Abstract
This scoping review identifies the roles of non-textual elements and how these roles have changed in sustaining the teaching and learning of English as an additional language (EAL) in the last five years. Much of the research regarding non-textual elements has shown that they have significantly contributed to learners’ motivation, active participation, and communication. However, a systematic synthesis of how these roles have changed over the last five years, in terms of the types of non-textual elements used as a result of the growing access to technologies, is lacking. Following Arksey and O’Malley’s framework, a scoping review of 50 studies from 2018 to 2022 was carried out, filtered from the ERIC, Scopus, and Google Scholar databases. The studies were compiled considering two characteristics: the roles and types of non-textual elements in enhancing English as a second language (ESL)/English as a foreign language (EFL) in classrooms. The results show that 29 out of the 50 studies used non-textual elements in complementary roles and 21 studies used them in supplementary roles to enhance the teaching and learning of ESL and EFL in recent years. Educators prefer to utilize non-textual elements in dominantly complementary roles rather than supplementary roles to create a sustainable EAL (ESL and EFL) learning environment. Non-textual elements help learners capture and recall information far longer than texts alone. A revised dual method using non-textual elements in a combination of both supplementary and complementary roles, and also utilizing both technologically driven and traditional approaches, is the way forward in sustaining effective EAL learning
1. Introduction
For the last few decades, the use of non-textual elements has been regarded as an effective teaching approach to support English as a second language (ESL)/English as a foreign language (EFL) learners in language learning. However, few studies have examined how non-textual elements interact with textual elements as a combined strategy for instructional resources and approaches in language classrooms. Recently, people have considered the use of non-textual elements differently, despite the emergence of technology in this 21st-century world. Past studies have revealed that the growth of technology also affects the types of non-textual elements used as teaching aids and approaches among educational practitioners. Ideologies and how teachers use non-textual elements have changed the teaching and learning processes in language classrooms.
Over the past five years, non-textual elements, such as photos, videos, graphics, pictures, multimedia, and flashcards have played supplementary and complementary roles in improving ESL and EFL learners’ learning performance. Supplementary materials, which are defined as materials designed to be used in addition to the core materials of a course [1], are significant in encouraging and sustaining learners’ effective learning outcomes [2]. “Supplementary” means that the non-textual element is not key to the process; it is something additional in the content. In other words, non-textual elements are used in supplementary ways to enhance learning, with extra value added to the learning process, and to improve or foster significant positive outcomes. “Complementary” is defined as a method or a combination of methods used to enhance or emphasize the qualities of another individual [3]. It refers to information that is built in to reinforce the learning process. In education, teachers often create and adapt complementary materials to enhance their lessons. The use of suitable supplementary materials has always been the main focus of language teaching [4]. Visualization formats can vary and complement motivation, memory, understanding, and attention [5]. Thus, the roles of non-textual elements positively contribute to ESL and EFL learning and the teaching process.
Past studies have reported that English educators or teachers often search for more impactful approaches to improve language classrooms. Language learning has become more varied as a result of incorporating non-textual elements and technology into class activities. In education studies, non-textual elements, such as pictures, photos, flashcards, videos, and infographics, have a vital function in supporting learning among English as a second language (ESL) and English as a foreign language (EFL) learners. Several studies conducted in education from primary to tertiary levels [6,7,8,9,10] have defined visuals as anything one person observes within a given frame. Our world is visually oriented, and most responses are stimulated non-verbally, with verbal information better processed through visual cues. The method that the learners use to observe and classify the information from their environment is defined as visual proficiency.
Moreover, Stafford (2011) defines a non-textual element as historical material which covers items that are not written and includes still and moving images, audio recordings, artefacts, and places [11]. Non-textual elements can also be characterized as illustrations that involve moving images. Collin MacArthur’s theory of iconography (1972; pp. 23–24), as cited in [12], also discusses how images on screen create a sense of genre for the audience. He points out that the ongoing forms of visual imagery support them in their understanding of the characters and elements of the plot and enable the audience to recognize swiftly the type of film they are watching. Similarly, moving images represented in audio-visual aids or videos, which are widely used by educators globally, act as a tool for enhancing and engaging students’ interest in learning. One of the non-textual elements commonly used in language classrooms is video. Teachers and students have various multimedia tools, such as YouTube videos, available as teaching and learning aids. Thus, the use of video for learning has been widely used among ESL and EFL teachers to arouse learners’ interest in learning.
The Importance of Non-Textual Elements
The use of non-textual elements in learning positively impacts learners’ comprehension of content, generates thoughts and ideas, and helps them to overcome learning difficulties through the use of video, pictures, flashcards, and other technologies. The roles of non-textual elements and how they are used can be highly engaging in the educational structure to develop ESL and ESL classrooms [13]. In recent years, non-textual elements in teaching strategies and approaches have been used extensively alongside education publications. The use of non-textual elements in language classrooms is a versatile method that can be utilized to cope with 21st-century learning.
