Abstract
China is currently the world’s largest energy consumer and carbon emitter. In order to reduce the harm of carbon dioxide to the global ecological environment, the use of natural gas instead of coal is a realistic choice for China to achieve the “dual carbon” goal. Opportunities also bring new challenges, and the price of natural gas is an important method of promoting the upstream and downstream industrial chains of natural gas, so it is of great practical significance to study the price of natural gas. This paper builds a three-level supply chain model consisting of suppliers in the natural gas market, city gas companies and consumers in the market and uses the Stackelberg game to study the decision-making models of different subjects under their own dominance and centralized decision-making; it also considers the pricing mechanism and profit situation of stakeholders in the natural gas market under the low-carbon preference of consumers and the level of corporate carbon emission reduction. The research results show that when considering consumers’ low-carbon preferences, the sales prices of various stakeholders in the market have increased, which is beneficial for all entities in the natural gas industry chain. At the same time, with the low-carbon transformation of energy companies, the production method drives the price of raw materials to rise in the process of low-carbon innovation, which, in turn, makes the price of various stakeholders in the natural gas market and the level of carbon emission reduction per unit show a positive relationship; in order to maximize the overall profit of the supply chain, the natural gas market should adopt a centralized decision-making method to further promote the reform of China’s natural gas marketization.
1. Introduction
Since human beings entered the era of industrialization, global carbon dioxide emissions have increased year by year, accompanied by global temperature rise, glacier melting, sea level rise and many other environmental problems [1]. According to the survey, more than 85% of carbon emissions come from energy activities, so the pace of the transition to green and low-carbon energy must be accelerated [2]. As the world’s largest energy consumer and carbon emitter, China’s “carbon peak and carbon neutrality” goal (hereinafter referred to as the “dual carbon” goal) will be the two milestones of China’s energy revolution within the next 40 years and an important stage in the construction of a new energy consumption system [3,4]. Using low-carbon or non-fossil energy to replace coal with high carbon emission is an effective way to reduce CO2. According to the statistics of the International Energy Agency, natural gas is a low-carbon, clean and efficient energy compared with coal and oil [5,6]. As a bridge from high carbon to low-carbon energy, natural gas is a realistic choice for China to achieve the goal of “dual carbon” in the future [7,8]. China’s future transformational trend is to take non-fossil energy as the core and natural gas as the transitional energy, so the reform of the system and mechanism of the natural gas market is particularly important [9]. The realization path of the natural gas industry under the “dual carbon” goal mainly involves upstream production, midstream trade and transportation and downstream consumption, which requires us to think about emission reduction from the perspective of the whole industry chain [10]. To be specific, innovation should be carried out in natural gas exploitation technology and natural gas market system and policy; the upstream, middle and downstream of the industrial chain should coordinate with each other; in the process of natural gas exploration and development, environmental damage and exhaust gas emission should be minimized [11]. The upstream exploration and development of the natural gas market should be low-carbon, clean and involve less environmental pollution; the midstream infrastructure is interconnected, economical and efficient; the downstream supply chain channels should be diversified and supply security should be guaranteed [12].
The price of natural gas is an important way to promote the development of upstream and downstream enterprises in the supply chain and this is related to the development of the natural gas market. Therefore, it is of great practical significance to study the price of natural gas. At present, the insufficient supply and high cost of natural gas are the most important problems to be solved, which is also a long-term problem to be faced, namely, to increase supply and reduce cost [13]. For a long time, the natural gas industry has been controlled by the Chinese government in all aspects and its price cannot be adjusted according to the current situation of market supply and demand. Compared with developed countries, the natural gas industry has a low degree of marketization. In terms of short-term goals for the future, the main goal of the Chinese government’s price policy is to adjust and optimize the price mechanism of natural gas to make it fluctuate in a reasonable range. Although the state strongly supports the development of natural gas, the development of natural gas still seriously lags behind expectations due to the pricing mechanism [14]. Therefore, it is necessary to continue to deepen the reform of natural gas price marketization and improve the market competitiveness of natural gas [15]. At present, there is still a big gap between the natural gas industry and the complete marketization: First, the pricing of pipeline transportation has not become a system; Second, the upstream exploration and production blocks of natural gas are monopolized by huge oil and gas enterprises, which makes it difficult to form a new situation in which competition is explored; Thirdly, the division of the marketization scope is complicated, which leads to the failure of regulated price policies to a certain extent [9]. To sum up, in order to optimize the natural gas market price mechanism, all enterprises in the industrial chain need to play their respective roles, deepen the division of labor and cooperation, make joint efforts to promote low-carbon emission reduction and establish a qualified price mechanism to promote the development of the natural gas market.
According to the summary of existing research on the natural gas pricing mechanism, the Stackelberg game model has been used to explore many research studies on the natural gas pricing mechanism. For example, some studies discussed the pricing strategy of natural gas, which only considered the game between natural gas production enterprises and industrial users [16] or the construction of two models of competitive pricing of natural gas, in which the advantage orientation of natural gas price in competition was obtained through comparative analysis [17,18]. Studies also analyzed natural gas output under different marginal costs in the energy industry and investigated the influence of a third-party access system on the natural gas pricing mechanism [19,20]. However, the content combining low-carbon emission reduction in previous studies is less. In addition, most previous studies have studied the secondary supply chain [16,21]. On this basis, we studied the three-level supply chain of natural gas, taking into account the upstream, middle and downstream stakeholders, which is more in line with the industrial chain structure of the natural gas market described above. Different from the previous literature, this paper considers consumers’ low-carbon preference and the unit carbon emission reduction parameters of various stakeholders in the natural gas market, because we know that consumers’ low-carbon preference and enterprises’ unit carbon emission reduction level will affect the price of natural gas [22,23]. Finally, the Stackelberg game model is established to analyze the pricing mechanism and profit under different dominant and centralized decision-making conditions, which further expands the relevant research on the pricing mechanism of the natural gas market.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows and relevant literature are listed in Section 2. In Section 3 and Section 4, we analyze and describe the problems and models in detail and analyze different situations in detail through the method of game. In Section 5, we assign parameters to the formula obtained after the model calculation and further verify the model through numerical simulation. In Section 6, we summarize the correct conclusions and put forward relevant policy recommendations for the reform of the pricing mechanism of China’s natural gas market under the “dual carbon” target. Additionally, we present the direction of future research.
