Research on Passengers’ Preference for High-Speed Railways (HSRs) and High-Speed Trains (HSTs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bibliometric Analysis
2.1. Scopus Database
2.2. Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) Model
3. Results
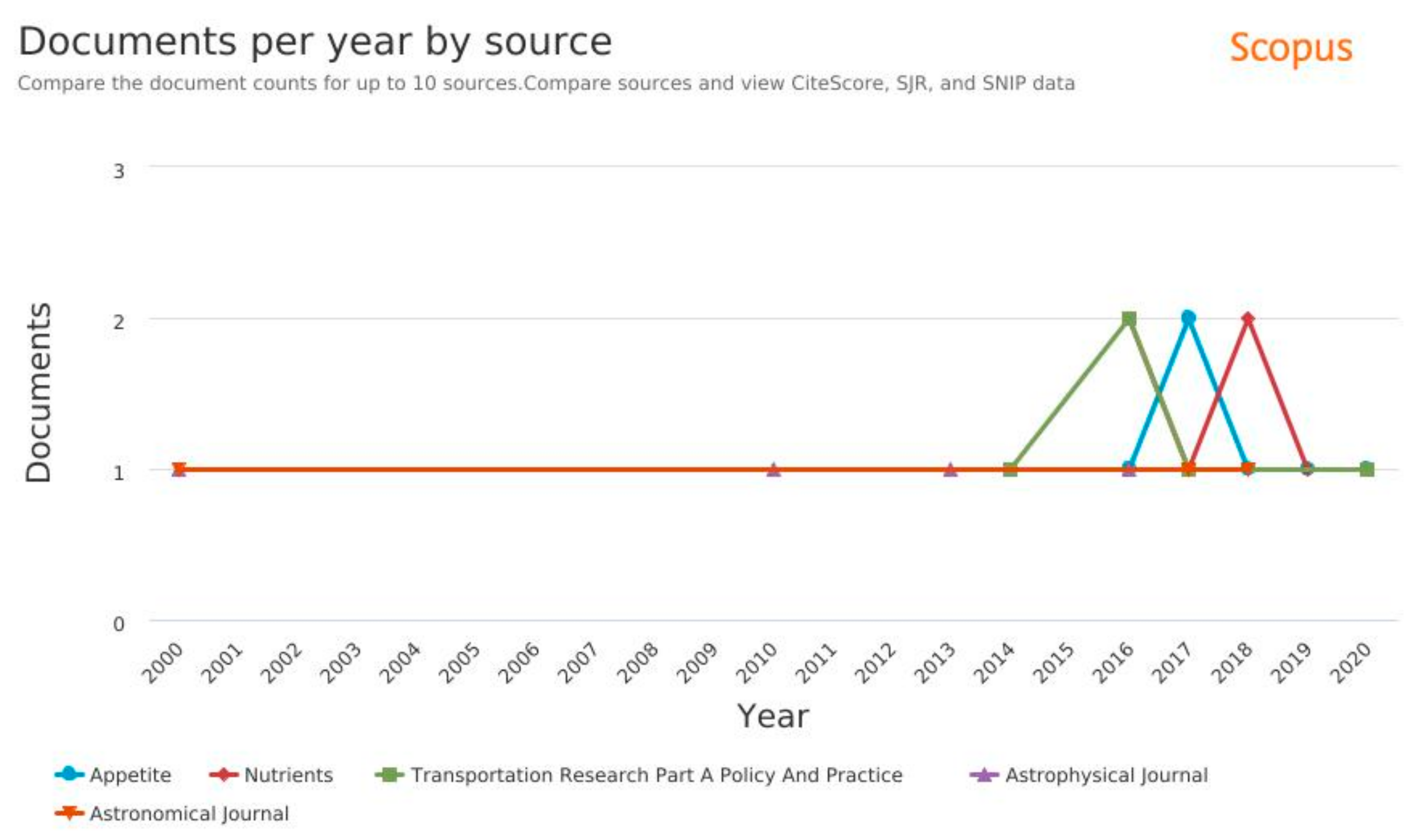
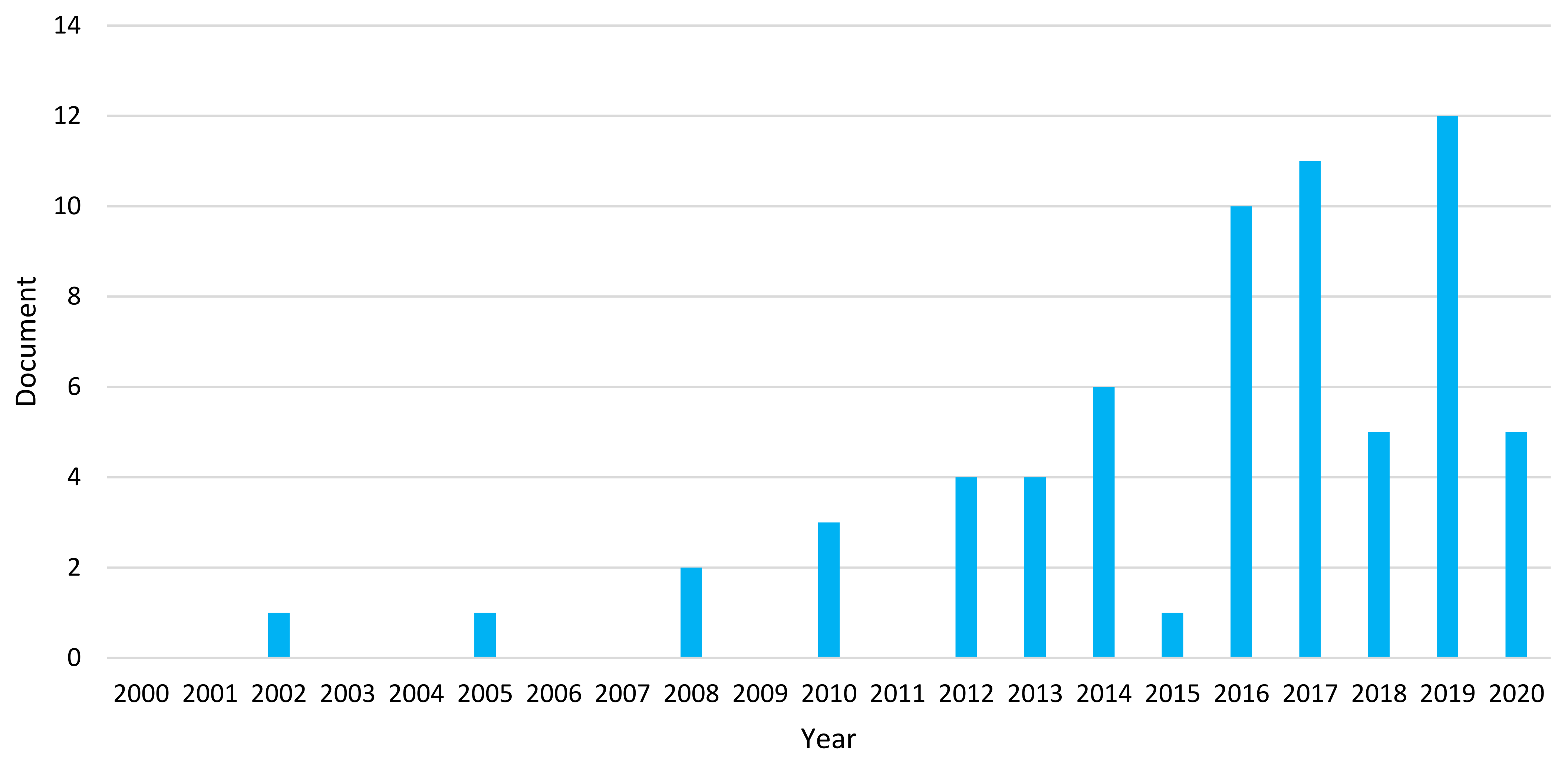
3.1. Results of the Database
3.2. Results of the Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) Model
3.3. A further Refinement of the Topics
4. Existing Gaps
4.1. Speed of HSRs
4.2. Competing Alternatives and Access to Terminals
4.3. Attributes for the Development of HSRs in Logistics
4.4. Attributes Related to Environmental Costs and Passengers’ Attitudes towards Climate Change
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Givoni, M. Development and Impact of the Modern High-speed Train: A Review. Transp. Rev. 2006, 26, 593–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evazzadeh, E.; Kheirkhah, A.; Shakeri, M. An Investigation of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Parallelism of the High-Speed Intercity Passenger Rail with Freeway. Int. J. Technol. Res. Eng. 2020, 8, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Cascetta, E.; Cartenì, A.; Henke, I.; Pagliara, F. Economic Growth, Transport Accessibility and Regional Equity Impacts of High-Speed Railways in Italy: Ten Years Ex Post Evaluation and Future Perspectives. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2020, 139, 412–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.H.; Zhao, Y. Research of High-Speed Rail Express Delivery Market Demand Prediction Problem in China. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2016, 851, 899–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banister, D.; Hall, P. The Second Railway Age. Built Environ. 1993, 19, 157. [Google Scholar]
- Schwanen, T. Transport Geography, Climate Change and Space: Opportunity for New Thinking. J. Transp. Geogr. 2019, 81, 102530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Shen, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. An Evaluation of the Low-Carbon Effects of Urban Rail Based on Mode Shifts. Sustainability 2017, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Lang, M.; Gao, Y.; Wang, K.; Su, C.-H.; Tsai, S.-B.; Huo, M.; Yu, X.; Li, S. An Empirical Study on the Design of China High-Speed Rail Express Train Operation Plan—From a Sustainable Transport Perspective. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armah, F.; Yawson, D.; Pappoe, A.A.N.M. A Systems Dynamics Approach to Explore Traffic Congestion and Air Pollution Link in the City of Accra, Ghana. Sustainability 2010, 2, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E.S.; Gomes, J.A.N.F. A Comparison of Scopus and Web of Science for a Typical University. Scientometrics 2009, 81, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, F.; Sherman, D. ScopusTM: The Product and Its Development. Ser. Libr. 2006, 49, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, T. Electrical Features of the New Tokaido Line. IEEE Spectr. 