Non-textual elements have been extensively used in lessons to improve learning. The use of illustrations as visual prompts can attract the student’s interest, encourage learning, and develop the growth of their critical intellectual support (Duchastel and Waller, 1979; Levie, 1987; Winn, 1982), as cited in [14]. In other words, the learners are easily engaged in an active learning process through using illustrations, and it can facilitate their understanding of a particular topic effectively. In this way, implementing non-textual elements as a teaching approach motivates the learners to desire to learn more. Furthermore, Nor Pazilah et al. (2019) reports that the use of visual aids can be adapted to modern and traditional ways of teaching, which could depend on students’ preferences and the school environment [15]. Many different types of non-textual elements support materials, classifying them according to form and function. Pictures with multimedia methods were used most in education articles between 2018 and 2022. The author of “Using Non-Textual Sources: A Historian’s Guide”, Armstrong (2016) also points out that the use of the Internet has revolutionized the way learners study using non-textual sources [12]. For instance, Abdul Samat and Abdul Aziz (2020) report that the use of multimedia in language learning is impactful in developing indigenous pupils’ comprehension skills [16]. Multimedia methods assist learners in visualizing information immediately while they are not overly dependent on their prior knowledge.
The issues related to incorporating non-textual elements into learning are widely known in ESL and EFL language classrooms. Most ESL and EFL learners still encounter challenges in mastering the four main language skills. For instance, Ahmad (2019) revealed that lack of student engagement is one of the causes of the reading comprehension problems encountered by EFL learners [17]. Poor competency in reading comprehension influences learners’ understanding of what they read and learn. Furthermore, reading strategies, lack of motivation, and unavailability of good materials are also factors that negatively affect EFL learners during reading comprehension [18]. Some studies have also reported that most ESL and EFL learners experience difficulty because of their restricted word choice [18,19,20]. In addition, the lack of motivation among ESL and EFL learners to speak the target language is one of the reasons why students cannot speak the English language in the language classrooms. Numerous studies have observed that motivation plays a fundamental role in speaking the English language [21,22,23]. One complaint that learners have is that they cannot speak from memory and are not motivated to express themselves. This complaint is supported by Leong and Mosaumeh (2017) who observed that learners do not have enough material for the subject matter their teachers choose and thus falter in expressing themselves [24]. Non-textual elements are one of the alternative approaches that language educators use to address this problem.
This analysis is driven by two questions as follows: “What are the roles of non-textual elements in the teaching of ESL and EFL?” and “How do the roles of non-textual elements change in sustaining the teaching and learning of ESL and EFL in relation to the types of non-textual elements used in language classrooms?” The importance of this review is emphasized as follows: First, the roles of non-textual elements as learning tools for supporting ESL and EFL learners in supplementary and complementary ways are addressed. They act as reinforcement, stimulus, and prompt to facilitate and improve the learners’ learning. Second, given the lack of emphasis on non-textual elements with the advance in technologies, the roles of non-textual elements have changed the types of these elements being utilized by educators in language classrooms.
2. Materials and Methods
In this review, we employed the most recent scoping review framework from Arksey and O’Malley (2005), which will also be discussed in the subsections below [25]. The methodology based on Arksey and O’Malley (2005) was used to analyze studies on the roles of non-textual elements and methods used in implementing non-textual elements in enhancing the learning of ESL and EFL learners in language classrooms. Five stages were employed in this scoping review: identifying the research question; identifying the relevant studies; study selection; charting the data; and summarizing and reporting the results [25]. Furthermore, the Preferred Reporting of Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) procedures presented by [25] were also used in planning and in selecting articles.
2.1. Scoping Review Research Questions
The review questions are used as the initial step in defining the analytical criteria, and the principles used in solving this question were described to explain the focus of this study [25]. The review questions consist of the following: “What are the roles of non-textual elements in the teaching of ESL and EFL?” and “How do the roles of non-textual elements change in sustaining the teaching and learning of ESL and EFL in relation to the types of non-textual elements used in language classrooms?”. In this review, we generalized the roles and the types of non-textual elements integrated to support ESL and EFL learners’ language learning. A comprehensive approach to the review limitations was adopted based on the characteristics of Arksey and O’Malley (2005). To comprehend the scope of studies in this field, the abstracts and literature aspects of articles were revised based on the selection criteria for research papers.
2.2. Relevant Studies
Previous studies were identified through keyword searches from three applicable databases: Scopus, ERIC, and Google Scholar. The selected databases limit access to numerous journal articles, and some allow downloading. Even though compiled articles from 2018 and 2022 were selected for this study, some related articles from 2017 were also used to gain more understanding of the topics related to the study. The search terms used for this review were as follows:
- i.
- The role of non-textual elements in ESL/EFL learning (104 results from Google Scholar; 7481 results from ERIC; 31 results from Scopus).
- ii.
- Using pictures in ESL/EFL learning (23,100 results from Google Scholar; 3452 results from ERIC; 64 results from Scopus);
- iii.
- Using flashcards in ESL/EFL learning (2930 results from Google Scholar; 2214 results from ERIC; 8 results from Scopus);
- iv.
- Using infographic in ESL/EFL learning (219 results from Google Scholar; 2203 results from ERIC; 1 result from Scopus);
- v.
- Using video in ESL/EFL learning (16,900 results from Google Scholar; 5702 results from ERIC; 158 results from Scopus);
- vi.
- Using visuals in ESL/EFL learning (18,100 results from Google Scholar; 4756 results from ERIC; 127 results from Scopus).
