Abstract
Globalization has led to a new paradigm where the traditional industries, such as agriculture, employ vanguard technologies to broaden its possibilities into what is known as smart farming and the agri-food industry 4.0. This industry needs to adapt to the current market through an efficient use of resources while being environmentally friendly. The most commonly used approaches for analyzing efficiency and sustainability on farms are production efficiency based analyses, such as Data Envelopment Analysis and Stochastic Frontier Analysis, since they allow to see how efficient the outputs are generated regardless of the units of measurement of the inputs. This work presents a real scenario for making farms more profitable and sustainable through the analysis of the Data Envelopment Analysis and the application of the Internet of Things and Edge Computing. What makes this model interesting is that it allows monitoring the ambient conditions with real-time data from the different sensors that have been installed on the farm, minimizing costs and gaining robustness in the transmission of the data to the cloud with Edge Computing, and then to have a complete overview in terms of monthly resource efficiency through the Data Envelopment Analysis. The results show that including the costs of edge and non-edge data transfer have an impact on the efficiency. This small-scale study set the basis for a future test with many farms simultaneously.
1. Introduction
In terms of agriculture production, the differences between developed and developing countries are becoming less noticeable as the market becomes increasingly globalized and competitive [1]. For European Union (EU) countries, the Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) [2] manages and finances, at European level, resources from the EU budget regarding the support for farmers’ incomes, market orientation and the environment. The CAP also regulates the evolution of quotas for agricultural industries. For example, in 2015 with the abolition of the milk quota and the correspondent policies [3], or more recently, the end to the sugar quota in 2017 [4], as well as evaluating the post-quota trade environment. Even though the quotas have come to an end, there are important concerns among agricultural lobbies and the real effects in time change of those quotas as well as the economic impact of years with a market in apparently perfect competition [5,6]. The European Union is one of the leading producers of dairy products worldwide [7]. However, Europe’s milking yields per dairy cow, for example, vary considerably among EU regions (5290 and 8702 kg/head in Ireland and Spain, respectively) [8]. Moreover, milk share is quite different for the milk of livestock other than cattle (15.2% in Spain, 5.4% in Portugal or 0% in Ireland). Furthermore, latest years demonstrate that the dairy industry is in continuous evolution (e.g., milk used in cheese production had a 24% share of total dairy in 1983 and a 40% in 2013) [8].
Nonetheless, the challenges faced by the European dairy industry are also applicable to dairy producers worldwide: a need to increase resource efficiency, become more environment-friendly and implement the latest technological trends that allow providing detailed information to the end consumer while ensuring the safety and quality of the final product. The transformation of the agricultural sector has become a new reality, and the level of technology used in production will gradually become comparable, and so will the challenges faced by producers [9]. Now, the agro-industry has to provide the food quality and safety standards which emerged mostly in the 1990s, when the modern agri-food industry began [10,11]. Technology requirements are increasing in the agricultural industry, as far as the challenges faced by producers when providing the product to end consumers increment. In this sense, end consumers are increasingly more concerned about process sustainability and product origin. Therefore, the possibility of tracking the value chain will also be a new challenge to be considered [12]. Those challenges not only apply to all dairy producers worldwide but also to other types of farms, such as crop-cultivating farms or mixed farms, i.e., those that grow crops and produce livestock. Moreover, mixed dairy farms tend to cultivate feed grain for cattle. Those industries, such as the agricultural, where meteorological changes have large effects will gradually benefit from the technology and possibility of forecasting the use of their resources according to future meteorological changes.
