Economical Productivity of Maize Genotypes under Different Herbicides Application in Two Contrasting Climatic Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Emergence
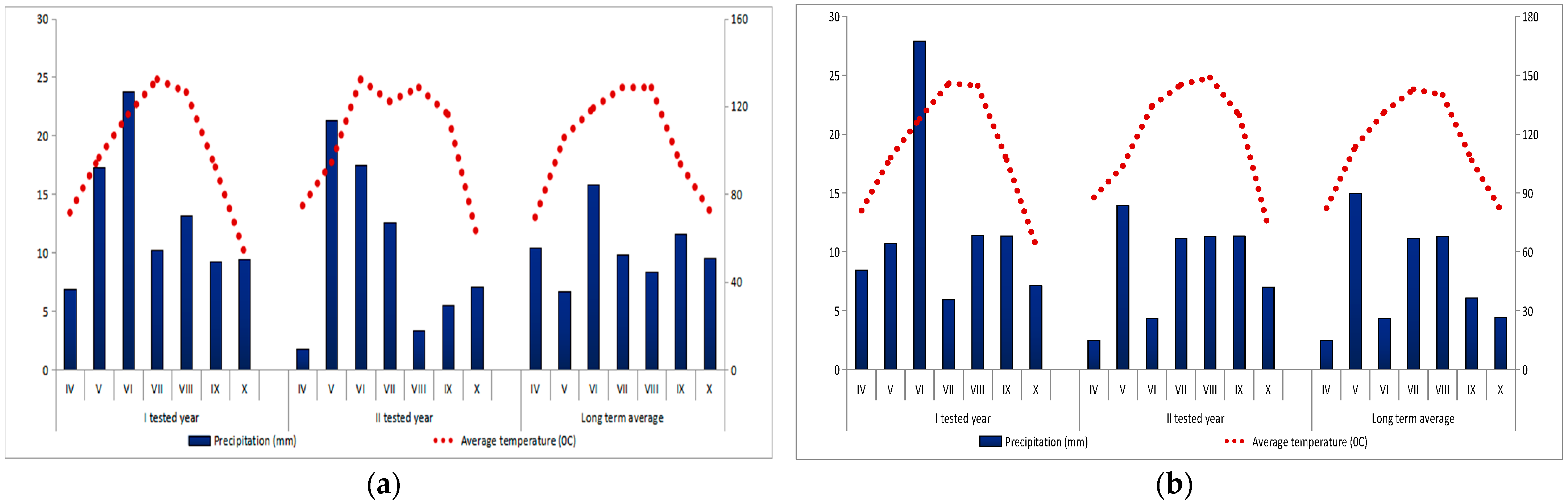
2.2. Meteorological Data
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mean Values of Grain Yield of Maize
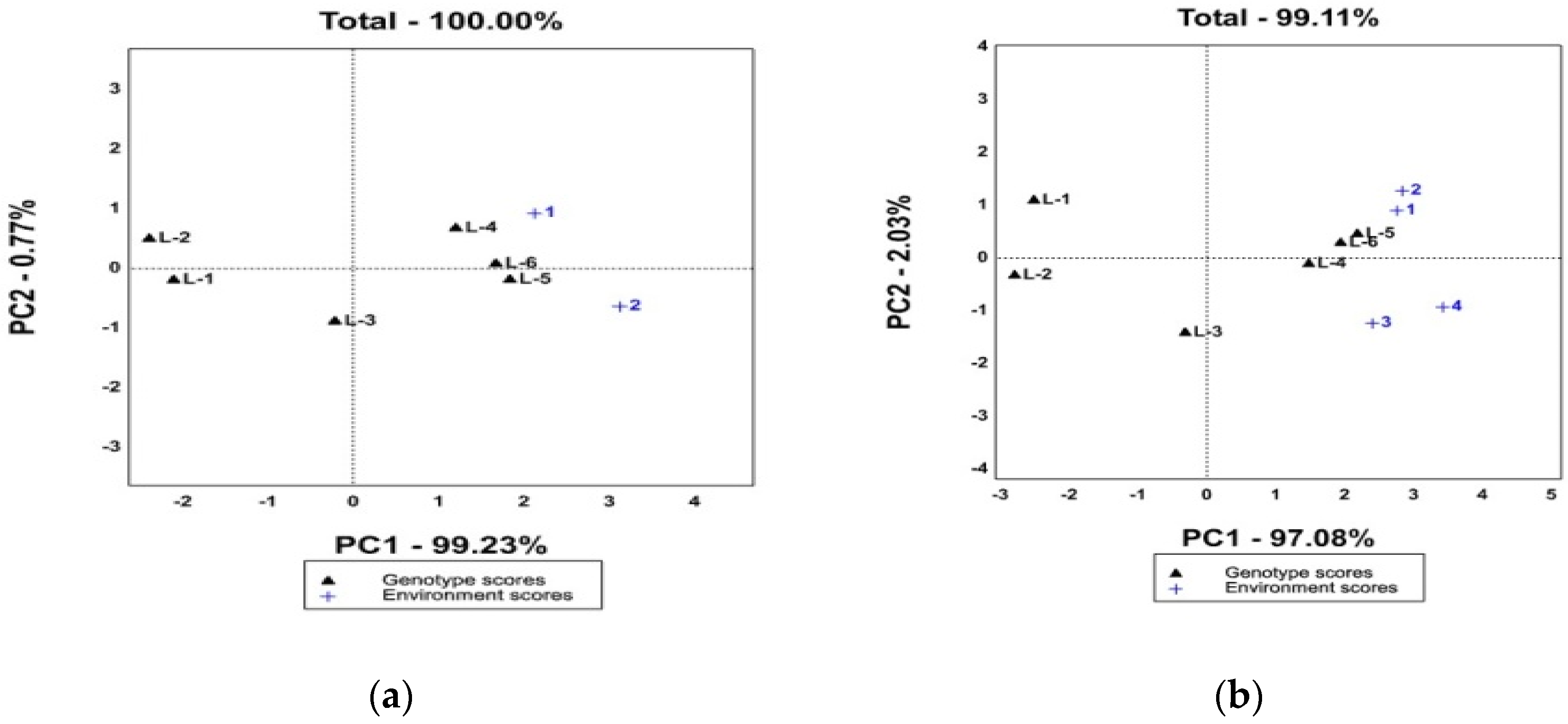
3.2. Mean Values of Hundred Grains Weight and Interaction IPCA1 and IPCA2
3.3. Analysis of Variance-ANOVA for Hundred Grains Weight of Maize (g)
3.4. Stability of Hundred Grains Weight of Maize
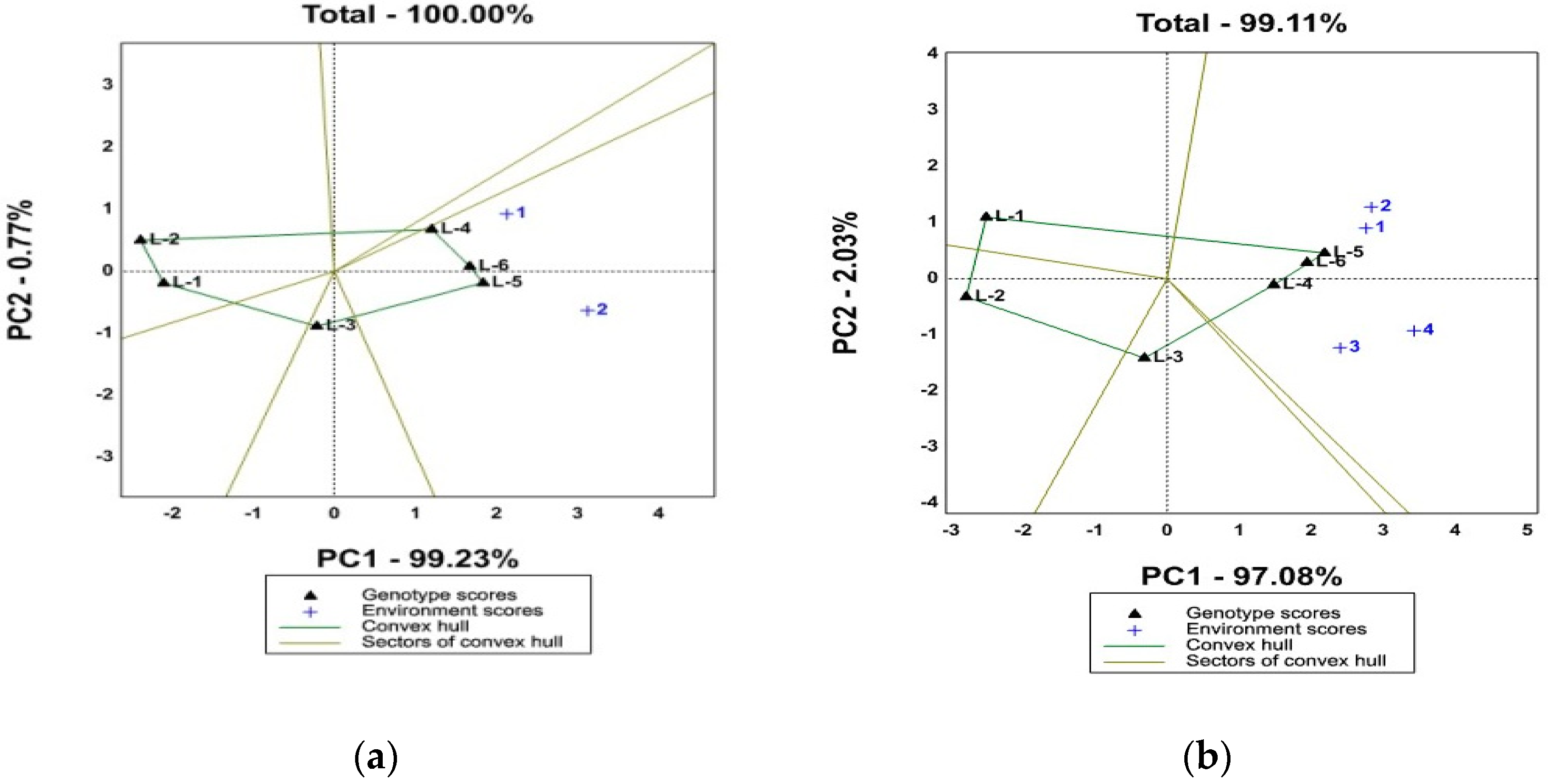
3.5. Stability of Hundred Grains Weight of Maize by Model “Which-Won-Where”
3.6. GGE Biplot Display of Hundred Grains Weight According to the Ideal Genotype Model Based on the Locality
3.7. Correlation Relations between Traits–Spearman’s Coefficient
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, S.; Wei, F.; Nguyen, J.; Bechner, M.; Potamousis, K.; Goldstein, S.A. Single Molecule Scaffold for the Maize Genome. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šarčević-Todosijević, L.; Živanović, L.; Popović, V.; Ikanović, J.; Popović, S.; Dražić, G. The Influence of Nitrogen Fertilizer on the Total Number of Microorganisms and Amino Auto-Troph Dynamics under “Ugar” and Sown Maize. Agric. For. 2016, 62, 185–196. [Google Scholar]
- Božović, D.; Živanović, T.; Popović, V.; Tatić, M.; Gospavić, Z.; Miloradović, Z.; Stanković, G.; Đokić, M. Assessment Stability of Maize Lines Yield by GGE-Biplot Analysis. Genetika 2018, 50, 755–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božović, D.; Popović, V.; Rajičić, V.; Kostić, M.; Filipović, V.; Kolarić, Lj.; Ugrenović, V.; Spalević, V. Stability of the Expression of the Maize Pproductivity Parameters by AMMI Models and GGE-Biplot Analysis. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2020, 48, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, V.; Kravić, N.; Vančetović, J.; Delić, N.; Žilić, S. Differences in Nutritive and Bioactive Compounds Content between Hybrid and Open-Pollinated Maize Varieties. Food Feed Res. 2020, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Office of the Republic of Serbia. Monthly Statistical Bulletin, 2019. Available online: https://www.stat.gov.rs/en-us/publikacije/publication/?p=12169 (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Trademap. Available online: