Abstract
In this study, a low-cost granular activated carbon doped with Fe2O3 nanoparticles (Fe–GAC) was prepared via a modified sol-gel technique and utilized for the elimination of lead (Pb(II)) and chromium (Cr(T)) ions from synthetic and actual brackish water. The effect of adsorption parameters on the removal of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions from the water was evaluated in batch adsorption tests. The characterization results validated the distribution of well-defined Fe2O3 nanoparticles onto the GAC surface. GAC loaded with 5 wt.% of Fe2O3 (Fe–GAC 5) exhibited a maximum surface area of 848.2 m2 g−1. The equilibrium data of Cr(T) adsorption were in close agreement with the Langmuir and Sips models with R2 values of 0.95 and 0.96, respectively. However, the R2 values of the equilibrium data for Pb(II) adsorption were greater than 0.91 for all four models, i.e., Langmuir, and Sips, Freundlich and Redlich-Peterson. The maximum Langmuir adsorption capacities of Pb(II) and Cr(T) by Fe–GAC 5 at pH 5.6 and room temperature were 11.9 and 22.1 mg g−1, respectively. Pseudo-second order (R2Pb(II) = 0.99, R2Cr(T) = 0.99) and Elovich kinetic models (R2Pb(II) = 1, R2Cr(T) = 1) were found the most suitable for describing the adsorption kinetics data of Pb(II) and Cr(T) using Fe–GAC 5. The adsorption/desorption studies illustrated that the Fe–GAC is reusable and can be regenerated using 1.0 M HCl. Moreover, the Fe–GAC 5 was found effective to reduce heavy metals loading in actual brackish water to the allowed international standards of drinking water. Accordingly, the Fe–GAC could be a promising material for large-scale applications for the elimination of heavy metals from water.
1. Introduction
Although heavy metals such as lead and chromium are naturally occurring elements found widely on the earth’s crust, their high degree of toxicity makes them a leading cause of significant harm to humans and the ecosystem, even at trace concentrations [1]. Lead, usually found in its divalent form, is highly toxic and is found widely in nature and industrial wastewater. Lead has the tendency to be absorbed through the skin, and respiratory and digestive systems, affecting the body’s physiological systems, and its accumulation over time can cause severe ecological and environmental problems in water reservoirs [2,3]. Wastewater discharged from electroplating, dye and paint, battery manufacturing and glass industries has been found to have elevated levels of Pb(II) ions, exceeding the World Health Organization (WHO) standards (i.e., 0.01 mg L−1). For instance, Otieno et al. reported elevated Pb(II) concentrations up to 0.321 mg L−1 in open drainage wastewater channels located in industrial areas [4]. On the other hand, Cr(T) is also non-biodegradable, persistent, carcinogenic, and toxic, and is mostly generated from the textile, leather tanning, electroplating, cement, mining, dyeing, fertilizer, and photography industries. The buildup of Cr(T) ions over time may lead to many diseases and malfunctions such as cancer in the digestive and respiratory tract, epigastric pain, nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, and hemorrhage. Typically, Cr(T) in aqueous solutions exists in different oxidation states, mainly trivalent chromium (Cr(III)) and hexavalent Chromium (Cr(VI)). Cr(VI) is far more toxic to living organisms than Cr(III) and has been found in ground and surface waters at values exceeding the WHO limit (50 µg L−1) [5]. In addition, Cr(III) species are considered non-toxic at minute concentrations, though when exceeded, they can be toxic [6].
The adsorption process is viewed as a highly promising technique in comparison to other traditional methods due to its simplicity in operation, flexibility in design, ability to regenerate the sorbent material, cost-effectiveness, high efficiency, and easy compatibility with large-scale application in water and other industries [7,8]. Comparatively, other techniques have been found to have some limitations such as high carbon footprint, high cost, low efficiency, demanding special reagents/chemicals, and challenges associated with the discharge of sludge [9,10]. Various adsorbents such as silica gel [11], activated alumina [12], activated carbon [13,14], fly ash [15], sugarcane bagasse [16], natural clay [17], zeolites [18], and nanomaterials [19,20] have been utilized for heavy metal ion elimination from water bodies. Among them, activated carbon (AC) has attracted significant attention in water treatment applications because of its relatively high surface area, stable structure, diverse functional groups, ease of modification, and regeneration ability. Commonly, ACs exist in two forms: granular and powdered activated carbon (GAC and PAC). GACs are known for their adsorption capacities for the removal of a wide variety of contaminants from both aqueous and gaseous systems. Moreover, GACs can also facilitate the removal of taste and odor-causing compounds, disinfection by-products, pharmaceutical products, organic molecules from decaying plants, and other naturally occurring matter. Regardless of the wide use of GACs in purification systems, it has been reported that GACs exhibit low adsorption capacities toward heavy metal ions. Metal oxide nanomaterials such as Fe2O3, on the other hand, are found to have a noteworthy efficiency and high affinity toward the elimination of heavy metals, which is generally ascribed to the surface functional groups onto the Fe2O3 nanoparticles [21,22,23,24]. However, different challenges have been associated with the use of nanomaterials as adsorbents, including the loss of material and agglomeration of Fe particles due to the magnetic field between the atoms, which is not recommended for the adsorption process. As such, doping the Fe2O3 nanoparticles onto the surface of GAC is said to overcome those challenges and contribute to the improvement of raw GAC adsorption capabilities. It has been reported that modifying the GACs with metal oxide nanoparticles improved the surface properties, selectivity, and adsorption uptake of the base material [25].
Among the different biomasses used to produce the GAC, the GACs obtained from coconut shells are found to have a high surface area and are fortunately widely available. However, there is an absence of data in the literature about the influence of Fe2O3 mass loading on the surface properties and morphology of coconut shell obtained GAC. Moreover, so far, the adsorptive elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions from artificial and actual brackish water by Fe2O3 doped coconut GAC is not reported yet. Hence, the current study discloses the influence of Fe2O3 on the surface properties of GACs, and experimentally investigates the application of Fe2O3 doped GAC for heavy metals elimination from water.
The key objectives of the current study are (i) preparing Fe2O3 doped GAC by the sol-gel method at different Fe2O3 loading, (ii) investigating the influence of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on the morphology and surface properties of GAC obtained from coconut shell, (iii) exploring the influence of adsorption parameters on the rejection of Cr(T) and Pb(II) ions from synthetic and actual brackish water, (iv) analyzing the adsorption isotherms, thermodynamics and kinetics of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions elimination by Fe–GAC 5, (v) experimentally investigates the desorption of heavy metals ions as well as the reusability of Fe–GAC 5, and finally, (vi) characterizing the spent Fe–GAC 5 to propose the adsorption mechanisms behind Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions elimination by Fe–GAC 5.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Marketable GAC produced from coconut shells was purchased (GAC, HY-101, China). Chemicals involved in the impregnation process include iron (III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O, ≥99%, Sigma-Aldrich, Gillingham, UK), ammonia solution (NH4OH, 35%, Fisher Scientific Chemicals, Loughborough, UK) and glacial acetic acid (CH3COOH, 99.7%, PanReac AppliChem, Barcelona, Spain). The initial solution pH (pHi) was regulated by adding sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 98%, Sigma-Aldrich, Bangalore, India) and hydrochloric acid (HCl, 37%, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). Potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7, 99.9%, Acros Organics, Geel, Belgium) and Lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2, Honeywell Riedel-de Haën, Seelze, Germany) were procured. Sodium Chloride (NaCl, Supelco®, Sigma-Aldrich, Gladsaxe Municipality, Denmark) was utilized for the determination of the zero point of charge (pHZPC). Deionized water (DI, 0.055 µS cm−1) was utilized for mixture preparations.
2.2. Fe–GAC Synthesis
A modified sol-gel method as defined somewhere else was adopted for the synthesis of Fe–GAC, with minor modifications [26]. In brief, 20 g of GAC was submerged in 900 mL DI. Based on the desired Fe2O3 loading (1, 5, and 20 wt.%), a specific amount of FeCl3·6H2O was dissolved in 100 mL DI. In the iron solution, diluted NH4OH solution was added to ensure that the mole ratio of hydroxides to iron in the solution is 3:1 to generate hydroxyiron (i.e., Fe(OH)3) accordingly. Further, the (Fe(OH)3) mixture was added dropwise to the GAC granules and stirred at 450 rpm for a period of 24 h. The mixture was then subjected to ultra-sonication (Hielscher Ultrasonics, UP400St, 24 kHz, Teltow, Germany) for 30 min, followed by further separation by vacuum filtration. The mixture was then washed with DI before allowing it to dry at 22 °C for 24 h. After that, the GAC mixture was then subjected to glacial acetic acid vapor in a temperature-controlled furnace at 80 °C for 2 h to control the nucleation of Fe nanoparticles. The reaction vessel was then left to dry at 80 °C for half hour to get rid of any remaining acetic acid. Next, the sample was calcined under air at 400 °C for 2 h to acquire Fe–GAC. The preparation procedure comes to an end by sieving the mixture utilizing (100 µm sieve) to eliminate any accumulated portions. The samples are termed as Fe–GACx, where x represents Fe content 1 wt.%. (Fe–GAC 1), 5 wt.% (Fe–GAC 5), and 20 wt.%. (Fe–GAC 20). Figure 1 summarizes the research methodology conducted throughout the current study.
