China’s Eco-Efficiency: Regional Differences and Influencing Factors Based on a Spatial Panel Data Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
3.1. The EBM DEA Model with Undesirable Outputs
3.2. Global Moran’s I
3.3. Spatial Durbin Model
4. Data Source and Indicator Selection
4.1. Indicators of EE Evaluation
4.2. Factors Influencing EE
5. Empirical Analysis
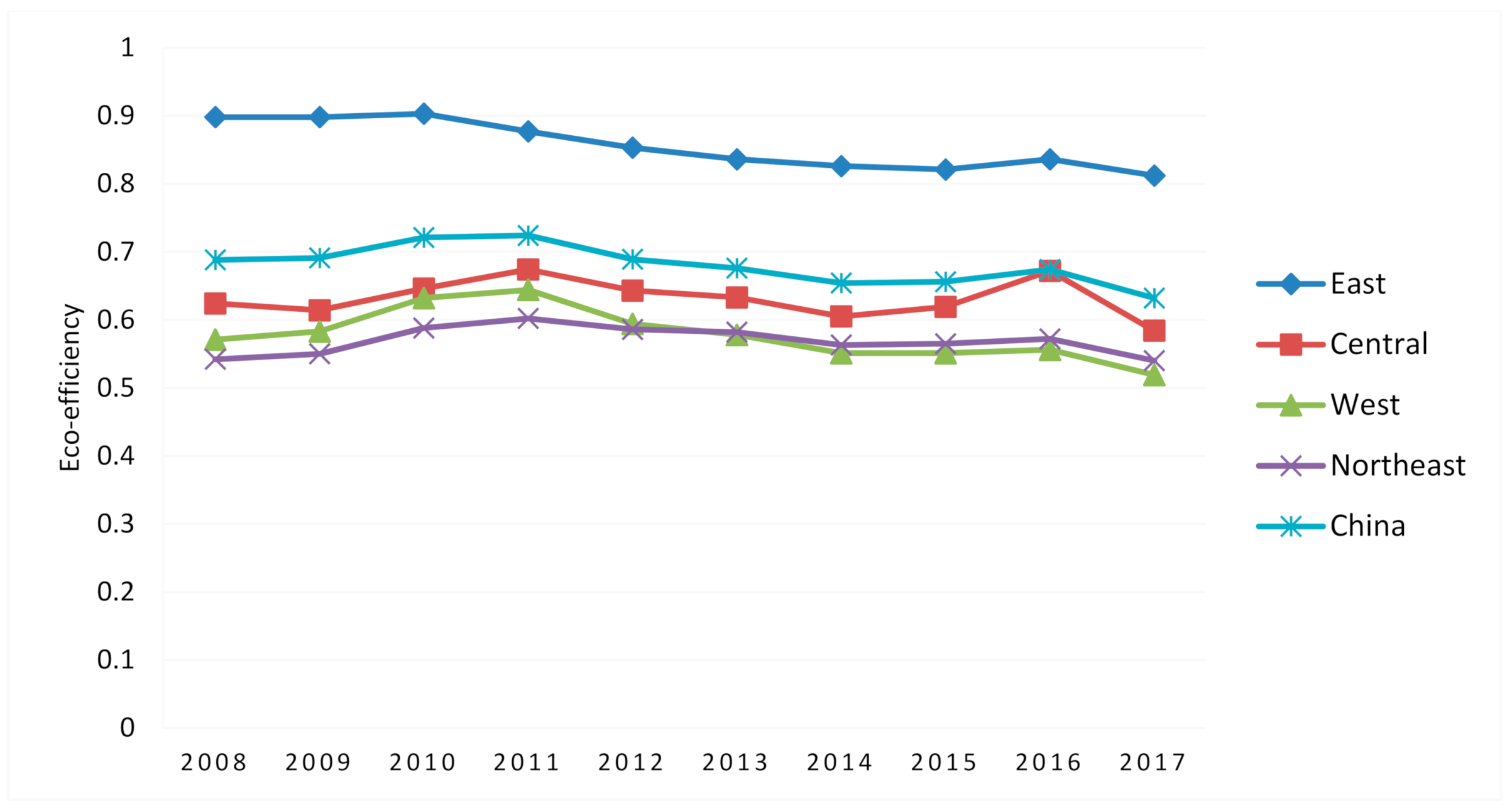
5.1. Overall Characteristics of Chinese EE
5.2. Regional Characteristics of EE
5.2.1. Eastern Area
5.2.2. Central Area
5.2.3. Western Area
5.2.4. Northeastern Area
5.3. Regression Results and Analysis
5.3.1. Smulticollinearity Test
5.3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Test
5.3.3. LM and Robust LM Tests
5.3.4. Wald and LR Tests
β5ULi,t + β6PDi,t +θ1WDELi,t +θ2WISi,t + θ3W*FTDi,t +θ4WTPi,t +
θ5WULi,t +θ6WPDi,t +εi,t εi,t ~ N(0, σ2i,t In),
5.3.5. Analysis Results
6. Conclusions and Policy Suggestions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. Chapter 8: Transport. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar5/wg3/transport/ (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Climate Change 2014 Synthesis Report: Summary for Policymakers. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/2018/02/AR5_SYR_FINAL_SPM.pdf (accessed on 13 March 2019).
