An Assessment Approaches and Learning Outcomes in Technical and Vocational Education: A Systematic Review Using PRISMA
Abstract
1. Introduction
- 1.
- What are the assessment approaches used to assess students in technical and vocational education?
- 2.
- What are the intended student learning outcomes of the educators’ assessment?
The Needs for a Systematic Literature Review Related to Student Learning Outcome from Assessment Approaches in TVET
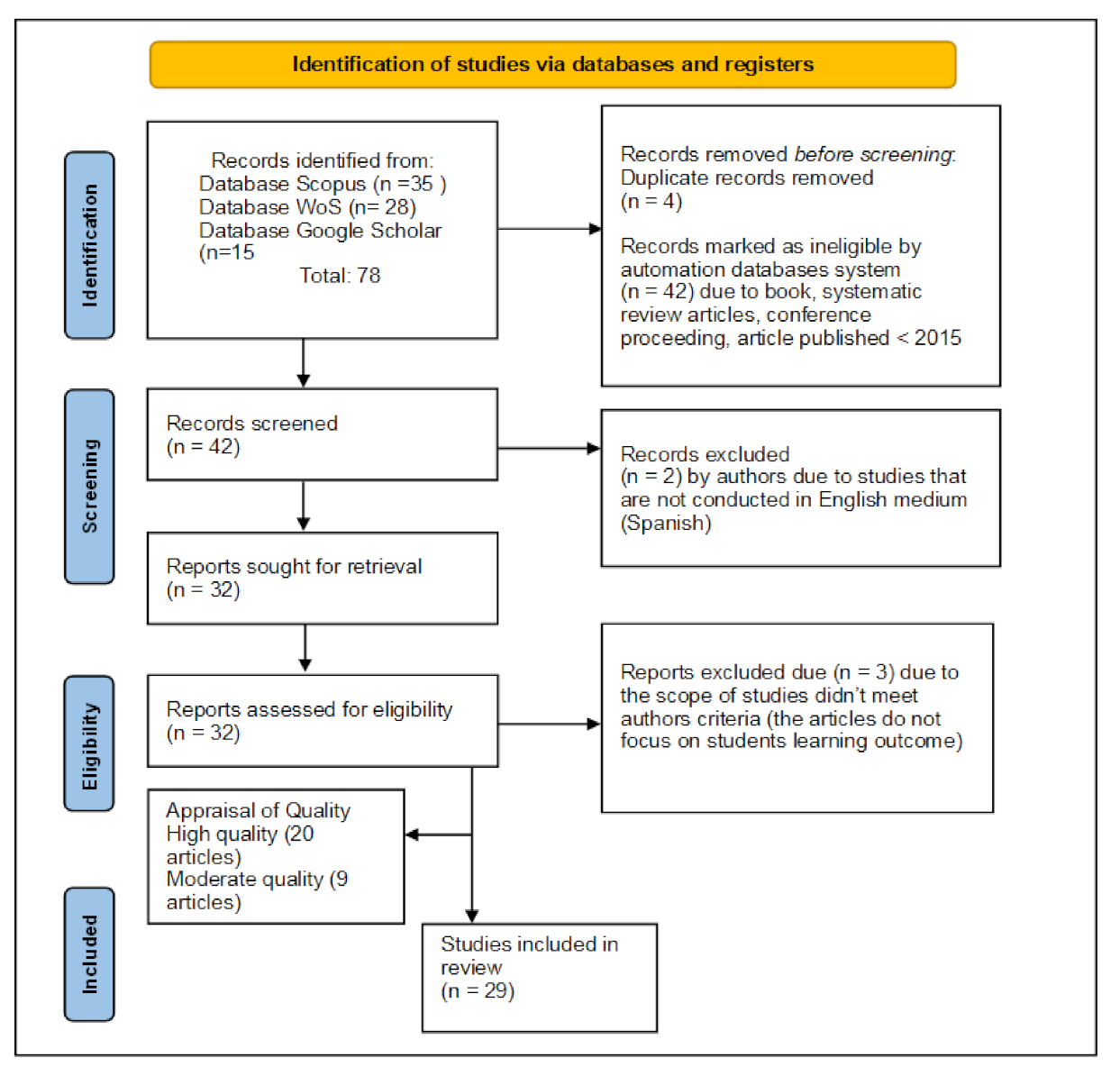
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preferred Reporting Items
2.2. Formulation of Research Questions
2.3. Systematic Searching Strategy
2.3.1. Identification
2.3.2. Screening Phase
2.3.3. Eligibility
2.4. Quality Appraisal
2.5. Data Extraction and Analysis
2.6. Strength and Limitation
3. Results
3.1. The Selected Studies’ General Context
3.2. The Assessment Approaches and Students’ Learning Outcomes
3.3. Assessment Approaches Used to Assess Students in Technical and Vocational Education
3.3.1. Competency-Based Assessment (CBA)
3.3.2. Performance-Based Assessment
3.3.3. Formative Assessment
3.3.4. Criteria-Based Assessment
3.3.5. E-Portfolio Assessment
3.3.6. School-Based assessment
3.3.7. Summative Assessment
3.3.8. Workplace Assessment
3.3.9. Computer-Based Assessment
3.3.10. Scenario-Based Assessment
3.3.11. Inclusive-Based Assessment
3.3.12. Classroom-Based Assessment
3.4. Development of Learning Outcomes of TVET Assessment
3.4.1. Building Student Competencies
3.4.2. Formation of Student Performances
3.4.3. Formation of the Impact of Assessment
4. Discussion and Conclusions
5. Implication and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campbell, M. UNESCO TVET Strategy 2016-2021; UNESCO: Hamburg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ra, S.; Chin, B.; Liu, A. Challenges and Opportunities for Skills Development in Asia; Changing Supply, Demand, and Mismatches; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2015; ISBN 9789292572204. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO Technical Vocational and Education Training (TVET) 1. Sub-Education Policy Review Report: Technical and Vocational and Training (TVET); UNESCO: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, M.; Winterton, J. Competence-Based Vocational and Professional Education; Mulder, M., Ed.; Springer: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2017; p. 1. ISBN 978-3-319-41713-4. [Google Scholar]
- Yunos, J.M.; Salleh, K.M.; Sern, L.C.; Sulaiman, N.L.; Mohamad, M.M.; Abidin, N.A.Z.; Sahdan, S. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 9th International Conference on Engineering Education, Kanazawa, Japan, 9–10 November 2017; pp. 128–131.
- Lassnigg, L. Technical and Vocational Education and Training Issues, Concerns and Prospects. In Competence-Based Vocational and Professional Education; Mulder, M., Ed.; Springer: Borne, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9783319417110. [Google Scholar]
- Hashim, S.; Zakariah, S.H.; Taufek, F.A.; Zulkifli, N.N.; Lah, N.H.C.; Murniati, D.E. An Observation on Implementation of Classroom Assessment in Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) Subject Area. J. Tech. Educ. Train. 2021, 13, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung-Blunden, V.; Khan, S.R. A Modified Peer Rating System to Recognise Rating Skill as a Learning Outcome. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2018, 43, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haolader, F.A.; Foysol, K.M. The Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching and Assessing: Current Practices at Polytechnics in Bangladesh and Its Effect in Developing Students’ Competences. Int. J. Res. Vocat. Educ. Train. 