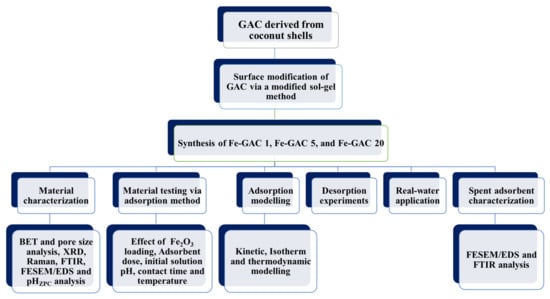
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram for the research methodology used in this study.
2.3. Adsorbate Preparation
Stock mixtures of Pb(II) and Cr(T) (1.0 g L−1) were prepared by weighing and immersing the needed mass of Pb(NO3)2 and K2Cr2O7 in DI. The solutions were further diluted to needed concentrations between 5 and 100 mg L−1. The residual concentration of Pb(II) and Cr(T) was acquired through Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES, Thermo Fisher Scientific TM iCAP TM 7400, Bend, OR, USA).
2.4. Characterization of Fe–GAC
The textural properties of GAC and Fe–GAC samples were acquired by nitrogen adsorption/desorption technique using Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) and Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) method (NOVATECH LX2 analyzer, Anton Paar, Austria) after degassing at 300 °C for 6 h. The crystallographic structures of raw and modified GAC materials were studied using a powder X-ray diffractometer (XRD, D8 Advance, Bruker, Bremen, Germany). The XRD was operated with CuKα radiation at a wavelength of 1.54056 Å and the data were collected within the range of 10 to 70°. The ordered and disordered crystal structures of GAC and Fe–GAC samples were studied using Raman spectroscopy within a spectral range between 200 and 3500 cm−1 (RENISHAW Raman Microscope, London, UK). The surface functional groups on the raw and modified GAC were explored utilizing a Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR, JASCO FTIR-6300, Tokyo, Japan), and the samples were prepared by the KBr pellet method. The morphologies and chemical compositions of raw GAC and Fe–GAC samples were inspected by a Field Emission-Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM, type: Apreo, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with an Energy Dispersive Spectrometer (EDS, Bruker Xflash 6/60, Bremen, Germany) with an accelerating voltage of approximately 15 kV. To produce high-quality images and avoid charging effects, the samples were gold sputtered before scrutiny. The pH drift method was employed to investigate the pHZPC of the Fe–GAC 5.
2.5. Adsorption and Desorption Experiments
Batch mode tests were acquired in 100 mL Erlenmeyer flasks, where 50 mL of Pb(II) and Cr(T) were added into separate flasks with pre-weighed masses of the Fe–GAC. The purpose of the experiments was to scrutinize the effect of Fe2O3 loading, adsorbent dosage, pHi, initial adsorbate concentration ([]), contact time (T), and temperature on the adsorption uptake of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions by GAC and Fe–GAC adsorbents. The sorption efficiency was studied under the following conditions: [] 40 mg L−1 (except for the adsorbent dosage and pH study, where the [] was 20 mg L−1), T 24 h and shaking speed of 200 rpm utilizing Kuhner Lab-Shaker LS-X (Model MAZ10661LAB, Birsfelden, Switzerland). When evaluating the effect of pHi, the solution pH was attuned utilizing 0.1 M HCl or/and 0.1 M NaOH. The impact of GAC dosage and [] was scrutinized between 1 and 5 g L−1 and from 5 to 100 mg L−1, respectively. The impact of experiment temperature was investigated at 25, 35, 45 and 55 ± 0.2 °C. For high temperature experiments (35–55 °C), an incubator shaker (Model ISF-7100, Seoul, Korea) was used for the adsorption experiments. An optimum sorbent dosage of 1.75 g L−1 was used for all adsorption tests for the elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions by Fe–GAC. Kinetic studies were conducted by testing the Pb(II) or Cr(T) concentration at various time slots between 1 and 1440 min. After each adsorption experiment, the samples were filtered using 0.45 µm filters before ICP analysis. Equations (1) and (2) shown below were utilized to calculate the elimination efficiency (%) and adsorption uptake (qe, mg g−1) of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions, respectively.
where Ci and Ce are the original and final concentrations of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions (mg L−1), V is the volume of the adsorbate solution in (L), and Ms is the GAC dose in (g).
Desorption of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions from Fe–GAC was assessed using HCl solution as an elution agent. For these experiments, 1.75 g L−1 of Fe–GAC was added to 50 mL of 40 mg L−1 of Pb(II) and Cr(T), each ion in a separate flask. The adsorption experiment was conducted over 24 h, shaking speed of 200 rpm, solution pH of 5.6 and under room temperature. Next, the resulting Fe–GAC was decanted and oven-dried at 80 °C for 2 h. After that, the dried samples of Fe–GAC were subjected to desorption experiments by the addition of 1.0 M, 0.1 M, 0.01 M, and 0.001 M HCl solutions in separate conical flasks, allowing them to agitate at 200 rpm for 1 h. The desorption effectiveness (%) was then estimated utilizing Equation (3).
2.6. Adsorption Modelling
2.6.1. Adsorption Isotherm
The adsorption equilibrium data for Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions onto Fe–GAC were fitted by four different isotherm models to gain information on the equilibrium state for the adsorption experiments. The isotherm models and their factors are tabulated in Table S1. Theoretically, the Langmuir isotherm model is founded on the assumption that the solid surface consists of a finite number of active binding sites with uniform energy and homogeneous distribution. Additionally, it is estimated that the adsorbed molecules have no direct interaction, resulting in the formation of a saturated layer and thus maximal adsorption. Hence, a monolayer typed adsorption process is assumed. Freundlich isotherm model describes multi-layer adsorption and is interpreted as adsorption to a heterogeneous surface or surfaces with different affinities. On the other hand, Sips and Redlich-Peterson isotherms are three-factor models that define the adsorption process based on incorporating both the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models. The Sips model accounts for the challenges associated with both the Langmuir and Freundlich equation when the concentration is sufficiently high and can fit heterogeneous surfaces, whereas the Redlich-Peterson isotherm model fits a big range of pollutants loadings and can fit homogeneous and heterogeneous surfaces.
Using the above-mentioned isotherm models, the isotherm experimental data were analyzed by minimizing the sum of the square of the errors (SSE) using the Excel solver (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). SSE function is given by the following equation:
where qi(exp) and qi(cal) are the adsorption uptakes in mg g−1 attained from the experimental data and the model values, respectively, and n is the number of the test points. Furthermore, the isotherm data were further confirmed and compared through the determination factor (R2).
2.6.2. Adsorption Kinetics
Adsorption kinetic investigations were considered to understand the adsorption dynamic mechanism of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions onto Fe–GAC. Moreover, the kinetics are very important to inspect the rate-determining step of the removal process. The experimental data were assessed using intra-particle diffusion, pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order and Elovich adsorption kinetic models. The mathematical and linearized forms of the kinetic models utilized to interpret the experimental data are listed in Table S2.
2.6.3. Adsorption Thermodynamics
Thermodynamic factors such as standard entropy , enthalpy and Gibbs free energy changes were evaluated to analyze the adsorption process of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions onto Fe–GAC. The can be determined by Equation (5):
where Kd is the thermodynamic coefficient, determined using the reduced equation stated below:
where Cs is the adsorption uptake of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions onto Fe–GAC and Ce is the concentration of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions at equilibrium. The of the adsorption process gives information on the heat of the adsorption process, whether the process is endothermic or exothermic in nature. The describes the degree of randomness and disorder of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions at the solid-liquid interface. These variables can be determined through the following Van’t Hoff Equation (7):
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterizations of the Prepared Activated Carbon
The textural characteristics of GAC and Fe-doped GACs are illustrated in Figure 2a,b, respectively. According to IUPAC categorization, the N2 adsorption/desorption isotherm of GAC and Fe–GAC samples can be categorized into Type IV isotherm with H4 hysteresis loop. Type IV isotherm indicates the mesoporous structure of GAC, initially starting with monolayer and multilayer adsorption followed by pore condensation (see Figure 2a). The specific surface areas of raw GAC, Fe–GAC 1, Fe–GAC 5, and Fe–GAC 20 were found to be 829.6, 831.9, 848.2, and 750.0 m2 g−1, respectively. The increased specific surface area of Fe–GAC 1 and Fe–GAC 5 is attributed to the contribution of Fe2O3 nanoparticles onto the GAC surface. It was also noticed that at higher loadings of Fe2O3 (Fe–GAC 20), the specific surface area decreased due to possible pore blockage via the exceeded amount of Fe2O3 nanoparticles [27]. The BJH pore size distribution of raw and modified GACs is presented in Figure 2b. The average pore sizes of raw GAC, Fe–GAC 1, Fe–GAC 5, and Fe–GAC 20 were found to be 2.31 nm, 2.40 nm, 2.37 nm, and 2.36 nm, respectively, confirming the presence of abundant mesoporous.
