Smart Rainwater Harvesting for Sustainable Potable Water Supply in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
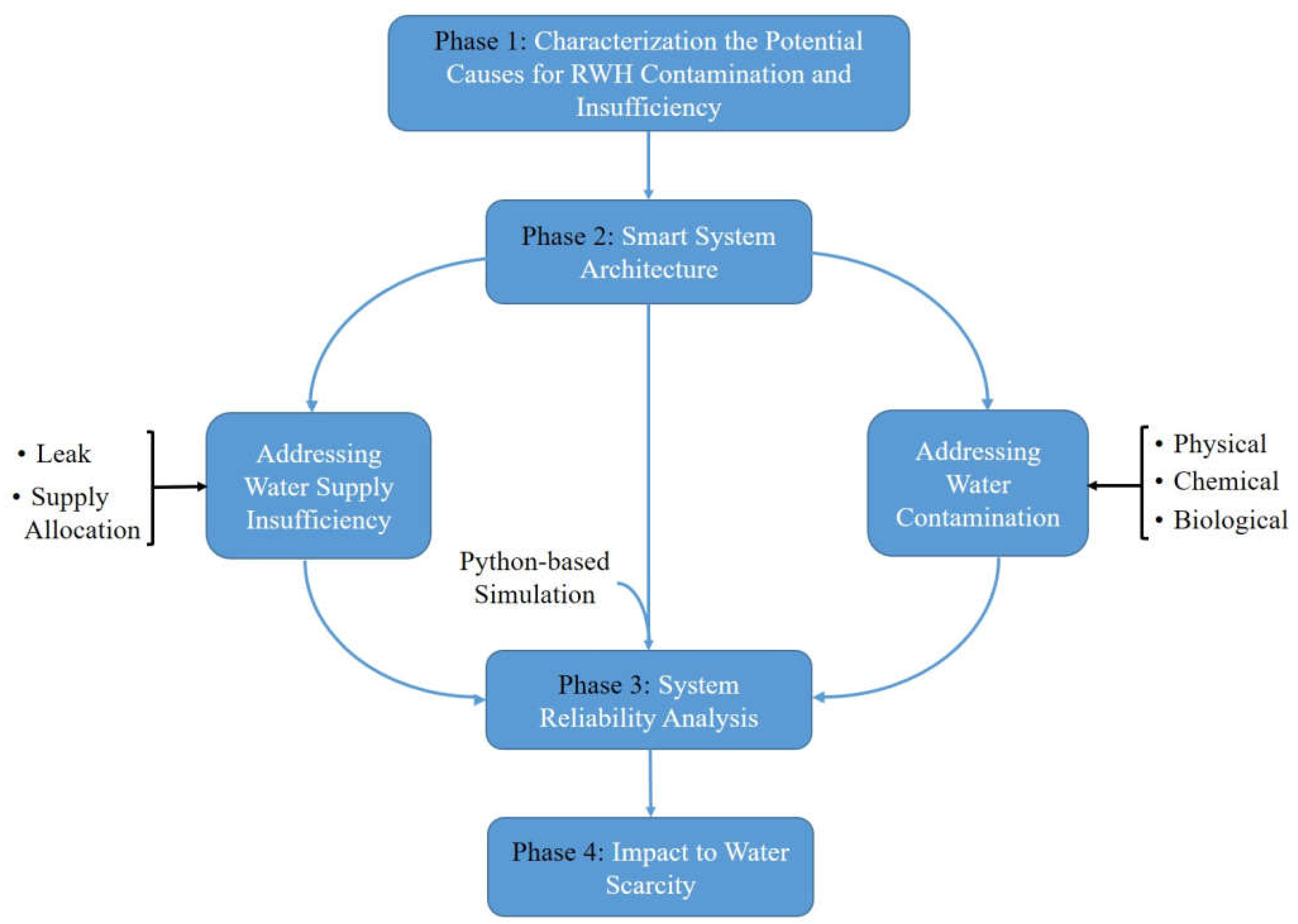
2. Materials and Methods
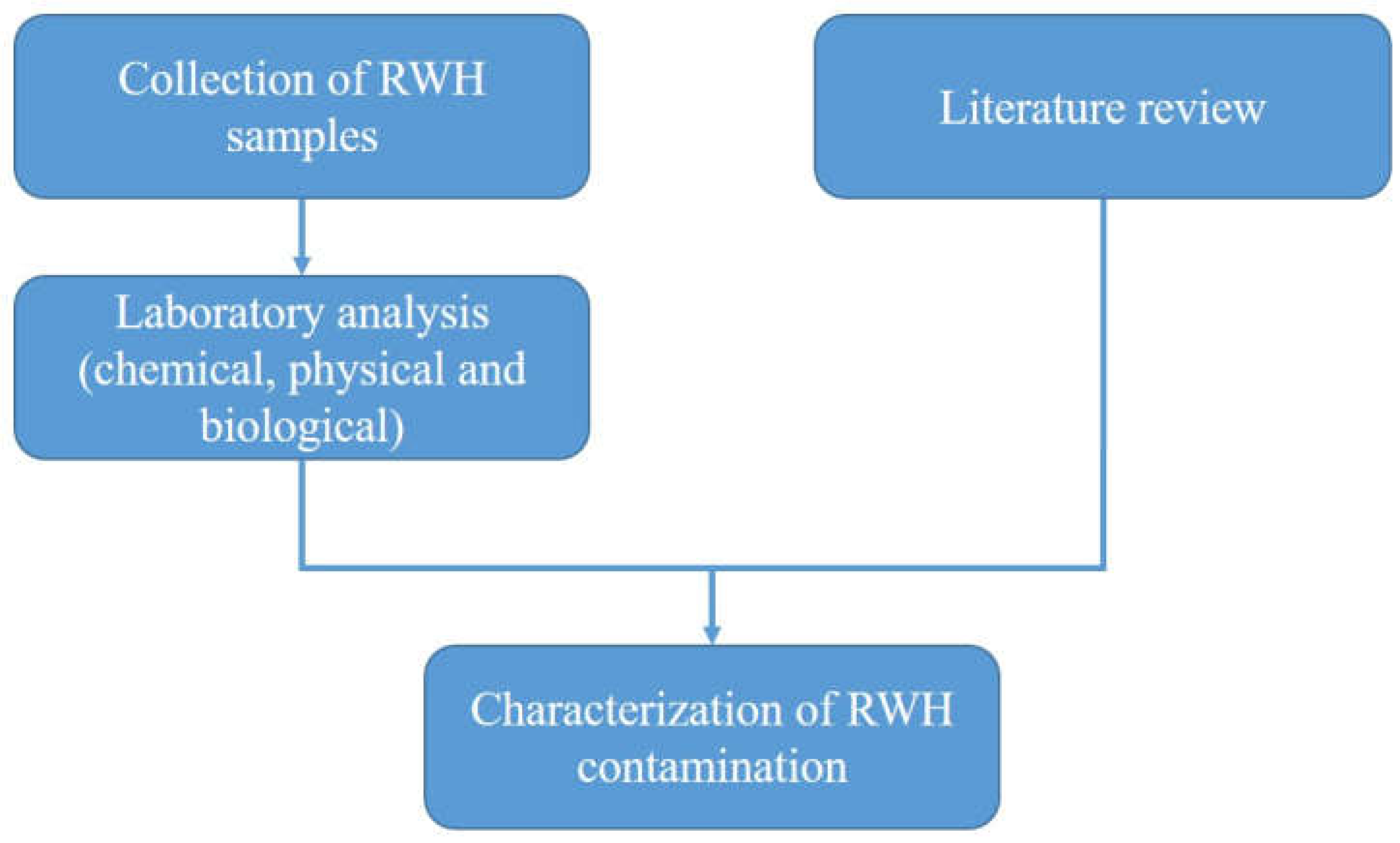
2.1. Assessment of Conventional RWH Shortcomings
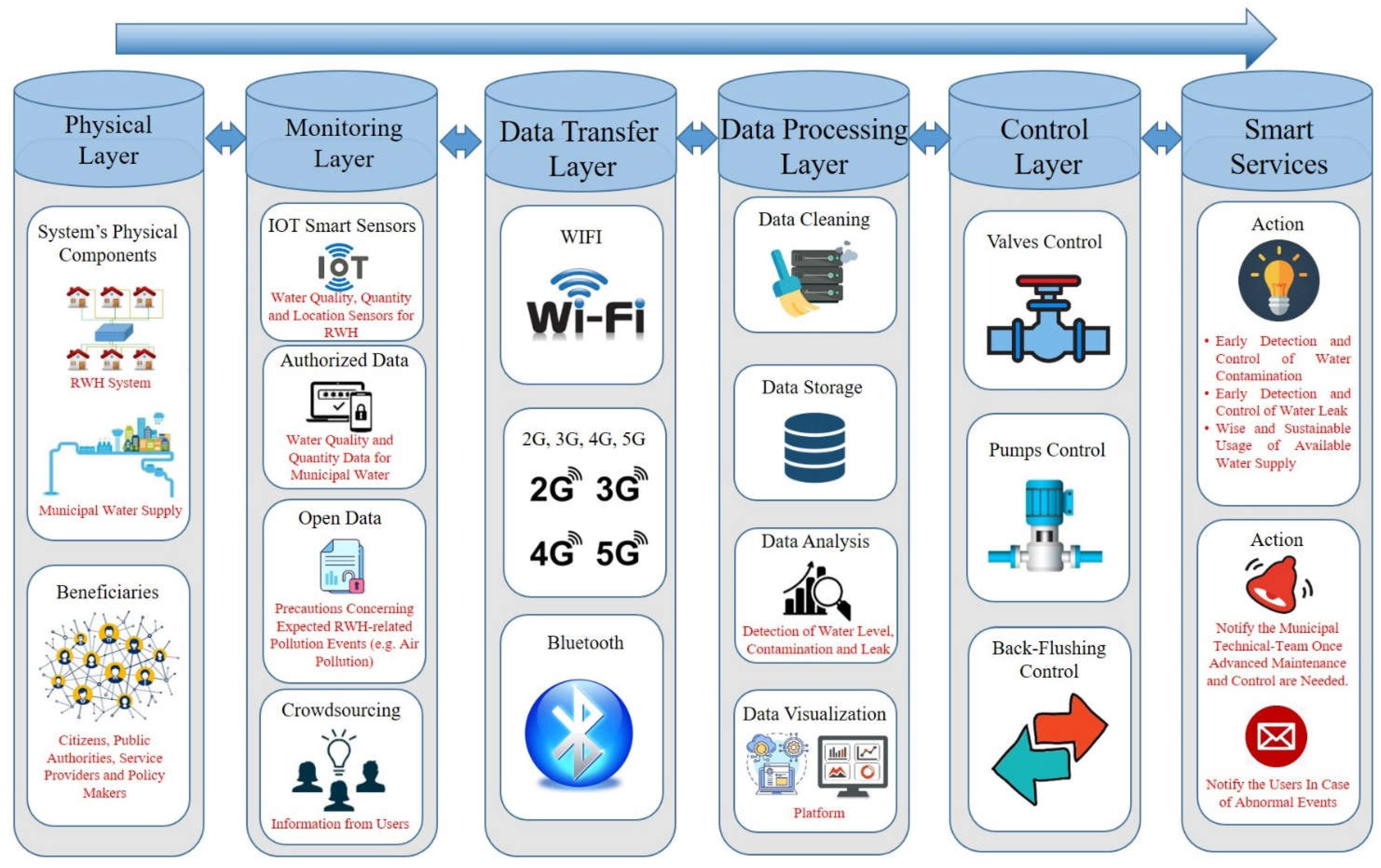
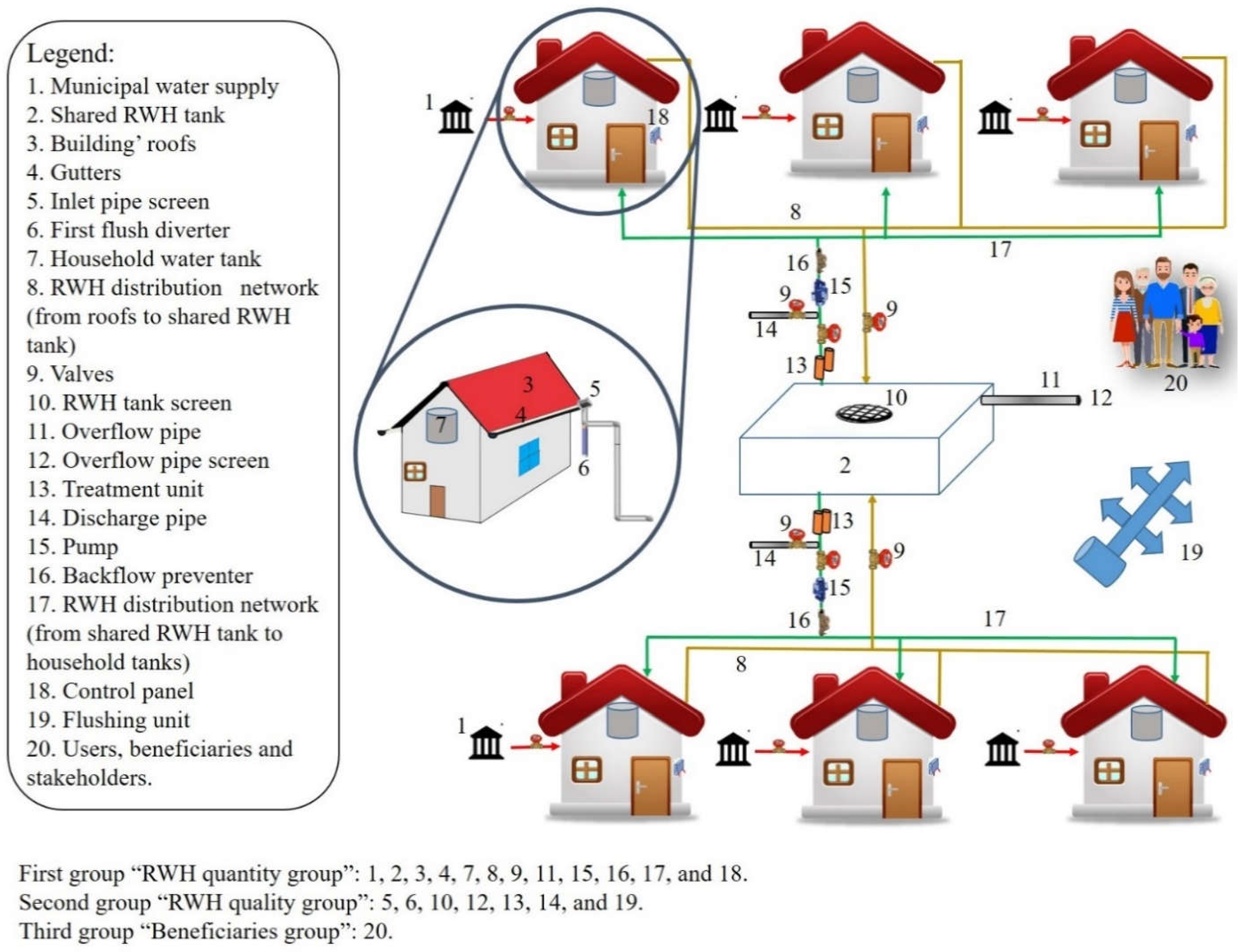
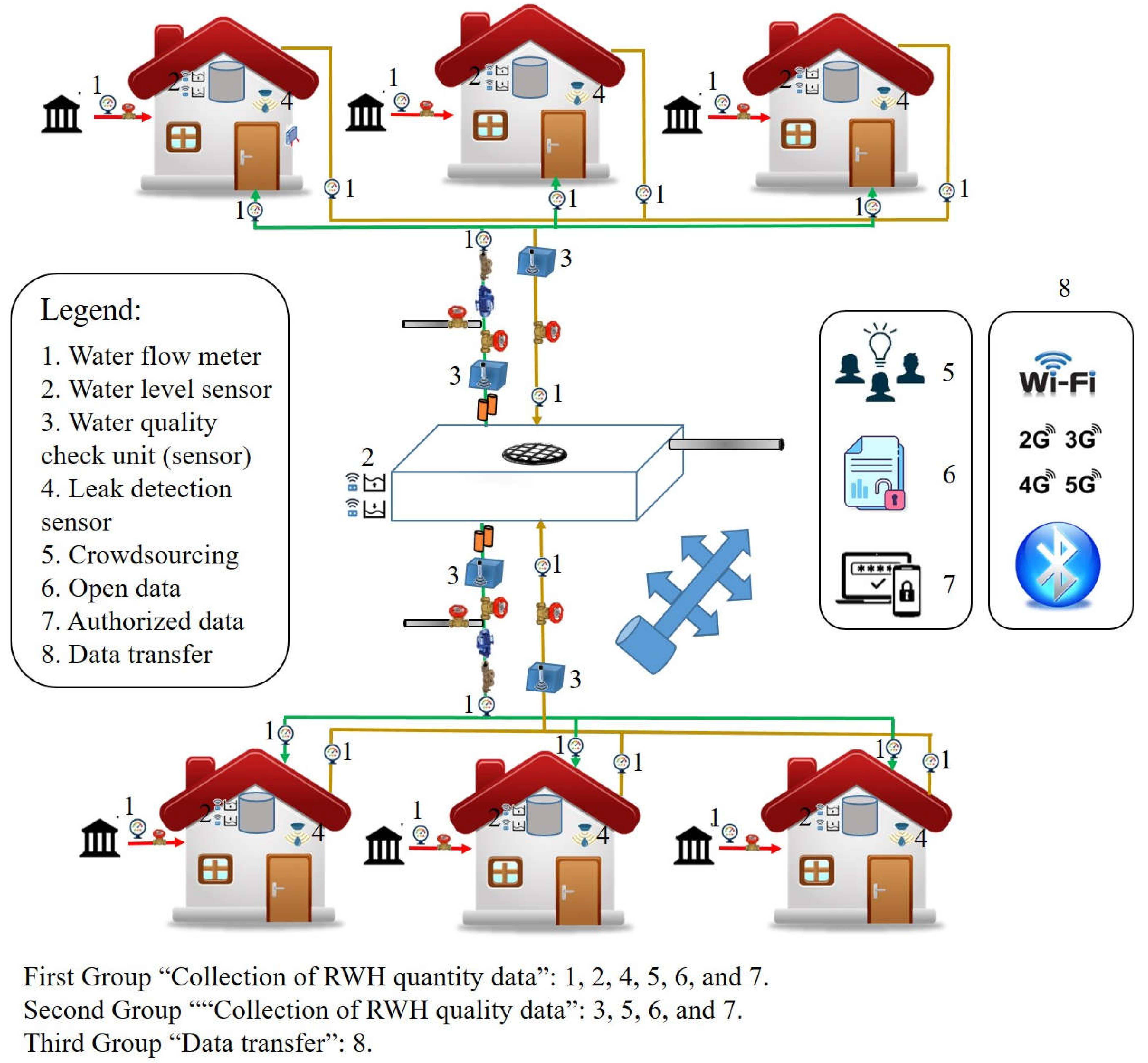
2.2. Smart RWH System Architecture
2.2.1. The Physical Layer
2.2.2. The Monitoring and Data Transfer Layer
2.2.3. Data Processing Layer
2.2.4. Control Layer and the Provided Smart Services
2.3. Smart System Reliability Analysis
- First step: Estimation of Dt and St
- Dt: the water demand on the t-th day (m3/day)
- DWCR: the daily per capita water consumption rate in liter/capita/day (L/c/d)
- POP: the resident’s statistics (capita)
- St: the potential daily RRWH volume for the shared system in the t-th day (m³/day)
- RFt: daily RF for the t-th day (m/day)
- Aj: area for the j-th rooftop (m²)
- RC: runoff and collection efficiency coefficient for the j-th rooftop [25]
- t: the day (1 to 365)
- j: the building number
- n: total number of buildings
- Second step: Estimation of Vt, Ot, and Xt
- Ot: daily overflow from the RWH tank (m³)
- Vt: daily water volume in the RWH tank in the current day
- Vt−1: daily water volume in the RWH tank in the previous day
- St: daily captured volume of rainwater at the roof (m³)
- Dt: daily water demand (m³)
- C: tank size/capacity (m³)
- Xt: daily shortage in covering the needed water demand (m³)
- t: day (1 to 365)
- Third step: Estimation of Re and Rv
- N: total days in a year (365 days)
- U: number of days with water shortage each year (Xt > 0) (in days)
- AWS: annual water supply from the system (in m3)
- AWD: annual water demand (in m3)
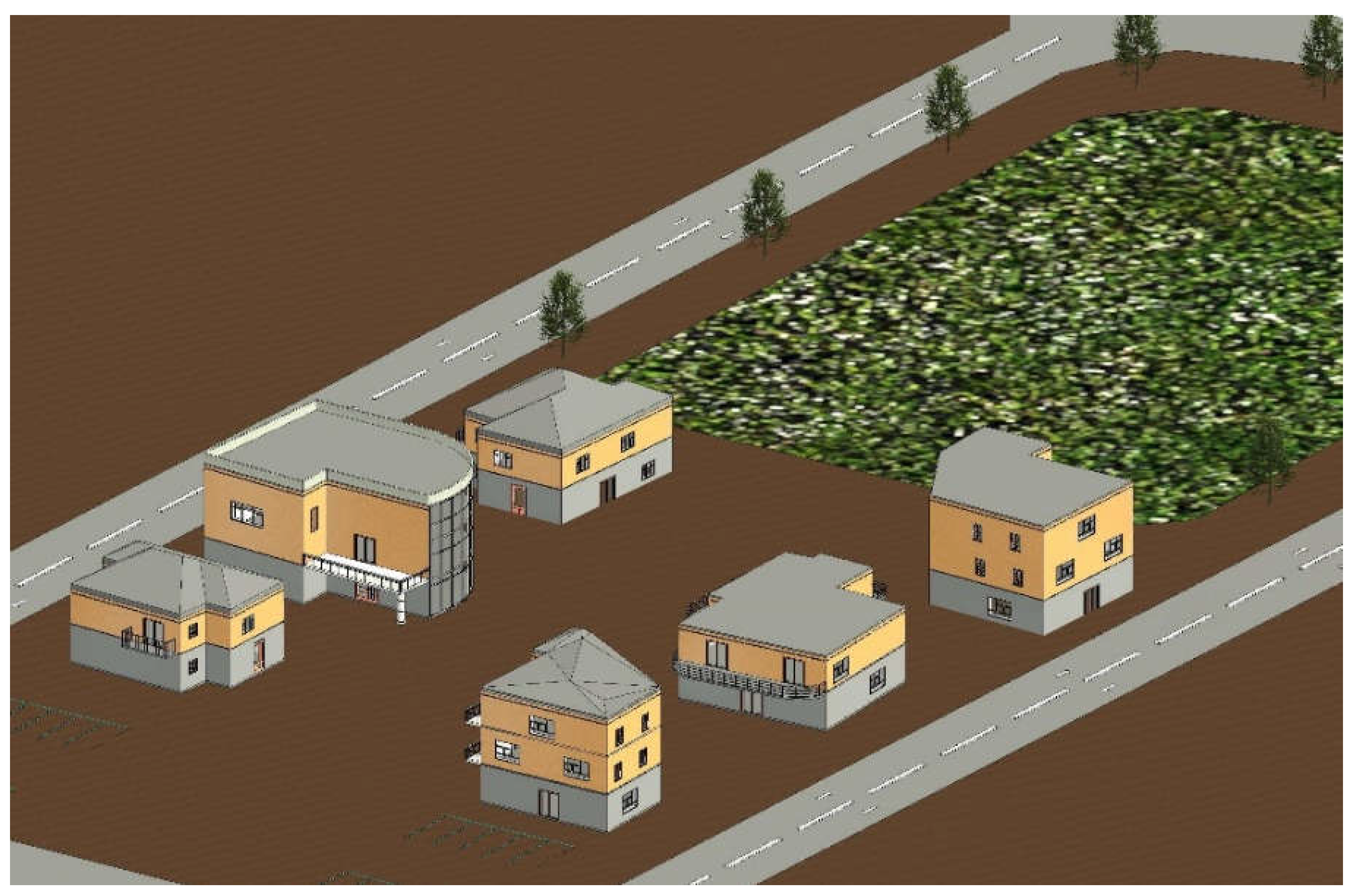
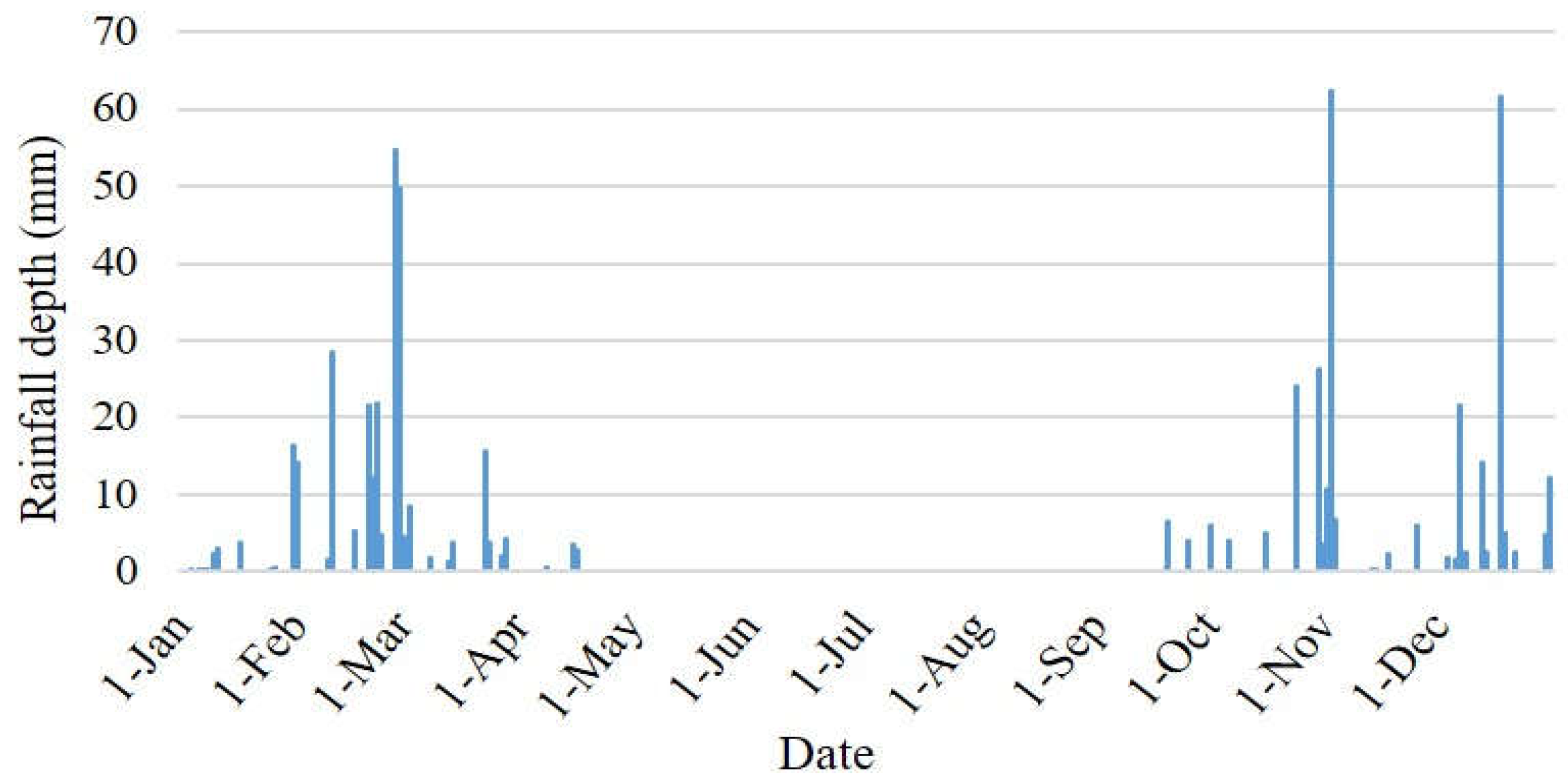
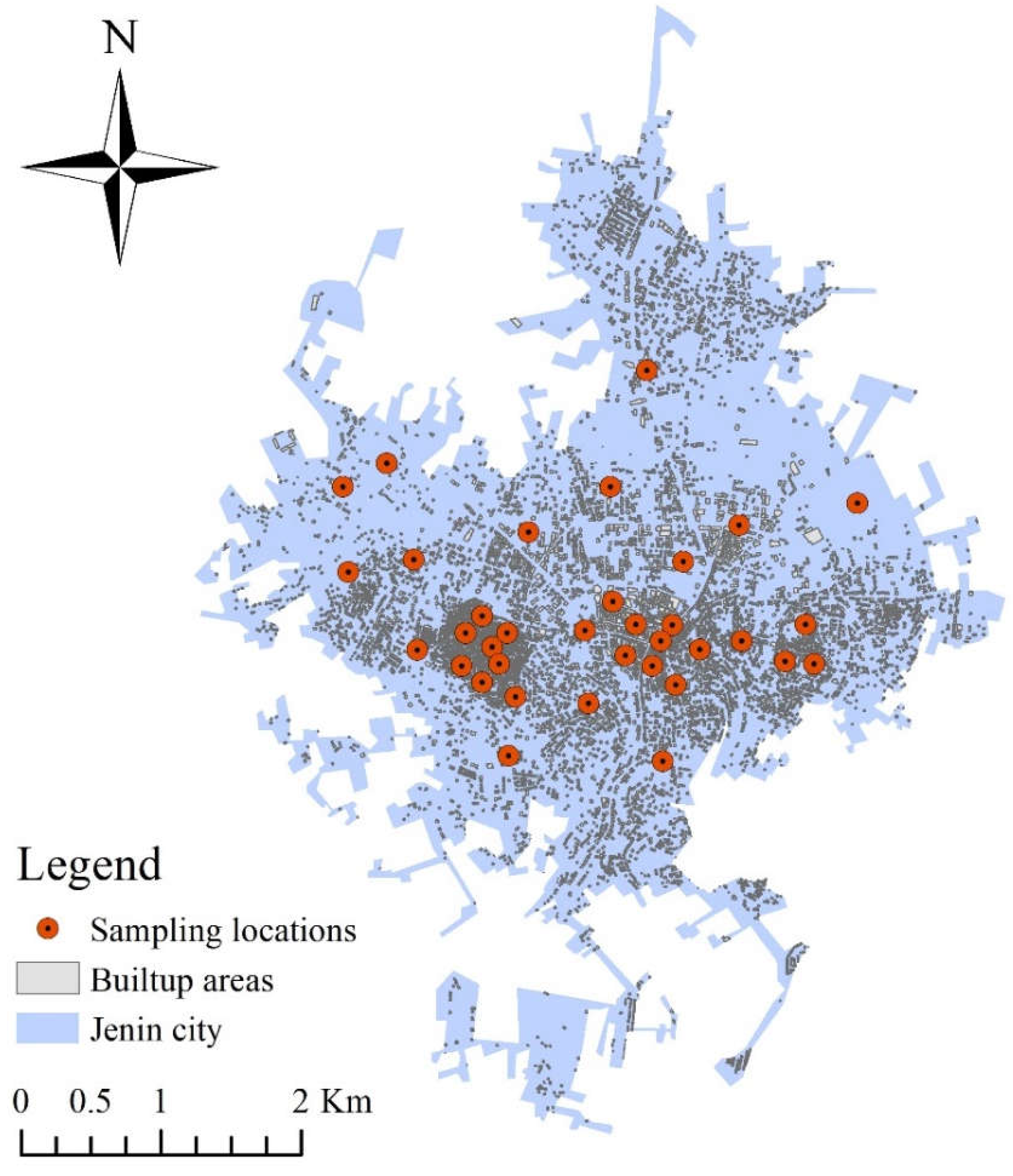
3. Case Study
4. Results
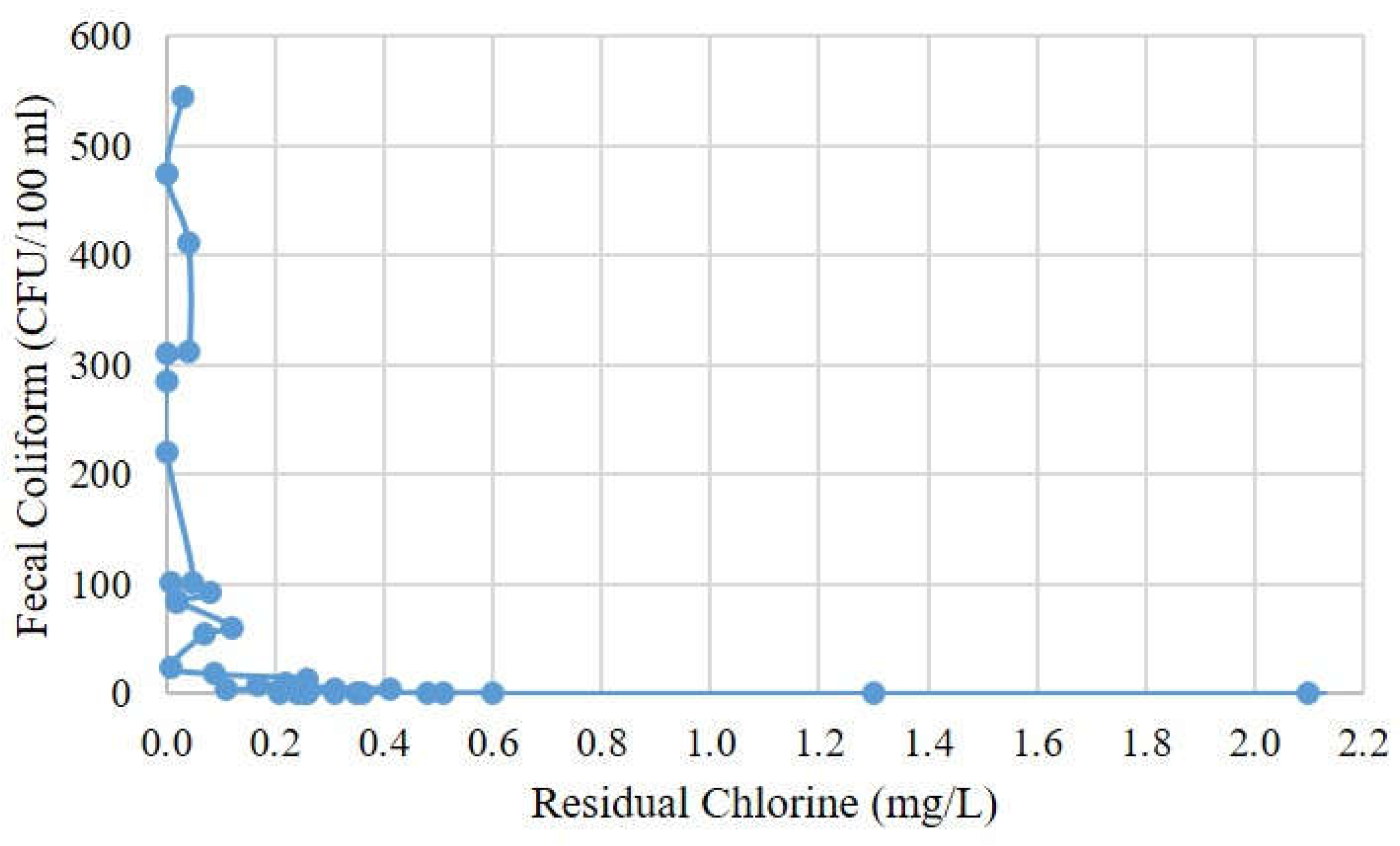
4.1. Smart RWH Quality Assessment and Control
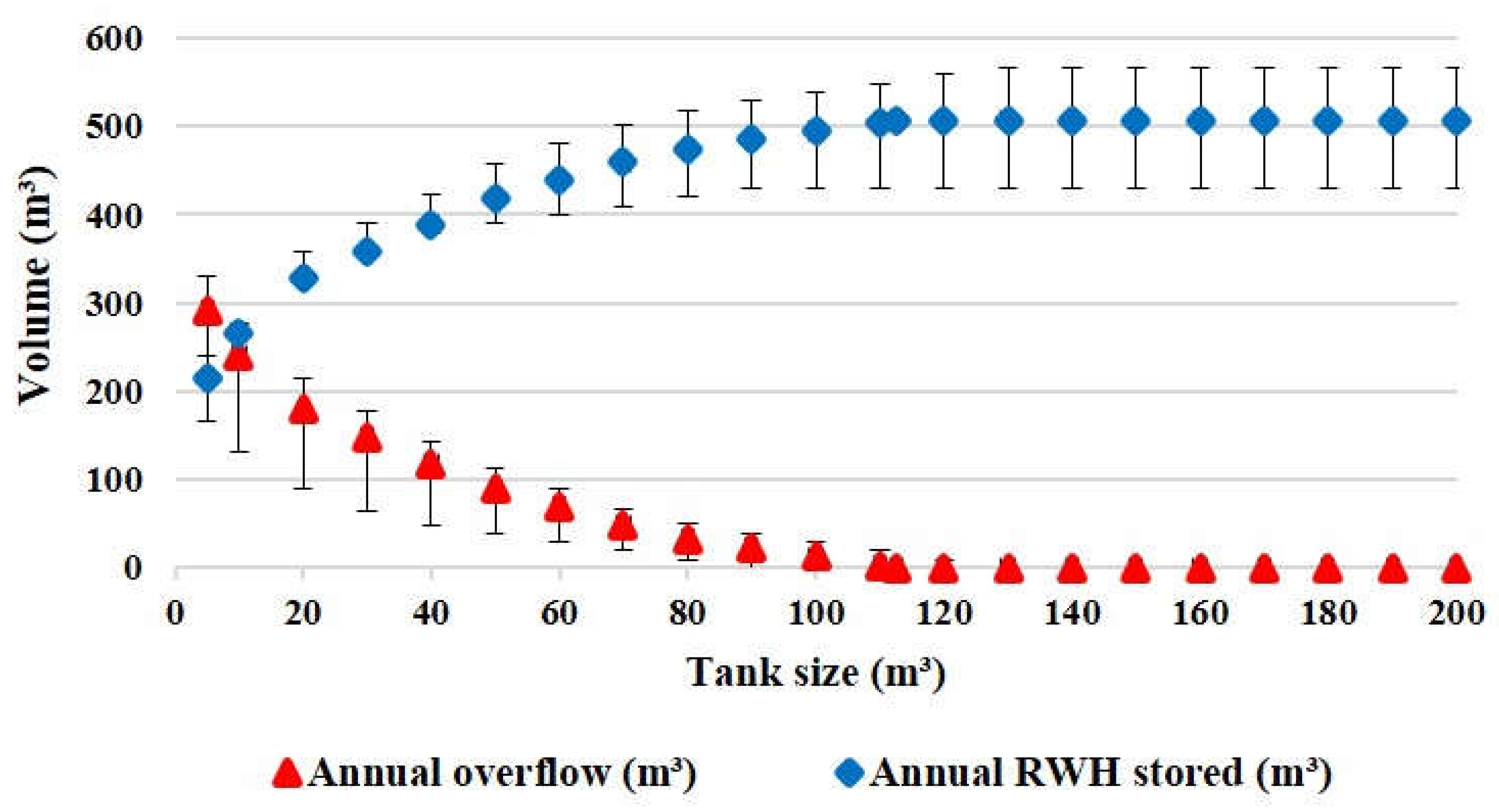
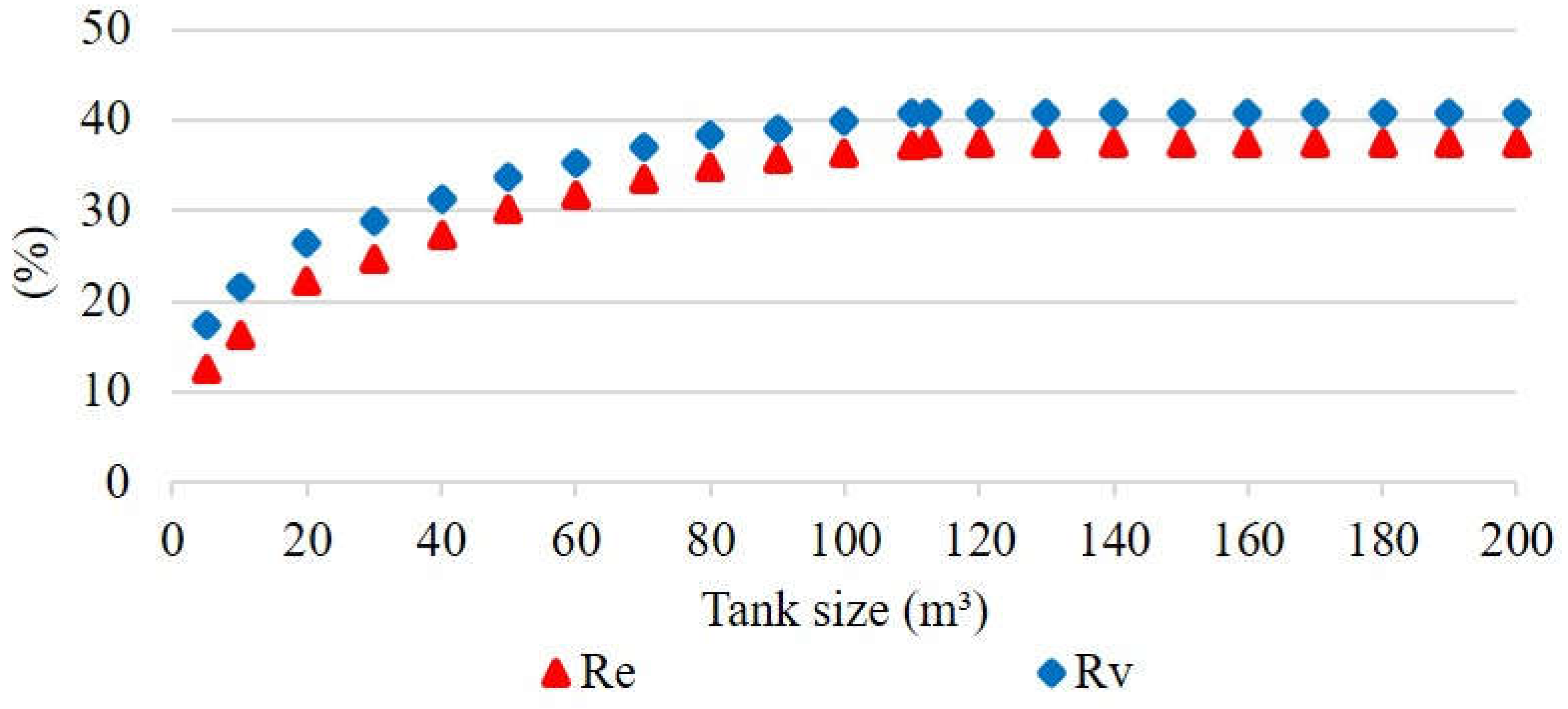
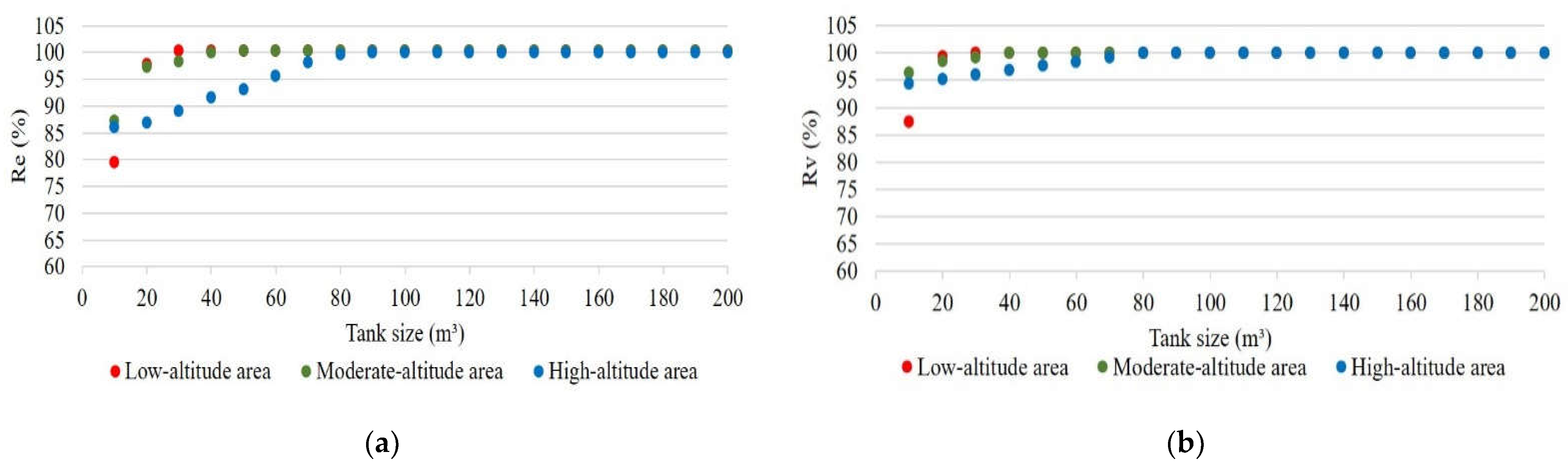
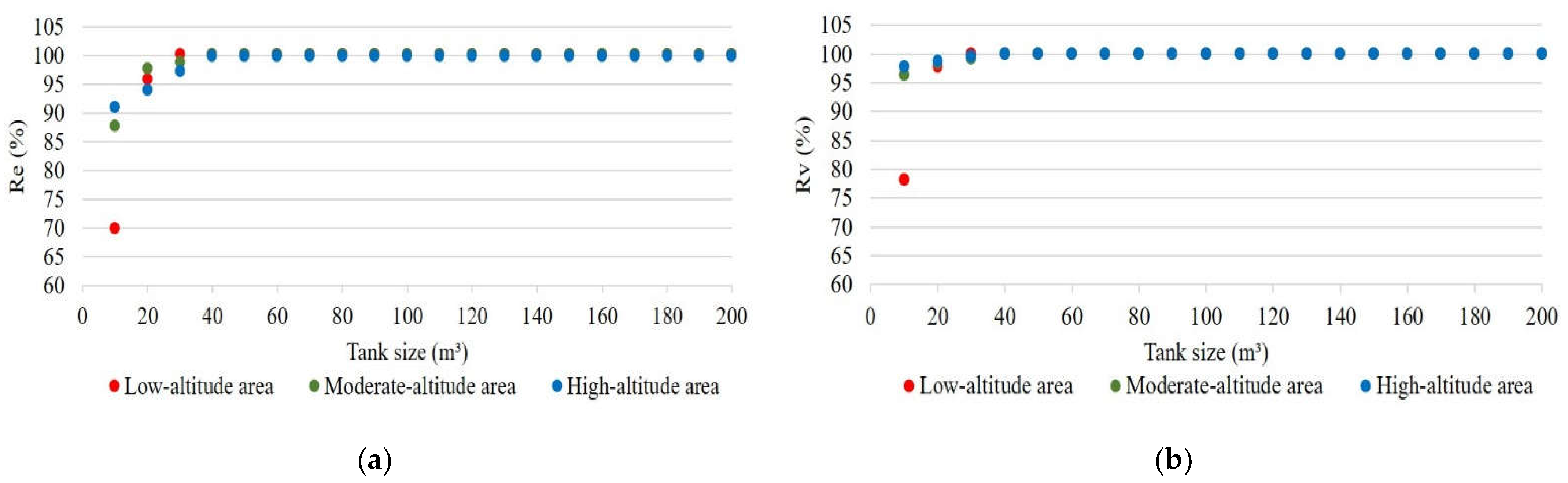
4.2. Smart RWH System Reliability
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gould, J.; Nissen-Petersen, E. Rainwater Catchment Systems for Domestic Supply: Design, Construction and Implementation; IT Publications: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, S.; Sahoo, S.; Debsarkar, A.; Pal, M. Assessment of Adoption Potential of Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting to Combat Water Scarcity: A Case Study of North Parganas District of West Bengal, India. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendanayake, S. Potential for Domestic Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting in the District of Colombo, Sri Lanka. Imp. J. Interdiscip. Res. IJIR 2016, 2, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Mundia, C. Assessing the Reliability of Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting for Domestic Use in Western Kenya. Master’s Thesis, Southern Illinois University, Carbondale, IL, USA, January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Malambo, T.; Huang, Q. Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting as an Alternative Domestic Water Resource in Zambia. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2016, 4, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boakye, E.; John-Jackson, N. Quantifying Rooftop Rainwater Harvest Potential: Case of Takoradi Polytechnic in Takoradi, Ghana. Int. J. Sci. Res. IJSR 2015, 5, 6–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Mahmood, M.; Yaseen, M. Assessing the Potential for Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting and Its Physio and Socioeconomic Impacts, Rawal Watershed, Islamabad, Pakistan. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 10, 17942–17963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, F.A. Rainwater Harvesting in Jordan: Potential Water Saving, Optimal Tank Sizing and Economic Analysis. Urban Water J. 2019, 17, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zreig, M.; Ababneh, F.; Abdullah, F. Assessment of Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting in Northern Jordan. Phys. Chem. Earth 2019, 114, 102794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, O.; Murakami, K. Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting and its Efficiency in Kabul New City. J. Jpn. Soc. Civ. Eng. 2017, 73, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gado, T.A.; El-Agha, D.E. Feasibility of Rainwater Harvesting for Sustainable Water Management in Urban Areas of Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. ESPR 2020, 27, 32304–32317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Mandal, B. Construction and Evaluation of Rainwater Harvesting System for Domestic Use in a Remote and Rural Area of Khulna, Bangladesh. Int. Sch. Res. Notices 2014, 2014, 751952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrão, C.; Moura, P.; de Almeida, A.T. Review of Smart City Assessment Tools. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourabi, H.; Nam, T.; Walker, S.; Gil-Garcia, J.R.; Mellouli, S.; Nahon, K.; Pardo, T.A.; Scholl, H.J. Understanding Smart Cities: An Integrative Framework. In Proceedings of the 45th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 January 2012; pp. 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preeti, P.; Rahman, A. A Case Study on Reliability, Water Demand and Economic Analysis of Rainwater Harvesting in Australian Capital Cities. Water 2021, 13, 2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaren, L.S.; Mondal, M.S. Assessing Water Poverty of Livelihood Groups in Peri-Urban Areas around Dhaka under a Changing Environment. Water 2021, 13, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar-Navascués, R.A.; Fragkou, M.C. Managing Water Scarcity Futures: Identifying Factors Influencing Water Quality, Risk Perception and Daily Practices in Urban Environments after the Introduction of Desalination. Water 2021, 13, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayt Ougougdal, H.; Yacoubi Khebiza, M.; Messouli, M.; Lachir, A. Assessment of Future Water Demand and Supply under IPCC Climate Change and Socio-Economic Scenarios, Using a Combination of Models in Ourika Watershed, High Atlas, Morocco. Water 2020, 12, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judeh, T.; Bian, H.; Shahrour, I. GIS-Based Spatiotemporal Mapping of Groundwater Potability and Palatability Indices in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas. Water 2021, 13, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judeh, T.; Haddad, M.; Özerol, G. Assessment of Water Governance in the West Bank, Palestine. Int. J. Glob. Environ. Issues 2017, 16, 119–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PCBS. Quantity of Water Supply for Domestic Sector, Water Consumed and Daily Consumption per Capita in the West Bank by Governorate in 2018. Available online: https://www.pcbs.gov.ps/Portals/_Rainbow/Documents/water-E9-2018.html (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Anayah, F.M.; Almasri, M.N. Trends and Occurrences of Nitrate in the Groundwater of the West Bank, Palestine. Appl. Geogr. 2009, 29, 588–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghara, A.; Al-Khatib, I.A.; Al-Jabari, M. Quality of Drinking Water from Springs in Palestine: West Bank as a Case Study. J. Environ. Public Health 2019, 2019, 8631732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaee, E.; Abbasi, A.A.; Tabatabaee Yazdi, J.; Ziyaee, M. Feasibility of Rainwater Harvesting and Consumption in a Middle Eastern Semiarid Urban Area. Water 2021, 13, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judeh, T.; Shahrour, I. Rainwater Harvesting to Address Current and Forecasted Domestic Water Scarcity: Application to Arid and Semi-Arid Areas. Water 2021, 13, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagnone, P.; Cea, L.; Comino, E.; Rosso, M. Rainwater Harvesting Techniques to Face Water Scarcity in African Drylands: Hydrological Efficiency Assessment. Water 2020, 12, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, F.; Abdulla, C.; Eslamian, S. Concept and Technology of Rainwater Harvesting. In Handbook of Water Harvesting and Conservation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słyś, D.; Stec, A. Centralized or Decentralized Rainwater Harvesting Systems: A Case Study. Resources 2020, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, D.A.; Tran, S.H.; Dang, H.T.T.; Nguyen, V.-A.; Nguyen, V.A.; Do, C.v.; Han, M. Assessment of Rainwater Harvesting and Maintenance Practice for Better Drinking Water Quality in Rural Areas. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua 2021, 70, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, S.A.; Talarico, V.C.; Pirouz, B. Optimizing Rainwater Harvesting Systems for Non-Potable Water Uses and Surface Runoff Mitigation BT-Numerical Computations: Theory and Algorithms; Sergeyev, Y.D., Kvasov, D.E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 570–582. [Google Scholar]
