Abstract
Abha city is distinguished by urbanization, infrastructure, deepening watercourses, and changes in runoff flow which encourage flash floods in the urban zones of many villages in the region. AlMahalah village is prone to flash flooding due to its geographic location near the outlet of convergence streams of significant flow. The Geographic Information System (GIS), Remote Sensing (RS), Water Modeling System (WMS), and Hydrologic Engineering Center-Hydrologic Modeling System (HEC-HMS) were used to assess the effects of flash floods on AlMahala village. Precipitation data from 1978 to 2020 was statistically processed and analysed to provide more information about flash flood hazards. With a 3-h lag time in both watersheds, the higher peak discharge in Wadi Abha than in Wadi Al Akkas indicates that flooding was a primary concern in Wadi Abha. With an average yearly rainfall of 520 mm, the hydrograph simulation from 1 to 5 April 2020 would contribute to the junction (outlet) point of AlMahala village with a peak discharge rate of 474.14 m3/s. The vegetation cover increased by 243 km2 in 2020 compared to 2016. The HEC-RAS model was used to calculate the water depth, velocity, and elevation of the water surface with and without dam installation. The study provides the administration with practical and reasonable procedures for avoiding flash flood destruction in urban areas.
1. Introduction
Flash floods occur when precipitation saturates the drainage ability of the catchment slopes, leading to damming of the drainage network and tremendously high discharge on the catchment outlets [1]. The rapid urbanization combined with climate change in recent years has resulted in numerous environmental issues and increased risks of natural disasters [2], including flooding and related fatalities of human lives and property [3]. Flood disasters are expected to become more common as a result of unplanned urbanization [4]. Flooding is one of the most expensive natural disasters, both in terms of human casualties and property damage [5]. Most floods have an impact on people because the fear of the consequences outweighs the actual effects [6]. According to Hassan [7], frequent flash floods have severely impacted the roadways and human actions along the Red Sea’s coastal plains. Several other research papers on flood hazards have been published in various areas, including Youssef et al. [8] and Youssef and Hegab [9]. Flash floods pose a significant threat to human life as well as infrastructure such as cities, streets, and railways. The economic cost of such disasters is enormous, and as a result, floods can bring pathogens into urban environments, causing microbial growth and diseases [10,11]. Flooding causes human injury or death, and preventing such events is advisable to compensating victims. According to Regmi et al. [12], large databases are frequently required in natural hazard research. According to Youssef et al. [1], the most influential contributors to flooding are natural factors such as hydrological and meteorological features, geological structures, soil types, geomorphology, and vegetation. Anthropogenic activities such as increasing impervious surfaces (roads and buildings) and cutting trees can hasten flooding.
Reliable forecasts of runoff in arid regions are difficult to obtain due to the paucity of hydrometeorological data, and flash flood gauging is extremely rare [13,14,15,16,17]. Runoff modeling can be a promising approach to improve the habitability of an area and any landscape surrounded by similar geographic conditions in the absence of flow data [18,19]. Soil Conservation Service Curve (SCS-CN) models are widely used to predict hydrologic responses in ungauged catchments [20]. Since then, this method has been adapted to measure infiltration losses in arid regions with similar climatic and geographical conditions [21,22,23,24]. When predicting rainfall-runoff in in gauged and ungauged catchments, SCS models are as good, if not better, then the more complex ones [24,25,26,27,28,29]. Hydrological Engineering Center-Hydrological Modeling System (HEC-HMS) is developed to simulate rainfall-runoff processes in watershed systems [30]. The input data for the HEC-HMS model setup includes rainfall, Digital Elevation Model (DEM), flow gauge data, land use/land cover (LULC), soil type, etc. The resulting hydrographic charts are used to study water availability, flow forecasting, urban drainage, floodplain regulation, effects of future urbanization, flood damage reduction, reservoir sewer design and system operation. The rates and amounts of floodwater flow are affected by interactions between numerous variables, including the morphometric properties of drainage basins (catchment shape, number, and length of streams); the frequency of rainfall and its properties; LULC characteristics; the physical properties of soil (texture, depth, and hydraulic conductivity); and anticipated conditions (soil moisture values) [31,32].
Various researchers have used RS and GIS techniques in the past to estimate flood risk impacts on urban regions, infrastructure, and agricultural areas with respect to land use land cover changes [33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. Others [31,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51] have investigated flood hazard susceptibility mapping using GIS techniques and RS data, as well as probabilistic, statistical, hydrologic, and fuzzy logic and stochastic neural networks. In a recent paper, Essel [44] and Portugués-Molla et al. [52] stated that hydrologic assessments could be conducted using geospatial tools to determine different hydrologic components, develop possible scenarios and prepare hydrologic designs to overcome the hazards of flash flooding.
Due to climate change, many areas around the world have experienced unprecedented rainstorm events (above-normal records) [53,54,55,56]. These occurrences result in disasters that cause human, property, and economic loss. Unprecedented events have hit the Saudi Arabia (KSA), causing significant damage to railroads, highways, urban areas, and agricultural lands [32]. The majority of flash flood hazards in the SA are caused by a combination of natural conditions (climate change and heavy rainfall) and human intervention (unplanned urban expansion and poor drainage systems) [57]. Heavy rains have recently caused flash floods in parts of the SA (Al Riyadh city in 2015 and 2018 and Jeddah city in 2009, 2011, 2015, 2017, and 2018). During November 2009 and January 2011, the most severely affected areas were in the country’s west, particularly in the city of Jeddah [31,51]. These events were marked by 70 and 111 mm of rain in 3 h, respectively, and were classified as catastrophic flash floods for Jeddah City. In 2009, they claimed the lives of 113 people, damaged over 10,000 homes, and destroyed approximately 17,000 vehicles [32]. Due to limited water resources and inadequate flash flood mitigation measures, the SA faces a number of challenges in implementing sustainable development plans. Several authors have addressed flash flood issues in various parts of the SA. In the design of sustainable development in the Alsail Alkabir area, El Shinnawy et al. [58] addressed flash floods. Elkhrachv [59] used satellite imagery and GIS to map flash flood areas in Najran City. Sharif et al. [60] investigated flood hazards in Riyadh City urban watersheds. In Ha’il City, Abdul Karim [61] assessed the effect of flood risk on urban growth and LULC changes. Al-Ghamdi et al. [62] investigated the effect of urban expansion on flood risk in Makkah City. ElAlfy [63] studied the impact of flash floods on Jizan’s urbanization.
Most of the cities in SA assessed for flash flood investigation are the Makkah, Jeddah, Hail, Jizan, Riyadh etc. [62,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73]. However, Abha (Figure 1), although an important city in the SA, has not been assessed and paid adequate attention. The city was distinguished by a scarcity of hydrological data, which facilitates the use of Water Modeling System software (WMS) procedures to simulate the characteristics of the watersheds in a flash flood and surface runoff potentiality events [74]. Therefore, the goal of this study was to assess the practical impact of flash floods on Abha City’s AlMahala region using a method based on RS, GIS, WMS, and HEC-HMS and to propose dam alternatives to mitigate the effects of flash flooding, as well as to evaluate hydrological models to detect flooding risks.
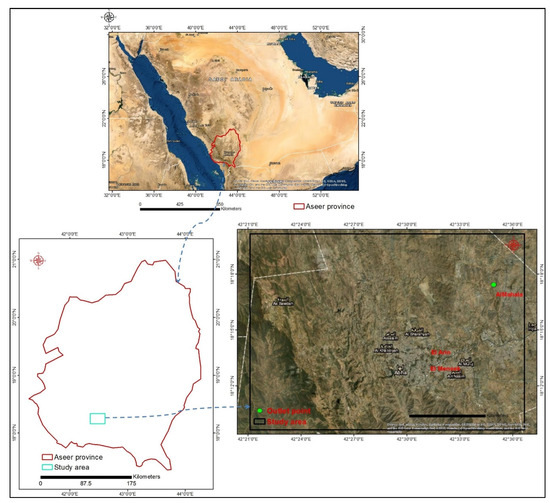
Figure 1.
