Effect of Supporting Base System on the Flexural Behavior and Toughness of the Lighting GFRP Poles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Work
2.1. Geometry and Material Properties of the Tested Specimens
2.2. Test Setup and Instrumentation
3. Experimental Results and Observations
4. Finite Element Analysis
4.1. Elements Types, Meshing, and Material Modeling
4.2. Interaction Properties
4.3. Loading and Boundary Conditions
4.4. Failure Criterion
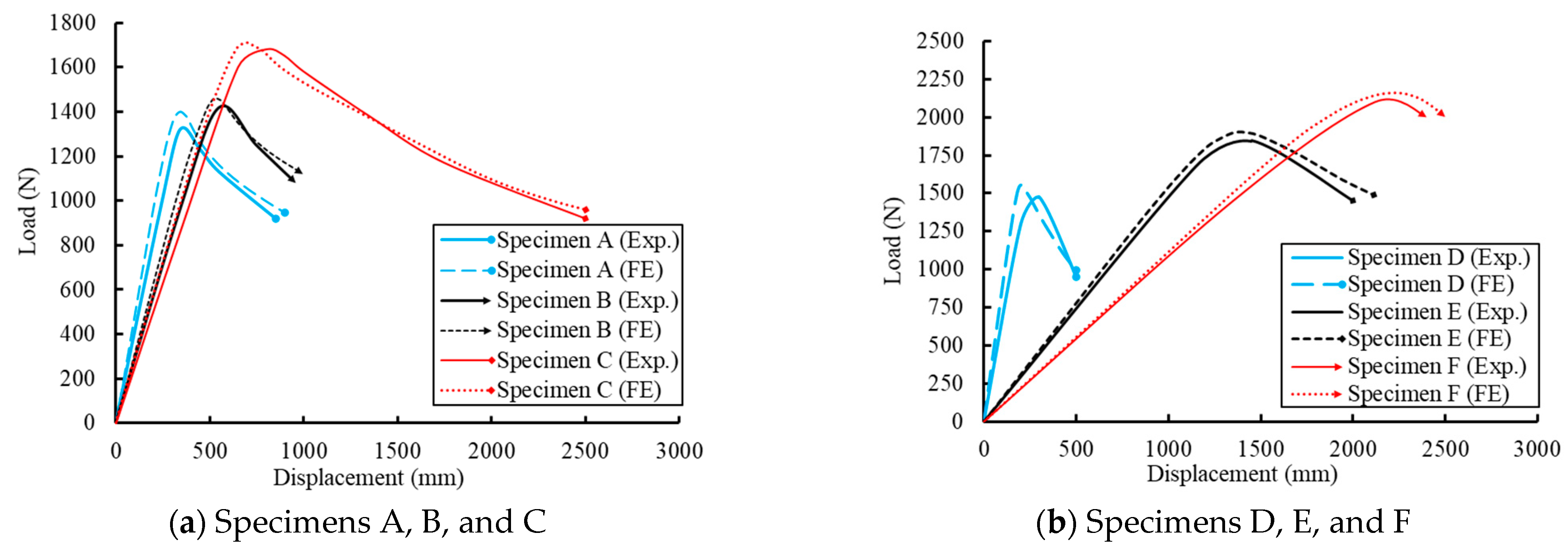
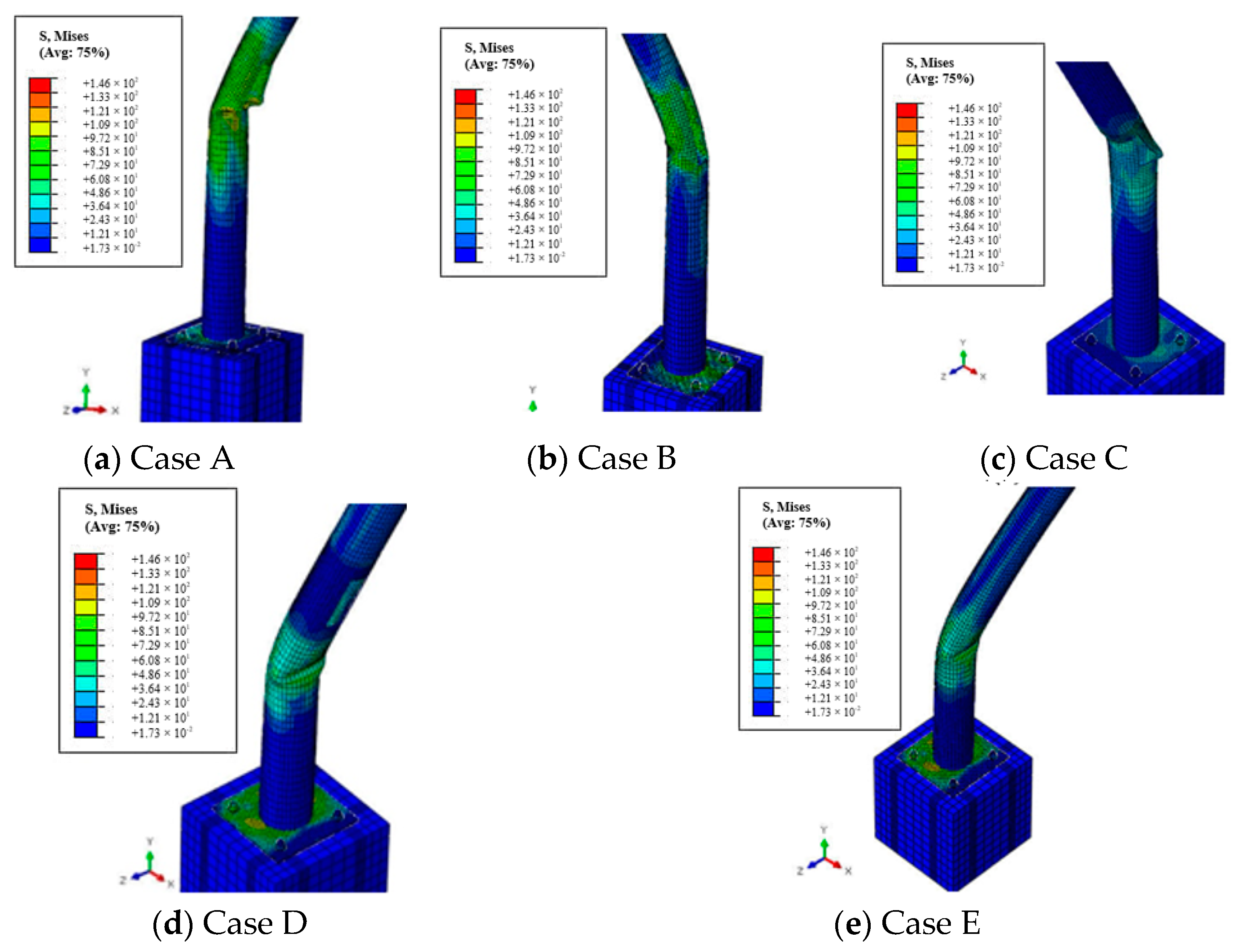