2. Literature Review
The relevant literature have the following three parts: the development status of the natural gas industry under the “dual carbon” goal, the research on the relationship between stakeholders in the natural gas market and the relevant research on the pricing mechanism of stakeholders in the natural gas market. In this section, we review the relevant literature and point out how our study differs from theirs.
2.1. Development Status of the Natural Gas Industry under the “Dual Carbon” Goal
Natural gas is one of the clean energy alternatives to coal and oil. “China’s 14th Five-Year Plan” clearly pointed out that in the future, the natural gas industry should constantly improve the production, supply, storage and marketing system based on the “dual carbon” goal and the new economic and social situation to meet the increasing demand for clean energy in social development and build a new pattern of energy development [24]. Based on the experience of Japan, the United States and other developed countries, it has been found that carbon emission reduction can be achieved by controlling the total amount of energy consumption and optimizing the consumption structure. From the perspective of the first change in global energy consumption structure, the proportion of clean energy has increased greatly [25]. Developed countries such as the United States, Japan and the United Kingdom have achieved substantial reductions in carbon emissions by vigorously developing clean energy [26].
In the process of realizing the “dual carbon” goal, how much development space is there for China’s natural gas market in the future, whether it can reach the carbon peak at the same time as the world, what is the peak level and what will happen after the peak is reached? These questions will all be discussed. These are issues that directly affect the enthusiasm for exploration, development and infrastructure investment in the natural gas market [2]. There are three challenges facing China’s natural gas industry. First, the natural gas infrastructure needs to be further improved. Although China attaches great importance to the construction of natural gas infrastructure, there is still a problem of insufficient pipeline interconnection, which affects the purchase of natural gas by downstream consumers. Secondly, the downstream distribution link of the natural gas market needs to be reformed. The monopoly of city gas companies is not conducive to the marketization of the natural gas industry and the decrease in upstream gas price cannot bring benefits to end consumers directly. Finally, with the expected future increase in natural gas consumption, the capacity of gas storage and peak regulation needs to be improved [27]. In the future, the focus of the natural gas industry is to reduce costs, improve and innovate in technology and further improve infrastructure construction in combination with the goal of low-carbon emission reduction [28]. With the “dual carbon” goal vigorously promoted, the natural gas industry will usher in a prosperous period of development opportunities in the next decade, providing sufficient development space for enterprises in the market, middle and downstream. Therefore, all stakeholders should cooperate to learn from each other and jointly realize low-carbon and sustainable development of the natural gas industry.
2.2. Research on the Relationship between Stakeholders in the Natural Gas Market
In the natural gas market, there are usually multiple stakeholders such as natural gas producers, city gas companies, governments, consumers and environmental protection departments [29]. From the perspective of the supply chain, the natural gas market is composed of the upstream supply market, the downstream consumption market, the pipeline transportation company and the city gas company in the middle. Upstream suppliers are responsible for the exploration, production and processing of natural gas, which is delivered to consumers in the downstream natural gas market through midstream pipeline companies. The pipeline transportation enterprise is responsible for the transportation and dispatching of the long-distance pipeline network, transporting natural gas to gas storage and city gate stations; city gas companies are responsible for buying gas from producers and selling it to the consumer market; consumers in the market generally refer to urban gate stations and downstream consumer markets, including industrial users and residents [30].
The game-based method has been widely used in the optimization of the natural gas supply chain [31]. Most of the existing studies focus on supply reliability, pricing decisions, overall optimization design of supply chain system, etc. We summarize scholars’ research on the natural gas supply chain in Table 1:

Table 1.
Related research on the natural gas supply chain.
In general, many scholars use the game method to analyze and optimize the supply chain of the natural gas industry, laying a certain foundation for further putting forward corresponding policies. Therefore, using the scientific game model and method from the perspective of the natural gas supply chain to explore the reasonable pricing of natural gas has very important guiding significance. In a word, under the “dual carbon” goal, the natural gas industry faces a practical problem in the new market environment: how to coordinate the allocation of upstream resources, improve transportation capacity, optimize the overall value of the sales business chain and on this basis, achieve the goal of maximizing the profit of all stakeholders in the supply chain, which is a considerable problem facing the natural gas industry.
2.3. Research on the Pricing Mechanism of Stakeholders in the Natural Gas Market
Price reform is the core of China’s natural gas market reform. With the increasing demand for natural gas, China needs to further improve the pricing mechanism of natural gas. Under the premise of considering the maximum bearing capacity of consumers, the difference in the cost of natural gas from different sources and the appropriate control of the cost of the downstream industry chain, this paper explores how to optimize the benefits and investment returns of all links of the natural gas industry chain. At the same time, the impact of alternative energy prices on the natural gas price system should also be considered and the price should be dynamically adjusted following the changes in market supply and demand [39,40]. According to the structure of the natural gas industry chain, its price involves three aspects: the upstream ex-factory price of natural gas, the midstream pipeline transportation cost and the downstream user price. In the natural gas development plan, it is proposed to give full play to the leverage of the price mechanism in regulating the relationship between supply and demand. Although the measures of natural gas market-oriented reform in different countries in the world are different, most of them are changing from a monopoly market to market pricing [20]. At present, in China’s natural gas market, producers monopolize the exploration and production of natural gas and also occupy the midstream transportation through the construction of transportation pipelines with a strong monopoly [41]. The focus of the natural gas market reform is to establish a dedicated pipeline transportation company to separate the upstream and middle reaches of the natural gas industry and to reduce the vertical integration of upstream producers. In the natural gas industry chain, CO2 emissions run throughout. Therefore, under the “dual carbon” target, the natural gas industry should vigorously develop low-carbon emission reduction technologies to promote sustainable development in the future.
