The Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling and Coordinated Development of Basic Public Services, Urbanization, and Tourism in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Area Overview and Research Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Evaluation System Construction
2.3. Data Selection and Evaluation System Construction
2.4. Research Methods
2.4.1. Comprehensive Evaluation Model
2.4.2. Coupling Coordination Degree Model
2.4.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Model
2.4.4. Geographical Detector
3. Analysis of the Results
3.1. Research on the Development of the Coupling Coordination Degree of Basic Public Services, Urbanization, and Tourism
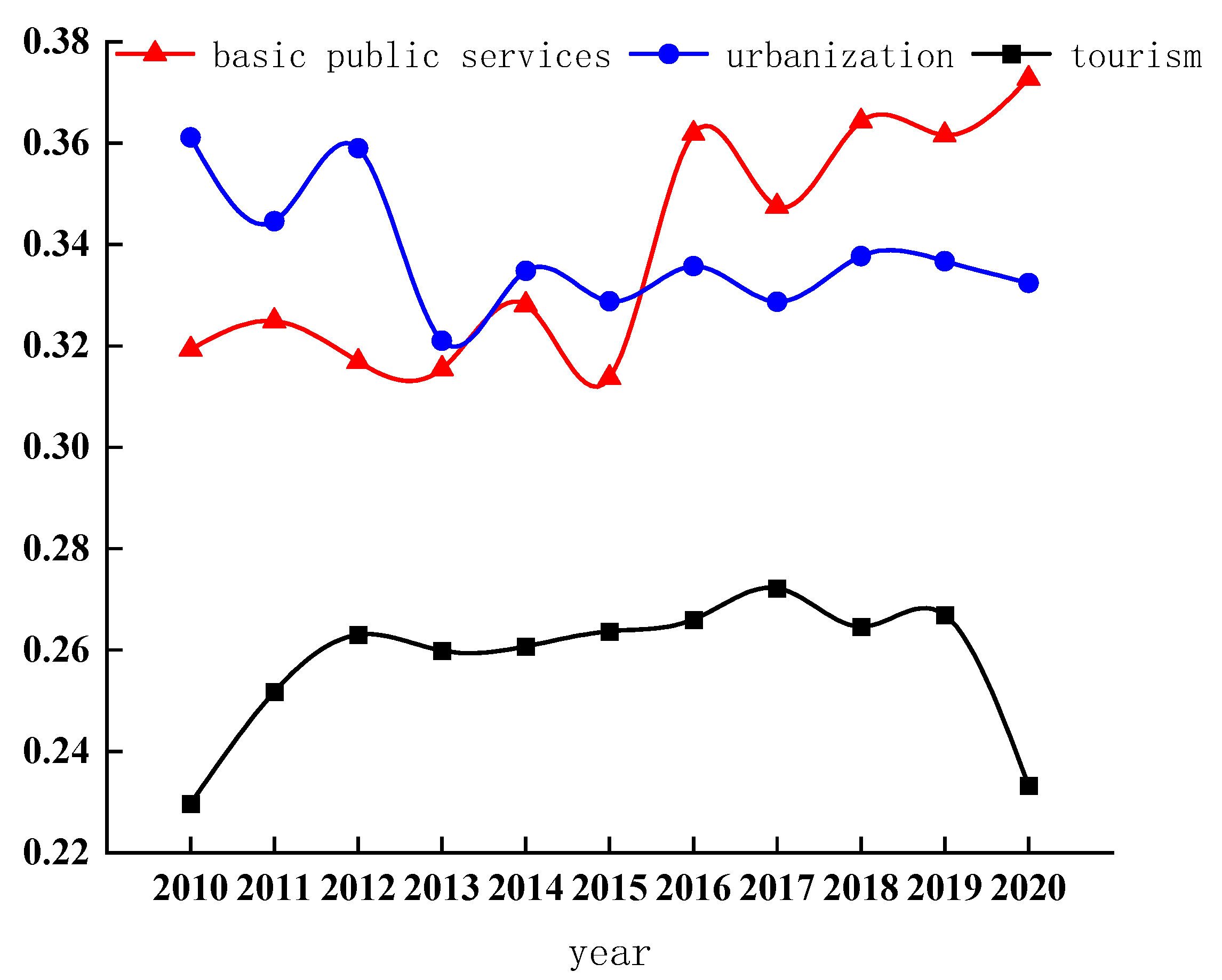
3.1.1. Time-Series Characteristics of the Comprehensive Development Index of Each Subsystem