4.5. FE Validations and Discussions
5. Parametric Study
5.1. Effect of the Handle Door Opening Position
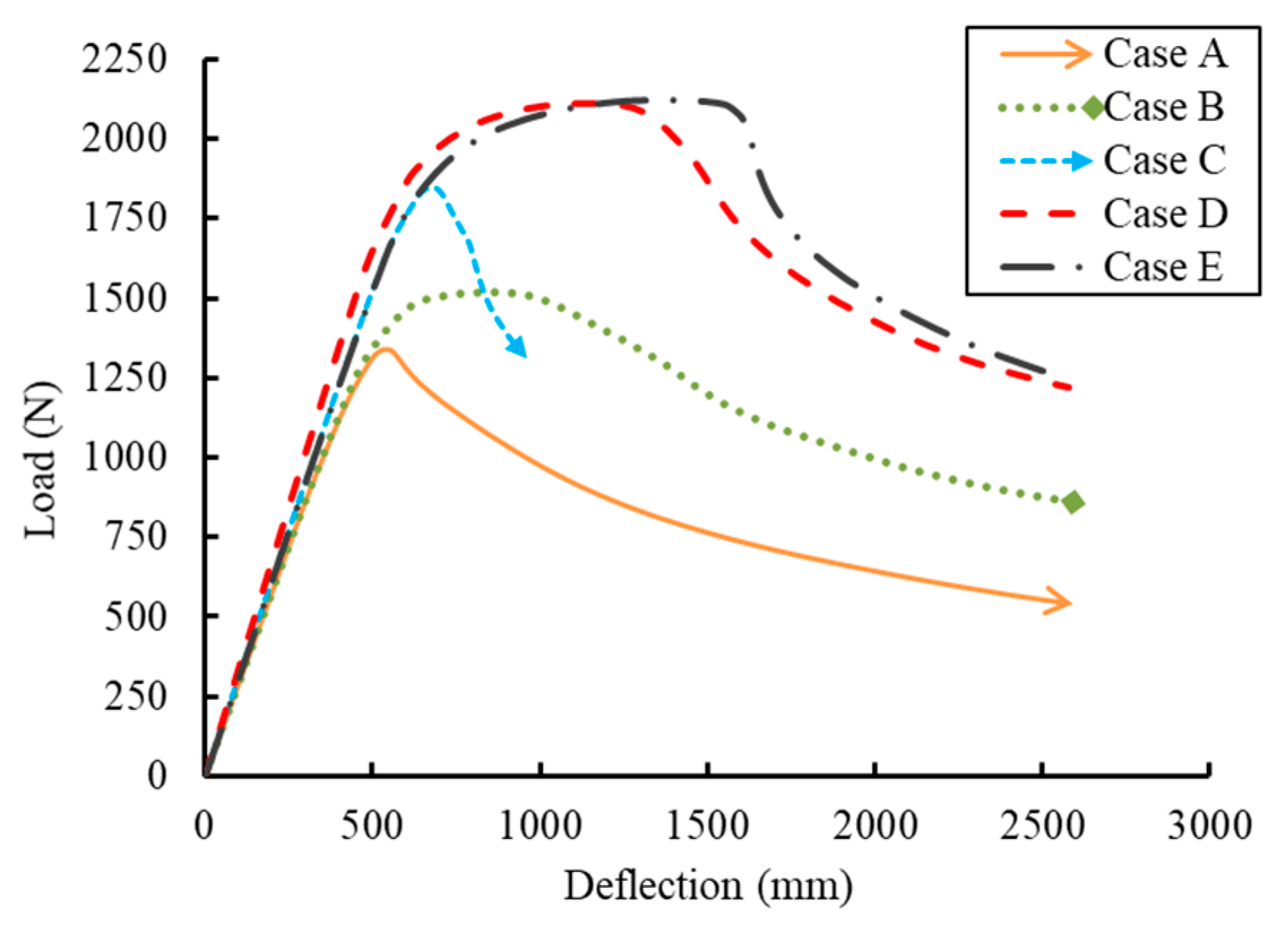
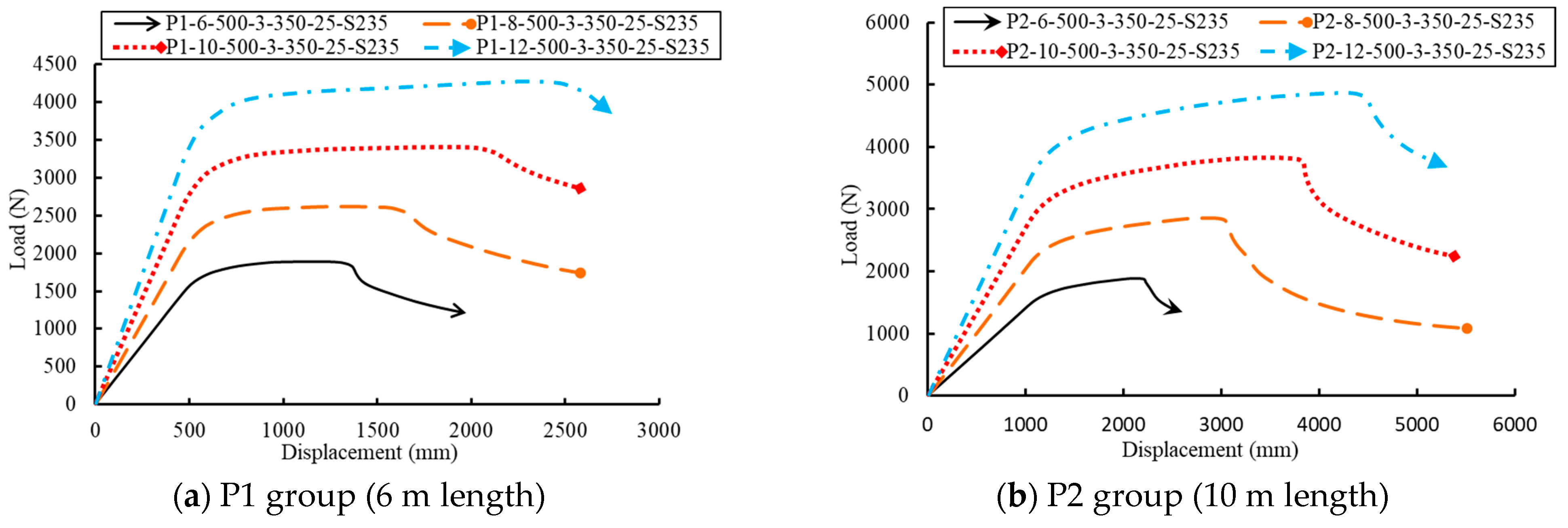
5.2. Effect of the GFRP Pole Wall Thickness (PT)
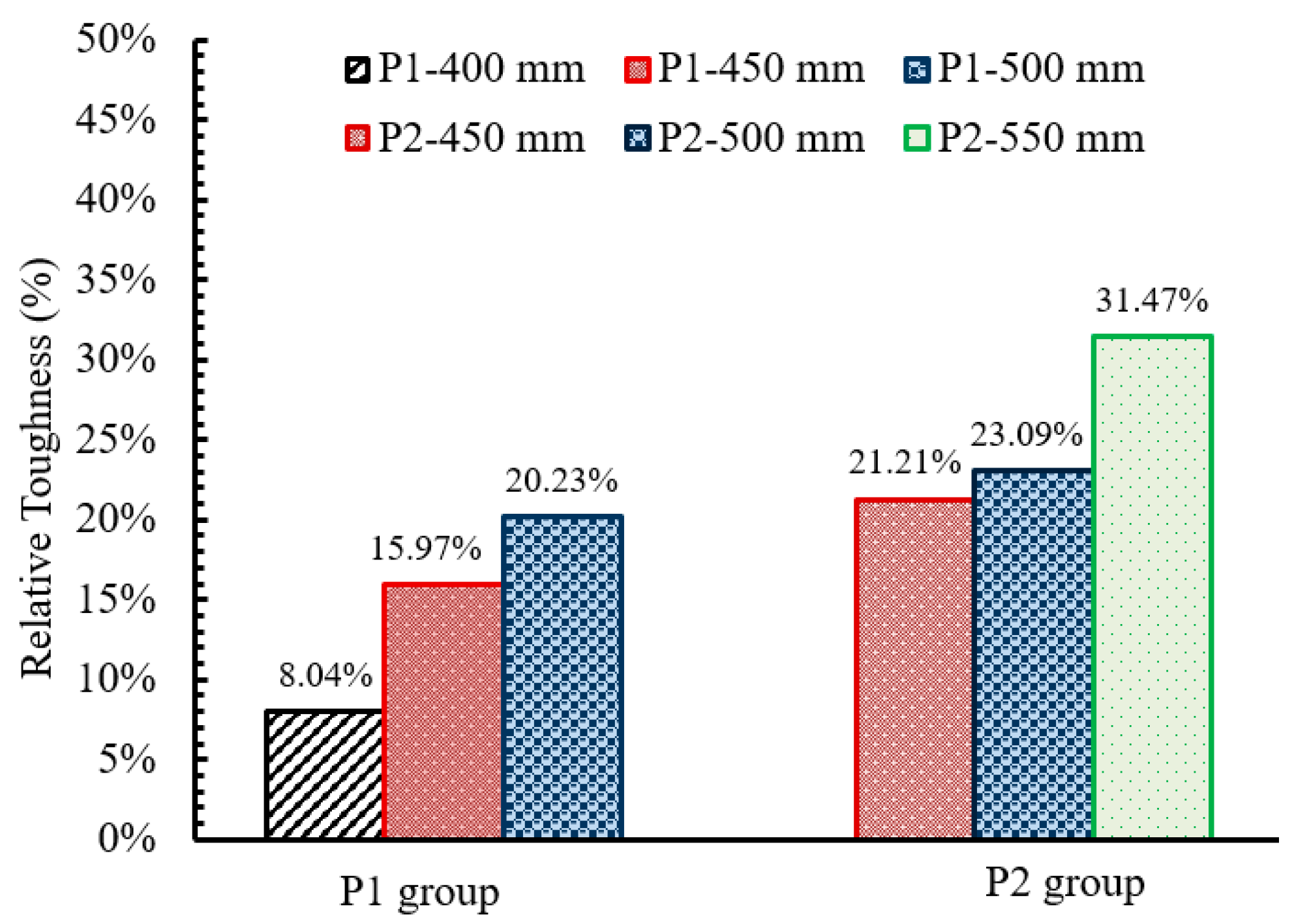
5.3. Effect of the Base Plate Dimensions (L and B)
5.4. Effect of the Base Plate Thickness (T)
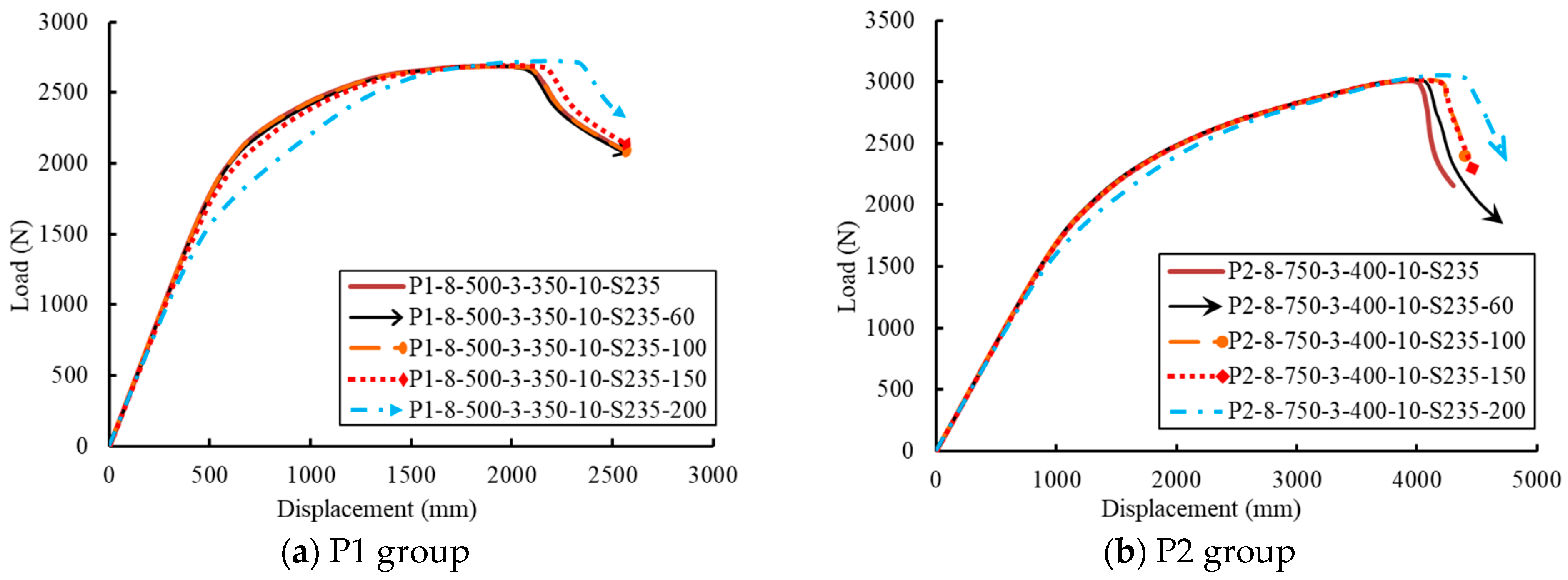
5.5. Effect of the Electric Cable Hole Diameter (HD)
5.6. Effect of the Base Plate Material Properties (SG)