https://www.trademap.org/Product_SelCountry_TS.aspx?nvpm=1%7c688%7c%7c%7c%7c1005%7c%7c%7c4%7c1%7c1%7c2%7c2%7c1%7c1%7c1%7c1%7c1 (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Millet, E.J.; Kruijer, W.; Coupel-Ledru, A.; Alvarez Prado, S.; Cabrera-Bosquet, L.; Lacube, S.; Charcosset, A.; Welcker, C.; van Eeuwijk, F.; Tardieu, F. Genomic Prediction of Maize Yield across European Environmental Conditions. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branković-Radojčić, D.; Babić, V.; Girek, Z.; Živanović, T.; Radojčić, A.; Filipović, M.; Srdić, J. Evaluation of Maize Grain Yield and Yield Stability by AMMI Analysis. Genetika 2018, 50, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, V.; Vučković, S.; Jovović, Z.; Rakaščan, N.; Kostić, M.; Ljubičić, N.; Mladenović Glamočlija, M.; Ikanović, J. Genotype by Year Interaction Effects on Soybean Morpho-Productive Traits and Biogas Production. Genetika 2020, 52, 1055–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, V. Influence of Agro-Technical and Agro-Ecological Practices on Seed Production of Wheat, Maize and Soybean. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Belgrade, Faculty of Agriculture, Belgrade, Serbia, 2010; pp. 30–60. [Google Scholar]
- Popović, V.; Ljubičić, N.; Kostić, M.; Radulović, M.; Blagojević, D.; Ugrenović, V.; Popović, D.; Ivošević, B. Genotype × Environment Interaction for Wheat Yield Traits Suitable for Selection in Different Seed Priming Conditions. Plants 2020, 9, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimović, L.; Popović, V.; Stevanović, P. Water and Irrigation Requirements of Field Crops Grown in Central Vojvodina, Serbia. Agric. For. 2018, 64, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.A.; Doerksen, T.K.; Kannenberg, L.W. An Empirical Method of Grouping Genotypes Based on a Linear Function of the Genotype-Environment Interaction. Herediry 2003, 34, 255–263. [Google Scholar]
- Foroozanfar, M.; Zeynali, H. Inheritance of Some Correlated Traits in Bread Wheat Using Generation Mean Analysis. Adv. Crop Sci. 2013, 3, 436–443. [Google Scholar]
- Ljubičič, N.; Petrović, S.; Dimitrijević, M.; Hristov, N. Gene Actions Involved in the Inheritance of Yield Related Traits in Bread Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Emir. J. Food Agric. 2016, 28, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbaji, M.I. Effects of N Rates and Intra Row Spacing on Local Maize (Zea mays L.) in the Southern Guinea. J. Sustain. Agric. Environ. 