Improving Irrigation Water Use Efficiency of Robusta Coffee (Coffea canephora) Production in Lam Dong Province, Vietnam
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection and Sampling
2.3. Empirical Models
2.3.1. Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA)
Determining Technical Efficiency (TE)
2.3.2. DEA Approach of IWUE
2.3.3. Regression Models
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Coffee Farmers
3.2. The Response of Robusta Coffee Productivity to the Level of Irrigation Water Used
3.3. The DEA Results-TE and IWUE Scores
3.4. Tobit Model Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amarasinghe, U.A.; Hoanh, C.; D’haeze, D.; Hung, T. Toward sustainable coffee production in Vietnam: More coffee with less water. Agric Syst. 2015, 136, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, S.; Hieu, S.P.; Kuit, M.; Von Enden, J.; Swinkels, R.; Vietnamese Coffee Competitiveness and Policy Options to Improve it. Conference Proceedings. 2002. Available online: http://ipsard.gov.vn/news/mispa/Nhom%20ca%20phe/Hop,%20Hoi%20thao/Hoi%20thao%20kha%20nang%20canh%20tranh%20cafe%20VN/Policy_brief__ver09__Hieu.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2017).
- World Bank (WB). The Socialist Republic of Vietnam. Coffee Sector Report. 2004. 29358-VN. Available online: https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/14405 (accessed on 22 August 2019).
- Marsch, A. Diversification by Smallholder Farmers: Vietnam Robusta Coffee; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Haggar, J.; Schepp, K. Coffee and Climate Change Impacts and Options for Adaption in Brazil, Guatemala, Tanzania and Vietnam. NRI Working Paper Series. 2012. Climate Change, Agriculture and Natural Resources No. 4. Natural Resources Institute. Available online: https://www.nri.org/publications/working-paper-series/4-coffee-and-climate-change/file (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Giungato, P.; Nardone, E.; Notarnicola, L. Environmental and socio-economic effects of intensive agriculture. Vietnam Case 2008, 47, 135–151. [Google Scholar]
- Dewbre, J. Improving Resource Allocation and Incomes in Vietnamese Agriculture. A Case Study of Farming in the Dong Nai River Basin; IFPRI Discussion Paper 00984; IFPRI: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- D’haeze, D.; Deckers, J.; Raes, D.; Phong, T.; Loi, H. Environmental and socio-economic impacts of institutional reforms on the agricultural sector of Vietnam: Land suitability assessment for Robusta coffee in the Dak Gan region. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A. An Institutional Analysis of Changes in Land Use Pattern and Water Scarcity in Dak Lak Province, Vietnam; Copenhagen, Denmark; NIAS Press: 2001. Available online: http://dlc.dlib.indiana.edu/dlc/bitstream/handle/10535/7903/ahmadviet.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 25 July 2019).
- Technoserve. Vietnam: A Business Case for Sustainable Coffee Production. 2013. Available online: www.sustainablecoffeeprogram.com/site/getfile.php?id=211 (accessed on 24 July 2019).
- Ministry of Natural Resource and Environment of Vietnam (MONRE). Climate Change, Sea Level Rise Scenarios for Vietnam; Vietnam Publishing House of Natural Resources, Environment and Cartography: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2016.
- Nguyen, H.A.; Bokelmann, W.; Ngo, T.T.; Do, T.N.; Nguyen, V.M. Smallholders’ preferences for different contract farming models: Empirical evidence from sustainable certified coffee production in Vietnam. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3799. [Google Scholar]
- Luong, Q.V.; Tauer, L.W. A real options analysis of coffee planting in Vietnam. Agric. Econ. 2006, 35, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.K.; Gerardo, H.; Jake, B. Vietnam-Netherlands Partnership Water for Food & Ecosystems; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MARD): Hanoi, Vietnam, 2009.
