Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Experiment on the Microscopic Mechanism of the Effect of Wax Crystals on the Burst and Drainage of Foams
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
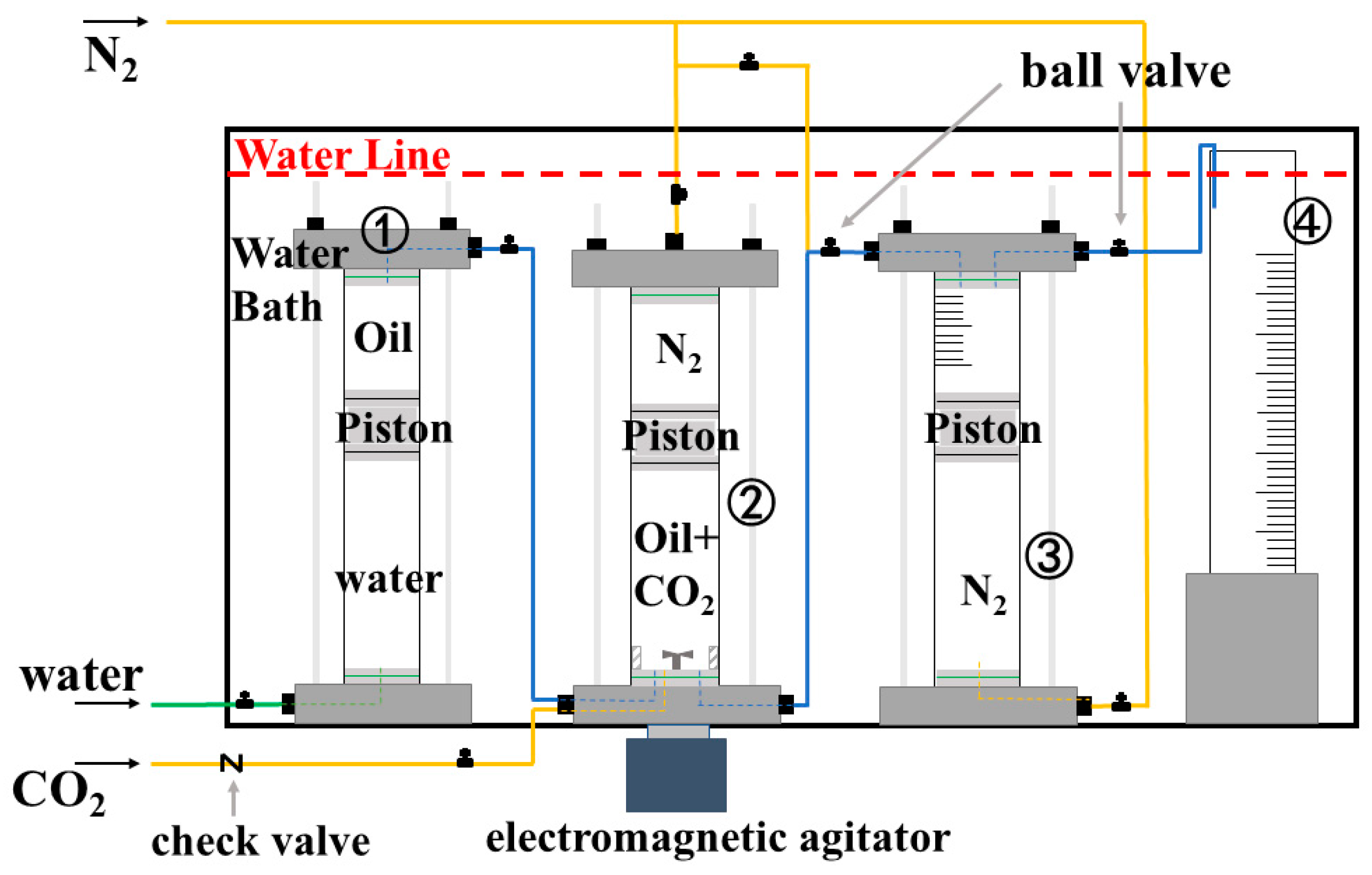
2.1. Experimental Section
2.1.1. Materials
2.1.2. Foam Preparation and Performance Tests
2.2. Simulation Section
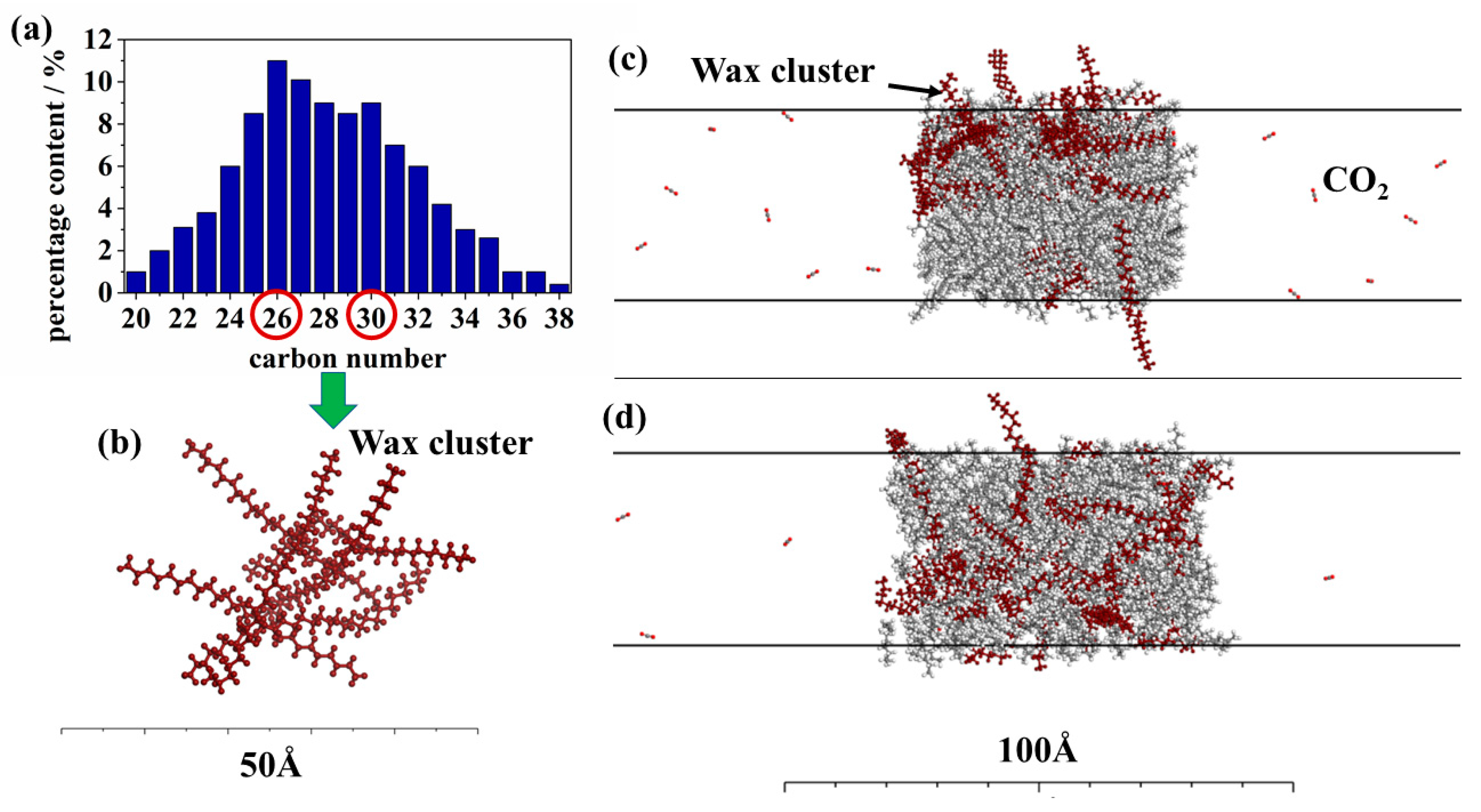
2.2.1. Model Construction
2.2.2. Simulation Methods
2.2.3. Parameters Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Wax Crystals on the Simulated Oil Foam
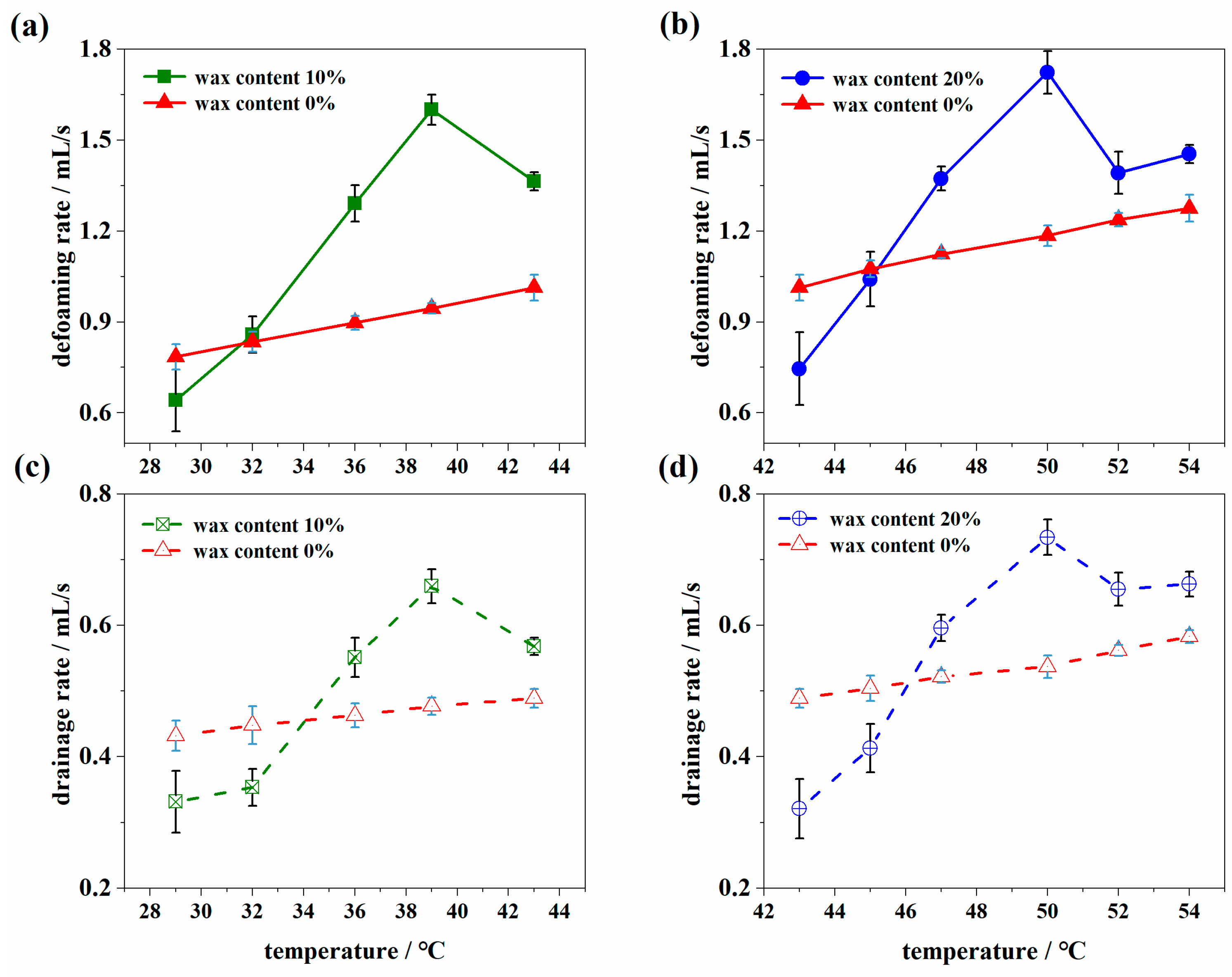
3.1.1. The Evolution of Defoaming and Drainage
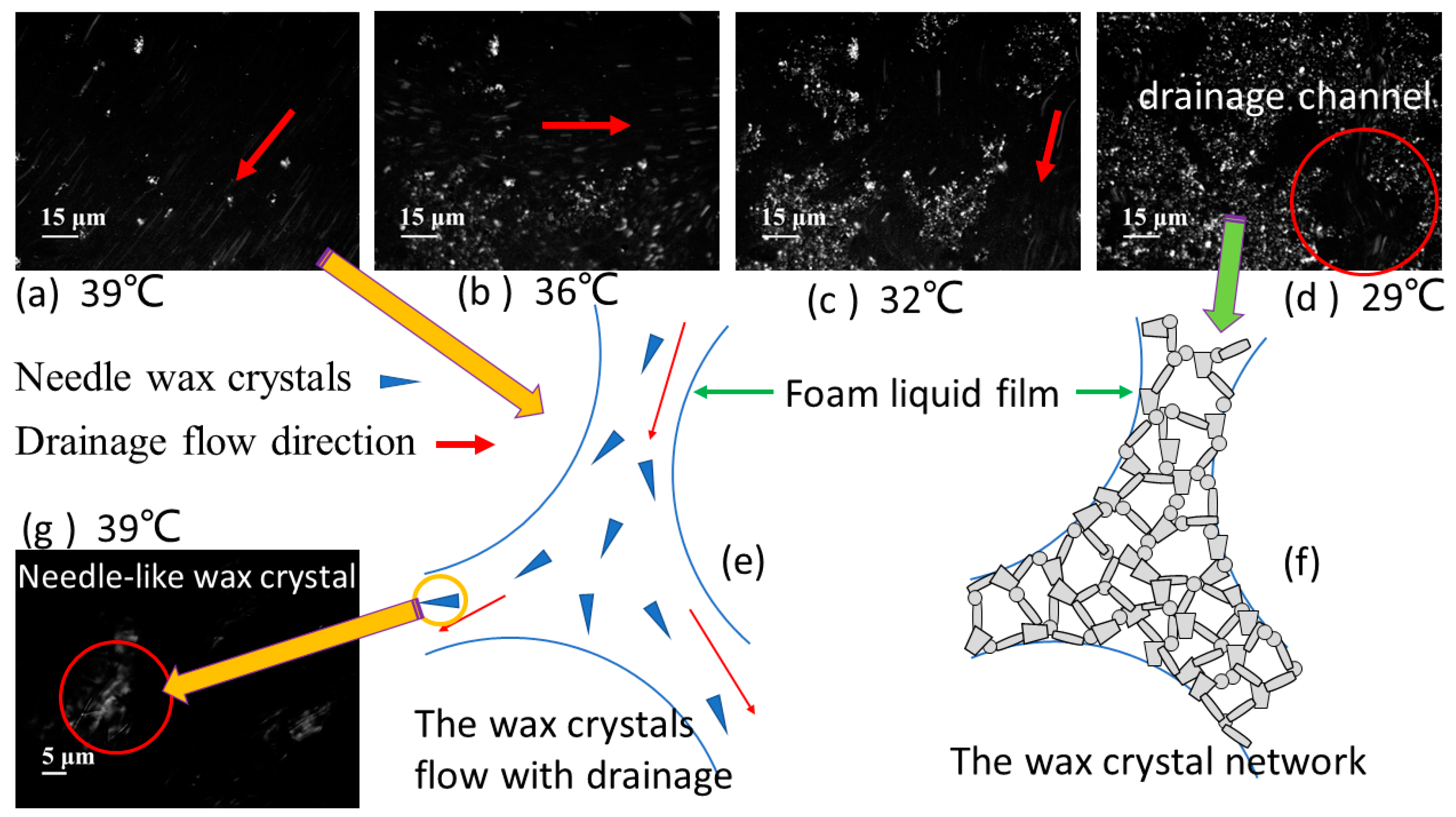
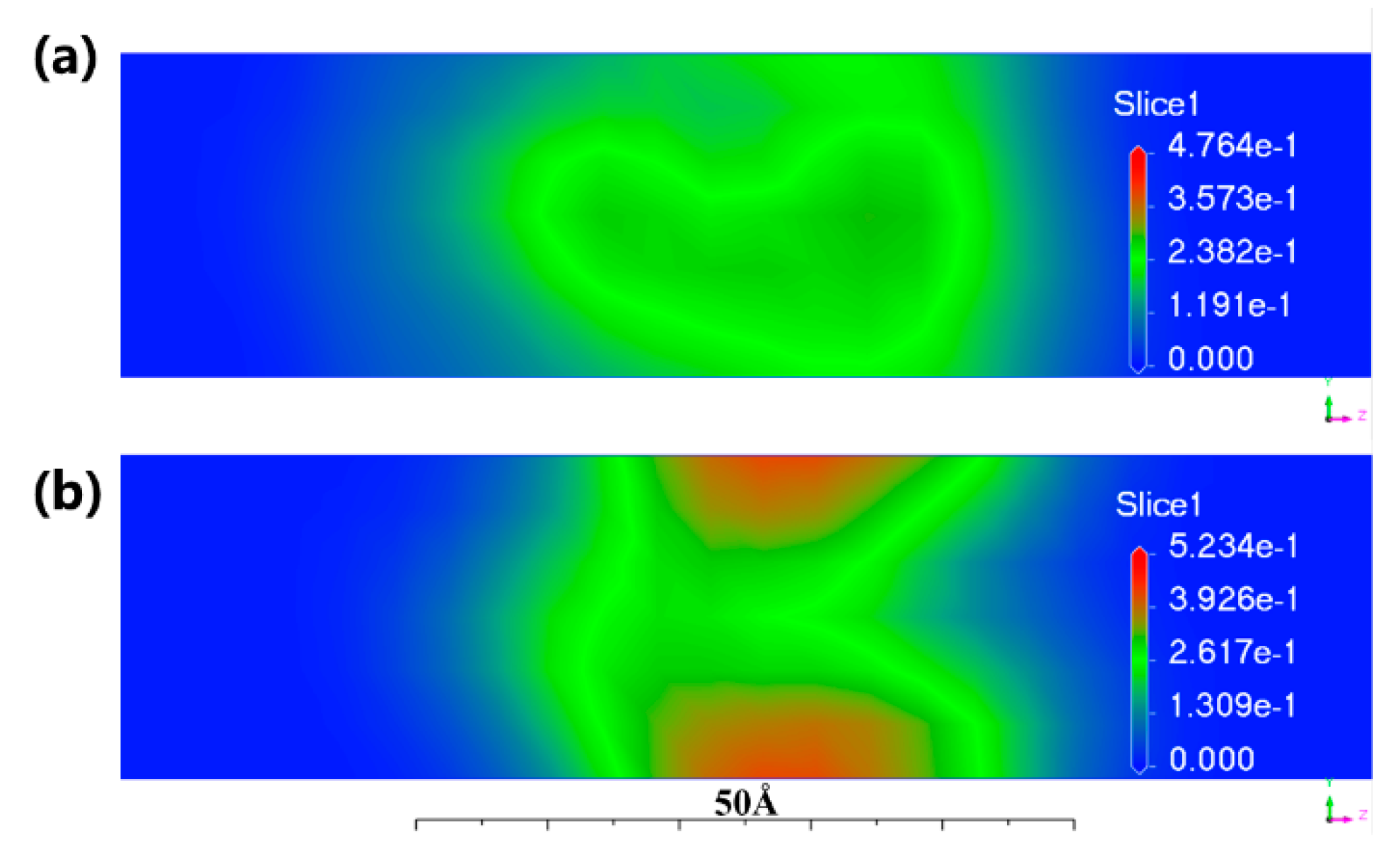
3.1.2. Microscopic Structure of Wax Crystals
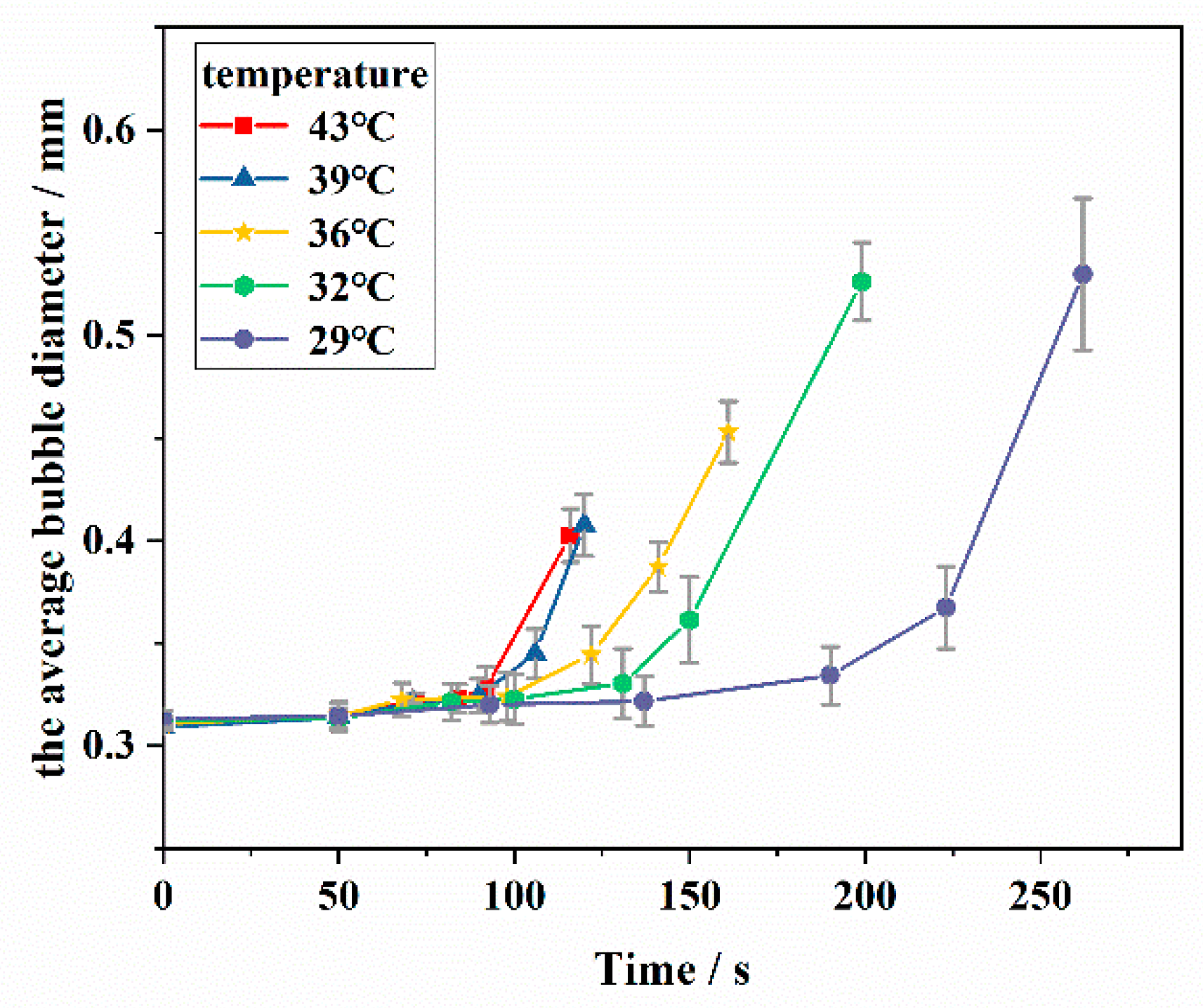
3.1.3. Bubble Diameter of the Simulated Oil Foam
3.2. The Effect of Wax Crystals on the Foam Film According to the MD Simulation
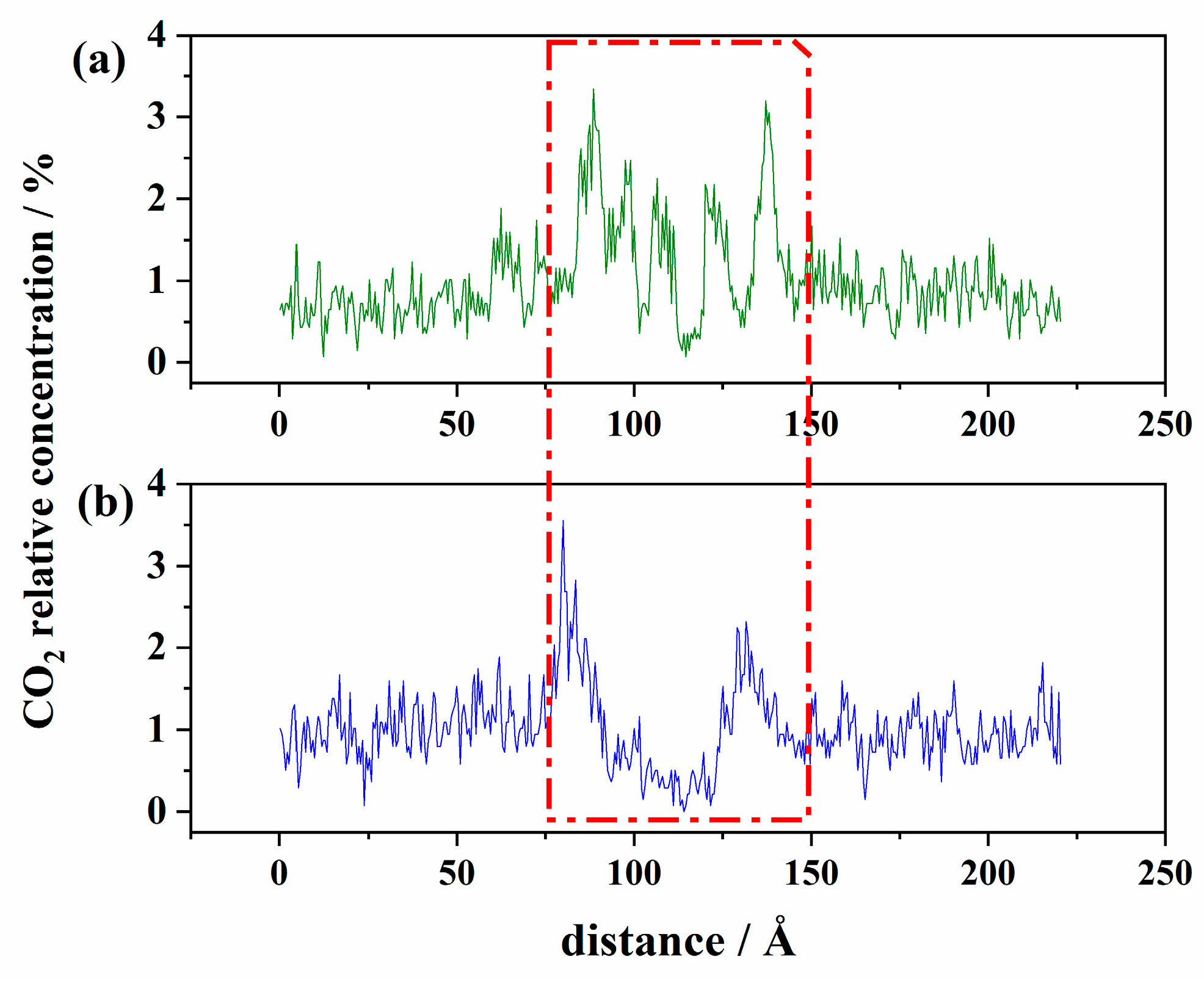
3.2.1. The Distribution of Wax Crystals
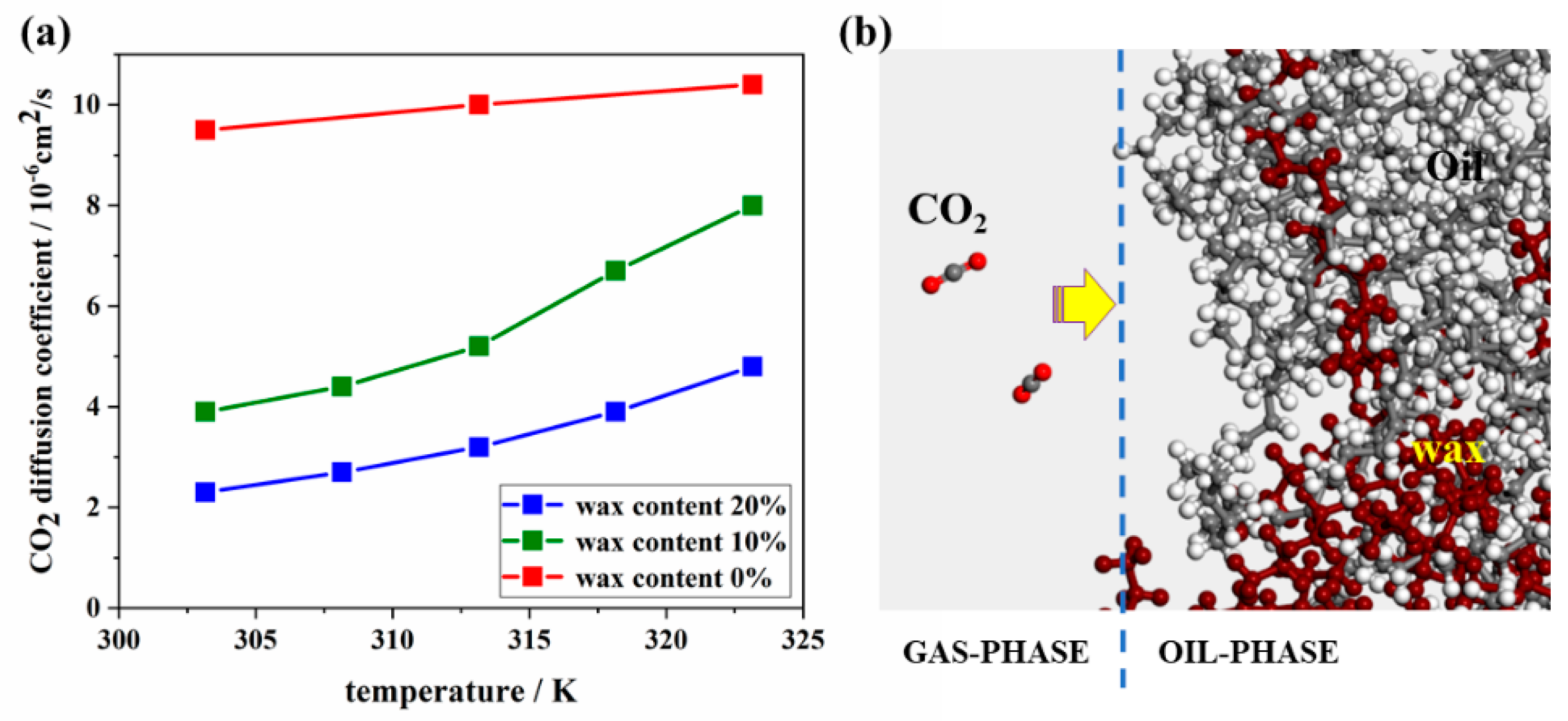
3.2.2. The Impediment of Wax Crystals on CO2
4. Conclusions
- Both the defoaming and drainage rates increase slightly as the temperature is lower than WAT and then decrease faster than that of pure white oil with a continuous decrease in temperature. The defoaming and drainage rates of waxy oil foam have an obvious inflection point with a wax crystal content of 0.2%.