2.3. Study Selection: Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The keyword searches generated 89,850 results as shown in Table 1. And includes redundant articles found from many searches. From the results, 37,798 articles were excluded, with 31,551 articles with full-text access remaining. The compiled articles were selected using two stages of evidence screening, following Moher et al. (2009) [26]. In the first stage, the titles and abstracts of the identified articles were screened. The abstracts were obtained to ascertain their relevance to the present topic. In the second stage, the full texts of the reviewed articles were screened. The inclusion criteria required articles retrieved from peer-reviewed publications, which were written between 2018 and 2022. Following this, the articles from 2018 to 2022 were selected for open-access criteria. Time-range decisions are important from a practical perspective in scoping reviews. Despite the topics of the articles being presented in different formats, an extra inclusion requirement was applied to ensure that the articles were relevant to the scope of the review. Therefore, all the theoretical articles were included in the review, such as the literature reviews and recommendations based on cited research, and the empirical articles, such as qualitative, quantitative, action research, or mixed-methods studies. The exclusion criteria were expressed during the article screening process to remove those articles that did not precisely emphasize the roles and methods used in non-textual elements as supporting materials in sustaining the learning of ESL and EFL learners. In this stage, an article was excluded from the review if exclusion criteria were fulfilled: first, if the article was not published between 2018 and 2022; second, if the article did not describe non-textual elements’ roles in language learning activities. The articles were screened based on how the roles of non-textual elements changed in sustaining the teaching and learning of ESL and EFL in relation to the types of non-textual elements used in language classrooms. After applying the criteria, 50 articles were selected to be included in the current review.

Table 1.
Summary of the search terms.
2.4. Charting the Data
After the selection process, each article was classified according to its main issues and themes based on its research questions [25]. The articles were divided into three emerging types based on their methods: traditional methods, dual methods, and multimedia methods. Figure 1 shows a PRISMA 2009 flow diagram that explains the steps of identifying the relevant studies involved in this review.
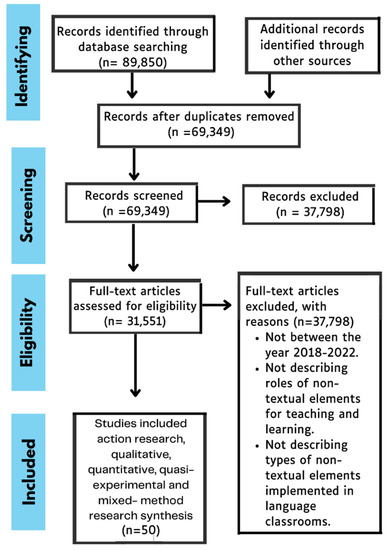
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram of the articles searches and study selection process (Moher, Liberati, Tetzlaff, Altman, and The PRISMA Group [26].
3. Results
A total of 50 articles were examined to investigate the two methods of addressing problems related to the use of non-textual elements in supporting the learning of ESL and EFL learners. Figure 2 shows the roles of non-textual elements in selected articles from 2018 to 2022. Table 2 provides a summary of the findings.
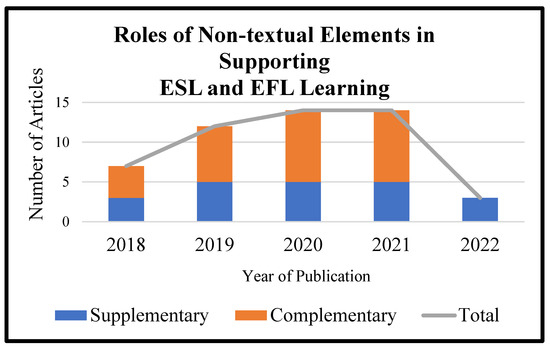
Figure 2.
Roles of non-textual elements in supporting ESL and EFL learning from 2018 to 2022.

Table 2.
Summary of the findings.
Based on the results illustrated in Figure 2 and Table 2, two methods of implementing non-textual elements in supporting ESL and EFL learners in language classrooms were identified: supplementary role and complementary role. Table 3 summarizes the 50 articles according to the year of publication, country, research design and sample, main findings, type of database from which the article was retrieved, types of non-textual elements used in the article, role of non-textual elements, and method used. The articles were predominantly from East Asia, the Middle East, South Asia, West Africa, South Africa, North America, Latin America, and Europe, published between 2018 and 2022, where authors used their first language and English as their second and foreign language.

Table 3.
Summary of information from the selected articles.
Based on these findings, the role of non-textual elements used in the retrieved articles were categorized into two characteristics: a supplementary role with 21 articles and complementary role with 29 articles. These characteristics play a vital role in learners’ language acquisition and influence the methods used to facilitate ESL and EFL language learning. Based on the type of non-textual elements studied, the fewest studies were found in relation to the use of multimedia, infographics, posters, and photographs as learning aids. Researchers tend to focus on using pictures and video in implementing non-textual elements as supporting materials in ESL and EFL classrooms.
Based on Table 4, studies on the use of multimedia in implementing non-textual elements have been utilized among educators in supporting ESL and EFL learning. Twenty-three studies endorsed the good engagement, interaction, and participation of ESL and EFL learners in learning through utilizing non-textual elements in a multimedia approach. The articles suggest that multimedia methods that include combining two or more methods or integrating ICT and using non-textual elements as learning instructional materials for language classrooms have been developed in sustaining language learning for the past five years. According to [65], the core of interactive learning is the independent acquisition of skills and knowledge by students under the guidance of a teacher, which can include student ICT skills. These multimedia methods using non-textual elements, such as Canva, digital posters, cartoon films, or videos, play a crucial role in motivating, engaging, and reinforcing learners to achieve positive learning outcomes.

