A Non-Isolated High Voltage Gain DC–DC Converter Suitable for Sustainable Energy Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Research Literature
- Higher voltage gain in comparison with others in the literature by the use of a coupled inductor and a voltage multiplier circuit.
- Reduced maximum voltage of the switch due to the existence of the voltage multiplier circuit used as a clamp unit.
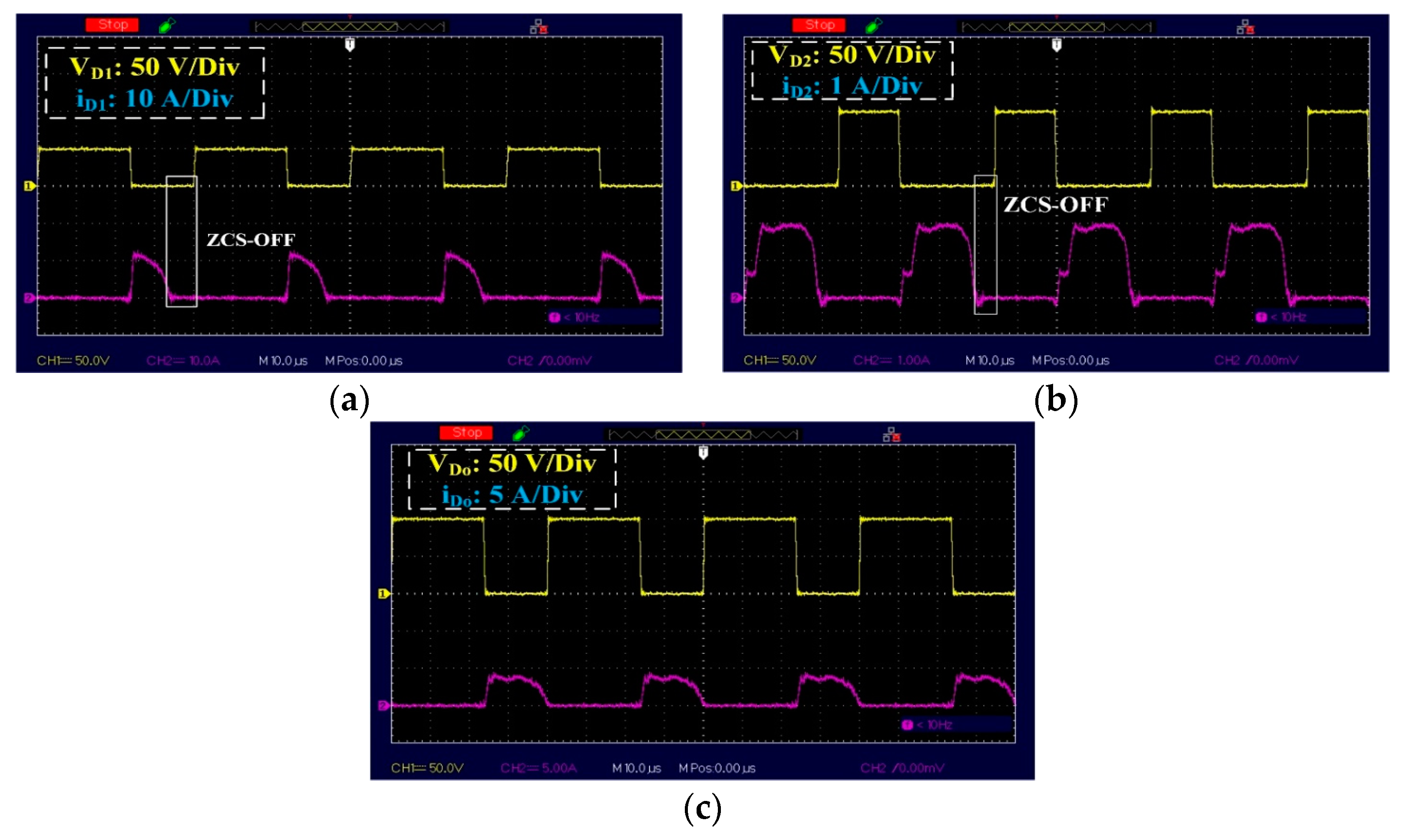
- Operation of the diodes under ZCS, which reduces their reverse recovery losses.
- Simple control system because of the one active switch used in the arrangement of the converter.