- With the precipitation of wax crystals, the needle-like wax crystals can destroy the stability of the simulated oil foam, and the network formed by wax crystal aggregation can reduce the drainage area, slow the drainage flow in the foam drainage channel and impede the diffusion of gas through liquid films of foam, leading to a decrease in the defoaming and drainage rates.
- The needle-like wax crystal destroyed the foam film and led to foam bursting before reaching the maximum bubble diameter, while the wax crystal network impeded the increase in bubble diameter by slowing down the rate of drainage and gas diffusion.
- It is clear from the molecular level that with the decrease in temperature, the insolubility between wax crystal and oil molecules and the wax crystal aggregation increased, hindering the diffusion of CO2 through liquid film and slowing down the coalescence between bubbles using MD simulation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blázquez, C.; Dalmazzone, C.; Emond, E.; Schneider, S. Crude oil foams. Part 1—A novel methodology for studying non-aqueous foams formed by depressurization. Fuel 2016, 171, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zuo, L.; Wu, C.; Sun, C.; Zhu, X. Effects of crude oil characteristics on foaming and defoaming behavior at separator during CO2 flooding. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 608, 125562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; He, L.; Luo, X.; Zhang, C. Foaming of crude oil: Effect of acidic components and saturation gas. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 553, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Q.; Gong, J.; Wang, W.; Gao, G. Study on the aging and critical carbon number of wax deposition with temperature for crude oils. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2015, 130, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anazadehsayed, A.; Rezaee, N.; Naser, J.; Nguyen, A.V. A review of aqueous foam in microscale. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 256, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boos, J.; Drenckhan, W.; Stubenrauch, C. Protocol for studying aqueous foams stabilized by surfactant mixtures. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2013, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Nguyen, A.V.; Farrokhpay, S. A critical review of the growth, drainage and collapse of foams. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 228, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Pal, N.; Jangir, A.K.; Manyala, D.L.; Varade, D.; Mandal, A.; Kuperkar, K. Dynamic interfacial properties and tuning aqueous foamability stabilized by cationic surfactants in terms of their structural hydrophobicity, free drainage and bubble extent. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 588, 124362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, E.; Drenckhan, W.; Salonen, A.; Langevin, D. Unusually stable liquid foams. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 205, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, C.G.; Noïk, C.; Dalmazzone, C.; Grossiord, J.L. Formation kinetics and viscoelastic properties of water/crude oil interfacial films. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. Rev. l’IFP 2009, 64, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, L.K.; Shrestha, R.G.; Sharma, S.C.; Aramaki, K. Stabilization of nonaqueous foam with lamellar liquid crystal particles in diglycerol monolaurate/olive oil system. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 328, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binks, B.P.; Rocher, A.; Kirkland, M. Oil foams stabilised solely by particles. Soft Matter. 2011, 7, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymans, R.; Tavernier, I.; Dewettinck, K.; van der Meeren, P. Crystal stabilization of edible oil foams. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 69, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, T.N.; Pugh, R.J.; Franks, G.V.; Jameson, G.J. The role of particles in stabilising foams and emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 137, 57–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binks, B.P.; Horozov, T.S. Aqueous foams stabilized solely by silica nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 3788–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptay, G. Interfacial criteria for stabilization of liquid foams by solid particles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2003, 230, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, S.; Suzuki, A.; Sato, K.; Ueno, S. Formation and microstructures of whipped oils composed of vegetable oils and high-melting fat crystals. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2016, 93, 1453–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binks, B.P.; Garvey, E.J.; Vieira, J. Whipped oil stabilised by surfactant crystals. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2621–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sethumadhavan, G.N.; Nikolov, A.D.; Wasan, D.T. Stability of liquid films containing monodisperse colloidal particles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 240, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madivala, B.; Vandebril, S.; Fransaer, J.; Vermant, J. Exploiting particle shape in solid stabilized emulsions. Soft Matter. 2009, 5, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, L.K.; Aramaki, K.; Kato, H.; Takase, Y.; Kunieda, H. Foaming properties of monoglycerol fatty acid esters in nonpolar oil systems. Langmuir 2006, 22, 8337–8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Sun, W.; Liu, Y. Molecular dynamics simulation of the microscopic mechanisms of the dissolution, diffusion and aggregation processes for waxy crystals in crude oil mixtures. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 179, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hou, L.