1966, 3, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponweiser, M. Latent Dirichlet Allocation in R. Diploma Thesis, Vienna University of Business and Economics, Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent Dirichlet Allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Blei, D.M.; Lafferty, J.D. Visualizing Topics with Multi-Word Expressions. arXiv 2009, arXiv:0907.1013. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, T.L.; Steyvers, M. Finding Scientific Topics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5228–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.C.; Hindle, A.; Stroulia, E. Latent Dirichlet Allocation: Extracting Topics from Software Engineering Data. In The Art and Science of Analyzing Software Data; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 139–159. ISBN 978-0-12-411519-4. [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro, T.; Medeiros Da Nobrega, R.V.; Nepomuceno, T.; Bian, G.-B.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C.; Filho, P.P.R. Performance Analysis of Google Colaboratory as a Tool for Accelerating Deep Learning Applications. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 61677–61685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tock, K. Google CoLaboratory as a Platform for Python Coding with Students. RTSRE Proc. 2019, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Heimerl, F.; Lohmann, S.; Lange, S.; Ertl, T. Word Cloud Explorer: Text Analytics Based on Word Clouds. In Proceedings of the 2014 47th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Waikoloa, HI, 6–9 January 2014; pp. 1833–1842. [Google Scholar]
- Elsevier Scopus Search API. Available online: https://www.scopus.com/search/ (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Grefenstette, G.; Tapanainen, P. What Is a Word, What Is a Sentence? Problems of Tokenization. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Computational Lexicography, Budapest, Hungary, 7–10 July 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur, W.J.; Sirotkin, K. The Automatic Identification of Stop Words. J. Inf. Sci. 1992, 18, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirunillai, S.; Tellis, G.J. Mining Marketing Meaning from Online Chatter: Strategic Brand Analysis of Big Data Using Latent Dirichlet Allocation. J. Mark. Res. 2014, 51, 463–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, C.D.; Raghavan, P.; Schutze, H. Introduction to Information Retrieval; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Dong, S. Comprehensive Sustainability Evaluation of High-Speed Railway (HSR) Construction Projects Based on Unascertained Measure and Analytic Hierarchy Process. Sustainability 2018, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sustainable Transport: Priorities for Policy Reform Development in Practice; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; ISBN 0-8213-3598-7.