Base map of the Abha city.
2. Study Area
The drainage basins of Abha are located in the southwestern part of the SA, between latitudes 18°09′ N–18°21′ N and longitudes 42°21′ E–42°36′ E. (Figure 1). The study area covers 533.93 km2 and is distinguished as the best tourist attraction. The southern and southwestern sections had the lowest elevation between 1136.2–1637.6 m above sea level (asl), while the central-northwestern sections had the highest elevation between 2408–2989 m asl (Figure 2a). The study area’s elevation ranged from 1136 to 2989 m asl (Figure 2a).
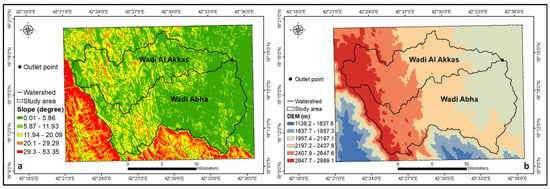
Figure 2.
The DEM (a) and slope (b) of the watersheds.
The slope ranged from 0.01 to 53.35 degrees (Figure 2b). The high elevation, high depth valleys [75], weather fluctuation, deep watercourses, and urbanization. As evident from Figure 2a, Abha has a variety of topographical elevations that result in urbanization. The average minimum and maximum temperatures were 19.3 °C and 29.7 °C, respectively, and the average precipitation within 25 years was 355 mm per year [76]. Most of the region of SA has a hot and dry climate, including high temperatures and light and variable rainfall. The Abha, in the southwest of SA, receives the most precipitation in the country due to its mountainous elevation. The surface observations at the Abha station from 1979 to 2009 show that the wet season (November-April) was followed by the dry season (June–September) [77] (Figure 3). The majority of Abha city was seen covered in runoff due to flash floods (Figure 4).
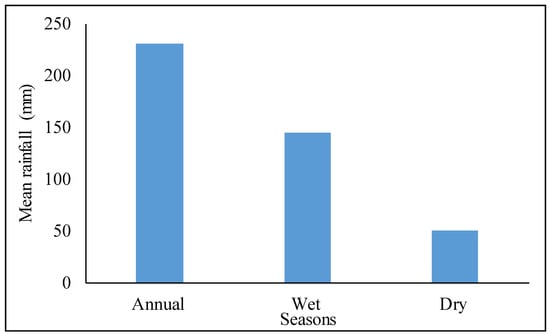
Figure 3.
Average rainfall of Abha city.

Figure 4.
Flood risk in El Arine (a) and El Mensek (b) during 2017 period, Abha city (after [75]).
The AlMahala area (facing the outlet point) was the confluence of several streams and was considered a permanently flooding zone [75]. Surface water elevations exceed 1.49 m between the AlMahala and Bani Mazen regions (Figure 1), particularly at river saddles and confluences. The soil clay is primarily composed of smectite, illite, and partially kaolinite, and it has a low permeability, which increases the risk of flooding (Figure 4). Flooding occurs even on gentle slopes and in agricultural areas due to soil clay sealing, distinguished by low permeability [78]. The study area was characterized by topographical fluctuation, dramatic changes in precipitation, extremely low soil permeability, and urbanization. It was jeopardized by flash flood risks and the short period between the event and decision-making.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Ideas
RS, WMS, and DEM were applied with precipitation data and field visits to determine various hydrological parameters of the drainage basins [79,80]. Flood hazard characteristics were analysed by combining RS and GIS with WMS, HEC-HMS, and HEC-RAS. It supports the decision-makers and planning management in taking the necessary action to protect Abha from flash floods. El Bastawesy et al. [16] used RS and DEM data in GIS to predict flash flooding in the Wadi Hudain catchment in southern Egypt. The RS precipitation determination was used in hydrological models, particularly when rain gauge data was limited or non-existent. GIS techniques were used to map flooding distribution in Makkah, Saudi Arabia [27]. Milzow et al. [81] used RS and GIS procedures to evaluate the hydrological parameters and interpret the catchment.
3.2. Satellite Data
The United States Geological Survey (USGS) website (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/; accessed on 23 April 2022) provided the satellite image of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM)-DEM. The Landsat 8 surface reflectance (L8SR) image with a resolution of 30 m (path 167/row 047; SCENE ID: LC81670472018326LGN00) was downloaded. The L8SR image contains 11 bands, and the cloud cover is low (0.02). Wavelengths, quick atmospheric pressure, UTM projection WSG84, and contrast stretching were all corrected in the image. The accuracy of the flood risk map is affected by the accuracy and quality of the data used. The more accurate the map produced, the higher the spatial resolution of the data [82]. RS technologies select the best spectral bands for detecting changes in the natural environment [83]. The normalized difference of vegetation index (NDVI) was determined from the L8SR image to display green vegetation. The digital number (DN) of the L8SR image was transformed to reflectance values according to the following equation:
Band specific reflectance multiplication band × DN values + reflectance additive band
It is corrected for sun angle by meta data included in the satellite images information as:
Reflectance/sin (sun elevation)
The NDVI was calculated by the following formula.
where, NIR = near infrared band and Red = red band
NDVI = (NIR − Red)/(NIR + Red)
The geological map was scanned and geo-referenced using L8SR images, and various rock units were digitized. The supervised image classification accuracy evaluation, Maximum Likelihood (ML) classifier, uses digitized geology as a valuable data source. To create a base map for the area analysed, land cover classes were extracted using L8SR images. The ENVI v 5.1 program was used for digital image processing and data pre-processing. ArcGIS v 10.3 software packages were employed to obtain the study area’s geology, slope, DEM, and NDVI. Lineaments were extracted with ENVI 5.1 software, followed by automatic extraction lineaments (PCI Line program), handling extraction lineaments (ArcGIS 10.3 software), and trend analysis (RockWork v 16 software). The principal component image (PCI) has the essential information and can be used to extract lineaments (PCI Geomatica). The LANDSAT 8 OLI/TIRS C1 Level-1 was collected from an image courtesy of the US Geological Survey between 2016 and 2020 to detect land cover change. The LANDSAT_SCENE_ID = LC81670472016289LGN01 and LC81670472020252LGN00 for 2016 and 2020 periods, respectively, the WRS_PATH = 167 and WRS_ROW = 47. The CLOUD_COVER = 0.00. The DATUM = “WGS84 and UTM_ZONE = 38.
3.3. Hydrological Data
HyfranPlus software was used to process rainfall data from 1978 to 2020 and to calculate the precipitation depth for the return periods of 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 years (Weibull, Gumbel, and GEV techniques). WMS software V. 9.1 was used to delineate and characterize the sub-basins, followed by HEC-HMS, which simulated the hydrographs for each sub-basin. The SCS surface runoff CN techniques are used to model the hydrological hydrograph features (SCS Type II curve), common in arid zones such as the current study [84]. The precipitation depth was assessed using SCS (CN) leakage techniques (loss and outflow). SCS techniques evaluated the precipitation depth—runoff relationship [85]. The runoff CN was the watershed’s discharge rate for flood water, or the predicted water volume runoff based on precipitation [86]. Because land characteristics in Saudi Arabia differ from those in America, the CN values for Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha are not automatically extracted from the US land features classification table [87]. They calculated 83, 67, and 86 CN for hard rocks, alluvium deposits, and urbanization zones, respectively. The percentage of three types of land uses was calculated for the two delineated sub-basins. The CN for each sub basin was estimated by the following equation.