3.1.2. Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Coupling Coordination Degree
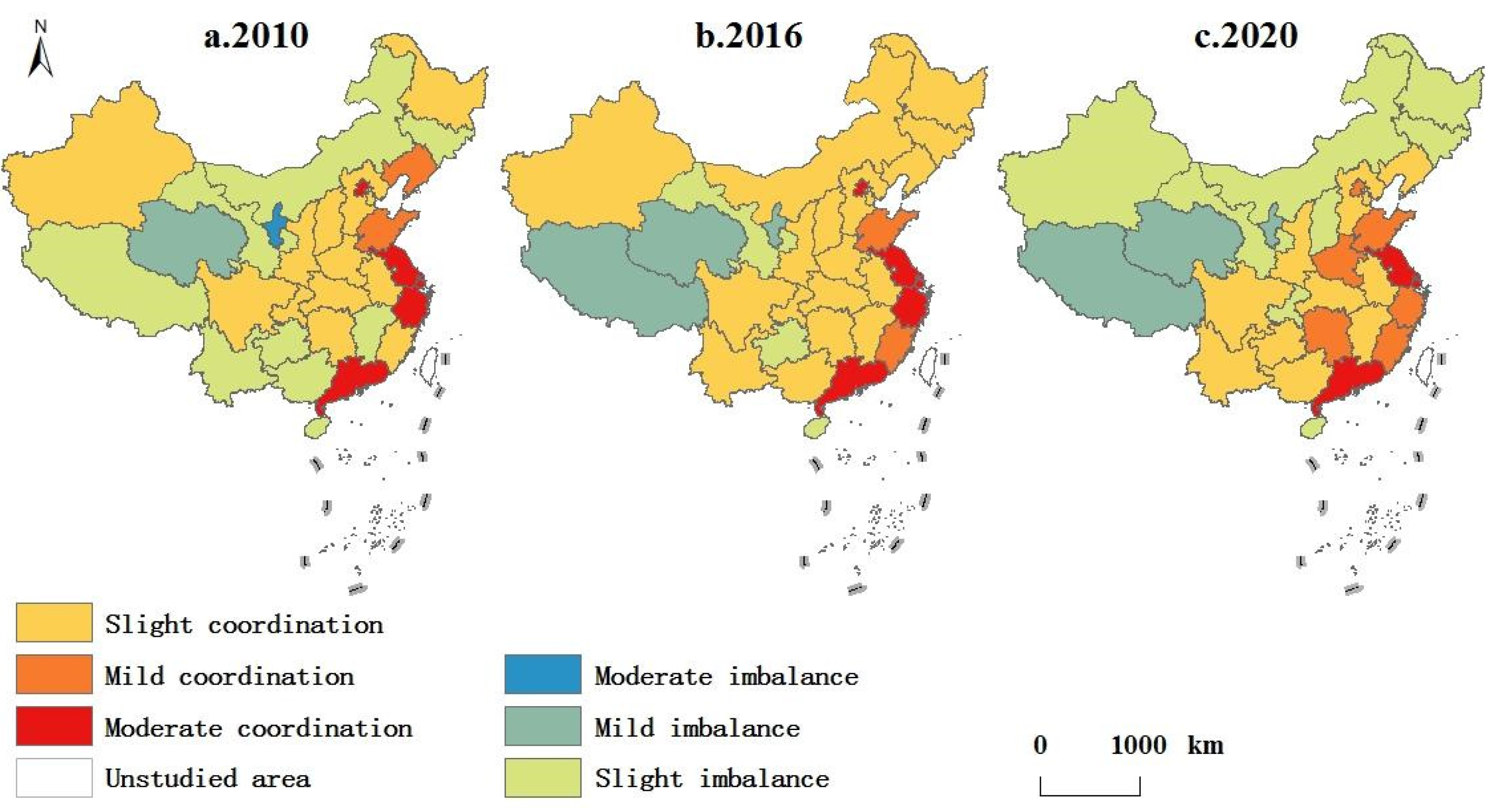
3.1.3. Spatial Evolution of Coupling Coordination Degree
3.2. Spatial Agglomeration of Basic Public Services–Urbanization–Tourism Coupling Coordination Degree
3.2.1. Overall Coordination Level and Spatial Agglomeration Characteristics
3.2.2. Spatial Differentiation of Local Autocorrelation
3.3. The Influencing Factors of the Coordinated Development of Basic Public Services, Urbanization, and Tourism
3.3.1. Analysis of Influencing Factors
3.3.2. Significant Interaction
4. Discussion
5. Suggestions
6. Conclusions
- (1)
- From 2010 to 2020, there was comprehensive development: basic public services showed a rising trend, urbanization experienced a declining and fluctuating stability, and the tourism industry demonstrated an inverted U-shaped trend of rising first and then falling.