- United Nations Climate Change Conference. The Paris Agreement. Available online: http://www.tanjiaoyi.com/apphtml/pdf/PARISAGREEMENT201512120830.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Fet, A.M. Eco-efficiency Reporting Exemplified by Case Studies. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2003, 5, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaltegger, S.; Sturm, A. Okologische rationalitat: Ansatzpunkte zur ausgestaltung yon okologieorienttierten management instrumenten. Die Unternehm. 1990, 4, 273–290. [Google Scholar]
- Hinterberger, F.K.; Schepelmann, F. Eco-Efficiency of Regions:Toward Reducing Total Material Input. Sustainable Europe Research Institute. 2001. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Friedrich_Hinterberger/publication/228597679_Eco-Efficiency_of_Regions_Toward_Reducing_Total_Material_Input/links/00463519fb6a1d7570000000.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- United Nations Statistics Division. World Statistics Pocketbook. Available online: https://unstats.un.org/unsd/publications/pocketbook/ (accessed on 7 November 2019).
- Zeng, L.E.; Lu, H.Y.; Liu, Y.P.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, H.Y. Analysis of Regional Differences and Influencing Factors on China’s Carbon Emission Efficiency in 2005–2015. Energies 2019, 12, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BP. Statistical Review of World Energy. Available online: https://www.nengapp.com/news/detail/2263237 (accessed on 7 November 2019).
- International Energy Agency. CO2 Emissions from Fuel Combustion: Highlights. Available online: https://webstore.iea.org/co2-emissions-from-fuel-combustion-2018-highlights (accessed on 7 December 2019).
- Yale Center for Environmental Law and Policy. Environmental Performance Index; International Earth Science Information. Available online: http://epi.yale.edu (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Xi, J.P. Full Text of Xi Jinping’s Report at 18th CPC National Congress. Available online: http://cpc.people.com.cn/n/2012/1204/c64387-19788313.html (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Chinese State Council. The Main Functional Area Planning. Available online: https://www.chinanews.com/gn/2011/06-09/3099774.shtml (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Ma, F.; Li, X.D.; Sun, Q.P.; Liu, F.; Wang, W.L.; Bai, L.L. Regional Differences and Spatial Aggregation of Sustainable Transport Efficiency: A Case Study of China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Chen, H.; Lin, T.-Y. Impact of Media Reports and Environmental Pollution on Health and Health Expenditure Efficiency. Healthcare 2019, 7, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, K.L.; Geng, J.C. China’s Regional Ecological Energy Efficiency and Energy Saving and Pollution Abatement Potentials: An Empirical Analysis Using Epsilon-Based Measure Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.; Tsutsui, M. An Epsilon-Based Measure of Efficiency in DEA-A Third Pole of Technical Efficiency. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 207, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chiu, Y.H.; Lin, T.Y. The Impact of Economic Growth and Air Pollution on Public Health in 31 Chinese Cities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.T.; Huang, J.H.; Zhang, N. Modeling the eco-efficiency of Chinese prefecture-level cities with regional heterogeneities: A comparative perspective. Ecol. Model. 2019, 402, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chiu, Y.H.; Lin, T.Y. Energy and Environmental Efficiency in Different Chinese Regions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Ren, F.R.; Xiao, Q.W.; Chiu, Y.H.; Lin, T.Y. Cross-Regional Comparative Study on Carbon Emission Efficiency of China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt Based on the Meta-Frontier. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Li, Y. CNG2020 Strategy and Airline Efficiency: A Network Epsilon-Based Measure with Managerial Disposability. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2018, 12, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.J.; Zeng, L.E.; Lu, H.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Wei, X.Y. Green economic efficiency and its influencing factors in China from 2008 to 2017: Based on the super-SBM model with undesirable outputs and spatial Dubin model. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 140026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Ecological Total-Factor Energy Efficiency and Their Drivers in China at the Prefecture Level. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Sun, Y.; Shen, H.; Jian, J.; Yu, Z. Does Environmental Tax Affect Energy Efficiency? An Empirical Study of Energy Efficiency in OECD Countries Based on DEA and Logit Model. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Lu, L.C. New Energy Development and Pollution Emissions in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesage, J.P.; Pace, P.K. Introduction to Spatial Econometrics; CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Liu, C. Regional disparity, spatial spillover effects of urbanisation and carbon emissions in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zuo, L.; Wang, X.; Hu, S.; Zhu, Z. Spatial Econometric Analysis of the Relationship between Urban Land and Regional Economic Development in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Coordinated Development Region. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Ouyang, S.S. The influencing factors and spatial spillover effects of CO2 emissions from transportation in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.C.; Tabak, B.M.; Cajueiro, D.O.; Dias, M.V.B. A comparison of DEA and SFA using micro– and macro–level perspectives: Efficiency of Chinese local banks. Physical A 2017, 469, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orea, L.; Wall, A. Measuring Eco-efficiency Using the Stochastic Frontier Analysis Approach. In Advances in Efficiency and Productivity. International Series in Operations Research & Management Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Chen, X. Eco-efficiency of grain production in China based on water footprints: A stochastic frontier approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.L.; Wan, K.D.; Yang, J.Y. Measurement and evolution of eco-efficiency of coal industry ecosystem in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, C. Estimation of Association between Healthcare System Efficiency and Policy Factors for Public Health. Appl. Sci 2018, 8, 2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Xing, Z. Re-Examining Regional Total-Factor Water Efficiency and Its Determinants in China: A Parametric Distance Function Approach. Water 2018, 10, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellnitz, A.; Kleine, A. Multiple input-output frontier analysis-From generalized deterministic to stochastic frontiers. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 135, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, W. Reconsidering heterogeneity in panel data estimators of the stochastic frontier model. J. Econ. 2005, 126, 269–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the Efficiency of Decision Making Units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Bai, B.; Qiao, Q.; Kang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J. Study on eco-efficiency of industrial parks in China based on data envelopment analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, J.T.; Hu, D.; Liao, W.W. Research on eco-efficiency of industrial parks in Taiwan. Energy Procedia 2018, 152, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutinho, V.; Fuinhas, J.A.; Marques, A.C.; Santiago, R. Assessing eco-efficiency through the DEA analysis and decoupling index in the Latin America countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybaczewska-Błażejowska, M.; Gierulski, W. Eco-Efficiency Evaluation of Agricultural Production in the EU-28. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, I.H.; Dong, L.; Park, H.S. Tracking urban sustainability transition: An eco-efficiency analysis on eco-industrial development in Ulsan, Korea. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K.A. Slacks-based Measure of Efficiency in Data Envelopment Analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. Dealing with Undesirable Outputs in DEA: A Slacks-Based Measure (SBM) Approach; North American Productivity Workshop: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2004; Available online: https://doc.guandang.net/s8615e0bc793c1a059a3db9f3.html (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Peng, H.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Tang, G.; Yan, B.; Xiao, X.; Han, Y. Eco-efficiency and its determinants at a tourism destination: A case study of huangshan national park, China. Tour. Manag. 