Distinguishing the Impacts of Human Activities and Climate Change on the Livelihood Environment of Pastoralists in the Qinghai Lake Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
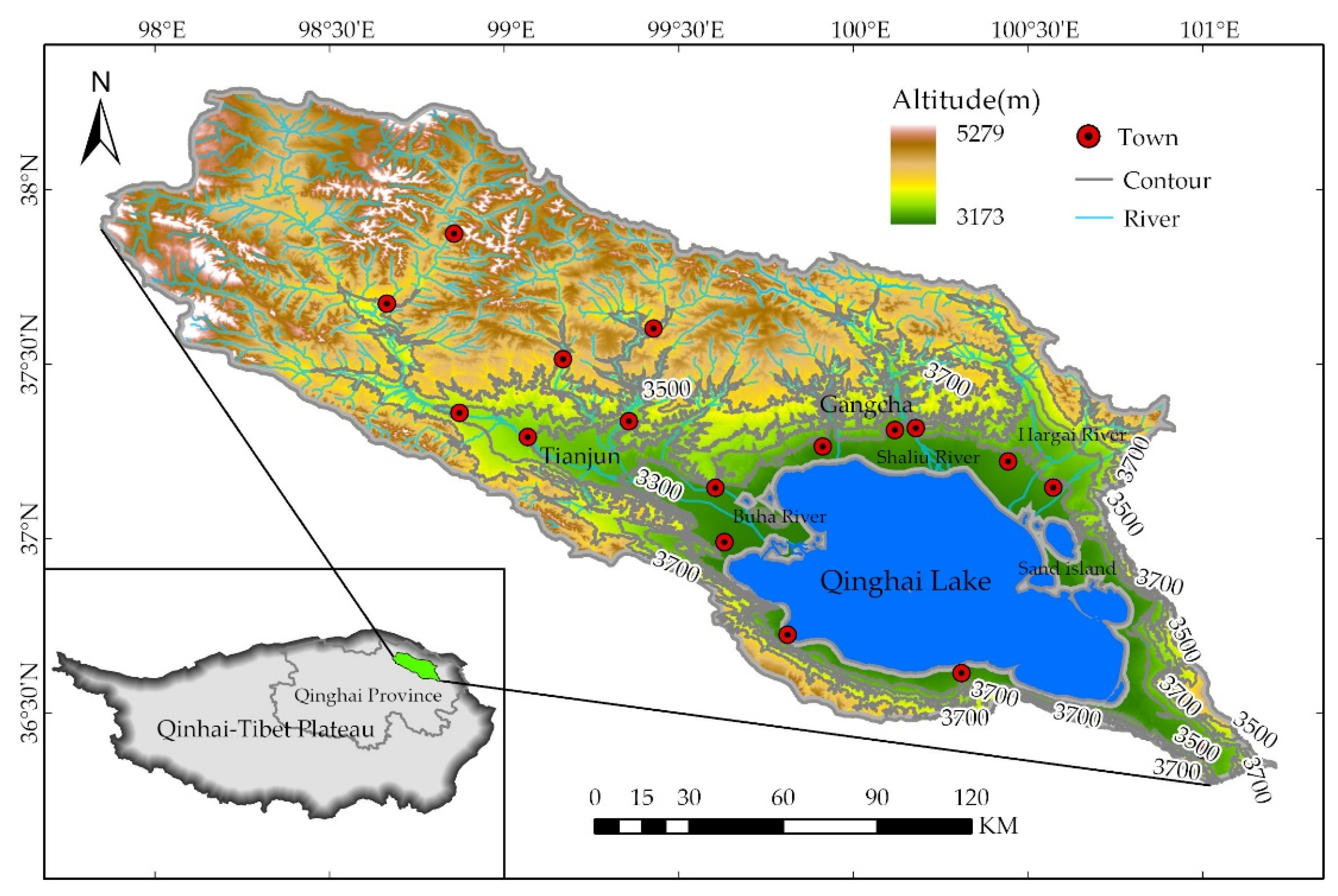
2.1. The Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
2.3. Research Methods
2.3.1. Trend Analysis of Vegetation Coverage and Climate Factors
2.3.2. Quantifying the Impact of Climate Change and Human Activities on Vegetation Cover
3. Results
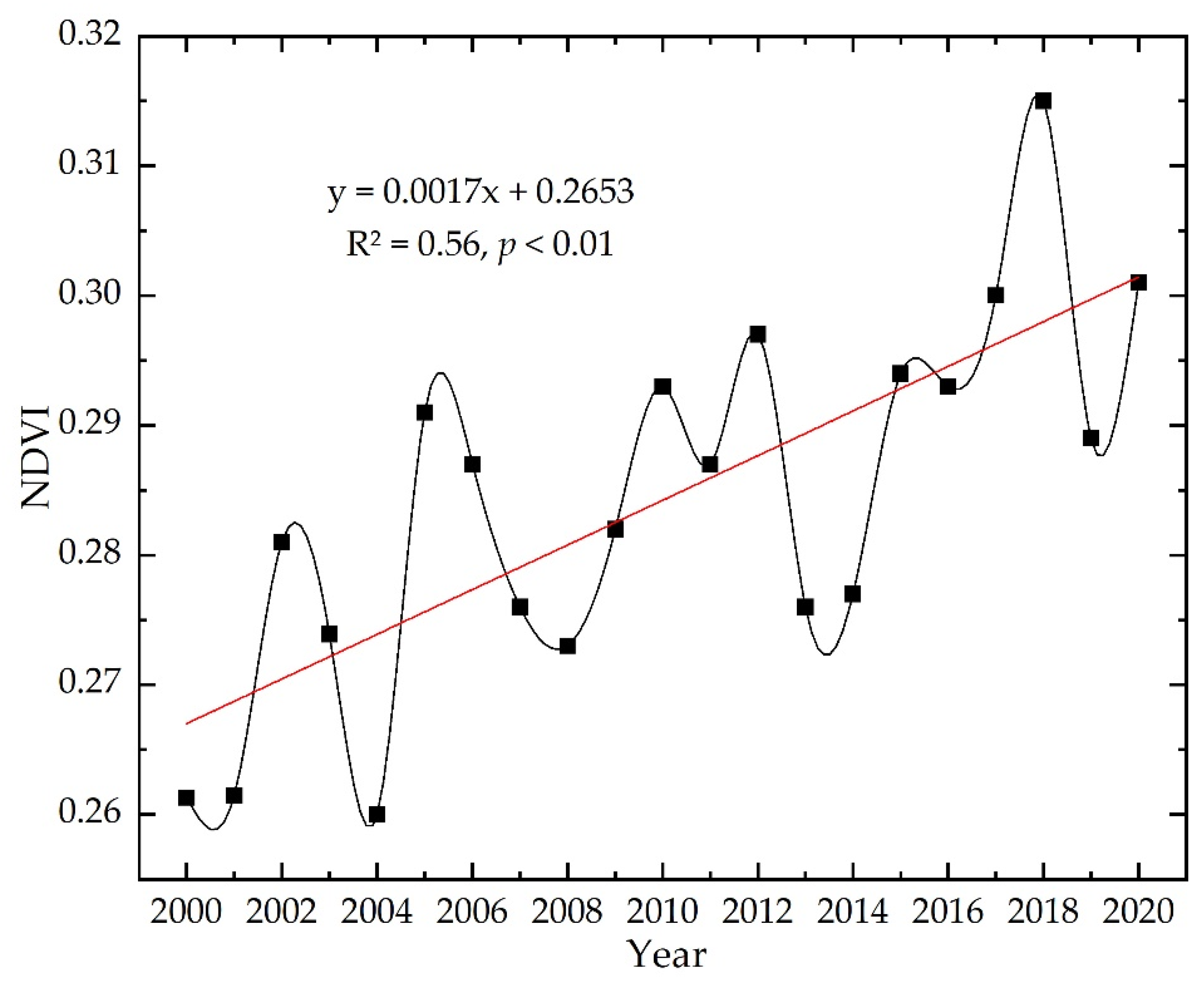
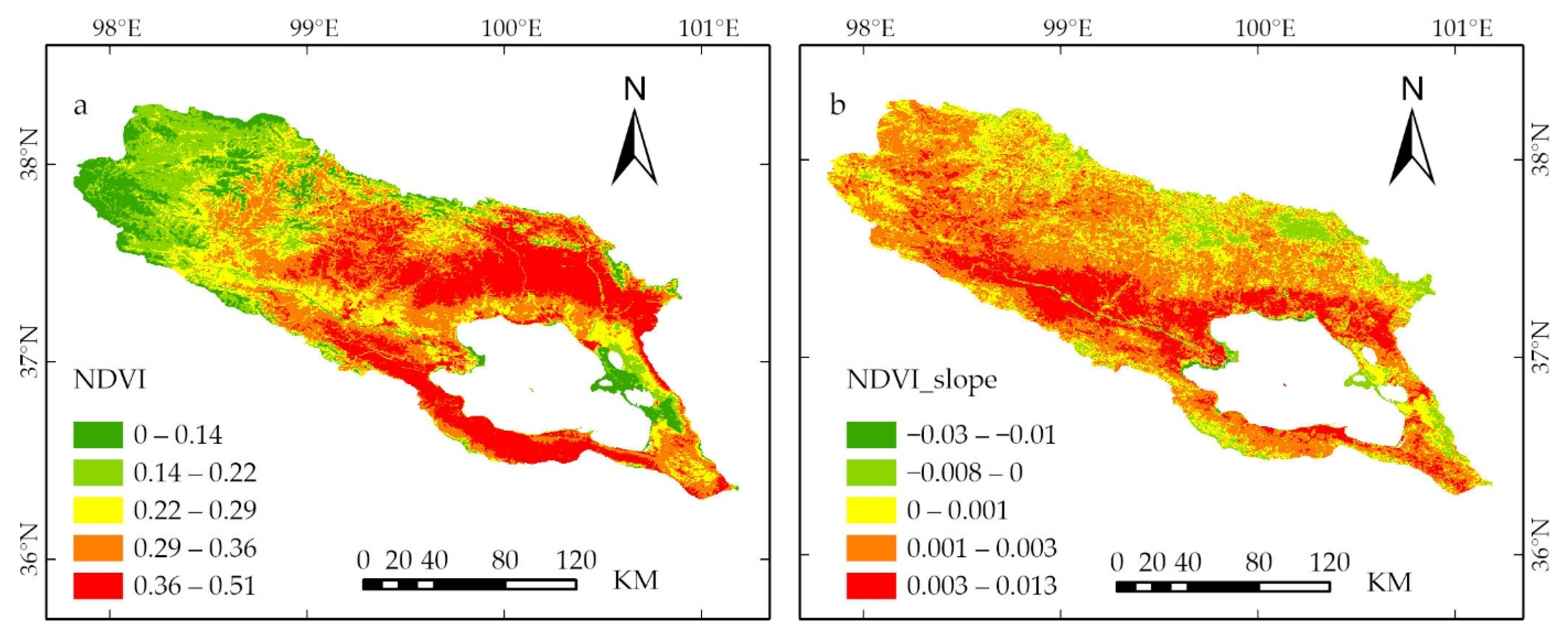
3.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Variation Trend of NDVI
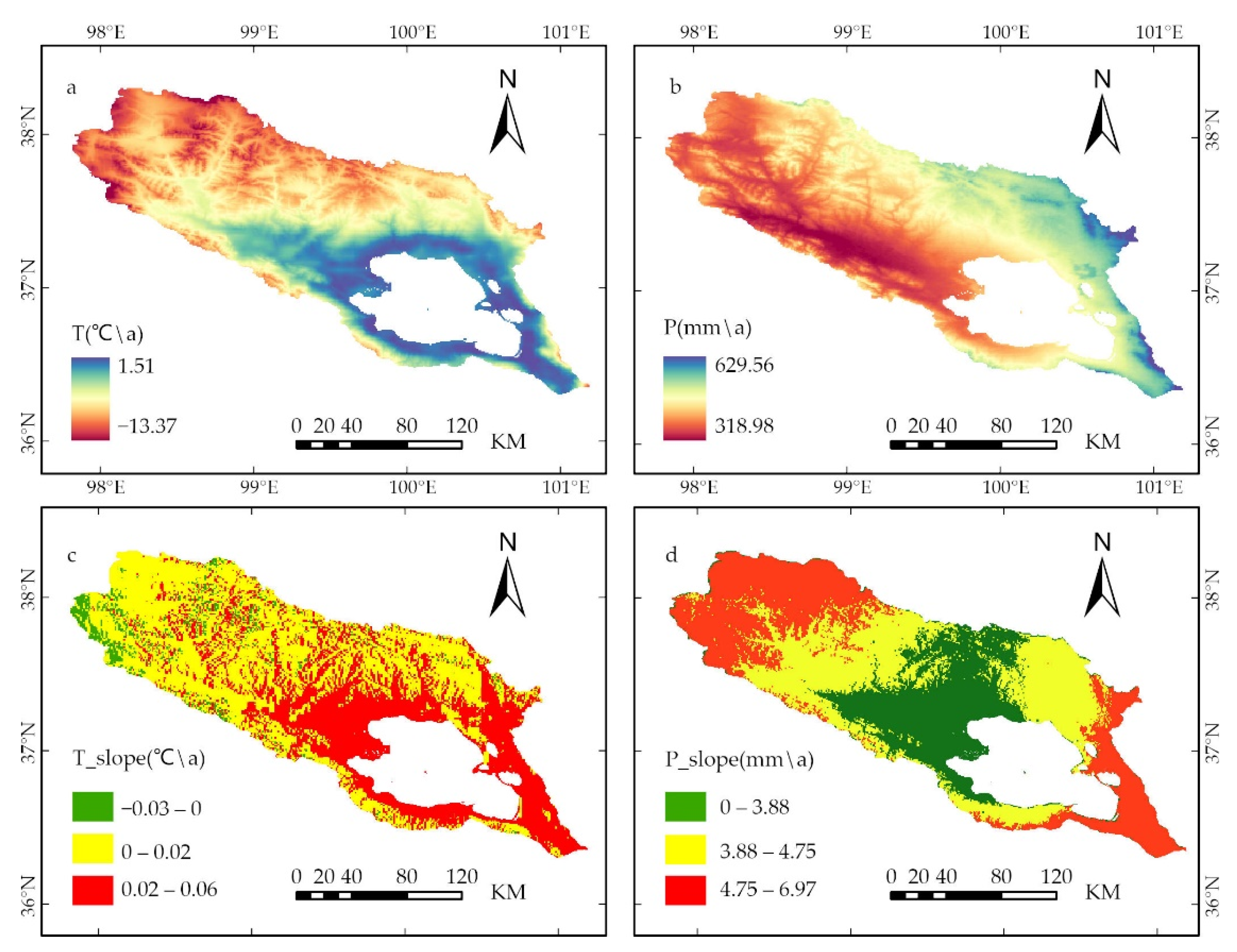
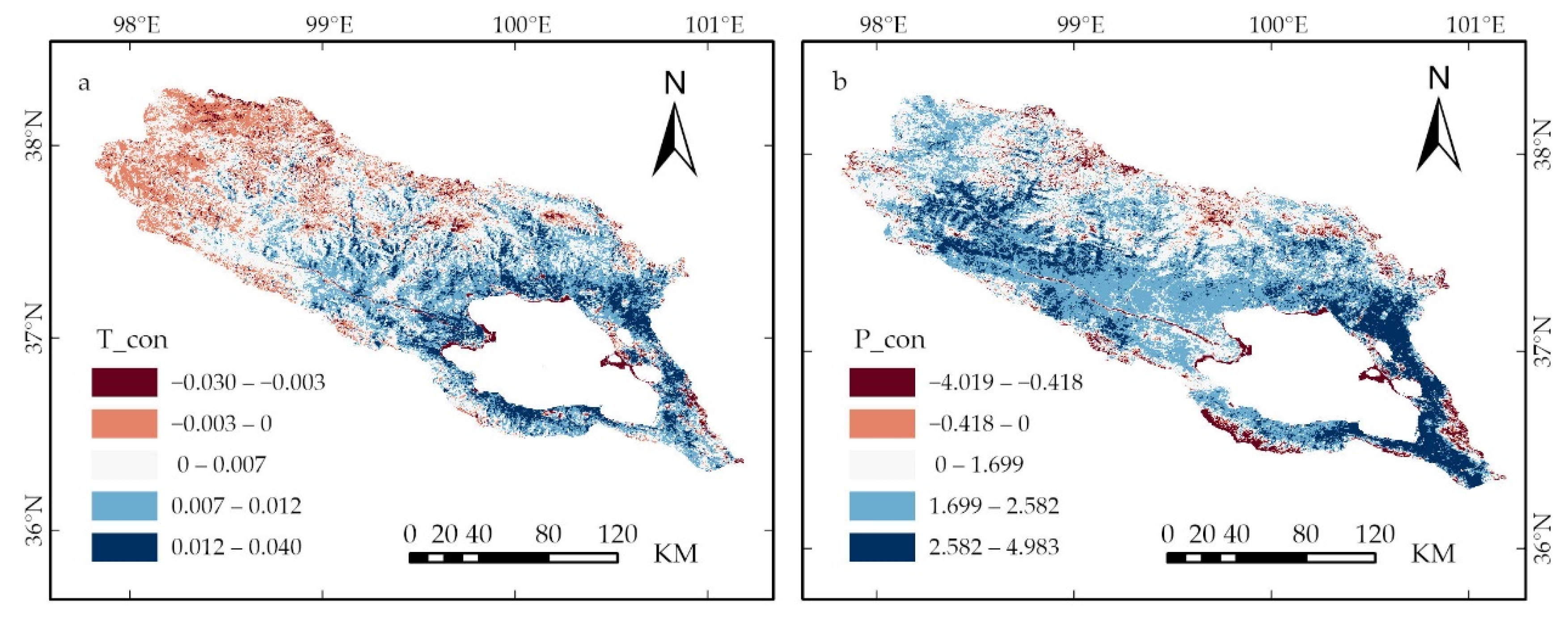
3.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics and Variation Trends of Climate Factors
3.3. Residual Trends of Human Activities
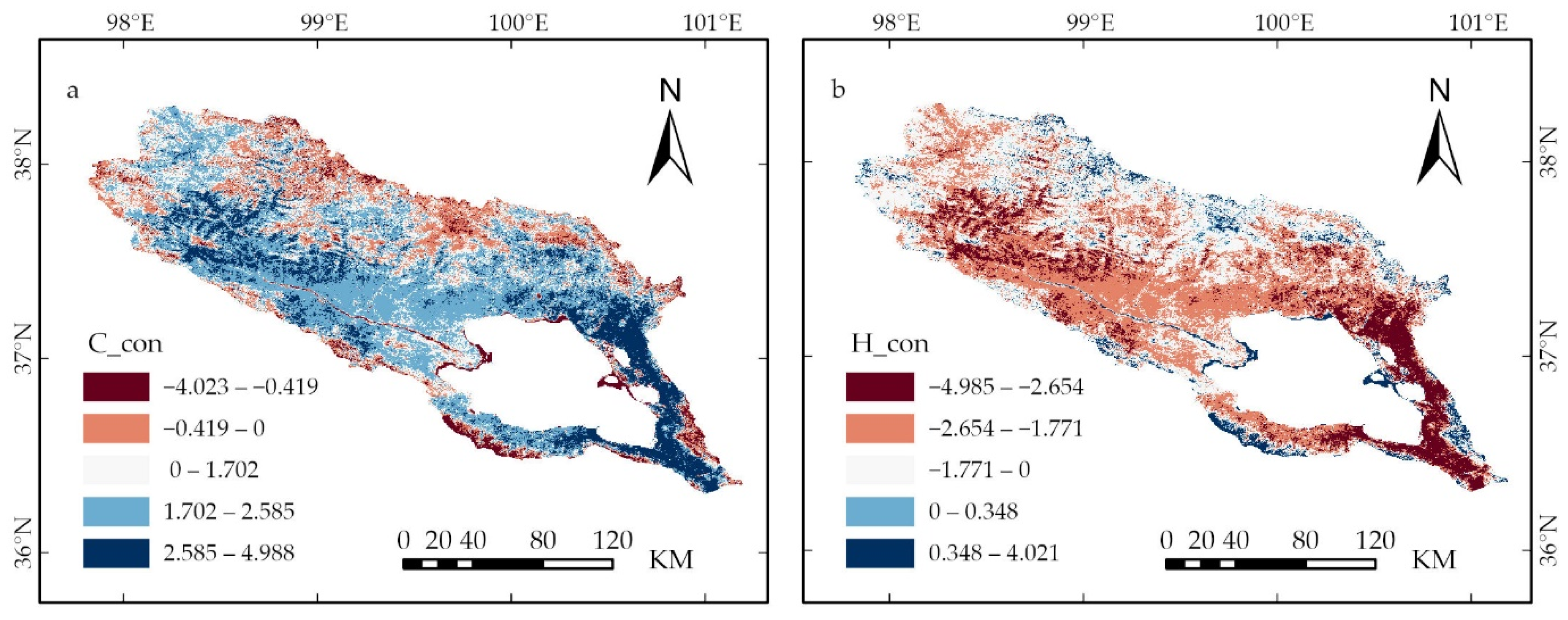
3.4. Contribution of Climate Change and Human Activities to Vegetation Cover
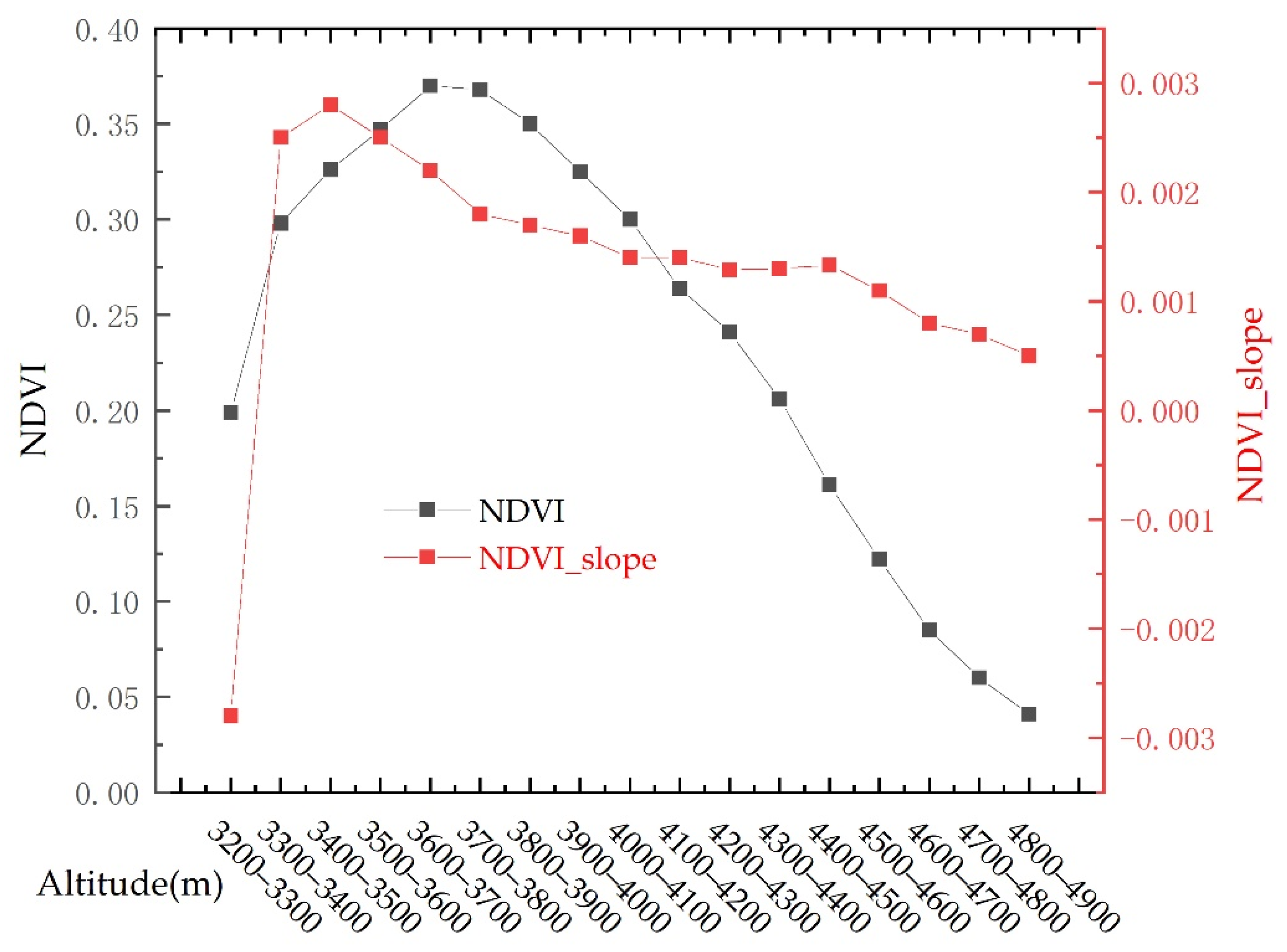
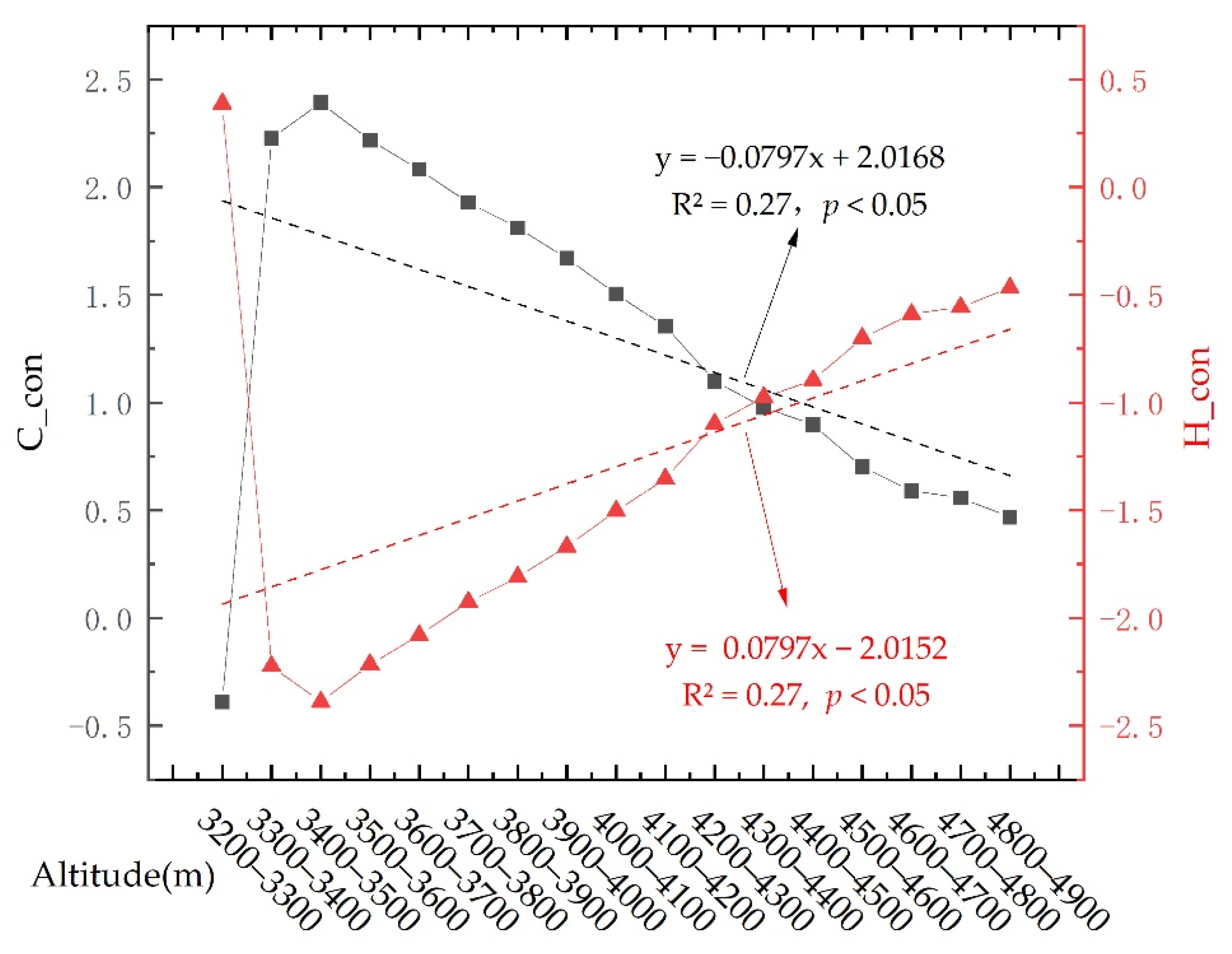
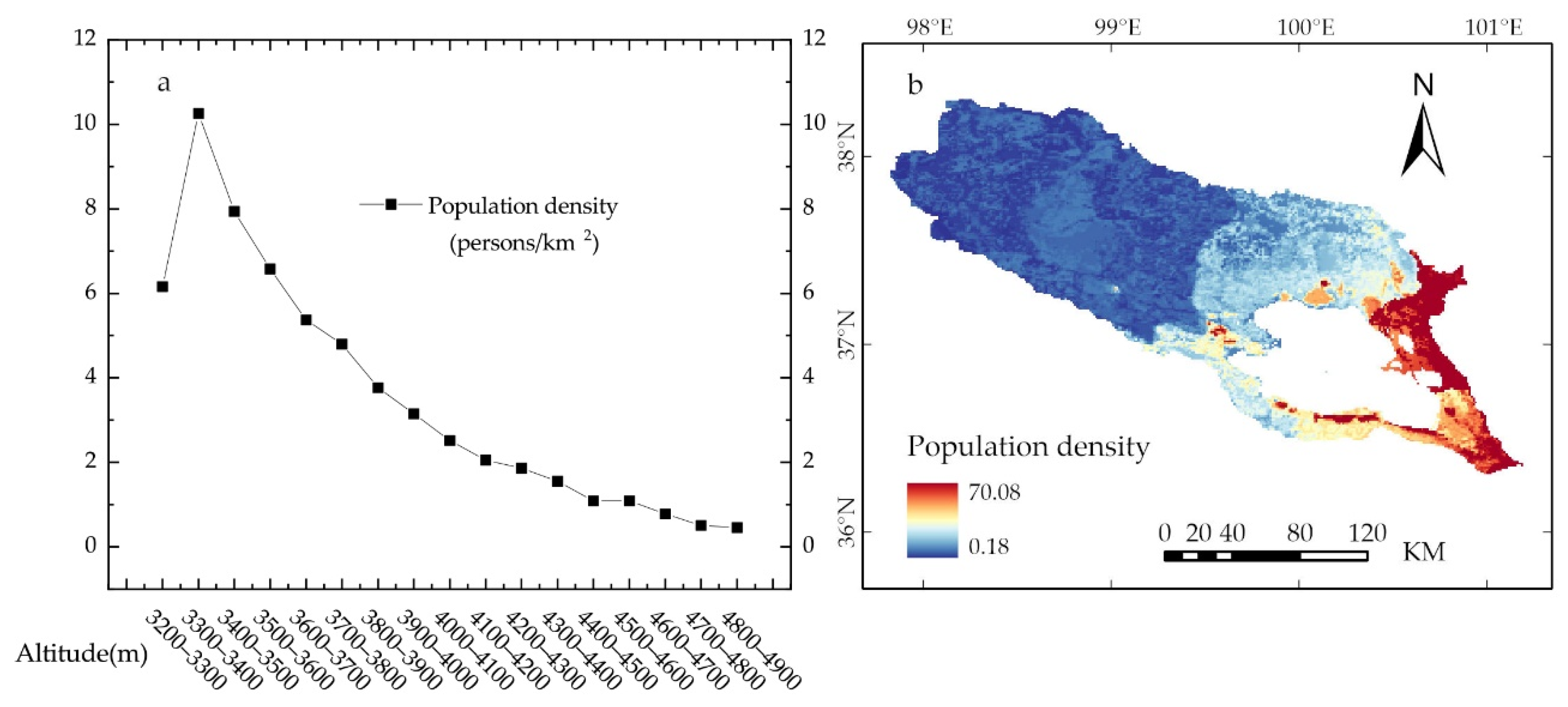
3.5. Distribution and Greening of Vegetation along the Altitude Gradient
4. Discussion
4.1. Three-Dimensional Distribution Pattern of Vegetation Cover