Summing the three CNs for three land-use types resulted in CN of the sub-basin.
The peak discharge and water volume collected were determined manually using the following equations [85].
where, Q: direct flood (inches); P: rainfall depth (inches); S: soil retention (inches)
where, qp: peak discharge; A: sub basin area; Tp: time to peak
where, TL; lag time; D: storm duration period (3 h in KSA)
where, Wv is Water collect volume
The HEC-HMS model determines the peak flow rates at the outlet point and sub-basins. The HEC-HMS model’s main components are the watershed structure, meteorological parameters, and control features. The model is influenced by watershed hydrological parameters, land use, moisture capacity, and average precipitation [88]. The outflow volume is estimated using the water losses (SCN-CN) method to estimate recession periods.
3.4. Land Cover Change
For land cover change detection, the LANDSAT_8 OLI/TIRS C1 Level-1 was collected within 2016 and 2020 periods from Image courtesy of the U.S. Geological Survey. The LANDSAT_SCENE_ID = LC81670472016289LGN01 and LC81670472020252LGN00 for 2016 and 2020 periods, respectively, the WRS_PATH = 167 and WRS_ROW = 47. The CLOUD_COVER = 0.00. The DATUM = WGS84 and UTM_ZONE = 38.
3.5. HEC-RAS 2D Software (Mitigation and Protection from Flooding Risks)
It uses a DEM, ARCGIS imagery, and a hydrograph of the outlet point area derived previously from the HEC-HMS software. As an inline structure, a dam was installed in HEC-RAS (weir contains spillway). Flooding was caused by unsteady surface water flow that shifted abruptly as flood waves passed. The unsteady flow from the outlet zone/or upstream (determined by HEC-HMS) to downstream of Wadi Abha and its surrounding zones was simulated using HEC-RAS. HEC-RAS is used to simulate unsteady state conditions using geometric data. The upstream boundary condition (outlet point) was simulated by hydrograph data in no dam simulation, whereas the downstream was at normal depth. The storage, perimeter, and outlet areas of the dam and no dam breach designs were traced in unsteady-state conditions. Following the run, the water surface elevation WSE at sites along the upstream and downstream boundaries was calculated and used to calculate the flooding distribution rate. The water depth and extension were estimated using the SWE and terrain model (DEM). HEC-RAS created the flood distribution map (water depth, water velocity, and WSE).
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Rainfall Trend
Precipitation was distributed locally rather than regionally. It is distinguished by high rainfall intensity in some areas (Figure S1). The average annual rainfall in the Abha area was 172.4 mm. In SA, Aseer has the highest mean precipitation (March–June), while rainfall is negligible in other months [89]. Rainfall is higher in the central-northwestern mountainous areas than in the rest zones (Figure 2a).
The statistical description of the 43 years (1978–2020) shows wide trend variation, with some rainfall values exceeding the mean and others falling below it (Table 1). Some rainfall values in the southwestern part exceed the mean by mountainous areas, while others fall below the mean due to topography, humidity, and temperature changes. In 1994, 2003 and 2019, the area experienced maximum and minimum precipitation of 693 and 90 mm/year, respectively (Figure 5). Weibull, Gumbel, and GEV models used annual precipitation data from the previous 43 years to determine precipitation depth for storms in returning periods of 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 years (Figure 6). Table 2 summarizes the three output results.

Table 1.
Statistics of the 24 h rainfall depths (mm) at Abha metrological station (Number of observations: 43 Y).
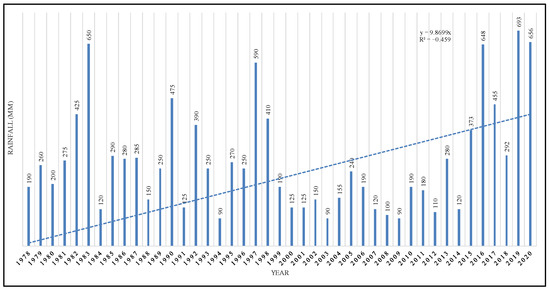
Figure 5.
Annual rainfall depth of the Abha meteorological station within 1978–2020.
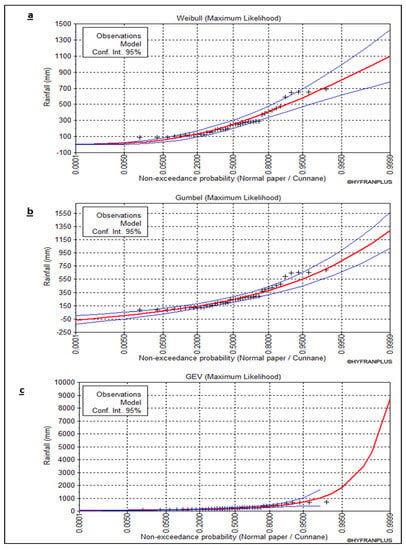
Figure 6.
(a–c) Weibull, Gumbel, and GEV graphs of rainfall depths for the model storms.

Table 2.
Twenty-four hours rainfall depths determined for different return periods at Abha meteorological station using Weibull, Gumbel, and GEV models.
4.2. Precipitation Analysis of Watersheds
Annual rainfall covering 1978 to 2020 (43 years) was recorded from the National Meteorology and Environment Centre and Worldwide Weather Forecasts and Climate Information (https://weather-and-climate.com; accessed on 20 May 2022). The precipitation hydrographs were created using rainfall events from two sub-basins that discharge directly into and around AlMahala village with return periods of 5, 10, 25, 50, and 100 years. The Weibull, Gumbel, and GEV methods produced the best-fit curves (Figure 6). The rainfall distribution between the two blue lines was included in the GEV technique (Figure 6c). As a result, it is the best method. Rainfall intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) curves for various return periods were also established using GEV techniques (Figure 7). The 5-min precipitation intensity ranged between 450 and 1608 mm/h for 2 and 100 years, respectively (Figure 7). The precipitation for the 50- and 100-year return periods of 60 min is 270.4 and 306.8 mm, respectively. They provide additional information when installing the safe drainage application, flood management evaluation, and flood risk area protection. Precipitation depths for return periods are shown in Table 2.
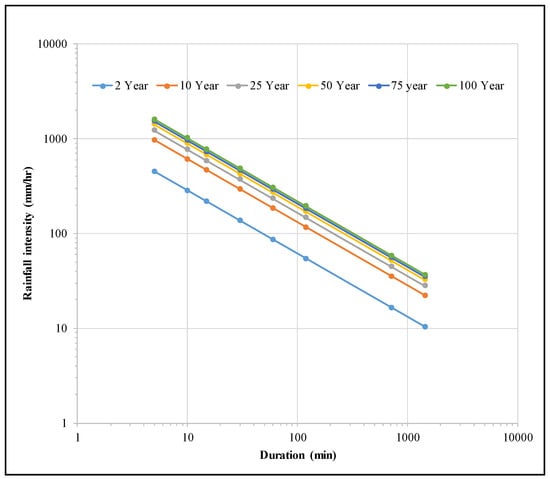
Figure 7.
Intensity–duration–frequency (IDF) curves of Abha City (intensity data within 1978–2020 periods).
4.3. Drainage Networks and Basins Characteristics
WMS delineates the drainage basins affecting the outlet point, located next to AlMahala village in Abha city (Figure S2). The outlet points collect inflow water and discharge it into Wadi AlMahala, Bani Malek (Aseer), and AlMahala village (Figure 1). Two drainage basins, Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha, with 4th order streams, were extracted (Figure S2a,b). Abha Dam is part of the wadi Abha, a barrier to surface runoff that recharges the alluvium aquifer. It has a capacity of 213 million cubic meters (MCM) and stands 32 m tall. The Ashran dam, which opened in 1985 and controls food probability, is located in Wadi Al Akkas. These dams will provide potable water for two million people by 2030 and water for approximately 15,000 ha [76].