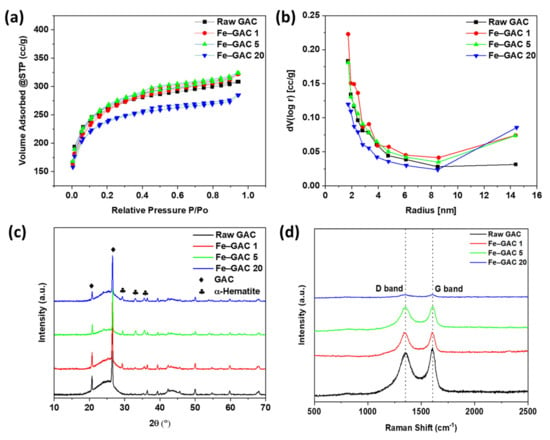
Figure 2.
(a) N2 adsorption/desorption isotherm, (b) BJH pore size distribution, (c) X-ray diffraction spectra, and (d) Raman spectra of raw GAC and Fe doped GACs.
The XRD patterns (Figure 2c) of raw GAC and Fe–GAC samples demonstrated crystalline peaks for GAC and Fe2O3 nanoparticles. The peaks located at 21.44° (002) and 26.74° (002) in GAC correspond to the graphitic carbon structures, typical for all carbon materials. For Fe–GAC samples, new characteristic diffraction peaks originated at 2θ of 33.1° (104), 35.54° (311), and 54.00° (422), respectively. These peak positions validated the formation of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on the surface of GAC.
Raman spectroscopy was used to investigate the ordered and disordered crystal structures of raw GAC and Fe–GAC samples, and the outcomes are clarified in Figure 2d. All the samples possessed two characteristic peaks of carbon materials denoted as D-band at 1337.20 cm−1 and G-band at 1598.71 cm−1, respectively. The G-band is linked with the stretching vibrations of the sp2-bonded pairs, suggesting full graphitization of the GAC [28]. On the other hand, the D-band is related to the sp3 defect sites, which indicates the existence of disorder in the structure of the carbon material [29]. According to Figure 2d, the intensities of D- and G-bands were seen to decrease with an increase in the Fe2O3 loadings, suggesting the successful doping of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on the GAC surface.
The FTIR spectra of GAC and Fe–GAC materials were inspected in the range of 4000–400 cm−1 and the outcomes are displayed in Figure 3. The peak at 3475 cm−1 signifies the presence of O-H stretching vibration corresponding to a hydroxyl functional group. The intensity of the -OH peak was seen to significantly improve with the Fe2O3 loadings, suggesting an increased number of O-H functional groups after the modification of GAC. The characteristic absorption peak at 2849 cm−1 can be assigned to an O-H stretching vibration. Fe–GAC materials exhibited a small peak at 1647 cm−1 that corresponds to the presence of either C=C or C=O stretching vibrations. A significantly broad peak at 1424 cm−1 was observed in Fe–GAC 20 and can be given to O-H bending vibration from either carboxylic acid or alcohol. Furthermore, the broad band at 1080 cm−1 can be given to C-H and C=C bending vibrations. The band at 665 cm−1 proves the successful doping of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on the GAC surface due to the existence of the FeOOH functional group. The presence of similar absorption peaks in raw GAC and Fe–GAC materials suggests that the GAC preserved its structure after modification by creating more functional groups on the surface. Furthermore, similar trends were observed in the literature suggesting the destruction of organic structures and the addition of more acidic groups on the GAC surface after modification [30]. Therefore, the presence of more acidic groups enhances the number of active binding sites, which in turn might offer more adsorption sites for the binding of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions.
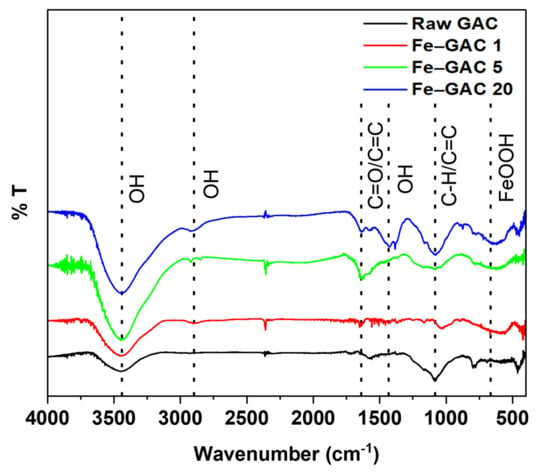
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of raw and Fe doped GACs.
The morphological properties and chemical composition of raw GAC and Fe–GAC samples were studied using FE-SEM and EDS, respectively, and the outcomes are demonstrated in Figure 4a–d. Raw GAC (Figure 4a) showed a porous morphology with a wide range of mesopores and macropores. Fe–GAC materials in Figure 4b–d clearly showed a well-defined distribution of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on the surface of the GAC with an average particle diameter ranging between 100–400 nm. EDS results displayed in Table 1 illustrate that raw GAC was primarily composed of trace amounts of silicon (Si), aluminum (Al), and iron (Fe) as impurities. It was noticed that after the loading of Fe2O3, the average mass of C decreased with increasing Fe2O3 loading, whereas corresponding masses of Fe increased to 1.84, 6.04, and 21.90 for Fe–GAC 1, Fe–GAC 5, and Fe–GAC 20, respectively.
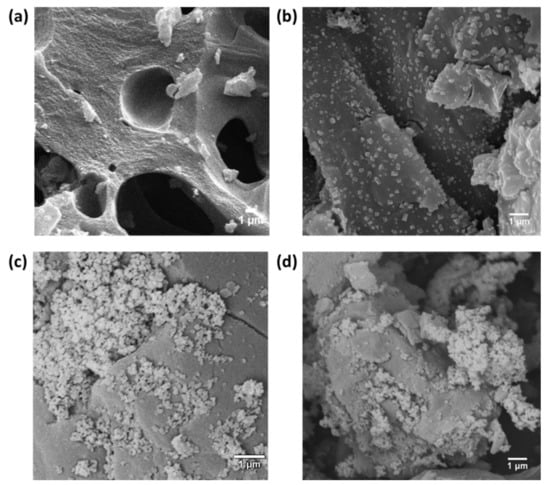

Figure 4.
FE-SEM micrographs of (a) Raw GAC, (b) Fe–GAC 1, (c) Fe–GAC 5, and (d) Fe–GAC 20.

Table 1.
EDS elemental atomic composition of raw GAC and Fe doped GACs.
3.2. Effect of Fe2O3 Loading on the Elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) Ions
Screening tests were performed to illustrate the ideal Fe2O3 loading for the adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions from water. The adsorption results presented in Figure 5 demonstrated an increase in the adsorption uptake of Pb(II) and Cr(T) by raising the Fe2O3 loading from 1 to 5 wt.%. A further increase in the Fe2O3 loading to 20 wt.% led to a drastic decrease in the adsorption uptake from 9.1 mg g−1 to 3.1 mg g−1 and 9.9 mg g−1 to 7.8 mg g−1 towards Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions, respectively, which is lower than that of raw GAC (i.e., 5.9 mg g−1 for Pb(II) and 8.8 mg g−1 for Cr(T). The reduction in the adsorption uptake of Fe–GAC 20 can be explained by the possible agglomeration of the Fe2O3 nanoparticles on the surface of the GAC, as seen in the SEM micrograph in Figure 4d. Similar outcomes were gained by Monika Jain et al., who reported that more surface-free binding sites are covered with increased metal ion concentration, causing a decline in the adsorption uptake [31]. The adsorption outcomes illustrated that Fe–GAC 5 (5 wt.%) showed good efficiency for both Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions as compared to raw GAC, Fe–GAC 1, and Fe–GAC 20. The adsorption uptake of Fe–GAC was highly dependent on the specific surface area and the existence of mesoporous structure. The higher adsorption uptake of Fe–GAC 5 accounted for the highest textural characteristics, which provided more adsorption sites for binding Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions. It is worth mentioning that doping Fe2O3 nanoparticles did improve the adsorption uptake of GAC, but to a certain limit, above which it exhibited a negative effect. Therefore, Fe–GAC 5 was picked up as the optimum modified GAC for subsequent studies.