- Aizaki, H.; Nakatani, T.; Sato, K. Stated Preference Methods Using R; The R Series; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-1-4398-9048-6. [Google Scholar]
- Bergantino, A.S.; Madio, L. Intermodal Competition and Substitution. HSR versus Air Transport: Understanding the Socio-Economic Determinants of Modal Choice. Res. Transp. Econ. 2020, 79, 100823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, A.L.; Widyastuti, H. Study of Willingness to Pay the Jakarta-Bandung Highspeed Train: A Case Study of Argo Parahyangan Train Passangers. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 650, 012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Deng, W.; Hu, Q. Modeling Passengers’ Preference on High-Speed Trains: Mixed Logit Model Development. In Proceedings of the CICTP 2019, Nanjing, China, 6–8 July 2019; pp. 5925–5936. [Google Scholar]
- Raturi, V.; Verma, A. Competition between High Speed Rail and Conventional Transport Modes: Market Entry Game Analysis on Indian Corridors. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2019, 19, 763–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Z.; Pan, X.-F. Determinants of College Students Choosing Railway during the Spring Festival Travel Rush in China: Preliminary Results Using Stated Preference Approach. In Proceedings of the CICTP 2019, Nanjing, China, 6–8 July 2019; pp. 5913–5924. [Google Scholar]
- Nurhidayat, A.Y.; Widyastuti, H.; Utomo, D.P. Model of Transportation Mode Choice between Aircraft and High Speed Train of Jakarta-Surabaya Route. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 202, 012002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggiero, L.; Pagliara, F.; Patrone, A.; Peruggini, F. Spatial Equity and High-Speed Rail Systems. Int. J. Transp. Dev. Integr. 2017, 1, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brida, J.G.; Martín, J.C.; Román, C.; Scuderi, R. Air and HST Multimodal Products. A Segmentation Analysis for Policy Makers. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2017, 17, 911–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartenì, A.; Pariota, L.; Henke, I. Hedonic Value of High-Speed Rail Services: Quantitative Analysis of the Students’ Domestic Tourist Attractiveness of the Main Italian Cities. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2017, 100, 348–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuma, A.; Tinumbia, N.; Leksono, P. The Characteristics of Potential Passengers of an Indonesian High-Speed Train (Case Study: Jakarta–Bandung). Int. J. Technol. 2017, 8, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Muro-Rodríguez, A.I.; Perez-Jiménez, I.R.; Gutiérrez-Broncano, S. Consumer Behavior in the Choice of Mode of Transport: A Case Study in the Toledo-Madrid Corridor. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raturi, V.; Verma, A. Analyzing Competition between High Speed Rail and Bus Mode Using Market Entry Game Analysis. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 25, 2373–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperry, B.R.; Burris, M.; Woosnam, K.M. Investigating the Impact of High-Speed Rail Equipment Visualization on Mode Choice Models: Case Study in Central Texas. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2017, 5, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascetta, E.; Coppola, P. Assessment of Schedule-Based and Frequency-Based Assignment Models for Strategic and Operational Planning of High-Speed Rail Services. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2016, 84, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-K.; Yoo, K.-E.; Song, K.-H. A Study on Travelers’ Transport Mode Choice Behavior Using the Mixed Logit Model: A Case Study of the Seoul-Jeju Route. J. Air Transp. Manag. 2016, 56, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-C.; Sheng, D. Forecasting Passenger Travel Demand for Air and High-Speed Rail Integration Service: A Case Study of Beijing-Guangzhou Corridor, China. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2016, 94, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhu, H.; Hu, D. High-Speed Rail Competitiveness Analysis in the Guangzhou-Zhaoqing Transport Corridor with Mixed RP/SP Data. In Proceedings of the CICTP 2016, Shanghai, China, 6–9 July 2016; pp. 478–490. [Google Scholar]
- Barreira, Á.; Reis, V.; Macário, R. Competitiveness of High-Speed Rail: Analysis for Corridor Between Lisbon, Portugal, and Madrid, Spain, Based on Discrete Choice Models. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2013, 2374, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.-W.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Feng, C.-M.; Yeh, W.-Y. Effects of Price Promotions on Potential Consumers of High-Speed Rail. Transp. Plan. Technol. 2013, 36, 722–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, E.J.; Yang, Q.R.; Zhang, Y.S.; Dai, H.N. A Study on Travel Demand for High-Speed Train Based on Nested Logit Model. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 361–363, 2096–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, E.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. A Study on High-Speed Rail Pricing Strategy in the Context of Modes Competition. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2013, 2013, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliara, F.; Vassallo, J.M.; Román, C. High-Speed Rail versus Air Transportation: Case Study of Madrid–Barcelona, Spain. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2012, 2289, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-W.; Sung, Y.-C. Constructing a Mixed-Logit Model with Market Positioning to Analyze the Effects of New Mode Introduction. J. Transp. Geogr. 2010, 18, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, E.; Morikawa, T.; Kurauchi, S.; Tokida, T. A Study on Nested Logit Mode Choice Model for Intercity High-Speed Rail System with Combined RP/SP Data. In Proceedings of the Traffic And Transportation Studies (2002), Guilin, China, 23–25 July 2002; pp. 612–619. [Google Scholar]
- Nationwide Shinkansen Railway Development Act; 1970; pp. 1–19. Available online: https://www.mlit.go.jp/english/2006/h_railway_bureau/Laws_concerning/05.pdf (accessed on 22 December 2021).