2003, 5, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Maqbool, M.M.; Tanveer, A.; Ali, A.; Abbas, M.N.; Imran, M.; Quayyum, M.A.; Ahmad, A.; Abid, A.A. Growth and Yield Response of Maize (Zea mays) to Inter and Intra-Row Weed Competition under Different Fertilizer Application Methods. Planta Daninha 2016, 34, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, M.; Babić, V.; Delić, N.; Anđelković, V.; Prodanović, S. The Comparison of Stability Parameters According to the Finlay-Wilkinson, Eberhart-Russell and AMMI Model. Sel. Semen. 2011, 7, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kolarić, Lj.; Popović, V.; Živanović, Lj.; Ljubičić, N.; Stevanović, P.; Šarčević Todosijević, Lj.; Simić, D.; Ikanović, J. Buckwheat Yield Traits Response as Influenced by Row Spacing, Nitrogen, Phosphorus and Potassium Management. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugrenović, V.; Popović, V.; Ugrinović, M.; Filipović, V.; Mačkić, K.; Ljubičić, N.; Popović, S.; Lakić, Ž. Black Oat (Avena strigosa Schreb.) Ontogenesis and Agronomic Performance in Organic Cropping System and Pannonian Environments. Agriculture 2021, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, M.; Čanak, P.; Vujošević, B.; Babić, V.; Stanisavljević, D. Significance of Field Trials Data Cleaning Process for Making More Reliable Breeder Decisions. Sel. Semen. 2019, 25, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badu-Apraku, G.B.; Oyekunele, M.; Fokorede, M.A.B.; Vroh, I.; Akinwale, R.O.; Aderounmu, M. Combiningability, Heterotic Patterns and Genetic Diversity of Extra-Early Yellow Inbreeds under Contrasting Environments. Euphytica 2013, 192, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M. Using Genotype-by-Environment Interaction for Crop Cultivar Development. Adv. Agron. 1998, 62, 199–252. [Google Scholar]
- Mitrović, B.; Drašković, B.; Stanisavljević, D.; Perišić, M.; Čanak, P.; Mitrović, I.; Tančić-Živanov, S. Environmental Modeling of Interaction Variance for Grain Yield of Medium Early Maturity Maize Hybrids. Genetika 2020, 52, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zečević, V.; Knežević, D.; Mićanović, D.; Madić, M. Genetic and Phenotypic Variability of Spike Length and Plant Height in Wheat. Kragujevac J. Sci. 2008, 30, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- Lu’quez, J.E.; Aguirrezabal, L.A.N.; Aguëro, M.E.; Pereyra, V.R. Stability and Adaptability of Cultivars in Non-balanced Yieldtrials: Comparison of Methods for Selecting ‘High Oleic’ Sunflower Hybrids for Grain Yield and Quality. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2002, 188, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.M.; Kang, M.S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, J.; Xu, C. Yield Stability of Maize Hybrids Evaluated in Multi-Environment Trials in Yunnan, China. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobel, R.W. A Powerful Statistical Model for Understanding Genotype by Environment Interaction. In Genotype by Environment Interaction and Plant Breeding; Kang, M.S., Ed.; Louisiana State University: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1990; pp. 126–140. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, M.; Kokten, K.; Akcura, M. Assessment of Genotype × Trait × Environment Interactions of Silage Maize Genotypes through GGE Biplot. Chilean J. Agric. Res. 2017, 77, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zobel, R.W.; Wright, M.J.; Gauch, H.G. Statistical Analysis of a Yield Trial. Agron. J. 1988, 80, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauch, H.G. Statistical Analysis of Yield Trials by AMMI and GGE. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodig, D.; Zorić, M.; Knežević, D.; King, S.; Šurlan-Momirović, G. Genotype × Environment Interaction for Wheat Yield in Different Drought Stress Conditions and Agronomic Traits Suitable for Selection. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2008, 59, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauch, H.G.; Moran, D.R. AMMISOFT for AMMI Analysis with Best Practices. Soil Crop. Sci. 2019, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Tier, W.Y. Application of GGE Biplot Analysis to Evaluate Genotype (G), Environment (E) and G × E Interaction on P. Radiata: A Case Study. In Proceedings of the Australasian Forest Genetics Conference Breeding for Wood Quality, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 11–14 April 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ilker, E.; Tonk, F.; Çaylak, Ö.; Tosun, M.; Özmen, İ. Assessment of Genotype X Enviroment Interactions for Grain Yield in Maize Hybrids Using AMMI and GGE Biplot Analyses. Turk. J. Field Crops 2009, 14, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Gauch, H.G. Statistical Analysis of Regional Yield Trials: AMMI Analysis of Factorial Designs; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; p. 278. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.L.; Yan, W.; Dwyer, L.M.; Frégeau-Reid, J.; Voldeng, H.D.; Dion, Y.; Nass, H. Graphic Analysis of Genotype, Environment, Nitrogen Fertilizer, and Their Interaction on Spring Wheat Yield. Agron. J. 2004, 96, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Faostat Database. 2022. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/site/567/default.aspx#ancor (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Rahimi Jahangirlou, M.; Akbari, G.A.; Alahdadi, I.; Soufizadeh, S.; Parsons, D. Grain Quality of Maize Cultivars as a Function of Planting Dates, Irrigation and Nitrogen Stress: A Case Study from Semiarid Conditions of Iran. Agriculture 2021, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdia, L.K.; Wadhwani, R.; Wadhawan, N.; Bajpai, P.; Shekhawat, S. Maize Utilization in India: An Overview. Am. J. Food Nutr. 2016, 4, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenov, V.; Dimitrijević, M.; Petrović, S.; Boćanski, J.; Banjac, B.; Kondić-Špika, A.; Trkulja, D. Genetic Analysis of Spike Length in Wheat. Genetika 2019, 51, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Kang, M.S.; Ma, B.L.; Woods, S.; Cornelius, P.L. GGE Biplot vs. AMMI Analysis of Genotype-by-Environment Data. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Reddy, P.S.; Rathore, A.; Reddy, B.; Panwar, V.S. Application GGE Biplot and AMMI Model to Evaluate Sweet Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) Hybrids for Genotype × Environment Interaction and Seasonal Adaptation. Indian J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 81, 438–844. [Google Scholar]
- Knežević, D.; Paunović, A.; Madić, M.; Djukic, N. Genetic Analysis of Nitrogen Accumulation in Four Wheat Cultivars and Their Hybrids. Cereal Res. Commun. 2007, 35, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoune-Tandzi, L.; Mutengwa, CS. Estimation of Maize (Zea mays L.) Yield Per Harvest Area: Appropriate Methods. Agronomy 2020, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, D.; Zečević, V.; Đukić, N.; Dodig, D. Genetic and Phenotypic Variability of Grain Mass per Spike of Winter Wheat Genotypes (Triticum aestivum L.). Kragujevac J. Sci. 2008, 30, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Borrás, L.; Gambín, B.L. Trait Dissection of Maize Kernel Weight: Towards Integrating Hierarchical Scales Using a Plant Growth Approach. Field Crop Res. 2010, 118, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.E.; Hou, P.; Xie, R.Z.; Li, S.K.; Zhang, H.B.; Ming, B.; Ma, D.L.; Liang, S.M. Spatial Adaptabilities of Spring Maize to Variation of Climatic Conditions. Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Yue, Y.; Sun, X.; Ding, Z.; Ma, W.; Zhao, M. Maize Kernel Weight Responses to Sowing Date-Associated Variation in Weather Conditions. Crop J. 2017, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, D.; Zečević, V.; Mićanović, D.; Đukić, N.; Milinković, J. Yield and Quality Parameters of Winter Wheat Lines (Triticum aestivum L.). In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium of Ecologist of Montenegro, Kotor, Montenegro, 20–24 September 2006; pp. 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Ben, L.H.B.; Peiter, M.X.; Robaina, A.D.; Parizi, A.R.C.; Silva, G.U.S. Influence of Irrigation Levels and Plant Density on Second-Season Maize. Revista Caatinga 2016, 29, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Serpa, M.S.; Silva, P.R.F.; Sangoi, L.; Vieira, V.; Marchesi, D.R. Densidade de Plantas em Híbridos de Milho Semeados no Final do Inverno em Ambientes Irrigados e de Sequeiro. Pesqui. Agropecuária Bras. 2012, 47, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauch, H.G. Simple Protocol for AMMI Analysis of Yield Trials. Crop Sci. 2013, 53, 1860–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanisavljević, D.; Mitrović, B.; Mirosavljević, M.; Ćirić, M.; Čanak, P.; Stojaković, M.; Ivanović, M. Identification of the Most Desirable Maize Testing Environments in Northern Serbia. Field Veg. Crops Res. 2013, 50, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Brankov, M. Effects of Herbicides and Foliar Fertilizer on Maize Lines; University of Belgrade: Zemun, Serbia, 2016; pp. 1–110. [Google Scholar]
- Oerke, E.C. Crop Losses to Pests. J. Agric. Sci. 2006, 144, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božović, D. Stability of Yield and Maize Compounds in Conditions of Stress under the Sulphonylurea. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Belgrade, Faculty of Agriculture, Zemun-Belgrade, Serbia, 2019; pp. 1–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gauch, H.G.; Piepho, H.P.; Annicchiarico, P. Statistical Analysis of Yield Trials by AMMI and GGE: Further Considerations. Crop Sci. 2008, 48, 866–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Kang, M.S. GGE Biplot Analysis: A Graphical Tool for Breeders, Geneticists, and Agronomists; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; p. 288. [Google Scholar]