In the study of natural gas pricing mechanisms, some scholars point out the existing problems of natural gas pricing mechanisms and corresponding measures. By learning from the experience of developed countries, building a competitive natural gas market is based on price marketization [42]. Due to problems such as insufficient upstream competitiveness and imperfect infrastructure, China’s natural gas market does not have the conditions to completely liberalize prices. To sum up, the current pricing mechanism has the following problems: the permitted rate of return of the natural gas pipeline is too high, the price management method of the “base price + floating range” still has room for optimization and there is still no influential benchmark price [43,44]. Therefore, the natural gas price reform needs to straighten out the original price, formulate reasonable prices for transportation, storage and gas transmission and distribution and accelerate the construction of a market trading center to form an influential market benchmark price [45]. Other scholars have discussed the role of speculation in natural gas pricing [46,47]. Manera et al. used the DCC multivariate GARCH model to analyze the future prices of energy commodities (including natural gas) and agricultural commodities; the results showed a spillover effect between commodities and a surge in the correlation between energy and agricultural commodities. In addition, they considered alternative measures of speculative activities in their research to assess the role of speculation in simulating commodity futures price volatility [48,49]. The research of comprehensive scholars has found that in recent years, energy and agricultural product markets have become the most concerning issues in various countries and the relationship between the two has become closer. Factors such as macroeconomic uncertainty, emergencies and speculation have a significant impact on natural gas prices. The quantitative easing monetary policies successively introduced in Europe and the United States have intensified global excess liquidity and the emergence of some crises has severely impacted the supply chains of commodities such as food and energy, which has further promoted global inflation. However, the green and low-carbon transformation provides a strong basis for the future market-oriented reform of domestic energy. In addition, some scholars have studied the emission reduction of the supply chain and analyzed the optimal emission reduction cost input and optimal subsidy rate of enterprises by constructing models of government subsidies for cooperative emission reduction between manufacturers and retailers under different game relationships [50]. Zhao considered relevant research on emission reduction investment strategies of the supply chain under equity concern and low-carbon preference [51]. Fan constructed a two-stage decision-making model between the government and supply chain enterprises and explored the similarities and differences between government subsidy strategies and enterprises’ carbon emission reduction decisions under different circumstances [52].
Through reading literature related to the natural gas supply chain and pricing mechanism, most scholars have pointed out the market-oriented direction of natural gas pricing reform in their studies but have not formed a systematic market-oriented pricing reform strategy. At the same time, the pricing reform schemes proposed in literature are mostly qualitative research, lacking quantitative analysis and data model verification. Moreover, considering the current “dual carbon” goal of China, the content of the natural gas supply chain combined with low-carbon emission reduction is reduced. Therefore, this study assigns relevant stakeholders in China’s natural gas market as the research object and builds a game model considering the carbon emission reduction of enterprises and consumers’ low-carbon preferences so as to further improve China’s natural gas price mechanism.
3. Problem Description and Model Assumptions
3.1. Problem Description
In order to facilitate the “dual carbon” goal as soon as possible and further improve the price system of the natural gas market, we will solve this problem from the perspective of the supply chain. This paper establishes a three-level supply chain model consisting of suppliers in the natural gas market, city gas companies and consumers in the market. The natural gas supplier is responsible for the exploration and exploitation of natural gas and sells the natural gas to the city gas company at a certain price . When the supplied natural gas is transported to the city gas company through the pipeline, certain pipeline transportation costs are incurred. The city gas company also sells to the natural gas market at a certain price and finally, the natural gas market sells the natural gas to the consumers in the market at a certain price .
By constructing this model, this paper focuses on the impact of consumers’ low-carbon preferences and corporate low-carbon emission reduction levels on the prices and profits of various stakeholders in the natural gas market. The three-level supply chain model of the natural gas market is shown in Figure 1:
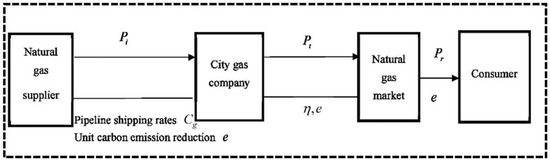
Figure 1.
Natural gas market supply chain model.
3.2. Model Assumptions
According to the natural gas three-tier supply chain model, the following are the assumptions:
Hypothesis 1 (H1).
Under the natural gas market conditions, all stakeholders are pursuing the maximization of their own interests. According to the “individual behavior rationality” criterion, there is bound to be strong non-cooperative competition and each supply chain member has decision-making power. In the context of China’s current “dual carbon” goal, the power of various stakeholders in the natural gas market varies; it is predicted that competition will be more significant under the pricing mechanism of the natural gas market in the future; that is, it is assumed that the pricing process is sequential and a dynamic process. Additionally, we assume that all stakeholders in the natural gas market are in a complete information environment and according to the information they have, they set the price of natural gas that already includes reasonable profits. This study does not consider the impact of the international market, domestic economic environment, related taxes and government regulations on the game model.
Hypothesis 2 (H2).
All stakeholders in the natural gas market produce according to the quantity determined by the market demand function. The natural gas market demand function is:[20,53]. Among them,represents the market size of the natural gas market (that is, the largest possible demand in the market),is the price sensitivity coefficient andis the market value of natural gas. Consumers are sensitive to the purchase of low-carbon products, and the inverse demand function of price has a linear relationship with the level of emission reduction. In the demand function,represents the low-carbon preference coefficient of consumers andrepresents the unit emission reduction.
Hypothesis 3 (H3).
Natural gas suppliers will adopt corresponding low-carbon emission reduction methods so that the carbon emission reduction per unit of natural gas is. Referring to various literature, it is concluded that the carbon emission reduction cost of natural gas suppliers is[54,55], the investment cost coefficient of carbon emission reduction is. That is to say, as the level of emission reduction increases, the cost of emission reduction for suppliers also increases. In order to encourage natural gas suppliers to reduce carbon emissions in the production process, city gas companies share the carbon emission reduction costs of suppliers. Therefore, the carbon emission reduction costs of city gas companies areandis the share of carbon emission reduction costs.
Hypothesis 4 (H4).
The rate at which a pipeline company transports natural gas per unit of production is[33]. The natural gas pipeline company operates as an independent third party and only bears the transportation cost of natural gas in the entire natural gas supply chain and the established unit transportation rate already includes reasonable profits.
3.3. Model Parameters
All parameters involved in this paper and their definitions are summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Symbol parameters.