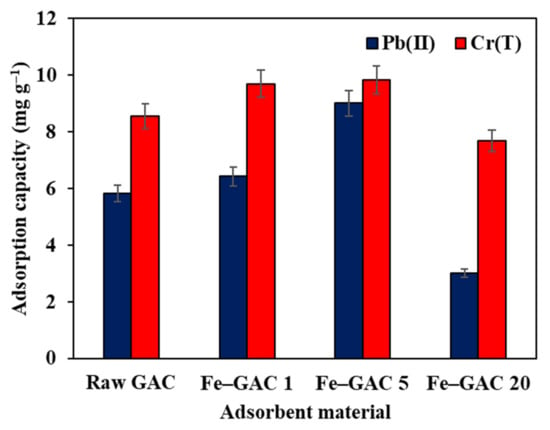
Figure 5.
Effect of Fe2O3 loadings on the adsorption uptake of Pb(II) and Cr(T) in aqueous systems ([] 40 mg L−1, adsorbent dose 1.75 g L−1, T 24 h, temperature 22 °C, pHi 5.6).
3.3. Effect of Fe–GAC 5 Dose
The impact of Fe–GAC 5 amount on the elimination efficiency and adsorption uptake of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions was investigated by fluctuating the Fe–GAC 5 dosage from 1 to 5 g L−1 and the outcomes are demonstrated in Figure 6a,b. The results reveal an increase in the elimination efficiency with raising Fe–GAC 5 dosage. For example, the elimination efficiency was found to increase from 53.3% to 90.8% for Pb(II) and from 74.8% to 98.2% for Cr(T) with increasing Fe–GAC dosage from 1 to 5 g L−1. However, further increasing the Fe–GAC 5 dosage from 3 to 5 g L−1 was found to have an insignificant effect on the elimination efficiency. The increase in the elimination efficiency with Fe–GAC 5 dosage is attributed to the accessibility of more Fe–GAC 5 surface area and the availability of active adsorption sites alongside fixed concentrations of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions in the water. On the other hand, the adsorption uptake was found to decrease with the Fe–GAC 5 dosage, most probably due to the opposite relationship between the adsorption uptake and the Fe–GAC 5 mass. Typically, at higher doses, a larger Fe–GAC 5 surface area becomes exposed for the adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions, which results in more competition for the ions to fill the active sites. This behavior causes many active sites on the Fe–GAC 5 surface to remain unsaturated, which therefore leads to a decreased adsorption uptake [32]. Similar trends were stated in the literature for the remediation of Cr(T) and Pb(II) ions using paper mill sludge and date pit ACs, respectively [33,34]. In this study, an Fe–GAC 5 dosage of 1.75 g L−1 is recommended for the rejection of both Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions from water and has been used for the remaining experiments.
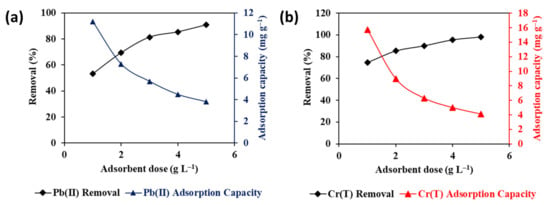
Figure 6.
Impact of Fe–GAC 5 dosage on the elimination efficiency and adsorption uptake of (a) Pb(II) and (b) Cr(T) ions from water ([] 20 mg L−1, T 24 h, temperature 22 °C, pHi 5.6).
3.4. Effect of pHi
The pHi of the solution plays a vibrant role in the rejection of pollutants due to the fact that the pH does not only change with the nature of the pollutant species but also affects the adsorbents’ surface charge in the liquid phase. At first, the pHZPC of raw GAC and Fe–GAC 5 were studied using the pH drift method and the results are displayed in Figure S1. The pHZPC is the pH point where the charge on the adsorbent surface is neutral (zero net charge). It was noticed that the surface of raw GAC was almost neutral, holding a pHZPC value of 7.2 while the pHZPC of Fe–GAC 5 was found to be 5.6. The influence of pHi on the adsorption uptake of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions from water using Fe–GAC 5 is displayed in Figure 7. The outcomes clearly show an increase in Pb(II) adsorption uptake by raising the pHi from 2.1 to 6.1. After that, the adsorption uptake was found to decrease at pH 8.2. At pH 2.1, the Fe–GAC 5 and Pb(II) ions are both holding positive charges, resulting in low adsorption uptake due to the electrostatic repulsions between the Fe–GAC 5 and the adsorbate. Raising the pHi from 2.1 to 5.6 undoubtedly decreased the magnitude of electrostatic repulsions, which in turn resulted in an improved adsorption uptake from 3.9 to 5.1 mg g−1. The maximum adsorption uptake of 5.6 mg g−1 was recorded at pH 6.1. At this pH, the Fe–GAC 5 is negatively charged since the solution pH exceeds the pHZPC (5.6) and Pb(II) ions have a positive charge, hence the electrostatic repulsions no longer exist, and the adsorption process is dominated by the electrostatic interactions. However, at pH 8.2, a high concentration of hydroxyl ions (OH−) competes with Pb(II) ions for the adsorption sites causing Pb(II) ions to precipitate, decreasing the adsorption uptake to 4.8 mg g−1 [35,36].
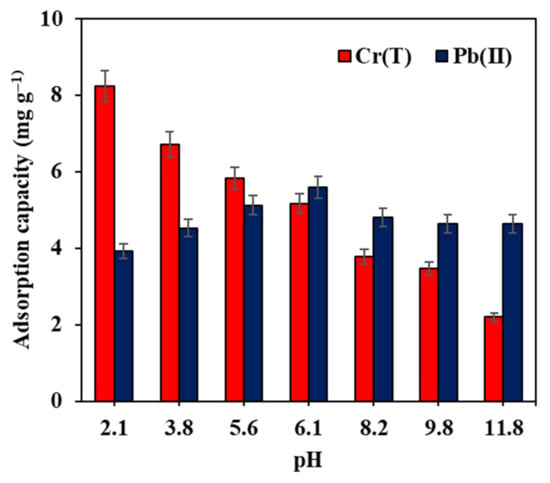
Figure 7.
Effect of pHi on the adsorption uptake of Pb(II) and Cr(T) by Fe–GAC 5, ([] 20 mg L−1, Fe–GAC 5 dose 1.75 g L−1, T 24 h, temperature 22 °C).
For Cr(T) removal (see Figure 7), a decrease in the adsorption uptake with increasing pH values was observed, indicating more adsorption uptake at low pH values. It is worth mentioning that Cr(T) ions generated from potassium dichromate salt exist in different forms (CrO42−, Cr2O72− and HCrO4−) by changing the pHi from 2.0 to 12.0, implying negatively charged Cr(T) ions within the pH range 2 to 12. The higher adsorption uptake at pH 2.1 was ascribed to the electrostatic interactions among the negatively charged Cr(T) ions and the positively charged Fe–GAC 5. The higher number of positive charges on the Fe–GAC 5 at pH 2.1 is generally accredited to the protonation of the functional groups on the Fe–GAC 5 surface owing to the high concentration of H+ ions. Moreover, the reduction of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) is more likely to take place at low pH such as pH 2.1, resulting in an improved adsorption uptake. Similar trends were observed by Yang et al. and Ihsanullah et al. [37,38]. It was also reported that Equation (8) is feasible to explain the higher adsorption uptake under acidic conditions.
Raising the pHi from 2.1 to 5.6 was found to decrease the adsorption uptake from 8.24 to 5.8 mg g−1. This is credited to the decline of the extent of electrostatic interactions between Cr(T) ions and Fe–GAC 5 surface. Further increasing the solution pH, higher than the pHZPC (>5.6) resulted in a negatively charged Fe–GAC 5. Moreover, the Cr(T) ions generated from potassium dichromate salt are available in water as CrO42− and Cr2O72−. As such, the adsorption uptake was found to decrease to 3.8 mg g−1 at pH 8.2 owing to the electrostatic repulsions. Further increase in the solution pH from 9.8 to 11.8 was found to decrease the adsorption uptake from 3.47 to 2.2 mg g−1. Typically, increasing the solution alkalinity would increase the magnitude of the negative charges on the Fe–GAC 5 surface, resulting in more electrostatic repulsions with the negatively charged Cr(T) ions and hence decreasing the adsorption capacity. Moreover, a high concentration of OH− ions would compete with Cr(T) ions on the accessible adsorption sites subsequent to a further decrease in the adsorption uptake.
3.5. Effect of Contact Time and Adsorption Kinetics
The impact of T on the adsorption uptake of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions onto the Fe–GAC 5 is displayed in Figure 8. As depicted, rapid adsorption had taken place in the first 1 h, then a slower rate of adsorption was observed until achieving equilibrium after 24 h. At the initial adsorption stages, the existence of high adsorbate concentration in the solution led to the diffusion of the ionic species from the bulk to the surface of the Fe–GAC 5, explaining the rapid increase in the adsorption uptake in the first 1 h. With increasing T, the surface adsorption binding site on the Fe–GAC 5 gets occupied with time, causing less improvement in the adsorption uptake as no more sites are available for binding. However, the adsorption uptake for Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions increased from 12.2 to 15.6 mg g−1 and from 9.4 to 12.7 mg g−1 by rising the T from 60 min to 1260 min, respectively. This slow improvement in the adsorption uptake is attributed to the diffusion of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions within the internal micropores and mesoporous of the Fe–GAC 5. Once equilibrium had been established, the adsorption sites were less likely to be occupied and the adsorption uptake gradually balanced after 24 h of adsorption.