Table 3 shows the morphometric characteristics of the two sub-basins. They cut through the southwest mountain ranges via the Jeddah group (andesite and diabase) (Figure 8). SB-2 is dominated by granite and syenite in the east, while Wadi Al Akkas 1 is dominated by chlorite sericite schist and amphibolite schist (Figure 8a). Figure 8b depicts the geological distribution areas within Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha. The highest geological distribution within the two sub-basins was marble-quartzite and chlorite sericite schist-amphibolite schist (Figure 8b). The lowest geological distributions were andesite and diabase, while the middle geological were greenstone-schistose greenstone and amphibolite-schist (Figure 8b).

Table 3.
Main morphological characteristics of the drainage basins.
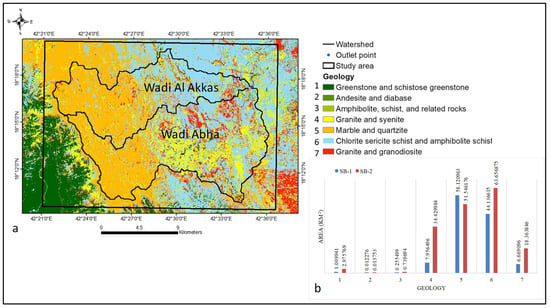
Figure 8.
(a) Digitized geologic map of the study area and (b) Geological area distribution in Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha (modified after [76]).
Due to the hardness of the rocks, the geology was characterized by scarce lineament structures (Figure S3). The shallow infiltration and high surface runoff of the low lineaments structures in two sub-basins aided the flooding process. Water flooded AlMahala village (near the outlet point) from two sub-basins, Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha (Figure S2b). Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha and 2 have 23.2 and 22 km lengths, respectively (Table 3), confirming that the basins were elongated. Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha have Sinuosity factors of 1.3 and 1.5, respectively (Table 3), indicating that tectonic activity has a greater influence on Wadi Abha than on SB-1. For Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha, the time lag, concentration-time, and peak time are (226.7, 250), (316.7, 340), and (945, 975) minutes, respectively (Table 3). Precipitation has an impact on the area (116.71, 172.67 km2), slope (0.1426, 0.1145), shape factor (4.66, 2.79), and land use of Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha, respectively. Peak discharge (2732.82 m3/s), area (172.67 km2), and CN (81.6) are higher in Wadi Abha than in Wadi Al Akkas. (Table 3). It confirms that Wadi Abha was more prone to flood than Wadi Al Akkas. The increased lag time allows for adequate time for warning, evacuation, and protection of downstream zones. The two sub-basins contributed to a high risk of flooding in AlMahala village. The long lag time allows for easier preparation, safety, warning, and evacuation of residents, particularly those living in downstream zones. Both sub-basins have lag times of more than three hours, with slight variation (Table 3). The higher peak discharge and longer lag time in Wadi Abha cause destructive waves in the outlet area than in Wadi Al Akkas.
4.4. Flooding Process
The flow peak rate from 5 to 100 years ranged from 370.3 to 1655.5 m3/s and 534 to 2289 m3/s for Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha, respectively (Table 4, Figure 9a,b). High peak discharges in two sub-basins were attributed to high rainfall, low lineament structures (Figure S3), urbanization prolongation (Figure S4), and villages spread across alluvial deposits. These villages are AlMahala, Shamsan, AlManhal, El Arin, El Mensek, AlNasim, AlMuftaha, Abha Jadida, Al Shifa, and Al Qura. These villages are part of Abha city, primarily in Wadi Abha. (Figure 1). The exposed hard rocks cover the majority of Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha, while sandy loam soil makes up the majority of Wadi Abha. (Figure S5a). The soil loam covers the western portion of both sub-basins (Figure S5b). Wadi Abha has a higher concentration of buildup and hard rocks than Wadi Al Akkas (Figure S5b), which increases flood risk faster than Wadi Al Akkas. The leakage through wadis sediments declines due to infrastructure activity and consequently improves the runoff, flash floods, and high collection of water volumes. Wadi Abha has higher peak discharge and water collection volume than Wadi Al Akkas, which can be attributed to more urbanization in the former. After a short period (5 years), the peak discharge and water collection volumes in Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha were (370 and 534 m3/s) and (33,845,900 and 52,319,010 m3), respectively (Table 4 and Figure 9). As a result, flash floods may occur within 5 years (a short period) and increase with rainfall. The high peak discharges indicate a negative impact on urbanization and people. The large volume of water collected in Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha (Table 4) is one of the most critical water resources for these villages and agricultural practices. It recommends constructing steps gravels damming to avoid evaporation, evapotranspiration, and water escape through wadi channels. The dams are made up of gravel and sand steps that protect against flooding, reduce water velocity, and recharge the aquifer system (triple functions). The injection wells were built to receive the water volumes collected at the outlet. They are distributed in appropriate locations to improve aquifer recharge and productivity.

Table 4.
Characteristics of floods in main drainage basins for different return periods.
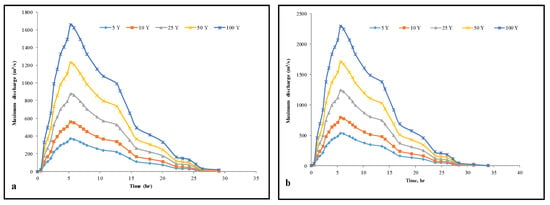
Figure 9.
Estimated peaks flow for 5–100-year events of (a) Wadi Al Akkas and (b) Wadi Abha.
4.5. Hydrograph Simulation
The HEC-HMS calculates the runoff of Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha between April 1 and 5, 2020, when there is the most rainfall (Figure 10). The red colour in Figure 10 represented total water lost by infiltration, while the blue colour represented storm surface runoff, which resulted in peak discharges. Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha have peak discharges of 1979 m3/s and 2776 m3/s, respectively (Table S1). The maximum outflow at the junction (outlet) was 4741.4 m3/s (Table S1). The volume of water discharged from Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha was 445.3 and 457.5 MM, respectively (Table S1). Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha have low soil infiltration and high outflow; the latter sub-basin had higher outflow values than the former (Figure 10). Most urbanization (villages) is concentrated in Wadi Abha (Figure S4), which has low infiltration and high surface runoff. The main geology in the investigated area was hard rocks, mainly granite and syenite, which are concentrated in the Wadi Abha’s eastern part. The latter area has very low permeability, which increases surface runoff in Wadi Abha more than in Wadi Al Akkas. The sink’s total hydrograph (outlet point) represented the total outflow from Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha (Figure 11).
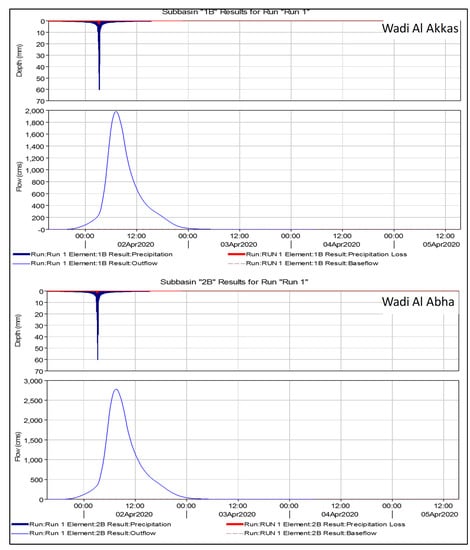
Figure 10.
HEC-HMS simulated hydrograph of Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha.