- Rostad, N.; Foti, R.; Montalto, F.A. Harvesting Rooftop Runoff to Flush Toilets: Drawing Conclusions from Four Major U.S. Cities. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2016, 108, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Nya, E.L.; Rahman, M.A.; Mwamila, T.B.; Cao, V.; Gwenzi, W.; Noubactep, C. Integrated Water Resource Management: Rethinking the Contribution of Rainwater Harvesting. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadian, K.; Kapelan, Z.; Mousavi, J.; Alani, A. Can Smart Rainwater Harvesting Schemes Result in the Improved Performance of Integrated Urban Water Systems? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 19271–19282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrolo, R.; Loscri, V.; Mitton, N. Towards a Smart City Based on Cloud of Things, a Survey on the Smart City Vision and Paradigms. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2015, 28, e2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Jara, A.J.; Skarmeta, A.F.G. Smart Lighting Solutions for Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops, Barcelona, Spain, 25–28 March 2013; pp. 1374–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratigea, A. The Concept of ‘Smart’ Cities—Towards Community Development? NETCOM 2012, 26, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriazis, D.; Varvarigou, T.A.; White, D.; Rossi, A.; Cooper, J. Sustainable Smart City IoT Applications: Heat and Electricity Management & Eco-Conscious Cruise Control for Public Transportation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 14th International Symposium on “A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks” (WoWMoM), Madrid, Spain, 4–7 June 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Şevik, S.; Aktaş, A. Performance enhancing and improvement studies in a 600 kW solar photovoltaic (PV) power plant; manual and natural cleaning, rainwater harvesting and the snow load removal on the PV arrays. Renew. Energy 2022, 181, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, B.; Butler, J.P.; Bock, R.G.; Portelli, J.P.; Bilén, S.G. IoT-Based Sanitizer Station Network: A Facilities Management Case Study on Monitoring Hand Sanitizer Dispenser Usage. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 979–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carminati, M.; Sinha, G.R.; Mohdiwale, S.; Ullo, S.L. Miniaturized Pervasive Sensors for Indoor Health Monitoring in Smart Cities. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Hariz, M.; Said, D.; Mouftah, H.T. A Dynamic Mobility Traffic Model Based on Two Modes of Transport in Smart Cities. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, T. A Predictive Vehicle Ride Sharing Recommendation System for Smart Cities Commuting. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehbe, R.; Shahrour, I. A BIM-Based Smart System for Fire Evacuation. Future Internet 2021, 13, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.; Patrão, C.; Moura, P.; de Almeida, A.T. A Review of Energy Modeling Tools for Energy Efficiency in Smart Cities. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 1420–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnu, S.; Ramson, S.R.J.; Senith, S.; Anagnostopoulos, T.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Fan, X.; Srinivasan, S.; Kirubaraj, A.A. IoT-Enabled Solid Waste Management in Smart Cities. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 1004–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudumbe, M.J.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M. Smart Water Meter System for User-Centric Consumption Measurement. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 13th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN), Cambridge, UK, 22–24 July 2015; pp. 