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Chen, Y. Molecular dynamics simulation of magnetic field influence on waxy crude oil. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Wu, N. Molecular dynamics simulation guiding the improvement of EVA-type pour point depressant. Fuel 2005, 84, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samieadel, A.; Oldham, D.; Fini, E.H. Multi-scale characterization of the effect of wax on intermolecular interactions in asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.H.; Blanco, M.; Creek, J.; Tang, Y.C.; Goddard, W.A. Wax inhibition by comb-like polymers: Support of the incorporation-perturbation mechanism from molecular dynamics simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 13173–13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Zuo, L.; Wu, C.; Zhu, X.; Sun, C. The evolution and influence factors of CO2 flooding crude oil defoaming behavior after depressurization. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 206, 108996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babamahmoudi, S.; Riahi, S. Application of nano particle for enhancement of foam stability in the presence of crude oil: Experimental investigation. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 264, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Martinez, F.J.; Fini, E.H.; Buehler, M.J. Molecular asphaltene models based on Clar sextet theory. Rsc. Adv. 2015, 5, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, C.; Hu, S. CO2/N2 switchable aqueous foam stabilized by SDS/C12A surfactants: Experimental and molecular simulation studies. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 209, 115218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yuan, C.; Ji, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, S.; Hu, S. Effects of head type on the stability of gemini surfactant foam by molecular dynamics simulation. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 682, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, T.; Zhao, L.; Hu, D. Ethanol enhanced anionic surfactant solubility in CO2 and CO2 foam stability: MD simulation and experimental investigations. Fuel 2020, 267, 117162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, J.G.; Domínguez, H.; Aray, Y.; Iza, P.; Zarate, X.; Schott, E. Structural and interfacial properties of the CO2-in-water foams prepared with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS): A molecular dynamics simulation study. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 578, 123615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Md. Azmi, N.S.; Abu Bakar, N.F.; Tengku Mohd, T.A.; Azizi, A. Molecular dynamics simulation on CO2 foam system with addition of SiO2 nanoparticles at various sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) concentrations and elevated temperatures for enhanced oil recovery (EOR) application. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2020, 184, 109937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Simulated Oils | Wax Content/wt% | White Oil/wt% |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 100 |
| 2 | 10 | 90 |
| 3 | 20 | 80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zuo, L.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, C.; Zhu, X.; Wu, C. Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Experiment on the Microscopic Mechanism of the Effect of Wax Crystals on the Burst and Drainage of Foams. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116778
Zuo L, Zhang Q, Sun C, Zhu X, Wu C. Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Experiment on the Microscopic Mechanism of the Effect of Wax Crystals on the Burst and Drainage of Foams. Sustainability. 2022; 14(11):6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116778
Chicago/Turabian StyleZuo, Lili, Qi Zhang, Chengwei Sun, Xiaosong Zhu, and Changchun Wu. 2022. "Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Experiment on the Microscopic Mechanism of the Effect of Wax Crystals on the Burst and Drainage of Foams" Sustainability 14, no. 11: 6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116778
APA StyleZuo, L., Zhang, Q., Sun, C., Zhu, X., & Wu, C. (2022). Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Experiment on the Microscopic Mechanism of the Effect of Wax Crystals on the Burst and Drainage of Foams. Sustainability, 14(11), 6778. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14116778






