A Simplified Equation for Calculating the Water Quality Index (WQI), Kalu River, Sri Lanka
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methodology
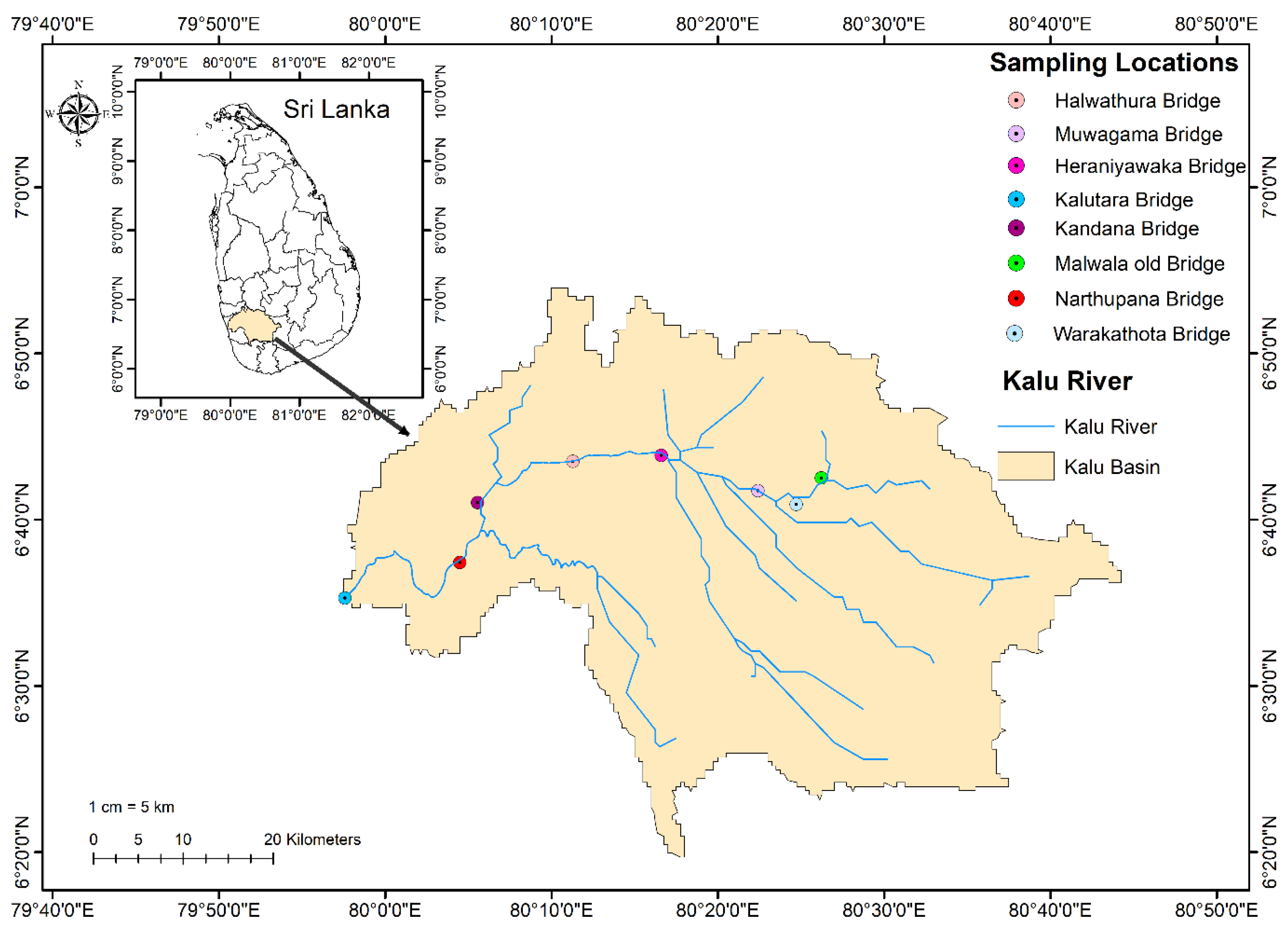
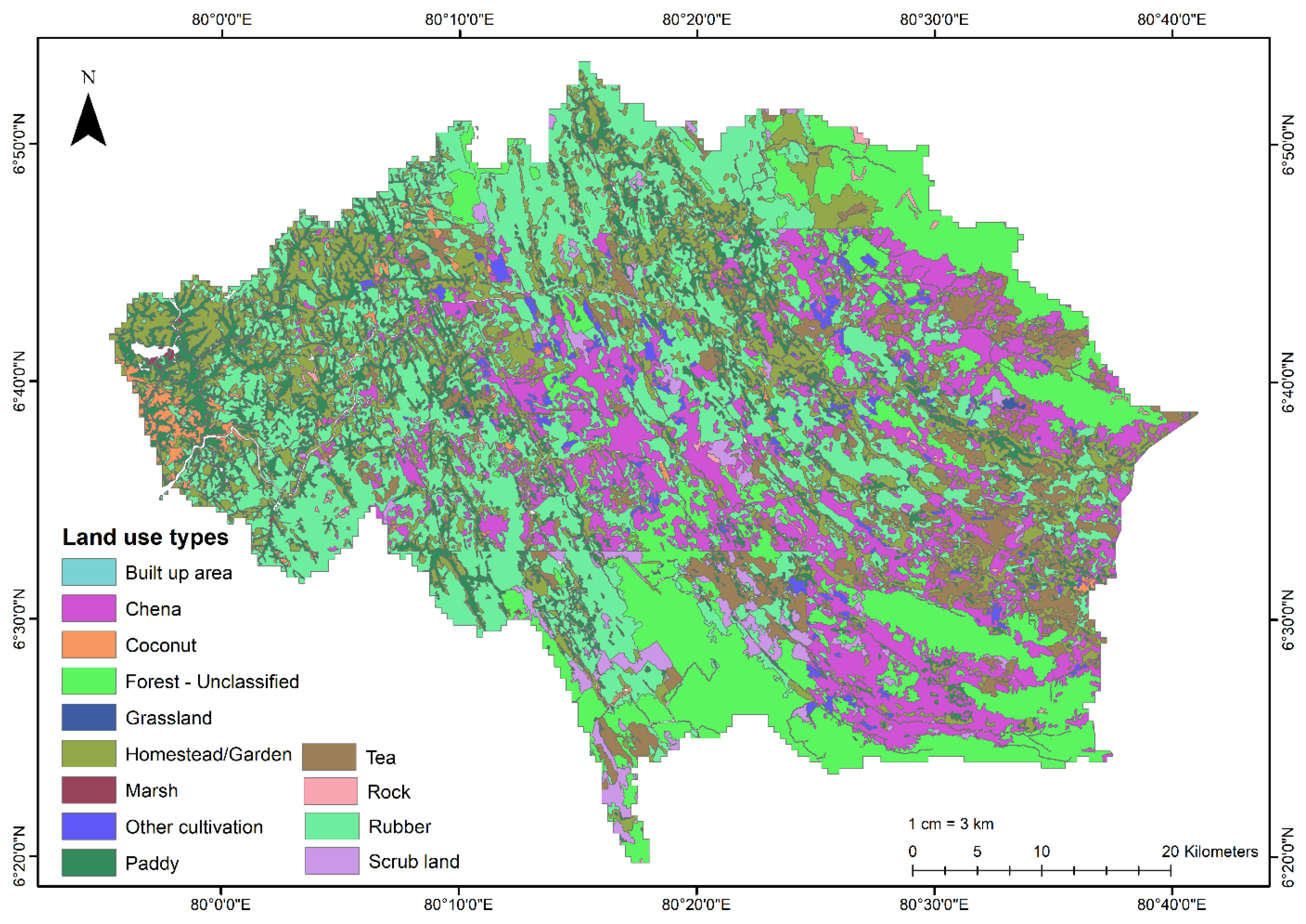
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Water Quality Data
2.3. Water Quality Index (WQI) Model Development
3. Results and Discussion
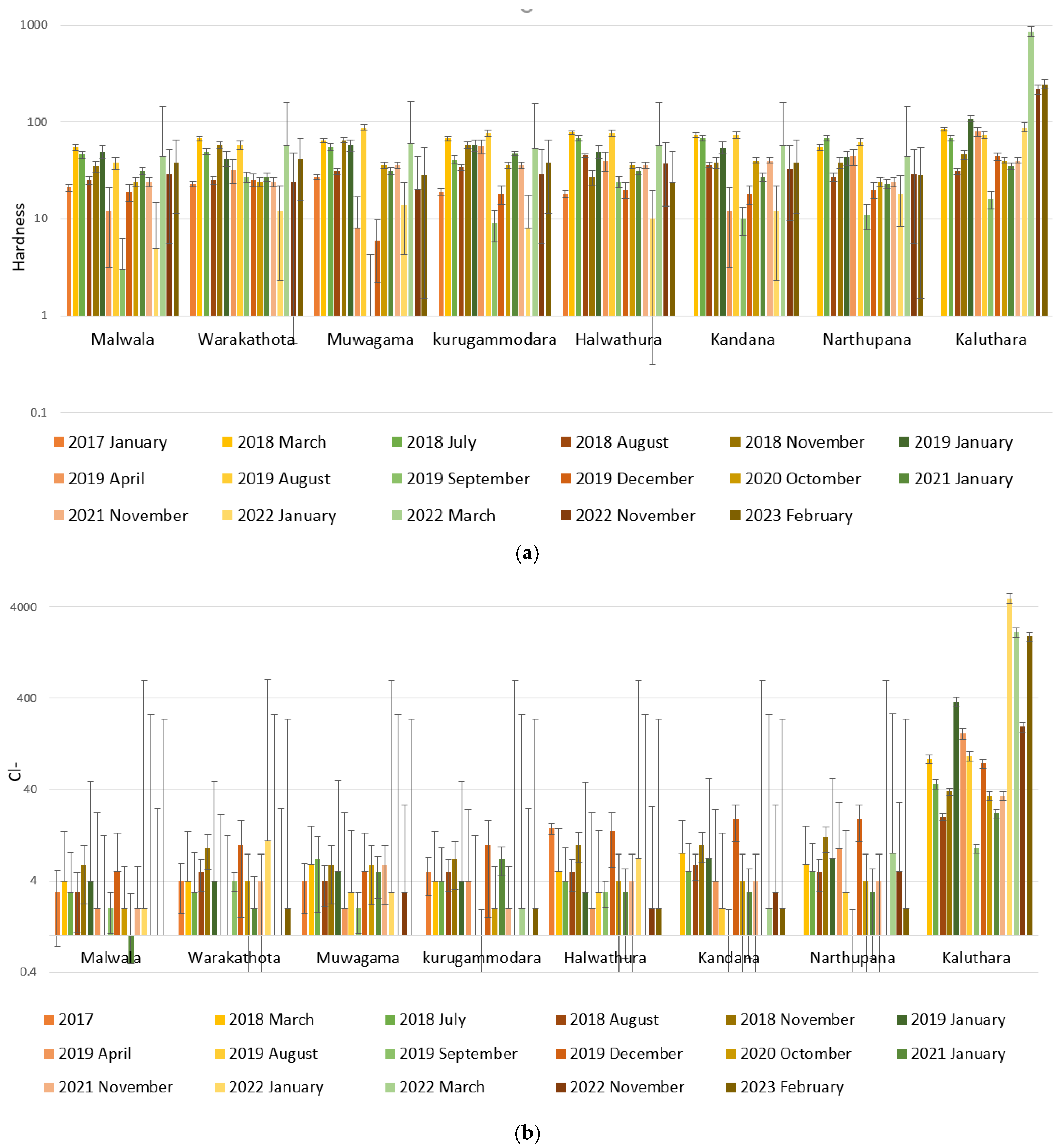
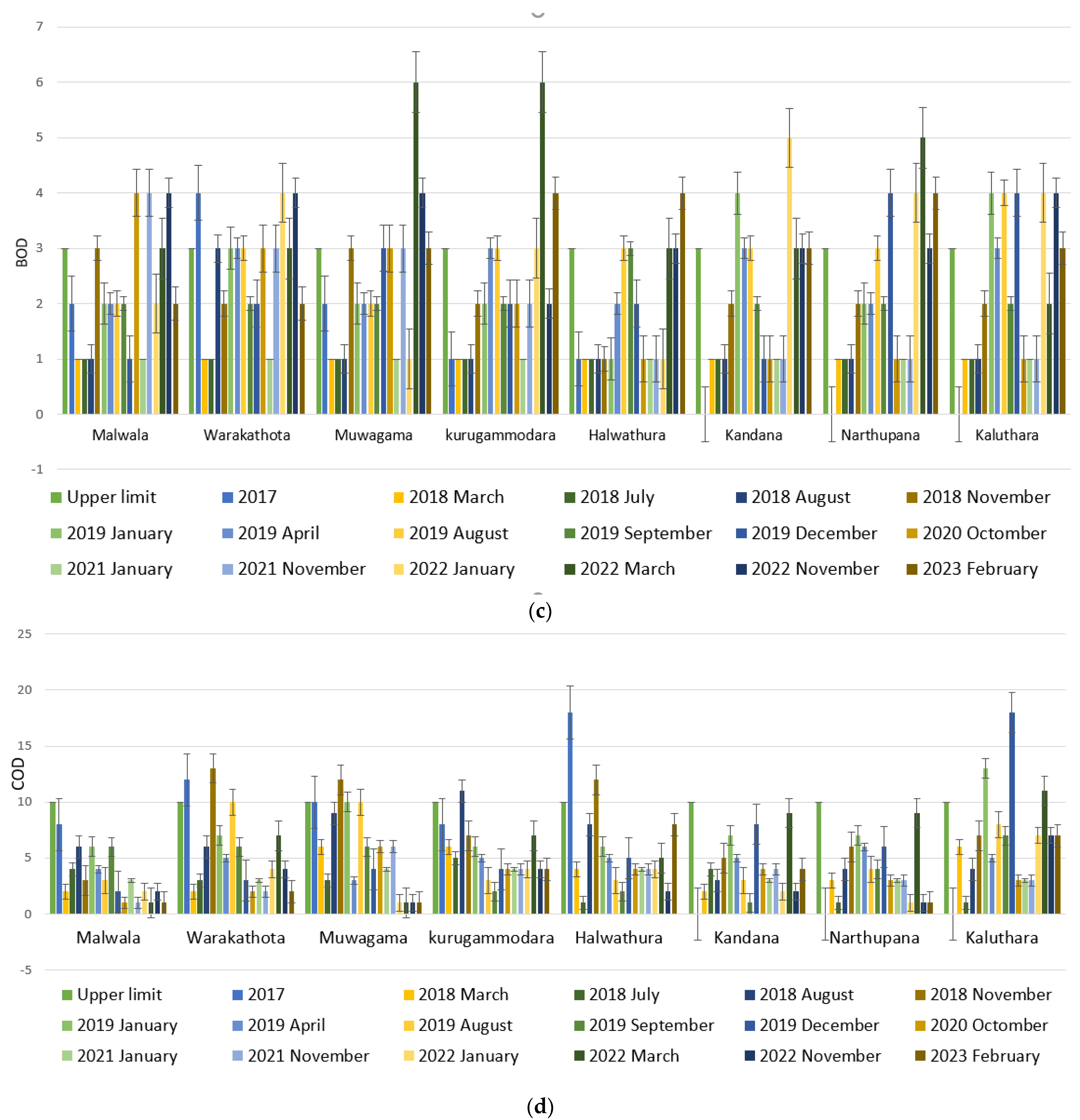
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variation of Water Quality Parameters
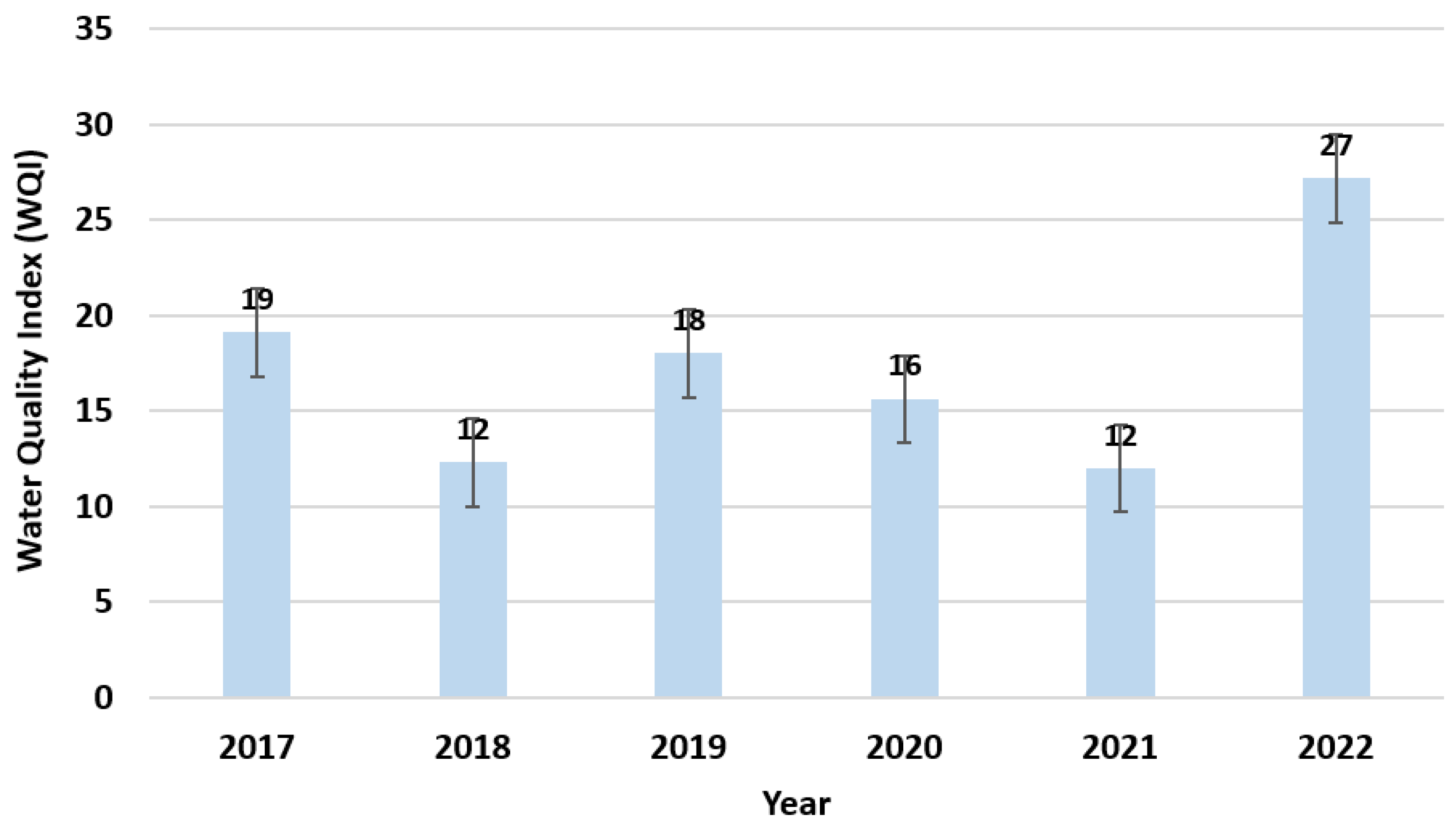
3.2. WQI Analysis
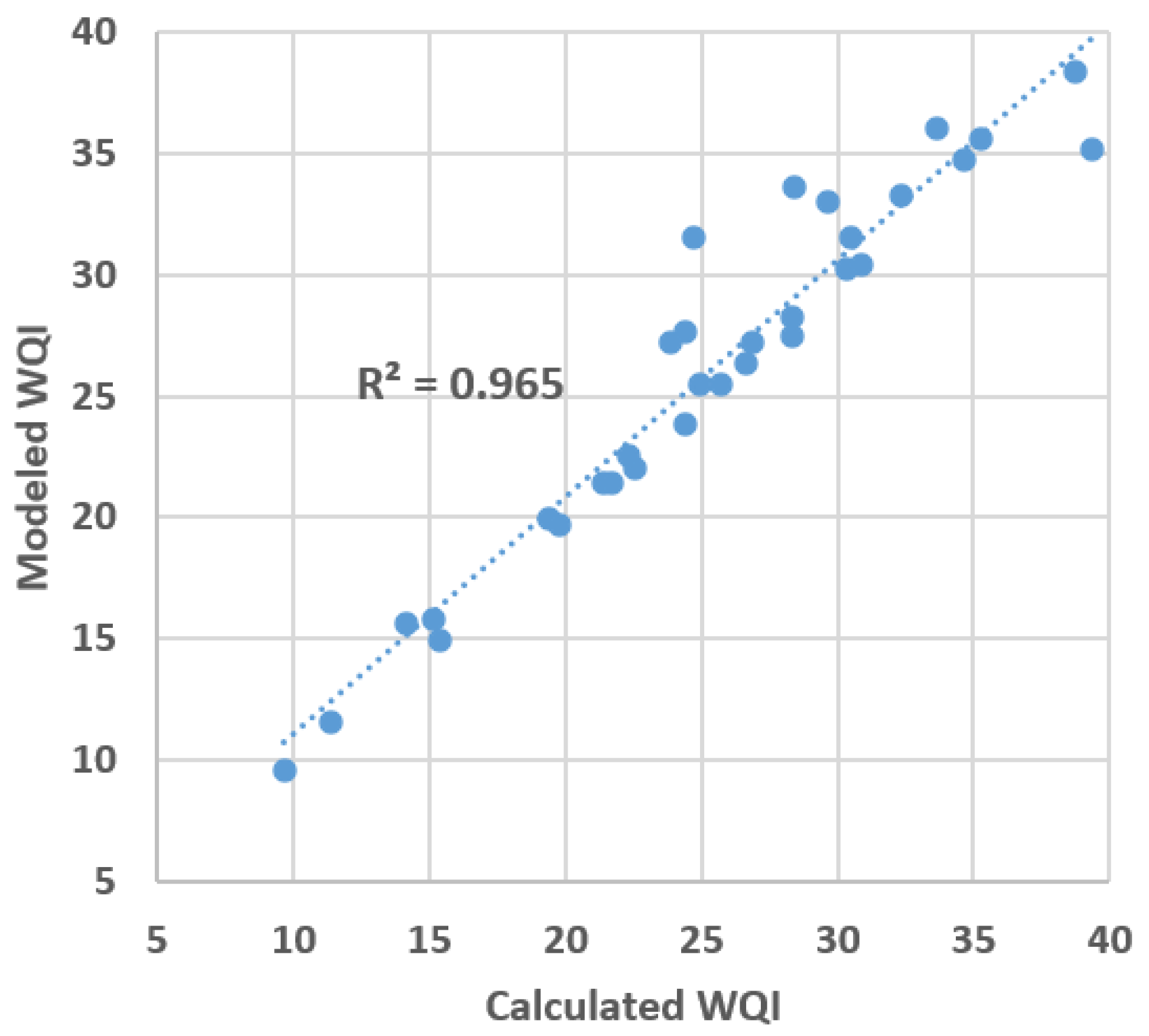
3.3. Development of Simplified Equation for WQI
3.4. Comparative Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Parameter | Unit | Standard | Ideal Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 6.5–8.0 | 7 |
| Temperature | Celsius | 25 | 25 |
| EC | mS/cm | 300 | 0 |
| COD | mg/L | 10 | 0 |
| BOD | mg/L | 3 | 0 |
| NO3− | mg/L | 10 | 0 |
| PO43− | mg/L | 0.7 | 0 |
| SO42− | mg/L | 250 | 0 |
| Cl− | mg/L | 400 | 0 |
| Total Hardness | mg/L | 600 | 0 |
References
- Gartsiyanova, K.; Varbanov, M.; Kitev, A.; Genchev, S. Water quality analysis of the rivers Topolnitsa and Luda Yana, Bulgaria using different indices. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2021, 1960, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edokpayi, J.N.; Odiyo, J.O.; Durowoju, O.S. Impact of wastewater on surface water quality in developing countries: A case study of South Africa. In Water Quality; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piazza, S.; Blokker, E.J.M.; Freni, G.; Puleo, V.; Sambito, M. Impact of diffusion and dispersion of contaminants in water distribution networks modeling and monitoring. Water Supply 2019, 20, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, U.S.; Tanyimboh, T.T. Optimal control of combined sewer systems using SWMM 5.0. WIT Trans. Built Environ. 2012, 122, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaccaro, M.M.; García-Liñeiro, A.; Fernández-Cirelli, A.; Volpedo, A.V. Life cycle assessment of water in sport equine production in Argentina: A case study. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, M.M.; Volpedo, A.V.; García Liñeiro, A.; Fernñandez Cirelli, A. Water quality in equine production in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Wilby, R.L.; Battarbee, R.W.; Keran, M.; Wade, A.J. A review of the potential impacts of climate change on surface water quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darko, H.F.; Ansa-Asare, O.; Paintsil, A. A number description of Ghanaian water quality—A case study of the southwestern and Coastal Rivers Systems of Ghana. J. Environ. Prot. 2013, 04, 1318–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokarram, M.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Huang, K.; Zhang, H. Investigation of water quality and its spatial distribution in the Kor River basin, Fars Province, Iran. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, M.N.; Hossain, M.S.; Latifa, G.A. Water quality assessment of balu river, Dhaka Bangladesh. Water Conserv. Manag. 2019, 3, 08–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tota-Maharaj, K.; Scholz, M. Combined permeable pavement and photocatalytic titani-um dioxide oxidation system for urban run-off treatment and disinfection. Water Environ. J. 2012, 27, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.; Tota-Maharaj, K. Laboratory studies on granular filters and their relationship to geotextiles for stormwater pollutant reduction. Water 2015, 7, 1595–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tota-Maharaj, K.; Paul, P. Sustainable approaches for stormwater quality improvements with experimental geothermal paving systems. Sustainability 2015, 7, 1388–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adeloju, S.B.; Khan, S.; Patti, A.F. Arsenic contamination of groundwater and its implications for drinking water quality and human health in under-developed countries and remote communities—A review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, P.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, Z.; Elumalai, V. Groundwater arsenic and fluoride and associated arsenicosis and fluorosis in China: Occurrence, distribution and management. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puntoriero, M.L.; Volpedo, A.V.; Fernández Cirelli, A. Arsenic, fluoride, and vanadium in surface water (chasicã3 lake, Argentina). Front. Environ. Sci. 2014, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batugedara, B.D.; Senanayake, S.A. Plankton diversity in coastal waters near Kalu Ganga river mouth; Sri Lanka. KDU J. Multidiscip. Stud. 2022, 4, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschke, S.; Avellán, T.; Bärlund, I.; Bogardi, J.J.; Carvalho, L.; Chapman, D.; Dickens, C.W.S.; Irvine, K.; Lee, S.; Mehner, T.; et al. Capacity challenges in water quality monitoring: Understanding the role of human development. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berthet, A.; Vincent, A.; Fleury, P. Water quality issues and agriculture: An International Review of Innovative Policy Schemes. Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, H.; Krueger, T.; Freer, J. Benchmarking observational uncertainties for hydrology: Rainfall, River Discharge and water quality. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 4078–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Barroso, L.A.; Rivas-Márquez, J.A.; Sosa-Tinoco, I.; Robles-Morúa, A. Design and implementation of a low-cost multiparameter probe to evaluate the temporal variations of water quality conditions on an estuarine lagoon system. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.M.; Klein, C.; Fünfrocken, E.; Kautenburger, R.; Beck, H.P. Real-time monitoring of water quality to identify pollution pathways in small and Middle Scale Rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2323–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeon, I.S.; Kim, J.H.; Jun, K.W. Application of artificial intelligence models in water quality forecasting. Environ. Technol. 2008, 29, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, P.; Cassidy, R. Perspectives on Water Quality Monitoring Approaches for Behavioral Change Research. Front. Water 2022, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Senf, C.; Jordan, P.; Krueger, T. Benchmarking inference methods for water quality monitoring and status classification. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tinnevelt, G.H.; Lushchikova, O.; Augustijn, D.; Lochs, M.; Geertsma, R.W.; Rijkeboer, M.; Kools, H.; Dubelaar, G.; Veen, A.; Buydens, L.M.; et al. Water quality monitoring based on chemometric analysis of high-resolution phytoplankton data measured with flow cytometry. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Janabi, S.; Al-Barmani, Z. Intelligent multi-level analytics of soft computing approach to predict water quality index (IM12CP-WQI). Soft Comput. 2023, 27, 7831–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Kumari, N.; Al Nawajish, S. Land use land cover (LULC) and surface water quality assessment in and around selected dams of Jharkhand using water quality index (WQI) and Geographic Information System (GIS). J. Geol. Soc. India 2023, 99, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El-Magd, S.A.; Ismael, I.S.; El-Sabri, M.A.; Abdo, M.S.; Farhat, H.I. Integrated machine learning–based model and WQI for groundwater quality assessment: ML, geospatial, and hydro-index approaches. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 53862–53875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumb, A.; Sharma, T.C.; Bibeault, J.-F. A review of Genesis and evolution of Water Quality Index (WQI) and some future directions. Water Qual. Expo. Health 2011, 3, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscuzza, C.; Volpedo, A.V.; Ojeda, C.; Cirelli, A.F. Water quality index as an tool for river assessment in agricultural areas in the pampean plains of Argentina. J. Urban Environ. Eng. 2007, 1, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Sharma, B.; Singh, P.; Dobhal, R. Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. Am. J. Water Resour. 2013, 1, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olubukola Ajoke Adelagun, R.; Edet Etim, E.; Emmanuel Godwin, O. Application of water quality index for the assessment of water from different sources in Nigeria. In Promising Techniques for Wastewater Treatment and Water Quality Assessment; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.G.; Nash, S.; Olbert, A.I. A review of water quality index models and their use for assessing surface water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukhabi, D.K.; Mensah, P.K.; Asare, N.K.; Pulumuka-Kamanga, T.; Ouma, K.O. Adapted water quality indices: Limitations and potential for water quality monitoring in Africa. Water 2023, 15, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machireddy, S.R. Assessment and distribution of groundwater quality using water quality index and geospatial technology in Vempalli Mandal of Andhra Pradesh, India. Water Resour. Manag. 