2017, 60, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ning, Z.; Zhang, H. Measuring Eco-Efficiency of State-Owned Forestry Enterprises in Northeast China. Forests 2018, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.F.; Hao, S.H.; Sun, C.Z.; Lyu, T. Spatial Correlation and Convergence Analysis of Eco-Efficiency in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Li, Y. Airline efficiency measures using a Dynamic Epsilon-based Measure model. Transp. Res. Part A 2017, 100, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Sun, Y.W.; Lan, Q.Q.; Jiang, F. Impacts of industrial agglomeration on pollution and ecological efficiency-A spatial econometric analysis based on a big panel dataset of China’s 259 cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, J. Estimation of relationships for limited dependent variables. Econometrica 1958, 26, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xia, B.; Dong, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Ba, D.; Zhang, W. Research on the Spatial Differentiation and Driving Forces of Eco-Efficiency of Regional Tourism in China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Dong, B.; Zhang, X.; Niu, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, R.; Yu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Ecological efficiency in China and its influencing factors—a super-efficient SBM metafrontier-Malmquist-Tobit model study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res 2018, 25, 20880–20898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Xu, L.X.; Tang, L.N.; Xiang, X.Q. Eco-efficiency of the Western Taiwan Straits Economic Zone: An evaluation based on a novel eco-efficiency model and empirical analysis of influencing factors. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhu, T.T. How does industrial policy affect the ecoefficiency of industrial sector? Evidence from China. Appl. Energy 2020, 272, 115206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.L.; Jiang, D.W.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Guo, A.J.; Ullah, A.; Yang, X.; Cheng, Q.P.; Zhang, Y.N.; Ding, X.J. Eco-efficiency of oasis seed maize production in an arid region, Northwest China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 268, 122220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.Y. Applying a data envelopment analysis game cross-efficiency model to examining regional ecological efficiency: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 267, 122031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Bera, A.K. Spatial Dependence in Linear Regression Models with an Introduction to Spatial Econometrics. Stat. Textb. Monogr. 1998, 155, 237–289. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Chen, B.Y.; Cao, X.; Li, T.; Li, P. The spatial characteristics and influencing factors of modal accessibility gaps: A case study for Guangzhou, China. J. Transport Geogr 2017, 60, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, T.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Wang, S.; Hu, S.; Yuan, L.; Wang, J.; Wen, M. Investigating the Impacts of Urbanization on PM2.5 Pollution in the Yangtze River Delta of China: A Spatial Panel Data Approach. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guang, W.; Xu, S.T. Study of spatial patterns and spatial effects of energy eco-efficiency in China. J. Geogr. Sci 2016, 26, 1362–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Deng, X.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z. Exploring the relationship between urbanization and urban eco-efficiency: Evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyżewski, B.; Smędzik-Ambroży, K.; Mrówczyńska-Kamińska, A. Impact of environmental policy on eco-efficiency in country districts in Poland: How does the decreasing return to scale change perspectives? Environ. Impact Assess. Rev 2020, 84, 106431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Luo, N.G. Effect of Urban Scale on Eco-efficiency and the Regional Difference Analysis. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2016, 26, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.H.; Huang, L.X.; Wang, X.B. Does Industrial Structure Upgrading Improve Eco-Efficiency? J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2016, 33, 40–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Qu, S.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, S. Spatial Effects and Nonlinear Analysis of Energy Consumption, Financial Development, and Economic Growth in China. Energies 2020, 13, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chiu, Y.H.; Li, Y.; Lin, T.Y. Production efficiency and geographical location of Chinese coal enterprises—Undesirable EBM DEA. Resour. Policy 2019, 64, 101527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Appolloni, A.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Measuring Green Growth Efficiency for Chinese Manufacturing Industries. Sustainability 2017, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.F.; Fang, C.L.; Li, G.D. Spatiotemporal characteristics and influential factors of eco-efficiency in Chinese prefecture-level cities: A spatial panel econometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 120787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Yu, T.H.E.; Cho, S.H.; Jensen, K.; Ugarte, D.D.L.T. Evaluating the spatial spillover effects of transportation infrastructure on agricultural output across the United States. J. Transp. Geogr. 