Clean Water Production Enhancement through the Integration of Small-Scale Solar Stills with Solar Dish Concentrators (SDCs)—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
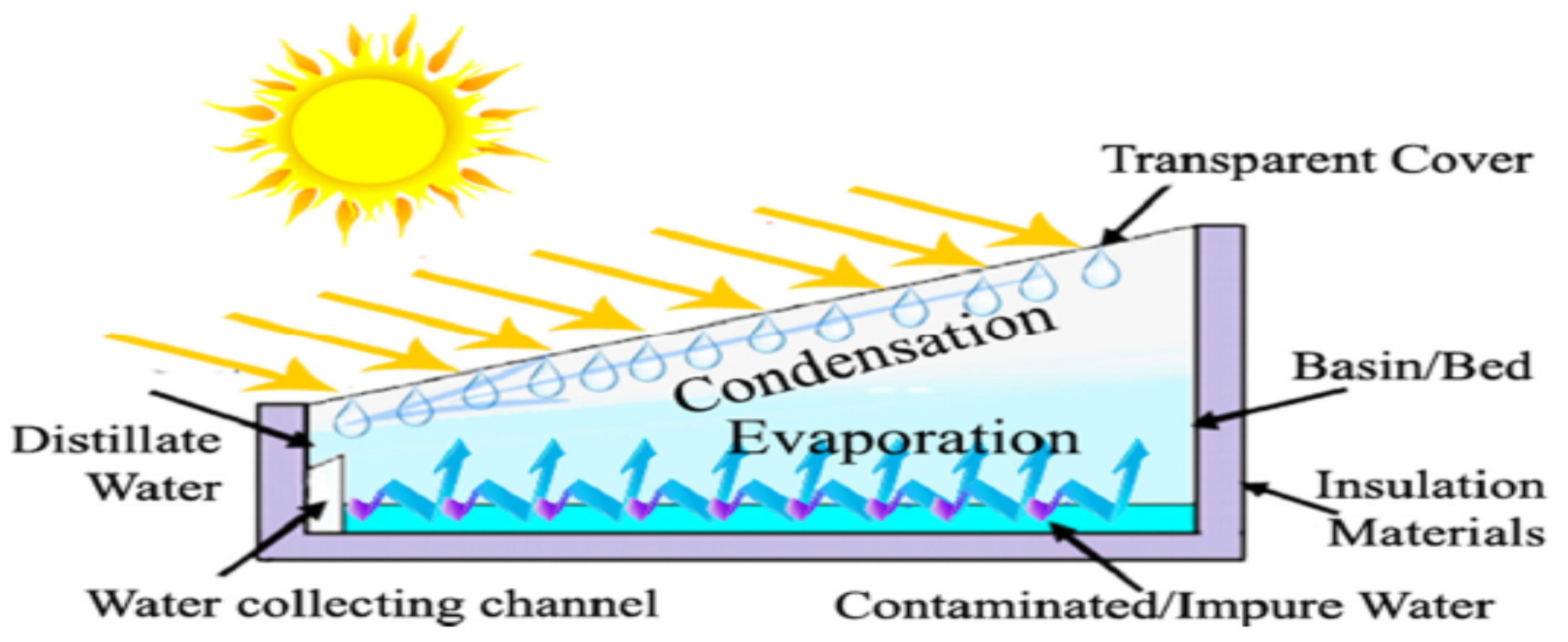
2. Performance of Passive Solar Desalination Still for Water Treatment
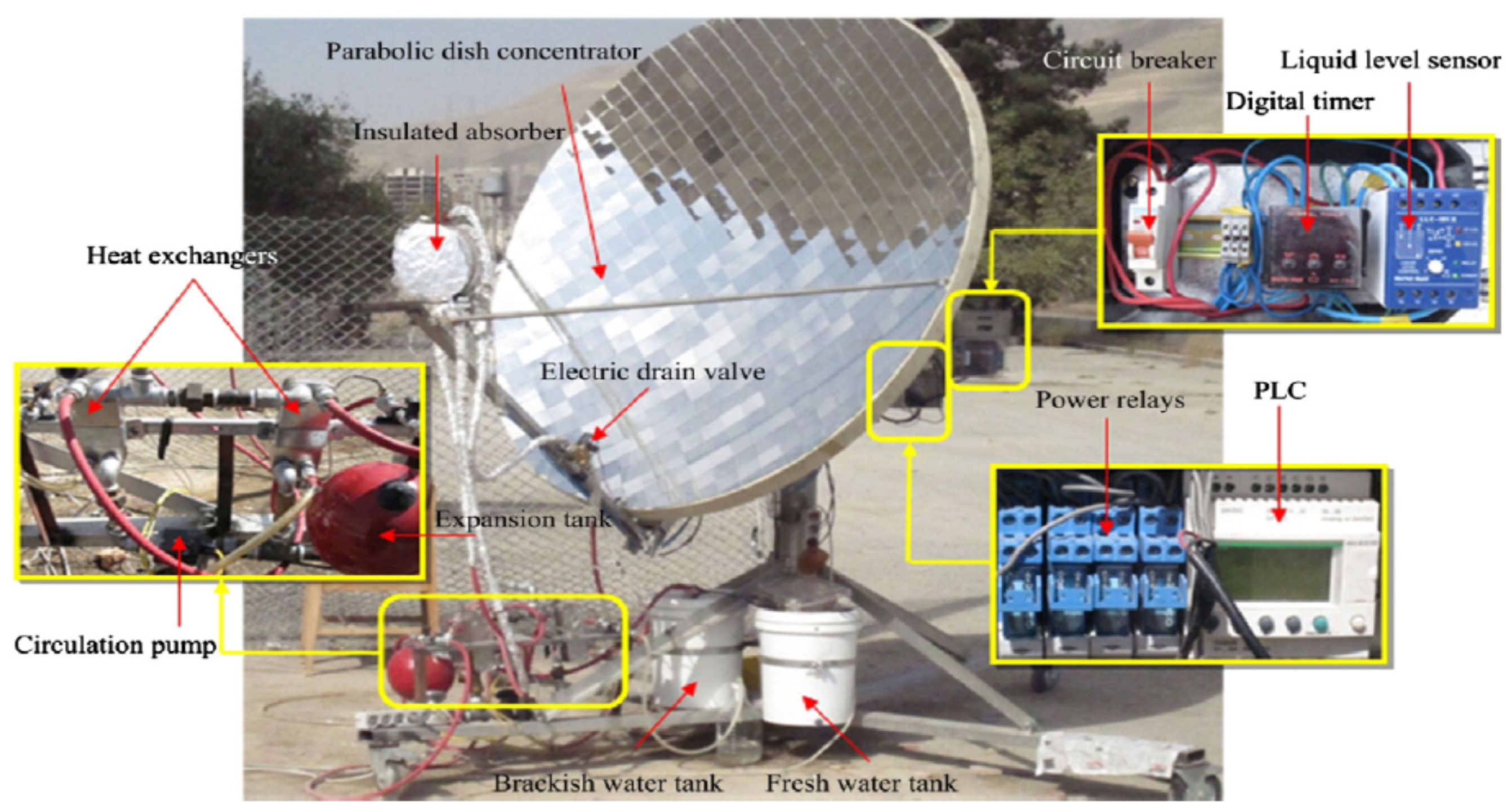
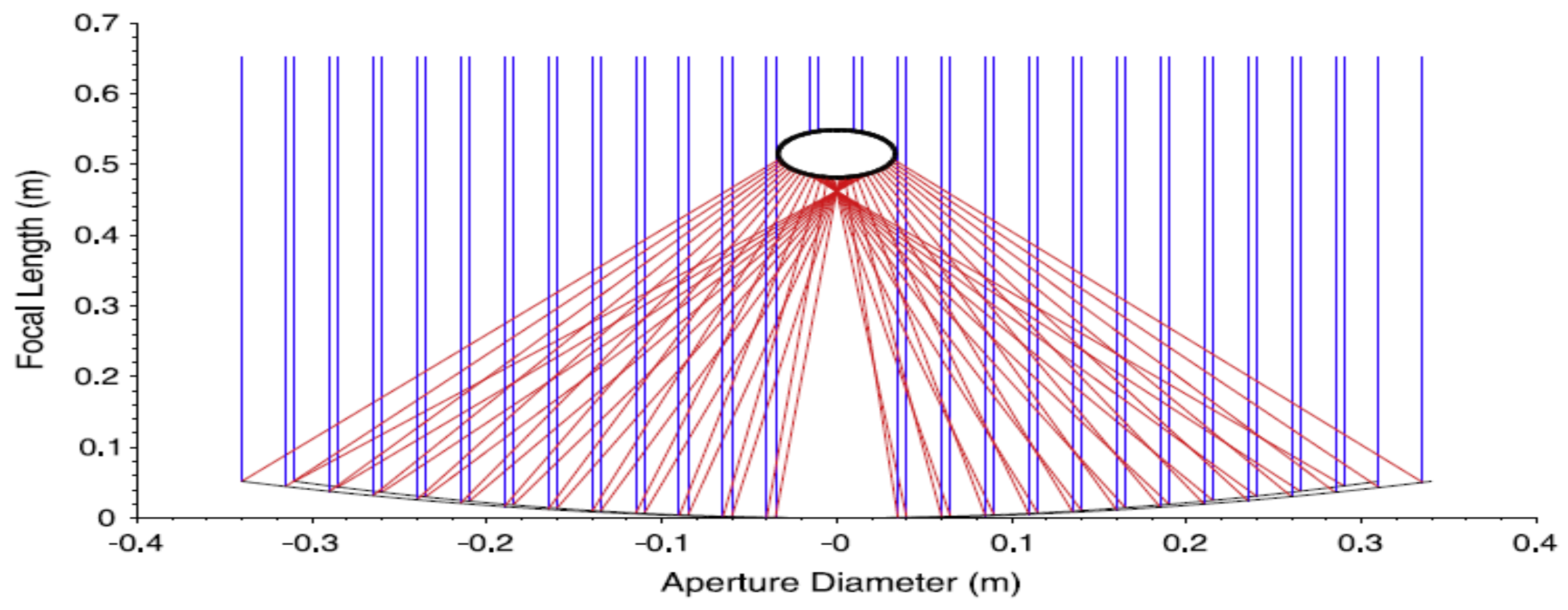
2.1. Description of Solar Dish Concentrator (SDC)
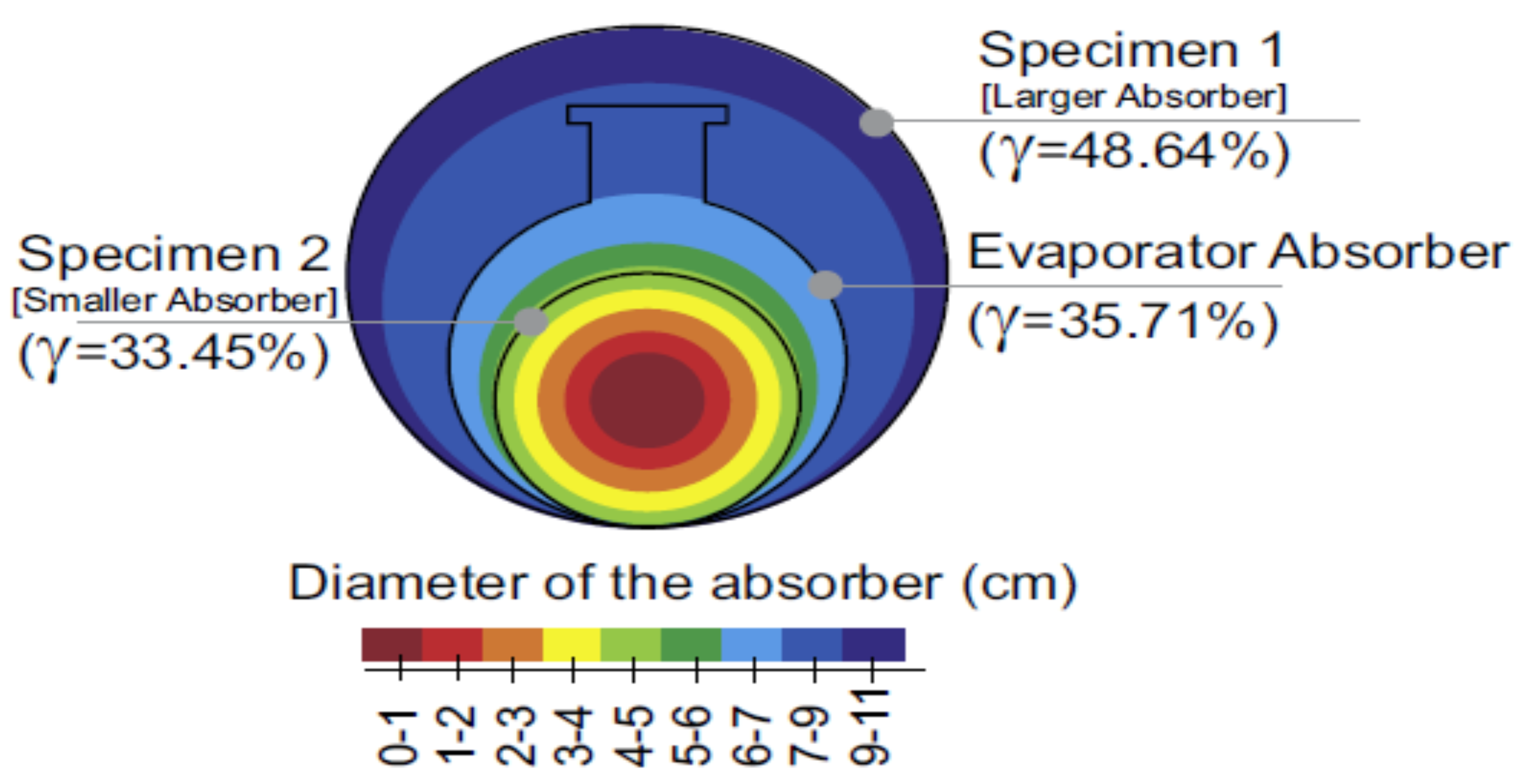
2.2. Recent Findings on SDCs Integrated with Solar Stills
2.2.1. SDCs Integrated with Solar Stills and the Sun-Tracking System (STS)
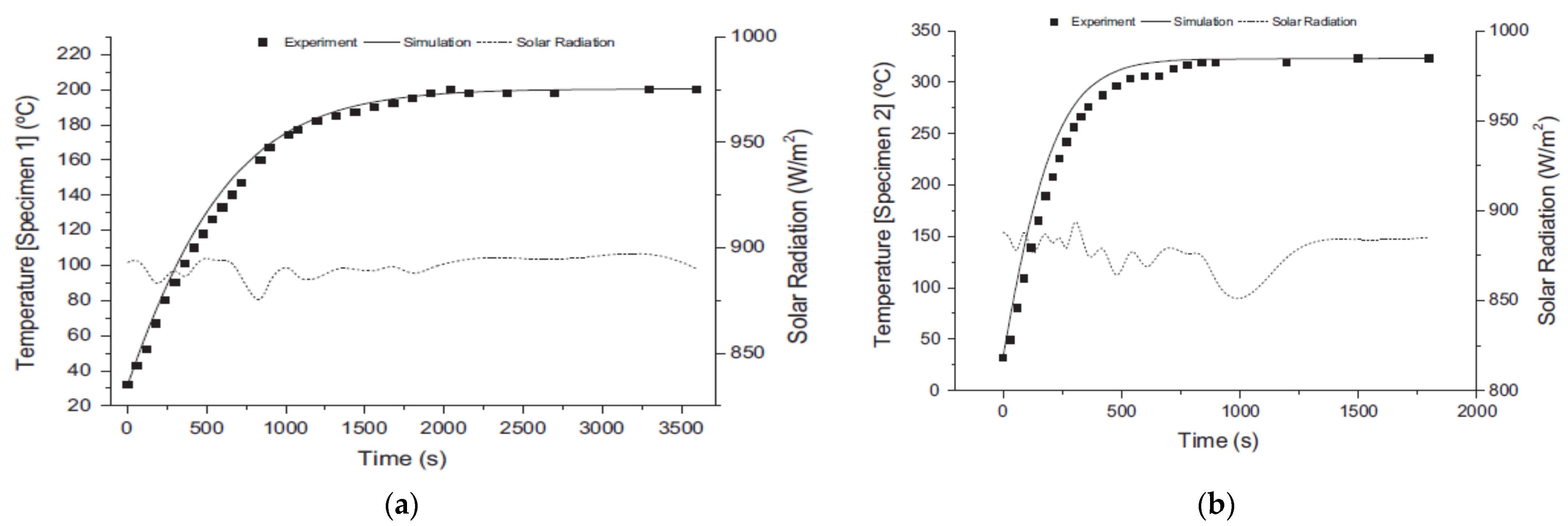
2.2.2. SDCs Integrated with Solar Stills without the Sun-Tracking System (STS)
2.3. Cost Per Liter (USD) of Small-Scale Passive Solar Stills (Absorbers) Integrated with SDCs