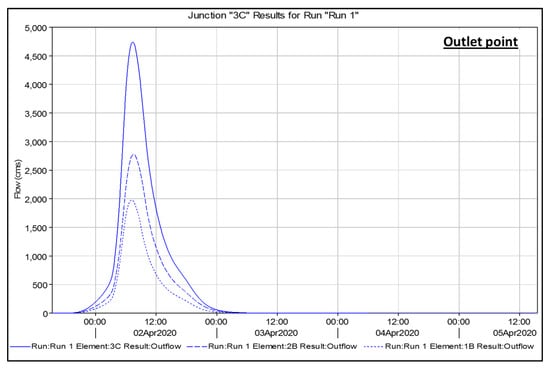
Figure 11.
HEC-HMS simulated hydrograph of outflow of the junction (outlet point) and Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha.
By entering the mean rainfall for each interval, the HEC-HMS model calculated the outflow and water collection volume (Table 5, Figure 12). Water volume decreased from 1978 to 2014 due to a decrease in average precipitation but increased dramatically from 2014 to 2020. (Figure 13). The most recent period generated a large amount of water (130.4 × 106 m3), the soil was primarily hard rocks (low infiltration), and topographical fluctuation and narrow channel widths contributed to high peak discharges. The peak discharges and outlet area of the two sub-basins varied from 387 m3/s to 4677 m3/s (Figure 13), while the time to peak in the two sub-basins went from 960 min to 990 min (Table 5).

Table 5.
Hydrograph estimation for mean rainfall (1978–2020).
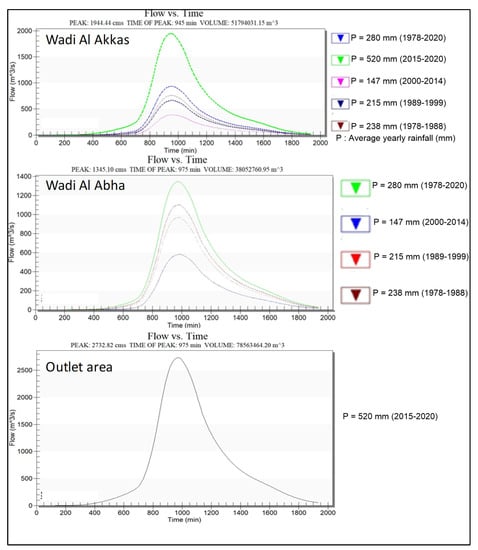
Figure 12.
Simulation runoff Hydrograph for means rainfall (1978–1988; 1989–1999; 2000–2014, 2015–2020, and 2020).
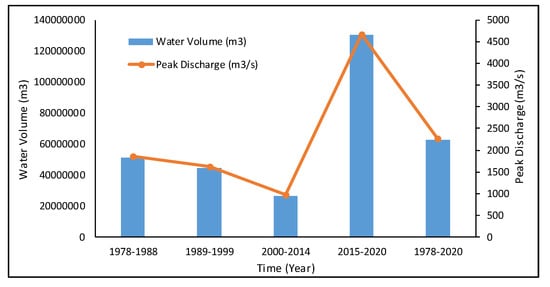
Figure 13.
Water volume and peak discharge of the outlet within different periods.
4.6. Agricultural Areas Change within 2006 and 2020 Periods
Bands 6, 5, and 4 highlight the vegetation distribution in green Figure S6a). The southwestern region had the most vegetation cover (green colour) (NDVI = 0.279–0.837). (Figure S6b). The vegetation cover increased in 2020 compared to 2016. (Figure 14a,b). ArcGIS was used to determine the differences in vegetation cover between 2016 and 2020. (Figure S7a,b). Approximately 243 km2 of agricultural land use area was increased in 2020 over the 2016 period, while 290.4 km2 of the land-use area remained unchanged (Figure S7a,b).
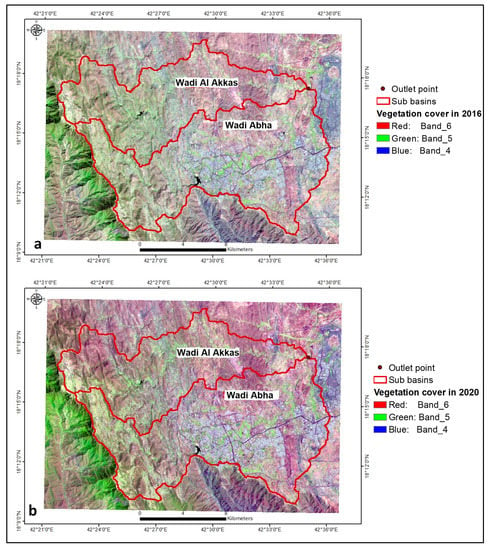
Figure 14.
Vegetation covers in (a) 2016 and (b) 2020 periods.
4.7. Maximum Flooding Probability (MFP)
Most of the flooding (130.4 × 106 m3) will be directed towards and around AlMahala village because the outlet point is not directly connected to Wadi Abha. They pose a threat to residents and can cause damage to infrastructure. A dam is built between the upstream storage area (Wadi Al Akkas and Wadi Abha) and the perimeter area (downstream, largely undeveloped) (Figure S8a,b) to slow the flow, force surface water to flow slowly into Wadi Abha, and reduce flooding. The Dam (Figure 15 and Figure S9) was constructed at the outlet point to direct surface water flow into the Wadi Abha channel, away from AlMahala village and its surroundings. The dam stores floodwater and causes surface water delay, allowing for water leakage and a long time for people to evacuate [90]. The HEC-RAS model simulates the proposed dam breach investigation based on the geometrical data (Figure 16).
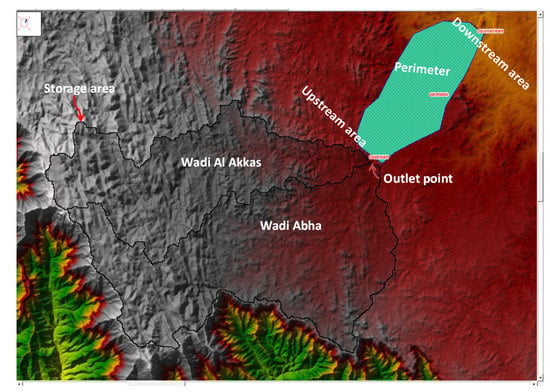
Figure 15.
Storage, perimeter, no dam installs, and outlet boundary.
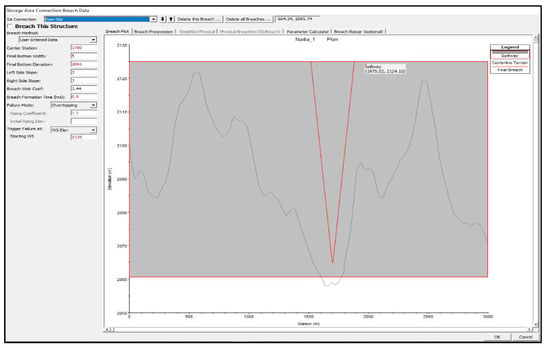
Figure 16.
Dam breach data of proposal dam in HEC-RAS.
The downstream perimeter area signifies normal depth, while the water surface gradient signifies a friction slope (HEC 2010). The initial condition (unsteady flow simulation) is made up of flow and various elevations of storage areas (DEM) (HEC 2010). There are two options for the flooding distribution rate: no dam installation and installing and designing the dam breach. In two scenarios, the perimeter area and shape of the periphery change (Figure S8 and Figure 15). It is primarily concentrated above Wadi Abha to fill it with surface water and reduce flooding and infrastructure damage. The perimeter’s outlet area also lies on Wadi Abha, allowing the drained water to fill the wadi. Instead of flooding AlMahala village or surrounding areas, the water inflow from the outlet point can be directed towards the wadi Abha. With no dam installed, the water depth is divided into four flooding probabilities: low (0–1.9 m), medium (2–3.8 m), high (3.9–5.5 m), and very high (5.6–11.4 m) (Figure 17a). With dam breach design, flooding depth is classified into four types: low (0–7.9 m), medium (8–16.6 m), high (16.7–26.5 m), and very high (26.6–40.3 m) (Figure 17b). Flooding distribution broadens as a result of dam construction. They are scattered throughout Wadi Abha, far from villages and industrial cities (Figure 17).