- Jolk, C.; Greassidis, S.; Jaschinski, S.; Stolpe, H.; Zindler, B. Planning and decision support tools for the Integrated Water Resources Management in Vietnam. Water 2010, 2, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omezzine, A.; Zaibet, L. Management of modern irrigation systems in Oman: Allocative vs irrigation efficiency. Agric. Water Manag. 1998, 37, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.E.; Grafton, R.Q.; Kirby, M.; Hanjra, M.A. Understanding irrigation water use efficiency at different scales for better policy reform: A case study of the Murray–Darling Basin, Australia. Water Policy 2011, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, M.; Ancev, T.; Hernández-Sancho, F. Efficient water use for sustainable irrigation industry. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 1683–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israelsen, O.W. Irrigation Principles and Practices, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1932; p. 422. [Google Scholar]
- El-Wahed, M.H.A.; Ali, E.A. Effect of irrigation systems, amounts of irrigation water and mulching on corn yield, water use efficiency and net profit. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 120, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Dawes, W.R.; Liu, C. Improving water use efficiency of irrigated crops in the north China plain–measurements and modelling. Agric. Water Manag. 2001, 48, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, C.M.; Styles, W.S. Drip and Micro Irrigation for Trees, Vines, and Row Crops, with Special Sections on Buried Drip; Irrigation Training and Research Center: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 1994; p. 261. [Google Scholar]
- Menga, F.Y.; Fanb, L.W.; Zhoua, P.; Zhoua, D.Q. Measuring environmental performance in China’s industrial sectors with non-radial DEA. Math. Comput. Model. 2012, 58, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueyoshi, T.; Goto, M. Returns to scale and damages to scale on U.S. fossil fuel power plants: Radial and non-radial approaches for DEA environmental assessment. Energy Econ. 2012, 34, 2240–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.; Huang, C.; Ting, C. A non-radial measure of different systems for Taiwanese tourist hotel’s efficiency assessment. CEJOR 2012, 20, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Sancho, F.; Molinos-Senante, M.; Sala-Garrido, R. Energy efficiency in Spanish wastewater treatment plants: A non-radial DEA approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2693–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Poh, K.L.; Ang, B.W. A non-radial DEA approach to measuring environmental performance. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 178, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lu, W.M. Performance benchmarking for Taiwan’s international tourist hotels. INFOR 2006, 44, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Lu, W.M. Evaluating the performance of the Taiwanese hotel industry using a weight slacks-based measure. Asia Pac. J. 2005, 22, 487–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.A. Measuring the Efficiency of Coffee Producers in Vietnam: Do Outliers Matter? Master’s Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Atici, K.; Podinovski, V.A. Review of Data Envelopment Analysis Studies in Agriculture. Ph.D. Thesis, Warwick Business School, University of Warwick, Coventry, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cheesman, J.; Son, T.V.H.; Bennett, J. Valuing Irrigation Water for Coffee Production in Dak Lak, Vietnam: A Marginal Productivity Analysis; Research Report, No. 6; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR): Bruce, Australia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Agriculture and Rural Development of Lam Dong (DARD). Available online: http://www.lamdong.gov.vn/vi-VN/Home/Pages/Default.aspx (accessed on 21 December 2017).
- General Statistics Office (GSO) of Vietnam. Area, Population and Population Density in 2013 by Province. Available online: http://www.gso.gov.vn/default_en.aspx?tabid=467&idmid=3&ItemID=15751 (accessed on 17 January 2015).
- Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA). Data Collection Survey on Water Resources Management in Central Highlands; Final Report; Nippon Koei Co. Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, M. The measurement of Productive Efficiency. J. R Stat. Soc. 1957, 120, 253–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochran, W.G. Sampling Technique, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1963; p. 413. [Google Scholar]
- Aigner, D.J.; Ameiya, T.; Poirier, P.J. On the estimation of production frontiers: Maximum likelihood estimation of the parameters of a discontinuous density function. Int. Econ. Rev. 1976, XVII, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelli, T. A Guild to DEAP, Version 2.1: A Data Envelopment Analysis Computer Program; Centre for Efficiency and Productivity Analysis: Armidale, Australia, 1988; Volume 96, pp. 1–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y. The productive efficiency of Chinese iron and steel industry. Resour. Policy 1996, 21, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of Decision-Making Units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGockin, J.T.; Gollehon, N.; Ghosh, S.C. Water conservation in irrigated agriculture: A stochastic production frontier model. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, S.; Lovell, C.A.K.; Thijssen, G. Econometric estimation of technical and environmental efficiency: An application to Dutch dairy farms. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 1999, 81, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, V.E.; Lovell, C.A.K.; Nehring, R.F.; Somwaru, A. Incorporating undesirable outputs into models of production: An application to US agriculture. Cah. D’economique Et Sociol. Rural. 1994, 31, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Lovell, C.A.K. Production Frontiers; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard, S.; Lovell, C.A.K.; Thijssen, G.J. Environmental efficiency with multiple environmentally detrimental variables; estimated with SFA and DEA. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2000, 121, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansink, O.A.; Pietola, K.; Bäckman, S. Efficiency and productivity of conventional and organic farms in Finland 1994–1997. Eur. Rev. Agric. Econ. 2002, 29, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilienfeld, A.; Asmild, M. Estimation of excess water use in irrigated agriculture: A data envelopment analysis approach. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 94, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frija, A.; Chebi, L.A.; Speelman, S.; Buysse, J.; Van Huylenbroeck, G. Water use and technical efficiencies in horticultural greenhouses in Tunisia. Agric. Water Manag. 2009, 96, 1509–1516. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A. Applications of Cobb-Douglas Production Function in Construction Time-Cost Analysis. Construction Systems. Master’s Thesis, University of Nebraska–Lincoln, Lincoln, NE, USA, 2012; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Simar, L.; Wilson, P.W. Two-stage DEA: Caveat emptor. J. Product. Anal. 2011, 36, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebil, A.; Frija, A.; Belhassen, A. Irrigation water use efficiency in collective irrigated schemes of Tunisia: Determinants and potential irrigation cost reduction. Greek Assoc. Agric. Econ. Agric. Econ. Rev. 2012, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Zhu, J.; Yan, Q.; Li, M.; Yu, G. Comparison of intrinsic water use efficiency between different aged Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica wide windbreaks in semiarid sandy land of northern China. Agroforest Syst. 2015, 89, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brienen, R.J.W.; Gloor, E.; Clerici, S.; Newton, R.; Arppe, L.; Boom, A.; Bottrell, S.; Callaghan, M.; Heaton, T.; Helama, S.; et al. Tree height strongly affects estimates of water-use efficiency responses to climate and CO2 using isotopes. Nat. Commun. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, N.G.; Bond, B.J.; Dickman, L.T.; Ryan, M.G.; Whitehead, D. Relationships between tree height and carbon isotope discrimination. Tree Physiol. 2011, 4, 255–286. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka-Oda, A.; Kenzo, T.; Koretsune, S.; Sasaki, H.; Fukud, K. Ontogenetic changes in water-use efficiency (d13C) and leaf traits differ among tree species growing in a semiarid region of the Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, Y.; Barnard, R.L.; Buchmann, N. Ontogeny and leaf gas exchange mediate the carbon isotopic signature of herbaceous plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terwilliger, V.J. Influence of phenotypic plasticity in photosynthetic functions on the spatial distributions of tropical trees. Phys. Geogr. 2003, 24, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobojonov, I.; Berg, E.; Franz-Vasdeki, J.; Martius, C.; Lamers, J.P.A. Income and irrigation water use efficiency under climate change: An application of spatial stochastic crop and water allocation model to Western Uzbekistan. Clim. Risk Manag. 2016, 13, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang’au, S.N.; Home, P.G.; Gathenya, J.M. Farm water use efficiency assessment for smallholder pumped irrigation systems in the arid and semi-arid areas of Kenya. Agric. Eng. Int. Cigr. J. 2011, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Meinzen-Dick, R.S.; Pradhan, R. Legal pluralism and dynamic property rights. In CAPRi Working Paper No. 22; International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI): Washington DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Meinzen-Dick, R. Property rights and sustainable irrigation: A developing country perspective. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 145, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cele, L.; Wale, E. The role of land- and water-use rights in smallholders’ productive use of irrigation water in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. Afr. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2018, 13, 345–356. [Google Scholar]
