Evaluation of PM Chemical Composition in Thessaloniki, Greece Based on Air Quality Simulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
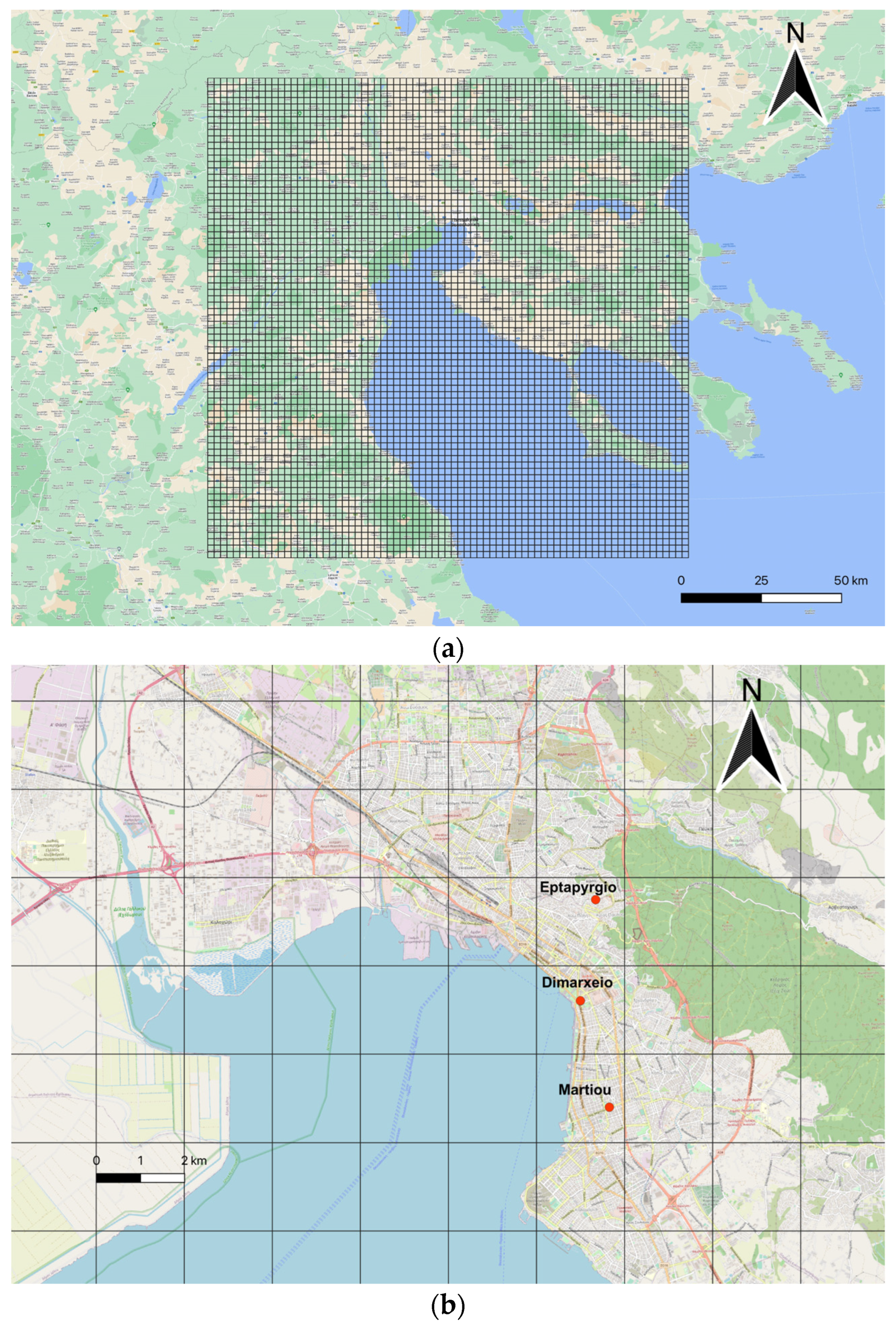
2.1. Modeling Application
2.2. Chemical Speciation
2.3. Evaluation
3. Results
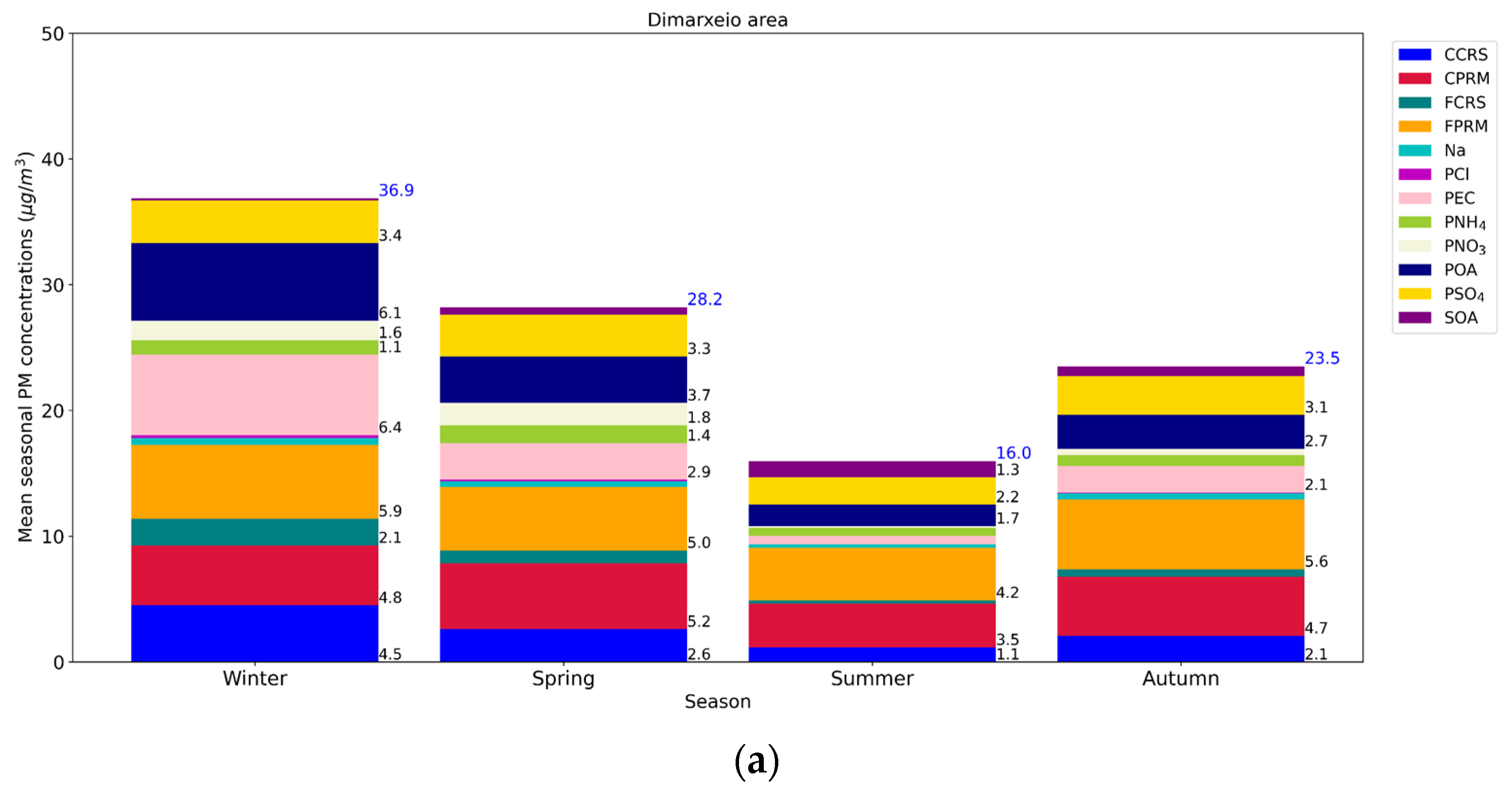
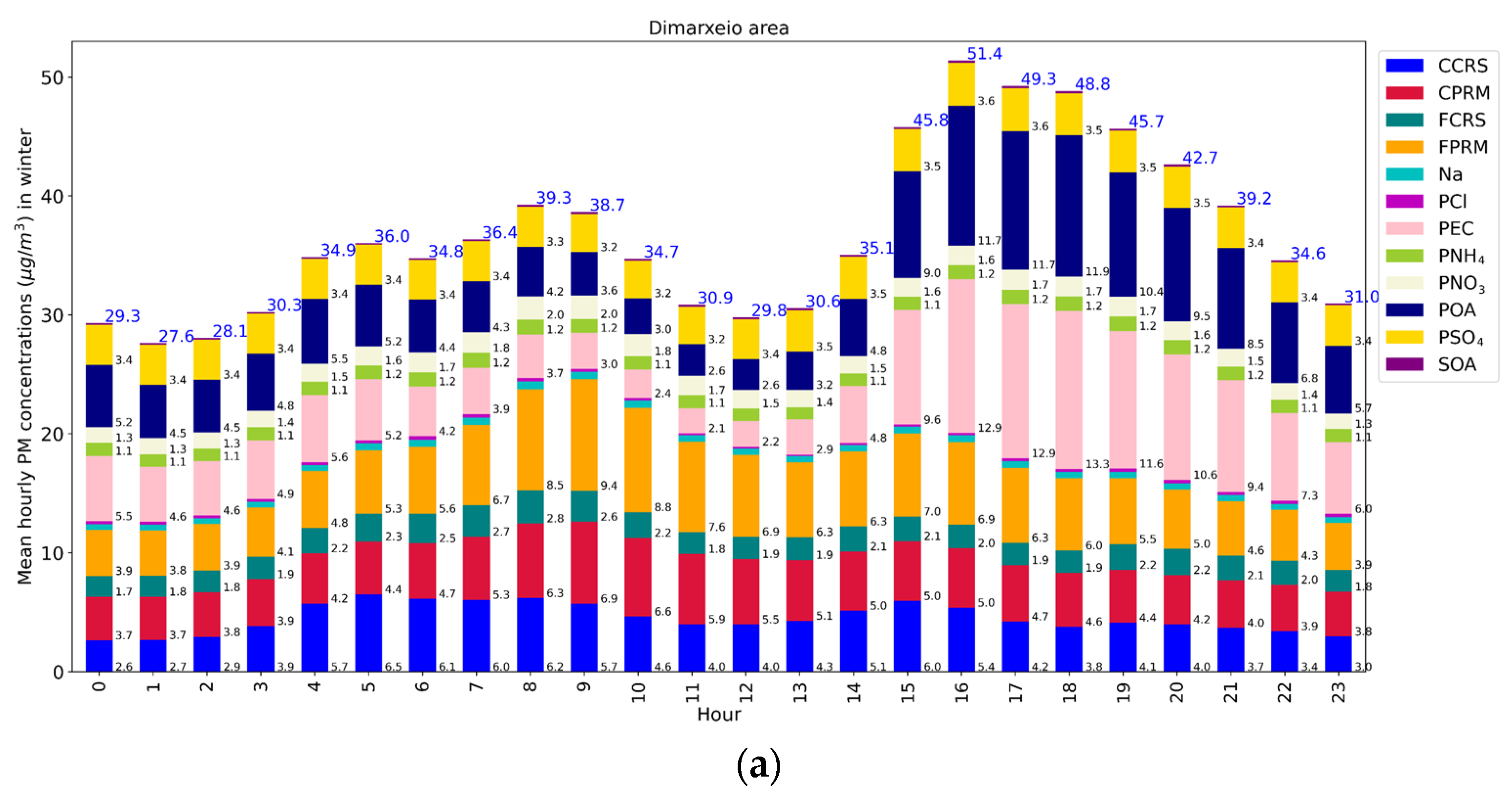
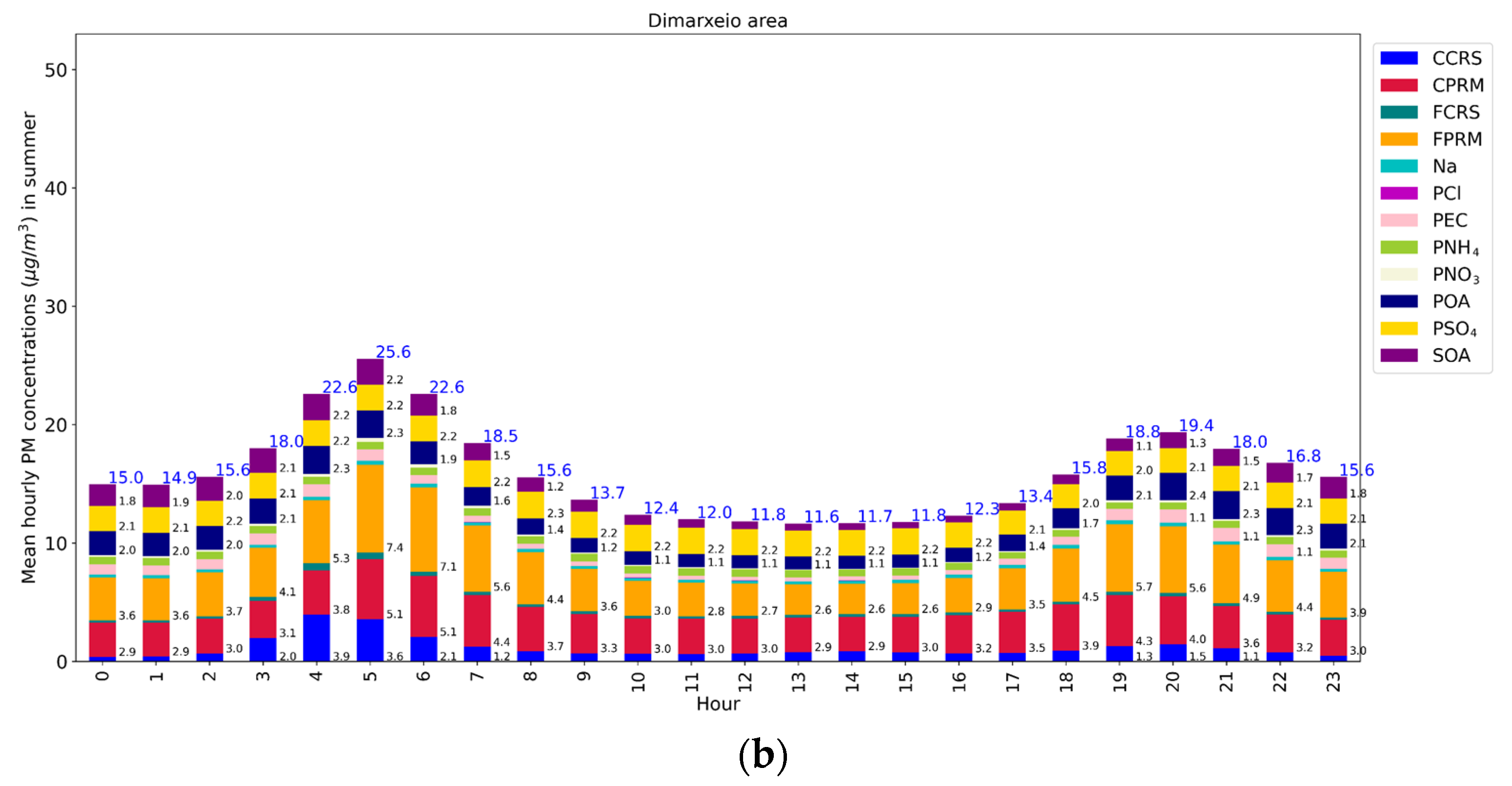
3.1. Seasonal Variation
3.1.1. Coarse and Fine Crustal Aerosols
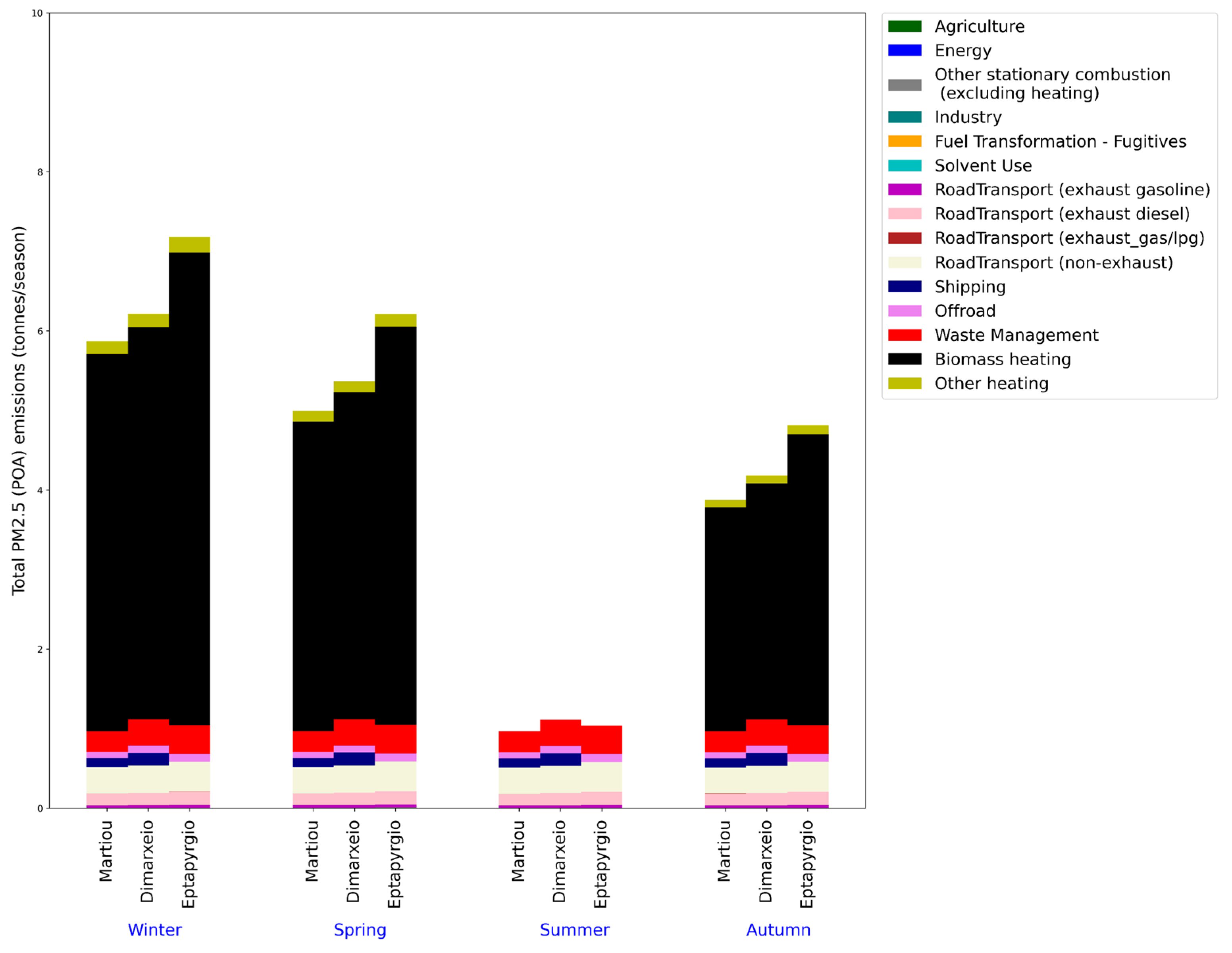
3.1.2. Coarse and Fine Other Primary Aerosols
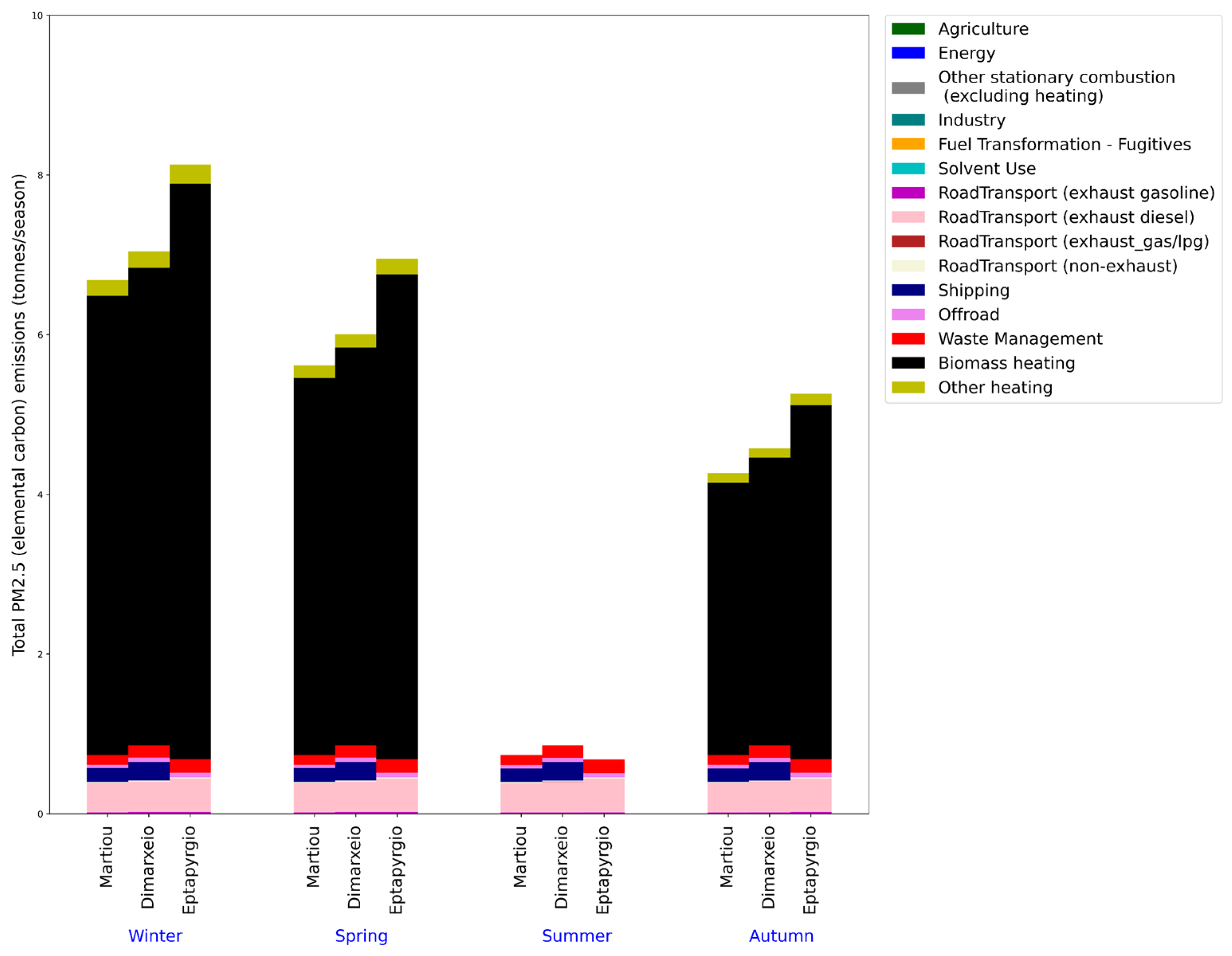
3.1.3. Carbonaceous Aerosols
3.1.4. Sulfate, Ammonium and Nitrate Aerosols
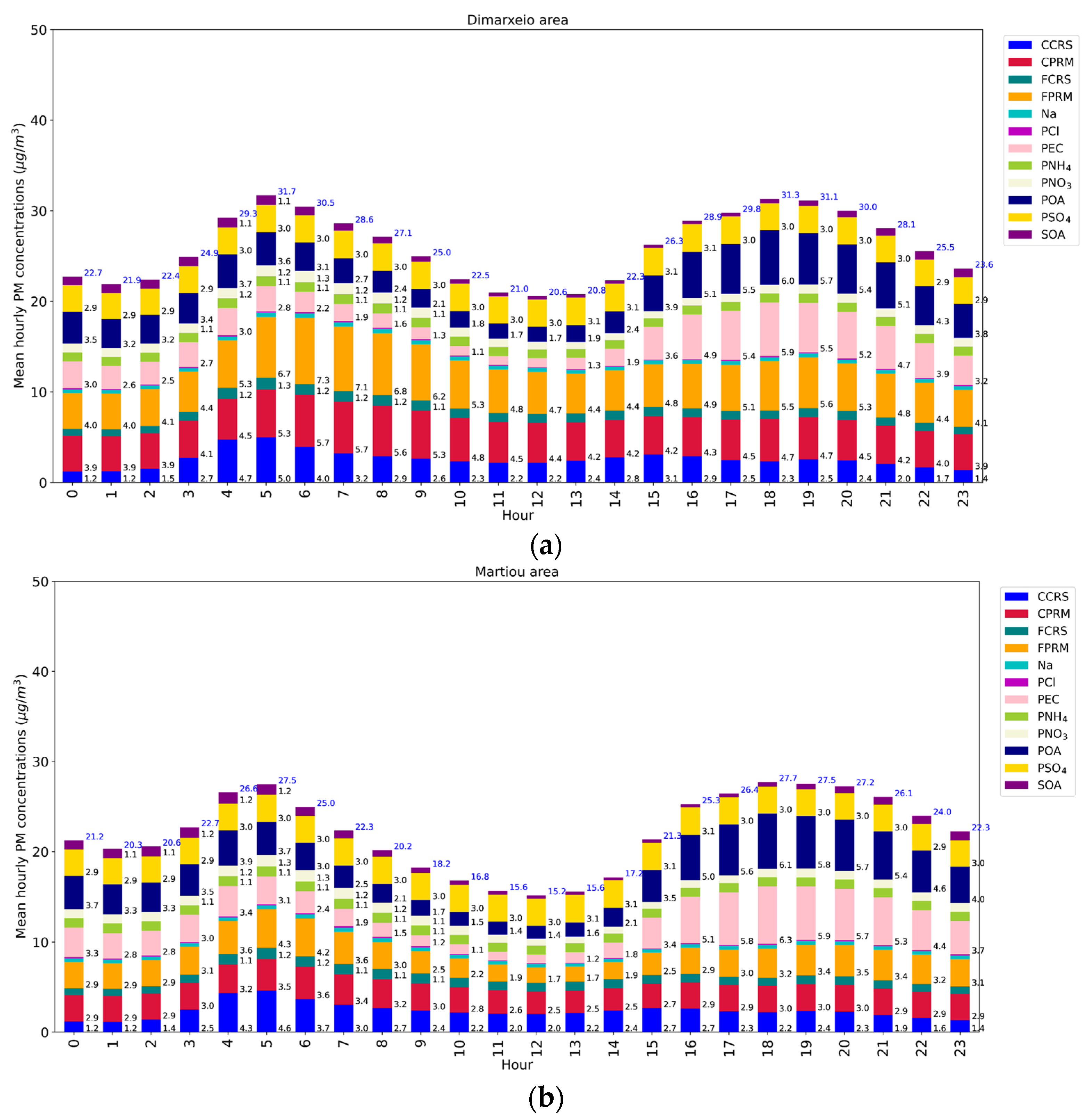
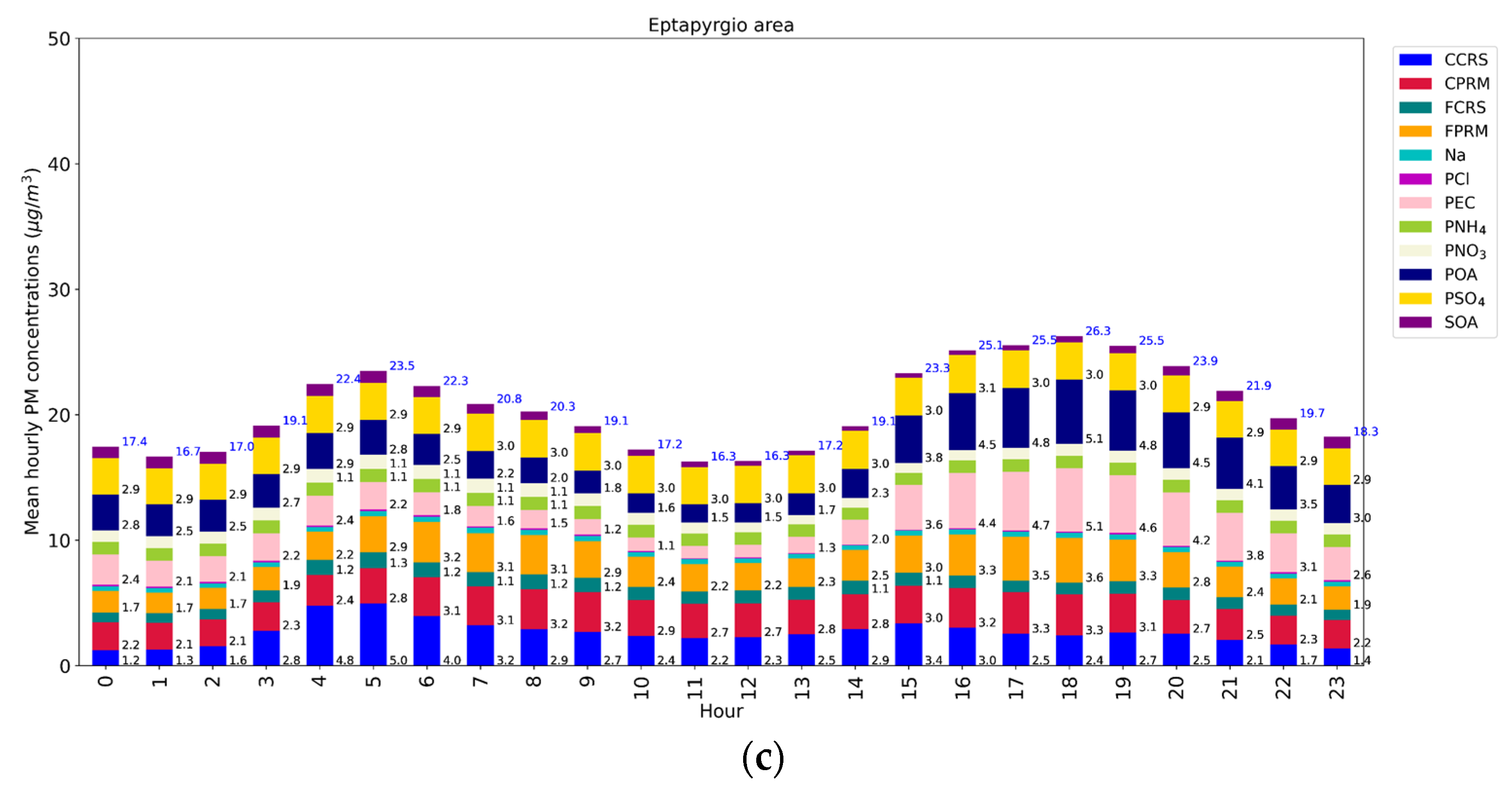
3.2. Hourly Variation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- A sensitivity analysis related to the different schemes for organic gas-aerosol partitioning and oxidation (e.g., SOAP versus VBS schemes used in CAMx model) and an improved emission inventory accounting also for SVOCs and IVOCs emissions, that have biomass burning as an important emission source, and lead to the production of SOA.
- The estimation of the emissions of minerals and other elements (e.g., Al, Si, S, K, V) and the simulation of their concentrations.
- The implementation of the Particulate Source Apportionment Technology (PSAT)) tool within CAMx for a more accurate identification of the major emissions sources contributing to PM levels.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moussiopoulos, N.; Vlachokostas, C.; Tsilingiridis, G.; Douros, I.; Hourdakis, E.; Naneris, C.; Sidiropoulos, C. Air quality status in Greater Thessaloniki Area and the emission reductions needed for attaining the EU air quality legislation. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1268–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markakis, K.; Poupkou, A.; Melas, D.; Tzoumaka, P.; Petrakakis, M. A Computational Approach Based on GIS Technology for the Development of an Anthropogenic Emission Inventory of Gaseous Pollutants in Greece. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 207, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, K.; Stavroulas, I.; Grivas, G.; Chatzidiakos, C.; Kosmopoulos, G.; Kazantzidis, A.; Kourtidis, K.; Karagioras, A.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Pandis, S.; et al. Intra- and inter-city variability of PM2.5 concentrations in Greece as determined with a low-cost sensor network. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 301, 119713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parliari, D.; Giannaros, C.; Papadogiannaki, S.; Melas, D. Short-Term Effects of Air Pollution on Mortality in the Urban Area of Thessaloniki, Greece. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psistaki, K.; Achilleos, S.; Middleton, N.; Paschalidou, A. Exploring the impact of particulate matter on mortality in coastal Mediterranean environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoke and Smog Health Effects of PM10. Available online: Https://Www.Marlborough.Govt.Nz/Environment/Air-Quality/Smoke-and-Smog/Health-Effects-of-Pm10 (accessed on 10 November 2022).
