Influence of Rainfall Events and Surface Inclination on Overland and Subsurface Runoff Formation on Low-Permeable Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
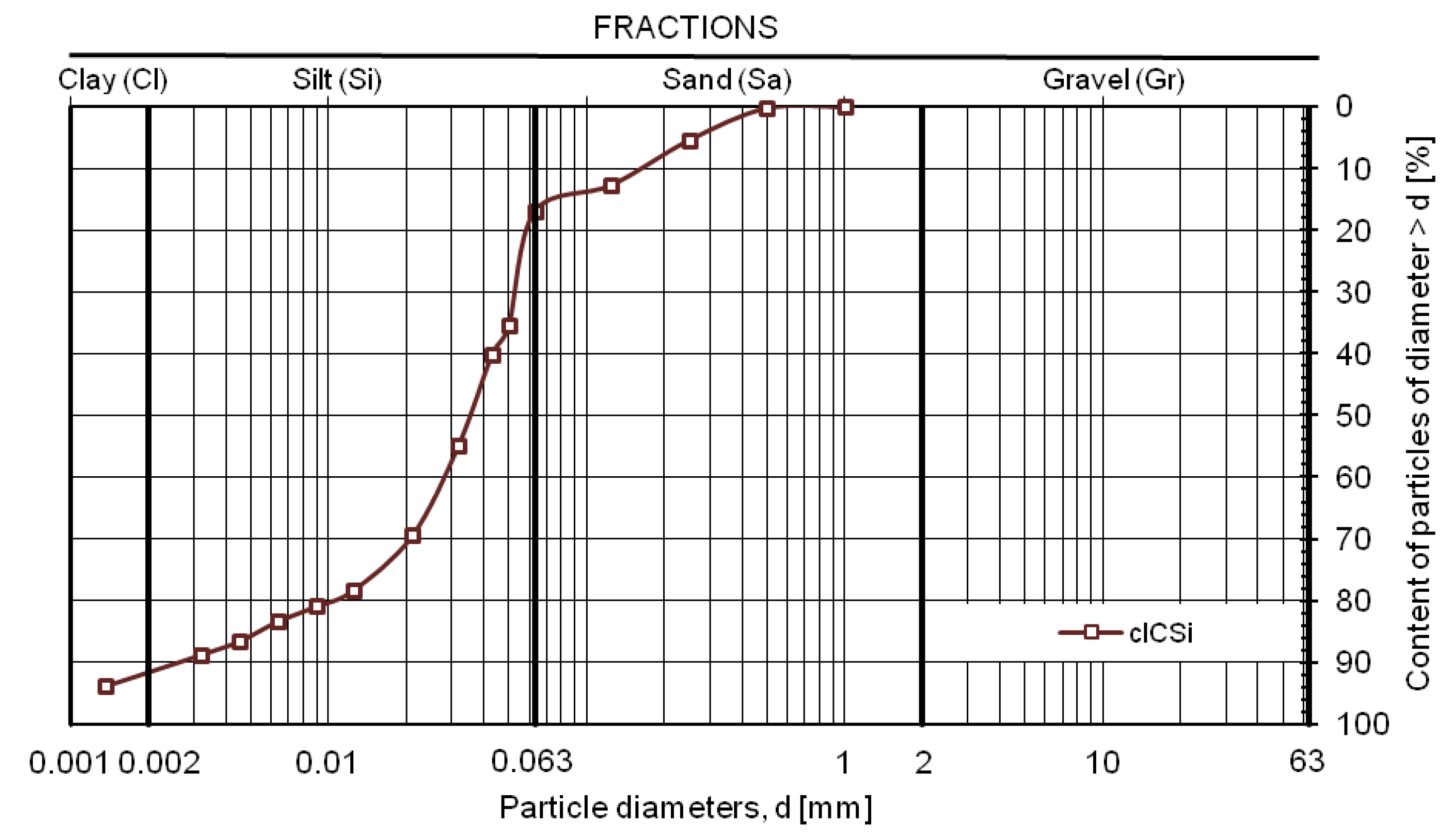
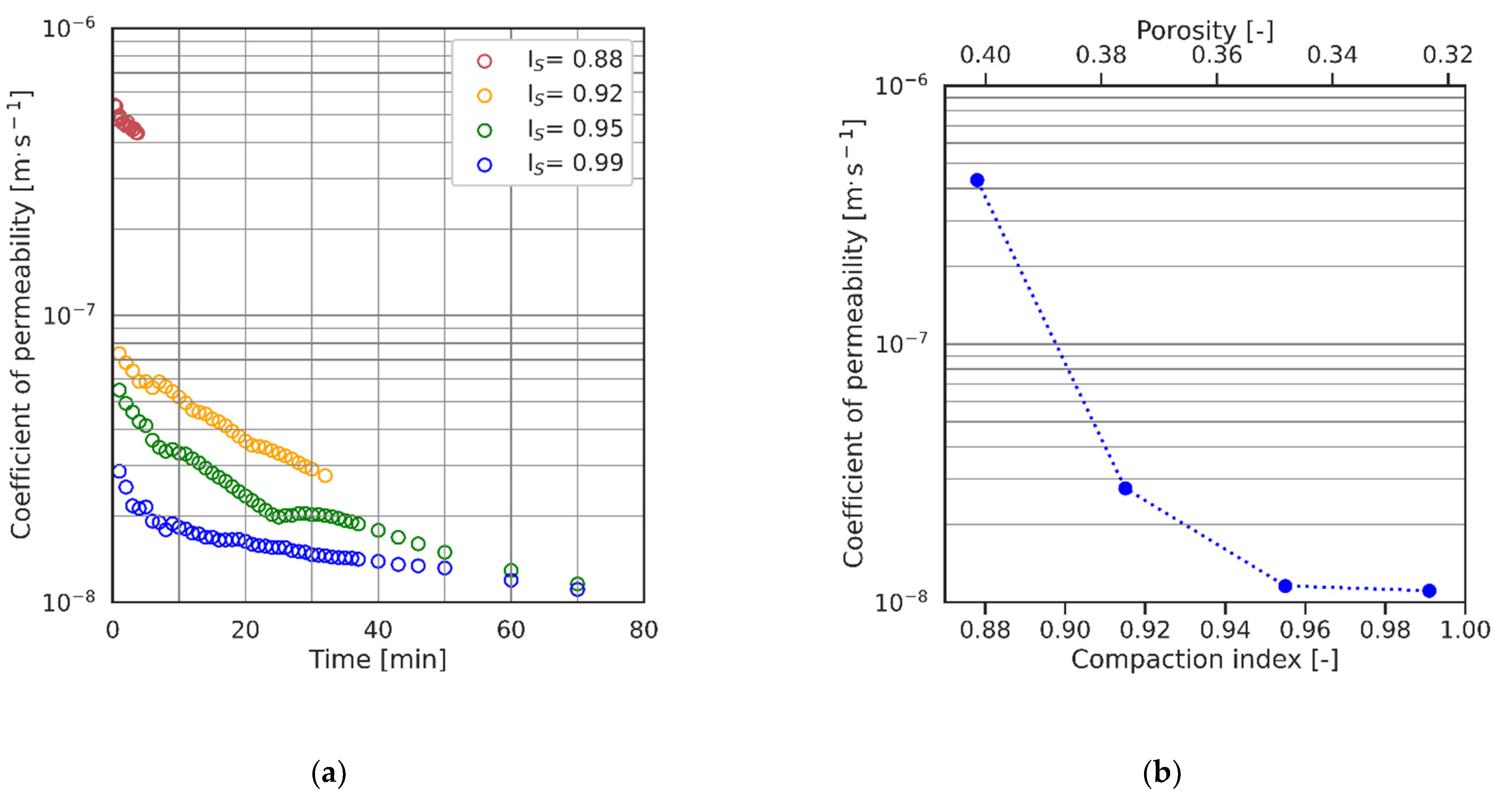
2.1. Research on Geotechnical Properties
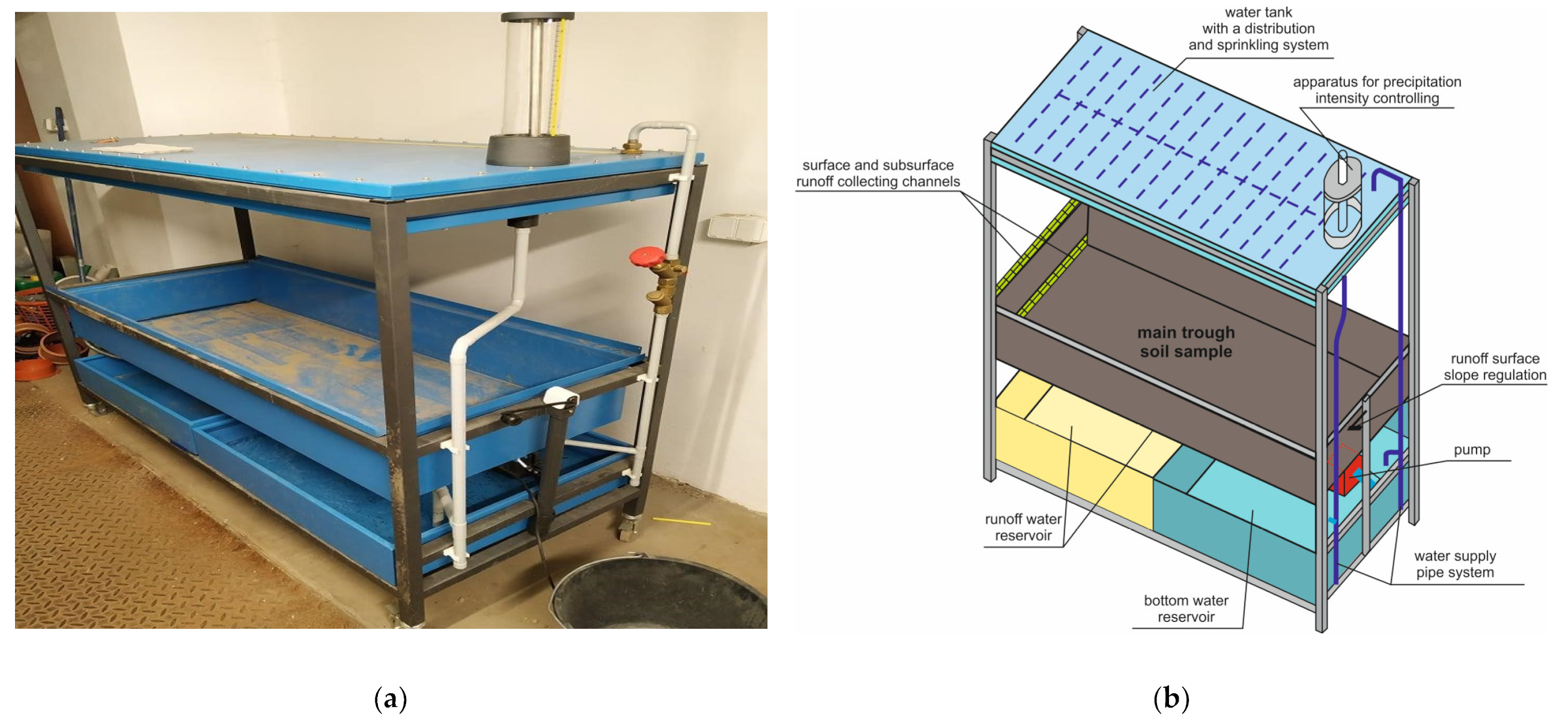
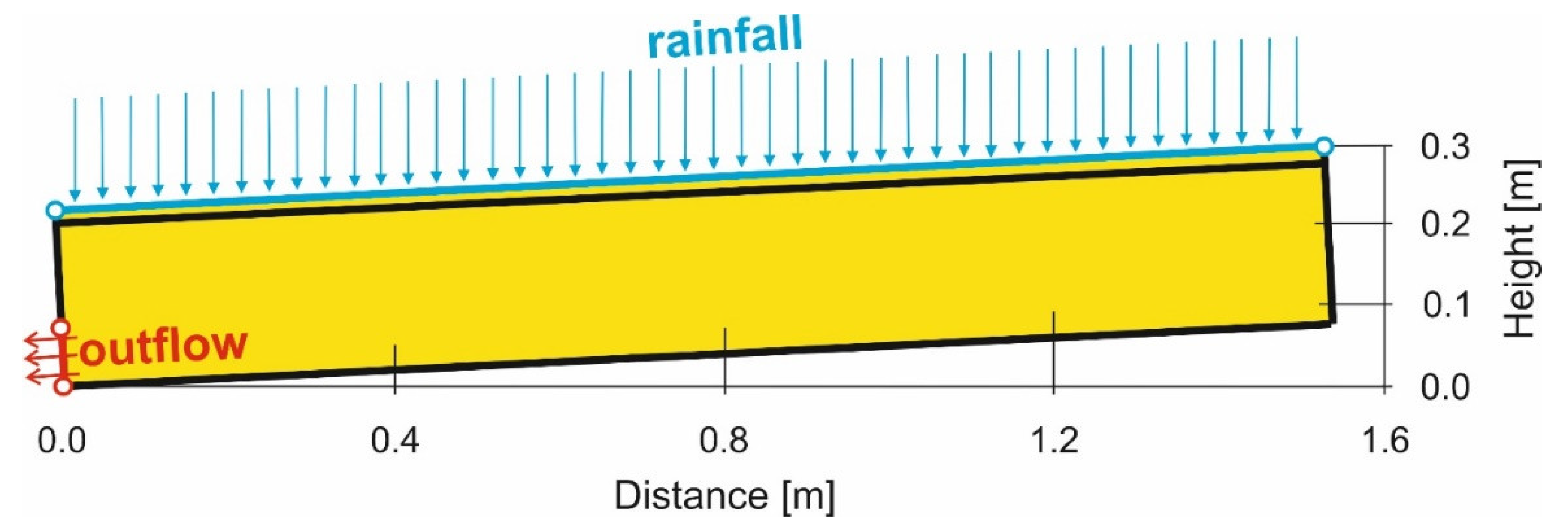
2.2. Surface and Subsurface Runoff Studies
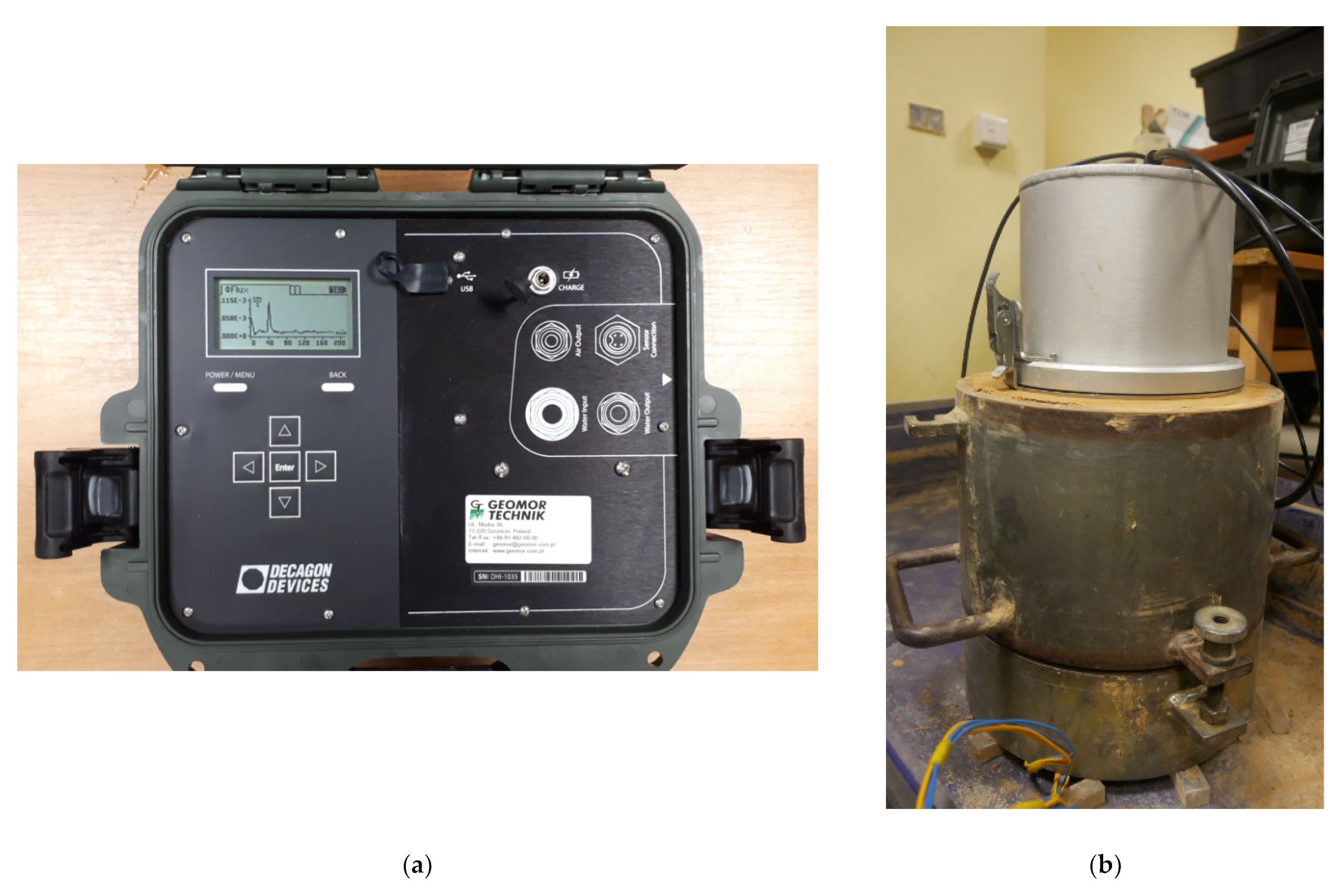
2.3. Monitoring of the Infiltration Process Using the EIS Method
2.4. Calculations of Overland and Subsurface Runoff with the Use of Models Taking into Account the Infiltration Process
2.5. Estimation of Overland and Subsurface Runoff Using the MSME Model
3. Results of Studies
3.1. Geotechnical Properties of Soil
3.2. Overland and Subsurface Runoff
3.3. Monitoring of Water Infiltration within the Soil
3.4. Verification of Calculation Models
3.4.1. Green–Ampt and Richards Models
3.4.2. MSME Model (Verification of Suitability for the Total Runoff Estimation)
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Egiazarova, D.; Kordzakhia, M.; Wałęga, A.; Drożdżal, E.; Milczarek, M.; Radecka, A. Application of Polish experience in the implementation of the flood directive in Georgia—Hydrological calculations. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2017, 16, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gądek, W.; Bodziony, M. The hydrological model and formula for determining the hypothetical flood wave volume in non-gauged basins. Meteorol. Hydrol. Water Manag. 2015, 3, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maidmend, D.R. Handbook of Hydrology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service. Hydrology. In National Engineering Handbook; Chapter 10; USDA Soil Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Karabová, B.; Sikorska, A.; Banasik, K.; Kohnová, S. Parameters determination of a conceptual rainfall-runoff model for a small catchment in Carpathians. Ann. Wars. Univ. Life Sci.-SGGW. Land Reclam. 2012, 44, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młyński, D.; Wałega, A.; Książek, L.; Florek, J.; Petroselli, A. Possibility of using selected rainfall-runoff models for determining the design hydrograph in mountainous catchments: A case study in poland. Water 2020, 12, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, S.; Petroselli, A. Do we still need the rational formula? An alternative empirical procedure for peak discharge estimation in small and ungauged basins. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscopia, R.; Petroselli, A.; Grimaldi, S. A software package for the prediction of design flood hydrograph in small and ungauged basins. J. Agric. Eng. 2015, 432, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petroselli, A.; Grimaldi, S. Design hydrograph estimation in small and fully ungauged basin: A preliminary assessment of the EBA4SUB framework. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2018, 11, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petroselli, A.; Grimaldi, S.; Piscopia, R.; Tauro, F. Design hydrograph estimation in small and ungauged basins: A comparative assessment of event based (EBA4SUB) and continuous (cosmo4sub) modelling approaches. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2019, 18, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, T.; Krężałek, K. Prognostic model of total runoff and its components from a partially urbanized small lowland catchment. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2018, 18, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Mitchell, J.K.; Hirschi, M.C.; Cooke, R.A. Modified SCS curve number method for predicting subsurface drainage flow. Trans. ASAE 2001, 44, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wałęga, A.; Amatya, D.M.; Caldwell, P.; Marion, D.; Panda, S. Assessment of storm direct runoff and peak flow rates using improved SCS-CN models for selected forested watersheds in the Southeastern United States. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2020, 27, 100645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, R.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Eldho, T.I. Performance evaluation of modified versions of SCS curve number method for two watersheds of Maharashtra, India. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 18, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, J.L.M.P.; Singh, V.P. Laboratory experiments on the influence of storm movement on overland flow. Phys. Chem. Earth 2003, 28, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Jin, C.; Pei, J. A modified hortonian overland flow model based on laboratory experiments. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Padmanabhan, G.; Bogart, D. Microrelief-controlled overland flow generation: Laboratory and field experiments. Hindawi Publ. Corp. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2015, 2015, 642952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danino, D.; Svoray, T.; Thompson, S.; Cohen, A.; Crompton, O.; Volk, E.; Argaman, E.; Levi, A.; Cohen, Y.; Narkis, K.; et al. Quantifying shallow overland flow patterns under laboratory simulations using thermal and LiDAR imagery. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Capillary conduction of liquids in porous mediums. Physics 1931, 1, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, W.H.; Ampt, G.A. Studies of soils physics I. The flow of air and water through soils. J. Agric. Sci. 1911, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Mein, R.G.; Larson, C.L. Modeling infiltration during a steady rain. Water Resour. Res. 1973, 9, 2, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chow, V.T.; Maidment, D.R.; Mays, L.W. Applied Hydrology; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Young, M.H. Green-Ampt infiltration model for sloping surfaces. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W07420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chormański, J.; Ignar, S.; Cabański, P. Zastosowanie modelu infiltracyjnego Green’a i Ampt’a oraz metod GIS do określania opadu efektywnego w modelowaniu opad-odpływ na przykładzie zlewni górnej wilgi. Zesz. Probl. Postępów Nauk. Rol. 2008, 532, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.E.; Lee, S.R. Evaluation of surficial stability for homogeneous slopes considering rainfall characteristics. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2002, 128, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.E. Infiltration analysis to evaluate the surficial stability of two-layered slopes considering rainfall characteristics. Eng. Geol. 2009, 105, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntohar, A.S.; Liao, H.J. Analysis of rainfall-induced infinite slope failure during typhoon using a hydrological—Geotechnical model. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, W.; Gil, E. Water circulation, soil erosion and chemical denudation in flysh catchment area. (In Polish: Procesy obiegu wody, erozji gleb i denudacji chemicznej w zlewni Bystrzanki). Przegląd Nauk. Inż. Kształt. Sr. 2007, 16, 28–42. [Google Scholar]