4.2. Methods to Quantitatively Assess Changes in Vegetation Caused by Climate Change and Human Activities
4.3. The Impact of Climate Change on Changes in Vegetation Cover
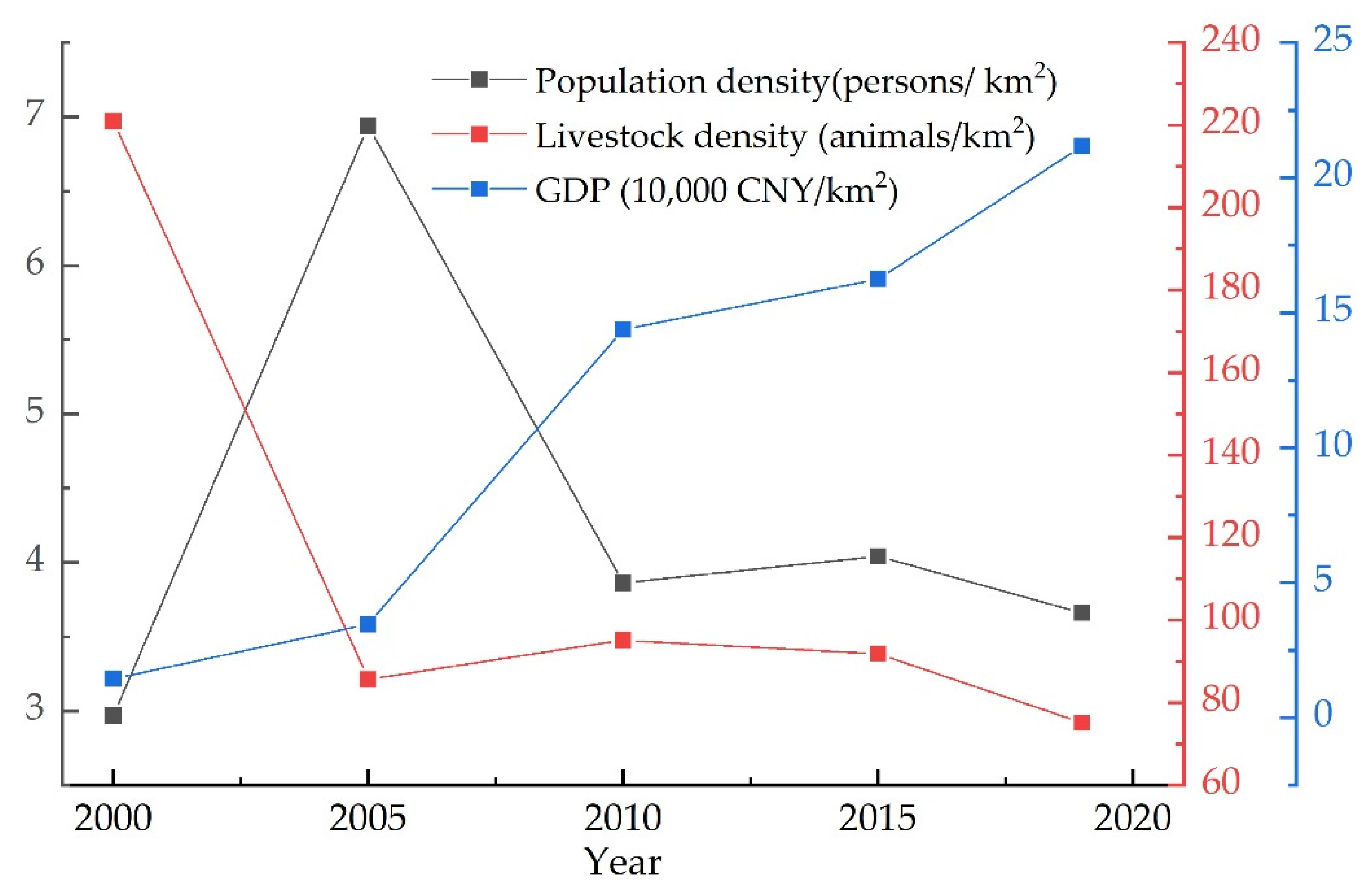
4.4. The Impact of Human Activities on Changes in Vegetation Cover
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piao, S.; Yin, G.; Tan, J.; Cheng, L.; Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Mao, J.; Myneni, R.B.; Peng, S. Detection and attribution of vegetation greening trend in China over the last 30 years. Global Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, W.; Miao, C. Hydrogeomorphic ecosystem responses to natural and anthropogenic changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Annu Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 45, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Ye, B.; Zhou, D.; Wu, B.; Foken, T.; Qin, J.; Zhou, Z. Response of hydrological cycle to recent climate changes in the Tibetan Plateau. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Ganopolski, A.; Chen, F.; Claussen, M.; Wang, H. Impacts of snow and glaciers over Tibetan Plateau on Holocene climate change: Sensitivity experiments with a coupled model of intermediate complexity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L17709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Z.; Piao, S.; Li, L.Z.; Zhou, L.; Ciais, P.