- Veldwisch, G.J.; Beekman, W.; Bolding, A. Smallholder irrigators, water rights and investments in agriculture: Three cases from rural Mozambique. Water Altern. 2013, 6, 125–141. [Google Scholar]
- Mogogana, B.P.; Olorunfemi, O.D.; Oladele, O.I. Knowledge and adoption of water use efficiency techniques among women: Evidence from South Africa. J. Agric. Environ. Int. Dev. 2018, 112, 271–295. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X. Irrigation Water Use Efficiency of Farmers and Its Determinants: Evidence from a Survey in Northwestern China. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Tan, Y.; Li, Z.; Aarnoudse, E.; Tu, Q. Agricultural Water Use Efficiency—A Case Study of Inland-River Basins in Northwest China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 10192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morote, Á.-F.; Hernández, M.; Olcina, J.; Rico, A.-M. Water Consumption and Management in Schools in the City of Alicante (Southern Spain) (2000–2017): Free Water Helps Promote Saving Water? Water 2020, 12, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafton, R.Q.; Kompas, T.; To, H.; Ward, M. Residential water consumption: A cross country analysis. Research report No.23. Environ. Econ. Res. Hub 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Yang, L.; Perren, K.; Zhang, Y. Household Water Consumption: Insight from a Survey in Greece and Poland. Procedia Eng. 2015, 119, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElwee, P. Forests are Gold: Trees, People, and Environmental Rule in Vietnam; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA; London, UK, 2016; p. 293. [Google Scholar]
- Shammout, M.W.; Qtaishat, T.; Rawabdeh, H.; Shatanawi, M. Improving water use efficiency under deficit irrigation in the Jordan Valley. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.G.; Mohd, R.I.; Kausar, H.; Marziah, M.; Ramlan, M.F. Plant water relations, crop yield and quality in coffee (Coffea arabica L.) as influenced by partial root zone drying and deficit irrigation. AJCS 2013, 7, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Mike, K.V.C. The water relations and irrigation requirements of coffee. Expl Agric. 2001, 37, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, R. Coffee Guide; Codeword Process and Printers: Mangalore, Karnataka, India, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.A.; Bokelmann, W.; Thi Nga, D.; Van Minh, N. Toward sustainability or efficiency: The case of smallholder coffee farmers in Vietnam. Economies 2019, 7, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.A.; Bokelmann, W. Determinants of smallholders’ market preferences: The case of sustainable certified coffee farmers in Vietnam. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2897. [Google Scholar]
- Ngango, J.; Kim, S.G. Assessment of Technical Efficiency and its potential determinants among small-scale coffee farmers in Rwanda. Agriculture 2019, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Abbreviation | Definitions |
|---|---|
| TE | Technical Efficiency |
| DEA | Data Envelopment Analysis |
| IWUE | Irrigation Water Use Efficiency |
| SFA | Stochastic Frontier Analysis |
| DMUs | Decision-Making Units |