2013, 30, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Kong, F.; Yu, Y. Measuring ecological total-factor energy efficiency incorporating regional heterogeneities in China. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, X. Assessing regional eco-efficiency from the perspective of resource, environmental and economic performance in China: A bootstrapping approach in global data envelopment analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 173, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, N. Industrial eco-efficiency, regional disparity, and spatial convergence of China’s regions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 872–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, G.Y.; Zhang, J.P. The Estimation of China’s Provincial Capital Stock: 1952–2000. Econ. Res. J. 2004, 10, 35–44. Available online: http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JJYJ200410004.htm (accessed on 7 December 2019).
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbooks(CSY)(2009–2018); China Statistical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2009–2018; Available online: http://tongji.oversea.cnki.net/oversea/engnavi/HomePage.aspx?id=N2017100312&name=YINFN&floor=1 (accessed on 24 April 2020).
- China Emission Accounts and Datasets. CO2 Emission Inventories for 30 Provinces (2008–2017). 2020. Available online: https://www.ceads.net/data/province/ (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Xu, X.E. Regional Differentials and Influence Factors of Eco-efficiency in China: An Empirical Analysis Based on the Perspective of Spatio-temporal Differences. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2018, 27, 2673–2683. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1y390mb04g6e0xr0va510e900b539949&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, W. Dynamics, differences, influencing factors of eco-efficiency in China: A spatiotemporal perspective analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 264, 110442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Kong, Y.; Sha, J.; Wang, H.K. The role of industrial structure upgrades in eco-efficiency evolution: Spatial correlation and spillover effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wang, J.J. Measurement and Evaluation of China’s Ecological Pressure and Ecological Efficiency Based on Ecological Footprint. China Ind. Econ. 2016, 5, 5–21. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=336feb244f88d5001b1fc00f5195b403&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Zhou, Y.; Kong, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, F. The impact of population urbanization lag on eco-efficiency: A panel quantile approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Shi, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, G. Estimation of eco-efficiency and its influencing factors in Guangdong province based on Super-SBM and panel regression models. Ecol. Indic 2018, 86, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, N.S.; Li, J.J.; Lu, F.Z. Empirical Analysis on the Relationship Between the China Urbanization and Regional Eco-efficiency. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2013, 23, 53–60. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=44ea6e594bafeee4666c2283b8c0407d&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Zhang, H.P.; Guan, S.; Wang, H.D. Differences in China’s Regional Ecological Efficiency and Influencing Factors. Econ. Survey 2017, 34, 1–6. Available online: https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=71edbf41b7e580e9278d1a81f889b26c&site=xueshu_se (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Díaz-Villavicencio, G.; Didonet, S.R.; Dodd, A. Influencing factors of eco-efficient urban waste management: Evidence from Spanish municipalities. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 164, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Shao, T.; Lai, H.; Shen, M.; Li, Y. Total-Factor Eco-Efficiency and Its Influencing Factors in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.T. What has caused regional inequality in China? China Econ. Rev. 2002, 13, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Teng, F. The air quality co-benefit of coal control strategy in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; An, Y. The government capacity on industrial pollution management in Shanxi province: A response impulse analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 223, 1037–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.G.; Lu, F. Spatial distribution characteristics and convergence of China’s regional energy intensity: An industrial transfer perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Duan, Z.; Shan, Y.; Duan, H.; Wang, S.; Song, J.; Wang, X. Low-carbon developments in Northeast China: Evidence from cities. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 1019–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorst, J.P. Spatial Panel Data Models. In Spatial Econometrics. SpringerBriefs in Regional Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.K.; Cheng, L.Y.; Zhang, T.B. Does foreign direct investment have the pollution halo effect? China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2017, 27, 74–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.; Xu, H.; Draz, M.U.; Ozturkc, I.; Chandio, A.A.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhang, D.W. The case of China’s fiscal decentralization and eco-efficiency: Is it worthwhile or just a bootless errand? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, H.; Tan, Q.; Zameer, H.; Tan, J.; Nawaz, K. Exploring the impact of technological innovation, environmental regulations and urbanization on ecological efficiency of China in the context of COP21. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 274, 111–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- State Council of the PRC. Outline of the National Medium and Long Term Science and Technology Development Program (2006–2020). Available online: http://www.gov.cn/jrzg/2006-02/09/content_183787_2.htm (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Zhang, X.L.; Jin, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Y. Research on the impact of higher education hierarchy in the process of new urbanization in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2020, 27, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounetas, K.E.; Polemisb, M.N.; Tzeremesd, N.G. Measurement of eco-efficiency and convergence: Evidence from a non-parametric frontier analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2020, 291, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
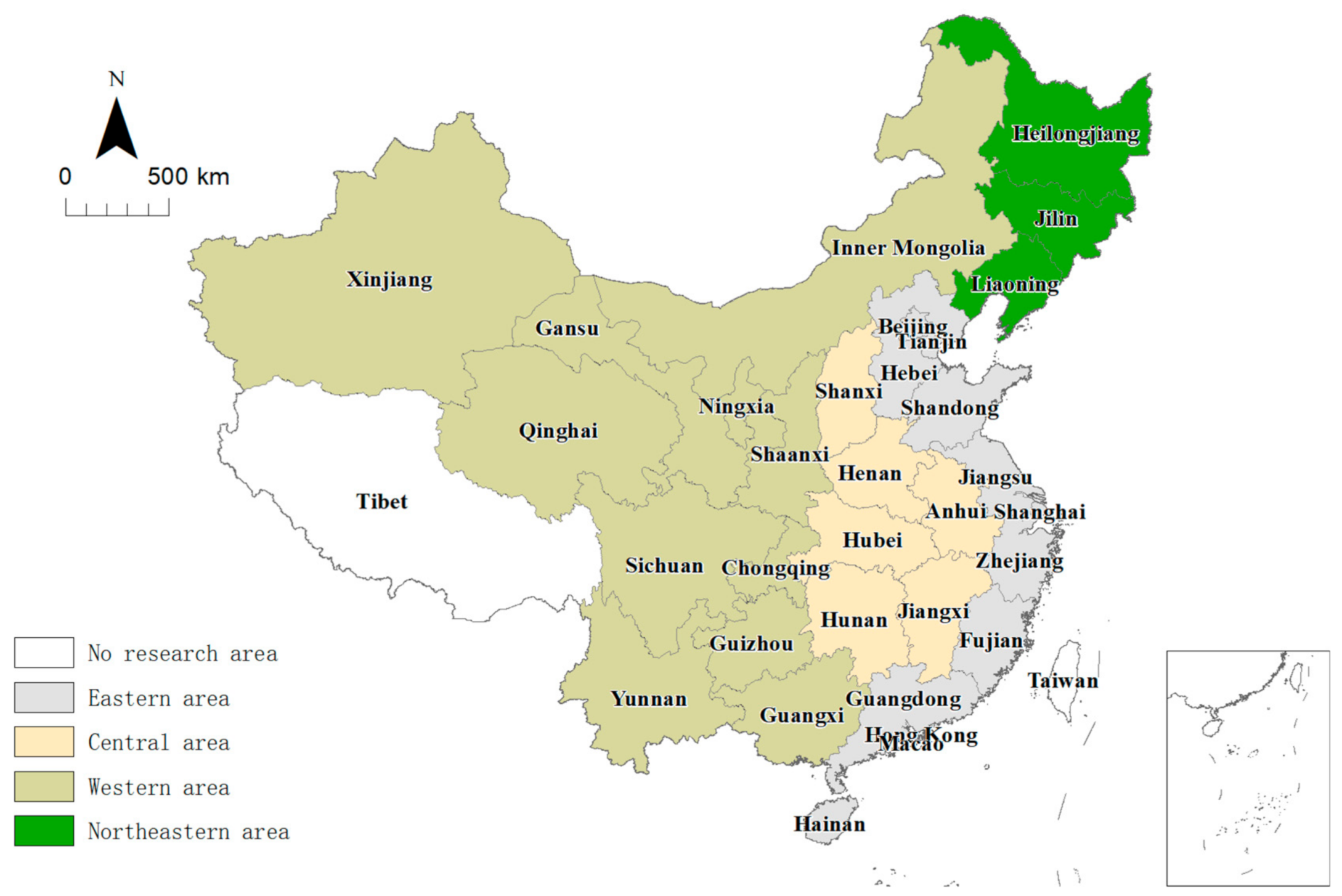

| Author | Methodology | Objects and Period | Variables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fan et al. [40] | CCR and BCC DEA models | The eco-efficiency levels of 40 Chinese industrial parks in 2012 | Input: Land, Energy, Water Desirable output: Industrial value added Undesirable output: Wastewater, Solid waste, COD, SO2 |
| Pai et al. [41] | CCR and BCC DEA models | Th eco-efficiencies of 60 industrial parks in Taiwan | Input: Site area, Labor force, Electricity, Water, Waste discharge, Airborne, Particles Output: The overall operating income |
| Moutinho et al. [42] | BCC DEA model | The eco-efficiency of the 16 Latin American countries from 1994 to 2013 | Input: Population density, labor productivity, Energy, Renewable energy, Gross capital formation productivity Output: The inverse ratio of carbon intensity |
| Rybaczewska-Bła˙ zejowsk and Gierulski [43] | Life cycle assessment (LCA) and BCC DEA model | Th eco-efficiencies of agricultural production in 28 member states of the European Union in 2015 | Input: Labor, Capital, Energy Desirable output: GDP Undesirable output: SO2 |
| Shah et al. [44] | CCR and BCC DEA models | The eco-efficiency at the industrial park/complex level of Ulsan metropolis and Korea in 2005, and 2010, and 2015 | Input: Land, Labor force, Energy Output: Gross output |
| Peng et al. [47] | The SBM DEA model with undesirable outputs | The eco-efficiency of the Huangshan National Park in China from 1981 to 2014 | Input: Average wage level of employees, New fixed asset investment, Energy, Water, Desirable output: Per capita tourism income Undesirable output: Garbage, Sewage, Waste gas |
| Ning et al. [48] | The SBM DEA model with undesirable outputs | The eco-efficiency of state-owned forestry enterprises in Northeast China from 2003 to 2015 | Input: Labor, Capital, Land Desirable output: Total output, Sale Undesirable output: Effluent, Exhaust, Solid-waste |
| Zheng et al. [49] | The SBM DEA model with undesirable outputs | The eco-efficiency of the Chinese 31 provinces from 2000 to 2015 | Input: Water footprint; Labor force; Capital, Cost of resource and environment, Land Desirable output: GDP Undesirable output: Gray water footprint, Environmental pollutants |