- Dunnivant, F.M.; Anders, E. A Basic Introduction to Pollutant Fate and Transport, an Integrated Approach with Chemistry, Modeling, Risk Assessment, and Environmental Legislation; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN -13. [Google Scholar]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Ueda, K.; Pozzer, A.; Lammel, G.; Kampf, C.J.; Fushimi, A.; Enami, S.; Arangio, A.M.; Fröhlich-Nowoisky, J.; Fujitani, Y.; et al. Aerosol Health Effects from Molecular to Global Scales. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 13545–13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateraki, S.; Assimakopoulos, V.; Maggos, T.; Fameli, K.; Kotroni, V.; Vasilakos, C. Particulate matter pollution over a Mediterranean urban area. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 508–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Payra, S.; Mishra, M.K.; Verma, S. An analysis of particulate pollution using urban aerosol pollution island intensity over Delhi, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, F.; Cassee, F.R.; van der Gon, H.A.D.; Gehrig, R.; Gustafsson, M.; Hafner, W.; Harrison, R.M.; Jozwicka, M.; Kelly, F.J.; Moreno, T.; et al. Urban air quality: The challenge of traffic non-exhaust emissions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 275, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liora, N.; Kontos, S.; Parliari, D.; Akritidis, D.; Poupkou, A.; Papanastasiou, D.K.; Melas, D. “On-Line” Heating Emissions Based on WRF Meteorology—Application and Evaluation of a Modeling System over Greece. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffari, A.; Daher, N.; Samara, C.; Voutsa, D.; Kouras, A.; Manoli, E.; Karagkiozidou, O.; Vlachokostas, C.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Shafer, M.M.; et al. Increased Biomass Burning Due to the Economic Crisis in Greece and Its Adverse Impact on Wintertime Air Quality in Thessaloniki. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13313–13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolis, E.I.; Saraga, D.E.; Lytra, M.K.; Papathanasiou, A.C.; Bougaidis, P.N.; Prekas-Patronakis, O.E.; Ioannidis, I.I.; Bartzis, J.G. Concentration and chemical composition of PM2.5 for a one-year period at Thessaloniki, Greece: A comparison between city and port area. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 113, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasopoulou, E.; Speyer, O.; Brunner, D.; Vogel, H.; Vogel, B.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Gerasopoulos, E. Changes in domestic heating fuel use in Greece: Effects on atmospheric chemistry and radiation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 17, 10597–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florou, K.K.; Pikridas, M.; Pandis, S.N. Wintertime Air Pollution and the Greek Financial Crisis. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 7–12 April 2013; p. 7091. [Google Scholar]