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleick, P.H. Water in Crisis: A Guide to the World’s Freshwater Resources; Oxford University Press Pacific: Oxford, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth, J. 18—Authorised EU health claims for water. In Foods, Nutrients and Food Ingredients with Authorised Eu Health Claims; Sadler, M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2014; pp. 373–395. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, J.R.; Whitford, W.G. Chihuahuan desert annuals: Importance of water and nitrogen. Ecology 1987, 68, 2032–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, S.C. Essentials of Animal Physiology, 4th ed.; New Age International Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2008; Available online: https://www.vet-ebooks.com/essentials-of-animal-physiology-4th-edition/ (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- Science Learning Hub—Pokapū Akoranga Pūtaiao. Earth’s Water Distribution. Available online: https://www.sciencelearn.org.nz/images/802-earth-s-water-distribution (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Cech, T.V. Principles of Water Resources: History, Development, Management, and Policy, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.V.; Bai, R.K. Performance study on solar still with enhanced condensation. Desalination 2008, 230, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.N.; Singh, H.N.; Tripathi, R. Present status of solar distillation. Sol. Energy 2003, 75, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vineis, P.; Chan, Q.; Khan, A. Climate change impacts on water salinity and health. J. Epidemiol. Glob. Health. 2011, 1, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guardian News & Media Limited. The Guardian for 200 Years. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2020/nov/26/more-than-3-billion-people-affected-by-water-shortages-data-shows (accessed on 26 November 2020).