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, D.; Vamvakeridou-Lyroudia, L.; Kapelan, Z. Smart Meters, Smart Water, Smart Societies: The IWIDGET Project. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasekh, A.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Mulchandani, S.; Modi, S.; Banks, M. Smart Water Networks and Cyber Security. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2016, 142, 1816004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Y.; El-Maghraby, M.; Pathak, S. Applications of Deep Learning for Smart Water Networks. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashhadi, N.; Shahrour, I.; Attoue, N.; el Khattabi, J.; Aljer, A. Use of Machine Learning for Leak Detection and Localization in Water Distribution Systems. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 1293–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, E.; Shahrour, I. Leakage Detection Using Smart Water System: Combination of Water Balance and Automated Minimum Night Flow. Water Resour. Manag. 2017, 31, 4821–4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, A.N.; Mamun, K.A.; Islam, F.R.; Haqva, H. Smart Water Quality Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 2nd Asia-Pacific World Congress on Computer Science and Engineering (APWC on CSE), Nadi, Fiji, 2–4 December 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, G.; Yan, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X. A Survey of Smart Water Quality Monitoring System. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 4893–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasika, S.; Gandla, S.T. Smart Water Quality Monitoring System with Cost-Effective Using IoT. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, H.M.; McNabola, A.; López-Jiménez, P.A.; Pérez-Sánchez, M. Smart Water Management towards Future Water Sustainable Networks. Water 2020, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Sarp, S.; Jeon, D.J.; Kim, J.H. Smart Water Grid: The Future Water Management Platform. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 55, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntuli, N.; Abu-Mahfouz, A. A Simple Security Architecture for Smart Water Management System. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 83, 1164–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, T.; Alcarria, R.; Martín, D.; Morales, A.; Navarro, M.; Calero, R.; Iglesias, S.; López, M. An Internet of Things-Based Model for Smart Water Management. In Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops, Victoria, BC, Canada, 13–14 May 2014; pp. 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, V.; Reddy, M.V.; Irshad, M.; Joshi, N. The Internet of Things (IOT) Based Smart Rain Water Harvesting System. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication (ICSC), Noida, India, 5–7 March 2020; pp. 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 1–631. [Google Scholar]
- Frichot, J.J.H.; Rubiyatno; Talukdar, G. Water Quality Assessment of Roof-Collected Rainwater in Miri, Malaysia. Trop. Aquat. Soil Pollut. 2021, 1, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otter, P.; Sattler, W.; Grischek, T.; Jaskolski, M.; Mey, E.; Ulmer, N.; Grossmann, P.; Matthias, F.; Malakar, P.; Goldmaier, A.; et al. Economic Evaluation of Water Supply Systems Operated with Solar-Driven Electro-Chlorination in Rural Regions in Nepal, Egypt and Tanzania. Water Res. 2020, 187, 116384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mac Mahon, J.; Gill, L.W. Sustainability of Novel Water Treatment Technologies in Developing Countries: Lessons Learned from Research Trials on a Pilot Continuous Flow Solar Water Disinfection System in Rural Kenya. Dev. Eng. 2018, 3, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddeo, V.; Scannapieco, D.; Belgiorno, V. Enhanced Drinking Water Supply through Harvested Rainwater Treatment. J. Hydrol. 2013, 498, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frechen, F.-B.; Exler, H.; Romaker, J.; Schier, W. Long-Term Behaviour of a Gravity-Driven Dead End Membrane Filtration Unit for Potable Water Supply in Cases of Disasters. Water Supply 2011, 11, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Nya, E.L.; Cao, V.; Gwenzi, W.; Rahman, M.A.; Noubactep, C. Universal Access to Safe Drinking Water: Escaping the Traps of Non-Frugal Technologies. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hu, R.; Ndé-Tchoupé, A.I.; Gwenzi, W.; Ruppert, H.; Noubactep, C. Designing the Next Generation of Fe0-Based Filters for Decentralized Safe Drinking Water Treatment: A Conceptual Framework. Processes 2020, 8, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, L. Water Quality of Rainwater Harvesting Systems; SOPAC: Suva, Fiji, 2005; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Gao, J.; Zhao, W.; Xu, X.; Yin, Y.; Wu, L. Quality Assessment of Rainwater and Harvested Rainwater Stored in Different Types of Cisterns. Water Supply 2016, 17, 652–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osayemwenre, G.; Osibote, O.A. A Review of Health Hazards Associated with Rainwater Harvested from Green, Conventional and Photovoltaic Rooftops. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2021, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chubaka, C.E.; Whiley, H.; Edwards, J.W.; Ross, K.E. Lead, Zinc, Copper, and Cadmium Content of Water from South Australian Rainwater Tanks. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, T.; Abbasi, S.A. Sources of Pollution in Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting Systems and their Control. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 2097–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alim, M.A.; Rahman, A.; Tao, Z.; Samali, B.; Khan, M.M.; Shirin, S. Suitability of Roof Harvested Rainwater for Potential Potable Water Production: A Scoping Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilane, T.; Simiso, G. An Assessment of the Quality of Rainwater Harvested Using Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting (RWH) Technologies in Swaziland. J. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2018, 3, 55–64. [Google Scholar]
- Tamimi, L. Rainwater Harvesting System: Quality and Impacts on Public Health. Master’s Thesis, Birzeit University, Ramallah, Palestine, February 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, N.; Driejana, D.; Sulaeman, A.; Ariesyady, H. Water Quality Indices for Rainwater Quality Assessment in Bandung Urban Region. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 669, 12044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Adeniyi, A.G. A Comprehensive Review of Water Quality Monitoring and Assessment in Nigeria. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D. A Case Study of Rainwater Harvesting: Its Desing, Factors Affecting and Cost Installation of AIIMS Hospital, Raipur. SSRN Electron. J. 2019, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuki, F.; Mikava, K.; Kurishu, H. Intelligent Water System for Smart Cities. Hitachi Rev. 2012, 61, 147–151. [Google Scholar]
- Rojek, I.; Studzinski, J. Detection and Localization of Water Leaks in Water Nets Supported by an ICT System with Artificial Intelligence Methods as a Way Forward for Smart Cities. Sustainability 2019, 11, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Xia, B.; Zhou, Y.; Bi, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Xia, S. Effect of Roof Materials and Weather Patterns on the Quality of Harvested Rainwater in Shanghai, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrour, I.; Xie, X. Role of Internet of Things (IoT) and Crowdsourcing in Smart City Projects. Smart Cities 2021, 4, 1276–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yen, N.Y.; Huang, R.; Zhou, X. Mobile Crowd Sensing and Computing: The Review of an Emerging Human-Powered Sensing Paradigm. ACM Comput. Surv. 2015, 48, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J. Data Cleaning and Feature Selection for Gravelly Soil Liquefaction. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 145, 106711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, S.B.; Yorke-Edwards, V.; Diaz-Montana, C.; Murray, M.L.; Masters, L.; Gabriel, M.; Joffe, N.; Sydes, M.R. Making a Distinction between Data Cleaning and Central Monitoring in Clinical Trials. Clin. Trials 2021, 18, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northcutt, C.; Jiang, L.; Chuang, I. Confident Learning: Estimating Uncertainty in Dataset Labels. J. Artif. Intell. Res. JAIR 2021, 70, 1373–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Rong, H. Toward Secure Distributed Data Storage with Error Locating in Blockchain Enabled Edge Computing. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2022, 79, 103560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robie, J. XML Processing and Data Integration with XQuery. IEEE Internet Comput. 2007, 11, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Chen, Z.; Hefferman, G.; Wei, T.; He, H.; Yang, Q. A Hierarchical Distributed Fog Computing Architecture for Big Data Analysis in Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the ASE Big Data & Social Informatics 2015, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 7–9 October 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhoseny, H.; Elhoseny, M.; el-din Riad, A.; Hassanien, A.E. A Framework for Big Data Analysis in Smart Cities. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Machine Learning Technologies and Applications 2018, Cairo, Egypt, 5–7 May 2018; pp. 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Xu, J.; Qiao, H.; Zhou, M.; Liang, B. Visual IoT: Enabling Internet of Things Visualization in Smart Cities. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Lopes, M.A.; Dória Neto, A.D.; de Medeiros Martins, A. Parallel T-SNE Applied to Data Visualization in Smart Cities. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 11482–11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.R.; Sakib, B.M.S.; Sakib, S.S.; Imteaz, M.A. Rainwater Harvesting Potentials in Commercial Buildings in Dhaka: Reliability and Economic Analysis. Hydrology 2021, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, L.v. A Simulation of Rainwater Harvesting Design and Demand-Side Controls for Large Hospitals. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basinger, M.; Montalto, F.; Lall, U. A Rainwater Harvesting System Reliability Model Based on Nonparametric Stochastic Rainfall Generator. J. Hydrol. 2010, 392, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursino, N.; Grisi, A. Reliability and Efficiency of Rainwater Harvesting Systems under Different Climatic and Operational Scenarios. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plan. 2017, 12, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Jing, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yue, T. Water Saving Efficiency and Reliability of Rainwater Harvesting Systems in the Context of Climate Change. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 1341–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenin Municipality (JM). Annual Report on Water Supply Service in Jenin Municipality; JM: Jenin, Palestine, 2019; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, G.; Bartram, J. Domestic Water Quantity, Service Level and Health; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Palestinian Metrological Authority (PMA). Climate Bulletin; PMA: Ramallah, Palestine, 2018; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, N.; Hogland, W.; Sokolov, M.; Rud, V.; Myazin, N. Assessment of Rainwater Harvesting for Domestic Water Supply in Palestinian Rural Areas. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 245, 6012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muoio, R.; Caretti, C.; Rossi, L.; Santianni, D.; Lubello, C. Water Safety Plans and Risk Assessment: A Novel Procedure Applied to Treated Water Turbidity and Gastrointestinal Diseases. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 223, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soros, A.; Amburgey, J.E.; Stauber, C.E.; Sobsey, M.D.; Casanova, L.M. Turbidity Reduction in Drinking Water by Coagulation-Flocculation with Chitosan Polymers. J. Water Health 2019, 17, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenazi, M.; Hashim, K.S.; Hassan, A.A.; Muradov, M.; Kot, P.; Abdulhadi, B. Turbidity Removal Using Natural Coagulants Derived from the Seeds of Strychnos Potatorum: Statistical and Experimental Approach. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 888, 12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Batsh, N.; Al-Khatib, I.A.; Ghannam, S.; Anayah, F.; Jodeh, S.; Hanbali, G.; Khalaf, B.; van der Valk, M. Assessment of Rainwater Harvesting Systems in Poor Rural Communities: A Case Study from Yatta Area, Palestine. Water 2019, 11, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, A.K.; Swaileh, K.M.; Hussein, R.M.; Matani, M. Quality Assessment of Roof-Harvested Rainwater in the West Bank, Palestinian Authority. J. Water Health 2011, 9, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, T.