- Vouitsis, I.; Amanatidis, S.; Ntziachristos, L.; Kelessis, A.; Petrakakis, M.; Stamos, I.; Mitsakis, E.; Samaras, Z. Daily and seasonal variation of traffic related aerosol pollution in Thessaloniki, Greece, during the financial crisis. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoratos, T.; Samara, C.; Voutsa, D.; Manoli, E.; Kouras, A. Chemical composition and mass closure of ambient coarse particles at traffic and urban-background sites in Thessaloniki, Greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7708–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remoundaki, E.; Bourliva, A.; Kokkalis, P.; Mamouri, R.E.; Papayannis, A.; Grigoratos, T.; Samara, C.; Tsezos, M. PM10 Composition during an Intense Saharan Dust Transport Event over Athens (Greece). Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4361–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querol, X.; Pey, J.; Pandolfi, M.; Alastuey, A.; Cusack, M.; Perez, N.; Moreno, T.; Viana, M.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Kallos, G.; et al. African Dust Contributions to Mean Ambient PM10 Mass-Levels across the Mediterranean Basin. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 4266–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippidis, F.T.; Gerovasili, V.; Millett, C.; Tountas, Y. Medium-term impact of the economic crisis on mortality, health-related behaviours and access to healthcare in Greece. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep46423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsouyanni, K. Health Effects of Air Pollution in Southern Europe: Are There Interacting Factors? Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafoggia, M.; Zauli-Sajani, S.; Pey, J.; Samoli, E.; Alessandrini, E.; Basagaña, X.; Cernigliaro, A.; Chiusolo, M.; DeMaria, M.; Díaz, J.; et al. Desert Dust Outbreaks in Southern Europe: Contribution to Daily PM10 Concentrations and Short-Term Associations with Mortality and Hospital Admissions. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Data-Analysis in Environmental and Traffic Data for Thessaloniki Greece. Available online: Https://Ikee.Lib.Auth.Gr/Record/320630/Files/GRI-2020-28133.Pdf (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Progiou, A.; Liora, N.; Sebos, I.; Chatzimichail, C.; Melas, D. Measures and Policies for Reducing PM Exceedances through the Use of Air Quality Modeling: The Case of Thessaloniki, Greece. Sustainability 2023, 15, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markakis, K.; Poupkou, A.; Melas, D.; Zerefos, C. A GIS based anthropogenic PM10 emission inventory for Greece. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2010, 1, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psefteli, M.; Kavvadas, D.; Karacosta, P.; Cheristanidis, S.; Dimitriadou, I.; Papamitsou, T. Air Quality Index Study in the Area of Thessaloniki a Valuable Public Health Tool. Arch. Hell. Med. 2022, 39, 838–843. [Google Scholar]