- Bochenek, W.; Gil, E. The diversity of overland flow and soil wash on experimental plots of different lengths (Szymbark, Low Beskidy Mts.) (In Polish: Zróżnicowanie spływu powierzchniowego i spłukiwania gleby na poletkach doświadczalnych o różnej długości (Szymbark, Beskid Niski)). Pr. Studia Geogr. 2010, 45, 265–278. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, G.; Weltz, M.; Pierson, F.B.; Spaeth, K.E.; Pachepsky, Y. Scale effects on runoff and soil erosion in rangelands: Observations and estimations with predictors of different availability. Catena 2017, 151, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounirou, L.A.; Zoure, C.O.; Yonaba, R.; Paturel, J.E.; Mahe, G.; Niang, D.; Yacouba, H.; Karambiri, H. Multi-scale analysis of runoff from a statistical perspective in a small Sahelian catchment under semi-arid climate. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolska, E. Runoff and soil erosion on sandy slope in the last-glacial area—Plots measurements (Suwałki Lake land, NE Poland. (in polish: Spływ wody i erozja gleby na piaszczystym stoku w obszarze młodoglacjalnym—Pomiary poletkowe (Pojezierze Suwalskie, Polska NE)). Pr. Studia Geogr. 2010, 45, 197–214. [Google Scholar]
- Święchowicz, J. Slopewash on agricultural foothill slopes in hydrological years 2007–2008 in Łazy (Wiśnicz Foothills). (In Polish: Spłukiwanie gleby na użytkowanych rolniczo stokach pogórskich w latach hydrologicznych 2007–2008 w Łazach (Pogórze Wiśnickie)). Pr. Studia Geogr. 2010, 45, 243–263. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, T.A.; Gitirana, G.F.N.J.; Rebolledo, J.F.R.; Vaz, E.F.; da Luz, M.P. Numerical evaluation of laboratory apparatuses for the study of infiltration and runoff. Braz. J. Water Resour. 2020, 25, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahardjo, H.; Lee, T.T.; Leong, E.C.; Rezaur, R.B. Response of a residual soil slope to rainfall. Can. Geotech. J. 2005, 42, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, S.; Naef, F.; Faeh, A.O.; Cordery, I. Formation of runoff at the hillslope scale during intense precipitation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poesen, J. The influence of slope angle on infiltration rate and Hortonian overland flow. Geomorphology 1984, 49, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Nassif, S.H.; Wilson, E.M. The influence of slope and rain intensity on runoff and infiltration (L’influence de l’inclinaison de terrain et de l’intensitéde pluie sur l’écoulement et l’infiltration). Hydrol. Sci. J. 1975, 20, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczak, P.; Kundzewicz, Z.W. Water-related conflicts in urban areas in Poland. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2011, 56, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skotnicki, M.; Sowiński, M. The influence of depression storage on runoff from impervious surface of urban catchment. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosińska, E. Local flooding in the USA, Europe, and Poland—An overview of strategies and actions in face of climate change and urbanisation. Infrastruct. Ecol. Rural. Areas 2016, 3, 801–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczykiewicz, T.; Skonieczna, M. Rainfall flooding in Urban areas in the context of geomorphological aspects. Geoseinces 2020, 10, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonaba, R.; Biaou, A.C.; Koïta, M.; Tazen, F.; Mounirou, L.A.; Zouré, C.O.; Queloz, P.; Karambiri, H.; Yacouba, H. A dynamic land use/land cover input helps in picturing the Sahelian paradox: Assessing variability and attribution of changes in surface runoff in a Sahelian watershed. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkel, L. Geomorphic hazards in the Polish Flysch Carpathians. Studia Geomorphol. Carpatho-Balc. 2006, 11, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bodziony, M.; Baziak, B. Heavy rain effects on the example of 1997 and 2005 floods in the Wielka Puszcza basin. (In Polish: Skutki deszczy nawalnych na przykładzie powodzi w zlewni rzeki Wielkiej Puszczy w latach 1997 i 2005). Czas. Tech. Sr. 2007, 2, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Wałega, A.; Cupak, A.; Amatya, D.M.; Drożdżal, E. Comparison of direct outflow calculated by modified SCS-CN methods for mountainous and high land catchments in upper vistula basin, Poland and lowland catchment in South Carlina, USA. Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2017, 16, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwagrzyk, M.; Kaim, D.; Price, B.; Wypych, A.; Grabska, E.; Kozak, J. Impact of forecasted land use changes on flood risk in the Polish Carpathians. Nat. Hazards 2018, 94, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gil, E. Water Circulation and Wash Down on the Flysch Slopes Used fo r Fanningpurposes in 1980–1990 Years (Results of Investigation on Experimental Plots at ResearchStation of Institute of Geography and Spatial Organization Polish Academy of Sciences in Szymbark) (In Polish: Obieg Wody i Spłukiwanie na Fliszowych Stokach Użytkowanych Rolniczo w Latach 1980–1990 (Wyniki Badań Przeprowadzonych na Poletkach Doświadczalnych na Stacji Naukowej IGiPZ PAN w Szymbarku)); Zeszyty IGiPZ PAN: Warszawa, Poland, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Moeyersons, J.; Makanzu, F.M.; Imwangana; Dewitte, O. Site- and rainfall-specific runoff coefficients and critical rainfall for mega-gully development in Kinshasa (DR Congo). Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, S203–S233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, S.H.; Mohammad, F.S.; Alazba, A.A. Determination of potential runoff coefficient for Al-Baha Region, Saudi Arabia using GIS. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 2041–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, J. Budowa geologiczna regionu Krakowa. Prz. Geol. 1989, 37, 302–308. [Google Scholar]
- Wójcik, A.; Kamieniarz, S.; Wódka, M.; Biajgo, A.; Janeczek, A.; Walatek, M. Atlas Osuwisk Miasta Krakowa; Urząd Miasta: Kraków, Poland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rutkowski, J. Szczegółowa Mapa Geologiczna Polski, Arkusz 973—Kraków; Państwowy Instytut Geologiczny: Warszawa, Poland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Kolasa, M. Geotechniczne Własności Lessów Okolic Krakowa; Wydawnictwa Geologiczne: Warszawa, Poland, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- PN-EN ISO 14688-2:2018-05; Rozpoznanie i Badania Geotechniczne. Oznaczanie i Klasyfikowanie Gruntów. Część 2: Zasady klasyfikowania. Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warszawa, Poland, 2018.
- Ziernicka-Wojtaszek, A.; Kopcińska, J. Variation in atmospheric precipitation in Poland in the years 2001–2018. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Meteorology and Water Management-National Research Institute (in Polish: Instytut Meteorologii i Gospodarki Wodnej—Państwowy Instutu Badawczy). Available online: https://danepubliczne.imgw.pl/#ostrzezenia-archiwalne (accessed on 16 February 2022).
