Permeable Pavement Systems for Effective Management of Stormwater Quantity and Quality: A Bibliometric Analysis and Highlights of Recent Advancements
Abstract
1. Introduction
- RQ1:
- What trends can be detected when analyzing studies investigating the use of PPS for stormwater management?
- RQ2:
- Who are the major contributors to research in the area of PPS for stormwater management?
- RQ3:
- What are the recent advancements and research gaps/future directions?
2. Background
3. Methods
3.1. Data Collection and Search Methods
3.2. Data Analysis
4. Results of Bibliometric Analysis
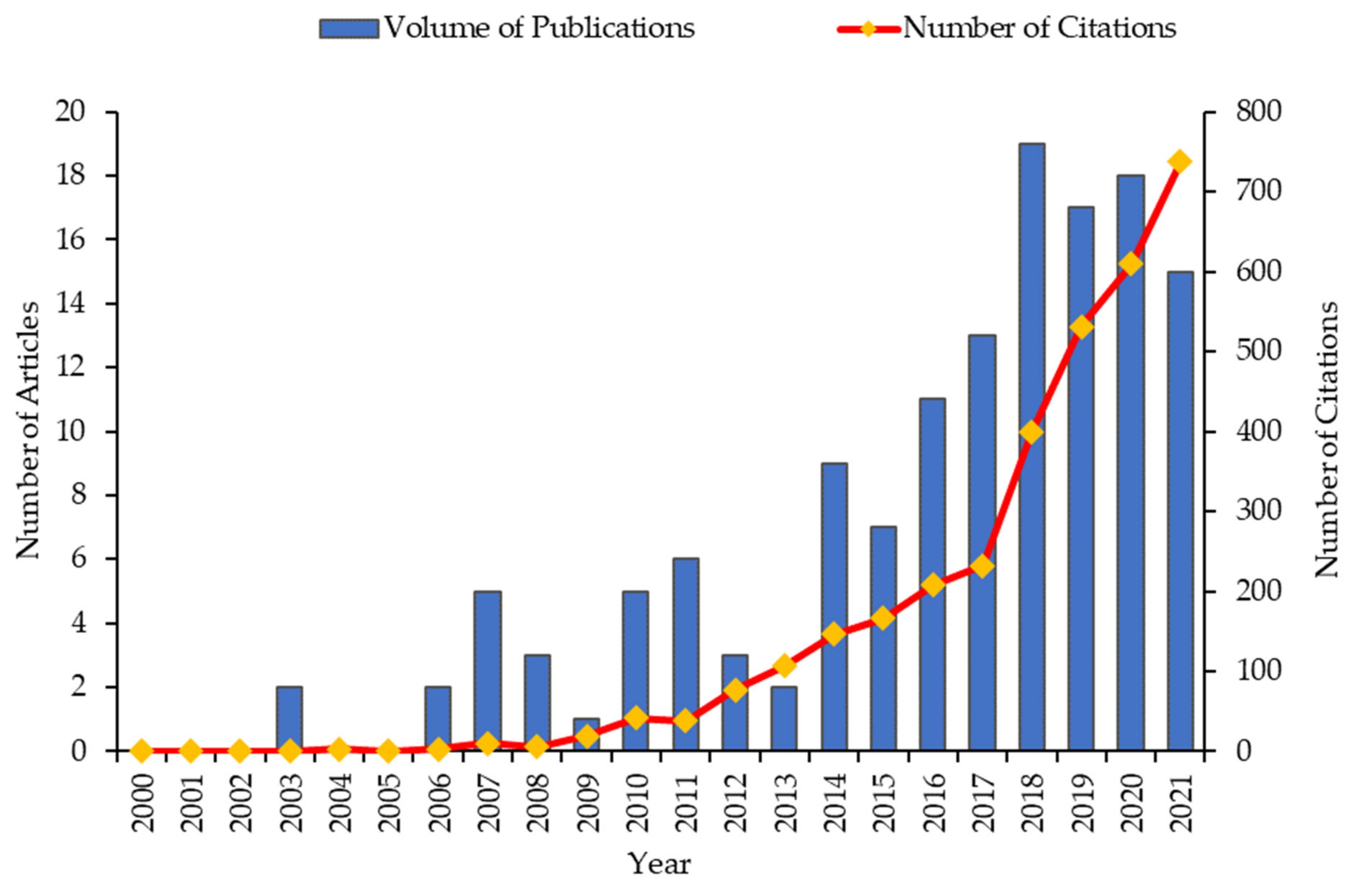
4.1. Data Overview
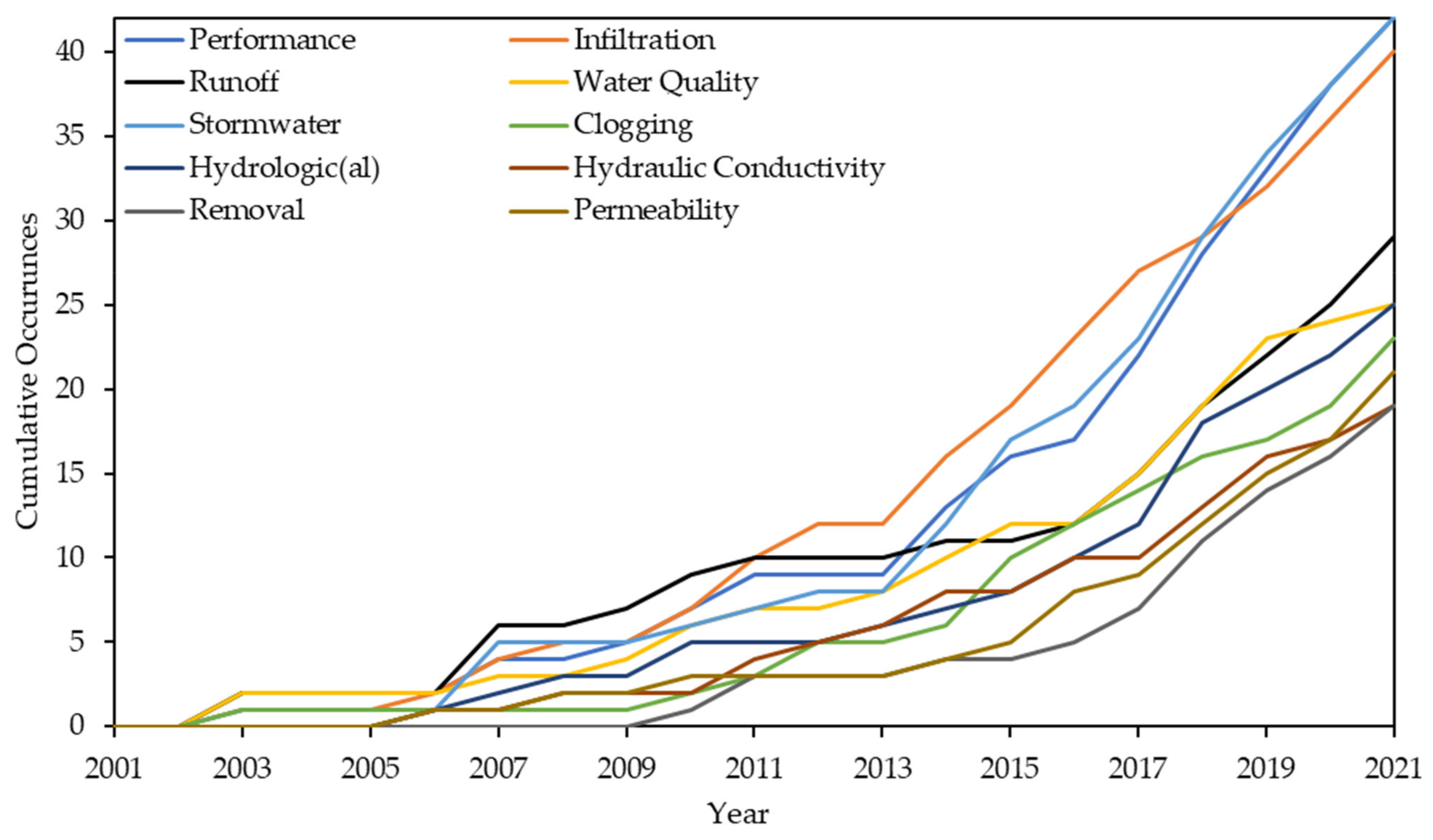
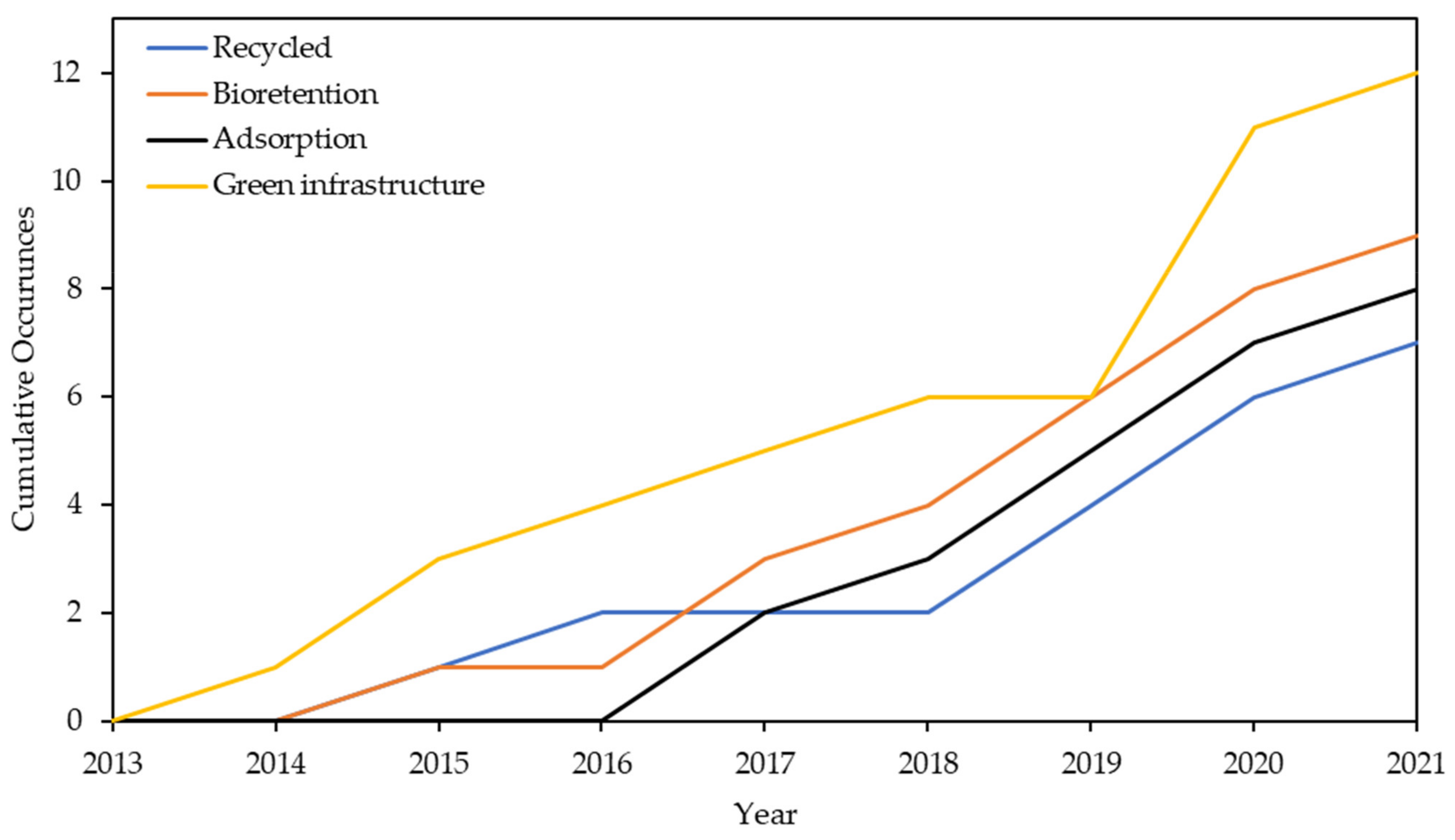
4.2. Keyword Analysis and Recent Research Trends
4.3. Major Contributors to Research in the Area of PPS for Stormwater Management
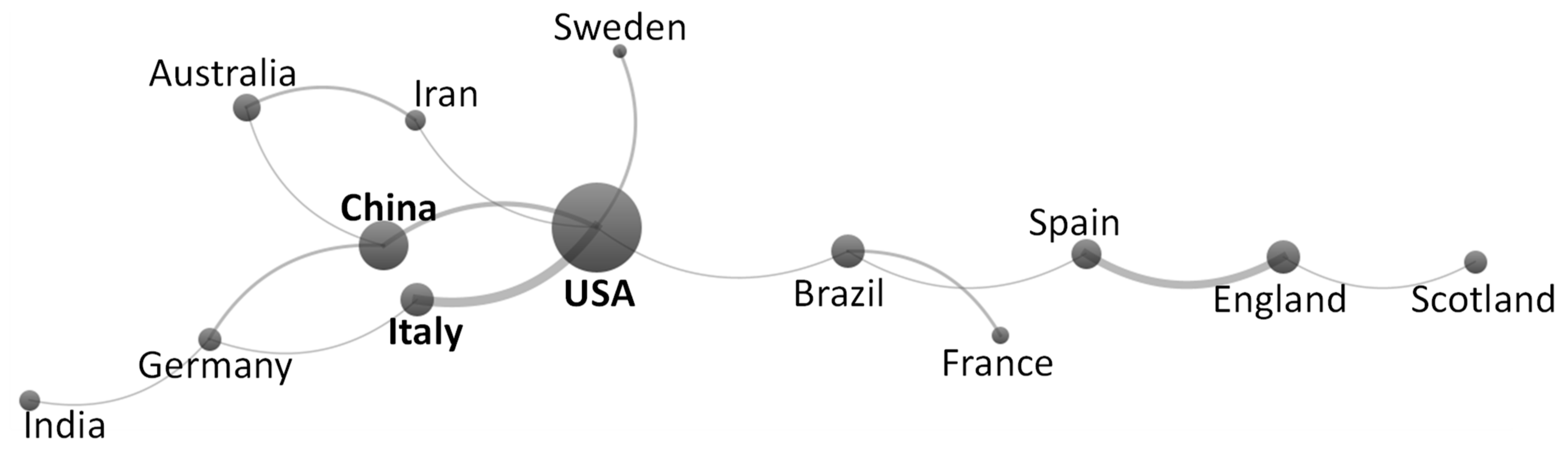
4.4. Nature of Collaboration in the Field of PPS
4.5. Co-Citation Analysis and Clustering
5. Discussion of Recent Developments
6. Conclusions and Way Forward