- (2)
- During the same period, for coupling coordinated development, the average value of the coupling coordination degree of the three systems was always in mild coordination and showed a slight upward trend; the stability of the coupling coordination degree for 18 provinces was low, and their levels changed. The coupling coordination degree for 13 provinces was relatively stable and remained unchanged. Spatially, the level of coupling coordination degree decreased from southeast to northwest, and the spatial heterogeneity of coupling coordination degree in each region was obvious. From 2010 to 2020, the coupling coordination degree of the eastern coastal and central regions increased slightly, while that of the northeast and western regions decreased slightly.
- (3)
- The spatial agglomeration of coupling coordination degree was revealed by the coupling coordination degree of the three systems, which demonstrates strong spatial autocorrelation, and with a tendency to gather in space; the agglomeration effect was obvious and interdependence between the systems exists; the coupling coordination degree of the three systems has an obvious spatial agglomeration effect, forming a hot-spot area with the southeast coast as the core, and a cold-spot area with the northwest inland area as the core. Both cold and hot spots gradually radiated outward, forming a spatial agglomeration distribution pattern of hot in the east and cold in the west.
- (4)
- In terms of influencing factors of coupling coordination degree, the coupling and coordinated development of China’s three systems is affected by many factors, and the influence of each factor is different in different years. The results of interaction detection showed different levels of Enhance, bi- and Enhance, nonlinear. The coupling and coordinated development of the three systems results from the combined effect of endogenous power (economic pulling power, infrastructure support power, industrial driving force, population agglomeration power) and exogenous power (government regulation power, market promotion power, social security power).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, W.; Wang, J.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y. High-quality development in China: Measurement system, spatial pattern, and improvement paths. Habitat Int. 2021, 118, 102458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q. Does the Equalization of Public Services Effect Regional Disparities in the Ratio of Investment to Consumption? Evidence From Provincial Level in China. SAGE Open 2022, 12, 21582440221085007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H. Evaluation and Analysis of High-Quality Development of New Urbanization Based on Intelligent Computing. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 6428970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Lian, Y.; Chen, H.; Qian, F. The impacts of energy resource and tourism on green growth: Evidence from Asian economies. Resour. Policy 2023, 81, 103359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Correlation Analysis between Tourism and Economic Growth Based on Computable General Equilibrium Model (CGE). J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 6497125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, Z. Quantitative measurement on urbanization development level in urban Agglomerations: A case of JJJ urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. The Measurement of High-Quality Development Level of Tourism: Based on the Perspective of Industrial Integration. Sustainability 2022, 14, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Tang, J.; Dombrosky, J.M. Coupling relationship of tourism urbanization and rural revitalization: A case study of Zhangjiajie, China. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2022, 27, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Cui, X.; Li, F. Exploring the multi-dimensional coordination relationship between population urbanization and land urbanization based on the MDCE model: A case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.L.; Yang, D.G.; Huo, J.W. Spatial-temporal pattern evolution and influencing factors of basic public service mismatch in Wuchang area. Arid. Land Geogr. 2019, 42, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, J.W.; Yang, L.; Li, J.J. Research on the influencing factors of the competitiveness of Sichuan-Tibet tourism industry based on DEMATEL. J. Arid. Land Resour. Environ. 2017, 31, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; Liang, C. Urbanization of county in China: Spatial patterns and influencing factors. J. Geogr. Sci. 2022, 32, 1241–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyzan, E. The distribution of urban public services. Cities 1997, 6, 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Carruthers, J.I.; Ulfarsson, G.F. Urban Sprawl and the Cost of Public Services. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2003, 30, 503–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y. Research on the coupling and coordinated development of basic public services and new urbanization in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Stat. Decis. 2023, 39, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubenko, S. Giants and midgets: The effect of public goods provision on urban population concentration. Cities 2020, 107, 102872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Wu, S.; Chen, D.; Cheng, M.; Yu, X.; Yan, D.; Dang, Y.; Peng, M. Can urban public services and ecosystem services achieve positive synergies. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, R.D.; Ferbrache, F.; Nikitas, A. Transport’s historical, contemporary and future role in shaping urban development: Re-evaluating transitoriented development. Cities 2020, 9, 102607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miriam, H.R. Does Urban Sprawl Increase the Costs of Providing Local Public Services? Evidence from Spanish Municipalities. Urban Stud. 2010, 47, 1513–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostovskaya, A.A.; Smirnova, E.A.; Shendrikova, S.P. Socio-economic Development of Tourism Infrastructure. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 459, p. 052064. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.Q.; Cai, X.W. Do transportation and tourism development really contribute to China’s economy? evidence from renewable and non-renewable energy consumption. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 25, 7189–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, P. Tourism Urbanization. Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 1991, 15, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burak, S.; Dogan, E.; Gazioglu, C. Impact of urbanization and tourism on coastal environment. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2004, 47, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Simon, M. Urban Heritage Tourism: The Global-local Nexus. Ann. Tour. Res. 1996, 23, 284–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anke, K. Impact of Tourism and Urbanization on Water Supply and Water Quality in Manali, Northern India. Can. Water Resour. J. 2013, 27, 383–400. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.X.; Yang, Q.; Sun, C.C.; Xie, X.L. Coupling Coordinated Evolution and Forecast of Tourism-Urbanization-Ecological Environment: The Case Study of Chongqing, China. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 7271637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, H.P. The Process of Urbanization and Its Implications for Tourism Sector: A Sustainability Approach: The Case of Famagusta/TRNC. Ph.D. Thesis, Eastern Mediterranean University, Famagusta, Cyprus, 2012; pp. 31–55. [Google Scholar]
- Amir, G. Tourism and Urbanization, An Interconnected Evolution. Sustain. Environ. 2021, 6, 96–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Han, D.; Wang, T.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Y. Coupled and Coordinated Development of the Tourism Industry and Urbanization in Marginal and Less Developed Regions—Taking the Mountainous Border Areas of Western Yunnan as a Case Study. Land 2023, 12, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Chen, H.; Pan, J.; Si, Y.; Law, R.; Zhang, M. Spatial Distribution Pattern and Influencing Factors of Sports Tourism Resources in China. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.J.; Xue, D.; Huang, J.C.; Liu, M.X.; Li, L. Identification of Coupling Relationship between Ecosystem Services and Ur-banization for Supporting Ecological Management: A Case Study on Areas along the Yellow River of Henan Province. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L. A study on the spatial and temporal differentiation of tourism industry-urbanization-ecological environment coordination in Yangtze River economic zone. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 33, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.Q.; Lian, Q.W.; Han, Z.L. Spatial-temporal evolution of coupling and coordinated development of basic public ser-vices-urbanization-regional economy. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, L. Research on temporal and spatial variations in the degree of coupling coordination of tourism–urbanization–ecological environment: A case study of Heilongjiang, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 8474–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Pérez, J.M.; Remond-Roa, R.; Rullan-Salamanca, O.; Vives-Miró, S. Urban growth and dual tourist city in the Caribbean. Urbanization in the hinterlands of the tourist destinations of Varadero (Cuba) and Bávaro-Punta Cana (Dominican Republic). Habitat Int. 2016, 58, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Ju, H. The spatial pattern and influencing factors of tourism development in the Yellow River Basin of China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Kang, L. Spatial–Temporal Heterogeneity of Urbanization and Ecosystem Services in the Yellow River Basin. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhao, Y.; Kong, X. Spatio-Temporal Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Basic Public Service Levels in the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Land 2022, 11, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.M.; Fang, C.L.; Mu, X.F.; Chen, D. Coupling and coordination analysis of urbanization and ecosystem service value in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.T.; Zhao, J.J.; Yan, S.W.; Zhu, M. Coupling coordination of new urbanization in Chinese urban agglomeration-characteristics and driving factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Li, J.F. Analysis on the Coupling Relationship and Coordinated Development between the Construction of Ethnic Minority Tourist Towns and the Tourism Industry. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Zhang, C.M.; Ren, Q.L. Interactive coupling mechanism and spatial-temporal characteristics of basic public services and economic development-Taking 13 cities in Jiangsu Province as an example. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Q. Comprehensive partitions and optimisation strategies based on tourism urbanisation and resources environment carrying capacity in the Yellow River Basin, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 23180–23193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principles and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
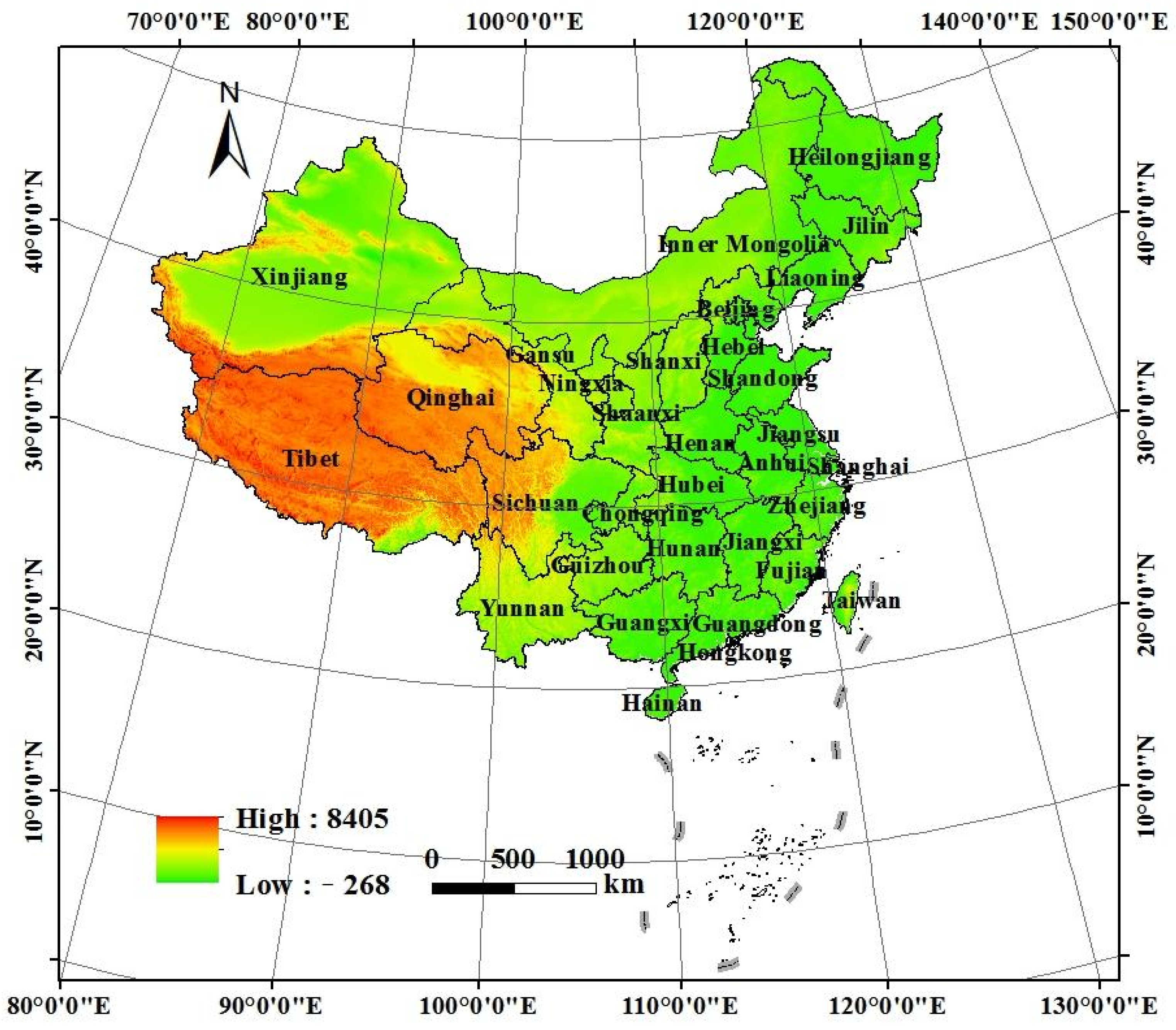


| Target Layer | Element Layer | Index Layer |
|---|---|---|
| Basic public services | education and cultural services | Local fiscal expenditure on education (CNY one hundred million) |
| Number of colleges and universities per ten thousand people (colleges/ten thousand people) | ||
| The number of students in regular institutions of higher learning (ten thousand people) | ||
| Number of full-time teachers in primary and secondary schools per ten thousand people (people) | ||
| Local fiscal expenditure on science and technology (CNY one hundred million) | ||
| The total collection of public libraries (ten thousand volumes) | ||
| health and social security services | Number of medical and health institutions per ten thousand people (numbers/ten thousand people) | |
| Number of beds in medical institutions per ten thousand people (numbers/ten thousand people) | ||
| Number of professional doctors (ten thousand people) | ||
| Number of social welfare homes per ten thousand people (numbers) | ||
| Medical insurance coverage for urban workers (%) | ||
| Basic pension insurance coverage of urban and rural residents (%) | ||
| ecological environmental services | Comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste (%) | |
| Urban sewage treatment rate (%) | ||
| Harmless treatment rate of municipal solid waste (%) | ||
| Industrial wastewater discharge (million tons) | ||
| Forest coverage (%) | ||
| infrastructure as a service | Public transport vehicles per ten thousand people (numbers) | |
| Urban water penetration rate (%) | ||
| Urban gas penetration rate (%) | ||
| Number of public toilets (numbers) | ||
| information service | Number of post offices per ten thousand people (numbers) | |
| Internet penetration (%) | ||
| The number of mobile phone users per ten thousand people (numbers) | ||
| Urbanization | population urbanization | Urbanization rate (%) |
| Urban population density (person/km2) | ||
| The proportion of employment in the second and third industries in the total employment (%) | ||
| economic urbanization | GDP per capita (CNY) | |
| The proportion of the tertiary industry in GDP (%) | ||
| Per capita disposable income of urban residents (CNY) | ||
| Urban fixed assets investment (one hundred million CNY) | ||
| social urbanization | Urban registered unemployment rate (%) | |
| The number of urban health technicians per ten thousand people (people) | ||
| Engel coefficient of urban households (%) | ||
| space urbanization | Urban built-up area per ten thousand people (km2/ten thousand people) | |
| Per capita urban road area (m2/people) | ||
| Green coverage rate of built-up area (%) | ||
| Tourism | tourist economy | Domestic tourism revenue (CNY one hundred million) |
| Foreign exchange earnings from tourism (USD ten thousand) | ||