2023, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Ishak, M.I.S.; Ahmad, M.I.; Umar, K.; Md Yusuff, M.S.; Anees, M.T.; Qadir, A.; Ali Almanasir, Y.K. Modification of the water quality index (WQI) process for simple calculation using the multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) method: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various natural and anthropogenic factors responsible for water quality degradation: A Review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhiri, L.; Mouni, L. Geochemical modeling of groundwater in the El Eulma area, Algeria. Desalination Water Treat. 2013, 51, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkhiri, L.; Mouni, L. Geochemical characterization of surface water and groundwater in Soummam Basin, Algeria. Nat. Resour. Res. 2014, 23, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, S.-L.; Yue, F.; Udeshani, C.; Chandrajith, R. Natural and anthropogenic controls of groundwater quality in Sri Lanka: Implications for chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDU). Water 2021, 13, 2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, N.; Tyagi, S. Influences of natural and anthropogenic factors on surface and groundwater quality in rural and urban areas. Front. Life Sci. 2014, 8, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, A.; Thejaswi, A.; Sreedhar, Y. Assessment of groundwater quality of Udayagiri area, Nellore district, Andhra Pradesh, South India using multivariate statistical techniques. Earth Sci. Res. J. 2016, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trabelsi, R.; Zouari, K. Coupled geochemical modeling and Multivariate Statistical Analysis Approach for the assessment of groundwater quality in irrigated areas: A study from North Eastern of Tunisia. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, C. How Many Countries Don’t Have Clean Water? Top 10 List and Facts. 