- For water quality improvements, different structural modifications, the addition of different sorbent materials, and modeling to predict the removal of contaminants could be promising in increasing the percentage removal of certain contaminants.
- Recent advancements in water quality improvements were investigated by the addition of adsorbents such as pozzolanic materials, nanomaterials, or cementitious materials. This was proven by the use of the keyword “adsorption” in recent years.
- Clogging characterization gained momentum in recent findings, especially using imaging techniques. The keywords associated with this topic included “clogging”, “hydraulic conductivity” and “permeability”.
- Improving the infiltration rate characterization and assessment of PPS has taken two routes: (1) concrete mix design modifications and (2) enhancing lab experiments to better represent field investigations.
- Innovative investigations and design considerations that included recycled aggregates within the PPS systems provided adequate mechanical and hydrologic properties while, importantly, being more sustainable in the long run.
- Leaching from PPS is an important aspect to investigate to safeguard the quality of the groundwater.
- A holistic approach is needed to incorporate the hydrological, mechanical, hydraulic, and water quality investigations to understand the overall functionality of the PPS.
- Developing a dataset of benchmark performance of PPS is essential for standardizing the PPS investigations.
- More on-site investigations need to be conducted to simulate the actual performance of PPS exposed to different wet and dry conditions, unlike lab-scale experimental investigations.
- There is a lack of models to predict the long-term performance of PPS. Hence, it would be important to incorporate both model and experimental simulations in future studies to simulate field experiments.
- Unifying testing parameters across conducted investigations is essential for assessing the viability of PPS.
- More investigations on the potential water savings from PPS harvesting schemes.