4. The Decision Model of Various Stakeholders in the Natural Gas Market
In this section, we make mathematical derivations based on the Stackelberg game model. According to the above, we have established a three-tier supply chain model consisting of suppliers in the natural gas market, city gas companies and consumers in the market. The Stackelberg model is a price leadership model and there are differences in the order of actions of each subject in the supply chain. We explore decision models for decentralized as well as centralized decision-making below. Under decentralized decision-making, we explored the situation of leadership by different leaders. The leader first decides one of its own outputs and then the rest of the followers decide their own output according to the observed output. In this model of the game, leaders determine their own output with full knowledge of how followers in the market will behave. This means that the leader can know the reaction function of the follower and then decide how to act on the premise of maximizing his own profit. When different stakeholders are dominant, we use backward induction to deduce, from the follower side to the leader side, how to get the relevant function. Under the centralized decision-making model, the main bodies of the natural gas supply chain make joint decisions and they take the maximization of the interests of the entire supply chain as the ultimate goal and then finally determine the market price of natural gas.
4.1. Game Research of Stakeholders in the Natural Gas Market under Decentralized Decision-Making
4.1.1. The Situation of the Natural Gas Supplier Is the Dominant Player
According to this assumption, city gas companies and natural gas suppliers will also produce according to the demand function under the condition of maximizing their own interests; then we solve the equilibrium solution of the Stackelberg model according to the idea of reverse induction.
According to the parameters in the table, the profit function of each stakeholder in the natural gas market can be obtained as follows:
Supplier’s profit:
Profits of city gas companies:
Consumer profits:
The first stage: Consumers in the natural gas market based on the price given by the city gas company is and to determine the price with the goal of maximizing Formula (3), obviously, is a concave function of and there is a maximum value. Letting , we can get:
The second stage: the city gas company based on the price given by the natural gas and the determined in the first stage, determined the price with the goal of maximizing Formula (2), and there is a maximum value. Letting , we can get:
The third stage: The gas supplier decides the price based on the and obtained in the first two stages with the goal of maximizing Formula (1). Similarly, is a concave function of and there is a maximum value. Letting , we can get:
By substituting into and , respectively, we get:
Substitute , and into , and , respectively, to get:
In summary, the total profit function of the natural gas supply chain is:
4.1.2. The Situation When the City Gas Company Is in a Dominant Position
In Section 4.1.2 and Section 4.1.3, in order to make the formulas look simpler and more intuitive, we added three new parameters (), which are the unit product margins of each stakeholder in the three-tier supply chain profit. Although in Section 4.1.2 and Section 4.1.3, we use different parameters than those in Section 4.1.1. However, what we want to explain here is that no matter whether the unit product profit or the price of each stakeholder is used for derivation, it will not affect the final derivation result and the deduced profit of the natural gas supplier is the same. Because as we all know, marginal profit = sales revenue − marginal cost.
The natural gas supplier determines the selling price based on the unit product profit margin ,
The city gas company determines the selling price according to the unit product profit margin ,
The consumer determines the acceptable price based on the profit margin per unit of product,
The profit of the natural gas supplier is:
The profit of the city gas company is:
The consumer’s profit is:
The first stage: According to the given by the city gas company, the natural gas supplier determines its own marginal profit with the goal of maximizing its own profit, that is, Formula (21) maximization. It can be seen from the above formula that is a concave function of , so there is a maximum value. Letting , we can get:
The second stage: According to the given by the city gas company, consumers also aim to maximize their own profit, that is, Formula (25) maximization in order to determine their own marginal profit . From the above formula, we can see that is a concave function of , so there is a maximum value. Letting , we can get:
The third stage: Since natural gas suppliers and consumers have unknowns when making decisions, they restrict each other, so for the simultaneous equations, let :
According to their interrelationships, the final simplification is:
The fourth stage: The city gas company aims at maximizing its own profit according to the above obtained and by maximizing the Equation (23) to determine the profit margin ; it can be seen from the above Formula (23) that is a concave function of , so there is a maximum. Letting , we can get:
By substituting into , we can get:
By substituting , and into the following three formulas: , and , we can get:
Then, by substituting , and into , and , we can get:
In summary, the total profit function of the natural gas supply chain is:
4.1.3. The Situation When the Consumer Is in the Main Position
In this section, the derivation content before the second stage is the same as the Formulas (17)–(26) in Section 4.1.2, so it is omitted here.
The second stage: According to the given by the consumer and the obtained in the first stage, the city gas company seeks with the goal of maximizing the Formula (23). From the above formula, we can see that is a concave function of and there is a maximum value; therefore, letting , we get:
The third stage: According to the and obtained in the first two stages, consumers aim to maximize their own profits, so they can find by maximizing Formula (25). It can be seen from the above equation that is a concave function of and has a maximum value. Therefore, letting , we get:
By substituting into , we get:
Then, by substituting and into , we get:
Then, by substituting into , , from the three formulas, we can get:
By substituting , and into , and , respectively, we can get:
In summary, the total profit function of the natural gas supply chain is:
4.2. Game Research of Natural Gas Stakeholders under Centralized Decision-Making
Under the centralized decision-making model, the main bodies of the supply chain cooperate closely to make decisions together. Taking the profit maximization of the entire supply chain as the ultimate goal of decision-making, the natural gas market price is jointly determined. Therefore, when natural gas suppliers, city gas companies and consumers in the natural gas market make joint decisions in the natural gas supply chain, the profit function of the entire natural gas market supply chain can be obtained as:
It can be seen from the above formula that is a concave function of and there is a maximum value, so let . We can obtain the equilibrium price under centralized decision-making as:
By substituting into the supply chain profit function, the maximum total profit of the natural gas market supply chain can be obtained as:
5. Numerical Simulation
In order to better verify the changing relationship between the parameters, this section will compare and analyze the parameters by assigning them. First, we describe and explain the parameters involved in the article in the third part of the problem description and model assumptions. Then, based on these descriptions, we refer to the previous relevant literature and set the values of the fixed parameters [52,56,57]. The values are explained as follows:, , , , , , , , , and . In the drawing in this section, under the decentralized decision-making model, the natural gas supplier-led model is represented by Model 1, the city gas company-led model is represented by Model 2 and the market consumer-led model is represented by Model 3. When the natural gas market is in centralized decision-making mode, it is represented by Model 4.