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Lian, X.; Wood, E.F.; Friedlingstein, P. Climate mitigation from vegetation biophysical feedbacks during the past three decades. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2017, 7, 432–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Li, S.; Yu, X.; Yang, P.; Yu, G.; Feng, R.; Zhuang, X. Chinese ecosystem research network: Progress and perspectives. Ecol. Complex. 2010, 7, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Lü, M. NDVI indicated long-term interannual changes in vegetation activities and their responses to climatic and anthropogenic factors in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Ma, Y.; Xue, Y.; Piao, S. Climate change trends and impacts on vegetation greening over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 7540–7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Pang, J. Quantifying influences of physiographic factors on temperate dryland vegetation, Northwest China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Dong, S.-K.; Wen, L.; Wang, X.-X.; Wu, Y. Soil carbon and nitrogen pools and their relationship to plant and soil dynamics of degraded and artificially restored grasslands of the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Geoderma 2014, 213, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Chen, Z. Comparison of broad-band and narrow-band red and near-infrared vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, K.; Liu, B.; Li, R.; Jiao, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, M. Spectral indices for estimating ecological indicators of karst rocky desertification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2115–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocic, M.; Trajkovic, S. Analysis of precipitation and drought data in Serbia over the period 1980–2010. J. Hydrol. 2013, 494, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Papadavid, G.; Agapiou, A.; Themistocleous, K.; Hadjimitsis, M.; Retalis, A.; Michaelides, S.; Chrysoulakis, N.; Toulios, L.; Clayton, C. Atmospheric correction for satellite remotely sensed data intended for agricultural applications: Impact on vegetation indices. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 10, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiegand, C.; Richardson, A.; Escobar, D.; Gerbermann, A. Vegetation indices in crop assessments. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 35, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Fang, J.; Zhou, L.; Guo, Q.; Henderson, M.; Ji, W.; Li, Y.; Tao, S. Interannual variations of monthly and seasonal normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) in China from 1982 to 1999. J. Geophys Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.R. A soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höpfner, C.; Scherer, D. Analysis of vegetation and land cover dynamics in north-western Morocco during the last decade using MODIS NDVI time series data. Biogeosciences 2011, 8, 3359–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, A. Spatial and temporal variations in vegetation coverage observed using AVHRR GIMMS and Terra MODIS data in the mainland of China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 4238–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Wang, X.; Yang, M. Using the NDVI to identify variations in, and responses of, vegetation to climate change on the Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2012. Quatern. Int. 2017, 444, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Halmy, M.W.A.; Dakhil, M.A.; Liang, P.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Pandey, B.; Pan, K.; El Kafraway, S.B. Monitoring the impact of climate change and human activities on grassland vegetation dynamics in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau of China during 2000–2015. J. Arid. Land 2019, 11, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, H.; Xue, X.; Wang, T.; Kang, W.; Liao, J.; Liu, S. Spatial and temporal differences in alpine meadow, alpine steppe and all vegetation of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and their responses to climate change. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chang, J.; Xu, C.-Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Jiang, S.; Duan, Z. The response of lake area and vegetation cover variations to climate change over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau during the past 30 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Fiedler, S.; Gao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, W.; Hassan, W.; Mărgărint, M.C.; Tarolli, P. Disentangling climatic and anthropogenic contributions to nonlinear dynamics of alpine grassland productivity on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 281, 111875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Li, M.; An, Y.; Shi, F. Spatial differentiation of the NPP and NDVI and its influencing factors vary with grassland type on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, S.-X.; Tao, H.-P. The relationship between normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and climate factors in the semiarid region: A case study in Yalu Tsangpo River basin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2014, 11, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Xu, Z. Greening implication inferred from vegetation dynamics interacted with climate change and human activities over the Southeast Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Yan, F.; Lu, Q. Spatiotemporal variation of vegetation on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and the influence of climatic factors and human activities on vegetation trend (2000–2019). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Pirani, A.; Conners, S.L.; Péan, C.; Berger, S.; Caud, N.; Chen, Y.; Goldfarb, L.; Gomis, M.I.; et al. Climate change 2021: The physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the sixth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. In Proceedings of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change AR6, Remote, 26 July–7 August 2021; Volume 2. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/ (accessed on 28 May 2022).