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Fecal Coliform Distribution and Health Risk Assessment in Surface Water in an Urban-Intensive Catchment. J. Hydrol. 2022, 604, 127204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Deng, Z. Modeling and Predicting Fecal Coliform Bacteria Levels in Oyster Harvest Waters along Louisiana Gulf Coast. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helbling, D.; Vanbriesen, J. Modeling Residual Chlorine Response to a Microbial Contamination Event in Drinking Water Distribution Systems. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.v.; Patel, H.M. Analysis of Residual Chlorine in Simple Drinking Water Distribution System with Intermittent Water Supply. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrudey, S.E.; Backer, L.C.; Humpage, A.R.; Krasner, S.W.; Michaud, D.S.; Moore, L.E.; Singer, P.C.; Stanford, B.D. Evaluating Evidence for Association of Human Bladder Cancer with Drinking-Water Chlorination Disinfection By-Products. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B 2015, 18, 213–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kali, S.; Khan, M.; Ghaffar, M.S.; Rasheed, S.; Waseem, A.; Iqbal, M.M.; Bilal khan Niazi, M.; Zafar, M.I. Occurrence, Influencing Factors, Toxicity, Regulations, and Abatement Approaches for Disinfection by-Products in Chlorinated Drinking Water: A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 281, 116950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Källén, B.A.J.; Robert, E. Drinking Water Chlorination and Delivery Outcome—A Registry-Based Study in Sweden. Reprod. Toxicol. 2000, 14, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, A.J.; Crider, Y.; Sultana, S.; Swarthout, J.; Goddard, F.G.B.; Anjerul Islam, S.; Sen, S.; Ayyagari, R.; Luby, S.P. Effect of In-Line Drinking Water Chlorination at the Point of Collection on Child Diarrhoea in Urban Bangladesh: A Double-Blind, Cluster-Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Glob. Health 2019, 7, e1247–e1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crider, Y.; Sultana, S.; Unicomb, L.; Davis, J.; Luby, S.P.; Pickering, A.J. Can You Taste It? Taste Detection and Acceptability Thresholds for Chlorine Residual in Drinking Water in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Lin, Y.; Xu, B.; Hu, C.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cao, T.; Gao, N. Factors Affecting the Water Odor Caused by Chloramines during Drinking Water Disinfection. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Salaymeh, A.; Al-Khatib, I.A.; Arafat, H.A. Towards Sustainable Water Quality: Management of Rainwater Harvesting Cisterns in Southern Palestine. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 1721–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.; Tamimi, L.M.A.; Al-Khatib, I.A.; Apul, D.S. Management of Rainwater Harvesting and Its Impact on the Health of People in the Middle East: Case Study from Yatta Town, Palestine. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafarzadeh, A.; Amanidaz, N.; Seyedghasemi, N. Relationship between Turbidity and Residual Chlorine and Microbial Quality of Drinking Water. Med. Lab. J. 2014, 8, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, S.; Hashmi, I.; Qazi, I.A.; Qaiser, S.; Rasheed, S. Monitoring of Coliforms and Chlorine Residual in Water Distribution Network of Rawalpindi, Pakistan. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 140, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, M.; Saleh, H.N.; Yaseri, M.; Mahvi, A.H.; Soleimani, H.; Saeedi, Z.; Zohdi, S.; Mohammadi, A.A. Data on Microbiological Quality Assessment of Rural Drinking Water Supplies in Poldasht County. Data Brief 2018, 17, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzhenry, K.; Barrett, M.; O’Flaherty, V.; Dore, W.; Cormican, M.; Rowan, N.; Clifford, E. The Effect of Wastewater Treatment Processes, in Particular Ultraviolet Light Treatment, on Pathogenic Virus Removal; EPA Research: Wexford, Ireland, 2016; pp. 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Akowanou, O.; Aina, M.; Groendijk, L.; Yao, B. Household Water Treatment in Benin: Current/Local Practices. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2016, 142, 246–256. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, D.; Lansey, K. Dual Water Distribution Network Design under Triple-Bottom-Line Objectives. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2012, 138, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burszta-Adamiak, E.; Spychalski, P. Water Savings and Reduction of Costs through the Use of a Dual Water Supply System in a Sports Facility. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Han, M.Y. Design of Dual Water Supply System Using Rainwater and Groundwater at Arsenic Contaminated Area in Vietnam. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. Aqua 2014, 63, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasoulkhani, K.; Mostafavi, A.; Cole, J.; Sharvelle, S. Resilience-Based Infrastructure Planning and Asset Management: Study of Dual and Singular Water Distribution Infrastructure Performance Using a Simulation Approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 48, 101577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.; Sharvelle, S.; Fourness, D.; Grigg, N.; Roesner, L.; Haukaas, J. Centralized and Decentralized Strategies for Dual Water Supply: Case Study. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2018, 144, 5017017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawna, S.; Shadeed, S. Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting to Alleviate Domestic Water Shortage in the West Bank, Palestine. An-Najah Univ. J. Res. A Nat. Sci. 2021, 35, 83–108. [Google Scholar]
- Shadeed, S.; Judeh, T.; Almasri, M. Developing a GIS-Based Water Poverty and Rainwater Harvesting Suitability Maps for Domestic Use in the Dead Sea Region (West Bank, Palestine). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadeed, S.; Alawna, S. Optimal Sizing of Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting Tanks for Sustainable Domestic Water Use in the West Bank, Palestine. Water 2021, 13, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Building Number | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Building 1 | Building 2 | Building 3 | Building 4 | Building 5 | Building 6 | |
| Roof area (m2) | 125.6 | 188.3 | 160.9 | 134.6 | 208.9 | 148.6 |
| Roof material | bricks | concrete | concrete | bricks | concrete | bricks |
| RC | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.85 | 0.9 | 0.85 |
| Residents’ number | 7 | 6 | 4 | 8 | 4 | 5 |
| Altitude | Supply Rate (m3/Day of Supply/Neighborhood) * | |
|---|---|---|
| Dry Season (May to October) | Rainy Season (November to April) | |
| High-altitude | 7 | 15 |
| Moderate-altitude | 10 | 25 |
| Low-altitude | 22 | 35 |
| Parameter | Min | Mean | Median | Max | WHO Standards | Number of Contaminated Samples (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 6.92 | 7.32 | 7.31 | 7.75 | 6.5–8.5 | 0 (0%) |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 0.18 | 3.37 | 0.95 | 28.50 | ≤5.00 | 7 (20%) |
| Chloride (mg/L) | 15.00 | 37.66 | 37.00 | 76.00 | ≤250.00 | 0 (0%) |
| Alkalinity (mg/L CaCO3) | 65.00 | 169.74 | 145.00 | 325.00 | ≤400.00 | 0 (0%) |
| TDS (mg/L) | 72.00 | 185.49 | 175.00 | 302.00 | ≤600.00 | 0 (0%) |
| FC (CFU/100 mL) | 0.00 | 92.23 | 9.00 | 545.00 | ≤10.00 | 17 (48.6%) |
| Residual Chlorine (mg/L) | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.17 | 2.10 | 0.2–0.8 | 20 (57.1%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Judeh, T.; Shahrour, I.; Comair, F. Smart Rainwater Harvesting for Sustainable Potable Water Supply in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159271
Judeh T, Shahrour I, Comair F. Smart Rainwater Harvesting for Sustainable Potable Water Supply in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas. Sustainability. 2022; 14(15):9271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159271
Chicago/Turabian StyleJudeh, Tariq, Isam Shahrour, and Fadi Comair. 2022. "Smart Rainwater Harvesting for Sustainable Potable Water Supply in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas" Sustainability 14, no. 15: 9271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159271
APA StyleJudeh, T., Shahrour, I., & Comair, F. (2022). Smart Rainwater Harvesting for Sustainable Potable Water Supply in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas. Sustainability, 14(15), 9271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159271