- PN-EN ISO 17892–4:2017-01; Rozpoznanie i Badania Geotechniczne. Badania Laboratoryjne Gruntów. Część 4: Badanie Uziarnienia Gruntów. Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warszawa, Poland, 2017.
- PN-EN ISO 17892-12:2018-08; Rozpoznanie i Badania Geotechniczne. Badania Laboratoryjne Gruntów. Część 12: Oznaczanie Granic Płynności i Plastyczności. Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warszawa, Poland, 2018.
- PN-EN 13286-2:2010; Mieszanki Niezwiązane i Związane Hydraulicznie. Część 2: Metody Badań Laboratoryjnych Gęstości na Sucho i Zawartości Wody. Zagęszczanie Metodą Proktora. Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warszawa, Poland, 2010.
- Kaczyński, R.R. Warunki Geologiczno-Inżynierski na Obszarze Polski; Państwowy Instytut Geologiczny: Warszawa, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lambor, J. Hydrologia Inżynierska; Arkady: Warszawa, Poland, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- PN-S-02204:1997; Drogi Samochodowe. Odwodnienie Dróg. Odwodnienie Dróg. Polski Komitet Normalizacyjny: Warszawa, Poland, 2018.
- Ziemiański, M.; Ośródka, L. Wpływ Zmian Klimatu na Środowisko, Gospodarka Społeczeństwo; Seria Publikacji Naukowo-Badawczych IMGW-PIB: Warszawa, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pařilková, J.; Gombos, M.; Talt, A.; Kandra, B. Calibration of Z-meter device for measurement of volumetric moisture of soils. In Proceedings of the Eureka 2009, 5th Working Session within the Frame of the International Program EUREKA, Project No.: E!3838. Research, Development and Processing of Computerized Measuring System of Soils Moisture with EIS Method, Brno, Czech Republic, 11–13 November 2009; pp. 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Morel-Seytoux, H.J.; Khanji, J. Derivation of an equation of infiltration. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntohar, A.S.; Liao, H.J. Rainfall infiltration: Infinite slope model for landslides triggering by rainstorm. Nat. Hazards 2010, 54, 967–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wałęga, A.; Amatya, D.M. Application of modified SME-CN method for predicting event runoff and peak discharge from a drained forest watershed on the North Carolina Atlantic Coastal Plain. Trans. ASABE 2020, 63, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wałęga, A.; Rutkowska, A.; Grzebinoga, M. Direct runoff assessment using modified SME method in catchments in the upper vistula river basin. Acta Geophys. 2017, 65, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.E.; Sutcliffe, J.V. River flow forecasting through conceptual models part I. A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, A.; Munoz-Carpena, R. Performance evaluation of hydrological models: Statistical significance for reducing subjectivity in goodness-of-fit assessments. J. Hydrol. 2013, 480, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskom, M.L. Seaborn: Statistical data visualization. Open J. 2021, 6, 3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.-B.; Sun, Y.-Z.; Zhu, Y.-T.; Yang, Z.-H.; Tian, D.-H. Study on permeability coefficient of saturated cohesive soil based on fractal theory. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 242, p. 062055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazdro, Z. Hydrogeologia Ogólna; Wydawnictwa Geologiczne: Warszawa, Poland, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Morbidelli, R.; Saltalippi, C.; Flammini, A.; Cifrodelli, M.; Corradini, C.; Govindaraju, R.S. Infiltration on sloping surfaces: Laboratory experimental evidence and implications for infiltration modelling. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, D.M.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Bruand, A. The effect of ponding depth on infiltration in a crusted surface depression. Catena 1998, 32, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijowska-Strugała, M.; Kiszka, K. Assessment of the splash on the foothill slope (Flysch carpathians, bystrzanka catchment) (In Polish: Ocena wielkości rozbryzgu gleby na stoku pogórskim (Karpaty fliszowe, zlewnia Bystrzanki)). Ann. Univ. Mariae Curie-Skłodowska Lub.—Pol. 2014, 69, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pařilková, J.; Pařilek, L. Monitoring of the earth-fill dam of the Hornice reservoir monitored by EIS. In Proceedings of the Eureka 2015 3rd Conference and Working Session within the Frame of the International Program EUREKA, Project No.: e!7614. A System of Monitoring of Selected Parameters of Porous Substances Using the EIS Method in a Wide Range of Applications, Jaromerice nad Rokytnou, Czech Republic, 15–16 October 2015; pp. 205–224. [Google Scholar]
- Pařilková, J.; Pařilek, L. Monitoring of the earth dam of a water reservoir by the method of electrical impedance spectrometry. In Proceedings of the Eureka 2008, 4th Working Session within the Frame of the International Program EUREKA; Project No.: E!3838. Research, Development and Processing of Computerized Measuring System of Soils Moisture with EIS Method, Brno, Czech Republic, 18–19 September 2008; pp. 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gruchot, A.; Zydroń, T.; Cholewa, M.; Koś, K. Using impedance spectroscopy method (EIS) to monitor filtration—Model tests. In Proceedings of the 4th Conference and Working Session within the Frame-Work of the International Programme EUREKA, Project No.: E!7614, Lednice, Czech Republic, 13–14 October 2016; pp. 82–90. [Google Scholar]
- Mounirou, L.A.; Yonaba, R.; Koïta, M.; Paturel, J.E.; Mahé, G.; Yacouba, H.; Karambiri, H. Hydrologic similarity: Dimensionless runoff indices across scales in a semi-arid catchment. J. Arid. Environ. 2021, 193, 104590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, W. Evaluation of precipitation at the IG&SO pas research station in Szymbark during 40-year period (1971–2010) and its impact on the variability of water runoff from the Bystrzanka stream basin. (In Polish: Ocena zmian warunków opadowych na stacji naukowo-badawczej IGiPZ PAN W Szymbarku w okresie 40 lat obserwacji (1971–2010) i ich wpływ na zmienność odpływu wody ze zlewni Bystrzanki). Woda-Sr.-Obsz. Wiej. 2012, 12, 29–44. [Google Scholar]