5.7. Effect of the Base Sleeve Height (SH)
5.8. Effect of the Base Sleeve Thickness (ST)
6. Significance of the Research
7. Conclusions
- By increasing the pole’s height by two times, the toughness was promoted at least three and half times approximately.
- The dominant failure mode of the GFRP pole with an anchored base system was local buckling around the handle door.
- The FE predictions of the load–displacement curves relative to the experimental results were generally by values less than 3.5% approximately.
- Strengthening the handle door with a steel ring increased the ultimate capacity of the GFRP pole and prevented the fracture of this region. Moreover, the base system became the most effective for pole deformation.
- The wall thickness of the GFRP pole had the most effective parameter that affected the ductility and toughness of the GFRP pole, while the base sleeve thickness had a slight effect.
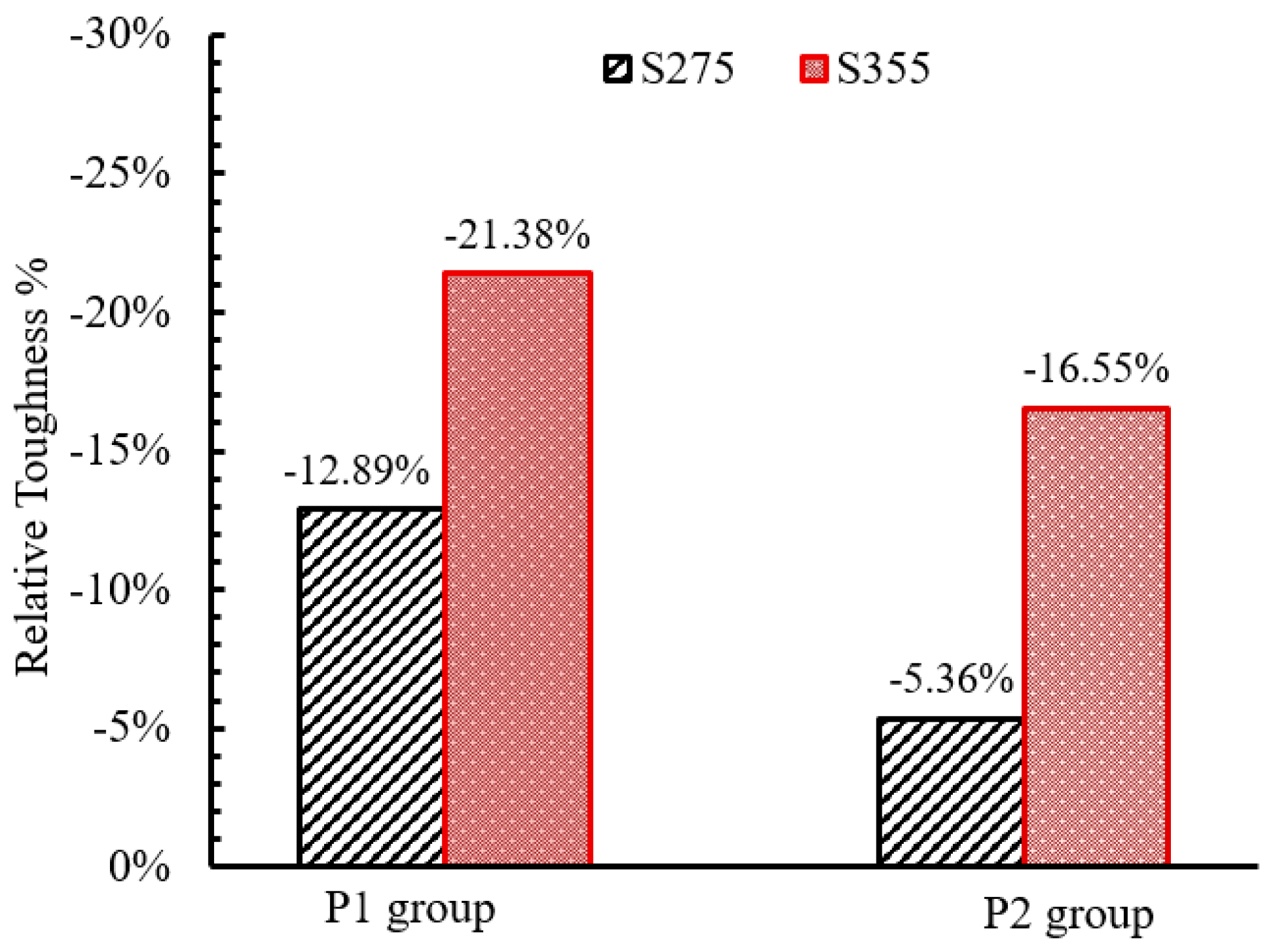
- Using mild steel for the base plate promoted the toughness of the GFRP pole.