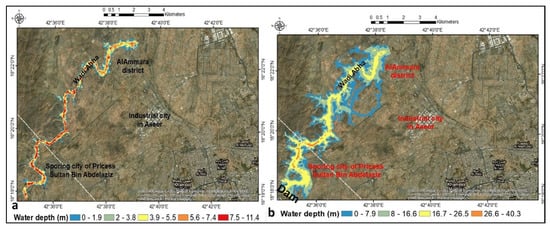
Figure 17.
(a) Water depth for no dam installation and (b) dam breach design.
Future urbanization should consider flooding classification areas to avoid high-risk flood zones (high to very high flooding). The dam’s main purpose is to deliver surface water far around Wadi Abha for irrigation rather than flowing entirely into Wadi Abha. As a result, agricultural income per capita will rise, and residents will have access to more water resources. The dam design and installation procedures in the model were modified to increase agricultural areas around Wadi Abha while keeping them away from the impact of urbanization flooding. Surface water velocity is classified into four types based on dam absence: low (0–2.1 m/s), medium (2.2–3.1 m/s), high (3.2–4.3 m/s), and very high (4.4–9.5 m/s) (Figure 18a). The dam design categorizes water velocity into four categories: low (0–3.95 m/s), medium (3.96–6.83 m/s), high (6.84–9.97 m/s), and very high (9.98–22.91 m/s) (Figure 18b).
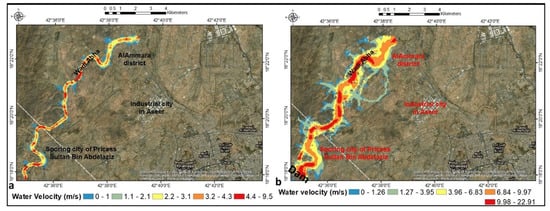
Figure 18.
(a) Water velocity for no dam installation and (b) dam breach design.
Wadi Abha had the fastest water velocity. As a result, most surface water flows through the wadi Abha, reducing its flooding capacity. The steeper Wadi Abha has higher water velocity and narrower channels, whereas the lower water velocity represents a gentle slope and wider zones (Wadi Abha peripheries). Without dam installation, the water surface elevation (WSE) is divided into four categories: low (1965–1981 m), medium (1981–2003 m), high (2003–2026 m), and very high (2026–2066 m) (Figure 19a). In the case of dam construction, the WSE was classified as low (1980–1999 m), medium (1999–2022 m), high (2022–2051 m), and extremely high (2051–2087 m) (Figure 19b)
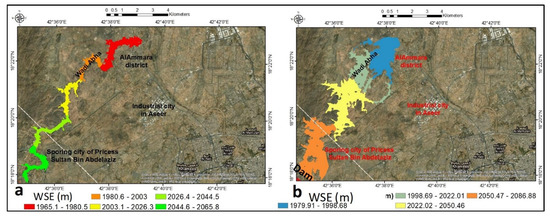
Figure 19.
(a) Water surface elevation (WSE) for no dam installation and (b) dam breach design.
Future urbanization should be located far from the downstream water surface flow (perimeter area). The dam will expand the wetted areas around Wadi Abha and the desert, allowing for more irrigation and increasing income/capita. In the case of dam construction, flooding is still far from urbanization. Under these geometrical conditions, the sporting city of Princess Sultan Bin Abdulaziz, the AlAmmara district, and the industrial city of Aseer were far from the flooding influences. Alternative mitigation methods included building subsurface cisterns to store floodwater for agricultural use.
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
The flood hazard map can determine the priority of the area for flood prevention, mitigation, and risk management planning. The methodology for increasing flood awareness is presented in this study. The goal was to reduce flood damage and improve the quality of life in the study area. The combination of GIS and hydraulic modelling provides a solution for long-term flood protection while also ensuring a cleaner and safer environment. The current study discusses the flourishing variety of scientific and practical experiences to demonstrate the efficacy of modelling techniques in engineering practice. In other words, it proves a well-functioning system of flood mitigation measures that improve the territory’s sustainability and environmental protection. Abha city is frequently seen and covered with runoff from flash floods. The statistical description of rainfall data from 1978 to 2020 reveals a wide variation range (90–693 mm/year). The hydrograph rainfall at AlMahala village, Abha, shows that the rainfall of 50 and 100 years with 60-min return periods is 270.4 and 306.8 mm, respectively. The morphometric characteristics of the extracted two sub-basins (wadis Al Akkas and Abha) were established and showed a lag time of more than 3 h with slight variation. Wadi Abha produces an enormous destructive wave at the outlet than Wadi Al Akkas. Peak discharge and water collection volume are more significant in Wadi Abha than in Wadi Al Akkas. The peak discharges and outlet area of the two sub-basins varied from 387 m3/s to 4677 m3/s, while the time to peak in the two sub-basins went from 960 min to 990 min. Approximately 243 km2 of agricultural land use area was increased in 2020 compared to 2016, while 290.4 km2 of land use area remained unchanged. The HEC RAS model was used to simulate water depth, velocity, and surface elevation at the outlet area (AlMahala village) without and with dam installation. They confirm that the Princess Sultan Bin Abdulaziz Sport City, AlAmmara district, and industrial city were not flooded. The study findings could lay the groundwork for more informed decisions and science-based recommendations in identifying river locations and developing more effective flood policies. Based on the current research findings, the specific proposals were that cooperation among hydrological, hydrogeological, and environmental programs resulted in good development with attractive dwellings.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su141610430/s1, Figure S1: Average annual precipitation map of Saudi Arabian (1960 to 2014) (Basahel and Mitri 2017); Figure S2: Flow direction (a) and stream orders (b) of the watersheds; Figure S3: Lineament detection in the watersheds; Figure S4: Urbanization distribution in selected study area; Figure S5: (a) Soil textures and (b) Land use land cover of the study area (modified after Mallick 2016); Figure S6: (a) Bands 6, 5, and 4 composites, and (b) NDVI distribution; Figure S7: (a) Vegetation differences in 2016 and 2020 and (b) vegetation zone areas; Figure S8: Storage, perimeter, dam site, and outlet boundary; Figure S9: Inflow Hydrograph of watershed area as a storage condition in HEC-RAS; Table S1: Summary results of the Wadi Al Akkas,2, and outlet point (1–5 April 2020).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.E. and M.Y.A.K.; methodology, M.E.; software, M.E.; validation, M.E.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Y.A.K. and M.E.; writing—review and editing, M.Y.A.K., A.M.S. and F.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia has funded this project, under grant no. (KEP-2-155-42).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Abdulaziz University Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, under grant no. KEP-2-155-42. The authors, therefore, acknowledge with thanks the DSR for technical and financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Youssef, A.M.; Pradhan, B.; Gaber, A.F.D.; Buchroithner, M.F. Geomorphological hazards analysis along the Egyptian Red Sea Coast between Safaga and Quseir. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 751–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, T.R. Modelling the impact of urbanization on flood frequency relationships in the UK. Hydrol. Res. 2010, 41, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwenzner, H.; Voigt, S. Improved estimation of flood parameters by combining space based SAR data with very high resolution digital elevation data. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrany, M.S.; Pradhan, B.; Mansor, S.; Ahmad, N. Flood susceptibility assessment using GIS-based support vector machine model with different kernel types. Catena 2015, 125, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D. Natural Disasters; UCL Press: London, UK, 1993; p. 631. [Google Scholar]
- Green, C.H.; Penning-Rowsell, E.C. Flooding and the quantification of intangibles. J. Inst. Water Environ. Man. 1989, 3, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, O.A. Salient geoenvironmental parameters of Ras Malaab—Abu Zenima Area, Gulf of Suez, Egypt, with an emphasis on flash flood potential and mitigative measures, Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2000, 3, 37–58. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, A.M.; Abdel Moneim, A.A.; Abu El-Maged, S.A. Flood hazard assessment and its associated problems using geographic information systems, Sohag Governorate, Egypt. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on the Geology of Africa, Assiut, Egypt, 15–16 November 2005; Volume 1, pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, A.M.; Hegab, M.A. Using geographic information systems and statistics for developing a database management system of the flood hazard for Ras Gharib area, Eastern Desert, Egypt. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on the Geology of Africa, Assiut, Egypt, 15–16 November 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, J.; Davies, M.; Clifton, D.; Ridley, I.; Biddulph, P. Flood management: Prediction of microbial contamination in large-scale floods in urban environments. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawod, G.M.; Mirza, M.N.; Al-Ghamdi, K.A. GIS-based estimation of flood hazard impacts on road network in Makkah city. Saudi. Arabia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 2205–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, A.D.; Yoshida, K.; Dhital, M.R.; Pradhan, B. Weathering and mineralogical variation in gneissic rocks and their effect in Sangrumba Landslide, East Nepal. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 71, 2711–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodier, J. Aspects of arid zone hydrology. In Facets of Hydrology; Rodda, J.C., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1985; Volume II, pp. 205–247. [Google Scholar]