5.1. The Impact of Consumers’ Low-Carbon Preferences on the Prices of Various Stakeholders in the Natural Gas Market
Through numerical simulation, the impact of consumers’ low-carbon preference on the prices of various stakeholders can be more clearly demonstrated. Under the “dual carbon” target, these values are substituted into Formulas (9), (33), (45) and (55) to obtain the change in the price of natural gas suppliers considering the dominance of different stakeholders and the centralized decision-making of the natural gas supply chain condition. As can be seen from Figure 2, with the increase in consumers’ low-carbon preference, the price of natural gas suppliers also shows an increasing trend and when using the centralized decision model, the ex-factory price of natural gas is the highest. Similarly, the values are substituted into Formulas (10), (34), (46) and (55) to obtain the price changes of the city gas companies in Figure 3. When natural gas suppliers dominate, city gas companies sell at higher prices than when city gas companies dominate the supply chain. In addition, the selling price of natural gas in the above-mentioned case is also higher than the price in the other two cases, namely the centralized decision-making and the market consumer-led situation. In a supplier-dominated and market consumer-dominated situation, the magnitude of changes in the price of city gas companies is larger than in the other two situations, which is the dominant and centralized decision-making model of the city gas company. As shown in Figure 4, by substituting the values into Formulas (11), (35), (47) and (55), it can be seen that with the increase in consumers’ low-carbon preference, the price of natural gas in the consumer market presents an increasing trend. When the natural gas supplier is in the dominant position, the market price is higher than the price in other situations. Under the background of the “dual carbon” target, natural gas suppliers carry out low-carbon innovation; the price of natural gas will rise as production technology is innovated, which will also run up prices for other stakeholders. Therefore, this also reflects the dominant position of natural gas suppliers in the pricing mechanism. The low-carbon innovation of suppliers also satisfies consumers’ low-carbon preference, which is conducive to the further development of the downstream consumer market of the natural gas industry and the improvement of consumers’ acceptable price.
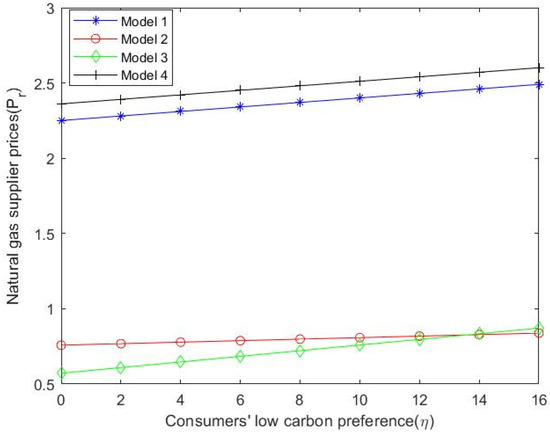
Figure 2.
with the changing trend of .
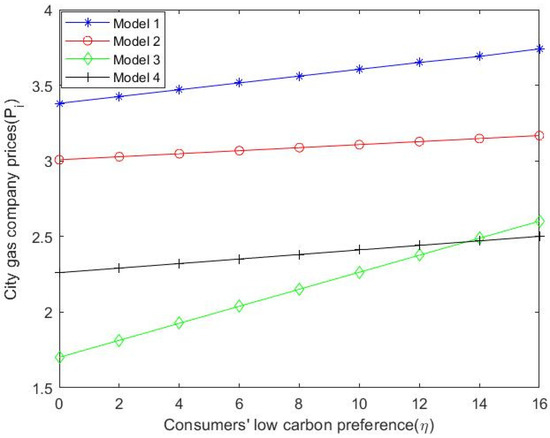
Figure 3.
with the changing trend of .
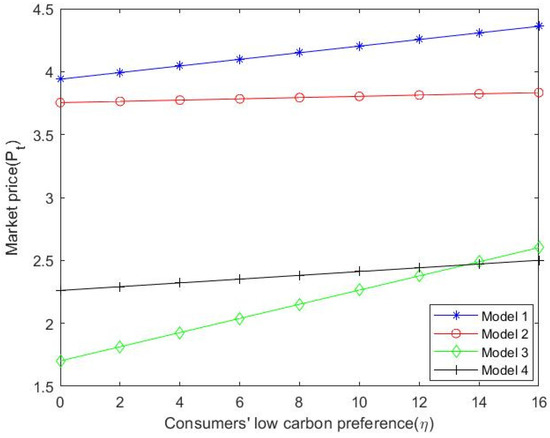
Figure 4.
with the changing trend of .
5.2. The Impact of Unit Carbon Emission Reduction Level on the Price of Various Stakeholders in the Natural Gas Market
As shown in Figure 5, by substituting numerical values, it can be seen that by comparing Formulas (10), (35), (55) and (64), gas suppliers have the highest pricing levels when city gas companies dominate. Additionally, with the increase in unit carbon emission reduction level, the price of each stakeholder shows an increasing trend. As can be seen in Figure 6, city gas companies have the highest pricing levels when natural gas suppliers dominate the supply chain. At the same time, when the market is dominated by consumers, with the increase in the level of carbon emission reduction per unit, the price of city gas companies fluctuates the most. Figure 7 shows that when suppliers are dominant, the natural gas market price increases with the level of unit carbon emission reduction and the market price at this time is greater than that when other stakeholders are dominant and supply chain decision-making is centralized. The total profit of the natural gas supply chain can be obtained by substituting the value into Formulas (15), (39) and (51).
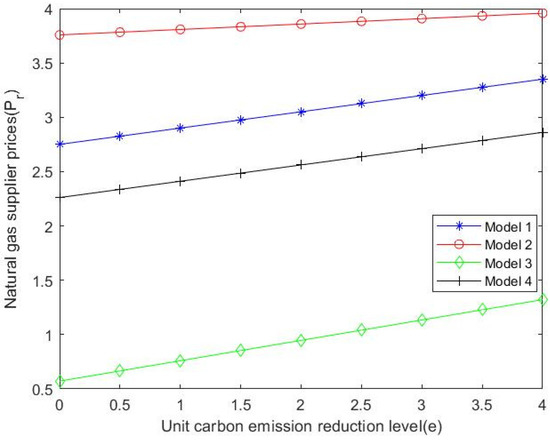
Figure 5.
with the changing trend of .