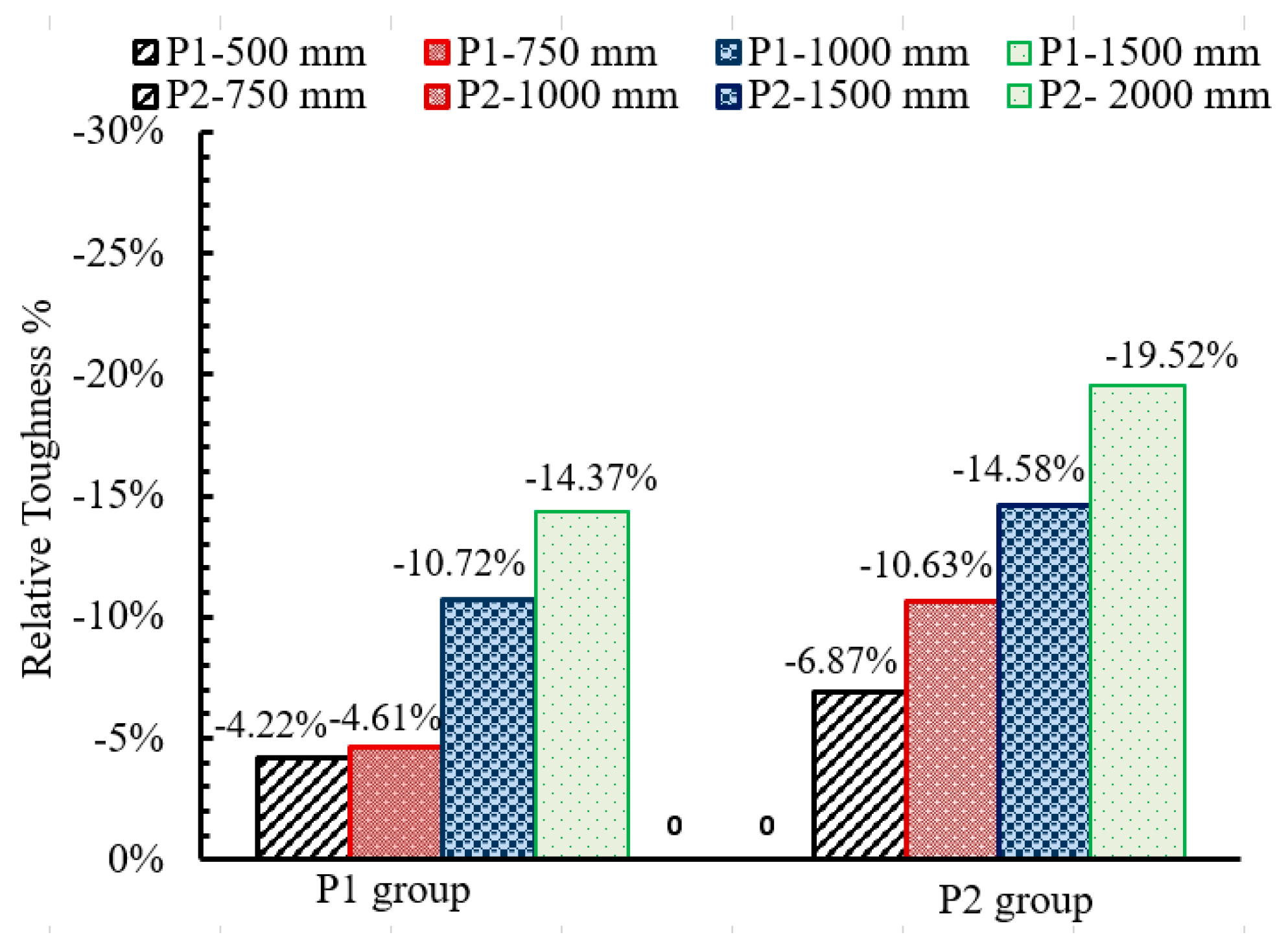
- Increasing the thickness of the base plate had a reverse effect on the ductility and toughness of the GFRP pole, while the base sleeve thickness had a slight direct effect.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elmarakbi, A.; Fielding, N. A new design of roadside pole structure: Crash analysis of different longitudinal tubes using LS-DYNA. In Proceedings of the 7th European LS-DYNA Conference 2009, Salzburg, Austria, 14–15 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bondok, D.H.; Salim, H.A. Numerical Modeling of Conventional Steel Stud Walls Static Resistance for Blast Response Predictions. Struct. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, M.T.; Arafa, I.T.; Elhosseiny, O.M.; El-Zohairy, A. Full static resistance of castellated steel beams with hexagonal web openings for blast response predictions. Eng. Struct. 2021, 245, 112844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Bhadauria, S.S.; Akhtar, S. Monitoring corrosion of steel bars in reinforced concrete structures. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 957904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirsayapov, I.; Yakupov SHassoun, M. About concrete and reinforced concrete corrosion. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 890, 012061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzois, D.; Ibrahim, S.; Burachynsky, V.; Hassan, S.K. Glass fiber-reinforced plastic poles for transmission and distribution lines: An experimental investigation. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Composite Materials, Paris, France, 5–9 July 1999; Available online: http://www.iccmcentral.org/Proceedings/ICCM12proceedings/site/papers/pap1201.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2022).