- There needs to be more collaboration between authors from different countries to assess the impact of different materials and climatic conditions on the performance of PPS.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.; Zhang, D.Q.; Su, J.; Trzcinski, A.P.; Dong, J.W.; Tan, S.K. Future Scenarios Modeling of Urban Stormwater Management Response to Impacts of Climate Change and Urbanization. Clean 2017, 45, 1700111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghussain, L. Global Warming: Review on Driving Forces and Mitigation. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2019, 38, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.; Zhang, X.; Zwiers, F.; Nature, G. Human Contribution to More-Intense Precipitation Extremes. Nature 2011, 470, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundzewicz, Z.; Radziejewski, M.; Research, I.P. Precipitation Extremes in the Changing Climate of Europe. Clim. Res. 2006, 31, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinge, G.; Hamouda, M.A.; Long, D.; Mohamed, M.M. Hydrologic Utility of Satellite Precipitation Products in Flood Prediction: A Meta-Data Analysis and Lessons Learnt. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, A.; Fernandes, J.N.; David, L.M. Key Issues for Sustainable Urban Stormwater Management. Water Res. 2012, 46, 6787–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechesne, M.; Barraud, S.; Bardin, J.P. Spatial Distribution of Pollution in an Urban Stormwater Infiltration Basin. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2004, 72, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.B.; Tia, M. An Experimental Study on the Water-Purification Properties of Porous Concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, C.; Newman, A.; Bond, P.C. Mineral Oil Bio-Degradation within a Permeable Pavement: Long Term Observations. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins Vaz, I.C.; Ghisi, E.; Thives, L.P. Life Cycle Energy Assessment and Economic Feasibility of Stormwater Harvested from Pervious Pavements. Water Res. 2020, 170, 115322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q. A Review of Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems Considering the Climate Change and Urbanization Impacts. Water 2014, 6, 976–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib Anwar, F.; El-Hassan, H.; Hamouda, M.; Hinge, G.; Hung Mo, K. Meta-Analysis of the Performance of Pervious Concrete with Cement and Aggregate Replacements. Buildings 2022, 12, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishigaki, M. Producing Permeable Blocks and Pavement Bricks from Molten Slag. Waste Manag. 2000, 20, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, W.; Langsdorff, V. The Use of Permeable Concrete Block Pavement in Controlling Environmental Stressors in Urban Areas. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Concrete Block Paving, Sun City, South Africa, 12–15 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Scholz, M.; Grabowiecki, P. Review of Permeable Pavement Systems. Build. Environ. 2007, 42, 3830–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.; Luo, P.; Zhu, W.; Wang, S.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M.; Huo, A.; Wang, Z. A Bibliometric Analysis of the Research on Sponge City: Current Situation and Future Development Direction. Ecohydrology 2021, 14, e2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Wróbel, K.; Montewka, J.; Goerlandt, F. A Bibliometric Analysis and Systematic Review of Shipboard Decision Support Systems for Accident Prevention. Saf. Sci. 2020, 128, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.; Hassini, S.; El-Dakhakhni, W. A Systematic Bibliometric Review of Optimization and Resilience within Low Impact Development Stormwater Management Practices. J. Hydrol. 2021, 599, 126457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to Conduct a Bibliometric Analysis: An Overview and Guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, N.; Lee, J. Changing Landscape of Emergency Management Research: A Systematic Review with Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 49, 101658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K.; Mukherjee, K.; Mondal, S.; Mitra, S. A Systematic Literature Review and Bibliometric Analysis Based on Pricing Related Decisions in Remanufacturing. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 310, 127265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Chen, G. Current Patterns and Future Perspectives of Best Management Practices Research: A Bibliometric Analysis. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 71, 98A–104A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qi, F.; Liu, L.; Chen, M.; Sun, D.; Nan, J. How Do Urban Rainfall-Runoff Pollution Control Technologies Develop in China? A Systematic Review Based on Bibliometric Analysis and Literature Summary. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpio, M.; González, Á.; González, M.; Verichev, K. Influence of Pavements on the Urban Heat Island Phenomenon: A Scientific Evolution Analysis. Energy Build 2020, 226, 110379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Types of Permeable Pavement—Minnesota Stormwater Manual. Available online: https://stormwater.pca.state.mn.us/index.php/Types_of_permeable_pavement (accessed on 13 July 2022).
- Razzaghmanesh, M.; Borst, M. Long-Term Effects of Three Types of Permeable Pavements on Nutrient Infiltrate Concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muttuvelu, D.V.; Kjems, E. A Systematic Review of Permeable Pavements and Their Unbound Material Properties in Comparison to Traditional Subbase Materials. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Hill, K. Effect of Permeable Pavement Basecourse Aggregates on Stormwater Quality for Irrigation Reuse. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 77, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.N.; Ghisi, E.; Thives, L.P. Permeable Pavements Life Cycle Assessment: A Literature Review. Water 2018, 10, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnadi, E.O.; Newman, A.P.; Coupe, S.J.; Mbanaso, F.U. Stormwater Harvesting for Irrigation Purposes: An Investigation of Chemical Quality of Water Recycled in Pervious Pavement System. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, A.; Delens, J.M.; Wong, H.S.; Cheeseman, C.R. Structural and Hydrological Design of Permeable Concrete Pavements. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachary Bean, E.; Frederick Hunt, W.; Alan Bidelspach, D. Evaluation of Four Permeable Pavement Sites in Eastern North Carolina for Runoff Reduction and Water Quality Impacts. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kia, A.; Wong, H.S.; Cheeseman, C.R. Clogging in Permeable Concrete: A Review. J Environ. Manag. 2017, 193, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.; Zhuge, Y.; Karunasena, K. Clogging Mechanism of Permeable Concrete: A Review. In Proceedings of the Concrete 2013: Understanding Concrete, Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 16–18 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kuruppu, U.; Rahman, A.; Rahman, M.A. Permeable Pavement as a Stormwater Best Management Practice: A Review and Discussion. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, G.; Thives, L.P.; Ghisi, E. Application of Stormwater Collected from Porous Asphalt Pavements for Non-Potable Uses in Buildings. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 222, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.N.; Thives, L.P.; Ghisi, E. Potential for Potable Water Savings in Buildings by Using Stormwater Harvested from Porous Pavements. Water 2016, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbig, W.R.; Buer, N. Hydraulic, Water-Quality, and Temperature Performance of Three Types of Permeable Pavement under High Sediment Loading Conditions; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legret, M.; Colandini, V. Effects of a Porous Pavement with Reservoir Structure on Runoff Water: Water Quality and Fate of Heavy Metals. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.J.; Arend, K.; Dorsey, J.D.; Hunt, W.F. Water Quality Performance of a Permeable Pavement and Stormwater Harvesting Treatment Train Stormwater Control Measure. Blue-Green Syst. 2020, 2, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braswell, A.S.; Winston, R.J.; Hunt, W.F. Hydrologic and Water Quality Performance of Permeable Pavement with Internal Water Storage over a Clay Soil in Durham, North Carolina. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 224, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, I.C.M.; Antunes, L.N.; Ghisi, E.; Thives, L.P. Permeable Pavements as a Means to Save Water in Buildings: State of the Art in Brazil. Sci 2021, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, B.; Beecham, S.; van Leeuwen, J.A. Water Quality with Storage in Permeable Pavement Basecourse. In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, London, UK, 25 May 2015; Volume 164, pp. 361–372. [Google Scholar]
- Brattebo, B.O.; Booth, D.B. Long-Term Stormwater Quantity and Quality Performance of Permeable Pavement Systems. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4369–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.; Bradford, A.; Research, J.M. Review of Environmental Performance of Permeable Pavement Systems: State of the Knowledge. Water Qual. Res. J. 2013, 48, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushton, B.T. Low-Impact Parking Lot Design Reduces Runoff and Pollutant Loads. J. Water Resour. Plan Manag. 2001, 127, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassman, E.A.; Blackbourn, S. Permeable Pavement Performance over 3 Years of Monitoring. Low Impact Development 2010: Redefining Water in the City. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Low Impact Development Conference, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 11–14 April 2010; pp. 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.M.; Huang, Z.L.; Guo, J.; Li, H.; Guo, X.R.; Nkeli, M.J. Bibliometric Analysis on Smart Cities Research. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegaard, O.; Wallin, J.A. The Bibliometric Analysis of Scholarly Production: How Great Is the Impact? Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1809–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranckutė, R. Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The Titans of Bibliographic Information in Today’s Academic World. Publications 2021, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apriliyanti, I.D.; Alon, I. Bibliometric Analysis of Absorptive Capacity. Int. Bus. Rev. 2017, 26, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, S.; Shah, H.; Lei, S.; Noor, S.; Anjum, A. Research Synthesis and New Directions of Prosumption: A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Sci. 2020, 31, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akintunde, T.Y.; Musa, T.H.; Musa, H.H.; Musa, I.H.; Chen, S.; Ibrahim, E.; Tassang, A.E.; Helmy, M.S.E.D.M. Bibliometric Analysis of Global Scientific Literature on Effects of COVID-19 Pandemic on Mental Health. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2021, 63, 102753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhao, R. Bibliometric Analysis of Research on Soil Health from 1999 to 2018. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.H.; Lei, S.; Ali, M.; Doronin, D.; Hussain, S.T. Prosumption: Bibliometric Analysis Using HistCite and VOSviewer. Kybernetes 2020, 49, 1020–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, E. From the Science of Science to Scientometrics Visualizing the History of Science with HistCite Software. J. Inf. 2009, 3, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrigos-Simon, F.J.; Narangajavana-Kaosiri, Y.; Lengua-Lengua, I. Tourism and Sustainability: A Bibliometric and Visualization Analysis. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva-Pareja, L.; Ramos-Pla, A.; Mercadé-Melé, P.; Espart, A. Evolution of Scientific Production on Health Literacy and Health Education—A Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gizzi, F.T.; Proto, M.; Potenza, M.R. The Basilicata Region (Southern Italy): A Natural and ‘Human-Built’ Open-Air Laboratory for Manifold Studies. Research Trends over the Last 24 Years (1994–2017). Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2019, 10, 433–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan van Eck, N.; Waltman, L. VOSviewer Manual. Available online: https://www.vosviewer.com/documentation/Manual_VOSviewer_1.6.18.pdf (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Goyal, K.; Kumar, S. Financial Literacy: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2021, 45, 80–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maditati, D.R.; Munim, Z.H.; Schramm, H.J.; Kummer, S. A Review of Green Supply Chain Management: From Bibliometric Analysis to a Conceptual Framework and Future Research Directions. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 139, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, R.R.; Hart, M.L.; Kevern, J.T. Enhancing the Ability of Pervious Concrete to Remove Heavy Metals from Stormwater. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2017, 3, 04017004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Sun, Z.; Bhaskar, N.R. Simulating the Long-Term Performance of Multifunctional Green-Pervious Concrete Pavement in Stormwater Runoff–Induced PAHs Remediation. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.J.; Arend, K.; Dorsey, J.D.; Johnson, J.P.; Hunt, W.F. Hydrologic Performance of a Permeable Pavement and Stormwater Harvesting Treatment Train Stormwater Control Measure. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2019, 6, 04019011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Mahmoud, E.; Yamin, M.; Patibandla, V.C. Experimental Study on Portland Cement Pervious Concrete Mechanical and Hydrological Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 50, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bean, E.Z.; Hunt, W.F.; Bidelspach, D.A. Field Survey of Permeable Pavement Surface Infiltration Rates. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassman, E.A.; Blackbourn, S. Urban Runoff Mitigation by a Permeable Pavement System over Impermeable Soils. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2010, 15, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarivate/Web of Science. Available online: http://help.incites.clarivate.com/incitesLiveESI/ESIGroup/indicatorsGroup/citationThresholds/thresholdsESI/countriesTerritoriesESI.html (accessed on 17 July 2022).