- Fratini, C.F.; Geldof, G.D.; Kluck, J.; Mikkelsen, P.S. Three points approach (3PA) for urban flood risk management: A tool to support climate change adaptation through transdisciplinarity and multifunctionality. Urban Water J. 2012, 9, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le, T.T.A.; Lan-Anh, N.T.; Daskali, V.; Verbist, B.; Vu, K.C.; Anh, T.N.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Nguyen, V.G.; Willems, P. Urban flood hazard analysis in present and future climate after statistical downscaling: A case study in Ha Tinh city, Vietnam. Urban Water J. 2021, 18, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zydroń, T.; Wałęga, A.; Bochenek, W. Application of selected hydrological models for the calculation of overland flow (In Polish: Zastosowanie wybranych modeli hydrologicznych do określania wielkości spływu powierzchniowego). Acta Sci. Pol. Form. Circumiectus 2014, 13, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Młyński, D. Analysis of problems related to the calculation of flood frequency using rainfall-runoff models: A case study in Poland. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



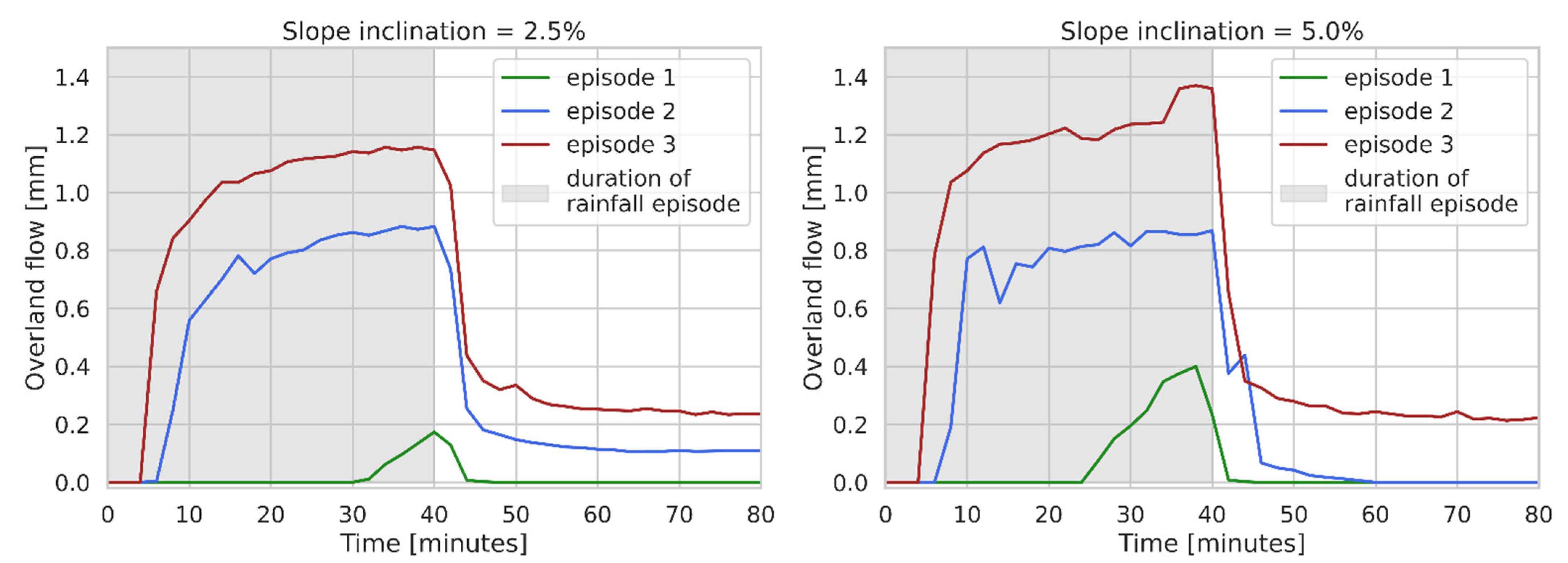
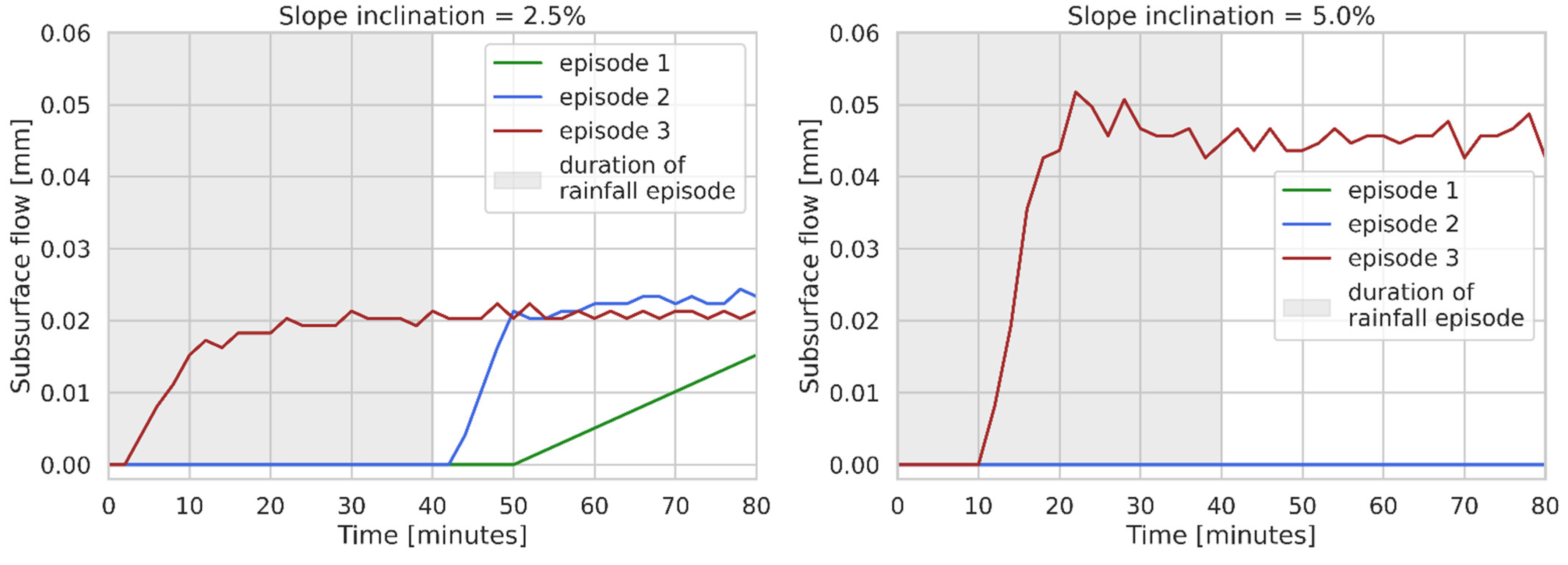
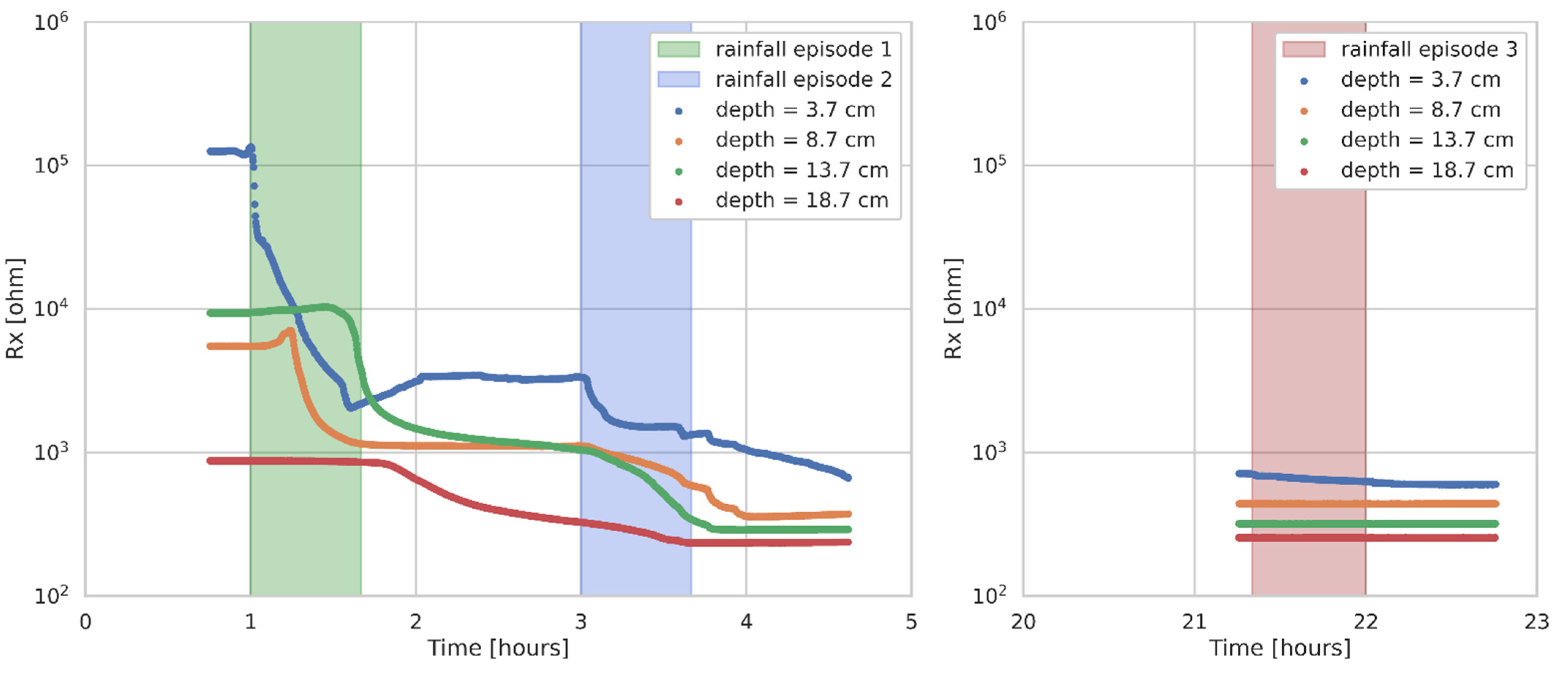


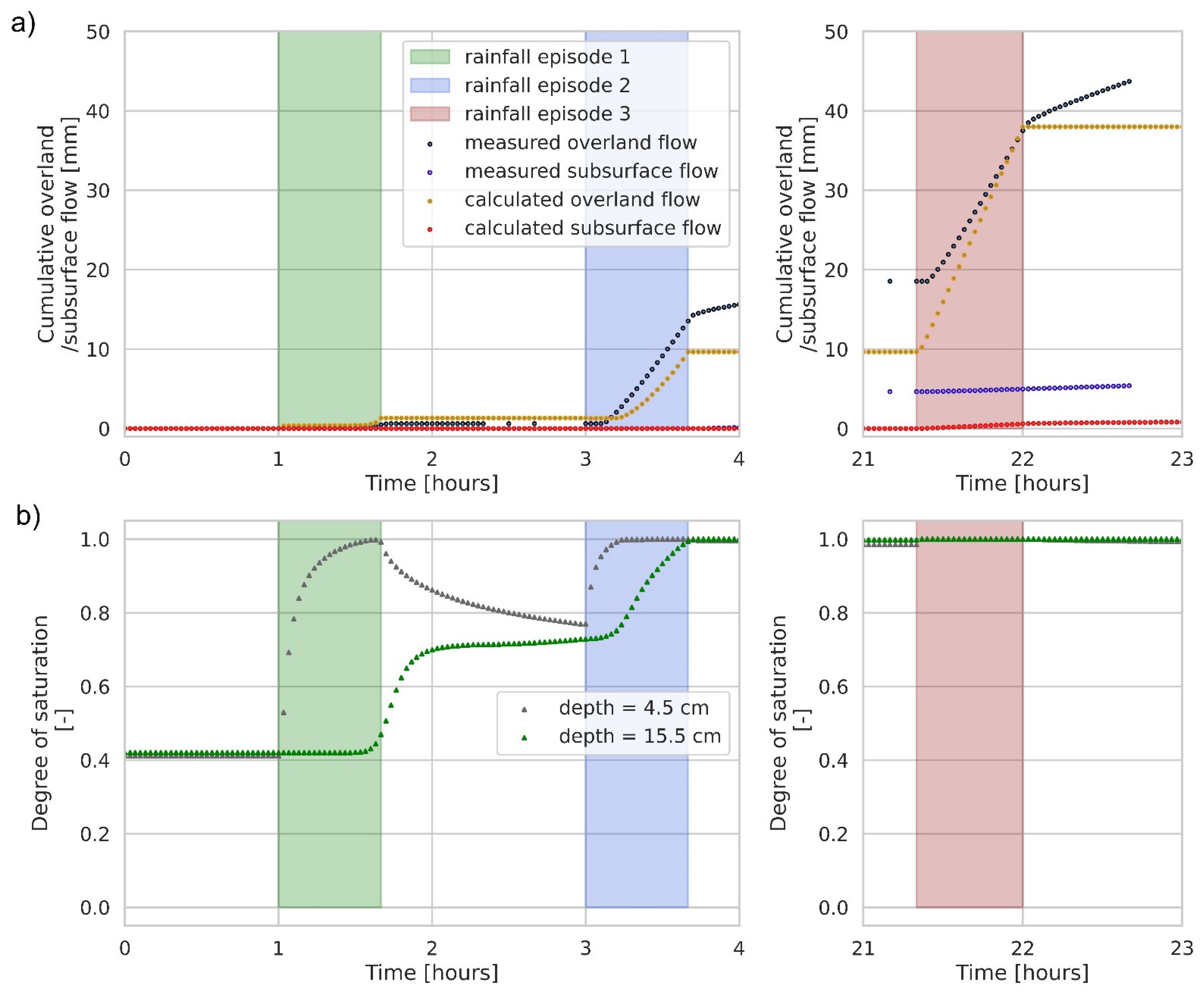
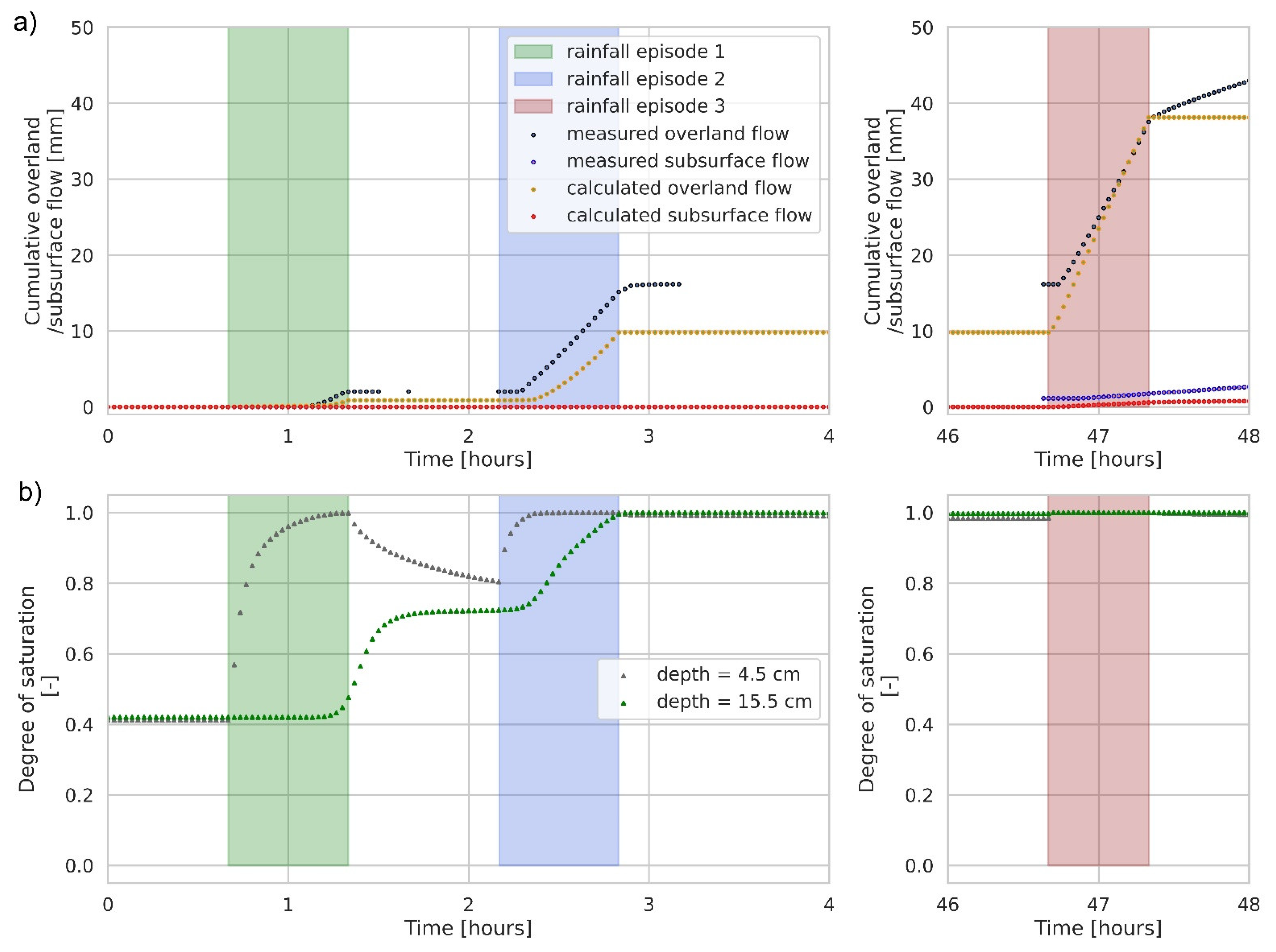
| Runoff Slope (%) | Rainfall Episode | Precipitation | Soil Moisture Content (1) before Rainfall (%) | Volumetric Soil Moisture Content (2) before/after the Examination (-) | Runoff Record | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Height (mm) | Duration (min) | Intensity (mm·min−1) | Overland | Subsurface | ||||
| 2.5 | 1 | 30 | 40 | 0.75 | 10.0 | 0.39/0.72 | yes | no |
| 2 | 24.2 | 0.72/0.92 | yes | yes | ||||
| 3 | 26.4 | 0.81/0.94 | yes | yes | ||||
| 5.0 | 1 | 10.0 | 0.39/0.71 | yes | no | |||
| 2 | 21.5 | 0.71/0.90 | yes | no | ||||
| 3 | 23.0 | 0.87/0.97 | yes | yes | ||||
| Number of the Rainfall Episode | Type of Runoff | Soil Coefficient of Permeability Used in the Calculations (m·s−1) | Inclination of Soil Surface | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5% | 5.0% | |||||||
| Observations | Model | Observations | Model | |||||
| Green–Ampt | Richards | Green–Ampt | Richards | |||||
| Runoff Value (mm) | ||||||||
| 1 | overland | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10−7 | 0.61 | 0.00 3.02 9.76 15.49 | 0.96 1.32 6.85 12.96 | 2.03 | 0.00 3.02 9.76 15.49 | 0.20 0.88 6.76 12.91 |
| subsurface | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10-7 | 0.00 | - | 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 | 0.0 | - | 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 | |
| 2 | overland | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10−7 | 16.11 | 6.83 14.24 19.37 22.78 | 7.38 8.33 14.46 19.32 | 14.15 | 6.10 13.59 18.87 22.41 | 8.25 8.95 15.27 19.91 |
| subsurface | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10−7 | 0.39 | - | 0.19 0.00 0.00 0.00 | 0.0 | - | 0.56 0.19 0.00 0.00 | |
| 3 | overland | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10−7 | 25.17 | 11.23 17.94 22.14 24.78 | 28.25 28.36 18.14 18.01 | 26.78 | 14.61 20.60 24.10 26.20 | 28.11 28.31 17.88 18.00 |