- Khayatazad, M.; De Pue, L.; De Waele, W. Detection of corrosion on steel structures using automated image processing. Dev. Built Environ. 2020, 3, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ožbolt, J.; Balabanić, G.; Oršanić, F. Modelling corrosion of steel reinforcement in concrete. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 615, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathishkumar, T.P.; Satheeshkumar, S.; Naveen, J. Glass fiber-reinforced polymer composites—A review. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2014, 33, 1258–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzuki, H.F.A.; Jaafar, M. Laminate Design of Lightweight Glass Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composite for Electrical Transmission Structure. Procedia Chem. 2016, 19, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, V.; Karakouzian, M. Effect of Fiber Reinforced Polymer Tubes Filled with Recycled Materials and Concrete on Structural Capacity of Pile Foundations. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudonis, E.; Timinskas, E.; Gribniak, V.; Kaklauskas, G.; Arnautov, A.K.; Tamulėnas, V. FRP Reinforcement for Concrete Structures: State-of-the-Art Review of Application and Design. Eng. Struct. Technol. 2013, 5, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglioni, C.; Imbimbo, M. Experimental Results on Centrifugated GFRP Poles for Electric Lifelines. J. Compos. Constr. 1999, 3, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, H.C. Method of Manufacturing a Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Lighting Pole. U.S. Patent 12/314 800, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Facultatis, A.; Zvolen, X. Investigation of modified wood as a material power transmission pole produced by self-pressing method. Acta Fac. Xylologiae Zvolen 2018, 60, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, F.H.; Mullinax, E.C. FRC Poles for Distribution Power Lines. In Proceedings of the Structure Congress 2000, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 8–10 May 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metiche, S.; Masmoudi, R. Full-Scale Flexural Testing on Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP) Poles. Open Civ. Eng. J. 2007, 1, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Metiche, S.; Masmoudi, R. Analysis and design procedures for the flexural behavior of glass fiber-reinforced polymer composite poles. J. Compos. Mater. 2013, 47, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.; Yuan, R. Investigation of bending/buckling characteristics for FRP composite poles. In Earth & Space 2006: Engineering, Construction, and Operations in Challenging Environment; 2006; Volume 146, pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Polyzois, D. Ovalization analysis of fiber-reinforced plastic poles. Compos. Struct. 1999, 45, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzois, D.; Ibrahim, S.; Raftoyiannis, I.G. Performance of fiber-reinforced plastic tapered poles under lateral loading. Compos. Mater. 1999, 33, 941–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urgessa, G.; Mohamadi, S. Structural Assessment of Fiber-reinforced Polymer Composite Electric Poles. Procedia Eng. 2016, 145, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masmoudi, R.; Mohamed, H.; Metiche, S. Finite element modeling for deflection and bending responses of GFRP poles. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2008, 27, 639–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broniewicz, M.; Broniewicz, F.; Broniewicz, E. A Full-Scale Experimental Investigation of Utility Poles Made of Glass Fibre Reinforced Polymer. Materials 2021, 14, 7398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, J.; Qiu, S.; Feng, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z. Experimental Study on Axial Compression Buckling of Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastics Solid Pole with Circular Cross-Section. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2022, 25, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siringoringo, D.M.; Fujino, Y.; Nagasaki, A.; Matsubara, T. Seismic Performance Evaluation of Existing Light Poles on Elevated Highway Bridges. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021, 17, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altanopoulos, T.I.; Raftoyiannis, I.G.; Polyzois, D. Finite Element Method for the Static Behavior of Tapered Poles Made of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2021, 28, 2141–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skender, A.; Domitran, Z.; Krokar, J. The Effective Flexural Modulus of Filament Wound GRP Tapered Poles. Teh. Vjesn. 2020, 27, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D 4923; American Society for Testing and Materials, Standard Specification for Reinforced Thermosetting Plastic Poles. American Association of State Highway and Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
- ANSI C 136; American National Standard Institute, Fiber-Reinforced Plastic (FRP) Lighting Poles. United States Department of Defense: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Abaqus, Abaqus 6.11, Computer Software for Finite Element Analysis; Dassault Systems Simulia: Johnston, RI, USA, 2011.
- LRFDLTS-1-I2-OL; Standard Specifications for Structural Supports for Highway Signs, Luminaires and Traffic 500 Signals. American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2001.