- Sorman, A.; Abdulrazzaq, J. Infiltration-recharge through wadi beds in arid region. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1993, 38, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qurashi, A.; McIntyre, N.; Wheater, H.; Unkrich, C. Application of the Kineros2 rainfall–runoff model to an arid catchment in Oman. J. Hydrol. 2008, 355, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bastawesy, M.; White, K.; Nasr, A. Integration of remote sensing and GIS for modelling flash floods in Wadi Hudain catchment, Egypt. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, M.; Copty, N.K.; Saysel, A.K. Modeling the impact of land use change on the hydrology of a rural watershed. J. Hydrol. 2013, 497, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheith, H.; Sultan, M. Construction of a hydrologic model for estimating Wadi runoff and groundwater recharge in the Eastern Desert, Egypt. J. Hydrol. 2002, 263, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M.; Ghoneim, E.M.; Arnell, N.W. Predicting locations sensitive to flash flooding in an arid environment. J. Hydrol. 2004, 292, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCS. National Engineering Handbook, Section 4, Hydrology; US Department of Agriculture, US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1972.
- Reich, B. Short-duration rainfall intensity estimation and other design aids for regions of spare data. J. Hydrol. 1963, 1, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, L. Fluvial Processes in Dryland Rivers; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1988; 387p. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, O. Transmission losses in arid region. Hydraul. Eng. 1990, 116, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalaf, A. Predicting Short-Duration, High-Intensity Rainfall in Saudi Arabia. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of the College of Graduate Studies, King Fahad University of Petroleum and Minerals, Dhahran, Saudi Arabia, 1997; 196p. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, J.; Sorooshian, S. Comparison of simple versus complex distributed runoff models on a midsized semiarid watershed. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener, T.; Wheater, H.; Gupta, H. Rainfall-Runoff Modelling in Gauged and Ungauged Catchments; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2004; 330p. [Google Scholar]
- Dawod, G.; Mirza, M.; Al-Ghamdi, K. GIS-based spatial mapping of flash flood hazards in Makkah city, Saudi Arabia. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2011, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dawod, G.M.; Koshak, N.A. Developing GIS-Based Unit Hydrographs for Flood Management in Makkah Metropolitan Area, Saudi Arabia. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2011, 3, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hublart, P.; Ruelland, D.; Atauri, I.G.D.C.; Ibacache, A. Reliability of a conceptual hydrological model in a semi-arid Andean catchment facing water-use changes. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2015, 371, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) 2010 HEC-HMS. User’s Manual Version 3.5; Hydrologic Engineering Center: Davis, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pradhan, B.; Sefry, S.A. Flash flood Susceptibility mapping in Jeddah city (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia) using bivariate and multivariate statistical models. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Sefry, S.A.; Pradhan, B.; Abu Alfadail, E. Analysis on causes of flash flood in Jeddah city (Kingdom of Saudi Arabia) of 2009 and 2011 using multi-sensor remote sensing data and GIS. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2016, 7, 1018–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, U.C.; Hofmann, P.; Willhauck, G.; Lingenfelder, I.; Heynen, M. Multi-resolution, object-oriented fuzzy analysis of remote sensing data for GIS-ready information. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2004, 58, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.; Vitvar, T.; McDonnell, J.; Hassett, J.; Duncan, J.; Kendall, C. Effects of suburban development on runoff generation in the Croton River basin, New York, USA. J. Hydrol. 2005, 311, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Herath, S. Trend of floods in Asia and a proposal for flood risk management with integrated river basin approach. In Proceedings of the Second International Conference of Asia–Pacific Hydrology and Water Resources Association, Singapore, 5–9 July 2004; Volume 1, pp. 128–137. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez, D.; Lutz, M. Urban flood hazard zoning in Tucumán Province, Argentina, using GIS and multicriteria decision analysis. Eng. Geol. 2010, 111, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaitan, S.; ten Veldhuis, M.-C.; van de Giesen, N. Spatial Distribution of Flood Incidents Along Urban Overland Flow-Paths. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 3387–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horritt, M. A methodology for the validation of uncertain flood inundation models. J. Hydrol. 2006, 326, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.C.; Bates, P.D.; Dall’ Amico, J.T. Calibration of uncertain flood inundation models using remotely sensed water levels. J. Hydrol. 2009, 368, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Simonovic, S. A three dimensional fuzzy methodology for flood risk analysis. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2011, 4, 53–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billa, L.; Shattri, M.; Mahmud, A.R.; Ghazali, A.H. Comprehensive planning and the role of SDSS in flood disaster management in Malaysia. Disaster Prev. Manag. Int. J. 2006, 15, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chormanski, J.; Van de Voorde, T.; De Roeck, T.; Batelaan, O.; Canters, F. Improving Distributed Runoff Prediction in Urbanized Catchments with Remote Sensing based Estimates of Impervious Surface Cover. Sensors 2008, 8, 910–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunderlik, J.M.; Burn, D.H. Analysis of the linkage between rain and flood regime and its application to regional flood frequency estimation. J. Hydrol. 2002, 261, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essel, B. The application of GIS in mapping of flood hazard areas and assessing of risk in kumasi, Ghana. J. Energy Nat. Resour. Manag. JENRM 2017, 3, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.-H.; Salas, J.; Boes, D. Regional flood frequency analysis based on a Weibull model: Part 2. Simulations and applications. J. Hydrol. 2001, 242, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knebl, M.R.; Yang, Z.-L.; Hutchison, K.; Maidment, D.R. Regional scale flood modeling using NEXRAD rainfall, GIS, and HEC-HMS/RAS: A case study for the San Antonio River Basin Summer 2002 storm event. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 75, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merwade, V.; Cook, A.; Coonrod, J. GIS techniques for creating river terrain models for hydrodynamic modeling and flood inundation mapping. Environ. Model. Softw. 2008, 23, 1300–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Shafie, M. Flood hazard assessment for cloud prone rainy areas in a typical tropical environment. Disaster Adv. 2009, 2, 7–15. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmati, O.; Zeinivand, H.; Besharat, M. Flood hazard zoning in Yasooj region, Iran, using GIS and multi-criteria decision analysis. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2017, 7, 1000–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, J.; Lu, X.X. Remote sensing and GIS-based flood vulnerability assessment of human settlements: A case study of Gangetic West Bengal, India. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 3699–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; Pradhan, B.; Hassan, A.M. Flash flood risk estimation along the St. Katherine road, southern Sinai, Egypt using GIS based morphometry and satellite imagery. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portugués-Mollá, I.; Bonache-Felici, X.; Mateu-Bellés, J.F.; Marco-Segura, J.B. A GIS-Based Model for the analysis of an urban flash flood and its hydrogeomorphic response. The Valencia event of 1957. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 582–596. [Google Scholar]