- Xiao, C.; Yang, Y.; Chi, G. Subway Development and Obesity: Evidence from China. J. Transp. Health 2021, 21, 101065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, M.; Mu, R.; Stead, D.; Ma, Y.; Xi, B. Introducing Public–Private Partnerships for Metropolitan Subways in China: What Is the Evidence? J. Transp. Geogr. 2010, 18, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Han, B.; Lu, F.; Wang, Z. Urban Rail Transit in China: Progress Report and Analysis (2008–2015). Urban Rail Transit 2016, 2, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, M.; He, S.; Xu, W. (Ato) Express Delivery with High-Speed Railway: Definitely Feasible or Just a Publicity Stunt. Transp. Res. Part Policy Pract. 2019, 120, 165–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

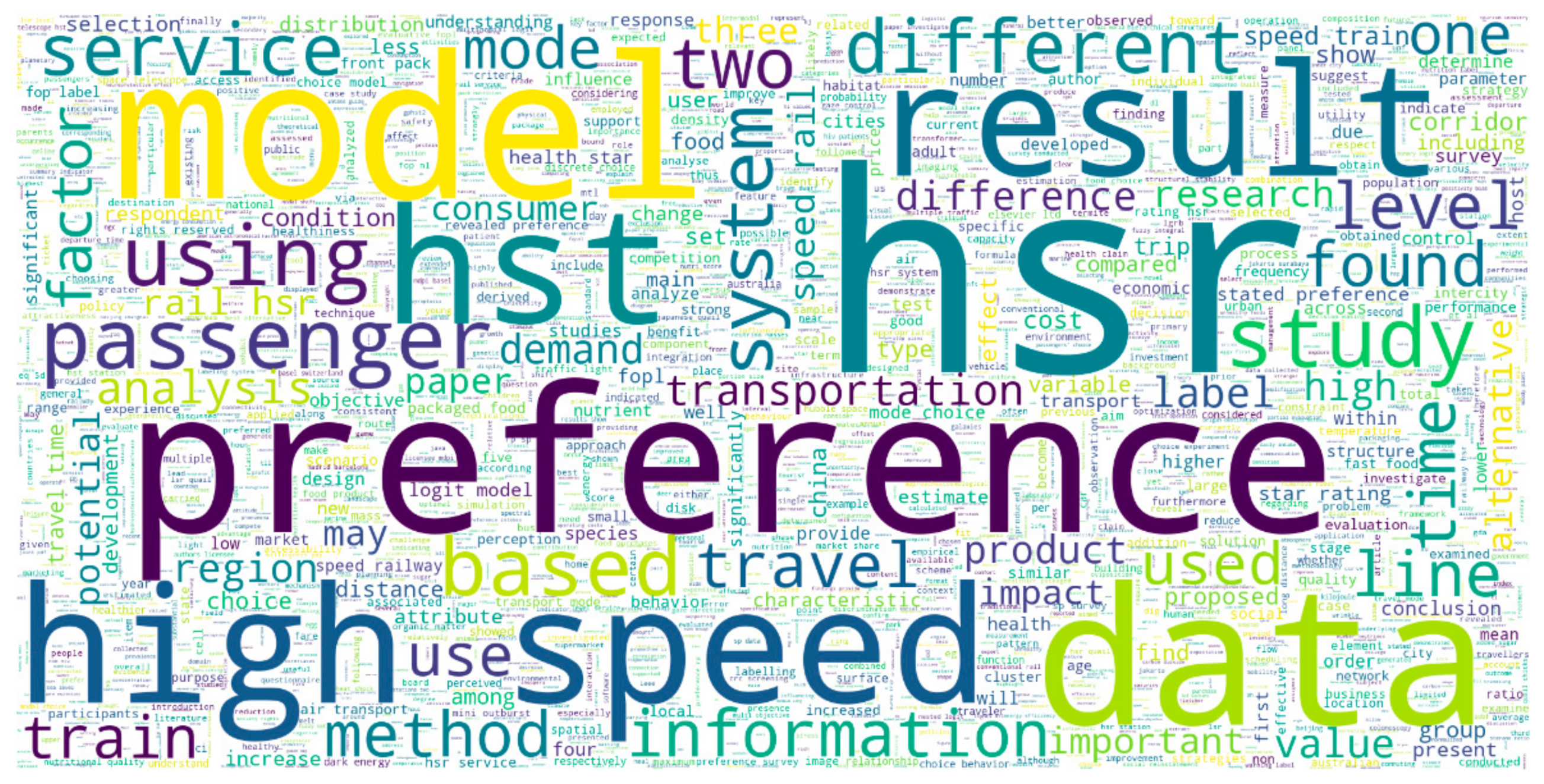


| i, me, my, myself, we, our, ours, ourselves, you, you’re, you’ve, you’ll, you’d, your, yours, yourself, yourselves, he, him, his, himself, she, she’s, her, hers, herself, it, it’s, its, itself, they, them, their, theirs, themselves, what, which, who, whom, this, that, that’ll, these, those, am, is, are, was, were, be, been, being, have, has, had, having, do, does, did, doing, a, an, the, and, but, if, or, because, as, until, while, of, at, by, for, with, about, against, between, into, though, during, before, after, above, below, to, from, up, down, in, out, on, off, over, under, again, further, then, once, here, there, when, where, why, how, all, any, both, each, few, more, most, other, some, such, no, nor, not, only, own, same, so, than, too, very, s, t, can, will, just, don, don’t, should, should’ve, now, d, ll, m, o, re, ve, y, ain, aren, aren’t, couldn, couldn’t, didn, didn’t, doesn’, doesn’t, hadn, hadn’t, hasn, hasn’t, haven, haven’t, isn, isn’t, ma, mightn, mightn’t, mustn, mustn’t, needn, needn’t, shan, shan’t, shouldn, shouldn’t, wasn, wasn’t, weren, weren’t, won, won’t, wouldn’, wouldn’t. |
| according, achieved, across, addition, additional, additionally, adopted, adopting, affect, affected, aim, al, allows, along, alongside, also, among, analyses, analysis, analyze, analyzed, answered, apparent, approach, appropriate, around, assessed, associated, assumed, atp, attempt, au, author, back, based, behalf, believed, best, calculated, ce, choosing, ci, cl, claim, claims, clearly, cm, cmb, col, collect, collected, combined, compete, conclusions, conducted, consider, considered, consistently, costs, cpcs, cr, criteria, current, currently, dce, demonstrate, demonstrated, depending, designed, detected, determine, determined, developed, dig, discussed, dls, dr, due, effect, eg, employing, eos, eq, er, error, estimate, estimates, et, eu, evaluated, even, ever, examined, example, exist, expected, explain, fact, far, fb, find, finding, findings, fine, following, fopls, found, front, gda, general, generally, generate, generated, given, good, gp, gphst, highly, however, hra, hree, hsp, identified, identify, ie, ii, implications, importance, important, improve, improved, improvement, imt, included, including, incorporate, increase, increased, indeed, indicated, indicators, influence, influenced, information, interpretive, introduced, investigate, investigated, investigation, ix, jeju, joint, kd, kj, labels, lccs, less, level, lgrbs, like, log, low, lower, lree, lsr, lt, main, make, mean, meaning, measure, method, methods, mini, modal, mode, model, models, mpacts, mrna, mtl, multi, near, new, nft, ngc, nice, nip, nl, non, novel, npsc, nutri, objective, objectives, obscured, observed, obtain, obtained, occur, occurring, od, one, optically, order, osa, overall, part, particularly, perceived, pgy, plp, point, potential, potentially, preferred, presence, present, presented, produced, product