| CRS | Constant Returns to Scale |
| VRS | Variable Returns to Scale |
| Variable Name | Explanation | Expected Sign |
|---|---|---|
| AGE | Age of trees (years) | Negative |
| DIS | Distance from the source of irrigated water to farm (m) | Negative |
| OWN | Ownership of irrigation system | Positive |
| EDU | Education level (dummy variable) | Positive |
| EXP | Farmer’s irrigation experience (years) | Positive |
| EXT | Extension contact (dummy variable) | Positive |
| CRE | Access to credit (dummy variable) | Positive |
| Variables | Kinh Group | Indigenous Group | All | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | S.D | Mean | S.D | Mean | S.D | |
| Age of household head (years) | 44.0 * | 11.0 | 42.0 * | 12.0 | 44.0 | 12.0 |
| Education level | 3.0 * | 0.7 | 2.0 * | 0.8 | 2.6 | 0.8 |
| Household size (people) | 5.0 * | 1.4 | 6.0 * | 2.2 | 5.0 | 1.7 |
| Experience (years) | 18.9 | 6.1 | 20.7 | 6.9 | 19.4 | 6.4 |
| Farm size (hectares) | 2.2 | 1.3 | 2.3 | 1.3 | 2.3 | 1.3 |
| Irrigation water use (m3) | 4719.6 | 3321.2 | 4766.8 | 3167.7 | 4733.0 | 3270.3 |
| Family labor (man-days/ha) | 66 | 43 | 78 | 60 | 69 | 49 |
| Working capital (1000 VND/ha) | 55,353.7 * | 40,801.2 | 46,465.2 * | 30,007.2 | 52,833.7 | 38,140.1 |
| Coffee productivity (Kg) | 5864.4 | 3487.6 | 5051.1 | 2857.3 | 5633.8 | 3334.2 |
| Independent Variable | Coefficient | Std. Err | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log constant | 4.581 * | 0.690 | 6.63 | 0.059 |
| Log working capital | 0.072 ** | 0.038 | 1.90 | 0.005 |
| Log labor | 0.175 ** | 0.062 | 2.84 | 0.001 |
| Log irrigation water use | 0.163 ** | 0.047 | 3.50 | 0.000 |
| Log farm size | 0.536 ** | 0.063 | 8.56 | 0.000 |
| R-square | 0.792 | |||
| Adjusted R-square | 0.788 | |||
| F (4, 189) | 180.24 | |||
| Prob > F | 0.0000 | |||
| Root MSE | 0.2928 | |||
| Efficiency (%) | TE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VRS | CRS | |||||
| Kinh Group | Indigenous Group | All | Kinh Group | Indigenous Group | All | |
| Summary Statistics | ||||||
| Mean | 0.76 | 0.81 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.75 | 0.66 |
| Minimum | 0.31 | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 0.21 |
| Maximum | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Std. Dev. | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.18 |
| Efficiency Interval | ||||||
| 100 | 23 (17) | 17 (31) | 21 (11) | 9 (6) | 9 (16) | 16 (8) |
| 90–100 | 14 (10) | 9 (16) | 24 (12) | 9 (6) | 6 (11.5) | 10 (5) |
| 80–90 | 27 (19) | 4 (7) | 24 (12) | 15 (11) | 11 (20) | 17 (9) |
| 70–80 | 16 (12) | 8 (15) | 31 (16) | 20 (14) | 6 (11.5) | 31 (15) |
| 60–70 | 28 (20) | 9 (16) | 32 (16) | 34 (25) | 9 (16) | 40 (21) |
| 50–60 | 23 (16) | 6 (11) | 44 (23) | 35 (25) | 9 (16) | 48 (25) |
| 40–50 | 4 (3) | 1 (2) | 11 (6) | 11 (8) | 4 (7) | 21 (11) |
| 30–40 | 4 (3) | 0 (0) | 6 (3) | 6 (4) | 0 (0) | 8 (4) |
| <30 | 0 (0) | 1 (2) | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (2) | 3 (2) |
| Total | 139 (100) | 55 (100) | 194 (100) | 139 (100) | 55 (100) | 194 (100) |
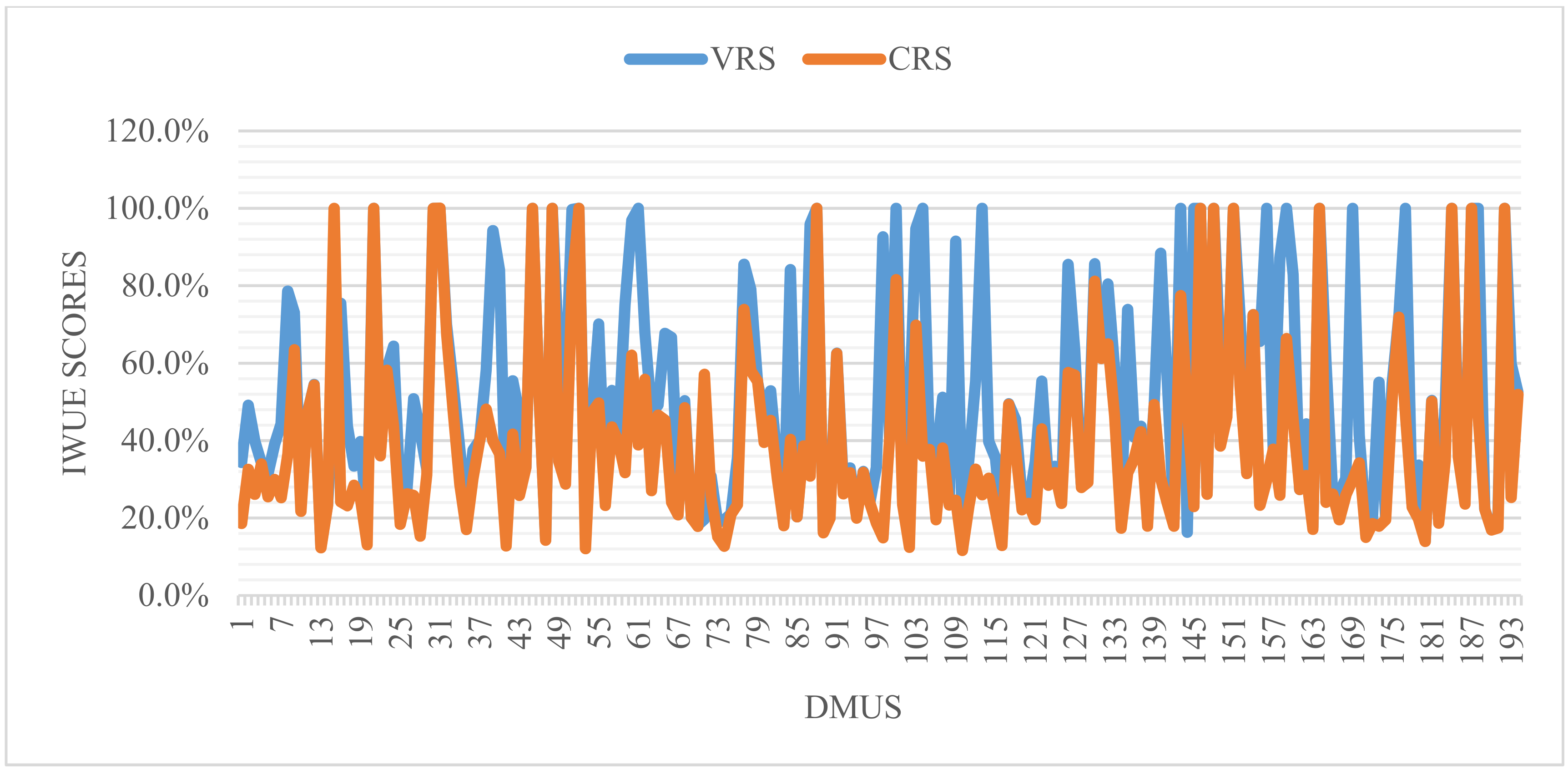