- Terzi, E.; Argyropoulos, G.; Bougatioti, A.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Nikolaou, K.; Samara, C. Chemical composition and mass closure of ambient PM10 at urban sites. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2231–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liora, N.; Markakis, K.; Poupkou, A.; Giannaros, T.M.; Melas, D. The natural emissions model (NEMO): Description, application and model evaluation. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosoglou, T.; Bais, A.F.; Zyrichidou, I.; Kouremeti, N.; Poupkou, A.; Liora, N.; Giannaros, C.; Koukouli, M.E.; Balis, D.; Melas, D. Comparisons of Ground-Based Tropospheric NO2 MAX-DOAS Measurements to Satellite Obser-vations with the Aid of an Air Quality Model over the Thessaloniki Area, Greece. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5829–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liora, N.; Poupkou, A.; Giannaros, T.M.; Kakosimos, K.E.; Stein, O.; Melas, D. Impacts of natural emission sources on particle pollution levels in Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 137, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marecal, V.; Peuch, V.-H.; Andersson, C.; Andersson, S.; Arteta, J.; Beekmann, M.; Benedictow, A.; Bergstrom, R.W.; Bessagnet, B.; Cansado, A.; et al. A regional air quality forecasting system over Europe: The MACC-II daily ensemble production. Geosci. Model Dev. 2015, 8, 2777–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontos, S.; Liora, N.; Giannaros, C.; Kakosimos, K.; Poupkou, A.; Melas, D. Modeling natural dust emissions in the central Middle East: Parameterizations and sensitivity. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 190, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontos, S.; Kakosimos, K.; Liora, N.; Poupkou, A.; Melas, D. Towards a Regional Dust Modeling System in the Central Middle East: Evaluation, Uncertainties and Recommendations. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Duda, M.G.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3; U.S. National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- ENVIRON. User’s Guide CAMx Comprehensive Air Quality Model with Extensions, 6., 5th ed.; Ramboll US Corporation: Novato, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Granier, C.; Darras, S.; van Der Gon, H.D.; Jana, D.; Elguindi, N.; Bo, G.; Michael, G.; Marc, G.; Jalkanen, J.P.; Kuenen, J.; et al. The Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service Global and Regional Emissions (April 2019 Version), Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS) Report; Laboratoire d’Aérologie: Toulouse, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Schaap, M.; Manders, A.M.M.; Hendriks, E.C.J.; Cnossen, J.M.; Segers, A.J.S.; Denier van Der Gon, H.A.C.; Jozwicka, M. Regional Modelling of Particulate Matter for The Netherlands; Research Program on Particulate Matter; PBL: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tolis, E.I.; Saraga, D.; Filiou, K.F.; Tziavos, N.; Tsiaousis, C.P.; Dinas, A.; Bartzis, J.G. One-year intensive characterization on PM2.5 nearby port area of Thessaloniki, Greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 6812–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.G.; Lee, T.; Roberts, P.T.; Collett, J.L., Jr. Variations in the OM/OC ratio of urban organic aerosol next to a major roadway. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2013, 63, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevopoulou, D.; Liakakou, E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Theodosi, C.; Mihalopoulos, N. Long-Term Characterization of Organic and Elemental Carbon in the PM2.5 Fraction: The Case of Athens, Greece. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13313–13325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guinot, B.; Shen, Z.; Ho, K.F.; Niu, X.; Xiao, S.; Huang, R.-J.; Cao, J. Characteristics of Organic and Elemental Carbon in PM2.5 and PM0.25 in Indoor and Outdoor Environments of a Middle School: Secondary Formation of Organic Carbon and Sources Identification. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 361–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskaoutis, D.G.; Grivas, G.; Theodosi, C.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Stavroulas, I.; Liakakou, E.; Gkikas, A.; Hatzianastassiou, N.; Wu, C.; et al. Carbonaceous Aerosols in Contrasting Atmospheric Environments in Greek Cities: Evaluation of the EC-tracer Methods for Secondary Organic Carbon Estimation. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katragkou, E.; Kazadzis, S.; Amiridis, V.; Papaioannou, V.; Karathanasis, S.; Melas, D. PM10 regional transport pathways in Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, K.; Kassomenos, P. A meteorological analysis of PM10 episodes at a high altitude city and a low altitude city in central Greece—The impact of wood burning heating devices. Atmos. Res. 2018, 214, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, K.; Kassomenos, P. Estimation of North African dust contribution on PM10 episodes at four continental Greek cities. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 106, 105530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics from Air Pollution to Climate Change; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; ISBN-13: 978-0-471-72018-8. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilatou, V.; Manousakas, M.; Gini, M.; Diapouli, E.; Scoullos, M.; Eleftheriadis, K. Long Term Flux of Saharan Dust to the Aegean Sea around the Attica Region, Greece. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanni NASA. Available online: Https://Giovanni.Gsfc.Nasa.Gov/Giovanni/ (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Worldview NASA. Available online: Https://Worldview.Earthdata.Nasa.Gov/ (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Diapouli, E.; Manousakas, M.; Vratolis, S.; Vasilatou, V.; Maggos, T.; Saraga, D.; Grigoratos, T.; Argyropoulos, G.; Voutsa, D.; Samara, C.; et al. Evolution of air pollution source contributions over one decade, derived by PM10 and PM2.5 source apportionment in two metropolitan urban areas in Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 164, 416–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salameh, D.; Detournay, A.; Pey, J.; Pérez, N.; Liguori, F.; Saraga, D.; Bove, M.C.; Brotto, P.; Cassola, F.; Massabò, D.; et al. PM2.5 chemical composition in five European Mediterranean cities: A 1-year study. Atmos. Res. 2015, 155, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scerri, M.M.; Weinbruch, S.; Delmaire, G.; Mercieca, N.; Nolle, M.; Prati, P.; Massabò, D. Exhaust and non-exhaust contributions from road transport to PM10 at a Southern European traffic site. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavroulas, I.; Bougiatioti, A.; Grivas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Zarmpas, P.; Liakakou, E.; Gera-sopoulos, E.; Mihalopoulos, N. Sources and Processes That Control the Submicron Organic Aerosol Composi-tion in an Urban Mediterranean Environment (Athens): A High Temporal-Resolution Chemical Composition Measurement Study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 901–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakakou, E.; Stavroulas, I.; Kaskaoutis, D.; Grivas, G.; Paraskevopoulou, D.; Dumka, U.; Tsagkaraki, M.; Bougiatioti, A.; Oikonomou, K.; Sciare, J.; et al. Long-term variability, source apportionment and spectral properties of black carbon at an urban background site in Athens, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 222, 117137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, C.; Voutsa, D.; Kouras, A.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Maggos, T.; Saraga, D.; Petrakakis, M. Organic and elemental carbon associated to PM10 and PM2.5 at urban sites of northern Greece. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 21, 1769–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraga, D.; Maggos, T.; Degrendele, C.; Klánová, J.; Horvat, M.; Kocman, D.; Kanduč, T.; Dos Santos, S.G.; Franco, R.; Gómez, P.M.; et al. Multi-city comparative PM2.5 source apportionment for fifteen sites in Europe: The ICARUS project. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 751, 141855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Special Issue “Secondary Organic Aerosol (SOA) Formation, Properties and Evolution in the Atmosphere”. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/journal/atmosphere/special_issues/SOA_Atmosphere (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Voutsa, D.; Samara, C.; Manoli, E.; Lazarou, D.; Tzoumaka, P. Ionic composition of PM2.5 at urban sites of northern Greece: Secondary inorganic aerosol formation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 21, 4995–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastos, P.T.; Larissi, I.K.; Grigoropoulos, K.N.; Antoniou, A.; Paliatsos, A.G. Indoor and Outdoor Particulate Matter Variability in Athens, Greece. Indoor Built Environ. 2012, 22, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, E.A.; Seltzer, K.M.; Murphy, B.N.; Qin, M.; Seinfeld, J.H.; Pye, H.O.T. Modeling secondary organic aerosol formation from volatile chemical products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 21, 18247–18261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Aksoyoglu, S.; El-Haddad, I.; Ciarelli, G.; van der Gon, H.A.C.D.; Canonaco, F.; Gilardoni, S.; Paglione, M.; Minguillón, M.C.; Favez, O.; et al. Sources of organic aerosols in Europe: A modeling study using CAMx with modified volatility basis set scheme. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 19, 15247–15270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, A.; Pirovano, G.; Gilardoni, S.; Lonati, G.; Colombi, C.; Gianelle, V.; Paglione, M.; Poluzzi, V.; Riva, G.; Toppetti, A. Investigating the role of chemical and physical processes on organic aerosol modelling with CAMx in the Po Valley during a winter episode. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 171, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoukis, C.; Megaritis, A.G.; Skyllakou, K.; Charalampidis, P.E.; Denier van Der Gon, H.A.C.; Crippa, M.; Prev Ot, A.S.H.; Fachinger, F.; Wiedensohler, A.; Pilinis, C.; et al. Simulating the Formation of Carbonaceous Aerosol in a European Megacity (Paris) during the MEGAPOLI Summer and Winter Campaigns. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 15, 25547–25582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, J.H.; Seinfeld, J.H. Chemistry of secondary organic aerosol: Formation and evolution of low-volatility organics in the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3593–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basla, B.; Agresti, V.; Balzarini, A.; Giani, P.; Pirovano, G.; Gilardoni, S.; Paglione, M.; Colombi, C.; Belis, C.A.; Poluzzi, V.; et al. Simulations of Organic Aerosol with CAMx over the Po Valley during the Summer Sea-son. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1996. Available online: Https://Www.Mdpi.Com/2073-4433/13/12/1996/Pdf (accessed on 24 June 2023). [CrossRef]