- Cvijanovic, G.; Udvardi, I.; Stepic, V.; Djuric, N.; Cvijanovic, V.; Djukic, V.; Dozet, G. Mass 1000 Grain and Yield of Maize Grain in Conventional and Organic Production. J. Inst. PKB Agroecon. 2018, 24, 123–129. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters | Quality Contents | Minerals | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 342.0 | Calcium (Ca, mg) | 10.0 |
| Energy (K) | 1399.1 | Zinc (Zn, mg) | 5.0 |
| Moisture (g) | 14.9 | Iron (Fe, mg) | 2.3 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 66.2 | Potasium (K, mg) | 286.0 |
| Protein (g) | 11.1 | Magnesium (Mg, mg) | 139.0 |
| Lipid (g) | 3.6 | Copper (Cu, mg) | 0.14 |
| Fibre (g) | 2.7 | Carotene (A, mg) | 90.0 |
| Ash (g) | 1.6 | Folates (B9, mg) | 39.4 |
| Total free sugars (g) | 1.7 | Niacin (B3, mg) | 2.2 |
| Minerals (mg) | 1.5 | Riboflavin (B2, mg) | 0.20 |
| Phosforus (P, mg) | 348.0 | Thiamine (B1, mg) | 0.42 |
| Sodium (Na, mg) | 15.9 | Pantothenic Acids (B5, mg) | 0.3 |
| Amino Acids (mg) | 1.8 | Pyridoxine (B6, mg) | 0.3 |
| Sulphur (S, mg) | 114.0 | Ascorbic acid (C, mg) | 0.12 |
| G * | HGW Mean | HGW CV(%) | Interactions | GY | GY | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G × Y | G × L | G × T | (kg ha−1) | CV (%) | ||||||
| IPCAg1 | IPCAg2 | IPCAg1 | IPCAg2 | IPCAg1 | IPCAg2 | |||||
| L-1 | 25.42 (7.70) | 18.31 | 0.338 | 0.000 | −0.778 | 0.000 | 1.287 | 0.781 | 2910 (493) | 18.26 |
| L-2 | 24.63 (7.65) | 22.58 | 0.338 | 0.000 | −1.366 | 0.000 | 0.649 | −0.558 | 2764 (680) | 24.16 |
| L-3 | 31.35 (8.83) | 12.42 | 0.655 | 0.000 | 0.503 | 0.000 | −0.301 | −1.463 | 3830 (462) | 12.66 |
| L-4 | 36.19 (4.37) | 11.95 | −0.835 | 0.000 | 0.061 | 0.000 | −0.830 | 0.174 | 4345 (602) | 13.85 |
| L-5 | 38.06 (3.07) | 8.64 | 0.469 | 0.000 | 0.915 | 0.000 | −1.099 | 0.898 | 4665 (315) | 7.11 |
| L-6 | 37.58 (2.41) | 7.17 | −0.965 | 0.000 | 0.665 | 0.000 | 0.295 | 0.168 | 4445 (337) | 8.11 |
| Sources of Variation * | DF | SS | SS (%) | MS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype (G) | 5 | 8801.20 | 64.70 | 1760.21 ** |
| Year (Y) | 1 | 609.60 | 4.39 | 609.60 ** |
| Location (L) | 1 | 437.60 | 3.02 | 437.60 ** |