- Tabrizi, F.F.; Sharak, A.Z. Experimental study of an integrated basin solar still with a sandy heat reservoir. Desalination 2010, 253, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghonemy, A.M.K. Water desalination systems powered by renewable energy sources: Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 1537–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampathkumar, K.; Arjunan, T.V.; Pitchandi, P.; Senthilkumar, P. Active solar distillation—A detailed review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 1503–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, T.; Raj, K.; Dsilva Winfred Rufuss, D.; Denkenberger, D.; Tingting, G.; Xuan, L.; Velraj, R. A review of efficient high productivity solar stills. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 101, 197–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. WHO/UNICEF Joint Monitoring Program (JMP) for Water Supply, Sanitation and Hygiene—Progress on Household Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene 2000–2020; IMI-SDG6 SDG 6 Progress Reports; United Nations: San Francisco, CA, USA; Available online: https://www.unwater.org/publications/who-unicef-joint-monitoring-program-for-water-supply-sanitation-and-hygiene-jmp-progress-on-household-drinking-water-sanitation-and-hygiene-2000-2020/ (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- World Health Organization. Global Costs and Benefits of Drinking-Water Supply and Sanitation Interventions to Reach the MDG Target and Universal Coverage, 1st ed.; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Jasrotia, S.; Kansal, A.; Kishore, V.V.N. Application of solar energy for water supply and sanitation in Arsenic affected rural areas: A study for Kaudikasa village, India. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 37, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, Incorporating First Addendum Vol. 1. Recommendations, 3rd ed.; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, P.; Welch, A.H.; Stollenwerk, K.G.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Bundschuh, J.; Panaullah, G. Arsenic in environment: Biology and chemistry. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 379, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahendra, P.; Yodit, A.; Angesom, H.; Sumitra, P.; Vijay, J.J. Public Health Hazards Due to Unsafe Drinking Water. Air Water Borne Dis. 2018, 7, 1000138. [Google Scholar]
- Adio, S.A.; Osowade, E.A.; Muritala, A.O.; Fadairo, A.A.; Oladepo, K.T.; Obayopo, S.O.; Fase, P.O. Solar distillation of impure water from four different water sources under the southwestern Nigerian climate. Drink. Water Eng. Sci. 2021, 14, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruss-Ustun, A.; Bos, R.; Gore, F.; Bartram, J. Safer Water, Better Health: Costs, Benefits and Sustainability of Interventions to Protect and Pro Mote Health; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cengel, Y.A.; Boles, M.A. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 8th ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2015; p. 712. [Google Scholar]
- Goosen, M.; Mahmoudi, H.; Ghaffour, N. Overview of renewable energy technologies for freshwater production. In Renewable Energy Applications for Freshwater Production; CRS Press: London, UK; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2012; pp. 25–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kalogirou, S.A. Concentrating solar power plants for electricity and desalinated water production. In Proceedings of the World Renewable Energy Congress, Linköping, Sweden, 8 May 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalogirou, S.A. Solar Energy Engineering: Processes and Systems; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UAE. World Resources Institute’s Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas August 2019 Report. Available online: https://www.thenationalnews.com/uae/environment/uae-water-resources-under-extreme-stress-new-report-finds-1.895660 (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Solar Power—Open Source Learning. Available online: https://mediawiki.middlebury.edu/wikis/OpenSourceLearning/images/5/53/Sunshine_Map.jpg (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Hanson, A.; Zachritz, W.; Stevens, K.; Mimbela, L.; Polka, R.; Cisneros, L. Disti late water quality of a single-basin solar still: Laboratory and field studies. Sol. Energy 2004, 76, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, A.; Yusof, K.W.; Isa, M.H.; Mahinder Singh, B.S.; Mustaffa, Z.; Ahsan, A.; Ul Mustafa, M.R.; Sapari, N.; Zahari, N.A.M. Potable water production using two solar stills having different cover materials and fabrication costs. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2018, 37, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, A.; Imteaz, M.; Thomas, U.A.; Azmi, M.; Rahman, A.; Nik Daud, N.N. Parameters affecting the performance of a low cost solar still. Appl. Energy 2014, 114, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.S.; Tiwari, G.N.; Kumar, A.; Sodha, M.S. Solar Distillation; Pergaman Press: Oxford, UK.; London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, G.N.; Madhuri. Effect of water depth on daily yield of the still. Desalination 1987, 61, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akash, B.A.; Mohsen, M.S.; Nayfeh, W. Experimental study of the basin type solar still under local climate conditions. Energy Convers. Manag. 2000, 41, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toure, S.; Meukam, P. A numerical model and experimental investigation for a solar still in climatic conditions in Abidjan (Côte d’Ivoire). Renew. Energy 1997, 11, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.M. Reliability of thermal desalination (solar stills) for water/wastewater treatment in light of COVID-19 (novel coronavirus “SARS-CoV-2”) pandemic: What should consider? Desalination 2021, 512, 115106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthu Manokar, A.; Prince Wiston, D.; Kabeel, A.E.; El-Agouz, S.A.