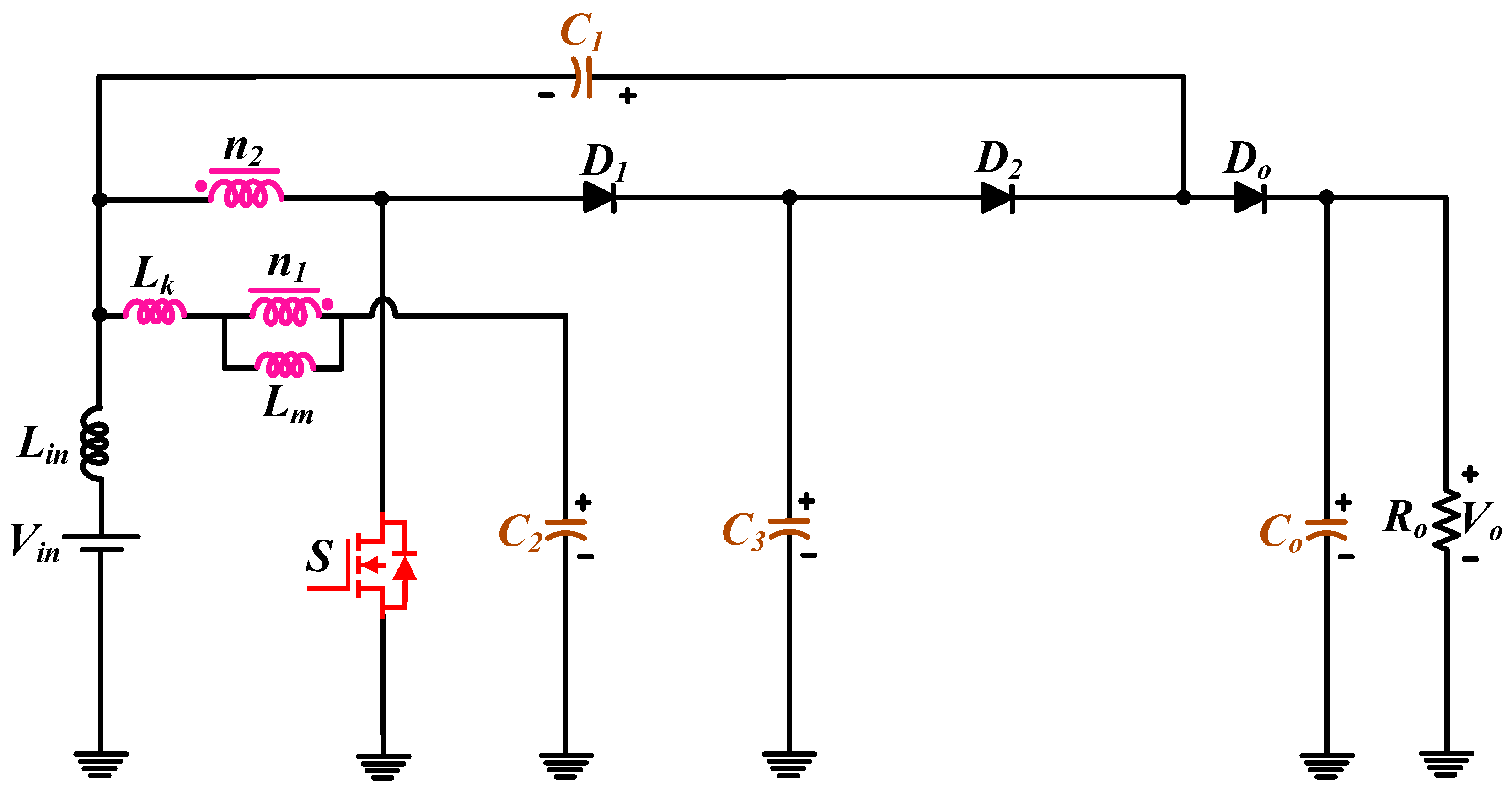
2. Material and Methods of Analysis the Proposed Converter
- The input DC source is consistent.
- The calculations do not consider the elements’ ESR values (capacitors and inductors), diode ohmic losses, and active switch conducting resistance.
- The intervals of transient state are ignored in the operating mode analysis.
- The leakage inductor (Lk) has a small value and may be ignored during the operation.