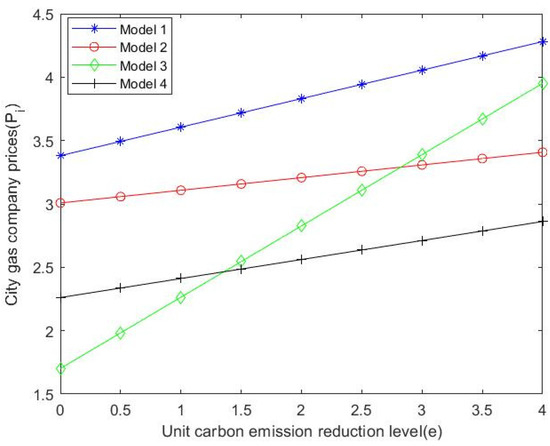
Figure 6.
with the changing trend of .
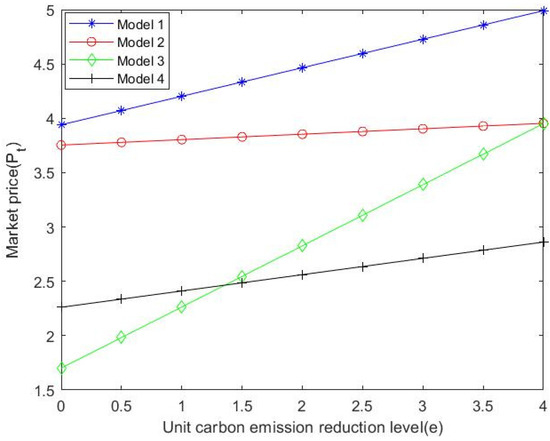
Figure 7.
with the changing trend of .
5.3. The Impact of Consumers’ Low-Carbon Preference and Unit Carbon Emission Reduction Level on the Total Profit of the Natural Gas Supply Chain
As shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9, the total profit of the supply chain increases with the increase in consumers’ low-carbon preference and the total profit level of the supply chain is positively related to the unit carbon reduction. Under the centralized decision model, the total profit of the natural gas supply chain is the largest. To sum up, in the natural gas market, the prices of various stakeholders in the natural gas market increase with the increase in consumers’ low-carbon preference; that is, the price of stakeholders in the natural gas market is proportional to consumers’ low-carbon preference. For the natural gas supply chain, natural gas suppliers are responsible for natural gas production, exploration, development and other activities, occupy a core position in the overall supply chain and have absolute dominance in the game with related enterprises in the middle and lower reaches. Therefore, it also reflects that the market price of city gas companies and consumers is often determined by supplier pricing.
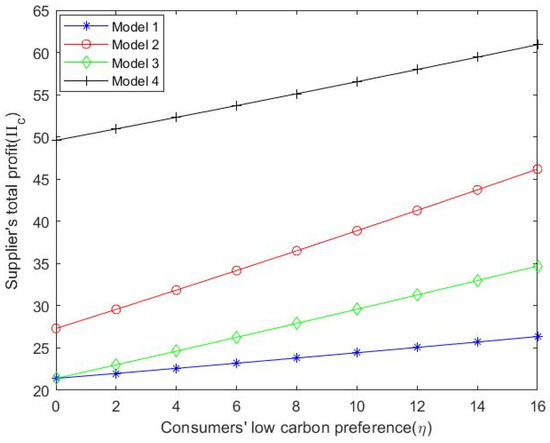
Figure 8.
with the changing trend of .
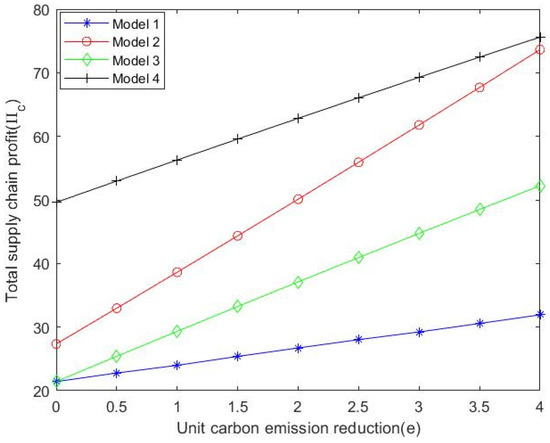
Figure 9.
with the changing trend of .
At present, the academic circle pays more and more attention to the low-carbon transformation of energy enterprises under the background of the “dual carbon” goal. With the adjustment of energy structure and the continuous promulgation of relevant policies for decarbonization in various countries, energy prices have been rising for a long time. Since the signing of the Paris Climate Agreement, all economies around the world will face the issue of green transition and the transition from fossil energy to non-fossil energy is a medium and long-term process. The transformation of energy companies to low-carbon production methods will drive up the prices of some raw materials. This also explains the reason for the consequent increase in selling prices for various stakeholders in the natural gas supply chain under the pricing model considering the unit carbon emission reduction level. China’s 2021 Sustainable Consumption Report focuses on low-carbon consumption trends in the context of “carbon peaking” and “carbon neutrality” goals. At present, China’s “dual carbon” goal and the concept of low-carbon development have become the consensus for all sectors of society and low-carbon consumption is also becoming the daily action for many people. The green and low-carbon products provided by energy companies have enriched the choices of consumers and the increasingly low-carbon preference of consumers in the market has also forced the low-carbon transformation of the production field. The two promote each other at both ends of the industrial chain. It is precisely because consumers’ increasing low-carbon consumption preference encourages enterprises to improve carbon emission reduction levels, the price of various stakeholders in the natural gas market and low-carbon preference show a positive relationship. In the future, low-carbon consumption will be the general trend. Only by taking the market as the guide and promoting the green and low-carbon transformation of products and value chains in the whole cycle can enterprises gain sustained growth and momentum in the low-carbon era.
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
6.1. Conclusions
Based on the current situation of natural gas pricing mechanisms at home and abroad, this paper analyzes the current natural gas pricing model in China, finds out the existing problems and provides relevant policies and suggestions for the market-oriented reform of natural gas pricing. This paper applies the Stackelberg game model under the “dual carbon” goal, aiming at the natural gas suppliers, city gas companies and consumers in the natural gas market, considering the decision-making model dominated by each stakeholder and the main body of the supply chain. Considering the impact of consumers’ low-carbon preference level and carbon emission reduction level on the three-level supply chain, numerical simulation and analysis of the model are carried out to study the impact on the price and profit of the natural gas market and the following conclusions are drawn:
- In the pricing model considering consumers’ low-carbon preference, when the natural gas supplier dominates, the selling price of each stakeholder in the natural gas supply chain reaches the maximum value. In the natural gas market, the prices of various stakeholders in the natural gas market increase with the increase in consumers’ low-carbon preference; that is, the price of stakeholders in the natural gas market is proportional to consumers’ low-carbon preference. However, compared with other stakeholders, the increase rate of city gas companies tends to be more stable.