Table 4.
Summary of methods used in implementing non-textual elements.
Twenty-two studies on the traditional methods of using non-textual elements were identified. Most of these articles used pictures, visual materials, infographics, posters, photographs, and graphics from language teachers and instructors, and their findings highly emphasized the important role of non-textual elements in supporting ESL and EFL learners in language classrooms, as suggested in many previous studies [7,8,9,15]. These articles described the treatment of non-textual elements in engaging learners in language learning through different types of media with illustrations. Furthermore, it is critical that students interact more with traditional lessons using non-textual elements during active learning.
Compared with multimedia methods and traditional or primary methods for implementing non-textual elements to support ESL and EFL learning, dual methods, such as the use of audio-visual elements or videos acting as moving images with audio in language classrooms, appeared in the fewest studies published between 2018 and 2022; for dual methods, there were only five studies, as indicated in Table 4. Dual methods combine two teaching methods to provide an impactful teaching approach for learners. Instructional materials that involve visual and audio-visual aids, concrete or non-concrete, are used by teachers to improve the quality of teaching and learning activities. The authors of “Implication of multimedia audio-visual aids in the English language classroom”, Wazeema and Kareema (2017) point out that multimedia audio-visual aids in the language learning classroom are important to increase interest in, knowledge of, and proficiency in the English language among students [66]. Nevertheless, dual methods are the least studied. No studies on dual methods were found for 2018. Furthermore, Inayah et al. (2022) observed that the usage of sequence pictures did not considerably increase EFL ability in respect of Indonesian tertiary students’ writing skills [64]. That study investigated the effectiveness of incorporating picture series for enhancing the student’s writing skills and comparing these with picture series introduced as the stimulus in a traditional method. No improvement was observed in the students’ writing performance after the treatment. In other words, the use of picture series in that study revealed the opposite results, as indicated in [7,15,58]. Students’ learning styles should be considered when incorporating non-textual elements in language classrooms. Educators should focus on producing instructional activities and developing learning materials that involve the entire body, providing students with interaction and experience depending on their learning styles [67]. Teachers need to identify students’ learning styles in order to provide an educational environment in which all of them can practice while simultaneously helping them improve their learning performance.
4. Discussion
In this section, the review questions are answered following our analysis and review of the 50 research papers.
RQ 1. What are the roles of non-textual elements in the teaching of ESL and EFL learning?
Non-textual elements, such as pictures, flashcards, infographics, motion pictures, or graphics, paint a thousand words in language learning. The question is, “What are the roles of non-textual elements in supporting ESL and EFL learners in language classrooms?” Similarly, in respect of practically any other teaching resource, non-textual elements can be used to enhance students’ motivation to learn and engage them in an active learning environment.
The importance of non-textual elements as a supplementary strategy must be recognized in the teaching and learning process, especially in ESL and EFL language classrooms. Studies have reported that non-textual elements have a positive impact on improving learners’ motivation and stimulating their active learning. Motivation has been extensively acknowledged as one of the main aspects influencing effective performance among ESL and EFL learners [68]. According to Gardner’s theory [69], motivation is the main aspect affecting learners’ cognition, and includes effort, willingness, and the desire to learn, as well as being the effect of their enjoyment of a certain task. Motivation is the primary driver for L2 learning and is probably the underlying factor. In addition, motivation is known as the main issue, given that high motivation usually leads to effective learning. For instance, the use of picture media improves learners’ motivation in learning English [58,59]. Through pictures, learners are encouraged to gain more information in language classrooms, particularly in terms of reading skills and vocabulary mastery.
The roles of non-textual elements in supporting language learning have been significant contributing factors to learner motivation and active participation in class activities and communication. The central idea of using learning materials in a supplementary way is to provide learners with extra resources to increase their interest and their motivation to learn [2]. Such experience is supported by [70], who points out that supplementary resources introduce the usage of real language via engaging and extended content, motivating and activating students in language learning through participation. In addition, Abbasi (2015) also remarks that the usage of supplementary materials helps learners improve their self-guided learning of English, bolstering comprehension in reading and various skills [71]. Furthermore, teachers should develop supplementary learning materials that will encourage learners and introduce contextualized and diversified teaching materials that can suit various types of learners [72].
Non-textual elements used in complementary strategies supporting ESL and EFL learning also contribute to positive learning outcomes. Non-textual elements play a significant role in engaging teachers and students to participate actively in the learning process. Generally, how a successful language classroom can further enhance learning depends on the degree of interesting, practical, realistic, and appealing instructional materials [64]. Effective non-textual elements provide students with opportunities in which to practice skills in new contexts with the help of visual, moving visual, or technology tools, which improve retention and help learners to see how different language skills are applied successfully. When ICT is used, student engagement is greatly increased [73], as it serves to attract their attention to learning.
The complementary role of using non-textual elements, such as visual elements, also helps learners capture and recall information longer than with texts alone. For instance, Singh et al. (2017) reported that students had positive experiences when using picture series in their guided writing activities [74]. The study reveals that the students encountered challenges when they were asked to write using only guided words and did not know what they should write. After using picture series in writing lessons, the students claimed they were interested in writing using pictures as visual aids. The technique also helped them to focus on the writing lessons. Wright (1989) observed that the experience of acquiring a target language will become more meaningful when visuals are significantly used as a stimulus related to learners’ lives [75]. Visuals also help activate the learners’ interest and motivation. They can also provide knowledge of the language context and a focused reference or stimulus [20]. Hence, visuals elements are crucial in supporting ESL and EFL learning efficiently.