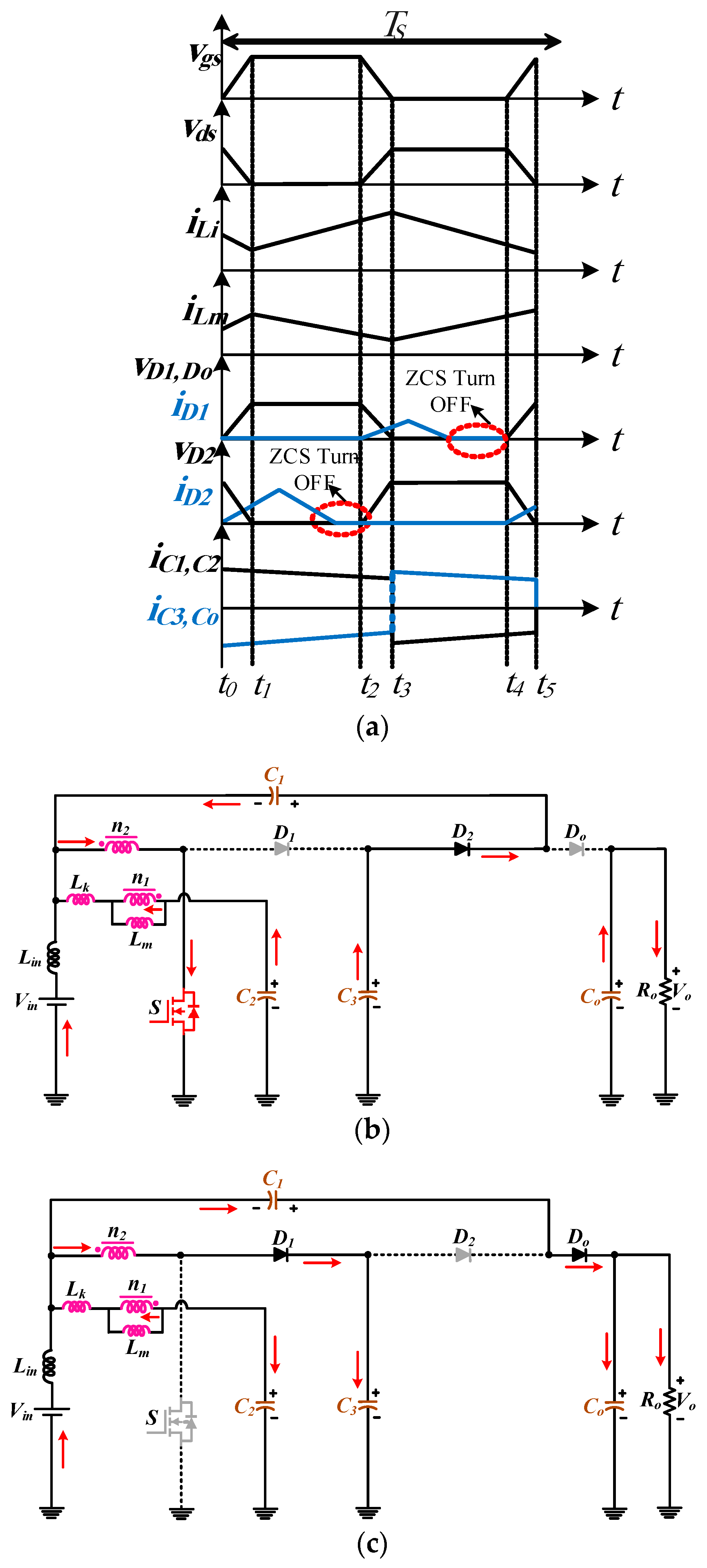
2.1. CCM Method Description
2.2. Current Calculation Method of the Components
2.3. Components Selection
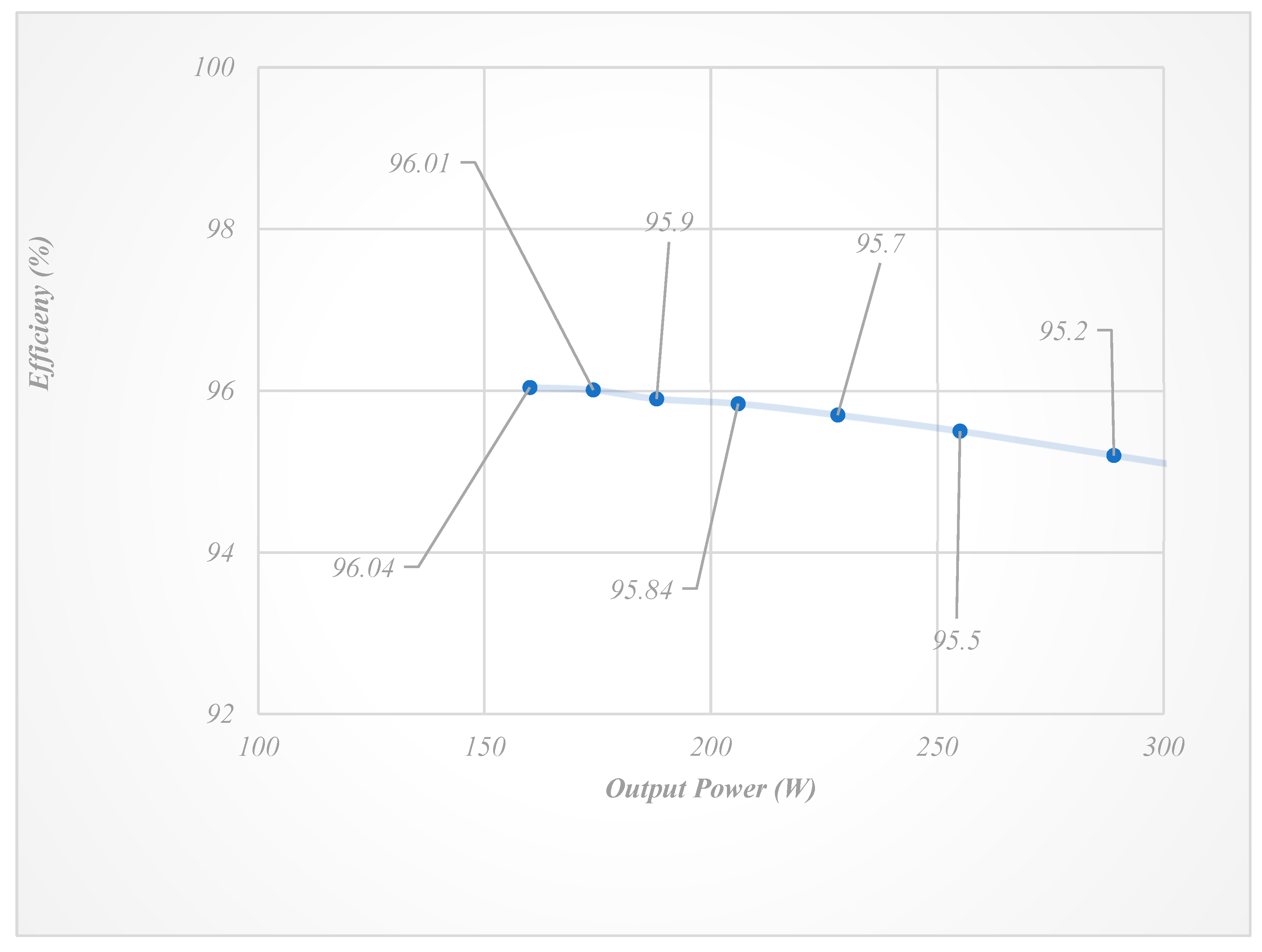
3. Efficiency Discussion of the Suggested Structure
4. Reliability Discussion and Method
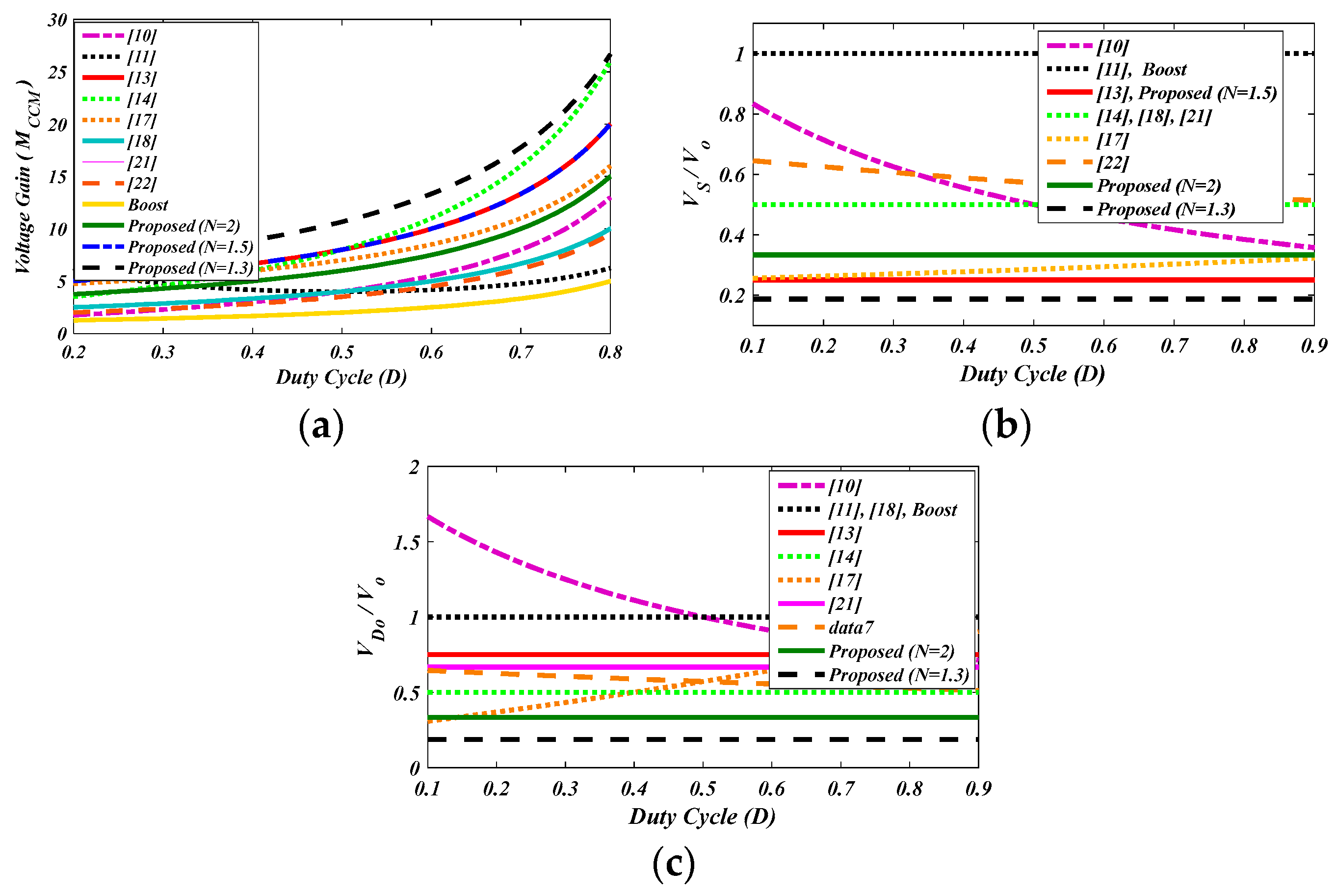
5. Discussion on the Feature Proposed Converter and Other Converters
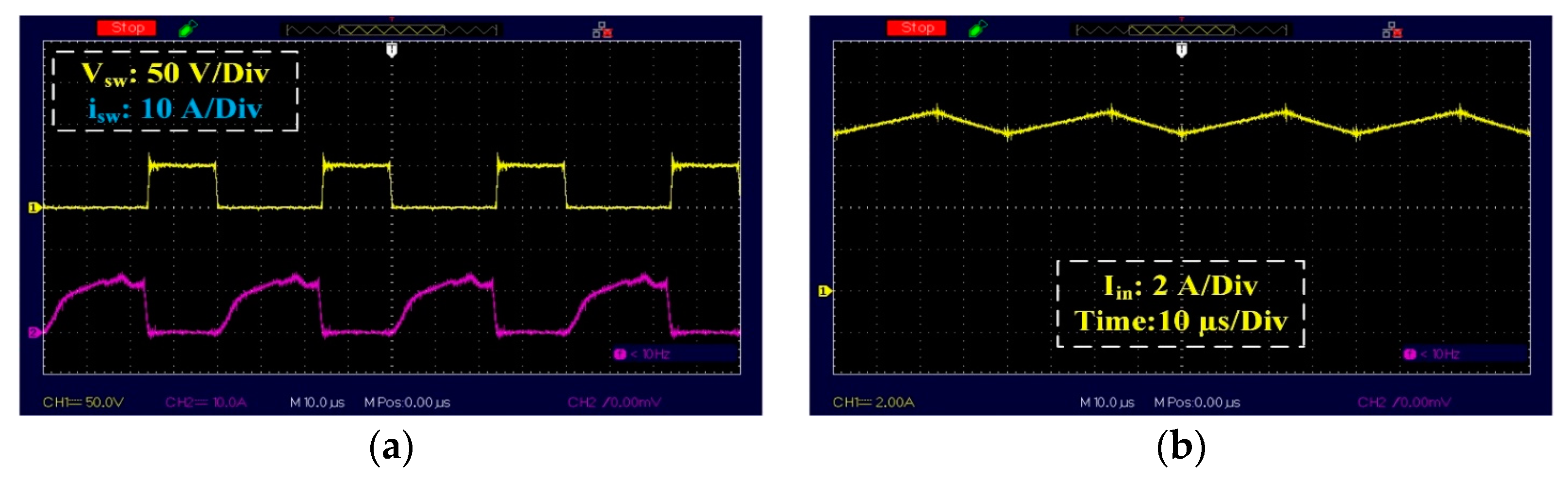
6. Result and Discussion
7. Conclusions
- A coupled inductor-based DC–DC converter with higher voltage gains in comparison with other topologies in the literature. As a result, the proposed converter can achieve higher voltage gains with smaller values of the duty cycles than others.
- Simple control system of the converter thanks to the existence of one switch.
- Reduced input current ripple, which can increase the lifetime of the used input source, such as a PV or a battery.
- Operation of the diodes under ZCS conditions reduces the reverse recovery losses of the regenerative diode.
- The lower peak voltage on the switch makes it possible to select a MOSFET switch with a lower nominal voltage which, in turn, can reduce the conduction and switching losses.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, N. High step-up DC–DC converter using coupled inductor voltage multiplier cell and differential connection method. IET Power Electron. 2023, 16, 542–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani SR, K.; Mostafaeipour, A.; Almutairi, K.; Dehshiri, S.J.H.; Dehshiri SS, H.; Techato, K. Predicting effect of floating photovoltaic power plant on water loss through surface evaporation for wastewater pond using artificial intelligence: A case study. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 50, 101849. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tao, Y.; Chen, W. Prospects and barriers analysis framework for the development of energy storage sharing. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 89, 104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh, S.M.; Marzang, V.; Pourjafar, S.; Hosseini, S.H. An ultra high step-up dual-input single-output DC–DC converter based on coupled inductor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 11023–11034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yang, M.