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Arunkumar, T.; Madhu, B.; Ahsan, A. Integrated PV/T solar still-A mini-review. Desalination 2018, 435, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, V.K.; Tiwari, G.N. Experimental validation of thermal model of a double slope active solar still under natural circulation mode. Desalination 2010, 250, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, A.; Wan, Y.K.; Mahinder Singh, B.S.; Isa, M.H.; Olisa, E.; Zahari, N.A.M. Sustainable potable water production using a solar still with photovoltaic modules-AC heater. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 14929–14944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, A.; Zakaria, N.A.; Isa, M.H.; Yusof, K.W.; Mahinder Singh, B.S.; Mustaffa, Z.; Takaijudin, H. Performance investigation of a solar still having polythene film cover and black painted stainless steel basin integrated with a photovoltaic module–direct current heater. Energy Environ. 2019, 30, 1521–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchanda, H.; Kumar, M. Study of water desalination techniques and a review on active solar distillation methods. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2018, 37, 444–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.P.; Winston, D.P.; Pounraj, P.; Manokar, A.M.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Kabeel, A.E. Experimental investigation on hybrid PV/T active solar still with effective heating and cover cooling method. Desalination 2018, 435, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, A.; Yusof, K.W.; Mahinder Singh, B.S.; Olisa, E.; Sapari, N.B.; Isa, M.H. The performance investigation of triangular solar stills having different heat storage materials. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2015, 6, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Garni, A.Z. Productivity enhancement of solar still using water heater and cooling fan. J. Sol. Energy Eng. Trans. ASME 2012, 134, 031006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadatare, M.K.; Verma, S.K. Influence of water depth on internal heat and mass transfer in a plastic solar still. Desalination 2007, 217, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, V.; Deenadayalan, C.K.; Vinod, H.; Srithar, K. Desalination of effluent using fin type solar still. Energy 2008, 33, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, H.; Patel, P.; Patel, N.; Thakkar, H. Performance analysis of solar still with different energy-absorbing materials. Int. J. Ambient. Energy 2017, 38, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, H. Performance investigation on variations of glass cover thickness on solar still: Experimental and theoretical analysis. Technol. Econ. Smart Grids Sustain. Energy 2016, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahsan, A.; Imteaz, M.; Rahman, A.; Yusuf, B.; Fukuhara, T. Design, fabrication and performance analysis of an improved solar still. Desalination 2012, 292, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.E.; Khalil, A.; Omara, Z.M.; Younes, M.M. Theoretical and experimental parametric study of modified stepped solar still. Desalination 2012, 289, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rehim, Z.S.; Lasheen, A. Improving the performance of solar desalination systems. Renew. Energy 2005, 30, 1955–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarawneh, M.S.K. Effect of water depth on the performance evaluation of solar still. Jordan J. Mech. Ind. Eng. 2007, 1, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Taamneh, Y.; Taamneh, M.M. Performance of pyramid-shaped solar still: Experimental study. Desalination 2012, 291, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aybar, H.S.; Assefi, H. Simulation of a solar still to investigate water depth and glass angle. Desalination Water Treat. 2009, 7, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 3rd ed.; WHO Press: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Balladin, D.A.; Headley, O.; Roach, A. Evaluation of a concrete cascade solar still. Renew. Energy 1999, 17, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KIkuchi, S.; Oyoda, H.T.; Akami, A.T.; Himada, S.S.; Oba, M.O.; Ekiyama, T.S. Simple solar still using solar energy and compost heat for family use. J. Arid L. Stud. 2012, 21, 207–210. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub, G.M.; Dahdah, L.; Alameddine, I.; Malaeb, L. Vapor-induced transfer of bacteria in the absence of mechanical disturbances. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, G.M.; Dahdah, L.; Alameddine, I. Transfer of bacteria via vapor in solar desalination units. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 53, 3199–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaeb, L.; Ayoub, G.M.; Al-Hindi, M.; Dahdah, L.; Baalbaki, A.; Ghauch, A. A biological, chemical and pharmaceutical analysis of distillate quality from solar stills. Energy Procedia 2017, 119, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.M.; Rahbar, A.; Javadi, Y.D.; Koleini, M.H.; Afrand, M.; Amidpour, M. Energy-matrices, exergy, economic, environmental, exergoeconomic, enviroeconomic, and heat transfer (6E/HT) analysis of two passive/active solar still water desalination nearly 4000 m: Altitude concept. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 261, 121243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbasi, R.; Esfahani, M.N. Multi-effect passive desalination system, an experimental approach. World Appl. Sci. J. 2010, 10, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar]