RQ 2. How have the roles of non-textual elements changed in sustaining the teaching and learning of ESL and EFL in relation to the types of non-textual elements used in language classrooms?
The use of non-textual elements in enhancing ESL and EFL learners’ language learning also provides an interactive atmosphere in language classrooms. The growing access to technology has become an important aspect of enhancing language learning in ESL and EFL learners’ learning settings. Most educators use technology in their classroom teaching and learning activities because it plays a major role in motivating and enhancing students’ language learning [76]. The incorporation of non-textual elements with technology are both supplementary and complementary in nature, supporting ESL and EFL learning outcomes. One effective method recommended in this study is the multimedia method used in non-textual elements for teaching in language classrooms. Compared with the traditional method of using non-textual elements in language classrooms, the multimedia method is a supplementary way of engaging and motivating students in learning via the integration of ICT. The learning process becomes engaging and collaborative through the emergence of technology in interactive classroom settings [77]. In this competitive world, mastering the English language is crucial to increasing the competence of ESL and EFL learners
The incorporation of user-friendly technology in teaching and learning has made a significant contribution to enhancing language learning, making it more interactive among the learners, and enabling the learning to go beyond the walls of the classroom. Past studies have revealed that English teachers often explore more impactful approaches to teaching ESL and EFL in classrooms. Educators are encouraged to create novel modern methods to improve on the shortcomings of normal teaching. They should change plain content into lively, engaging, audio-visual, and dynamic language-learning content. The impact of incorporating technology and non-textual elements into teaching is positive. They stimulate learners’ thinking, inspire their paths of thinking, and strengthen their discovery capacity and problem-solving abilities. Even though the aforementioned non-textual elements can result in positive experiences in respect of their uses, education practitioners should be aware of whether the types of materials selected suit the learners’ interests and needs in language lessons. For instance, Abdul Samat and Abdul Aziz (2017) pointed out that educators should note students’ interests before choosing multimedia content to avoid a mental block in understanding the materials [16]. In considering the roles of non-textual elements in supporting ESL and EFL learning, educators and practitioners also need to develop suitable and appropriate types of non-textual elements with which to prepare visually rich materials.
5. Conclusions
Overall, we examined 50 studies relating to the roles of non-textual elements and how they have changed in sustaining the teaching and learning of ESL and EFL in relation to the types of non-textual elements used in language classrooms over the past 5 years. In this scoping review, 29 out of 50 studies employed non-textual elements in complementary roles and 21 studies employed them in supplementary roles to enhance the teaching and learning of ESL and EFL. English educators prefer to utilize non-textual elements in dominantly complementary roles rather than supplementary roles to create a sustainable EAL (ESL and EFL) learning environment. The emphasis on the roles of non-textual elements in supporting ESL and EFL learning is observed to be timely in this review. Using non-textual elements is known as an effective teaching approach with which to support and sustain an ESL and EFL learning environment. Nonetheless, few studies have examined how non-textual elements interact with textual elements as a combined strategy for instructional resources and approaches in language classrooms. Past studies have revealed that the growth of technology has affected the types of non-textual elements being used as teaching aids and approaches among educational practitioners. The reviewed and analyzed studies have shown the use of non-textual elements in a complementary role in ESL and EFL language classrooms, and we have scrutinized their significant role in stimulating and prompting learning; their use in a supplementary role provides reinforcement.
This review provides insights that can help curriculum planners, educators, and researchers to understand the role of non-textual elements and the types of non-textual elements in supporting EAL learners in language classrooms. Having an awareness of the importance of non-textual elements in learning is crucial for learners as they can acquire and improve their learning efficiently. Future studies should focus on certain aspects, such as when and how to use non-textual elements in language classrooms, to provide an overview of the future of teaching using non-textual elements in language classrooms. Lessons should be prepared based on learners’ familiarity with the lessons, and their interest and motivation in learning should be triggered by technology integration. In this way, educators or teachers can completely utilize technology in ESL and EFL language classrooms, and learners can be provided with an interesting, fun, and proactive environment.
This review is however, not without its limitations. We used precise inclusion and exclusion criteria via three databases: Google Scholar, ERIC, and Scopus. This was done to obtain specific articles and verify their relevance to the scope of research. Particular inclusion and exclusion criteria have excluded some articles from review. Potential articles from other databases like Research Gate and SAGE Journals could be included for more comprehensive findings.
We also examined studies from several countries, such as Asian countries, i.e., Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand, China, Japan, South Korea, India, Sri Lanka; Middle Eastern countries, i.e., Iran, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Jordan, UAE and Egypt; African countries, i.e., West Africa and South Africa; one European country, i.e., Turkey; and North American and Latin American countries, i.e., USA and Colombia. Nevertheless, 52% of the reviewed articles were from Southeast Asian countries, namely Malaysia, Indonesia, and Thailand, showing limited coverage of other countries, such as the USA and European countries. Limited coverage of studies in Malaysia that focus on primary education students’ perception of using non-textual elements in ESL and EFL language classrooms was also observed. Hence, most studies were from Asian countries. To present an extensive and inclusive conclusion, articles from other countries should be included as they may offer new perspectives on the data analyzed.