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, J. A novel high-gain dc-dc converter applied in fuel cell vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 12763–12774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palleswari, Y.T.R. A Novel Hybrid High Gain DC-DC converter for Renewable Energy Applications. Int. J. Renew. Energy Res. (IJRER) 2022, 12, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Pourjafar, S.; Shayeghi, H.; Hashemzadeh, S.M.; Sedaghati, F.; Maalandish, M. A non-isolated high step-up DC–DC converter using magnetic coupling and voltage multiplier circuit. IET Power Electron. 2021, 14, 1637–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayeghi, H.; Pourjafar, S.; Hashemzadeh, S.M.; Blaabjerg, F. A high efficiency soft-switched DC–DC converter with high voltage conversion ratio. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2021, 49, 244–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.T.; De, D. Effective leakage energy recycling in high gain DC-DC converter with coupled inductor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2022, 69, 3284–3288. [Google Scholar]
- Naderi, A.; Abbaszadeh, K. High step-up DC–DC converter with input current ripple cancellation. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 2394–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjafar, S.; Sedaghati, F.; Shayeghi, H.; Maalandish, M. High step-up DC–DC converter with coupled inductor suitable for renewable applications. IET Power Electron. 2018, 12, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abkenar, P.P.; Samimi, M.H.; Marzoughi, A.; Samavatian, V.; Iman-Eini, H.; Naghibzadeh, Y. A highly reliable low-cost single-switch resonant dc–dc converter with high gain and low component count. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 2556–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.S.; Liang, T.J.; Lee, H.C.; Chen, J.F. Novel high step-up DC–DC converter with coupled-inductor and voltage-doubler circuits. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 4196–4206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwakoti, Y.P.; Blaabjerg, F. Single switch no isolated ultra-step-up DC–DC converter with an integrated coupled inductor for high boost applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 8544–8558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayeghi, H.; Pourjafar, S.; Hashemzadeh, S.M.; Sedaghati, F. A DC-DC Converter with High Voltage Conversion Ratio Recommended for Renewable Energy Application. J. Oper. Autom. Power Eng. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siva, A.; Rajendran, V. A novel auxiliary unit based high gain DC-DC converter for solar PV system with MPPT control. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2022, 13, 2386. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, M.Z.; Tirth, V.; Ali, A.; Farooq, A.; Algahtani, A.; Verma, R.; Islam, S.; Irshad, K.; Abdalla, A.N. Efficient Topology for DC-DC Boost Converter Based on Charge Pump Capacitor for Renewable Energy System. Int. J. Photoenergy 2021, 2021, 6675720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghaythi, M.L.; O’Connell, R.M.; Islam, N.E.; Khan, M.M.S.; Guerrero, J.M. A High Step-Up Interleaved DC–DC Converter with Voltage Multiplier and Coupled Inductors for Renewable Energy Systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 123165–123174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemzadeh, S.M.; Hosseini, S.H.; Babaei, E.; Sabahi, M. A soft switched high step-up DC-DC converter based on VMC and coupled inductor for photovoltaic energy applications. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2023, 17, 1583–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri Revathi, B.; Joseph Samuel, V.; Mahalingam, P. High step-up DC-DC converter based on double self-lift switched-coupled-inductor. Int. J. Electron. 2023, 110, 686–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Babu, N.R. Design and Development of Single Switch High Step-Up DC–DC Converter. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2018, 6, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.Z.; Farh, H.M.; Al-Shaalan, A.M.; Al-Shamma’a, A.A.; Alhelou, H.H. A novel single-input-multi-output converter for flexible-order power-distributive with MPPT capability. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 131020–131032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Ramos, J.; Mota-Varona, R.; Ortiz-Lopez, M.G.; Diaz-Saldierna, L.H.; Langarica-Cordoba, D. Control Strategy of a Quadratic Boost Converter With Voltage Multiplier Cell for High-Voltage Gain. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2017, 5, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M.F.; Giridhar, A.V.; Narasimharaju, B.L. Active switched-capacitor based ultra-voltage gain quadratic boost DC-DC converters. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2023, 51, 1389–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalandish, M.; Hosseini, S.H.; Ghasemzadeh, S.; Babaei, E.; Alishah, R.S.; Jalilzadeh, T. Six-phase interleaved boost dc/dc converter with high-voltage gain and reduced voltage stress. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 1904–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.Z.; Zhang, S.; Hong, Y.; Alwahkyan AR, A.Y.; Ali, A.; Farooq, A. A Coupled Inductor-Based Bidirectional DC-DC Converter with Step-Up Step-Down Operation for Electric Vehicle Applications. Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst. 2023, 2023, 9277881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, T.; Hosseini, S.H.; Babaei, E.; Ebrahimi, J. Interleaved high step-up DC–DC converter based on three-winding high-frequency coupled inductor and voltage multiplier cell. IET Power Electron. 2014, 8, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navauga, A.; Navamani, J.D.; Lavanya, A.; Vijayakumar, K. Comparison of high gain topologies of non-isolated dc-dc converters for fuel cell application. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Green Computing, Communication and Conservation of Energy (ICGCE), Chennai, India, 12–14 December 2013; pp. 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, K.V.; Vinay, K.S.; Chakraborty, P. Peer-to-Peer Sharing of Energy Storage Systems under Net Metering and Time-of-Use Pricing. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 3118–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghaythi, M.L.; O’Connell, R.M.; Islam, N.E. Design of a High Step-up DC-DC Power Converter with Voltage Multiplier Cells and Reduced Losses on Semiconductors for Photovoltaic Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Electric Ship Technologies Symposium (ESTS), Arlington, VA, USA, 14–16 August 2019; pp. 214–218. [Google Scholar]
- Dehshiri, H.; Jalaladdin, S.; Amiri, M. An integrated multi-criteria decision-making framework under uncertainty for evaluating sustainable hydrogen production strategies based on renewable energies in Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 46058–46073. [Google Scholar]
- Dehshiri, H.; Jalaladdin, S.; Zanjirchi, S.M. Comparative analysis of multicriteria decision-making approaches for evaluation hydrogen projects development from wind energy. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 46, 13356–13376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, J.W. Revision of MIL-HDBK-217, reliability prediction of electronic equipment. In Proceedings of the 2010 Proceedings-Annual Reliability and Maintainability Symposium (RAMS), San Jose, CA, USA, 25–28 January 2010; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]