| Wang et al. [50] | The SBM DEA model with undesirable outputs | The eco-efficiency of regional tourism in Chinese 31 provinces from 1997 to 2016 | Input: Labor, Capital, Water, Energy Desirable output: Revenue from tourism Undesirable output: Tourism effluent discharge Tourism waste discharge Tourism SO2, Tourism CO2, |
| Yang et al. [16] | The EBM DEA model | The ecological energy efficiency of in Chinese 30 provinces from 2007 to 2015 | Input: Labor, Capital, Energy, SO2, NOX Desirable output: GDP |
| Chen et al. [51] | The EBM DEA model with undesirable outputs | The ecological efficiency of in Chinese 259 cities from 2007 to 2016 | Input: Labor, Capital, Energy, Water, Land Desirable output: GDP Undesirable output: Industrial discharged wastewater, Industrial sulfur dioxide emission, Industrial soot (dust) emission |
| Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators | Mean | Std. Dev | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inputs | Capital stock (unit: 108 yuan) | 68,357.9 | 46,755.2 | 5832 | 231,280 |
| Labor force (unit: 104) | 2666.7 | 1744.7 | 301 | 6767 | |
| Total energy consumption (unit: 104 tons of SCE) | 13,624.5 | 8157.9 | 1135 | 38,899 | |
| Total water consumption (unit: 108 L) | 201 | 142 | 22.3 | 591.3 | |
| Urban construction land (unit: sq.km) | 1567.1 | 1078.1 | 109 | 5577 | |
| Desired outcomes | GDP (unit: 108 yuan) | 18,559.3 | 15,297.9 | 1019 | 80,956 |
| Undesired outcomes | CO2 emissions (unit: 106 tons) | 300.5 | 192.2 | 25 | 842 |
| SO2 emissions (unit: 104 tons) | 63 | 40.7 | 1.43 | 182.7 | |
| Smoke and dust emissions (unit: 104 tons) | 58.9 | 43. | 5.75 | 198.3 | |
| COD emissions (unit: 104 tons) | 43.4 | 31.1 | 1.47 | 179.8 | |
| Ammonia nitrogen (unit: 104 tons) | 6.25 | 4.51 | 0.56 | 23.09 |
| Explanatory Variable | Variables’ Definition and Unit | Key References | Pre-Judgment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic development level (EDL) | GDP per capita (104 RMB) | [55,58,79,80] | Positive |
| Industrial structure (IS) | The proportion of the added value of the tertiary industry to provincial GDP (%) | [55,81,82] | Positive |
| Foreign trade dependence(FTD) | The proportion of the total import and export trade to provincial GDP (%) | [54,79,80,83] | Unknown |
| Technological progress (TP) | Proportion of R&D expenditure to provincial GDP (%) | [58,80,84] | Positive |
| Urbanization level (UL) | The proportion of city population in total population (%) | [85,86] | Negative |
| Population density(PD) | Ratio of the total regional population to regional area (person/sq.km) | [62,84,87,88] | Unknown |
| Regions | Provinces | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East | Beijing | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Tianjing | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Hebei | 0.751 | 0.696 | 0.732 | 0.738 | 0.69 | 0.666 | 0.634 | 0.643 | 0.641 | 0.593 | 0.678 | |
| Shanghai | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Jiangsu | 0.889 | 0.884 | 0.893 | 0.855 | 0.811 | 0.789 | 0.78 | 0.761 | 0.773 | 0.75 | 0.818 | |
| Zhejiang | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.905 | 0.874 | 0.814 | 0.805 | 0.861 | 0.893 | 0.831 | 0.898 | |
| Fujian | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.852 | 0.792 | 0.771 | 0.755 | 0.743 | 0.778 | 0.7 | 0.839 | |
| Shandong | 0.772 | 0.759 | 0.8 | 0.783 | 0.734 | 0.738 | 0.697 | 0.695 | 0.713 | 0.682 | 0.737 | |
| Guangdong | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Hainan | 0.569 | 0.645 | 0.607 | 0.635 | 0.631 | 0.581 | 0.589 | 0.509 | 0.558 | 0.56 | 0.588 | |
| Mean | 0.898 | 0.898 | 0.903 | 0.877 | 0.853 | 0.836 | 0.826 | 0.821 | 0.836 | 0.812 | 0.898 | |
| Central | Shanxi | 0.66 | 0.619 | 0.633 | 0.662 | 0.614 | 0.597 | 0.57 | 0.564 | 0.546 | 0.517 | 0.598 |
| Anhui | 0.535 | 0.543 | 0.591 | 0.62 | 0.605 | 0.597 | 0.569 | 0.582 | 0.591 | 0.558 | 0.579 | |
| Jiangxi | 0.623 | 0.624 | 0.659 | 0.684 | 0.649 | 0.632 | 0.622 | 0.612 | 0.619 | 0.581 | 0.631 | |
| Henan | 0.703 | 0.686 | 0.706 | 0.708 | 0.662 | 0.644 | 0.614 | 0.622 | 0.652 | 0.626 | 0.662 | |
| Hubei | 0.565 | 0.59 | 0.599 | 0.635 | 0.613 | 0.625 | 0.574 | 0.618 | 0.626 | 0.563 | 0.601 | |
| Hunan | 0.657 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.736 | 0.713 | 0.706 | 0.68 | 0.715 | 1 | 0.661 | 0.718 | |
| Mean | 0.624 | 0.614 | 0.646 | 0.674 | 0.643 | 0.633 | 0.605 | 0.619 | 0.672 | 0.584 | 0.624 | |
| West | Inner Mongolia | 0.666 | 0.665 | 0.661 | 0.674 | 0.639 | 0.632 | 0.604 | 0.637 | 0.699 | 0.658 | 0.653 |
| Guangxi | 0.55 | 0.607 | 0.639 | 0.664 | 0.601 | 0.582 | 0.567 | 0.566 | 0.565 | 0.525 | 0.587 | |
| Chongqing | 0.629 | 0.616 | 0.649 | 0.68 | 0.702 | 0.705 | 0.672 | 0.666 | 0.678 | 0.647 | 0.664 | |