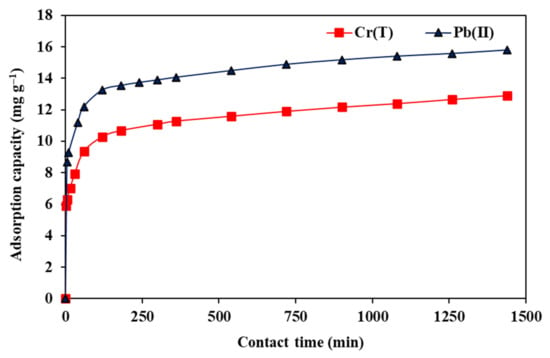
Figure 8.
Influence of T on the adsorption uptake of Pb(II) and Cr(T) by Fe–GAC 5 from water, ([] 40 mg L−1, Fe–GAC 5 dose 1.75 g L−1, room temperature 22 °C, pHi 5.6).
Data generated from the kinetic adsorption studies for Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions were fitted to several kinetic models. Table 2 shows all calculated kinetic model factors and correlation factor (R2) for the tested models. The pseudo-first order model (see Figure S2a) for Pb(II) and Cr(T) removal exhibited low values of R2 (<0.97). Moreover, the qe value obtained from the model did not match or fit the experimental qe value, implying that the pseudo-first order model does not define the elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions by Fe–GAC 5. The pseudo-second order model (see Figure S2b for the trend line fits) demonstrated an R2 value > 0.99 for Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions. Additionally, the calculated qe value from the model was seen to approach the experimental qe for Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions onto the Fe–GAC 5. The pseudo-second order rate constant K2 was found to be higher for Pb(II) adsorption than Cr(T), suggesting that Pb(II) was adsorbed at a faster rate by Fe–GAC 5 than Cr(T) ions. These outcomes validated that both Pb(II) and Cr(T) kinetics obeyed the pseudo-second order model.

Table 2.
Statistical parameters and adsorption kinetic models factors of Pb(II) and Cr(T) onto Fe–GAC 5.
The intra-particle diffusion model (see Figure S2c) was applied to inspect the mechanism of the adsorption process. Typically, the intra-particle diffusion controls the adsorption process if the trend line between qt and t1/2 forms a straight line and passes through the origin. The R2 value generated from the intra-particle diffusion model fit was found to be 0.77 and 0.85 for Pb(II) and Cr(T), respectively, suggesting that the adsorption of both ionic species onto the Fe–GAC 5 was controlled by different steps (i.e., intra-particle diffusion and surface film diffusion). The adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions onto the Fe–GAC 5 initially took part at the external surface of the Fe–GAC 5, which then diffused into the inner porous structure until equilibrium was reached.
The Elovich kinetic model (see Figure S2d) was found to produce an R2 value = 1, indicating the compliance between the kinetic data and the Elovich model. Moreover, the Elovich model stands for the heterogeneous surfaces and chemisorption process. Accordingly, the kinetic results generated from this work suggest a chemisorption process for the elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions onto the heterogeneous adsorption sites on the Fe–GAC 5 surface. However, the adsorption mechanism will be further investigated in the following sections.
3.6. Adsorption Isotherm
The isotherm curves optimized by the Excel solver are displayed in Figure 9a,b. Table 3 displays the model parameters and statistical evaluations (SSE and R2) of each fitted model. According to Table 3, Sips (R2 = 0.96; SSE = 7.10) and Langmuir (R2 = 0.95; SSE = 8.67) models best fitted the equilibrium data for Cr(T) removal, proposing a monolayer coverage of the Cr(T) ions onto the surface of the Fe–GAC 5 with some likely heterogeneity in the adsorption sites. For Pb(II) removal, all isotherm models were in agreement with the equilibrium data representing R2 values greater than 0.99 and SSE values less than or equal to 1.5, suggesting different removal mechanisms in the adsorption process. Accordingly, the agreement of different models for the elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions suggests a combination of chemical and physical adsorption processes on the Fe–GAC 5 surface. The Freundlich coefficient nF values for both Pb(II) and Cr(T) ion adsorption were found to be greater than 1, signifying favorable removal of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions by Fe–GAC 5. Typically, the value 1/ns in the sips model gives information on the homogeneity (1/ns ≈ 1) and heterogeneity (1/ns > 1) of the active adsorbent sites. The values of 1/ns obtained from this study indicated the heterogeneous and homogeneous adsorption sites of the Fe–GAC 5 towards Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions. The maximum adsorption capacities obtained from the Langmuir equation were found to be 11.9 and 22.1 mg g−1 for Pb(II) and Cr(T) by Fe–GAC 5, respectively.
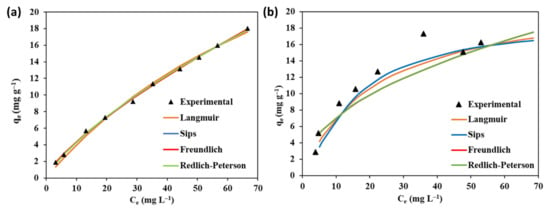
Figure 9.
Adsorption isotherms for (a) Pb(II) and (b) Cr(T) elimination by Fe–GAC 5, (Fe–GAC 5 dose 1.75 g L−1, T 24 h, room temperature 22 °C, pH 5.6 and varying [] from 5–100 mg L−1).

Table 3.
Isotherm modeling parameters and their related statistical factors for Pb(II) and Cr(T) elimination by Fe–GAC 5.
Table 4 displays a comparison between our Fe–GAC 5 and other carbon-based materials in terms of preparation technique, experimental conditions, and corresponding adsorption capacities for the rejection of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions from water. It can be seen that the Fe–GAC 5 illustrated one of the best-stated adsorption uptakes for Pb(II) ions compared to other carbonaceous materials. Moreover, the adsorption uptake of Cr(T) onto the Fe–GAC 5 is also comparable to the adsorption uptakes onto other adsorbents.

Table 4.
Comparison of adsorbent preparation, adsorption uptakes, and investigational conditions for Pb(II) and Cr(T) elimination with related literature.
3.7. Effect of Temperature
The elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions by Fe–GAC 5 was evaluated by varying the temperature between 25 and 55 °C. As revealed in Figure 10, it was noticed that the adsorption uptake of Cr(T) ions gradually improved with rising temperatures, whereas a decline in the adsorption uptake was noticed for Pb(II) removal. The increase in the adsorption uptake with temperature suggested an endothermic adsorption process for the elimination of Cr(T) by Fe–GAC 5. By increasing the temperature, the mobility of the ions is said to increase due to the interaction among the Cr(T) ions and Fe2O3 nanoparticles on the GAC surface, allowing the Cr(T) particles to diffuse into the pores of the Fe–GAC 5, resulting in an improved adsorption uptake [46]. On the other hand, the adsorption uptake of Fe–GAC 5 towards Pb(II) ions was found to drop from 5.6 to 5.0 mg g−1 with raising the temperature from 25 to 55 °C. The decrease in the adsorption uptake and the removal efficiency suggests the dominance of the exothermic and chemisorption process [47]. At higher temperatures, the migration of Pb(II) ions from the solid phase to the water phase is promoted, resulting in a decrease in the adsorption uptake. Moreover, it was also reported that the electrostatic interactions among the Pb(II) ions and the Fe–GAC 5 surfaces are weakened with temperature, which in turn decreases the adsorption uptake [48].
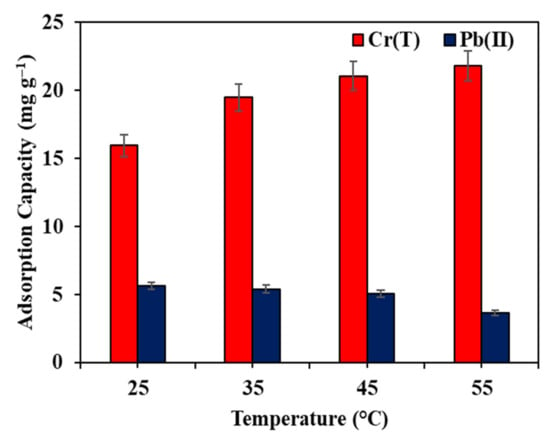
Figure 10.
Influence of experiment temperature on the elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) by Fe–GAC 5 from water, ([] 40 mg L−1, Fe–GAC 5 dose 1.75 g L−1, T 24 h, pH 5.6).