2015, 2, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattalitan, J.A. The Implications of Learning Theories to Assessment and Instructional Scaffolding Techniques. Am. J. Educ. Res. 2016, 4, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, R.K.; Garg, N.; Yadav, S.K. Quality Assessment Framework for Educational Institutions in Technical Education: A Literature Survey. Horizon 2018, 26, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boahin, P.; Hofman, A. A Disciplinary Perspective of Competency-Based Training on the Acquisition of Employability Skills. J. Vocat. Educ. Train. 2013, 65, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnam-Lim, C.T.L.; Tan, K.H.K. Large-Scale Implementation of Formative Assessment Practices in an Examination-Oriented Culture. Assess. Educ. Princ. Policy Pract. 2015, 22, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengist, W.; Soromessa, T.; Legese, G. Method for Conducting Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis for Environmental Science Research. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Watson, M. Guidance on Conducting a Systematic Literature Review. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2019, 39, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.-A.; Hopfenbeck, T.N.; Newton, P.; Stobart, G.; Steen-Utheim, A.T. State of the Field Review Assessment and Learning; Norwegian Knowledge Centre for Education: UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Black, P.; Wiliam, D. Classroom Assessment and Pedagogy. Assess. Educ. Princ. Policy Pract. 2018, 25, 551–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, L.A. Classroom Assessment to Support Teaching and Learning. Ann. Am. Acad. Political Soc. Sci. 2019, 683, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusalam, N.R.; Munawar, W.; Hardikusumah, I. Development of Authentic Assessment in TVET. Adv. Soc. Sci. Educ. Humanit. Res. 2019, 299, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillis, S.; Patrick, G. Competency Assessment Approaches to Adult Education. David Barlow Publ. 2008, 1, 227–250. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C. The Cochrane Collaboration’s Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.; Dennen, V.P.; Bonk, C.J. A Synthesis of Systematic Review Research on Emerging Learning Environments and Technologies. Educ. Technol. Res. Dev. 2020, 68, 1613–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández del Amo, I.; Erkoyuncu, J.A.; Roy, R.; Palmarini, R.; Onoufriou, D. A Systematic Review of Augmented Reality Content-Related Techniques for Knowledge Transfer in Maintenance Applications. Comput. Ind. 2018, 103, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffril, H.A.M.; Samah, A.A.; Samsuddin, S.F. Guidelines for Developing a Systematic Literature Review for Studies Related to Climate Change Adaptation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22265–22277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halevi, G.; Moed, H.; Bar-Ilan, J. Suitability of Google Scholar as a Source of Scientific Information and as a Source of Data for Scientific Evaluation—Review of the Literature. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, W. A Tale of Two Databases: The Use of Web of Science and Scopus in Academic Papers. Scientometrics 2020, 123, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Q.N.; Fàbregues, S.; Bartlett, G.; Boardman, F.; Cargo, M.; Dagenais, P.; Gagnon, M.P.; Griffiths, F.; Nicolau, B.; O’Cathain, A.; et al. The Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT) Version 2018 for Information Professionals and Researchers. Educ. Inf. 2018, 34, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using Thematic Analysis in Psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowell, L.S.; Norris, J.M.; White, D.E.; Moules, N.J. Thematic Analysis: Striving to Meet the Trustworthiness Criteria. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2017, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, K.; Booth, A.; Garside, R.; Tunçalp, Ö.; Noyes, J. Qualitative Evidence Synthesis for Complex Interventions and Guideline Development: Clarification of the Purpose, Designs and Relevant Methods. BMJ Glob. Health 2019, 4, e000882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim Mukhtar, M.; Ahmad, J. Assessment for Learning: Practice in TVET. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 204, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, H.; Mohd Puad, M.H.; Rashid, A.M.; Jamaluddin, R. Workplace Skills and Teacher Competency from Culinary Arts Students’ Perspectives. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2021, 29, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Musid, N.; Mohd Affandi, H.; Husain, S.H.; Mustaffa Kamal, M.F.; Abas, N.H. The Delevopment of On Job Training Assessment Constructs and Elements for Construction Technology Students in Malaysian Vocational College. J. Tech. Educ. Train. 2019, 11, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlogar, H.; Stanić, N.; Jerin, K. Self-Assessment of Entrepreneurial Competencies of Students of Higher Education. Zbor. Veleuč. U Rij. 2021, 9, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Shin, H.Y.; Woo, H.; Kim, J. Further Training Needs for TVET Trainers: Lessons from a National Survey on Rwandan TVET Trainers’ Instructional Competencies. J. Tech. Educ. Train. 2019, 11, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazin, K.A.; Norman, H.; Nordin, N.; Ibrahim, R. Student Self-Recording Videos for TVET Competency in MOOCs. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogara, G.; Kamin, Y.B.; Saud, M.S.B. The Impact of Assessment Techniques on the Relationship between Work-Based Learning and Teamwork Skills Development. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 59715–59722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyanto, S.; Setiawan, A.; Hamidah, I.; Ana, A. Integration of Mobile Learning and Project-Based Learning in Improving Vocational School Competence. J. Tech. Educ. Train. 2020, 12, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulikers, J.T.M.; Runhaar, P.; Mulder, M. An Assessment Innovation as Flywheel for Changing Teaching and Learning. J. Vocat. Educ. Train. 2018, 70, 212–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.F.; Lim, S.C.J.; Lai, C.S. Assessment of Teaching Practice Competency among In-Service Teacher Degree Program (PPG) in Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia. J. Tech. Educ. Train. 2020, 12, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekri, R.M.; Ruhizan, M.Y.; Norazah, M.N.; Norman, H.; Nur, Y.F.A.; Ashikin, H.T. The Formation of an E-Portfolio Indicator for Malaysia Skills Certificate: A Modified Delphi Survey. Procedia -Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 174, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ab Rahman, A.; Muhammad Hanafi, N.; Yusof, Y.; Ibrahim Mukhtar, M.; Awang, H.; Yusof, A.M. The Effect of Rubric on Rater’s Severity and Bias in Tvet Laboratory Practice Assessment: Analysis Using Many-Facet Rasch Measurement. J. Tech. Educ. Train. 2020, 12, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifried, J.; Brandt, S.; Kögler, K.; Rausch, A. The Computer-Based Assessment of Domain-Specific Problem-Solving Competence—A Three-Step Scoring Procedure. Cogent Educ. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Ali, S.; Nordin, N.; Ismail, M.E. The Effect of Computerized-Adaptive Test on Reducing Anxiety towards Math Test for Polytechnic Students. J. Tech. Educ. Train. 