, promote, proposed, provide, psg, published, ras, ratings, rc, recently, reduce, ree, reflect, regardless, related, relatively, relevant, represent, research, reserved, respectively, result, resulted, results, review, scoring, second, selected, show, showed, shown, significantly, similar, slight, small, smaller, snia, snls, sobf, sr, ssb, stage, strategies, strategy, strong, studies, study, suggest, suggests, supporting, ta, terms, testing, therefore, thsr, thus, tll, together, total, towards, typically, understand, understanding, us, used, using, uv, versus, viewed, visuals, vs, warning, web, well, whether, widely, without, would, wr, york. |
| Topic | Keywords |
|---|---|
| 1 | hsr; fast; packaged; food; organic; hst; price; marine; sea; healthier |
| 2 | hsr; eggs; oviposition; foods; life; sugar; dose; fat; baby; age |
| 3 | railway; line; city; flows; transportation; net; speed; hst; gas; preference |
| 4 | hsr; utility; time; adult; trips; rail; travel; cost; line; commuting |
| 5 | hsr; fuzzy; humanoid; hst; genes; robots; navigation; cells; pyroptosis; functions |
| 6 | energy; hst; stars; telescope; luminosity; space; spectrum; galaxy; daylighting; hubble |
| 7 | temperature; health; hsr; heat; quails; salmon; arctic; tolerance; age; animal |
| 8 | hsr; social; line; choice; host; passengers; air; distribution; regions; discrimination |
| 9 | hsr; speed; high; travel; system; transportation; regions; workers; rail; distance |
| 10 | hsr; services; choice; rail; parents; transport; trip; demand; tourist; train |
| 11 | energy; neutrino; parameter; cosmological; number; hubble; cosmic; time; density; helium |
| 12 | elites; habitat; deer; passengers; ticket; crisis; Europeanness; wild; landscape; hsr |
| 13 | hsr; food; health; nutrition; consumers; products; star; quality; healthiness; daily |
| 14 | species; hsr; habitat; plant; savanna; termite; woody; sugar; soil; forest |
| 15 | hsr; high; rail; speed; travel; passengers; train; transport; conventional; intercity |
| 16 | stations; hst; train; hsr; surface; location; speed; urban; fast; transformer |
| 17 | hsr; hst; stability; structural; speed; intercity; rp; sp; corridor; train |
| 18 | travel; choice; train; hsr; passengers; distance; service; frequency; demand; pathway |
| 19 | travel; speed; choice; high; hsr; hst; transportation; time; passengers; train |
| 20 | hsr; transport; preference; speed; passengers; exclusion; rail; travel; air; access |
| Meanings of “HSR” or “HST” | Number of Documents |
|---|---|
| High-speed railway or high-speed train | 65 |
| Health Star Rating (HSR) | 18 |
| Hubble Space Telescope (HST) | 10 |
| High levels of Social Reinstatement behavior (HSR) | 5 |
| HanSaRam-IX (HSR-IX) | 3 |
| Hottest Spot Temperature (HST) | 2 |
| highstand systems tract (HST) | 2 |
| hydrostatic transmission | 1 |
| hump-shaped oviposition regulation (HSR) | 1 |
| human speech recognition (HSR) | 1 |
| human Serine racemase (hSR) | 1 |
| Hubble constant (HST) | 1 |
| HST/STIS | 1 |
| HST/GOODS | 1 |
| HST WFPC2 observations | 1 |
| HST solar cells | 1 |
| HST Guide Star Catalog | 1 |
| HSD and HST | 1 |
| host star | 1 |
| homogeneously staining region (HSR) | 1 |
| homogeneous shear turbulence (HST) | 1 |
| home stool test (HST) | 1 |
| home sleep testing (HST) | 1 |
| home safety toolkit (HST) | 1 |
| High-silica rhyolites (HSR) | 1 |
| highly specialized technology (HST) | 1 |
| Higher Specialist Training (HST) | 1 |
| high structural stability regions (HSRs) | 1 |
| high school class (HSR) | 1 |
| hierarchical structures for recommender systems | 1 |
| Herbaceous Species Richness (HSR) | 1 |
| Hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation (HSR) | 1 |
| heat storage tanks (HSTs) | 1 |