3.8. Thermodynamic Modeling
Table 5 reveals the thermodynamic factors for the elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) by Fe–GAC 5. was estimated using Equation (5), while and were determined from the slope and the intercept of the plot 1/T versus Ln Kd. As depicted in Table 5, all values were found to be positive and increasing with temperature, suggesting a non-spontaneous adsorption process for the rejection of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions by Fe–GAC 5 [49]. The exothermic adsorption process of Pb(II) ions was confirmed by the negative value of , while an endothermic process was observed in the case of Cr(T) adsorption. The negative value of for Pb(II) adsorption indicates a reduction in the randomness at the solid/liquid interface while the positive value of for Cr(T) adsorption suggests an increase in the disorder at the solid–liquid interface between Cr(T) atoms and the Fe–GAC 5 surface.

Table 5.
Thermodynamic factors of Pb(II) and Cr(T) adsorption by Fe–GAC 5.
3.9. Desorption Experiments
The regeneration of the Fe–GAC 5 was investigated by studying the influence of HCl concentration on the desorption efficacy of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions. Figure 11 illustrates the desorption effectiveness of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions with respect to the concentration of HCl solution. The outcomes disclosed an increase in the desorption efficiency of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions by increasing the concentration of HCl solution. For instance, the desorption efficiency increased from 46.3% to 96.3% for Pb(II) and from 0.0% to 55.1% for Cr(T) with increasing HCl concentration from 0.001 M to 1.0 M. The effectiveness of HCl in regenerating the spent Fe–GAC 5 is attributed to the substitution of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions by H+ ions on the Fe–GAC 5 surface [34]. Regardless of the concentration of HCl used for desorption, the desorption efficiency of Pb(II) ions was found to be more than Cr(T). This might be explained by the strong chemical bond formation between Cr(T) ions and Fe–GAC 5 surface, which in turn resulted in a lower desorption efficiency of Cr(T) compared to Pb(II) ions. However, more than 50% of the adsorbed Cr(T) ions and 95% of Pb(II) ions can still be desorbed/removed using 1.0 M HCl, suggesting the reusability of Fe–GAC 5 for Cr(T) ions. It is worth mentioning that though most of the studies are reporting the reusability of the sorbent material by investigating the elimination efficiency and adsorption uptake with adsorption/desorption cycles, the desorption efficiency is limited in the literature.
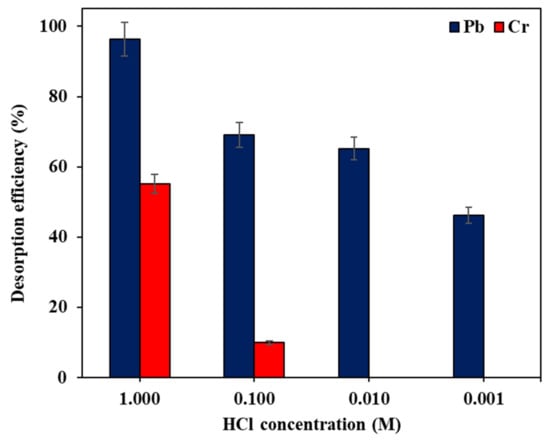
Figure 11.
The desorption effectiveness of Pb(II) and Cr(T) from Fe–GAC 5 at different molar concentrations of HCl, ([] 40 mg L−1, Fe–GAC 5 dose 1.75 g L−1, adsorption 24 h and desorption T 1 h, room temperature 22 °C, pH 5.6).
3.10. Removal of Pb(II) and Cr(T) from Real Brackish Water
Adsorptive rejection of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions was performed on real brackish water, collected from underground water well in Ras Al Khaimah, United Arab Emirates. The in-house characterization of the obtained water was, conductivity 6.6 μS cm−1, total organic carbon 1.09 mg L−1, chemical oxygen demand 13.8 mg L−1, and total dissolved solids 5.3 g L−1. In two different beakers, 1 L of this water was spiked with 1 mg L−1 Pb(II) and another liter was injected with 300 µg L−1 Cr(T). These concentrations of Cr(T) ions were selected based on the in-house analysis of different wells in Ras Al Khaimah areas while Pb(II) ions were not detected; hence, it was spiked with 1 mg L−1. The influence of Fe–GAC 5 dosage on the elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions from the actual well water is demonstrated in Figure 12. The outcomes illustrated that the elimination efficiency drastically improved with increasing the Fe–GAC 5 dose. The Fe–GAC 5 doses of 9 and 3 g L−1 were sufficient to decrease the concentrations of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions to 0.0 and 0.027 mg L−1, respectively. Fortunately, these results were in agreement with WHO standards of Pb(II) and Cr(T) in drinking water [50]. In comparison to the elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) from synthetic water, the Fe–GAC 5 dose of 1.75 g L−1 was able to achieve a removal between 60–80% for [] of 40 mg L−1. The increased Fe–GAC 5 dose required to remove pollutants in real water was due to the presence of other organic pollutants competing for the Fe–GAC 5s’ active sites, leading to higher chances of pore blockage.
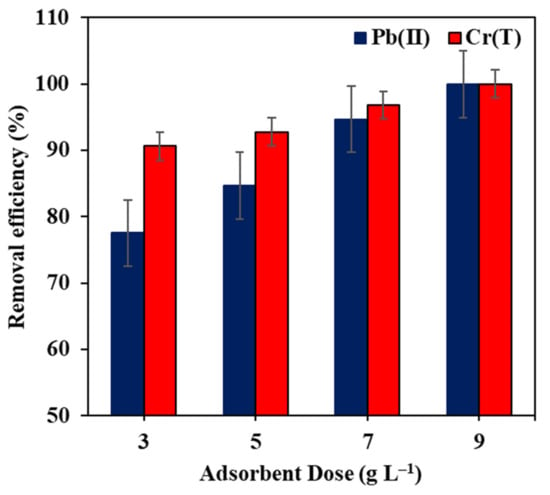
Figure 12.
Effect of Fe–GAC 5 dose on the elimination of Pb(II) and Cr(T) from actual brackish water, ([] Pb(II) 1 mg L−1 and Cr(T) 300 µg L−1, T 24 h, room temperature 22 °C, pH 5.6).
3.11. Spent Adsorbent Characterization and Removal Mechanism
Figure 13a,b shows the FE-SEM images of Fe–GAC 5 after the adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions, respectively. The EDS analysis of Fe–GAC 5 after adsorption indicated the presence of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions on the Fe–GAC surface, suggesting the successful removal of the ionic species by Fe–GAC 5 (Table 6). After the adsorption of Cr(T), the increased oxygen to carbon (O/C) ratio on the Fe–GAC 5 indicated the oxidation of the carbon material with a likely reduction of Cr(IV) ions to Cr(III).
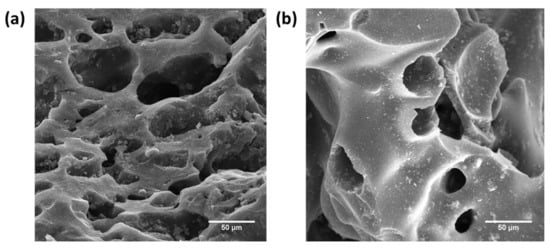
Figure 13.
FE-SEM images of (a) Pb(II)-loaded Fe–GAC 5 and (b) Cr(T)-loaded Fe–GAC 5.

Table 6.
EDS elemental content (%) on the surface of Fe–GAC 5 samples after Pb(II) and Cr(T) adsorption.
Figure 14 presents the FTIR spectra of Fe–GAC 5 over the adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions. A minor move in the position of the O-H group from 3475 cm−1 to 3433 cm−1 and 3450 cm−1 and mere disappearance of the peak stretch was observed upon the adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions by Fe–GAC 5, respectively. This is due to the complexation of the -OH group with Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions [51]. Similarly, the peak at 1647 cm−1 was also found to decrease to 1577 cm−1 and 1588 cm−1 after the adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions, respectively. This can be elucidated based on the complexation of the C=O surface groups on the Fe–GAC 5 surface with Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions. In addition, peaks at 2849 and 1080 cm−1 showed no noteworthy shift after Pb(II) ad Cr(T) adsorption, which suggests that C-H and C=C groups on the Fe–GAC 5 surface did not participate in any complexation with the ionic species. It is worth mentioning that the red shifts of the bands with decreasing intensities are attributed to the successful adhesion of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions on the Fe–GAC 5 surface [52]. Moreover, the appearance of new peaks at 470 and 793 cm−1 can be attributed to the stretching vibration of the M-O (Pb-O and Cr-O) and M-O-M (Fe-O-Pb and Fe-O-Cr) bond, implying that the adsorption and interaction of the metal ions to the Fe–GAC 5 surface was achieved. Similar observations were reported in previous studies [30,31,50,51].