No matter the type of farm, the critical resource in agriculture is water. Its use, therefore, must be optimized and monitored. According to Eurostat, in 2016 the total irrigable area in EU-28 was around 15.5 Mha (8.9% of the total); however, only 10.2 Mha (5.9% of the total) was irrigated [13]. This is another problem faced not only by European farmers but globally. Full irrigation (i.e., applied in irrigation farming, as opposed to rain-fed crops or dry-land farming) is necessary for different types of agricultural production in countries of southern Europe. Moreover, in 2016, Italy and Spain were the countries with the largest irrigable areas, in absolute terms (4.1 and 3.6 Mha, respectively) [13]. Cyprus, Malta, Italy and Greece had the largest share of irrigable utilized agricultural area in 2016 (between 34.1% and 29.7%). Moreover, the majority of the 69 European Union regions, mostly southern or eastern EU Member States, generated an average standard output worth less than €25k [14]. Not only in terms of resources consumption but also regarding environmental efficiency, water plays a key role in that industry. Simar and Wilson [15] introduced the variability of meteorological conditions (levels of temperature and precipitation) to capture the effect of production uncertainty on environmental efficiency, founding that it has a significant impact on environmental efficiency. The most recent scope of work for the CAP includes water resources and how to manage them effectively. With the technological advances, farms in both developed and developing countries can benefit from the implementation of low-cost technologies [16].
In this sense, the Internet of Things (IoT) and, more specifically, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), are presented as a key enabling technology for the implementation of monitoring and resource management solutions in a variety of Industry 4.0 scenarios, including smart farming environments [17]. The IIoT can be used in combination with other technologies, such as cloud computing, big data, artificial intelligence or distributed ledger technologies (e.g., blockchain) to implement solutions that improve the traceability and productivity of industrial processes [18]. Nevertheless, when transmitting data to the cloud, several challenges arise in terms of data privacy, energy consumption or costs associated with the use of cloud services [19]. In this regard, service providers charge users according to the amount of data that is transferred, stored and processed in the cloud [20]. By using Edge Computing technologies, it is possible to reduce the volume of traffic transferred between the IoT layer and the cloud [21]. Furthermore, this technology allows the execution of machine learning models at the edge of the network, reducing response time and providing a certain level of service even if communication with the cloud is interrupted; something frequent in scenarios where the Internet connectivity is limited (e.g., farming environments in rural areas) [12].