| High Gain Converters | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| High gain DC–DC structure with magnetic coupling | The extended input voltage, low price | In kilowatt levels, the efficiency is low (due to inductive elements) |
| High gain DC–DC structure with switched capacitors | High efficiency | High current stress of switches |
| High gain DC–DC structure with inductors and magnetizing inductors | Low peak voltage of the switch in comparison with the boost structure, high efficiency | High ripple of the input current and output voltage |
| High gain DC–DC structure with magnetic coupling and switching capacitors | Low maximum voltage on switch | High ripple contents |
| High gain interleaved converters | Low input ripple | Low output voltage rate, the high maximum voltage throughout the switch, high current ripple of the switch |
| Abbreviation/Variable | Description | Abbreviation/Variable | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC | Direct current | Base failure rate with a constant value | |
| VM | Voltage multiplier | Application factor | |
| PV | Photovoltaic | Quality factor | |
| ZCS | Zero current switching | Environmental factor | |
| EMI | Electromagnetic interference | Temperature factor | |
| ZVS | Zero voltage switching | Ambient thermal resistance | |
| CCM | Continuous conduction mode | Ta | Ambient temperature |
| ESR | Equivalent series resistant | PLoss_S | Total power switches loss |
| MTTF | Mean time to failure | Diodes voltage stress factor | |
| FR | Failure rate | Diodes contact construction factor | |
| TS | Switching period | Applied voltage of diodes/rated voltage | |
| D | Duty cycle | THS | Hot spot temperature |
| Average rise in temperature | Capacitors’ voltage stress factor | ||
| AL | Radiating surface magnetic device’s area | Capacitance factor | |
| Series resistance factor | SC | Operating voltage of capacitors/rated voltage |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| for switches | 0.012 | 8 | |
| for diodes | 0.0038 | πE | 1 |
| for capacitors | 0.002 | 1 | |
| for magnetics | 0.004 | 1 | |
| Ta | 25 °C | AL | 7 |
| for switches | 40.5 °C/W | z | 2.43 |
| for diodes | 62 °C/W | n | 3 |
| πA | 8 | m | 0.23 |