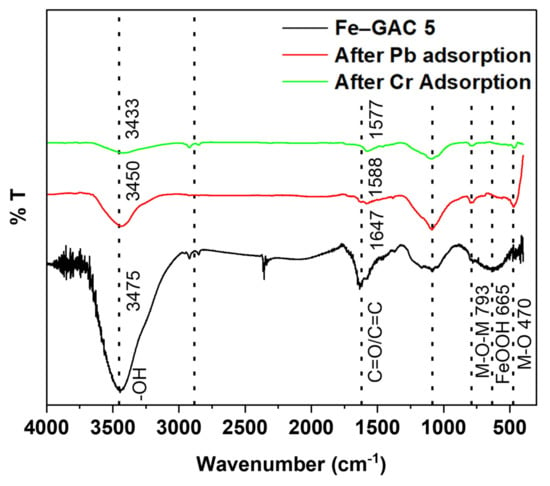
Figure 14.
FTIR spectra of Fe–GAC 5, Pb(II) loaded Fe–GAC 5 and Cr(T) loaded Fe–GAC 5.
According to the adsorption results, different adsorption mechanisms were found to control the deletion process of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions by the Fe–GAC composite. The isotherm modeling indicated that both chemical and physical adsorption processes occurred. Moreover, the kinetic data demonstrated that both surface film diffusion and intra-particle diffusion processes participated in the adsorption process. As revealed from the pH study, the elimination of both Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions was driven by electrostatic interactions. It was also suggested that possible reduction of Cr(IV) to Cr(III) took place at very low pH (under acidic conditions). Furthermore, desorption experiments suggested that Cr(T) removal involved chemisorption due to the lower desorption efficiency of HCl solutions caused by the strong chemical bond formation between the Cr(T) ions and Fe–GAC material. Additionally, the FTIR analysis after Pb(II) and Cr(T) adsorption suggested a surface complexation of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions onto the surface of the Fe–GAC 5.
4. Conclusions
In this study, GAC obtained from coconut shells was successfully doped with Fe2O3 nanoparticles via an altered sol-gel method for the rejection of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions from water. The textural, physical, and chemical features of raw and Fe2O3 doped GAC were thoroughly explored using several techniques including BET, XRD, Raman, FTIR, FESEM, and EDS. The BET analysis demonstrated that 5 wt.% of Fe2O3 doped GAC (Fe–GAC 5) possessed the highest surface area and pore volume. Additionally, the appearance of new characteristic diffraction peaks at 2θ of 33.1°, 35.5°, and 54.0° and the existence of the FeOOH functional group at wavelength 665 cm−1 affirmed the formation of Fe2O3 nanoparticles on the GAC surface. Fe–GAC 5 was found to exhibit the highest elimination efficiency and adsorption uptake towards Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions at an optimal dose of 1.75 g L−1 at 22 °C. The adsorption of Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions from water was extremely pH-dependent, where the highest removals were observed at pH 6.0 and 2.2 for Pb(II) and Cr(T), respectively. Furthermore, the maximum Langmuir adsorption capacities of Fe–GAC 5 were calculated to be 11.9 and 22.1 mg g−1, for Pb(II) and Cr(T), respectively. Adsorption isotherm data were in excellent agreement with several isotherm models, which indicated various adsorption mechanisms for Pb(II) and Cr(T) deletion by Fe–GAC 5. According to the calculated thermodynamic parameters, the elimination of Pb(II) by Fe–GAC 5 was seen to be exothermic in nature, while it was endothermic for Cr(T) rejection. Desorption results demonstrated that 1.0 M HCl effluent was suitable for desorbing Pb(II) (96%) and Cr(T) (55%) ions. Moreover, the Fe–GAC 5 was able to reduce the Pb(II) and Cr(T) content from actual brackish water to WHO limits. It was also found that the remediation of Pb(II) and Cr(T) by Fe–GAC 5 was controlled by electrostatic attractions and complexation chemisorption processes. Accordingly, the Fe–GAC 5 could be a promising adsorbent for the rejection of heavy metals such as Pb(II) and Cr(T) ions from actual water and wastewater streams.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su141710877/s1, Table S1. List of the isotherm models used for surfactants equilibrium data interpretation; Table S2. Kinetic models used for experimental data interpretation; Figure S1. Determination of pHpzc of raw GAC and Fe–GAC 5; Figure S2. (a) Pseudo-first order, (b) Pseudo-second order, (c) Intra-particle diffusion and (d) Elovich kinetic models for Pb(II) and Cr(T) adsorption onto Fe–GAC 5 adsorbent in an aqueous system. References [52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59] are cited in Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
L.J., writing, original draft, conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis; I.I., writing, conceptualization, review and editing; I.W.A., writing, conceptualization, data curation, review and editing, formal analysis; S.N.B., writing, conceptualization, data curation, review and editing, formal analysis; A.A., investigation, data curation; A.K.A.K., investigation, data curation; H.A., supervision, conceptualization; A.S., supervision, conceptualization; M.A.A., visualization, methodology, supervision, conceptualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are very appreciative of the Research Institute of Sciences & Engineering (RISE), the Center for Advanced Materials Research (CAMR) Laboratory, the environmental laboratory in the civil and environmental engineering department, and the environmental analytical laboratory at the University of Sharjah.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ihsanullah; Abbas, A.; Al-Amer, A.M.; Laoui, T.; Al-Marri, M.J.; Nasser, M.S.; Khraisheh, M.; Atieh, M.A. Heavy Metal Removal from Aqueous Solution by Advanced Carbon Nanotubes: Critical Review of Adsorption Applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 157, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Cabral-Pinto, M.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Shabnam, A.A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Gupta, D.K.; Malyan, S.K.; Kumar, S.S.; et al. Lead Toxicity: Health Hazards, Influence on Food Chain, and Sustainable Remediation Approaches. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almanassra, I.W.; Khan, M.I.; Atieh, M.A.; Shanableh, A. Adsorption of Lead Ions from an Aqueous Solution onto NaOH-Modified Rice Husk. Desalin. Water Treat. 2022, 254, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otieno, J.; Kowal, P.; Mąkinia, J. Monitoring Lead Concentration in the Surrounding Environmental Components of a Lead Battery Company: Plants, Air and Effluents—Case Study, Kenya. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, H.; Eskikaya, O.; Bilici, Z.; Dizge, N.; Balakrishnan, D. Comparison of Cr(VI) Adsorption and Photocatalytic Reduction Efficiency Using Leonardite Powder. Chemosphere 2022, 300, 134492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, N.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Rezania, S.; Radwan, N.; Alam, J. Chromium Contamination and Effect on Environmental Health and Its Remediation: A Sustainable Approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.K.A.; Dweiri, F.; Almanassra, I.W.; Chatla, A.; Atieh, M.A. Mg-Al Layered Double Hydroxide Doped Activated Carbon Composites for Phosphate Removal from Synthetic Water: Adsorption and Thermodynamics Studies. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isik, Z.; Saleh, M.; M’barek, I.; Yabalak, E.; Dizge, N.; Deepanraj, B. Investigation of the Adsorption Performance of Cationic and Anionic Dyes Using Hydrochared Waste Human Hair. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.; Heo, J.; Han, J.; Her, N.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, J.; Ryu, J.; Yoon, Y. Hexavalent Chromium Removal by Various Adsorbents: Powdered Activated Carbon, Chitosan, and Single/Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 106, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiopoulou, E.; Gikas, P. Effects of Chromium on Activated Sludge and on the Performance of Wastewater Treatment Plants: A Review. Water Res. 2012, 46, 549–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Basu, H.; Bassan, M.K.T.; Singhal, R.K. Thiol Functionalised Silica Microsphere Loaded Polymeric Hydrogel: Development of a Novel Hybrid Sorbent for Removal of Lead and Cadmium. Chemosphere 2022, 286 Pt 1, 131659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadollahzadeh, H.; Zabihi, M. Competitive Adsorption of Methylene Blue and Pb (II) Ions on the Nano-Magnetic Activated Carbon and Alumina. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 248, 122893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waly, S.M.; El-Wakil, A.M.; El-Maaty, W.M.A.; Awad, F.S. Efficient Removal of Pb(II) and Hg(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Amine and Thiol Modified Activated Carbon. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2021, 25, 101296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah; Al-Khaldi, F.A.; Abusharkh, B.; Khaled, M.; Atieh, M.A.; Nasser, M.S.; Laoui, T.; Saleh, T.A.; Agarwal, S.; Tyagi, I.; et al. Adsorptive Removal of Cadmium(II) Ions from Liquid Phase Using Acid Modified Carbon-Based Adsorbents. J. Mol. Liq. 2015, 204, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Zou, D.; Wu, C.; Li, T.; Gao, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Shimaoka, T. Comparative Study on Inorganic Cl Removal of Municipal Solid Waste Fly Ash Using Different Types and Concentrations of Organic Acids. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeonuegbu, B.A.; Machido, D.A.; Whong, C.M.Z.; Japhet, W.S.; Alexiou, A.; Elazab, S.T.; Qusty, N.; Yaro, C.A.; Batiha, G.E.S. Agricultural Waste of Sugarcane Bagasse as Efficient Adsorbent for Lead and Nickel Removal from Untreated Wastewater: Biosorption, Equilibrium Isotherms, Kinetics and Desorption Studies. Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 30, e00614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, V.P.; Nguyen, P.T.; Tran, M.C.; Luu, A.T.; Hung, N.Q.; Luu, T.T.; Kiet, H.A.T.; Mai, X.T.; Luong, T.B.; Nguyen, T.L.; et al. HTDMA-Modified Bentonite Clay for Effective Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solution. Chemosphere 2022, 286 Pt 3, 131766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ogata, F.; Saenjum, C.; Nakamura, T.; Kawasaki, N. Adsorption/Desorption Capability of Potassium-Type Zeolite Prepared from Coal Fly Ash for Removing of Hg2+. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I. MXenes (Two-Dimensional Metal Carbides) as Emerging Nanomaterials for Water Purification: Progress, Challenges and Prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 388, 124340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Jiang, P.; You, S.; Ding, N.; Guo, Q.; Lin, F. Applications of Nanomaterials for Heavy Metal Removal from Water and Soil: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hou, B.; Wang, J.; Tian, B.; Bi, J.; Wang, N.; Li, X.; Huang, X. Nanomaterials for the Removal of Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Ali, D.; Khan, S.H.; Gnanamoorthy, G.; Choudhary, N.; Yadav, K.K.; Thai, V.N.; Hussain, S.A.; Manhrdas, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Amorphous Iron Oxide Nanoparticles by the Sonochemical Method and Their Application for the Remediation of Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Zavaleta, K.; Chacon-Laiza, Y.; Asmat-Campos, D.; Raquel-Checca, N. Green Synthesis of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Eucalyptus Globulus Extract and Their Application in the Removal of Heavy Metals from Agricultural Soil. Molecules 2022, 27, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatla, A.; Almanassra, I.W.; Jaber, L.; Kochkodan, V.; Laoui, T.; Alawadhi, H.; Ali, M. Influence of Calcination Atmosphere on Fe Doped Activated Carbon for the Application of Lead Removal from Water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 652, 129928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariana, M.; Abdul, A.K.; Mistar, E.M.; Yahya, E.B.; Alfatah, T.; Danish, M.; Amayreh, M. Recent Advances in Activated Carbon Modification Techniques for Enhanced Heavy Metal Adsorption. J. Water Process. Eng. 2021, 43, 102221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasri, D.A.; Saleh, N.B.; Atieh, M.A.; McKay, G.; Ahzi, S. Adsorption of Phosphate on Iron Oxide Doped Halloysite Nanotubes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, W.; Zhang, L.; Kong, Q.; Wang, W. Efficient Adsorption of Sulfamethazine onto Modified Activated Carbon: A Plausible Adsorption Mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.; Yadav, M.; Kohout, T.; Lahtinen, M.; Garg, V.K.; Sillanpää, M. Development of Iron Oxide/Activated Carbon Nanoparticle Composite for the Removal of Cr(VI), Cu(II) and Cd(II) Ions from Aqueous Solution. Water Resour. Ind. 2018, 20, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabaane, L.; Tahiri, S.; Albizane, A.; El Krati, M.; Cervera, M.L.; de la Guardia, M. Immobilization of Vegetable Tannins on Tannery Chrome Shavings and Their Use for the Removal of Hexavalent Chromium from Contaminated Water. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzin, F.; Bahri Rasht Abadi, M.M. Adsorption of Cr(VI) from Aqueous Solution by Adsorbent Prepared from Paper Mill Sludge: Kinetics and Thermodynamics Studies. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krishnamoorthy, R.; Govindan, B.; Banat, F.; Sagadevan, V.; Purushothaman, M.; Show, P.L. Date Pits Activated Carbon for Divalent Lead Ions Removal. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 128, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boujelben, N.; Bouzid, J.; Elouear, Z. Removal of Lead(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Manganese Oxide-Coated Adsorbents: Characterization and Kinetic Study. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2009, 27, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouni, L.; Merabet, D.; Bouzaza, A.; Belkhiri, L. Adsorption of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solutions Using Activated Carbon Developed from Apricot Stone. Desalination 2011, 276, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, C.; Yang, B.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Z. Study on Adsorption of Chromium (VI) by Activated Carbon from Cassava Sludge. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Banda Aceh, Indonesia, 26–27 September 2018; Volume 128, p. 012017. [Google Scholar]
- Ihsanullah; Al-khaldi, F.A.; Abu-sharkh, B.; Mahmoud, A.; Qureshi, M.I.; Laoui, T.; Atieh, M.A. Effect of Acid Modification on Adsorption of Hexavalent Chromium (Cr(VI)) from Aqueous Solution by Activated Carbon and Carbon Nanotubes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 7232–7244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramutshatsha-Makhwedzha, D.; Mbaya, R.; Mavhungu, M.L. Application of Activated Carbon Banana Peel Coated with Al2O3-Chitosan for the Adsorptive Removal of Lead and Cadmium from Wastewater. Materials 2022, 15, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabede, P.M.; Shooto, N.D.; Naidoo, E.B. Removal of Methylene Blue Dye and Lead Ions from Aqueous Solution Using Activated Carbon from Black Cumin Seeds. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 33, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neolaka, Y.A.B.; Lawa, Y.; Naat, J.; Riwu, A.A.P.; Darmokoesoemo, H.; Widyaningrum, B.A.; Iqbal, M.; Kusuma, H.S. Indonesian Kesambi Wood (Schleichera Oleosa) Activated with Pyrolysis and H2SO4 Combination Methods to Produce Mesoporous Activated Carbon for Pb(II) Adsorption from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjuladevi, M.; Anitha, R.; Manonmani, S. Kinetic Study on Adsorption of Cr(VI), Ni(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Activated Carbon Prepared from Cucumis Melo Peel. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, F.; Lancia, A.; Molino, A.; Musmarra, D. Removal of Chromium Ions Form Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption on Activated Carbon and Char. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 145, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljerf, L. High-Efficiency Extraction of Bromocresol Purple Dye and Heavy Metals as Chromium from Industrial Effluent by Adsorption onto a Modified Surface of Zeolite: Kinetics and Equilibrium Study. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 225, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Liang, M.; Ding, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Han, L. Synthesis, Optical Characterization, and Adsorption of Novel Hexavalent Chromium and Total Chromium Sorbent: A Fabrication of Mulberry Stem Biochar/Mn-Fe Binary Oxide Composite via Response Surface Methodology. Front. Environ. Chem. 2021, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, N.N. Rapid Removal and Recovery of Pb(II) from Wastewater by Magnetic Nanoadsorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohubedu, R.P.; Diagboya, P.N.E.; Abasi, C.Y.; Dikio, E.D.; Mtunzi, F. Magnetic Valorization of Biomass and Biochar of a Typical Plant Nuisance for Toxic Metals Contaminated Water Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirtom, V.N.; Dinçer, A.; Becerik, S.; Aydemir, T.; Çelik, A. Removal of Lead (II) Ions from Aqueous Solution by Using Crosslinked Chitosan-Clay Beads. Desalin. Water Treat. 2012, 39, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.M.; Awwad, N.S.; Aboterika, A.H.A. Removal of Synthetic Reactive Dyes from Textile Wastewater by Sorel’s Cement. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 162, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumings, J.N. Biochemical Aspects. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1962, 55, 1023–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzin, F.; Ghoreyshi, A.A. Synthesis of a New Low-Cost Activated Carbon from Activated Sludge for the Removal of Cr (VI) from Aqueous Solution: Equilibrium, Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Desorption Studies. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalhruaitluanga, H.; Jayaram, K.; Prasad, M.N.V.; Kumar, K.K. Lead(II) Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions by Raw and Activated Charcoals of Melocanna Baccifera Roxburgh (Bamboo)-A Comparative Study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Sterbinsky, G.E.; Prigiobbe, V.; Meng, X. Mechanistic Study of Lead Adsorption on Activated Carbon. Langmuir 2018, 34, 13565–13573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharififard, H.; Pepe, F.; Soleimani, M.; Aprea, P.; Caputo, D. Iron-Activated Carbon Nanocomposite: Synthesis, Characterization and Application for Lead Removal from Aqueous Solution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 42845–42853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The Constitution and Fundamental Properties of Solids and Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M. Freundlich Over the Adsorption in Solution. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–471. [Google Scholar]
- Sips, R. On the Structure of a Catalyst Surface. J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redlich, O.; Peterson, D.L. A Useful Adsorption Isotherm. J. Phys. Chem. 1959, 63, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S. Citation Review of Lagergren Kinetic Rate Equation on Adsorption Reactions. Scientometrics 2004, 59, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-Second Order Model for Sorption Processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.H.; Clayton, W.R. Application of Elovich Equation to the Kinetics of Phosphate Release and Sorption in Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).