- In the pricing model considering the unit carbon emission reduction level, the sales price of each stakeholder in the natural gas market increases with the increase in the unit carbon emission reduction level. When the city gas company is in the dominant position, the supplier sells the highest price at this time. When the natural gas supplier is in a dominant position, the city gas company and the sales price in the market are maximized.
- For the natural gas industry, all stakeholders in the supply chain will gain more benefits under the centralized decision-making model. In the case considering consumers’ low-carbon preference and the unit carbon emission reduction level, the total profit of the natural gas supply chain is positively proportional to the low-carbon preference and the unit carbon emission reduction level; that is, it increases with the increase in low-carbon preference and unit carbon emission. Moreover, the income of the natural gas industry chain under the centralized decision model is greater than that under the dominance of city gas companies and greater than that under the market consumer and natural gas suppliers.
Based on the above conclusions and corresponding analysis, with the vigorous advancement of the “dual carbon” goal, the natural gas suppliers responsible for exploration and production and the city gas companies responsible for transporting and storing natural gas will vigorously promote low-carbon emission reductions. With the improvement in the level of carbon emission reduction per unit and the increase in low-carbon preference due to the improvement of consumers’ awareness of environmental protection, the sales prices of various players in the natural gas market will further increase. On the whole, in order to maximize the overall profit of the supply chain, the natural gas market should adopt a centralized decision-making method to ensure the interests of all parties and further promote the reform of China’s natural gas marketization. On the basis of the above research, the following suggestions are put forward, hoping to provide some help for the formulation of relevant price policies for China’s natural gas industry: First, the natural gas industry should further strengthen the internal management of the market and promote the implementation of price; secondly, under the condition of ensuring the steady supply of our country’s natural gas market, the natural gas price should be in line with international standards as soon as possible; finally, the natural gas industry should improve and optimize the user market structure and strengthen price management innovation research.
6.2. Future Directions
Limitations and future prospects resulting from this study: First, future research can explore how to maximize the benefits among the main bodies of the supply chain and further improve the innovation level of low-carbon emission reduction under the encouragement of various preferential policies of the government for the natural gas industry. Second, future research should focus on solving the problem of upstream oligopoly and the lack of a benchmark, step-by-step in order to solve control pricing to market pricing, introducing a competitive mechanism to form a diversified market competition structure, translating dynamic price adjustment mechanisms into practice, strengthening the construction of supporting facilities, all of which will lead to the steady and healthy development of China’s natural gas industry. Finally, with the continuous development of the global natural gas trade, in the future, the pricing mechanism of natural gas may tend to be globally integrated. Looking at the future of the natural gas industry, in areas such as equipment development, energy consumption and environmental protection, low-carbon methods and technologies and investment profits are the key points and difficulties that the natural gas industry needs to solve in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.C. and X.G.; methodology, X.G.; software, X.G. and Y.C.; validation, X.G., X.Z. and H.Z.; formal analysis, C.C., X.G. and Y.C.; investigation, X.Z. and H.Z.; resources, C.C.; data curation, X.G. and Y.C.; writing—original draft preparation, C.C. and X.G.; writing—review and editing, C.C. and X.G.; visualization, Y.C., X.Z. and H.Z.; supervision, C.C.; project administration, H.Z.; funding acquisition, C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Shandong Provincial Key Research and Development Program (Soft Science) (2020RKE28013) and the Qingdao Social Science Planning Research Project (QDSKL2101039).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the reviewers and the editor-in-charge for their valuable time spent on this article. We are also grateful to all the foundations that support us.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
References
- Zou, C.N.; Xiong, B.; Xue, H.Q. The role and role of new energy in carbon neutrality. PED 2021, 48, 411–420. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.H.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y. Development of China’s “14th Five-Year Plan” natural gas industry under the background of carbon neutrality. NGI 2021, 41, 171–182. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, J.P. Delivers an Important Speech at the General Debate of the 75th Session of the United Nations (UN) General Assembly (22 September 2020, Beijing). People’s Daily Overseas Edition. Available online: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1678590270030743941&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 22 September 2020).
- Zhou, S.W.; Zhu, J.L. Exploring the path to help the strategy of “carbon peaking and carbon neutrality”. NGI 2021, 41, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- IEA. Global CO2 Emissions in 2019 [EB/OL]. (11 February 2020). Available online: https://wwwjea.org/articles/global-co2-emissions-in-2019 (accessed on 19 February 2021).
- IEA. CO2 Emissions Statistics [EB/OL]. (16 November 2020). Available online: https://wwwjea.org/subscribe-to-data-services/co2-emissions-statistics (accessed on 19 February 2021).