- Giani, P.; Balzarini, A.; Pirovano, G.; Gilardoni, S.; Paglione, M.; Colombi, C.; Gianelle, V.L.; Belis, C.A.; Poluzzi, V.; Lonati, G. Influence of Semi- and Intermediate-Volatile Organic Com-pounds (S/IVOC) Parameterizations, Volatility Distributions and Aging Schemes on Organic Aerosol Modelling in Winter Conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strader, R.; Lurmann, F.W.; Pandis, S.N. Evaluation of Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation in Winter. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 4849–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.; Knipping, E.; Yarwood, G. 1.5-Dimensional volatility basis set approach for modeling organic aerosol in CAMx and CMAQ. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ye, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; et al. Aqueous production of secondary organic aerosol from fossil-fuel emissions in winter Beijing haze. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022179118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


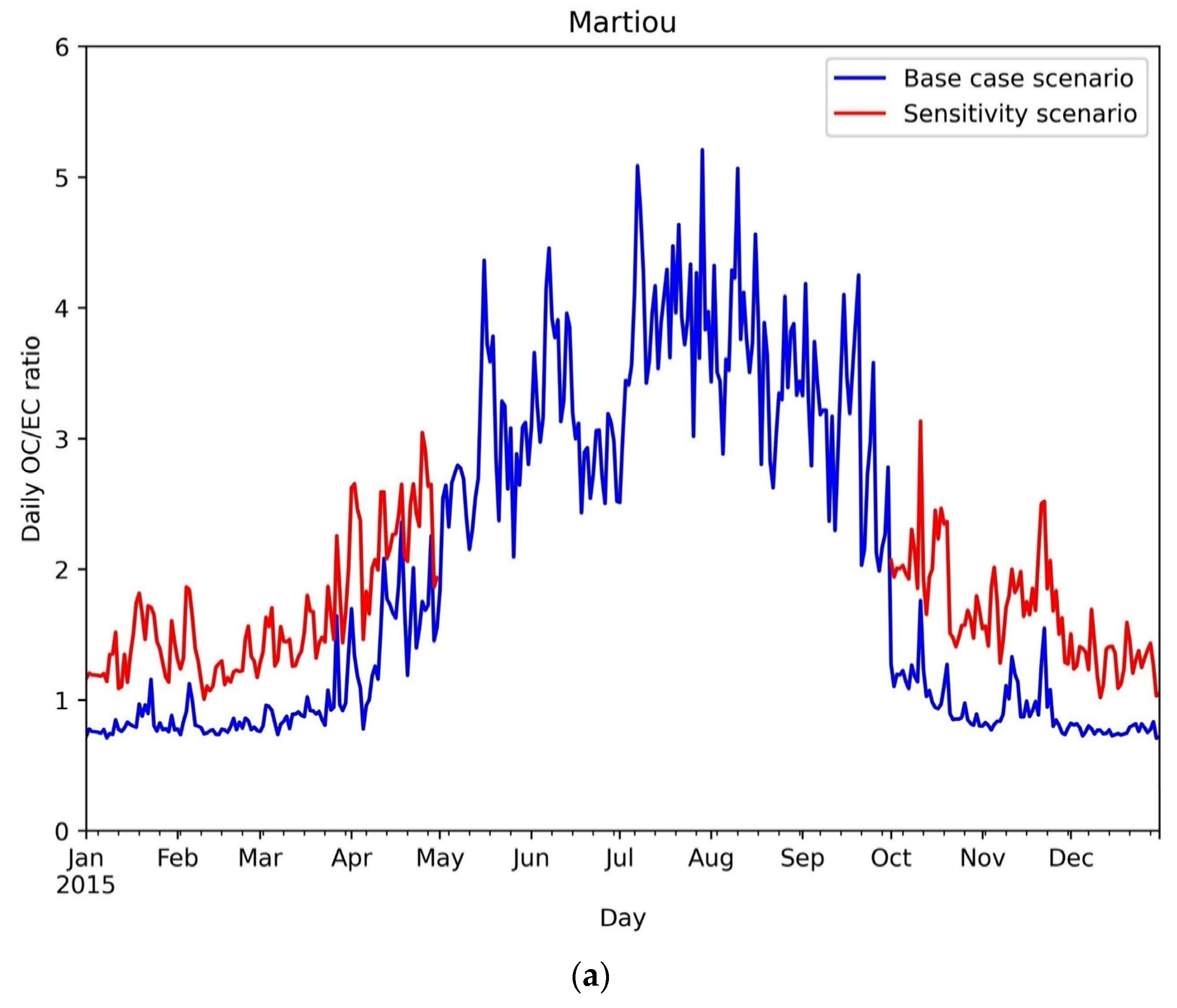
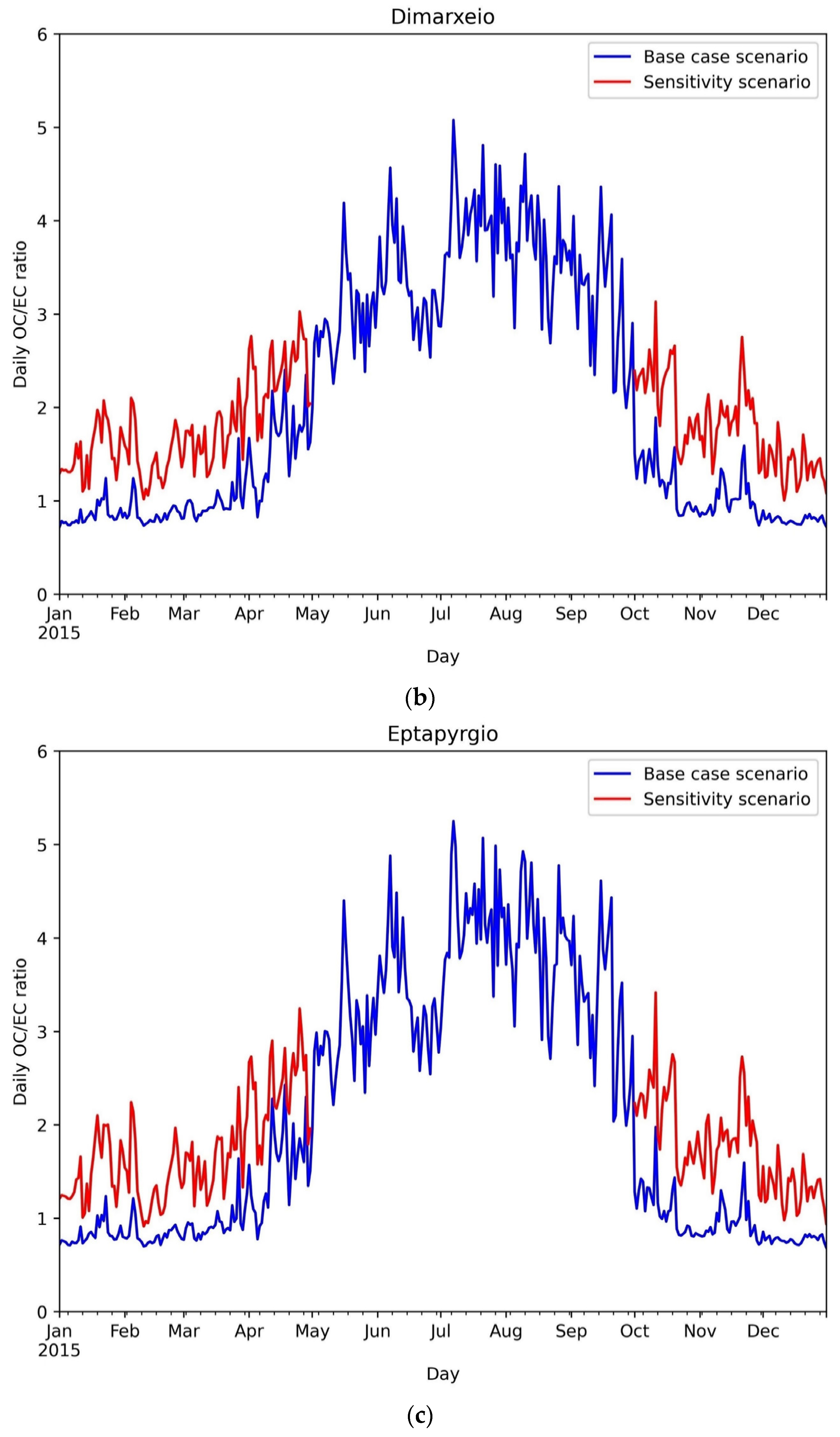
| Internal Label | Name |
|---|---|
| PSO4 | Particulate Sulfate |
| PNO3 | Particulate Nitrate |
| PNH4 | Particulate Ammonium |
| Na | Sodium |
| PCl | Particulate Chloride |
| PEC | Primary Elemental Carbon |
| FPRM | Fine Other Primary () |
| FCRS | Fine Crustal () |
| POA | Primary Organic Aerosol |
| SOA | Secondary Organic aerosol |
| CPRM | Coarse Other Primary (2.5 μm ) |
| CCRS | Coarse Crustal (2.5 μm ) |
| Base Case * (Dimensionless) | Sensitivity Scenario ** (Dimensionless) | |
|---|---|---|
| POA | 0.42 | 0.8 |
| PEC | 0.51 | 0.1 |
| Other species | 0.07 | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsiaousidis, D.T.; Liora, N.; Kontos, S.; Poupkou, A.; Akritidis, D.; Melas, D. Evaluation of PM Chemical Composition in Thessaloniki, Greece Based on Air Quality Simulations. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10034. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310034
Tsiaousidis DT, Liora N, Kontos S, Poupkou A, Akritidis D, Melas D. Evaluation of PM Chemical Composition in Thessaloniki, Greece Based on Air Quality Simulations. Sustainability. 2023; 15(13):10034. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310034
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsiaousidis, Dimitrios Theodoros, Natalia Liora, Serafim Kontos, Anastasia Poupkou, Dimitris Akritidis, and Dimitrios Melas. 2023. "Evaluation of PM Chemical Composition in Thessaloniki, Greece Based on Air Quality Simulations" Sustainability 15, no. 13: 10034. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310034
APA StyleTsiaousidis, D. T., Liora, N., Kontos, S., Poupkou, A., Akritidis, D., & Melas, D. (2023). Evaluation of PM Chemical Composition in Thessaloniki, Greece Based on Air Quality Simulations. Sustainability, 15(13), 10034. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151310034