The findings emphasized the roles of non-textual elements and how these have changed in sustaining the teaching and learning of ESL and EFL in relation to the types of non-textual elements used in language classrooms. These critical findings provide a clear educational proposal for future language curriculum development. This review also highlights and reiterates the importance of non-textual elements in improving the learning efficiency and acquisition of ESL and ESL learners.
For future research, a revised dual approach of combining technology and traditional approaches in language learning would enable learners to experience more enhanced learning. Using non-textual elements in both roles—complementary and supplementary—will further sustain learning. This is the way forward. Future research should also look into the impact of non-textual elements on language learning and examine the factors that promote or inhibit the use of such elements in the English language classroom.
In future research, all suggestions should be considered to balance practicality with available resources in revealing further evidence and relevant findings in the scoping review.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.H.T. and B.L.; methodology, K.H.T.; validation, N.-E.M.S., M.H., N.M. and K.H.T.; formal analysis, K.H.T. and B.L.; investigation, N.-E.M.S.; resources, N.-E.M.S., M.H. and N.M.; writing—original draft preparation, K.H.T. and B.L.; writing—review and editing, K.H.T. and B.L.; visualization, N.M.; supervision, K.H.T.; funding acquisition, M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Hubei University of Economics, China, grant number XJ20BS38.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tomlinson, B. Materials Development in Language Teaching, 2nd ed.; Cambridge Univiversity Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Available online: https://assets.cambridge.org/97805217/62854/frontmatter/9780521762854_frontmatter.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Dodd, A.; Camacho, G.; Morocho, E.; Paredes, F.; Zuniga, A.; Pinza, E.; Toro, L.; Vargas, A.; Benitez, C.; Rogers, S. The Use of Supplementary Materials in English Foreign Language Classes in Ecuadorian Secondary Schools. Engl. Languange Teach. 2015, 8, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Free Dictionary. Available online: https://www.thefreedictionary.com/complementary (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Barzan, P.; Kooti, M.S.; Heidary, B. The Impact of Supplementary Materials on Students’ English Language Learning and Cultural Conceptualization. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Humanities, Social Sciences and Lifestyle, Nice, France, 17–19 June 2022; pp. 1–10. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/351985813 (accessed on 12 July 2022).
- Eppler, M.J. A Comparison between Concept Maps, Mind Maps, Conceptual Diagrams, and Visual Metaphors as Complementary Tools for Knowledge Construction and Sharing. Inf. Vis. 2006, 5, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelia, L.C.H.; Abidin, M.J.Z. Young ESL learners’ perception on the effects of using digital storytelling application in English language learning. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2018, 26, 179–198. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, Y.L.P.K.; Yunus, M.M. The Use of Pictures in Improving Students’ Writing. Mod. J. Lang. Teach. Methods 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasibuan, S.; Pricilia, G.M.; Waruwu, S.M. The effect of using flashcard media on students’ vocabulary mastery. J. Liner Inst. Pendidik. Tapanuli Selatan 2020, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mathura, S.; Zulu, F.Q.B. Using flashcards for English second language creative writing in Grade 1. Read. Writ. 2021, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.; Jabeen, I. Prompting Cognition for Creativity in EFL Context: An Experimental Study on Use of Infographics for Teaching Writing Skill. J. Lang. Linguist. Stud. 2022, 18, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, T. Teaching Visual Literacy in the Primary Classroom, Comic Books, Film, Television and Picture Narratives; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, C. Introduction. In Using Non-Textual Sources: A Historian’s Guide; Bloomsbury Academic: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Halwani, N. Visual Aids and Multimedia in Second Language Acquisition. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2017, 10, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, L. L2 Writing: Using Pictures as a Guided Writing Environment. In Proceedings of the Rocky Mountain Modern Language Association Conference, New York, NY, USA; 1994. No. Ed 386951. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED386951.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2022).
- Nor Pazilah, F.; Hashim, H.; Yunus, M.M.; Rafiqah Rafiq, K.M. Improving narrative writing in ESL Classroom using picture series. J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2019, 4, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul Samat, M.S.; Abdul Aziz, A. The Effectiveness of Multimedia Learning in Enhancing Reading Comprehension among Indigenous Pupils. Arab World Engl. J. 2020, 11, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.Z. Digital Posters to Engage EFL Students and Develop Their Reading Comprehension. J. Educ. Learn. 2019, 8, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, A.; Saed, A.; Shahi, Y. The Effect of Using Video Technology on Improving Reading Comprehension of Iranian Intermediate EFL Learners. Adv. Lang. Lit. Stud. 2018, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kondal, B.; Prasad, V.D. Poster Presentations for Promoting Vocabulary Learning among Tertiary Level Students. Int. J. Engl. Lit. 2019, 9, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, D.S.M.; Albakri, M.M.H.; Adnan, M.A.A.; Shaq, A.H.M.; Shah, M.S.Y. The Application of Visual Vocabulary for ESL Students’ Vocabulary Learning. Arab. World Engl. J. 2020, 11, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agung, A.; Arsana, P.; Maharani, P. The Use of Flashcard in English Vocabulary Learning. JOSELT (J. Stud. Engl. Lang. Teach.) 2021, 2, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Huwari, I.F. Problems faced by Jordanian undergraduate students in speaking English. Int. J. Innov. Creat. Chang. 2019, 8, 203–217. [Google Scholar]
- Yeboah, S.; Amoah, J. The speaking difficulties of Chinese EFL learners and their motivation towards speaking the English language. J. Lang. Linguist. Stud. 2021, 7, 56–69. [Google Scholar]
- Leong, L.M.; Masoumeh, S.M. An Analysis of Factors Influencing Learners’ English Speaking Skill. Int. J. Res. Engl. Educ. 2017, 2, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework. Int. J. Soc. Res. Methodol. Theory Pract. 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jang, B.G.; Roy-Campbell, Z. Optimum input mode in the modality and redundancy principles for university ESL students’ multimedia learning. Comput. Educ. 2018, 127, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, L.N.H. Utilizing Jolly Phonics Songs and Flash Cards to Teach Iraq EFL Primary School Pupils’ Language. PalArch’s J. Archaeol. Egypt/Egyptol. 2020, 17, 16701–16709. Available online: https://archives.palarch.nl/index.php/jae/article/view/7534/7118 (accessed on 21 May 2022).