- Luo, Z.X. Carbon neutralization activates the potential of natural gas demand in many fields. Energy 2020, 11, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.O.; Zhang, B.S.; Xu, T. Forecasting of China’s natural gas production and its policy implications. Pet. Sci. 2016, 13, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Yi, B.W. Laws of Energy Transformation, Driving Mechanisms and China’s Path. Manag. Wld. 2021, 37, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D. Prospects of the international natural gas market in the post-epidemic era. Sino-Foreign Energy 2021, 26, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.Z.; Xiao, Y.T.; Li, J.Y. Evaluation of high-quality development of my country’s natural gas market based on principal component analysis. J. CHA Univ. Petro. 2021, 37, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y. China’s natural gas supply security assessment and countermeasures. J. CHA Univ. Petro. 2015, 31, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J. City gas companies should do a good job in expanding natural gas consumption. Sinopec 2019, 10, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D. Deepening the reform of natural gas prices and promoting the development of clean energy in China. CHN Petro. Chem. Ind. 2017, 1, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Some thoughts on building my country’s 5A-level natural gas industry chain. NET Econ. 2018, 12, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.D.; Kuang, J.C. Research on Natural Gas Pricing Strategy Based on Game Theory. N G Econ. 2004, 3, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S. Game Analysis of Natural Gas Competitive Strategy. J. Xihua Univ. 2004, 136–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Trang, D.T.Q.; Tan, T.S. Competition and cooperation in the natural gas market: A game-theoretic demand-base analysis. AEJ 2021, 19, 21–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y. Game Analysis of Natural Gas Industry Competitive Strategy. Mark. MOD 2009, 563, 256–257. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, G.H. Research on Natural Gas Pricing Mechanism Based on Stackelberg Game. J. CHA Univ. Petro. 2013, 37, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Bazyar, A.; Zarrinpoor, N.; Safavian, A. Optimal design of a sustainable natural gas supply chain network under uncertainty. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2021, 176, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Tong, F.; Yang, G. Challenges of using natural gas as a carbon mitigation option in China. Energy Policy 2018, 117, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.J.; Zhu, S.L.; Fu, S.X. The impact of low-carbon development on China’s energy price reform. Teach. Res. 2015, 5, 14–23. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, G. “China Natural Gas Development Report (2021)” released. NGI 2021, 41, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, H.Y.; Lu, G. Centennial change of world energy and national energy security. J. Nat. Res. 2020, 35, 2803–2820. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.N.; Peng, T.D.; Xiang, Z.J. Analysis of China’s energy transition path under the carbon neutrality goal. Int. Petro Econ. 2021, 29, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Q.; Liu, W.; Luo, H.H. Development Opportunities and Challenges of China’s Natural Gas Industry under the “Dual Carbon” Target. Int. Petro Econ. 2021, 29, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.N.; Ni, Z.; Tian, Z. Challenges and Opportunities of Carbon Neutral Vision to Oil and Gas Industry. Petro Tech. Econ. 2021, 37, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Guo, J.; Zheng, Z. Development and suggestion of natural gas market under the independent opening of pipeline network. Macroecon. Manag. 2021, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.Z.; Wu, D.S.; Gong, N.J. The potential impact and path of China’s upstream natural gas market-oriented reform. Environ. Econ. Res. 2019, 4, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y. Impact of unconventional natural gas development on regional water resources and market supply in China from the perspective of game analysis. Energy Policy 2020, 145, 111750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.C.; Yuan, Y.H. Research on natural gas supply chain network problems from the perspective of supply side. Sta. Dec. 2017, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Liu, Z.H. Analysis of natural gas pricing decision considering fairness concerns. Nat. Gas. Tech. Econ. 2017, 11, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, K.; Sun, R.; Wu, J. The growth and development of natural gas supply chains: The case of China and the US. Energy Policy 2018, 123, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, D.J.G.; Giarola, S.; Hawkes, A.D. A dynamic model of global natural gas supply. Appl Energy 2018, 218, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, N.; Zhang, X.Q.; Zhang, H.R. Overall Optimization of Natural Gas Supply Chain. Oil Gas. Storage Trans. 2020, 39, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Li, S. The natural gas import game between China and the EU under the influence of reserve preference. J. Syst. Manag. 2021, 30, 729–742. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, B.; Zeng, X.Y. The impact of supply security on the natural gas game from the perspective of infrastructure. CHA J. Sys. Engr. 2021, 36, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Dang, L.R.; Du, X.T. Sustainable Development Mechanism of Natural Gas Industry. NGI 2019, 39, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.P. Perfecting the natural gas pricing mechanism must take into account the interests of multiple parties. Price Theory Pract. 2016, 380, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Xiao, X.Z.; Jiang, C.H. The “Trinity” Theory of Natural Monopoly. Contemp. Financ. 2004, 8, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M.; Liu, R.; Wang, S.Y. Research on Competitive Natural Gas Market Construction and Price Formation Mechanism—and Analysis of Main Experience and Practice of Natural Gas Market Construction in Typical Countries. Price Theory Pract. 2020, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.D.; He, C.L.; Dong, Z.Y. Paths and policies to improve my country’s natural gas pricing mechanism. Nat. Gas. Tech. Econ. 2021, 15, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, S.; Zhang, P.C.; Dong, Z.Y. The key direction of my country’s natural gas price reform during the “14th Five-Year Plan” period and enterprise countermeasures. NGI 2020, 40, 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, B.G.; He, C.L.; Zhang, Y. Reconstructing the price formation mechanism of China’s natural gas production, supply, storage and sales—and on the central task of China’s “14th Five-Year Plan” natural gas price reform. NGI 2020, 40, 126–133. [Google Scholar]
- Sifat, I.; Ghafoor, A.; Mand, A.A. The COVID-19 pandemic and speculation in energy, precious metals, and agricultural futures. J. Behav Exp. Financ. 2021, 30, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, Y. Macroeconomic uncertainty, speculation, and energy futures returns: Evidence from a quantile regression. Energy 2022, 241, 122517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manera, M.; Nicolini, M.; Vignati, I. Financial speculation in energy and agriculture futures markets: A multivariate GARCH approach. Energy J. 2013, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manera, M.; Nicolini, M.; Vignati, I. Modelling futures price volatility in energy markets: Is there a role for financial speculation? Energy Econ. 2016, 53, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.D.; Zhao, D.Z.; Xia, L.J. Government subsidy strategy under vertical emission reduction cooperation in low carbon supply chain. Ops. Res. Mgt 2014, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Jian, S.F. Research on investment strategies for supply chain emission reduction under fairness concerns and low-carbon preference. Ind. Tech. Econ. 2020, 39, 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.D.; Xu, Q. Analysis of corporate carbon emission reduction and government subsidy decision-making under different power structures. Soft Sci. 2018, 32, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.T. Low-carbon dual-channel supply chain pr icing and emission reduction strategies based on consumer preferences. Ops. Res. Manag. 2020, 29, 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Qian, Q.H.; Zhou, S.F. Research on supply chain low-carbon emission reduction mechanism based on green financial loans and cost sharing. Financ. Theory Pract. 2019, 1, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Che, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.G. Study on Emission Reduction Strategies of Dual-Channel Supply Chain Considering Green Finance. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.M.; He, L.H.; Chen, X.D. A study on the profit distribution mechanism of the resource-Based supply chain considering low-carbon constraints and ecological restoration. Resour. Por. 2021, 74, 101539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.G. The impact of different government subsidy methods on low-carbon emission reduction strategies in dual-channel supply chain. Complexity 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).