| Converter | [10] | [11] | [13] | [14] | [17] | [18] | [21] | [22] | Boost | Proposed Converter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage conversion ratio | ||||||||||
| Mswitch | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | |||||||
| Mdiode | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| No of Diodes | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| No of Switches | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| No of capacitors | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 4 |
| No of inductors | 2 | 2 | - | 0 | - | 1 | - | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| No of coupled inductors | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| Total devices no. | 9 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 6 | 11 | 8 | 11 | 4 | 10 |
| Efficiency | 94 | 94.2 | 92.5 | 92.8 | 93.6 | 96.2 | 94 | 92.25 | 90 | 96 |
| Soft Switch | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | - | Yes |
| Parameter | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Output Power (Po) | 150 W |
| Power supply voltage (Vin) | 20 V |
| Load voltage (Vo) | 150 V |
| Operation frequency of the switch (fs) | 25 kHz |
| Turn ratio of the coupled inductor N(N1/N2) | 2/1 |
| Magnetizing inductance (Lm) | 250 µH |
| Input inductor (Lin) | 500 |
| MOSFET (S) | STW55NM60 |
| Diodes | RHRP15120 |
| The used capacitors (C1, C2, C3) | 100 µF/220 V |
| Output capacitor (Co) | 470 µF/400 V |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alghaythi, M.L. A Non-Isolated High Voltage Gain DC–DC Converter Suitable for Sustainable Energy Systems. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12058. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512058
Alghaythi ML. A Non-Isolated High Voltage Gain DC–DC Converter Suitable for Sustainable Energy Systems. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):12058. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512058
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlghaythi, Mamdouh L. 2023. "A Non-Isolated High Voltage Gain DC–DC Converter Suitable for Sustainable Energy Systems" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 12058. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512058
APA StyleAlghaythi, M. L. (2023). A Non-Isolated High Voltage Gain DC–DC Converter Suitable for Sustainable Energy Systems. Sustainability, 15(15), 12058. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512058