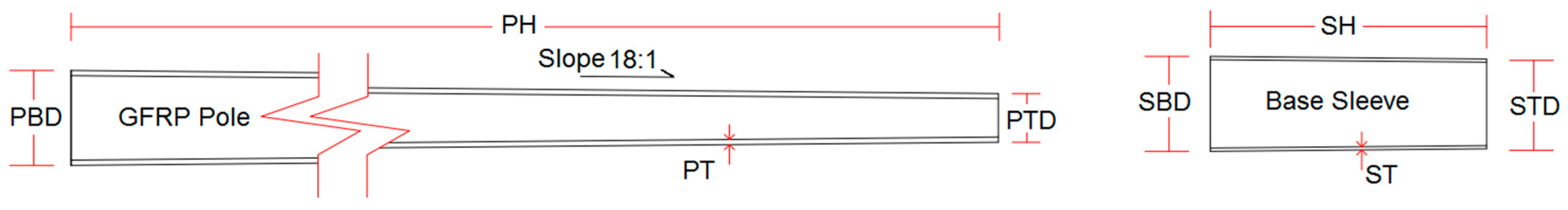

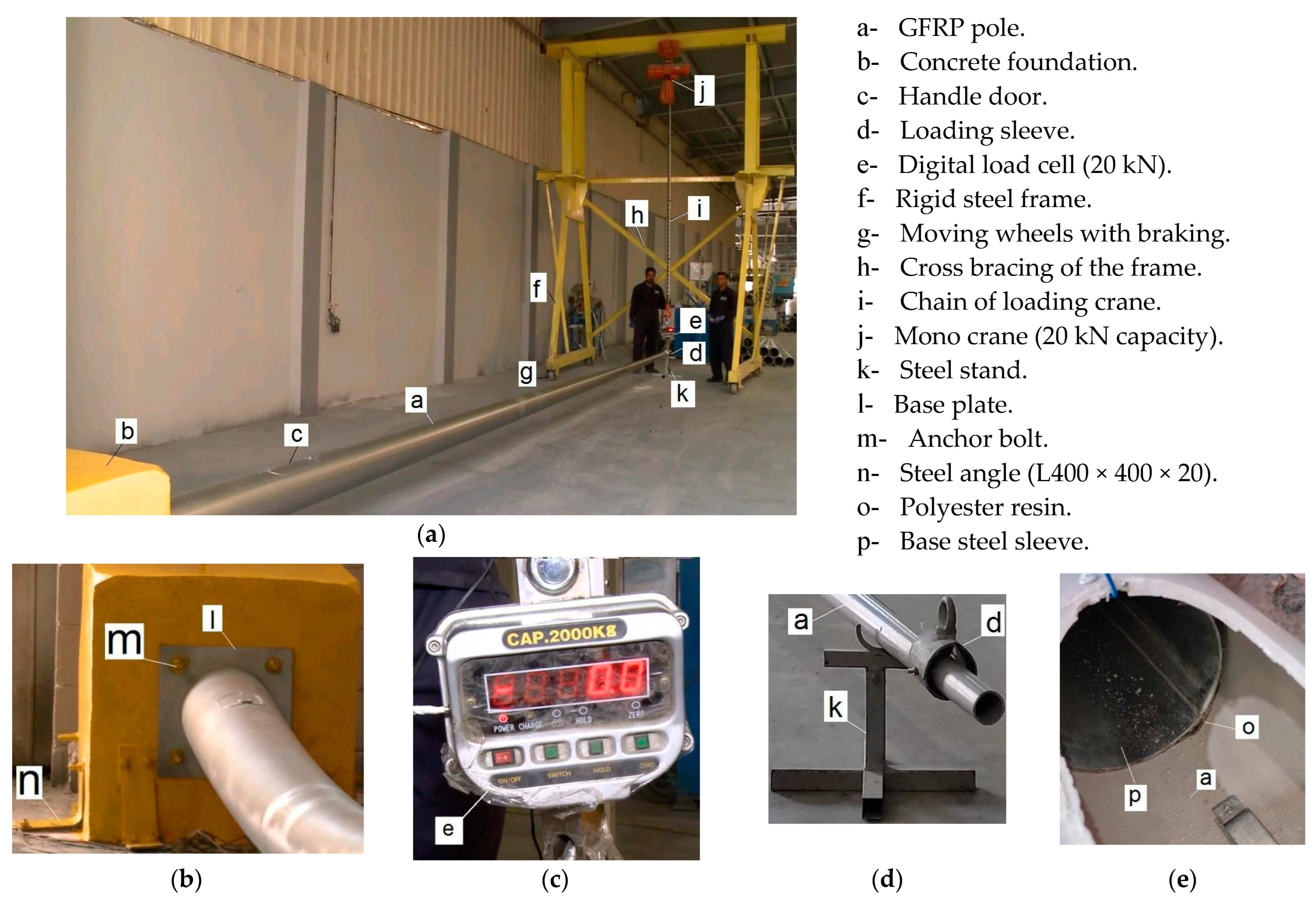
















| Specimen | PH (mm) | PTD (mm) | PBD (mm) | PT (mm) | SH (mm) | STD (mm) | SBD (mm) | ST (mm) | Base Plate Dimensions (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Specimen A | 4000 | 76 | 148 | 6 | 250 | 114 | 118 | 3 | 250 × 250 × 10 |
| Specimen B | 6000 | 76 | 184 | 6.6 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 × 350 × 10 |
| Specimen C | 8000 | 94 | 238 | 7.2 | 500 | 195 | 213 | 3 | 350 × 350 × 10 |
| Specimen D | 10,000 | 76 | 256 | 8.6 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 × 400 × 15 |
| Specimen E | 12,000 | 76 | 292 | 8.4 | 1000 | 252 | 270 | 4 | 400 × 400 × 15 |
| Specimen F | 16,000 | 94 | 364 | 8.7 | 1200 | 317 | 339 | 5 | 500 × 500 × 20 |
| PH: Total length of the pole. | SH: Total height of the steel sleeve. | ||||||||
| PTD: Top diameter of the pole. | STD: Top diameter of the sleeve. | ||||||||
| PBD: Bottom diameter of the pole. | SBD: Bottom diameter of the sleeve. | ||||||||
| PT: average wall thickness of the pole. | ST: sleeve wall thickness. | ||||||||
| Properties | E-Glass | # 90 Isophthalic Polyester Resin | Equivalent GFRP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (gm/cm3) | 2.54 | 1.08 | 1.85 |
| Poisson’s ratio (v) | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.25 |
| Tensile modulus (GPa) | 72 | 3.4 | 18 |
| Shear modulus (GPa) | 30 | 1.37 | 4.8 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 1500 | 79 | 370 |
| Flexural strength (MPa) | -- | -- | 365 |
| Percent of glass fiber by weight | -- | -- | 45% |
| Material | Base Sleeve, Base Plate | Anchor Bolt |
|---|---|---|
| Density (gm/cm3) | 7.8 | 7.8 |
| Poisson’s ratio (v) | 0.26 | 0.26 |
| Tensile modulus (GPa) | 207 | 207 |
| Shear modulus (GPa) | 80 | 80 |
| Tensile strength (MPa) | 360 | 520 |
| Yield strength (MPa) | 240 | 360 |
| Specimen | Max. Deflection (mm) | Failure Load (N) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆Exp. | ∆FE | % Change | PExp. | PF.E | % Change | |
| A (4 m) | 450 | 455 | 1.11 | 1320 | 1359 | 2.95 |
| B (6 m) | 550 | 557 | 1.35 | 1420 | 1456 | 2.54 |
| C (8 m) | 800 | 828 | 3.52 | 1680 | 1733 | 3.15 |
| D (10 m) | 300 | 310 | 3.23 | 1475 | 1517 | 2.85 |
| E (12 m) | 1450 | 1468 | 1.23 | 1845 | 1885 | 2.15 |
| F (16 m) | 2120 | 2152 | 1.52 | 2100 | 2142 | 1.98 |
| Case Study | FE pole (P-PT-SH-ST-B-T-SG-HD) | GFRP Pole | Base Sleeve | Base Plate | Toughness (kN·mm) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH (m) | PTD (mm) | PBD (mm) | PT (mm) | SH (mm) | STD (mm) | SBD (mm) | ST (mm) | L (mm) | B (mm) | T (mm) | HD (mm) | SG | |||
| GFRP pole thickness | P1-6-500-3-350-25-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 6 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 25 | - | S235 | 1656 |
| P1-8-500-3-350-25-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 25 | - | S235 | 2773 | |
| P1-10-500-3-350-25-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 10 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 25 | - | S235 | 5389 | |
| P1-12-500-3-350-25-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 12 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 25 | - | S235 | 8628 | |
| P2-6-750-3-400-30-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 6 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 30 | - | S235 | 2690 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-30-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 30 | - | S235 | 8248 | |
| P2-10-750-3-400-30-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 10 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 30 | - | S235 | 10,711 | |
| P2-12-750-3-400-30-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 12 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 30 | - | S235 | 16,916 | |
| Base plate dimensions | P1-8-500-3-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 4075 |
| P1-8-500-3-400-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 4403 | |
| P1-8-500-3-450-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 450 | 450 | 10 | - | S235 | 4726 | |
| P1-8-500-3-500-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 500 | 500 | 10 | - | S235 | 4899 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 8464 | |
| P2-8-750-3-450-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 450 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 10,260 | |
| P2-8-750-3-500-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 500 | 500 | 10 | - | S235 | 10,419 | |
| P2-8-750-3-550-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 550 | 550 | 10 | - | S235 | 11,128 | |
| Base plate thickness | P1-8-500-3-350-8-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 8 | - | S235 | 4875 |
| P1-8-500-3-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 4075 | |
| P1-8-500-3-350-12-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 12 | - | S235 | 2965 | |
| P1-8-500-3-350-16-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 16 | - | S235 | 2741 | |
| P1-8-500-3-350-20-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 20 | - | S235 | 2737 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-8-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 8 | - | S235 | 10,207 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 8464 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-12-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 12 | - | S235 | 6950 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-16-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 16 | - | S235 | 6264 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-20-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 20 | - | S235 | 6184 | |