2020. Available online: https://lifewater.org/blog/how-many-countries-dont-have-clean-water-top-10-list-and-facts (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Easterly, W. How the millennium development goals are unfair to Africa. World Dev. 2009, 37, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlet, L.; Polya, D.A. Arsenic in shallow, reducing groundwaters in Southern Asia: An Environmental Health Disaster. Elements 2006, 2, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, F.; Akhtar, M.M.; Ehsan, M. Evaluating urbanization impact on Stressed Aquifer of Quetta Valley, Pakistan. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 222, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, C.; Yamada, K. Impact of population growth on the water quality of natural water bodies. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandara, N.J.G.J. Water and wastewater related issues in Sri Lanka. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 47, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarathunga, A.A.D.; Kazama, F. Impact of land use on surface water quality: A case study in the Gin River Basin, Sri Lanka. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2016, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narangoda, C.; Amarathunga, D.; Dangalle, C.D. Evaluation of water quality in the upper and lower catchments of the Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Water Pr. Technol. 2023, 18, 716–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narangoda, C.N.; Dangalle, C.D.; Amarathunga, D. Selected freshwater fish species for assessing the water quality of the lower catchment of the Kelani River, Sri Lanka. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaratne, M.M.T.N.; Bandara, N.J.G.J.; Goonewardene, N.P. Water Quality in Selected Locations of the Kalu Ganga. In Proceedings of the 17th International Forestry and Environment Symposium 2012, Nugegoda, Sri Lanka, 16–17 November 2012; Volume 17. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnayake, N.P.; Silva, K.B.; Kumara, I.G. Chloride contamination in construction aggregates due to periodic saline water intrusion: A case study in the Kaluganga River estuary, Sri Lanka. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 69, 2529–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panditharathne, D.L.; Abeysingha, N.S.; Nirmanee, K.G.; Mallawatantri, A. Application of revised universal soil loss equation (Rusle) model to assess soil erosion in “Kalu ganga” river basin in Sri Lanka. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2019, 2019, 4037379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ampitiyawatta, A.; Guo, S. Precipitation trends in the Kalu Ganga Basin in Sri Lanka. J. Agric. Sci. 2010, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samarasinghe, S.M.J.S.; Nandalal, H.K.; Weliwitiya, D.P.; Fowze, J.S.M.; Hazarika, M.K.; Samarakoon, L. Application of Remote Sensing and GIS for Flood Risk Analysis: A Case Study at Kalu-Ganga River, Sri Lanka. International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Science, Volume XXXVIII (Part 8), Kyoto, Japan. 2010. Available online: https://www.isprs.org/publications/archives.aspx (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Bora, M.; Goswami, D.C. Water quality assessment in terms of Water Quality Index (WQI): Case study of the Kolong River, Assam, India. Appl. Water Sci. 2016, 7, 3125–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Bora, P. Water Quality Assessment Using Water Quality Index and Principal Component Analysis: A Case Study of Historically Important Lakes of Guwahati City, North-East India. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 207–2017. [Google Scholar]
- Makumbura, R.; Meddage, D.P.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Pandey, M.; Rathnayake, U. A simplified mathematical formulation for water quality index (WQI): A case study in the Kelani River Basin, Sri Lanka. Fluids 2022, 7, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radin Nizar, F.S.; Mohd Ghazi, R.; Awang, N.R.; Muhammad, M. Assessment of kelantan river water quality using water quality index (WQI). IOP Conf. Series Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 842, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, National Environmental Act No. 47 of 1980 1–4. 2019. The Gazette of the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka. Available online: http://citizenslanka.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/02/National-Environmental-Act-No-47-0f-1980-E.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2023).