| Treatment (T) | 3 | 145.00 | 1.07 | 48.33 ** |
| G × Y | 5 | 150.60 | 1.01 | 30.12 ** |
| IPCA1 | 5 | 150.60 | 100.00 | 30.12 ** |
| IPCA2 | 3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| G × L | 5 | 385.40 | 2.74 | 77.10 ** |
| IPCA1 | 5 | 385.40 | 100.00 | 77.10 ** |
| IPCA2 | 3 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| G × T | 15 | 413.50 | 3.04 | 27.62 ** |
| IPCA1 | 7 | 207.00 | 50.06 | 29.57 |
| IPCA2 | 5 | 185.00 | 44.74 | 37.00 |
| Y × L | 7 | 207.00 | 1.32 | 29.57 ** |
| Y × T | 3 | 64.70 | 0.29 | 21.60 ** |
| L × T | 3 | 154.40 | 1.04 | 51.50 ** |
| G × Y × L | 5 | 145.20 | 1.07 | 29.01 ** |
| G × Y × T | 15 | 216.20 | 1.39 | 14.40 ** |
| G × L × T | 15 | 256.70 | 1.69 | 17.12 ** |
| Y × L × T | 3 | 211.90 | 1.36 | 70.64 ** |
| G × Y × L × T | 15 | 403.60 | 2.77 | 26.91 ** |
| Error | 192 | 1236.00 | 9.10 | 6.42 |
| Sum | 287 | 13,581.90 | 100.00 |
| Parameters | Grain Yield | IPCAG1 (G × Y) | IPCAG1 (G × L) | IPCAG1 (G × T) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HGW | 1.000 ** | 0.600 * | 0.257 ns | 0.086 |
| GY | - | - | 0.086 ns | 0.943 ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Božović, D.; Popović, D.; Popović, V.; Živanović, T.; Ljubičić, N.; Ćosić, M.; Spahić, A.; Simić, D.; Filipović, V. Economical Productivity of Maize Genotypes under Different Herbicides Application in Two Contrasting Climatic Conditions. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095629
Božović D, Popović D, Popović V, Živanović T, Ljubičić N, Ćosić M, Spahić A, Simić D, Filipović V. Economical Productivity of Maize Genotypes under Different Herbicides Application in Two Contrasting Climatic Conditions. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095629
Chicago/Turabian StyleBožović, Dragan, Dragana Popović, Vera Popović, Tomislav Živanović, Nataša Ljubičić, Milivoje Ćosić, Anđela Spahić, Divna Simić, and Vladimir Filipović. 2022. "Economical Productivity of Maize Genotypes under Different Herbicides Application in Two Contrasting Climatic Conditions" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095629
APA StyleBožović, D., Popović, D., Popović, V., Živanović, T., Ljubičić, N., Ćosić, M., Spahić, A., Simić, D., & Filipović, V. (2022). Economical Productivity of Maize Genotypes under Different Herbicides Application in Two Contrasting Climatic Conditions. Sustainability, 14(9), 5629. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095629