| The proportion of total tourism income to GDP (%) | ||
| tourism market | Number of domestic tourists (one hundred million people) | |
| The number of inbound tourists (ten thousand people) | ||
| The growth rate of tourists (%) | ||
| tourism resources | A-level scenic spot quality total score (score) | |
| Total quality score of star hotels (score) | ||
| tourism public services | Number of travel agencies (numbers) | |
| The number of tourism practitioners (people) |
| Coordination Degree | Coordination Type | Coordination Degree | Coordination Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00~0.09 | Extreme imbalance | 0.50~0.59 | Slight coordination |
| 0.10~0.19 | Serious imbalance | 0.60~0.69 | Mild coordination |
| 0.20~0.29 | Moderate imbalance | 0.70~0.79 | Moderate coordination |
| 0.30~0.39 | Mild imbalance | 0.80~0.89 | High coordination |
| 0.40~0.49 | Slight imbalance | 0.90~1.00 | Extreme coordination |
| Judgment Basis | Interaction |
|---|---|
| q(X1X2) < min [q(X1),q(X2)] | Weaken, nonlinear |
| min [q(X1),q(X2)] < q(X1∩X2) < max [q(X1),q(X2)] | Weaken, uni- |
| q(X1∩X2) > max [q(X1),q(X2)] | Enhance, bi- |
| q(X1∩X2) = q(X1) + q(X2) | Independent |
| q(X1∩X2) > q(X1) + q(X2) | Enhance, nonlinear |
| Province | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 0.7601 | 0.7709 | 0.7536 | 0.7555 | 0.7585 | 0.7431 | 0.7504 | 0.7226 | 0.7401 | 0.7162 | 0.6840 |
| Tianjin | 0.5483 | 0.5576 | 0.5501 | 0.5550 | 0.5594 | 0.5531 | 0.5853 | 0.5490 | 0.5052 | 0.5072 | 0.5050 |
| Hebei | 0.5264 | 0.5334 | 0.5339 | 0.5136 | 0.5198 | 0.5155 | 0.5479 | 0.5427 | 0.5580 | 0.5587 | 0.5273 |
| Shanxi | 0.4915 | 0.4984 | 0.5200 | 0.5159 | 0.5122 | 0.5108 | 0.5405 | 0.5071 | 0.5159 | 0.5152 | 0.4765 |
| Inner Mongolia | 0.4766 | 0.4819 | 0.4914 | 0.4926 | 0.5012 | 0.4948 | 0.5275 | 0.5179 | 0.5144 | 0.5376 | 0.4831 |
| Liaoning | 0.6219 | 0.6274 | 0.6223 | 0.6226 | 0.6238 | 0.5762 | 0.5834 | 0.5670 | 0.5596 | 0.5539 | 0.5201 |
| Jilin | 0.4552 | 0.4608 | 0.4715 | 0.4761 | 0.4707 | 0.4751 | 0.5030 | 0.4707 | 0.4721 | 0.4711 | 0.4773 |
| Heilongjiang | 0.5146 | 0.4986 | 0.5189 | 0.4885 | 0.4856 | 0.4922 | 0.5006 | 0.4853 | 0.4759 | 0.4781 | 0.4696 |
| Shanghai | 0.7516 | 0.7232 | 0.7043 | 0.6888 | 0.6920 | 0.6759 | 0.7042 | 0.6756 | 0.6793 | 0.6528 | 0.7176 |
| Jiangsu | 0.7140 | 0.7343 | 0.7314 | 0.7016 | 0.7213 | 0.7033 | 0.7140 | 0.7107 | 0.7115 | 0.7068 | 0.7155 |
| Zhejiang | 0.7041 | 0.7151 | 0.7139 | 0.7055 | 0.7177 | 0.7134 | 0.7096 | 0.7153 | 0.7038 | 0.7003 | 0.6896 |
| Anhui | 0.4970 | 0.5252 | 0.5348 | 0.5097 | 0.5226 | 0.5202 | 0.5487 | 0.5521 | 0.5608 | 0.5711 | 0.5577 |
| Fujian | 0.5681 | 0.5751 | 0.5904 | 0.5767 | 0.5839 | 0.5799 | 0.5956 | 0.5984 | 0.5895 | 0.5958 | 0.6369 |
| Jiangxi | 0.4736 | 0.4989 | 0.5110 | 0.4874 | 0.5076 | 0.5080 | 0.5375 | 0.5397 | 0.5699 | 0.5481 | 0.5509 |
| Shandong | 0.6544 | 0.6732 | 0.6643 | 0.6527 | 0.6600 | 0.6543 | 0.6655 | 0.6638 | 0.6693 | 0.6599 | 0.6380 |
| Henan | 0.5357 | 0.5344 | 0.5463 | 0.5225 | 0.5385 | 0.5337 | 0.5615 | 0.5603 | 0.5795 | 0.5812 | 0.6105 |
| Hubei | 0.5400 | 0.5413 | 0.5501 | 0.5406 | 0.5601 | 0.5571 | 0.5822 | 0.5739 | 0.5768 | 0.5773 | 0.5587 |
| Hunan | 0.5156 | 0.5127 | 0.5152 | 0.5073 | 0.5325 | 0.5284 | 0.5536 | 0.5572 | 0.5650 | 0.5801 | 0.5928 |
| Guangdong | 0.7684 | 0.7709 | 0.7756 | 0.7585 | 0.7635 | 0.7686 | 0.7832 | 0.7788 | 0.7911 | 0.7815 | 0.7268 |
| Guangxi | 0.4536 | 0.4636 | 0.4735 | 0.4551 | 0.4651 | 0.4690 | 0.4964 | 0.5162 | 0.5324 | 0.5447 | 0.5367 |
| Hainan | 0.4150 | 0.4364 | 0.4280 | 0.4128 | 0.4148 | 0.4110 | 0.4277 | 0.4105 | 0.4153 | 0.4088 | 0.4386 |