2019, 11, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Otchia, C.S.; Taniguchi, K. Explaining Differing Perceptions of Employees’ Skill Needs: The Case of Garment Workers in Ethiopia. Int. J. Train. Dev. 2018, 22, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, S.E.; Baharun, S.B.; Mahrin, M.N. Skills Bio-Chart as Novel Instrument to Measure TVET Students’ Progressive Performances. In Proceedings of the 2017 7th World Engineering Education Forum, WEEF 2017-In Conjunction with: 7th Regional Conference on Engineering Education and Research in Higher Education 2017, RCEE and RHEd 2017, 1st International STEAM Education Conference, STEAMEC 201, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–16 November 2017; pp. 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levanova, E.A.; Galustyan, O.V.; Seryakova, S.B.; Pushkareva, T.V.; Serykh, A.B.; Yezhov, A.V. Students’ Project Competency within the Framework of STEM Education. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2020, 15, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-Cuesta, V.; Skaf, M.; Manso, J.M.; Ortega-López, V. Student Perceptions of Formative Assessment and Cooperative Work on a Technical Engineering Course. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim Mukhtar, M.; Baharin, M.N.; Mohamad, M.M.; Yusof, Y. Innovative Approaches to Assessment: Develop a Sense of Direction to Promote Students Learning. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2017, 25, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Avdarsol, S.; Rakhimzhanova, L.B.; Bostanov, B.G.; Sagimbaeva, A.Y.; Khakimova, T. Criteria-Based Assessment as the Way of Forming Students’ Functional Literacy in Computer Science. Period. Tche Quim. 2020, 17, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, B.; Thompson, M. A Teacher’s Influence on Student Engagement: Using Smartphones for Creating Vocational Assessment EPortfolios. J. Inf. Technol. Educ. Res. 2019, 18, 113–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, S.; Abdul Rahman, M.H.; Nincarean, D.; Jumaat, N.F.; Utami, P. Knowledge Construction Process in Open Learning System among Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) Practitioners. J. Tech. Educ. Train. 2019, 11, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzembe, A. Access, Participation and Success: The Tri-Dimensional Conundrum of Academic Outcomes in a South African TVET College. Acad. J. Interdiscip. Stud. 2018, 7, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlback, J.; Olstad, H.B.; Sylte, A.L.; Wolden, A.C. The Importance of Authentic Leadership. Dev. Learn. Organ. Int. J. 2020, 7, 302–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, A.; Seifried, J.; Wuttke, E.; Kögler, K.; Brandt, S. Reliability and Validity of a Computer-Based Assessment of Cognitive and Non-Cognitive Facets of Problem-Solving Competence in the Business Domain. Empir. Res. Vocat. Educ. Train. 2016, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewing, B. An Exploration of Assessment Approaches in a Vocational and Education Training Courses in Australia. Empir. Res. Vocat. Educ. Train. 2017, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkalane, P.K. Inclusive Assessment Practices in Vocational Education: A Case of a Technical Vocational Education and Training College. Int. J. Divers. Educ. 2018, 17, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sephokgole, D.; Makgato, M. Student Perception of Lecturers’ Assessment Practices at Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET) Colleges in South Africa. World Trans. Eng. Technol. Educ. 2019, 17, 398–403. [Google Scholar]
- Ana, A.; Yulia, C.; Jubaedah, Y.; Muktiarni, M.; Dwiyanti, V.; Maosul, A. Assessment of Student Competence Using Electronic Rubric. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2020, 15, 3559–3570. [Google Scholar]