- Das Kangabam, R.; Bhoominathan, S.D.; Kanagaraj, S.; Govindaraju, M. Development of a water quality index (WQI) for the Loktak Lake in India. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Howladar, M.F.; Al Numanbakth, M.A.; Faruque, M.O. An application of Water Quality Index (WQI) and multivariate statistics to evaluate the water quality around Maddhapara granite mining industrial area, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environ. Syst. Res. 2017, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.; Mahessar, A.A.; Memon, S.A.; Ansari, K.; Qureshi, A.L. Impact assessment of groundwater quality using WQI and geospatial tools: A case study of islamkot, Tharparkar, Pakistan. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. Res. 2020, 10, 5288–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| WQI | WQS | Intended Usage | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drinking | Irrigation | Industrial | ||
| 0–25 | Suitable | Suitable | Suitable | |
| 25–50 | Good | Suitable | Suitable | Suitable |
| 50–75 | Poor | Not Suitable | Suitable | Suitable |
| 75–100 | Very poor | Not Suitable | Suitable | Not Suitable |
| Above 100 | Not suitable for drinking or fish culture | Proper treatment is required | ||
| Parameter | Coefficient | Parameter | Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1.86 | NO−3 (mg/L) | 0.4188 |
| EC (mS/cm) | −0.018 | PO4−3 (mg/L) | 96.04 |
| Temperature (°C) | 0.1643 | SO4−2 (mg/L) | 0.000619 |
| COD (mg/L) | 0.4454 | Cl− (mg/L) | 0.0004 |
| BOD (mg/L) | 5.16 | Hardness (mg/L) | 0.009218 |
| Country | Basin | Methodology | Results | Suggested Solutions | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sri Lanka | Kelani River Basin | Weighted arithmetic index method to calculate WQI | Kelani River WQI average values varying by 35.9 (2011)–58.7 (2012) (considered time period, 2005–2012); water is not fit for drinking | Establish a water quality monitoring strategy, public awareness campaigns, and some policy decisions addressing the quality of water near industrial zones, such as imposing new legislation on industries that discharge effluents into natural streams. | [61] |
| India | Loktak Lake | Weighted arithmetic index method to calculate WQI | WQI values range from 64 to 77, indicating that the Loktak Lake water is not fit for drinking | The study recommends the urgent need for continuous monitoring of the lake water and identifying the pollution sources to protect the largest freshwater lake from further contamination. | [64] |
| Bangladesh | Maddhapara Granite Mining Industrial Area, Dinajpur | Weighted arithmetic index method to calculate WQI multivariate statistical analysis | Water quality index analysis revealed that 96.77% of the water samples fell under excellent quality and the rest 3.23% of the water samples were of good quality types | Monitor activities for further water quality management to prevent pollution. | [65] |
| Pakistan | Islamkot, Tharparkar | Weighted arithmetic index method to calculate WQI | The computed WQI values range from 98 to 153 under the very poor category | Water quality monitoring and health impact assessment must be conducted constantly. | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Siriwardhana, K.D.; Jayaneththi, D.I.; Herath, R.D.; Makumbura, R.K.; Jayasinghe, H.; Gunathilake, M.B.; Azamathulla, H.M.; Tota-Maharaj, K.; Rathnayake, U. A Simplified Equation for Calculating the Water Quality Index (WQI), Kalu River, Sri Lanka. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512012
Siriwardhana KD, Jayaneththi DI, Herath RD, Makumbura RK, Jayasinghe H, Gunathilake MB, Azamathulla HM, Tota-Maharaj K, Rathnayake U. A Simplified Equation for Calculating the Water Quality Index (WQI), Kalu River, Sri Lanka. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):12012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512012
Chicago/Turabian StyleSiriwardhana, Kushan D., Dimantha I. Jayaneththi, Ruchiru D. Herath, Randika K. Makumbura, Hemantha Jayasinghe, Miyuru B. Gunathilake, Hazi Md. Azamathulla, Kiran Tota-Maharaj, and Upaka Rathnayake. 2023. "A Simplified Equation for Calculating the Water Quality Index (WQI), Kalu River, Sri Lanka" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 12012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512012
APA StyleSiriwardhana, K. D., Jayaneththi, D. I., Herath, R. D., Makumbura, R. K., Jayasinghe, H., Gunathilake, M. B., Azamathulla, H. M., Tota-Maharaj, K., & Rathnayake, U. (2023). A Simplified Equation for Calculating the Water Quality Index (WQI), Kalu River, Sri Lanka. Sustainability, 15(15), 12012. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151512012