| heat shock response (HSR) | 1 |
| Health system responsiveness (HSR) | 1 |
| health services research (HSR) | 1 |
| Harvard Step Test (HST) | 1 |
| Handover Served Ratio (HSR) | 1 |
| Habitat Sharing Ratio (HSR) | 1 |
| H. syriacus (HSR) | 1 |
| local measurements (HST) | 1 |
| guinea pig adrenal hydroxysteroid sulfotransferase (gpHST2) | 1 |
| Others | 3 |
| Total number of documents | 143 |
| Topic | Keywords |
|---|---|
| 1 | hsr; transportation; transport; tourism; business; service; futuroscope; speed; safety; leisure |
| 2 | train; hsr; passengers; air; transport; speed; infrastructure; services; environment; accessibility |
| 3 | hsr; trips; rail; services; travel; trip; business; distance; air; income |
| 4 | hsr; train; transfer; station; distance; railway; waiting; speed; travel; destination |
| 5 | hsr; speed; transportation; tourism; intercity; carbon; emissions; economic; capacity; security |
| 6 | revenue; hsr; train; railway; classes; fare; time; seats; transportation; speed |
| 7 | hsr; transport; economic; exclusion; rail; travellers; services; car; accessibility; speed |
| 8 | speed; trains; travel; railway; machine; software; class; seats; income; harmony |
| 9 | rail; passengers; integration; speed; air; economic; energy; sustainable; schedule |
| 10 | hsr; travel; speed; intercity; business; rail; future; security; tourism; economic |
| 11 | hsr; services; travel; tourist; trip; tourism; access; emissions; dioxide; carbon |
| 12 | corridor; competition; hsr; speed; welfare; cost; technology; business; bus; fare |
| 13 | hsr; speed; travel; intercity; service; fuzzy; economic; capacity; tourism; security |
| 14 | train; frequency; accessibility; cities; techniques; distribution; connectivity; speed; transportation; vehicles |
| 15 | exclusion; hsr; time; transport; speed; economic; rail; mobility; stations; passengers |
| 16 | high; travel; speed; trains; railway; software; machine; income; transportation; age |
| 17 | hsr; fare; speed; high; train; pricing; ticket; capacity; aircraft; seat |
| 18 | speed; hst; hsr; train; workers; fuzzy; energy; commuting; reliability; comfort |
| 19 | hsr; spatial; speed; rail; transport; equity; accessibility; economic; sp; rp |
| 20 | speed; intercity; travel; train; railway; trips; car; fuzzy; machine; software |
| No. | Authors (Year) |
|---|---|
| (1) | Bergantino A. S. and Madio L. (2020) [29] |
| (2) | Cheng Q., Deng W., and Hu Q. Z. (2019) [31] |
| (3) | Putri A. L. and Widyastuti H. (2019) [30] |
| (4) | Raturi V. and Verma A. (2019) [32] |
| (5) | Zuo Z. and Pan X. F. (2019) [33] |
| (6) | Nurhidayat A. Y., Widyastuti H., and Utomo D. P. (2018) [34] |
| (7) | Biggiero L., Pagliara F., Patrone A., and Peruggini F. (2017) [35] |
| (8) | Brida J. G., Martín J. C., Román C., and Scuderi R. (2017) [36] |
| (9) | Cartenì A., Pariota L., and Henke I. (2017) [37] |
| (10) | Kusuma A., Tinumbia N., and Bakdirespati P. L. (2017) [38] |
| (11) | Muro-Rodríguez A. I., Perez-Jiménez I. R., and Gutiérrez-Broncano S. (2017) [39] |
| (12) | Raturi V. and Verma A. (2017) [40] |
| (13) | Sperry B. R., Burris M., and Woosnam K. M. (2017) [41] |
| (14) | Cascetta E. and Coppola P. (2016) [42] |
| (15) | Lee J. K., Yoo K. E., and Song K. H. (2016) [43] |
| (16) | Li Z. C. and Sheng D. (2016) [44] |
| (17) | Zhao W. Y., Zhu H. G., and Hu D. W. (2016) [45] |
| (18) | Barreira Á., Reis V., and Macário R. (2013) [46] |
| (19) | Kuo Y. W., Hsieh C. H., Feng C. M., and Yeh W. Y. (2013) [47] |
| (20) | Yao E. J., Yang Q. R., Zhang Y. S., and Dai H. N. (2013) [48] |
| (21) | Yao E. J., Yang Q. R., Zhang Y. S., and Sun X. (2013) [49] |
| (22) | Pagliara F., Vassallo J. M., and Román C. (2012) [50] |
| (23) | Yang C. W. and Sung Y. C. (2010) [51] |