- Okolie, U.C.; Elom, E.N.; Igwe, P.A.; Binuomote, M.O.; Nwajiuba, C.A.; Igu, N.C.N. Improving Graduate Outcomes: Implementation of Problem-Based Learning in TVET Systems of Nigerian Higher Education. High. Educ. Ski. Work. -Based Learn. 2020, 11, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ana, A.; Widiaty, I.; Murniati, D.E.; Deauansavanh; Saripudin, S.; Grosch, M. Applicability of Competency-Based Assessment for TVET Interns: Comparing between Indonesia and Laos. J. Tech. Educ. Train. 2019, 11, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalath, J.; Esichaikul, V. Gamification to Enhance Motivation and Engagement in Blended ELearning for Technical and Vocational Education and Training. Technol. Knowl. Learn. 2020, 27, 91–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehner, M.M. High Quality Teaching and Assessing in TVET: The Road to Enhanced Learning Outcomes 2017, 2, pp. 1–232. Available online: https://www.academia.edu/35212852/High_Quality_Teaching_and_Assessing_in_TVET_The_Road_to_Enhanced_Learning_Outcomes_High_Quality_Teaching_and_Assessing_in_TVET_Series_on_Quality_in_TVET_Volume_2_Tertiary_and_Vocational_Education_Commission (accessed on 8 February 2022).
- ILO; UNESCO. The Digitization of TVET and Skills Systems; ILO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 9789220327296. [Google Scholar]

| Databases | Keywords Used | Identification Phase | Included Phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| SCOPUS | TITLE-ABS-KEY ((“assessment” OR “competency * assessment” OR “performance * assessment”) AND (“student * learning outcome *” OR “student * performances *” OR “students * competency *” AND (“technical and vocational education” OR “technical education” OR “vocational education” OR “TVET”)) | 35 | 14 |
| WoS | TS = ((“assessment” OR “competency * assessment” OR “performance * assessment”) AND (“student * learning outcome *” OR “student * performances *” OR “students * competency *” AND (“technical and vocational education” OR “technical education” OR “vocational education” OR “TVET”)) | 28 | 10 |
| Google Scholar | Using specific keywords from Scopus and WoS, as well as Boolean operators, phrase searches, and field code functions (either together or individually) as appropriate | 15 | 5 |
| Publications earned | 78 | 29 |
| Criterion | Eligibility | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Literature type | Journal (research articles) | Book, book series, chapter in book, systematic review articles, conference proceeding |
| Language | English | Non-English |
| Timeline | Between 2015 and 2021 | 2014 and earlier |
| Country/territory | World |
| Authors/Country | Main Study Design | Assessment Approaches | Students Learning Outcome | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Competency Development | Performance Development | Positive Impact of Assessment | |||
| Ibrahim Mokhtar et al., (2017)—Malaysia | QL | FA | 1. Enhance learning (EL) 2. Succeed in achieving learning outcomes (SLO) 3. Build positive attitude (PA) | ||
| Okolie et al., (2020)— Nigeria | QL | CBA | Employability skill (ES) | 1. Integrating theory and practice (ITP) 2. Enhance learning (EL) 3. Allow students to construct learning on their own (CL) | |
| Hegarty et al., (2019)— New Zealand | MM | E-PA | 1. Build confident (BC) 2. Build networking (BN) 3. Reduced student fail (RSF) | ||
| Ana et al., (2019)— Indonesia | MM | CBA | Technical competency (TC) Generic competency (GC) Industrial competency (IC) | ||
| Mohamed et al., (2021)— Malaysia | QN | CBA | Work skill competency (WSC) | ||
| Revilla-Cuesta et al., (2020)— Spain | MM | FA | Professional competencies (PC) | ||
| Abdul Musid et al., (2019)— Malaysia | QL | CBA | Technical skill (TC) soft skill (GC) | ||
| Slogar et al., (2021)— Croatia | QN | CBA | Leadership skills (LS) entrepreneurial competencies (ECS) | ||
| Levanova et al., (2020)—Rusia | QL | CRBA | Project competency (PC) | ||
| Yamada et al., (2018)— Ethiopia | QN | PBA | Comprehensive skills (CS) | ||