- Pounraj, P.; Prince Winston, D.; Kabeel, A.E.; Praveen Kumar, B.; Manokar, A.M.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Christabel, S.C. Experimental investigation on Peltier based hybrid PV/T active solar still for enhancing the overall performance. Energ. Conver. Manag. 2018, 168, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, T.; Kabeel, A.E.; Raj, K.; Denkenberger, D.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Ragupathy, P.; Velraj, R. Productivity enhancement of solar still by using porous absorber with bubble-wrap insulation. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Yadav, P.; Dev, R.; Singh, D. Performance analysis of modified basin type double slope multi–wick solar still. Desalination 2017, 422, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Tiwari, A. Design, fabrication and performance evaluation of a hybrid photovoltaic/ thermal (PV/T) double slope active solar still. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev, R.; Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Tiwari, G.N. Performance study of the inverted absorber solar still with water depth and total dissolved solid. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Tiwari, G.N. Energy matrices, exergo-economic and enviro-economic analysis of an active single slope solar still integrated with a heat exchanger: A comparative study. Desalination 2018, 443, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohani, A.; Hoseinzadeh, S.; Berenjkar, K. Experimental analysis of innovative designs for solar still desalination technologies; an in-depth technical and economic assessment. J. Energy Storage. 2021, 33, 101862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripath, R.; Tiwari, G.N. Effect of water depth on heat and mass transfer in a solar still: In summer climate condition. Desalination 2006, 217, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, R.; Tiwari, G.N. Thermal modelling of passive and active solar stills for different depths of water by using the concept of solar fraction. Sol. Energy 2006, 80, 956–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Kumar, S.; Tiwari, G.N. Design, fabrication and performance evaluation of a hybrid photovoltaic thermal (PVT) double slope active solar still. Desalination 2011, 277, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, G.B.; David, P.W.; Mariappan, R.K.; Kabeel, A.E.; Athikesavan, M.M.; Sathyamurthy, R. Improvising the efficiency of single-sloped solar still using thermally conductive nano-ferric oxide. Environ. Sci. Pollute. Res. 2020, 27, 32191–32204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, A.W.H.; Chu, J.T.S.; Perera, M.R.A.; Hui, K.P.Y.; Yen, H.L.; Chan, M.C.W.; Peiris, M.; Poon, L.L.M. Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.H.; Sridhar, S.; Zhang, R.R.; Chu, H.; Fung, A.Y.F.; Chan, G.; Chan, J.F.W.; To, K.K.W.; Hung, I.F.N.; Cheng, V.C.C.; et al. Factors affecting stability and infectivity of SARS-CoV-2. J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 106, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Peel, G.K.; Cheema, F.H.; Lawrence, W.S.; Bukreyeva, N.; Jinks, C.W.; Peel, J.E.; Peterson, J.W.; Paessler, S.; Hourani, M.; et al. Catching and killing of airborne SARS-CoV-2 to control spread of COVID-19 by a heated air disinfection system. Mater. Today Phys. 2020, 15, 100249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Sun, B.C.; Wang, J.X.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.W.; Fang, Y.; Yue, W.H.; Liu, S.M.; Liu, K.Y.; Zeng, X.F.; et al. Can masks be reused after hot water decontamination during the COVID-19 pandemic? Engineering 2020, 6, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Bertsch, P.M.; Bibby, K.; Haramoto, E.; Hewitt, J.; Huygens, F.; Gyawali, P.; Korajkic, A.; Riddell, S.; Sherchan, S.P.; et al. Decay of SARS-CoV-2 and surrogate murine hepatitis virus RNA in untreated wastewater to inform application in wastewater-based epidemiology. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaouchi, B.; Zrelli, A.; Gabsi, S. Desalination of brackish water by means of a parabolic solar concentrator. Desalination 2007, 217, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, Z.; Eltawil, M.A. Hybrid of solar dish concentrator, new boiler and simple solar collector for brackish water desalination. Desalination 2013, 326, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorjian, S.; Ghobadian, B.; Tavakkoli Hashjin, T.; Banakar, A. Experimental performance evaluation of a stand-alone point-focus parabolic solar still. Desalination 2014, 352, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, G.O.; Vieira, L.G.M.; Damasceno, J.J.R. Solar dish concentrator for desalting water. Sol. Energy 2016, 136, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuigan, K.G.; Conroy, R.M.; Mosler, H.-J.; du Preez, M.; Ubomba-Jaswa, E.; Fernandez-Ibanez, P. Solar water disinfection (SODIS): A review from bench-top to roof-top. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 235–236, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljabair, S.; Habeeb, L.J.; Ali, A.M. Experimental analysis of parabolic solar dish with radiator heat exchanger receiver. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2020, 15, 437–454. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Kecskemethy, A.; Arif, A.F.M.; Dubowsky, S. A Novel Approach for Designing Parabolic Mirrors Using Optimized compliant Bands. In Proceedings of the International Design Engineering Technical Conference and Computers and Information in Engineering, IDETC, Washington, DC, USA, 28 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Aliman, O.; Daut, I.; Isa, M.; Adzman, M.R. Simplification of sun tracking mode to gain high concentration solar energy. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2007, 4, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Bhatnagar, V.P.; Tiwari, G.N. Design parameters for concentrator assisted solar distillation system. Energy Convers. Manag. 1996, 37, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riffat, S.; Mayere, A. Performance evaluation of v-trough solar concentrator for water desalination applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 50, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinitsyn, S.; Panchenko, V.; Kharchenko, V.; Vasant, P. Oprimization of parquetting of the concentrator of photovoltaic thermal module. In Intelligent Computing and Optimization. ICO 2019. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Vasant, P., Zelinka, I., Weber, G.W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 1072. [Google Scholar]
- Panchenko, V. Photovoltaic thermal module with paraboloid type solar concentrators. Int. J. Energy Optim. Eng. (IJEOE) 2021, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H.P.; Prakash, J. Solar Energy Fundamentals and Applications, 1st ed.; McGraw Hill: Delphi, Greece, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, G.; Lovegrove, K.; Luzzi, A. Optical performance of spherical reflecting elements for use with paraboloidal dish concentrators. Sol. Energy 2003, 74, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichan, M.T.; Kazem, H.A. Water solar distiller productivity enhancement using concentrating solar water heater and phase change material (PCM). Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2015, 5, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nuwayhid, R.Y.; Mrad, F.; Abu-Said, R. The realization of a simple solar tracking concentrator for university research applications. Renew. Energy 2001, 24, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushika, N.D.; Reddy, K.S. Performance of a low cost solar paraboloidal steam generating system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2000, 41, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics, 5th ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrami, M.; Avargani, V.M.; Bonyadi, M. Comprehensive experimental and theoretical study of a novel still coupled to a solar dish concentrator. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2019, 151, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, T.; Denkenberger, D.; Velraj, R.; Sathyamurthy, R.; Tanaka, H.; Vinothkumar, K. Experimental study on a parabolic concentrator assisted solar desalting system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srithar, K.; Rajaseenivasan, T.; Karthik, N.; Periyannan, M.; Gowtham, M. Standalone triple basin solar desalination system with cover cooling and parabolic dish concentrator. Renew. Energy 2016, 90, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badran, A.A.; Al-Hallaq, A.A.; Eyal Salman, I.A.; Odat, M.Z. A solar still augmented with a flat plate collector. Desalination 2005, 172, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, V.; Gopalakrishnan, M.; Raghu, R.; Srithar, K. Single basin solar still with fin for enhancing productivity. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 2602–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Tiwari, G.N. Life cycle cost analysis of single slope hybrid (PV/T) active solar still. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, V.; Kumaran, S.S.; Prabhu, V.N.; Srithar, K. Productivity enhancement of stepped solar still performance analysis. Therm. Sci. 2008, 12, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Samee, M.; Mirza, U.K.; Majeed, T.; Ahmad, N. Design and performance of a simple single basin solar still. Renew. Sustain. Energ. Rev. 2007, 11, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sebaii, A.A.; Ramadan, M.R.I.; Aboul-Enein, S.; Salem, N. Thermal performance of a single-basin solar still integrated with a shallow solar pond. Energy Convers. Manag. 2008, 49, 2839–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeel, A.E.; Dawood, M.M.K.; Ramzy, K.; Nabil, T.; Elnaghi, B.; Elkassar, A. Enhancemnet of single solar still integrated with solar dishes: An experimental approach. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 196, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
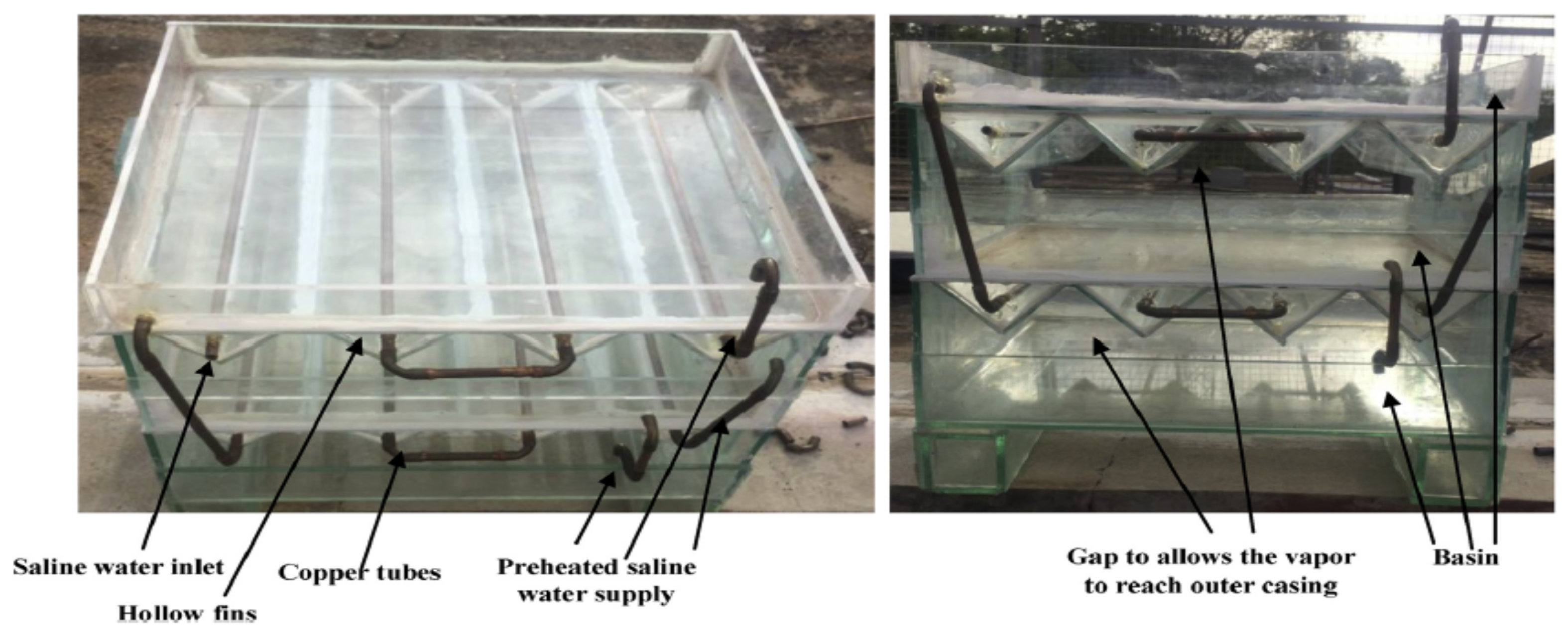
















| Water Quality Parameters | PSS [30] | GSS [30] | SSSB [17] | TrSS [31] | WHO Standards for Drinking Water [55] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.51 | 6.53 | 7.14 | 7.7 | 6.5–8.0 |
| Total dissolved solids (TDS) mg/L | 95 | 28 | 45 | 7.52 | 600 |
| Total Arsenic (mg/L) | ---- | ---- | ≤0.01 | ---- | 0.01 |
| Salinity (ppt) | 0.1 | 0 | Na | 0.006 | <0.25 |
| Nitrate (mg/L) | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.74 | ---- | <50 |
| Nitrite (mg/L) | 0.03 | 0.01 | Na | ---- | <0.05 |
| Fluoride (mg/L) | ---- | ---- | 0.02 | ---- | 1.5 |
| Chloride (mg/L) | ---- | ---- | 10.99 | ---- | 250 |
| Hardness (mg/L) | ---- | ---- | 33.81 | ---- | 200 |
| Iron (mg/L) | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.00 | ---- | 0.3 |
| Sulfate (mg/L) | ---- | ---- | 0.72 | ---- | 250 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 1.37 | 0.92 | Na | ---- | <5 |
| Electrical conductivity (EC) (μS/cm) | 52.5 | 15.66 | Na | 11.6 | <250 |
| Solar Still Type | Modified/Incorporated with | Basin Water Temperature of the Distiller (°C) | Initial Productivity (L/m2) of the Distiller Corresponded to the Basin Water Temperature | Countries/ Year of Experiment | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passive, double slope | Polythene film cover and black painted Perspex sheet basin | 32 °C | 0.01 L/m2 | Malaysia/2014 | [31] |