- Coumou, D.; Rahmstorf, S. A decade of weather extremes. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Aadhar, S.; Shah, H.L.; Mishra, V. Projected Increase in Hydropower Production in India under Climate Change. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, H.J.; Cooley, D.; Sain, S.R.; Thurston, M. Detecting change in UK extreme precipitation using results from the climateprediction.net BBC climate change experiment. Extremes 2010, 13, 241–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundzewicz, Z.; Kanae, S.; Seneviratne, S.; Handmer, J.; Nicholls, N.; Peduzzi, P.; Mechler, R.; Bouwer, L.M.; Arnell, N.; Mach, K.; et al. Flood risk and climate change: Global and regional perspectives. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkarim, A.; Gaber, A.F.D. Flood Risk Assessment of the Wadi Nu’man Basin, Mecca, Saudi Arabia (During the Period, 1988–2019) Based on the Integration of Geomatics and Hydraulic Modeling: A Case Study. Water 2019, 11, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shinnawy, I.; Bestawy, A.; Tahawy, T.E. Assessment and Management of Flash Floods for Sustainable Development in Al-Sail Al Kabir Area, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2017, 12, 2807–2814. [Google Scholar]
- Elkhrachv, I. Flash Flood Hazard Mapping Using Satellite Images and GIS Tools: A case study of Najran City, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). Egypt. J. Remote. Sens. Space Sci. 2015, 18, 261–278. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, H.O.; Al-Juaidi, F.H.; Al-Othman, A.; Al-Dousary, I.; Fadda, E.; Jamal-Uddeen, S.; Elhassan, A. Flood hazards in an urbanizing watershed in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2014, 7, 702–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Karim, A.A.A. Effect of spatial changes of urban growth and land uses on increasing flood risks in the Saudi City: Case Study of Ha’il city Using Geographical Information Systems and Remote Sensing (GIS & RS). Arab. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. Saudi Geogr. Soc. 2013, 6. Available online: http://abjdh.com/mag/wp-content/uploads/2016/12/ABSTRACTSISSUE12622014Last.pdf (accessed on 28 February 2019).
- Al-Ghamdi, K.; Elzahrany, R.; Mirza, M.; Dawod, G. Impacts of urban growth on flood hazards in Makkah City, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Water Resour. Environ. Eng. 2012, 4, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- El Alfy, M. Assessing the Impact of Arid Area Urbanization on Flash Floods Using GIS, Remote Sensing, and HEC-HMS Rainfall–Runoff Modeling. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 1142–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shwehdi, M.H. Reliable Maps of LightningThunderstorms for Saudi Arabia. IEEE Ransactions Power Deliv. 2006, 21, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qari, M.H. Geomorphology of Jeddah Governate, with emphasis on drainage systems JKAU. Earth Sci. 2009, 20, 93–116. [Google Scholar]
- Subyani, A.M.; Qari, M.H.; Matsah, M.E.; Al-Modayan, A.A.; Al-Ahmadi, F.S. Utilizing Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques to Reduce Hydrological and Environmental Hazards in some Wadis, Western Saudi Arabia (JeddahYanbu); Project No. APR 25/101; King Abdulaziz City for Sciences and Technology: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Subyani, A. Hydrologic behavior and flood probability for selected arid basins in Makkah area, western Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2010, 4, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledraa, T.; Al-Ghamidi, A.M. Planning and Management Issues and Challenges of Flash Flooding Disasters in Saudi Arabia: The Case of Riyadh City. J. Archit. Plan. 2020, 32, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashammari, E.Z.; Ruslan, R.B.; Int Abdurrahman, A.; Abdulkadir, M. Flash flood causes in Ha’il city kingdom of Saudi Arabia using Remote Sensing data and GIS. J. Crit. Rev. 2020, 7, 144–153. [Google Scholar]
- Alamri, Y.A. Rains and floods in Saudi Arabia. Crying of the sky or of the people? Saudi. Med. J. 2011, 32, 311–313. [Google Scholar]
- Alqahtani, F.; Qaddah, A.A. GIS digital mapping of flood hazard in Jeddah–Makkah region from morphometric analysis. Arabian J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Saud, M. Flood Control Management for the City and Surroundings of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia; The Springer Natural Hazards: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Aldosary, A.S.; Nahiduzzaman, K.M.; Reza, I. Vulnerability of flash flooding in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Nat. Hazards 2016, 84, 1807–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, S.; Radhakrishnan, N. Flood hazard delineation in an ungauged catchment by coupling hydrologic and hydraulic models with geospatial techniques—A case study of Koraiyar basin, Tiruchirappalli City, Tamil Nadu, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansar, A.; Naima, A. Mapping of Flood Zones in Urban Areas through a Hydro-climatic Approach: The Case of the City of Abha. Earth Sci. Res. 2021, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J. Geospatial-based soil variability and hydrological zones of Abha semi-arid mountainous watershed, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanean, H.; Almazroui, M. Rainfall: Features and Variations over Saudi Arabia, A Review. Climate 2015, 3, 578–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Menaa el Amri, A. Pedological Characteristics of the Soil in Wadi Bisha. Master’s Thesis, King Saoud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Scipal, K.; Scheffler, C.; Wagner, W. Soil moisture-runoff relation at the catchment scale as observed with coarseresolution microwave remote sensing. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2005, 9, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milzow, C.; Kgotlhang, L.; Kinzelbach, W.; Meier, P.; Bauer-Gottwein, P. The role of remote sensing in hydrological modelling of the Okavango Delta, Botswana. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioresita, F.; Puissant, A.; Stumpf, A.; Malet, J.-P. A Method for Automatic and Rapid Mapping of Water Surfaces from Sentinel-1 Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, H.; Najafzadeh, M. Flood Risk Mapping by Remote Sensing Data and Random Forest Technique. Water 2021, 13, 3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, H.; Esmaeily, A.; Najafzadeh, M. Flood monitoring by integration of Remote Sensing technique and Multi-Criteria Decision Making method. Comput. Geosci. 2022, 160, 105045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheater, S.; Bell, N. Northern Oman flood study. Proc. Inst. Civ. Engrs 1983, 2, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. Urban Hydrology for Small Watersheds; US Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Services, Conservation Engineering Division: London, UK, 1986; 164p.
- Gabr, S.S.; Alkhaldy, I.A.; El-Saoud, W.A.; Habeebullah, T.M. Flash flood modeling and mitigation of Al-Hussainiyah area, Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagha, M.O.; Gutub, S.A. Estimation of nrcs curve number from watershed morphometric parameters: A case study of Yiba watershed in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. 2016, 7, 247–265. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Singh, V. Long-term hydrological simulation based on the Soil Conservation Service curve number. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 1291–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheater, H.S.; Larentis, P.; Hamilton, G.S. Design rainfall characteristics for south-west of Saudi Arabia. In Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers, Part 2; Institution of Civil Engineers: London, UK, 1989; pp. 517–538. [Google Scholar]
- Sadek, M.; Li, X.; Mostafa, E.; Dossou, J.F. Monitoring flash flood hazard using modeling-based techniques and multi-source remotely sensed data: The case study of Ras Ghareb City, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).