- Fan, Z.; Bai, X. Scenarios of potential vegetation distribution in the different gradient zones of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under future climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 148918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zu, J.; Zhang, J. The influences of climate change and human activities on vegetation dynamics in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, S.; Dong, S.; Su, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X. Analysis of vegetation change associated with human disturbance using MODIS data on the rangelands of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Rangel. J. 2015, 37, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Ma, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, S.; Xu, J.; Long, Y.; Ma, D.; Zhang, Z. The impacts of climate change and human activities on alpine vegetation and permafrost in the Qinghai-Tibet Engineering Corridor. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Chai, L.; Hou, F.; Chang, S.; Ma, Y.; Tsunekawa, A.; Cheng, Y. Quantifying grazing intensity using remote sensing in Alpine Meadows on Qinghai-Tibetan plateau. Sustainability 2019, 11, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Li, S. Spatial pattern of non-stationarity and scale-dependent relationships between NDVI and climatic factors—A case study in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 20, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y. Research progress in man-land relationship evolution and its resource-environment base in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 899–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, S.; Cao, G. The Effect of Vegetative Coverage and Altitude on the Vegetation Water Consumption in the Alpine Inland River Basin of the Northeastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Water 2022, 14, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ni, X.; Jing, D.; Li, S. Spatial-temporal patterns of vegetation dynamics and their relationships to climate variations in Qinghai Lake Basin using MODIS time-series data. J. Geog. Sci. 2014, 24, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunlong, C.; Smit, B. Sustainable agriculture: Its status quo and trend in China. J. Chin. Geogr. 1996, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- China International Engineering Consulting Corporation. The Qinghai Lake Ecological Protection Plan (2021–2035); Qinghai Lake Scenic Area Protection and Utilization Administration: Xining, China, 2021; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Naudiyal, N.; Wu, N.; Cui, X.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Q. Multiple Effects of Topographic Factors on Spatio-Temporal Variations of Vegetation Patterns in the Three Parallel Rivers Region, Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Bai, J.; Ma, G.; Yan, J. Vegetation phenological changes in multiple landforms and responses to climate change. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2020, 9, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Evans, J.; Geerken, R. Discrimination between climate and human-induced dryland degradation. J. Arid. Environ. 2004, 57, 535–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Yu, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, K. Quantitative contributions of climate change and human activities to vegetation changes over multiple time scales on the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderick, M.L.; Rotstayn, L.D.; Farquhar, G.D.; Hobbins, M.T. On the attribution of changing pan evaporation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L17403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, X.; Wen, Y.; Ou, J. Quantitative analysis of the contributions of climatic and human factors to grassland productivity in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 103, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Myneni, R.B.; Chen, A.; Chevallier, F.; Dolman, A.J.; Janssens, I.A.; Penuelas, J.; Zhang, G. Asymmetric effects of daytime and night-time warming on Northern Hemisphere vegetation. Nature 2013, 501, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Li, L.; Liu, Q. Temporal variation of reference evapotranspiration during 1961–2005 in the Taoer River basin of Northeast China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2010, 150, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yu, D.; Chen, K. Evolution and Prediction of Landscape Patterns in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Land 2021, 10, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; de Jong, R.; Schmid, B.; Wulf, H.; Schaepman, M.E. Changes in grassland cover and in its spatial heterogeneity indicate degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 119, 106641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, B.; Yan, J. Spatial variation patterns of plant herbaceous community response to warming along latitudinal and altitudinal gradients in mountainous forests of the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 172, 103983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wan, L.; Zhang, Y.-K.; Hu, G.; Schaepman, M.E.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Su, Z.B. Quantification of spatial distribution of vegetation in the Qilian Mountain area with MODIS NDVI. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 5751–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Deng, X.; Jin, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, C. The impacts of climate change and human activities on grassland productivity in Qinghai Province, China. Front. Earth Sci. Chin. 2014, 8, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Han, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, P.; Ban, C.; Sun, W.; Pang, B.; Peng, D.; Kan, G.; Zhang, R. Time-lag effects of climatic change and drought on vegetation dynamics in an alpine river basin of the Tibet Plateau, China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Liu, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y. The trend of vegetation greening and its drivers in the Agro-pastoral ecotone of northern China, 2000–2020. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liang, E.; Liu, R.; Babst, F.; Camarero, J.J.; Fu, Y.H.; Piao, S.; Rossi, S.; Shen, M.; Wang, T. An earlier start of the thermal growing season enhances tree growth in cold humid areas but not in dry areas. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 6, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Gu, S.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, J.; Tang, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, S. High positive correlation between soil temperature and NDVI from 1982 to 2006 in alpine meadow of the Three-River Source Region on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Zu, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, M.; Paudel, B. Increasing sensitivity of alpine grasslands to climate variability along an elevational gradient on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jönsson, P.; Tamura, M.; Gu, Z.; Matsushita, B.; Eklundh, L. A simple method for reconstructing a high-quality NDVI time-series data set based on the Savitzky–Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 91, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, C. The use of ‘altitude’in ecological research. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cui, G.; Liu, X.; Zheng, K.; Lu, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, G.; An, Z. Greening of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and Its Response to Climate Variations along Elevation Gradients. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, J.; Peng, S.; Piao, S.; Ciais, P.; Betts, R. Changes in productivity and carbon storage of grasslands in China under future global warming scenarios of 1.5 °C and 2 °C. J. Plant Ecol. 2019, 12, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Long, H.; Li, X.; Yu, F. Evaluation of changes in ecological security in China’s Qinghai Lake Basin from 2000 to 2013 and the relationship to land use and climate change. Env. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Ma, Y.-J.; Xu, H.-Y.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhang, D.-S. Impact of land use and land cover change on environmental degradation in lake Qinghai watershed, Northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land Degrad. Develop. 2009, 20, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhuo, G.; Zhang, Y. Regional-scale vegetation-climate interactions on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Ecol. Inf. 2021, 65, 101413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liang, T.; Xie, H.; Huang, X.; Lin, H. Climate-driven changes in grassland vegetation, snow cover, and lake water of the Qinghai Lake basin. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 036017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, G.; Jia, Z.; Song, X.; Wang, X. Study on the Shoreline Evolution of Qinghai Lake and its Socio-economic Impact under the Background of Global Climate Change. Plateau Sci. Res. 2021, 5, 1–9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.; Gao, Z.; Yang, X.; Ge, Y. Distinguishing the Impacts of Human Activities and Climate Change on the Livelihood Environment of Pastoralists in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8402. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148402
Song Z, Gao Z, Yang X, Ge Y. Distinguishing the Impacts of Human Activities and Climate Change on the Livelihood Environment of Pastoralists in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Sustainability. 2022; 14(14):8402. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148402
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zhiyuan, Ziyi Gao, Xianming Yang, and Yuejing Ge. 2022. "Distinguishing the Impacts of Human Activities and Climate Change on the Livelihood Environment of Pastoralists in the Qinghai Lake Basin" Sustainability 14, no. 14: 8402. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148402
APA StyleSong, Z., Gao, Z., Yang, X., & Ge, Y. (2022). Distinguishing the Impacts of Human Activities and Climate Change on the Livelihood Environment of Pastoralists in the Qinghai Lake Basin. Sustainability, 14(14), 8402. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148402