| Active, double slope | Photovoltaic modules-AC heater | 47 °C | 0.138 L/m2 | Malaysia/2016 | [39] |
| Active, double slope | A photovoltaic module-DC heater | 49 °C | 0.32 L/m2 | Malaysia/2019 | [40] |
| Active, single slope | Hybrid PV/T with cover cooling method | 25.5 °C | 0.08 L/m2 | India/2018 | [42] |
| Passive, double slope | Black soil heat absorption materials | 35 °C | 0.048 L/m2 | Malaysia/2015 | [43] |
| Passive, double slope | Black painted basin | 37 °C | 0.15 L/m2 | Saudi Arabia/2012 | [44] |
| Active, double slope | Two immersed AC water heaters | 49 °C | 0.50 L/m2 | Saudi Arabia/2012 | |
| Passive, single slope | Fin and sand as heat storing materials | 35 °C | 0.05 L/m2 | India/2008 | [46] |
| Passive, single slope | Marble pieces in basin | 34 °C | 0.035 L/m2 | India/2017 | [47] |
| Passive, single slope | Glass cover with 4 mm thickness | 33 °C | 0.04 L/m2 | India/2016 | [48] |
| Passive, tubular shape | Polythene film cylindrical cover | 20 °C | 0.02 L/m2 | Japan, 2012 | [49] |
| Passive, single slope | 39 °C | 0.07 L/m2 | Egypt/2012 | [50] | |
| Active, single slope | Vacuum tube collector and stepped basin | 48 °C | 0.15 L/m2 | ||
| Active, single slope | A photovoltaic module-Rotating shaft | 36 °C | 0.05 L/m2 | Egypt/2005 | [51] |
| Active, pyramid shape | A photovoltaic module-DC fan | 25 °C | 0.06 L/m2 | Jordan/2012 | [53] |
| Active, single slope | Hybrid PV/T and flat plate collector (FPC) | 18.9 °C | 0.08 L/m2 | India/2018 | [63] |
| Passive, single slope | Porous absorber and carbon foam | 49.2 °C | 0.10 L/m2 | India/2018 | [64] |
| Passive, double slope | Multi wicks heat storage materials | 18 °C | 0.062 L/m2 | India/2017 | [65] |
| Active, single slope | PV/T | 15 °C | 0.04 L/m2 | India/2010 | [66] |
| Active, single slope | Inverted absorber | 34.6 °C | 0.06 L/m2 | Oman/2011 | [67] |
| Active, single slope | Hybrid PV/T and heat exchanger | 9.25 °C | 0.0014 L/m2 | India/2018 | [68] |
| Active, single slope | Reflectors | 21.6 °C | 0.0017 L/m2 | Iran/2021 | [69] |
| Passive, single slope | 19.3 °C | 0.03 L/m2 | India/2006 | [70] | |
| Passive, single slope | 12.2 °C | 0.007 L/m2 | India/2006 | [71] | |
| Active, single slope | Flat plate collector (FPC) | 25 °C | 0.016 L/m2 | ||
| Active, double slope | Flat plate collector (FPC) | 26.6 °C | 0.032 L/m2 | India/2011 | [72] |
| Passive, single slope | Micro coated and nano-ferric oxide particles in basin | 39 °C | 0.13 L/m2 | India/2020 | [73] |
| Types of Solar Still | Maximum Daily Water Production (L/m2) | Cost per Liter (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| CSS with SDC with sun-tracking system and vapor condensing technique, Egypt [80] | 6.70 | 0.028 |
| CSS with SDC with sun-tracking system (PPSS) and vapor condensing method, Iran [81] | 3.56 | 0.012 |
| CSS with SDC with sun-tracking system and water heater/PV modules, Egypt [106] | 13.63 | 0.25 |
| SDC integrated with an evaporator and solar tracking system, Iran [97] | 6.5 | NA |
| Triple-basin solar still with SDC, charcoal in basins and cover cooling method without sun-tracking system, India [99] | 16.94 | 0.084 |
| SSSS with SDC, PCM balls, and cover cooling method without sun-tracking system, India [98] | 3.80 | 0.0085 |
| Conventional passive solar still, Egypt [80] | 3.00 | 0.048 |
| Conventional passive solar still, PSS, Malaysia [40] | 3.21 | 0.015 |
| Passive solar still (PSS) coupled with a PV module-DC heater, ACSS, Malaysia [40] | 4.36 | 0.045 |
| Single slope passive solar still, Pakistan [104] | 3.25 | 0.063 |
| Single slope hybrid (PV/T) active solar still, India [102] | 1.91 | 0.14 |
| Passive solar still coupled with a flat plate collector, Jordan [100] | 4.69 | 0.103 |
| Fin-type passive solar still, India [46] | 4.00 | 0.054 |
| Passive solar still with wick and fin in the basin, India [101] | 4.06 | 0.065 |
| Stepped passive solar still with fins and sponges in the basin, India [103] | 3.03 | 0.064 |
| Passive solar still with a shallow solar pond, Egypt [105] | 4.65 | 0.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yusof, M.F.; Zainol, M.R.R.M.A.; Sandu, A.V.; Riahi, A.; Zakaria, N.A.; Shaharuddin, S.; Aziz, M.S.A.; Mohamed Noor, N.; Vizureanu, P.; Zawawi, M.H.; et al. Clean Water Production Enhancement through the Integration of Small-Scale Solar Stills with Solar Dish Concentrators (SDCs)—A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5442. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095442
Yusof MF, Zainol MRRMA, Sandu AV, Riahi A, Zakaria NA, Shaharuddin S, Aziz MSA, Mohamed Noor N, Vizureanu P, Zawawi MH, et al. Clean Water Production Enhancement through the Integration of Small-Scale Solar Stills with Solar Dish Concentrators (SDCs)—A Review. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5442. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095442
Chicago/Turabian StyleYusof, Mohd Fazly, Mohd Remy Rozainy Mohd Arif Zainol, Andrei Victor Sandu, Ali Riahi, Nor Azazi Zakaria, Syafiq Shaharuddin, Mohd Sharizal Abdul Aziz, Norazian Mohamed Noor, Petrica Vizureanu, Mohd Hafiz Zawawi, and et al. 2022. "Clean Water Production Enhancement through the Integration of Small-Scale Solar Stills with Solar Dish Concentrators (SDCs)—A Review" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5442. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095442
APA StyleYusof, M. F., Zainol, M. R. R. M. A., Sandu, A. V., Riahi, A., Zakaria, N. A., Shaharuddin, S., Aziz, M. S. A., Mohamed Noor, N., Vizureanu, P., Zawawi, M. H., & Ikhsan, J. (2022). Clean Water Production Enhancement through the Integration of Small-Scale Solar Stills with Solar Dish Concentrators (SDCs)—A Review. Sustainability, 14(9), 5442. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095442