| Chongqing | 0.5011 | 0.5063 | 0.5222 | 0.4824 | 0.5037 | 0.4975 | 0.5159 | 0.5169 | 0.5243 | 0.5207 | 0.4827 |
| Sichuan | 0.5099 | 0.5173 | 0.5372 | 0.5176 | 0.5324 | 0.5227 | 0.5490 | 0.5538 | 0.5830 | 0.5868 | 0.5816 |
| Guizhou | 0.4195 | 0.4136 | 0.4356 | 0.4269 | 0.4273 | 0.4323 | 0.4783 | 0.4910 | 0.5123 | 0.5178 | 0.4977 |
| Yunnan | 0.4698 | 0.4715 | 0.4867 | 0.4686 | 0.4845 | 0.4769 | 0.5081 | 0.5252 | 0.5345 | 0.5519 | 0.5334 |
| Tibet | 0.4014 | 0.3818 | 0.4171 | 0.3986 | 0.3834 | 0.4209 | 0.3805 | 0.3551 | 0.3722 | 0.3737 | 0.3733 |
| Shaanxi | 0.5190 | 0.5308 | 0.5432 | 0.5278 | 0.5409 | 0.5313 | 0.5428 | 0.5443 | 0.5569 | 0.5591 | 0.5166 |
| Gansu | 0.3914 | 0.4018 | 0.4391 | 0.4164 | 0.4113 | 0.4220 | 0.4389 | 0.4464 | 0.4447 | 0.4422 | 0.4333 |
| Qinghai | 0.3198 | 0.3383 | 0.3243 | 0.3428 | 0.3514 | 0.3567 | 0.3786 | 0.3854 | 0.3779 | 0.4136 | 0.3886 |
| Ningxia | 0.2838 | 0.3131 | 0.3554 | 0.3802 | 0.3057 | 0.3207 | 0.3477 | 0.4152 | 0.3093 | 0.3739 | 0.3807 |
| Xinjiang | 0.5111 | 0.4935 | 0.4937 | 0.4741 | 0.4789 | 0.4764 | 0.4921 | 0.4984 | 0.4972 | 0.5154 | 0.4728 |
| mean value | 0.5262 | 0.5323 | 0.5405 | 0.5282 | 0.5332 | 0.5304 | 0.5500 | 0.5467 | 0.5483 | 0.5517 | 0.5411 |
| Year | M (I) | Z (I) | P (I) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 0.196 | 2.983 | 0.003 |
| 2016 | 0.222 | 3.328 | 0.001 |
| 2020 | 0.247 | 3.619 | 0.000 |
| Regional Type | 2010 | 2016 | 2020 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Proportion | Amount | Proportion | Amount | Proportion | |
| high significant hot spots | 2 | 6.44 | 2 | 6.44 | 3 | 9.66 |
| medium significant hot spots | 2 | 6.44 | 3 | 9.66 | 3 | 9.66 |
| low significant hot spots | 1 | 3.22 | 2 | 6.44 | 2 | 6.44 |
| not significant | 20 | 64.58 | 18 | 58.14 | 16 | 51.7 |
| low significant cold spots | 2 | 6.44 | 1 | 3.22 | 2 | 6.44 |
| medium significant cold spots | 4 | 12.88 | 4 | 12.88 | 4 | 12.88 |
| high significant cold spots | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3.22 | 1 | 3.22 |
| unstudied area | 3 | - | 3 | - | 3 | - |
| Year | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | |||||||||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||
| 2020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Gong, J.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J. The Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling and Coordinated Development of Basic Public Services, Urbanization, and Tourism in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11753. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511753
Zhang Z, Gong J, Ma H, Zhang J. The Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling and Coordinated Development of Basic Public Services, Urbanization, and Tourism in China. Sustainability. 2023; 15(15):11753. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511753
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhongwu, Jian Gong, Huiqiang Ma, and Jinyuan Zhang. 2023. "The Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling and Coordinated Development of Basic Public Services, Urbanization, and Tourism in China" Sustainability 15, no. 15: 11753. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511753
APA StyleZhang, Z., Gong, J., Ma, H., & Zhang, J. (2023). The Spatial and Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling and Coordinated Development of Basic Public Services, Urbanization, and Tourism in China. Sustainability, 15(15), 11753. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151511753