- Collins, K.A.; Hunt, W.F.; Hathaway, J.M. Hydrologic Comparison of Four Types of Permeable Pavement and Standard Asphalt in Eastern North Carolina. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2008, 13, 1146–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, F.; Haselbach, L. Measuring Hydraulic Conductivity in Pervious Concrete. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2006, 23, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansalone, J.; Kuang, X.; Ranieri, V. Permeable Pavement as a Hydraulic and Filtration Interface for Urban Drainage. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2008, 134, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.; Bradford, A.; van Seters, T. Stormwater Quality of Spring–Summer-Fall Effluent from Three Partial-Infiltration Permeable Pavement Systems and Conventional Asphalt Pavement. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 139, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Imteaz, M.A.; Arulrajah, A.; Piratheepan, J.; Disfani, M.M. Recycled Construction and Demolition Materials in Permeable Pavement Systems: Geotechnical and Hydraulic Characteristics. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 90, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, M.; Kakuturu, S.; Ballock, C.; Spence, J.; Wanielista, M. Effect of Rejuvenation Methods on the Infiltration Rates of Pervious Concrete Pavements. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 15, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowski, M.; Welker, A.L.; Traver, R.G.; Vanacore, M.; Ladd, T. Evaluation of an Infiltration Best Management Practice Utilizing Pervious Concrete1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 1208–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupic, I.; Čater, T. Bibliometric Methods in Management and Organization. Organ Res Methods 2014, 18, 429–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, H. Co-Citation in the Scientific Literature: A New Measure of the Relationship between Two Documents. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. 1973, 24, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetscherin, M.; Heinrich, D. Consumer Brand Relationships Research: A Bibliometric Citation Meta-Analysis. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alon, I.; Anderson, J.; Munim, Z.H.; Ho, A. A Review of the Internationalization of Chinese Enterprises. Asia Pac. J. Manag. 2018, 35, 573–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamore, S.; Ohene Djan, K.; Alon, I.; Hobdari, B. Credit Risk Research: Review and Agenda. Emerg. Mark. Financ. Trade 2018, 54, 811–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfield, E. The HistCite System for Mapping and Bibliometric Analysis of the Output of Searches Using the ISI Web of Knowledge. In Proceedings of the 65th Annual Meeting of the American Society for Information Science & Technology (ASIS&T), Austin, TX, USA, 3–8 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Øyna, S.; Alon, I. A Review of Born Globals. Int. Stud. Manag. Organ. 2018, 48, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemirovsky, E.M.; Welker, A.L.; Lee, R. Quantifying Evaporation from Pervious Concrete Systems: Methodology and Hydrologic Perspective. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, C.L.; Comino-Mateos, L. In-Situ Hydraulic Performance of a Permeable Pavement Sustainable Urban Drainage System. Water Environ. J. 2003, 17, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tota-Maharaj, K.; Scholz, M. Efficiency of Permeable Pavement Systems for the Removal of Urban Runoff Pollutants under Varying Environmental Conditions. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2010, 29, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lori, A.R.; Hassani, A.; Sedghi, R. Investigating the Mechanical and Hydraulic Characteristics of Pervious Concrete Containing Copper Slag as Coarse Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, X.; Sansalone, J.; Ying, G.; Ranieri, V. Pore-Structure Models of Hydraulic Conductivity for Permeable Pavement. J. Hydrol. 2011, 399, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Xu, M.; Vieira Netto, R.; Wille, K. Influence of Pore Tortuosity on Hydraulic Conductivity of Pervious Concrete: Characterization and Modeling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.; Šimůnek, J.; Piro, P. A Comprehensive Numerical Analysis of the Hydraulic Behavior of a Permeable Pavement. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 1146–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turco, M.; Kodešová, R.; Brunetti, G.; Nikodem, A.; Fér, M.; Piro, P. Unsaturated Hydraulic Behaviour of a Permeable Pavement: Laboratory Investigation and Numerical Analysis by Using the HYDRUS-2D Model. J. Hydrol. 2017, 554, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, J.P.; Campbell, C.D.; Mays, D.C. Infiltration and Clogging by Sand and Clay in a Pervious Concrete Pavement System. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayhanian, M.; Anderson, D.; Harvey, J.T.; Jones, D.; Muhunthan, B. Permeability Measurement and Scan Imaging to Assess Clogging of Pervious Concrete Pavements in Parking Lots. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 95, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.J.; Al-Rubaei, A.M.; Blecken, G.T.; Viklander, M.; Hunt, W.F. Maintenance Measures for Preservation and Recovery of Permeable Pavement Surface Infiltration Rate—The Effects of Street Sweeping, Vacuum Cleaning, High Pressure Washing, and Milling. J Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danz, M.E.; Selbig, W.R.; Buer, N.H. Assessment of Restorative Maintenance Practices on the Infiltration Capacity of Permeable Pavement. Water 2020, 12, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulu, A.; Jacob, P.; Dwarakish, G.S. Hydraulic Performance of Pervious Concrete Based on Small Size Aggregates. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2973255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, K.A.; Hunt, W.F.; Hathaway, J.M. Side-by-Side Comparison of Nitrogen Species Removal for Four Types of Permeable Pavement and Standard Asphalt in Eastern North Carolina. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 15, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.J.; Dorsey, J.D.; Smolek, A.P.; Hunt, W.F. Hydrologic Performance of Four Permeable Pavement Systems Constructed over Low-Permeability Soils in Northeast Ohio. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2018, 23, 04018007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhouse, P.W.; Srubar, W.V. Material Characterization and Hydraulic Conductivity Modeling of Macroporous Recycled-Aggregate Pervious Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 110, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.G.; Bortoletto, M.; Bigotto, S.A.M.; Akasaki, J.L.; Soriano, L.; Tashima, M.M. Effect of Wastes from Sugar Cane Industry on the Mechanical and Hydraulic Properties of Pervious Concrete. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2021, 23, 1981–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeyawardana, P.; Nanayakkara, N.; Gunasekara, C.; Karunarathna, A.; Law, D.; Pramanik, B.K. Improvement of Heavy Metal Removal from Urban Runoff Using Modified Pervious Concrete. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, V.; Maghfouri, M.; Nourmohammadi, D.; Azarsa, P.; Gupta, R.; Saberian, M. Stormwater Runoff Treatment Using Pervious Concrete Modified with Various Nanomaterials: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Villar, R.; Lizárraga-Mendiola, L.; Coronel-Olivares, C.; López-León, L.D.; Bigurra-Alzati, C.A.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, G.A. Effect of Photocatalytic Fe 2 O 3 Nanoparticles on Urban Runoff Pollutant Removal by Permeable Concrete. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 242, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H. Evaluation of Modified Permeable Pavement Systems with Coal Gangue to Remove Typical Runoff Pollutants under Simulated Rainfall. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathollahi, A.; Coupe, S.J.; El-Sheikh, A.H.; Sañudo-Fontaneda, L.A. The Biosorption of Mercury by Permeable Pavement Biofilms in Stormwater Attenuation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junling, W.; Jiangtao, W.; Xueming, W.; Cuimin, F.; Tao, C.; Lihua, S.; Junqi, L. The Adsorption Capacity of the Base Layer of Pervious Concrete Pavement Prepared with Additives for Typical Runoff Pollutants. Curr. Sci. 2018, 114, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y. Runoff Purification Effects of Permeable Concrete Modified by Diatomite and Zeolite Powder. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1081346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Chen, W.; Gao, Q.; Liu, S.; Deng, C.; Ma, Y.; Ji, G. Research on the Reduction Performance of Surface Runoff Pollution Through Permeable Pavement with Different Structures. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Gan, H.; Xiao, M.; Huang, B.; Zhu, D.Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Lin, Y.; Hou, Y.; Peng, S.; et al. Performance of Permeable Pavement Systems on Stormwater Permeability and Pollutant Removal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 28571–28584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, T.K.; Davis, A.P. Evaluation of an Enhanced Treatment Media and Permeable Pavement Base to Remove Stormwater Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Metals under Simulated Rainfall. Water Res. 2019, 166, 115071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yan, H.; Xin, K.; Li, S.; Schmidt, A.R.; Tao, T. Development and Application of Regression Models for Predicting the Water Quality Performance of Permeable Pavement. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, H.; Rockaway, T.D.; Rivard, J.; Abdollahian, S. Assessment of Surface Infiltration Performance and Maintenance of Two Permeable Pavement Systems in Louisville, Kentucky. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2017, 3, 04017009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isis, T.; Veldkamp, E.; Cornelis Boogaard, F.; Kluck, J. Unlocking the Potential of Permeable Pavements in Practice: A Large-Scale Field Study of Performance Factors of Permeable Pavements in The Netherlands. Water 2022, 14, 2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winston, R.J.; Asce, M.; Al-Rubaei, A.M.; Blecken, G.T.; Hunt, W.F.; Wre, D. A Simple Infiltration Test for Determination of Permeable Pavement Maintenance Needs. J. Environ. Eng. 2016, 142, 06016005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesh, A.; Ong, G.P.; Su, Y.-M. Development of Discharge-Based Thresholding Algorithm for Pervious Concrete Pavement Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, G.; Ming, R.; Cui, X.; Li, L.; Xu, H. Numerical Study on Seepage Flow in Pervious Concrete Based on 3D CT Imaging. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, G.F.B.; Galobardes, I.; de Moura, A.C.; Toralles, B.M. Hydraulic Behavior Variation of Pervious Concrete Due to Clogging. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 13, e00354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; He, Z.; Liu, P.; He, Z.; Li, G.; Jiang, H.; Oeser, M. Estimation of Hydraulic Properties in Permeable Pavement Subjected to Clogging Simulation. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 5091895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghmanesh, M.; Beecham, S. A Review of Permeable Pavement Clogging Investigations and Recommended Maintenance Regimes. Water 2018, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, C.F.; McCarthy, D.T.; Deletic, A. Predicting Physical Clogging of Porous and Permeable Pavements. J. Hydrol. 2013, 481, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radfar, A.; Rockaway, T.D. Clogging Prediction of Permeable Pavement. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2016, 142, 04015069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShareedah, O.; Nassiri, S. Spherical Discrete Element Model for Estimating the Hydraulic Conductivity and Pore Clogging of Pervious Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 305, 124749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, S.P.; Rowe, A.; Guo, Q. Laboratory Scale Study to Quantify the Effect of Sediment Accumulation on the Hydraulic Conductivity of Pervious Concrete. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.G.; Borst, M.; Brown, R.A.; Rossman, L.; Simon, M.A. Modeling the Hydrologic Processes of a Permeable Pavement System. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 04014070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaddy, P.; Singh, A.; Sampath, P.V.; Biligiri, K.P. Multi-Scale in Situ Investigation of Infiltration Parameter in Pervious Concrete Pavements. J. Test. Eval. 2020, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xie, X.; Liu, R.; Lin, C.; Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Comparison of Field Infiltration Test Methods for Permeable Pavement: Towards an Easy and Accurate Method. Clean 2019, 47, 1900174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lederle, R.; Shepard, T.; de La Vega Meza, V. Comparison of Methods for Measuring Infiltration Rate of Pervious Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 244, 118339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, T.K.; Aydilek, A.H.; Davis, A.P. High-Flow Structural Media for Removing Stormwater-Dissolved Phosphorous in Permeable Paving. J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. 2019, 5, 04019001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manan, A.; Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, F.; Basit, A.; Ayaz Khan, M.N. Experimental Investigation of Compressive Strength and Infiltration Rate of Pervious Concrete by Fully Reduction of Sand. Civ. Eng. J. 2018, 4, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, S.V.; da Silva Magalhães, M.; da Nóbrega Tavares, M.E. Mechanical Behavior and Water Infiltration of Pervious Concrete Incorporating Recycled Asphalt Pavement Aggregate. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 14, e00473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeo, S.K.; Ransinchung, G.D.R.N. Hydrological and Strength Characteristics of Pervious Concrete Mixes Containing Rap Aggregates and Sugarcane Bagasse Ash. Adv. Civ. Eng. Mater. 2022, 11, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.A.; Goh, Y.; Ng, Z.A.; Yap, S.P.; Mo, K.H.; Yuen, C.W.; Abutaha, F. Hydraulic and Strength Characteristics of Pervious Concrete Containing a High Volume of Construction and Demolition Waste as Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hassan, H.; Kianmehr, P. Pervious Concrete Pavement Incorporating GGBS to Alleviate Pavement Runoff and Improve Urban Sustainability. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2018, 19, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.N.; Ghisi, E.; Severis, R.M. Environmental Assessment of a Permeable Pavement System Used to Harvest Stormwater for Non-Potable Water Uses in a Building. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C1701; Standard Test Method for Infiltration Rate of In Place Pervious Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. Available online: https://www.astm.org/c1701_c1701m-17a.html (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- ASTM C1781; Standard Test Method for Surface Infiltration Rate of Permeable Unit Pavement Systems. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.astm.org/c1781_c1781m-21.html (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Gersson, G.F.; Pieralisi, R.; Dall Bello de Souza Risson, K.; Campos de Moura, A.; Toralles, B.M. Clogging Phenomenon in Pervious Concrete (PC): A Systematic Literature Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Fwa, T.F. Evaluation of Surface Infiltration Performance of Permeable Pavements. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 238, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.; Tang, B.; Fwa, T.F. Evaluation of Functional Characteristics of Laboratory Mix Design of Porous Pavement Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 191, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbig, W.R.; Buer, N.; Danz, M.E. Stormwater-Quality Performance of Lined Permeable Pavement Systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 251, 109510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Chui, T.F.M. Factors Influencing Stormwater Mitigation in Permeable Pavement. Water 2017, 9, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, Y.; Guo, K.; Qi, W.; Hinkelmann, R. Experimental Study for Effects of Terrain Features and Rainfall Intensity on Infiltration Rate of Modelled Permeable Pavement. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ranked by TP * | Ranked by TC * | Ranked by CPP * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Journal Name | TP | Rank | Journal Name | TC | Rank | Journal Name | CPP |
| 1 | Constr. Build. Mater. | 13 | 1 | J. Hydrol. Eng. | 541 | 1 | Water Res. | 103 |
| 2 | J. Hydrol. Eng. | 9 | 2 | J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. | 508 | 2 | J. Hydrol. Eng. | 60 |
| 3 | J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. | 9 | 3 | Constr. Build. Mater. | 426 | 3 | J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. | 56 |
| 4 | J. Environ. Manag. | 8 | 4 | Water Res. | 410 | 4 | J. Hydrol. | 45 |
| 5 | J. Environ. Eng. | 6 | 5 | J. Environ. Manag. | 290 | 5 | J. Environ. Manag. | 36 |
| 6 | Water Sci. Technol. | 6 | 6 | J. Hydrol. | 178 | 6 | Constr. Build. Mater. | 33 |
| 7 | Water | 6 | 7 | Environ. Eng. | 75 | 7 | JOEE | 13 |
| 8 | J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. | 5 | 8 | Water Sci. Technol. | 59 | 8 | Water Sci. Technol. | 10 |
| 9 | J. Test. Eval | 5 | 9 | Water | 53 | 9 | Water | 9 |
| 10 | Water Res. | 4 | 10 | J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. | 38 | 10 | J. Sustain. Water Built Environ. | 8 |
| Ranked by TP | Ranked by TC | Ranked by CPP | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Country | TP | Rank | Country | TC | Rank | Country | CPP |
| 1 | USA | 61 | 1 | USA | 2315 | 1 | Canada | 49 |
| 2 | China | 20 | 2 | Italy | 395 | 2 | Italy | 40 |
| 3 | England | 10 | 3 | Canada | 293 | 3 | USA | 38 |
| 4 | Brazil | 10 | 4 | China | 231 | 4 | Australia | 27 |
| 5 | Italy | 10 | 5 | Australia | 187 | 5 | Scotland | 20 |
| 6 | Spain | 8 | 6 | England | 143 | 6 | England | 14 |
| 7 | Australia | 7 | 7 | Scotland | 98 | 7 | China | 12 |
| 8 | Canada | 6 | 8 | Spain | 79 | 8 | Germany | 11 |
| 9 | Scotland | 5 | 9 | Germany | 57 | 9 | Spain | 10 |
| 10 | Germany | 5 | 10 | Brazil | 50 | 10 | Brazil | 5 |
| Ranked by Normalized Citation Score (NCS) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Author | Affiliation | Country | NCS |
| 1 | William Hunt | North Carolina State University | USA | 13 |
| 2 | Ryan Winston | Ohio State University | USA | 9 |
| 3 | Xuheng Kuang | Tsinghua University | China | 5 |
| 4 | Vittorio Ranieri | Politecnico di Bari University | Italy | 5 |
| 5 | John Sansalone | University of Florida | USA | 5 |
| 6 | Jay Dorsey | Ohio State University | USA | 4 |
| 7 | Krishna Biligiri | Indian Institute of Technology (IIT)—Tirupati | India | 4 |
| 8 | Luis Sanudo-Fontaneda | University of Oviedo | Spain | 3 |
| 9 | Haiyan Li | China University of Mining & Technology | China | 3 |
| 10 | Xiaoran Zhang | Beijing Adv Innovat Ctr Future Urban Design | China | 3 |
| 11 | Ziyang Zhang | Beijing University of Civil Engineering & Architecture | China | 3 |
| Ranked by Global Citations | Ranked by Local Citations | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Article | Global Citations | Rank | Article | Local Citations |
| 1 | Brattebo and Booth (2003) [44] | 318 | 1 | Brattebo and Booth (2003) [44] | 44 |
| 2 | Fassman and Blackbourn (2010) [68] | 169 | 2 | Bean et al. (2007a) [67] | 29 |
| 3 | Collins et al. (2008) [70] | 167 | 3 | Collins et al. (2008) [70] | 28 |
| 4 | Bean et al. (2007a) [67] | 165 | 4 | Bean et al. (2007b) [32] | 25 |
| 5 | Ibrahim et al. (2014) [66] | 134 | 5 | Fassman and Blackbourn (2010) [68] | 19 |
| 6 | Bean et al. (2007b) [32] | 126 | 6 | Montes and Haselbach (2006) [71] | 18 |
| 7 | Sansalone et al. (2008) [72] | 115 | 7 | Drake et al. (2014) [73] | 12 |
| 8 | Rahman et al. (2015) [74] | 84 | 8 | Sansalone et al. (2008) [72] | 11 |
| 9 | Montes and Haselbach (2006) [71] | 83 | 9 | Chopra et al. (2010) [75] | 11 |
| 10 | Drake et al. (2014) [73] | 79 | 10 | Kwiatkowski et al. (2007) [76] | 11 |
| Research Theme | Recent Advancement | Research Opportunity |
|---|---|---|
| Improving and predicting the removal of contaminants |
|
|
| Characterizing and minimizing the effects of clogging |
|
|
| Improvements for IR assessment and characterization |
| |
| Sustainability Considerations |
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singer, M.N.; Hamouda, M.A.; El-Hassan, H.; Hinge, G. Permeable Pavement Systems for Effective Management of Stormwater Quantity and Quality: A Bibliometric Analysis and Highlights of Recent Advancements. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13061. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013061
Singer MN, Hamouda MA, El-Hassan H, Hinge G. Permeable Pavement Systems for Effective Management of Stormwater Quantity and Quality: A Bibliometric Analysis and Highlights of Recent Advancements. Sustainability. 2022; 14(20):13061. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013061
Chicago/Turabian StyleSinger, Mohamed N., Mohamed A. Hamouda, Hilal El-Hassan, and Gilbert Hinge. 2022. "Permeable Pavement Systems for Effective Management of Stormwater Quantity and Quality: A Bibliometric Analysis and Highlights of Recent Advancements" Sustainability 14, no. 20: 13061. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013061
APA StyleSinger, M. N., Hamouda, M. A., El-Hassan, H., & Hinge, G. (2022). Permeable Pavement Systems for Effective Management of Stormwater Quantity and Quality: A Bibliometric Analysis and Highlights of Recent Advancements. Sustainability, 14(20), 13061. https://doi.org/10.3390/su142013061