| Hashim et al., (2019)— Malaysia | MM | SBA | Develop knowledge construction process (KCP) | ||
| Nzembe (2018)— South Africa | QL | SA | 1. Students were happy in the way they were assessed (AT) 2. They expressed satisfaction on the way they are assessed (AT) | ||
| Kim et al., (2019)— Rwanda | QN | CBA | Developing content knowledge skill (CKS) and Instructional skills (IS) | ||
| Mazin et al., (2020)—Malaysia | MM | CBA | Learning competency (LC) | Learning analytics (LA) | |
| Hui et al., (2017)— Malaysia | QN | PBA | Progressive performance and technology innovation performances (PTIP) | ||
| Mohd Ali et al., (2019)— Malaysia | QN | PBA | Students’ performance in Mathematic (SPM) | Reduces students’ anxiety towards math (AT) | |
| Ab Rahman et al., (2020)— Malaysia | MM | PBA | Student performance in item laboratory assessment (PLA) | ||
| Bekri et al., (2015)— Malaysia | QN | CBA | Development of 4 domains; in ICT Skills (ICTS) | ||
| Dogara et al., (2020)—Nigeria | QN | FA | Soft skills and teamwork skills (GS) | ||
| Sugiyanto et al., (2020)— Indonesia | MM | CBA | Project competency including (PC) | ||
| Dahlback et al., (2020)— Norway | QL | WBA | Teaching practice competency (TPC) | Integrating both theory and practice (ITP) | |
| Gulikers et al., (2018) —The Netherlands | QL | CBA | 1. Student learned a lot from the assessment (EL) 2. Student motivational for their preparation for VET (AT) | ||
| Rausch et al., (2016)—German | QN | COMA | Problem solving competency (PSC) | ||
| Seifried et al., (2020)—German | QN | PBA | Problem solving competency (PSC) | ||
| Lee at al. (2020)— Malaysia | QL | CBA | Teaching practice competency (TPC) | ||
| Ewing et al., (2017)—Australia | MM | SCBA | Competency in mathematics and numeracy (SPM) | ||
| Nkalane (2018)—South Africa | QL | IA | Student’s success in learning (EL) | ||
| Avdarsol et al., (2020)—Kazakhstan | QL | CRBA | Student’s functional literacy in computer science (ICTC) | ||
| Sephokgole et al., (2019)— South Africa | QN | CLBA | Student knowledge and skills to meet real life situation (BKS) | ||
| CBA | PBA | FA | CRBA | E-PA | SBA | SA | WBA | COMA | SCBA | IA | CLBA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] | [43,44,45,46,47] | [48,49,50] | [51] | [52] | [53] | [54] | [55] | [56] | [57] | [58] | [59] | ||
| ES ITP EL CL TC GC LS ECS CKS IS LC | LA ICTS GS PC EL AT TPC IC WSC PC TC GC | CS PTIP SPM | AT PLA PSC | EL AT | PC ICTS | BC BN RSF | KCP | ATA | TPC ITP | PSC | SPM | EL | BKS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yusop, S.R.M.; Rasul, M.S.; Mohamad Yasin, R.; Hashim, H.U.; Jalaludin, N.A. An Assessment Approaches and Learning Outcomes in Technical and Vocational Education: A Systematic Review Using PRISMA. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5225. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095225
Yusop SRM, Rasul MS, Mohamad Yasin R, Hashim HU, Jalaludin NA. An Assessment Approaches and Learning Outcomes in Technical and Vocational Education: A Systematic Review Using PRISMA. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):5225. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095225
Chicago/Turabian StyleYusop, Siti Raudhah M., Mohammad Sattar Rasul, Ruhizan Mohamad Yasin, Haida Umiera Hashim, and Nur Atiqah Jalaludin. 2022. "An Assessment Approaches and Learning Outcomes in Technical and Vocational Education: A Systematic Review Using PRISMA" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 5225. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095225
APA StyleYusop, S. R. M., Rasul, M. S., Mohamad Yasin, R., Hashim, H. U., & Jalaludin, N. A. (2022). An Assessment Approaches and Learning Outcomes in Technical and Vocational Education: A Systematic Review Using PRISMA. Sustainability, 14(9), 5225. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14095225