| subsurface | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10−7 | 0.75 | - | 0.90 0.77 0.00 0.00 | 1.53 | - | 1.42 0.77 0.00 0.00 | |
| Total | overland | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10−7 | 43.72 | 18.1 35.2 51.3 63.1 | 36.59 38.00 39.46 50.29 | 42.96 | 20.71 37.21 52.73 64.10 | 36.56 38.14 39.91 50.82 |
| subsurface | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10−7 | 5.20 | - | 1.49 0.91 0.00 0.00 | 2.66 | - | 2.42 0.78 0.00 0.00 | |
| Type of Runoff | Soil Coefficient of Permeability Used in the Calculations (m.s−1) | Inclination of Soil Surface | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5% | 5.0% | ||||
| Model | Model | ||||
| Green–Ampt | Richards | Green–Ampt | Richards | ||
| Root Mean Square Error, RMSE (mm) (Equation (21)) | |||||
| overland | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10−7 | 162.15 35.38 59.77 153.62 | 49.50 41.10 52.57 123.60 | 125.29 22.79 51.50 144.27 | 23.07 17.70 59.35 132.08 |
| subsurface | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10−7 | - | 0.25 0.30 0.63 0.63 | - | 0.19 0.33 1.35 1.35 |
| Modeling efficiency, EF [-] (Equation (22)) | |||||
| overland | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10−7 | 0.09 0.80 0.66 0.14 | 0.72 0.77 0.70 0.31 | 0.74 0.95 0.89 0.70 | 0.95 0.96 0.87 0.72 |
| subsurface | 4.0 × 10−6 2.0 × 10−6 1.0 × 10−6 5.0 × 10−7 | - | −0.54 −0.86 −2.86 −2.86 | - | 0.79 0.64 −0.50 −0.50 |
| Slope Inclination | Qsurfobs | Qsubsurfobs | Qtotobs | Qsurcalc | Qsubsurfcalc | Qtotcalc | CN | M | Sa | Sb | Ia1 | Ia2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | mm | - | mm | |||||||||
| 2.5 | 10.8 | 0.40 | 11.16 | 11.19 | 0.21 | 11.40 | 89.7 | 0.00 | 27.1 | 787.1 | 22.9 | 122.6 |
| 5.0 | 12.1 | 0.47 | 12.53 | 11.91 | 0.59 | 12.51 | 93.0 | 0.00 | 18.2 | 654.7 | 16.5 | 62.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gruchot, A.; Zydroń, T.; Wałęga, A.; Pařílková, J.; Stanisz, J. Influence of Rainfall Events and Surface Inclination on Overland and Subsurface Runoff Formation on Low-Permeable Soil. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4962. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094962
Gruchot A, Zydroń T, Wałęga A, Pařílková J, Stanisz J. Influence of Rainfall Events and Surface Inclination on Overland and Subsurface Runoff Formation on Low-Permeable Soil. Sustainability. 2022; 14(9):4962. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094962
Chicago/Turabian StyleGruchot, Andrzej, Tymoteusz Zydroń, Andrzej Wałęga, Jana Pařílková, and Jacek Stanisz. 2022. "Influence of Rainfall Events and Surface Inclination on Overland and Subsurface Runoff Formation on Low-Permeable Soil" Sustainability 14, no. 9: 4962. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094962
APA StyleGruchot, A., Zydroń, T., Wałęga, A., Pařílková, J., & Stanisz, J. (2022). Influence of Rainfall Events and Surface Inclination on Overland and Subsurface Runoff Formation on Low-Permeable Soil. Sustainability, 14(9), 4962. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14094962