| Efficiency (%) | IWUE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VRS | CRS | |||||
| Kinh Group | Indigenous Group | All | Kinh Group | Indigenous Group | All | |
| Summary Statistics | ||||||
| Mean | 0.54 | 0.69 | 0.52 | 0.40 | 0.52 | 0.39 |
| Minimum | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.12 |
| Maximum | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Std. Dev. | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.24 |
| Efficiency Interval | ||||||
| 100 | 15 (11) | 14 (25) | 17 (9) | 5 (4) | 6 (11) | 9 (5) |
| 90–100 | 14 (10) | 7 (13) | 15 (8) | 7 (5) | 3 (5) | 6 (3) |
| 80–90 | 8 (6) | 5 (9) | 9 (5) | 1 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (1) |
| 70–80 | 3 (2) | 1 (2) | 11 (6) | 4 (3) | 3 (5) | 5 (3) |
| 60–70 | 8 (6) | 4 (7) | 10 (5) | 6 (4) | 8 (15) | 8 (4) |
| 50–60 | 18 (13) | 6 (11) | 24 (12) | 10 (7) | 6 (11) | 13 (7) |
| 40–50 | 14 (11) | 4 (7) | 24 (12) | 16 (12) | 7 (13) | 24 (12) |
| 30–40 | 21 (15) | 9 (16) | 32 (16) | 28 (20) | 8 (15) | 37 (19) |
| <30 | 38 (27) | 5 (9) | 52 (27) | 62 (45) | 14 (25) | 90 (46) |
| Total | 139 (100) | 55 (100) | 194 (100) | 139 (100) | 55 (100) | 194 (100) |
| Variables | Coefficient | Std. Dev | t-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −0.155 NS | 0.116 | −1.34 | 0.183 |
| Age of coffee plant (AGE) | 0.002 NS | 0.28 | 0.85 | 0.395 |
| Distance to water source (DIS) | −0.00009 * | 0.00003 | −2.56 | 0.011 |
| Ownership of irrigation system (OWN) | 0.060 ** | 0.019 | 3.11 | 0.002 |
| Education level (EDU) | 0.066 ** | 0.025 | 2.66 | 0.008 |
| Experience (EXP) | 0.007 * | 0.003 | 2.31 | 0.022 |
| Extension contact (EXT) | 0.123 * | 0.043 | 2.89 | 0.004 |
| Access to credit (CRE) | 0.122 * | 0.041 | 2.94 | 0.004 |
| Number of observations | 194 | |||
| LR chi2 (7) | 59.38 | |||
| Prob > chi2 | 0.0000 | |||
| Pseudo R2 | 0.3912 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, D.N.L.; Nguyen, T.D.; Pham, T.T.; Rañola, R.F., Jr.; Nguyen, T.A. Improving Irrigation Water Use Efficiency of Robusta Coffee (Coffea canephora) Production in Lam Dong Province, Vietnam. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6603. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126603
Tran DNL, Nguyen TD, Pham TT, Rañola RF Jr., Nguyen TA. Improving Irrigation Water Use Efficiency of Robusta Coffee (Coffea canephora) Production in Lam Dong Province, Vietnam. Sustainability. 2021; 13(12):6603. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126603
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Duyen Nhat Lam, Tien Dinh Nguyen, Thuy Thu Pham, Roberto F. Rañola, Jr., and Thinh An Nguyen. 2021. "Improving Irrigation Water Use Efficiency of Robusta Coffee (Coffea canephora) Production in Lam Dong Province, Vietnam" Sustainability 13, no. 12: 6603. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126603
APA StyleTran, D. N. L., Nguyen, T. D., Pham, T. T., Rañola, R. F., Jr., & Nguyen, T. A. (2021). Improving Irrigation Water Use Efficiency of Robusta Coffee (Coffea canephora) Production in Lam Dong Province, Vietnam. Sustainability, 13(12), 6603. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13126603