| (24) | Yao E. J., Morikawa T., Kurauchi S., and Tokida T. (2002) [52] |
| Year | Counts | Papers |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 1 | (1) |
| 2019 | 4 | (2–5) |
| 2018 | 1 | (6) |
| 2017 | 7 | (7–13) |
| 2016 | 4 | (14–17) |
| 2013 | 4 | (18–21) |
| 2012 | 1 | (22) |
| 2010 | 1 | (23) |
| 2002 | 1 | (24) |
| Country | Counts | Papers |
|---|---|---|
| China | 8 | (2,5,16,17,19,20,21,23) |
| Italy | 4 | (1,7,9,14) |
| Spain | 3 | (8,11,22) |
| Indonesia | 3 | (3,6,10) |
| India | 2 | (4,12) |
| Japan | 1 | (24) |
| South Korea | 1 | (15) |
| United States | 1 | (13) |
| Spain and Portugal | 1 | (18) |
| Alternative | Counts | Papers |
|---|---|---|
| HSRs | 23 | (1–7,9–24) |
| Road Transport | 15 | (1,4,7,10,11,12,14,17–24) |
| Air transport | 13 | (1,4,6,7,14,15,16,18,20–24) |
| Conventional rail | 11 | (1,4,5,7,9,10,17,20,21,23,24) |
| Multimodal Air–HSR | 2 | (8,16) |
| Air–Air | 1 | (8) |
| (a) HSR | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Attributes | Counts | Papers | |
| Time | 24 | (1–24) | |
| Travel time | 16 | (2,5,6,9–15,19–24) | |
| Access/egress time | 5 | (7,8,14,16,23) | |
| In-vehicle time | 4 | (1,4,8,16) | |
| Total travel time | 3 | (3,11,18) | |
| Departure time | 2 | (2,23) | |
| Connecting time | 2 | (8,16) | |
| Waiting time | 2 | (17,23) | |
| Out-vehicle travel time | 1 | (4) | |
| Ticket sold-out time | 1 | (5) | |
| After-train time | 1 | (5) | |
| Arrival time | 1 | (5) | |
| Prob. of 2 h delay | 1 | (5) | |
| Average headway | 1 | (14) | |
| Cost | 24 | (1–24) | |
| Travel cost | 16 | (3,4,7,8,10,11,13,15,16,17,19,20,21,22,23,24) | |
| Access/egress cost | 1 | (7) | |
| Operating cost | 1 | (12) | |
| Cost reimbursed/not reimbursed | 1 | (14) | |
| Early/late schedule penalty | 1 | (14) | |
| Price (Cost) | 10 | (1,2,4,5,6,7,8,9,15,18) | |
| Fare integration | 1 | (8) | |
| Frequency | 9 | (1,3,4,9,15,18,22,23,24) | |
| Service | 4 | (9,13,14,17) | |
| Reliability | 3 | (1,19,22) | |
| Comfort | 3 | (17,19,22) | |
| Accessibility | 2 | (3,19) | |
| Ticket type | 2 | (5,23) | |
| Safety | 2 | (15,17) | |
| Companion | 1 | (5) | |
| Baggage integration | 1 | (8) | |
| Distance | 1 | (9) | |
| Capacity | 1 | (12) | |
| High professional condition | 1 | (14) | |
| Rapidness | 1 | (17) | |
| Convenience | 1 | (17) | |
| Seat pitch | 1 | (18) | |
| Hand luggage space | 1 | (18) | |
| Noise level | 1 | (18) | |
| Efficiency | 1 | (19) | |
| (b) Bus | |||
| Attributes | Counts | Papers | |
| Time | 11 | (1,4,7,10,11,12,18,20,21,22,23) | |
| Travel time | 8 | (10,11,12,18,20,21,22,23) | |
| In-vehicle time | 2 | (1,4) | |
| Out-vehicle travel time | 1 | (4) | |
| Access/egress time | 1 | (7) | |
| Total travel time | 1 | (18) | |
| Cost | 10 | (4,7,10,11,12,20,21,22,23,24) | |
| Travel cost | 9 | (4,7,10,11,20,21,22,23,24) | |
| Access/egress cost | 1 | (7) | |
| Operating cost | 1 | (12) | |
| Frequency | 4 | (1,18,23,24) | |
| Price (Cost) | 3 | (1,7,18) | |
| Reliability | 1 | (1) | |
| Capacity | 1 | (12) | |
| Seat pitch | 1 | (18) | |
| Hand luggage space | 1 | (18) | |
| Noise level | 1 | (18) | |
| (c) Air Transport | |||
| Attributes | Counts | Papers | |
| Time | 13 | (1,6,7,8,14,15,16,18,20–24) | |
| Travel time | 7 | (6,14,15,20–23) | |
| Access/egress time | 5 | (1,7,8,14,16) | |
| In-vehicle time | 3 | (1,8,16) | |
| Connecting time | 2 | (8,16) | |
| Average headway | 1 | (14) | |
| Total traveling time | 1 | (18) | |
| Line-haul time | 1 | (24) | |
| Terminal time | 1 | (24) | |
| Cost | 10 | (7,8,14,15,16,20–24) | |
| Travel cost | 9 | (7,8,15,16,20–24) | |
| Access/egress cost | 1 | (7) | |
| Cost reimbursed/not reimbursed | 1 | (14) | |
| Early/late schedule penalty | 1 | (14) | |
| Price (Cost) | 6 | (1,6,7,8,15,18) | |