- Yawiloeng, R. Second Language Vocabulary Learning from Viewing Video in an EFL Classroom. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2020, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T. The impact of written visual materials in the development of speaking skills in English language among secondary level students. J. Lang. Linguist. Stud. 2021, 17, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Lornklang, T. The Use of Picture-word Inductive Model and Readers’ Theater to Improve Chinese EFL Learners’ Vocabulary Learning Achievement. Adv. Lang. Lit. Stud. 2021, 12, 120. Available online: https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1307957 (accessed on 21 May 2022). [CrossRef]
- Utami, Y.; Suriyani, D. Students’ Motivation in Writing Class Using of Canva: Students’ Perception. Engl. J. 2021, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winasih, W.W.; Cahyono, B.Y.; Prayogo, J.A. Effect of Project-Based Learning Using E-Poster on Indonesian EFL Students’ Speaking Ability across Personality Types. Arab World Engl. J. 2019, 10, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicen, H.; Beheshti, M. Assessing perceptions and evaluating achievements of ESL students with the usage of infographics in a flipped classroom learning environment. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2022, 30, 498–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, J.; Cuellar, M. The Use of Plotagon to Enhance the English Writing Skill in Secondary School Students. Profile Issues Teach. Prof. Dev. 2019, 21, 139–153. [Google Scholar]
- Aprianto, D.; Syarifaturrahman, W.K. ESL learners’ perception on the use of the graphic organizers (Gos) as class presentation strategies. Expo. J. Pendidik. Bhs. Ingg. 2020, 9, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madzlan, N.A. Use of Video Blogs in Alleviating Public Speaking Anxiety among ESL Learners. J. Educ. e-Learn. Res. 2020, 7, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olagbaju, O.O.; Popoola, A.G. Effects of Audio-visual Social Media Resources-supported Instruction on Learning Outcomes in Reading. Int. J. Technol. Educ. 2020, 3, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.A.L.; Lee, B.C.; Adi Kasuma, S.A.; Ganapathy, M. Picture superiority effect: Using images for vocabulary enhancement among year one Malaysian ESL learners. Pertanika J. Soc. Sci. Humanit. 2020, 28, 177–196. [Google Scholar]
- Altakhaineh, A.R.M.; Shahzad, N.M. Using pictures in teaching metaphorical expressions to Arabic-speaking EFL learners. Asian J. Appl. Linguist. 2020, 7, 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, U.; Chinokul, S. Effect of the scaffolded reading experience using a graphic novel on the English reading comprehension and reading motivation of Thai EFL students. Learn J. Lang. Educ. Acquis. Res. Netw. 2020, 13, 158–175. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.A. The impact of using Readers Theatre on improving EFL Reading prosody among Primary Stage Pupils. J. Fac. Educ. 2020, 122, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansyah, N. The influence of flash card toward students’ English vocabulary mastery during COVID-19. J. Syntax Fusion 2021, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahardika, I.G.N.W.; Widiati, U.; Bhastomi, Y.; Suryanti, N. Camera Roll, Action! Non-specialist Undergraduate English Learners’ Perceptions of Using Video Production in Learning English Camera Roll, Action! J. Univ. Teach. Learn. Pract. 2021, 18, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaid, A. ICT multimedia learning affordances: Role and impact on ESL learners’ writing accuracy development. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saed, H.A.; Haider, A.S.; Al-Salman, S.; Hussein, R.F. The use of YouTube in developing the speaking skills of Jordanian EFL university students. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynar, N.; Sadik, O. The Effects of Authentic and Interactive Video Tasks on Students’ Extra Listening Practices. J. Theor. Educ. Sci. 2021, 14, 291–307. Available online: https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1307354.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2022). [CrossRef]
- Tamer, M.A.A. The Effectiveness of Using Cartoon Films in Enhancing Primary School EFL Pupils’ Writing Skills. 2021. Available online: https://jsep.journals.ekb.eg/article_215243_8827c023d8c13fd427bd256a4c667337.pdf (accessed on 18 June 2022).