| Diameter of the electric cable hole | P1-8-500-3-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 4075 |
| P1-8-500-3-350-10-S235-60 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | 60 | S235 | 4042 | |
| P1-8-500-3-350-10-S235-100 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | 100 | S235 | 4074 | |
| P1-8-500-3-350-10-S235-150 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | 150 | S235 | 4241 | |
| P1-8-500-3-350-10-S235-200 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | 200 | S235 | 4562 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 8464 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S235-60 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | 30 | S235 | 8609 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S235-100 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | 60 | S235 | 8828 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S235-150 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | 100 | S235 | 8828 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S235-200 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | 150 | S235 | 9155 | |
| Steel grades of the base plate | P1-8-500-3-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 4075 |
| P1-8-500-3-350-10-S275 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S275 | 3550 | |
| P1-8-500-3-350-10-S355 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S355 | 3204 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 8464 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S275 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S275 | 8011 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S355 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S355 | 7063 | |
| Base sleeve height | P1-8-300-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 300 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 4255 |
| P1-8-500-3-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 4075 | |
| P1-8-750-3-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 750 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 4059 | |
| P1-8-1000-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 1000 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 3798 | |
| P1-8-1500-3-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 1500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 3643 | |
| P2-8-300-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 300 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 9088 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 8464 | |
| P2-8-1000-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 1000 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 8122 | |
| P2-8-1500-3-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 1500 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 7763 | |
| P2-8-2000-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 2000 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 7314 | |
| Base sleeve thickness | P1-8-500-3-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 3 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 4075 |
| P1-8-500-5-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 5 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 4047 | |
| P1-8-500-8-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 8 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 3946 | |
| P1-8-500-12-350-10-S235 | 6 | 76 | 184 | 8 | 500 | 142 | 160 | 12 | 350 | 350 | 10 | - | S235 | 3791 | |
| P2-8-750-3-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 3 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 8464 | |
| P2-8-750-5-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 5 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 8529 | |
| P2-8-750-8-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 8 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 8074 | |
| P2-8-750-12-400-10-S235 | 10 | 76 | 256 | 8 | 750 | 214 | 232 | 12 | 400 | 400 | 10 | - | S235 | 8230 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nawar, M.T.; Kaka, M.E.; El-Zohairy, A.; Elhosseiny, O.; Arafa, I.T. Effect of Supporting Base System on the Flexural Behavior and Toughness of the Lighting GFRP Poles. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12614. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912614
Nawar MT, Kaka ME, El-Zohairy A, Elhosseiny O, Arafa IT. Effect of Supporting Base System on the Flexural Behavior and Toughness of the Lighting GFRP Poles. Sustainability. 2022; 14(19):12614. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912614
Chicago/Turabian StyleNawar, Mahmoud T., Mostafa E. Kaka, Ayman El-Zohairy, Osama Elhosseiny, and Ibrahim T. Arafa. 2022. "Effect of Supporting Base System on the Flexural Behavior and Toughness of the Lighting GFRP Poles" Sustainability 14, no. 19: 12614. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912614
APA StyleNawar, M. T., Kaka, M. E., El-Zohairy, A., Elhosseiny, O., & Arafa, I. T. (2022). Effect of Supporting Base System on the Flexural Behavior and Toughness of the Lighting GFRP Poles. Sustainability, 14(19), 12614. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141912614