| Sichuan | 0.655 | 0.637 | 0.672 | 0.703 | 0.672 | 0.661 | 0.63 | 0.627 | 0.616 | 0.58 | 0.645 | |
| Guizhou | 0.551 | 0.549 | 0.619 | 0.622 | 0.588 | 0.573 | 0.554 | 0.544 | 0.527 | 0.469 | 0.56 | |
| Yunnan | 0.598 | 0.598 | 0.623 | 0.617 | 0.6 | 0.604 | 0.564 | 0.555 | 0.538 | 0.491 | 0.579 | |
| Shaanxi | 0.683 | 0.782 | 1 | 1 | 0.718 | 0.682 | 0.654 | 0.664 | 0.682 | 0.621 | 0.749 | |
| Gansu | 0.508 | 0.51 | 0.546 | 0.557 | 0.541 | 0.542 | 0.512 | 0.523 | 0.524 | 0.507 | 0.527 | |
| Qinghai | 0.604 | 0.6 | 0.633 | 0.654 | 0.599 | 0.538 | 0.499 | 0.49 | 0.502 | 0.475 | 0.559 | |
| Ningxia | 0.364 | 0.368 | 0.413 | 0.413 | 0.397 | 0.391 | 0.377 | 0.366 | 0.364 | 0.343 | 0.38 | |
| Xinjiang | 0.472 | 0.477 | 0.499 | 0.502 | 0.472 | 0.452 | 0.424 | 0.422 | 0.423 | 0.392 | 0.454 | |
| Mean | 0.571 | 0.583 | 0.632 | 0.644 | 0.594 | 0.578 | 0.551 | 0.551 | 0.556 | 0.519 | 0.571 | |
| Northeast | Liaoning | 0.565 | 0.578 | 0.615 | 0.639 | 0.618 | 0.605 | 0.59 | 0.597 | 0.592 | 0.55 | 0.595 |
| Jilin | 0.51 | 0.511 | 0.541 | 0.539 | 0.535 | 0.55 | 0.54 | 0.539 | 0.552 | 0.526 | 0.534 | |
| Heilongjiang | 0.552 | 0.561 | 0.607 | 0.628 | 0.605 | 0.591 | 0.559 | 0.56 | 0.571 | 0.544 | 0.578 | |
| Mean | 0.542 | 0.55 | 0.588 | 0.602 | 0.586 | 0.582 | 0.563 | 0.565 | 0.572 | 0.54 | 0.542 | |
| Average EEs in Chinese provinces | 0.688 | 0.691 | 0.721 | 0.724 | 0.689 | 0.676 | 0.654 | 0.656 | 0.674 | 0.632 | 0.680 | |
| InEE | InDEL | InIS | InFTD | InTP | InUL | InPD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| InEE | 1 | ||||||
| InDEL | 0.5409 *** | 1 | |||||
| InIS | 0.3723 *** | 0.5964 *** | 1 | ||||
| InFTD | 0.7037 *** | 0.5694 *** | 0.5214 *** | 1 | |||
| InTP | 0.6892 *** | 0.6621 *** | 0.5329 *** | 0.6349 *** | 1 | ||
| InUL | 0.5991 *** | 0.9122 *** | 0.6726 *** | 0.7089 *** | 0.7090*** | 1 | |
| InPD | 0.6723 *** | 0.4279 *** | 0.4240 *** | 0.6707 *** | 0.7078*** | 0.5293 *** | 1 |
| InDEL | InIS | InFTD | InTP | InUL | InPD | Mean VIF | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIF | 6.63 | 1.86 | 2.80 | 3.01 | 9.66 | 2.51 | 4.41 |
| 1/VIF | 0.150881 | 0.537701 | 0.357327 | 0.331950 | 0.103474 | 0.398968 |
| Year | Moran’s I | Z-Score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2008 | 0.423 *** | 3.696 | 0.000 |
| 2009 | 0.417 *** | 3.653 | 0.000 |
| 2010 | 0.299 *** | 2.682 | 0.007 |
| 2011 | 0.257 ** | 2.364 | 0.018 |
| 2012 | 0.381 *** | 3.406 | 0.001 |
| 2013 | 0.343 *** | 3.102 | 0.002 |
| 2014 | 0.380 *** | 3.411 | 0.001 |
| 2015 | 0.318 *** | 2.890 | 0.004 |
| 2016 | 0.285 ** | 2.591 | 0.010 |
| 2017 | 0.327 *** | 2.977 | 0.003 |
| Spatial Error: | Spatial Lag | |
|---|---|---|
| Moran’s I | 3.707 *** | |
| Lagrange multiplier | 189.649 *** | 50.831 *** |
| Robust Lagrange multiplier | 139.848 *** | 1.030 |
| Fixed Effects | Random Effects | |
|---|---|---|
| Wald test spatial lag | 501.84 *** | 127.34 *** |
| LR test spatial lag | 134.89 *** | 134.89 *** |
| Wald test spatial error | 22.27 *** | 7.13 *** |
| LR test spatial error | 30.65 *** | 30.65 *** |
| Spatial Fixed-Effects | Time Fixed-Effects | Spatial and Time Fixed-Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|
| InDEL | 0.397 *** | 0.053 | 0.402 *** |
| InIS | 0.091 ** | −0.200 *** | 0.092 |
| InFTD | 0.026 * | 0.124 *** | 0.027 * |
| InTP | 0.080 * | 0.078 | 0.080 * |
| InUL | −0.105 | 0.125 | −0.127 |
| InPD | −0.046 *** | −0.040 * | −0.044 *** |
| WInDEL | −0.306 *** | −0.064 | −0.259 |
| WInIS | −0.008 | 0.141 | −0.003 *** |
| WInFTD | −0.024 | −0.095 *** | −0.041 |
| WInTP | −0.067 | −0.037 | −0.045 |
| WInUL | −0.046 | −0.035 | −0.012 |
| WInPD | 0.069 *** | 0.042 | 0.055 |
| Spatial rho | 0.772 *** | 0.684 *** | 0.701 *** |
| Variance sigma2_e | 0.005 | 0.010 | 0.005 |
| R-squared | 0.775 | 0.640 | 0.672 |
| Log-likelihood | 335.771 | 249.772 | 338.962 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, L. China’s Eco-Efficiency: Regional Differences and Influencing Factors Based on a Spatial Panel Data Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063143
Zeng L. China’s Eco-Efficiency: Regional Differences and Influencing Factors Based on a Spatial Panel Data Approach. Sustainability. 2021; 13(6):3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063143
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Liangen. 2021. "China’s Eco-Efficiency: Regional Differences and Influencing Factors Based on a Spatial Panel Data Approach" Sustainability 13, no. 6: 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063143
APA StyleZeng, L. (2021). China’s Eco-Efficiency: Regional Differences and Influencing Factors Based on a Spatial Panel Data Approach. Sustainability, 13(6), 3143. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13063143