- Durongbhandhu, N.; Suwanasilp, D. Effectiveness of Multimodal Glossing Reading Program on English Vocabulary Acquisition. Engl. Lang. Teach. 2021, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damayanti, L.S.; Nitiasih, P.K.; Santosa, M.H. Character-Based Extensive English Reading Materials Development of English Teachers and Students of Secondary Education In Bali: Needs Analysis. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on English Across Culture, Bali, Indonesia, 19–20 October 2019; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334507492 (accessed on 21 June 2022).
- Hamzah, A. Picture Word Inductive Model in Vocabulary Learning. Engl. Educ. Appl. Linguist. J. 2018, 138, 138–141. Available online: https://journal.institutpendidikan.ac.id/index.php/eeal/article/view/139/161 (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Yeom, E.Y. How Visual Thinking Strategies Using Picture Book Images Can Improve Korean Secondary EFL Students’ L2 Writing. Engl. Teach. 2018, 73, 23–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyani, L.; Solihat, D.; Hanifah, I. The Influence of Picture and Picture Model on Indonesian Writing Skills. Indonesia J. Learn. Instr. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.; Pandian, A.; Rethinasamy, S.; Tan, D.A.L. Effects of PWIM in the ESL Classroom: Vocabulary Knowledge Development Among Primary Malaysian Learners. 3L Southeast Asian J. Engl. Lang. Stud. 2019, 25, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M. The Impact of Visual Literacy Awareness Education on Verbal and Writing Skills of Middle School Students. Int. J. Educ. Lit. Stud. 2020, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, B. Cognitive processing of second language idiom comprehension: A comparative study. J. Lang. Linguist. Stud. 2019, 15, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, S. Cartoons as an Authentic Supplementary Teaching Tool in English as a Second Language Classrooms. Adv. Lang. Lit. Stud. 2019, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdana, H.; Nor Hasanah, I. The Effectiveness of Scanning Technique in Teaching Reading At the Eighth Grade of Smp Negeri 5 Alalak School Year 2019/2020. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Social Sciences & Humanity, Economic, and Politics, South Sulawesi, Indonesia, 16–17 October 2020; Volume 1, pp. 137–139. [Google Scholar]
- Almekhlafy, S.S.A.; Alqahtani, A.A.J. The visual memory development technique: A remedial and pre-reading activity to enhance EFL learners’ Motivation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.; Son, J.B. English Vocabulary Learning with Simplified Pictures. Electron. J. Engl. A Second. Lang. 2020, 24, n3. [Google Scholar]
- Ngalang, M.; Yamat, H. Generating Ideas for Writing Using Photography among Level 2 Rural Primary ESL Pupils. Int. J. Acad. Res. Prog. Educ. Dev. 2021, 10, 392–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.S.; Izzah, L.; Putra, A.D. Analysis of the Use of Banksy Image in Improving Students’ Writing Skill. J. Lang. Lang. Teach. 2021, 9, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febriyanti, B.; Kiptiyah, M.; Wahyudi, M.A. The Implementation of Using Flash Card in Teaching Writing. SELL 2022, 7, 80–90. [Google Scholar]
- Inayah, N.; Adzim, S.; Mayasari, A.; Aulinnia; Info, A. The Influence Sequence Picture on Indonesian ELT. Indonesia J. Res. Educ. Rev. 2022, 1, 217–224. [Google Scholar]
- Nafosat, Z.; Nasiba, A.; Ozoda, N.; Baktior, D. Interactive Strategies and Methods of Education. Int. J. Recent Technol. Eng. 2019, 8, 7667–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazeema, T.M.F.; Kareema, M.I.F. Implication of multimedia audio-visual aids in the English language classroom. In Proceedings of the International Symposium 2017 on Multidisciplinary Research for Sustainable Development, Rome, Italy, 6–7 September 2017; pp. 433–442. Available online: http://192.248.66.13/handle/123456789/3028 (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Park, C.C. Learning Style Preferences of Southeast Asian Students. Urban Educ. 2000, 35, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.F.; Ng, P.K. A Review of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Motivations of ESL Learners. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Culture, Languages and Literature, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 9–10 June 2015; Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/278025827 (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Gardner, R.C. Motivation and Second Language Acquisition: The Socio-Educational Model; Peter Lang Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Thakur, V.S. Using Supplementary Materials in the Teaching of English: Pedagogic Scope and Applications. Engl. Languange Teach. 2015, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, Z. The Effect of Supplementary Materials on Reading Comprehension Improvement of Iranian Female High School EFL Learners Based on Gaj and Khate Sefid Text books. Adv. Lang. Lit. Stud. 2015, 6, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edward, C.; Jimenez, F.; Csee. Motivating Factors of Teachers in Developing Supplementary Learning Materials (SLMs). Int. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 8, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, M.M.; Salehi, H.; Embi, M.A. Effects of Using Digital Comics to Improve ESL Writing. Res. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2012, 4, 3462–3469. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, C.K.S.; Mei, T.P.; Abdullah, M.S.; Othman, W.M.; Mostafa, N.A. ESL Learner’ Perspectives on the Use of Picture Series in Teaching Guided Writing. Int. J. Acad. Res. Progress. Educ. Dev. 2017, 6, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A. Pictures for Language Learning; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.J.; Tan, K.H.; Awang, M.M. Generic digital Equity Model in Education: Mobile-Assisted Personalized Learning (MAPL) through e-Modules. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, K.K.W.; Tan, K.H. ESL teachers intention in adopting online educational technologies during COVID-19 pandemic. J. Educ. e-Learn. Res. 2020, 7, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).