| Fare integration | 1 | (8) | |
| Frequency | 6 | (1,15,18,22,23,24) | |
| Reliability | 2 | (1,22) | |
| Baggage integration | 1 | (8) | |
| High professional condition | 1 | (14) | |
| Safety | 1 | (15) | |
| Duty-free shopping availability | 1 | (15) | |
| Seat pitch | 1 | (18) | |
| Hand luggage space | 1 | (18) | |
| Noise level | 1 | (18) | |
| Comfort | 1 | (22) | |
| (d) Conventional Rail | |||
| Attributes | Counts | Papers | |
| Time | 11 | (1,4,5,7,9,10,17,20,21,23,24) | |
| Travel time | 6 | (5,9,10,20,21,23) | |
| In-vehicle Time | 2 | (1,4) | |
| Out-vehicle travel time | 1 | (4) | |
| Ticket sold-out time | 1 | (5) | |
| After-train time | 1 | (5) | |
| Arrival time | 1 | (5) | |
| Prob. of 2 h Delay | 1 | (5) | |
| Access/egress time | 1 | (7) | |
| Waiting time | 1 | (17) | |
| Line-haul time | 1 | (24) | |
| Terminal time | 1 | (24) | |
| Cost | 8 | (4,7,10,17,20,21,23,24) | |
| Travel cost | 8 | (4,7,10,17,20,21,23,24) | |
| Access/egress cost | 1 | (7) | |
| Price (Cost) | 4 | (1,5,7,9) | |
| Frequency | 4 | (1,9,23,24) | |
| Reliability | 1 | (1) | |
| Ticket type | 1 | (5) | |
| Companion | 1 | (5) | |
| Distance | 1 | (9) | |
| Comfort | 1 | (17) | |
| Safety | 1 | (17) | |
| Service | 1 | (17) | |
| Rapidness | 1 | (17) | |
| Convenience | 1 | (17) | |
| (e) Private Car | |||
| Attributes | Counts | Papers | |
| Time | 9 | (1,4,7,10,11,14,18,20,21) | |
| Travel time | 5 | (10,11,14,20,21) | |
| In-vehicle time | 2 | (1,4) | |
| Access/egress time | 2 | (7,14) | |
| Out-vehicle travel time | 1 | (4) | |
| Average headway | 1 | (14) | |
| Total travel time | 1 | (18) | |
| Cost | 7 | (4,7,10,11,14,20,21) | |
| Travel cost | 5 | (4,7,10,11,20,21) | |
| Access/egress cost | 1 | (7) | |
| Cost traveling alone/with party | 1 | (14) | |
| Early/late schedule penalty | 1 | (14) | |
| Price (Cost) | 3 | (1,7,18) | |
| Reliability | 1 | (1) | |
| High professional condition | 1 | (14) | |
| Service | 1 | (14) | |
| Frequency | 1 | (18) | |
| Seat pitch | 1 | (18) | |
| Hand luggage space | 1 | (18) | |
| Noise level | 1 | (18) | |
| Variables | Counts | Papers |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 12 | (1,2,3,8,13,16,17,19–23) |
| Income | 12 | (1,2,3,6,8,13,16,17,20–23) |
| Trip purpose | 12 | (1,3,6,8,15–18,20,21,22,24) |
| Career | 8 | (1,2,3,6,17,20,21,23) |
| Gender | 8 | (1,2,3,6,8,13,17,23) |
| Education | 5 | (2,6,8,13,19) |
| Trip frequency | 4 | (1,3,8,17) |
| Household vehicles | 2 | (13,19) |
| Number of children in household | 2 | (13,19) |
| Financial source | 1 | (2) |
| Consideration of ease of mode and mobility | 1 | (3) |
| Consideration of time and speed | 1 | (3) |
| Pieces of checked bags | 1 | (8) |
| Image package viewed | 1 | (13) |
| Number of adults in household | 1 | (13) |
| Driving experience | 1 | (19) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, D.; Martín, J.C. Research on Passengers’ Preference for High-Speed Railways (HSRs) and High-Speed Trains (HSTs). Sustainability 2022, 14, 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031473
Wu D, Martín JC. Research on Passengers’ Preference for High-Speed Railways (HSRs) and High-Speed Trains (HSTs). Sustainability. 2022; 14(3):1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031473
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Di, and Juan Carlos Martín. 2022. "Research on Passengers’ Preference for High-Speed Railways (HSRs) and High-Speed Trains (HSTs)" Sustainability 14, no. 3: 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031473
APA StyleWu, D., & Martín, J. C. (2022). Research on Passengers’ Preference for High-Speed Railways (HSRs) and High-Speed Trains (HSTs). Sustainability, 14(3), 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14031473