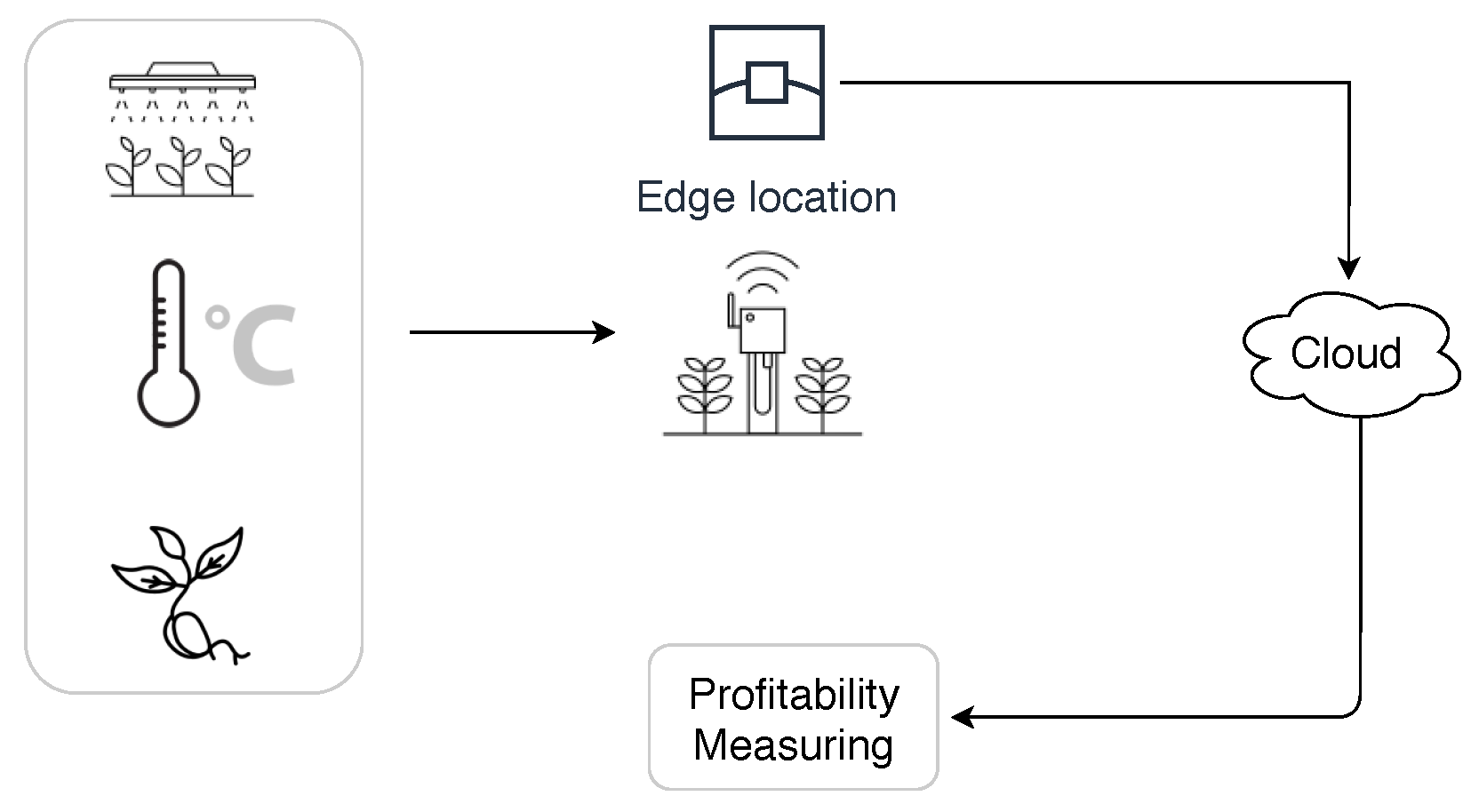
This research aims to develop a strategy on how farms can track their environmental efficiency and evaluate their possibilities for increasing their profitability as is shown in Figure 1.
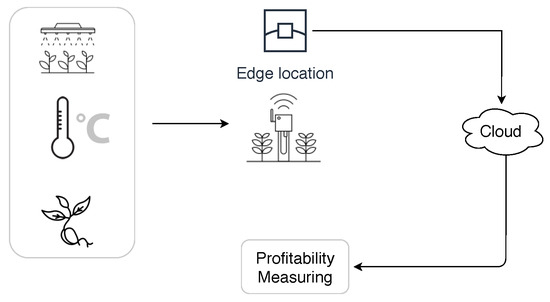
Figure 1.
Working flow of the different procedures involved in the objectives of this research.
Due to all the regulations and production levels allowed and their implications, this research presents an efficiency-oriented case study on a mixed farm in Spain. In this regard, there are many different approaches to measure the profitability and the environmental efficiency, being the Stochastic Frontier Analysis (SFA) and the Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) two of the most practiced, as Lansink and Wall [22] shown. The DEA is a data-driven approach to evaluate the performance of different units, known as Decision Making Units (DMU) [23]. DMU represent how efficiently are the inputs converted into outputs. Equally, the inputs and outputs can be measured in different units, being used in many studies in the field of environmental and ecological efficiency [24,25], and also, which makes it an interesting approach for the current efficiency analysis.
Considering the previous mentioned advances in research, this work presents the analysis of profitability and environmental monitoring in a mixed dairy farm where an Edge-IoT platform has been implemented to monitor livestock and crops, as well as to manage farming resources (i.e., irrigation and data transfer). The platform has been presented by Alonso et al. [12] and its design follows the Global Edge Computing Architecture, specially designed for the implementation of Edge Computing (EC) solutions in Industry 4.0 scenarios [26]. To conduct the analysis, two main components have been developed. On the one hand, the track of the meteorological conditions is performed by placing different sensors connected to the Edge-IoT platform. On the other hand, the efficiency of the inputs’ analysis is conducted through the DEA. Moreover, the efficiency measures provided by the DEA permit to rank the different DMU [27].
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents a review of the state-of-the-art of economic and environmental effects of technology in the agricultural industry. Section 3 describes how IoT and EC can help to increase the efficiency and profitability in Smart Farming scenarios. After that, Section 4 analyzes the profitability and environmental performance of an Edge-IoT platform in a Smart Farming scenario. Section 5 covers the experimentation and initial results. Lastly, Section 6 presents the conclusions and future work.
2. Economic and Environmental Effects of Information Technology in the Agricultural Industry
There is strong evidence that new technologies and incentives for sustainable production have had an economic impact in the agricultural industry, which affect production efficiency [28]. In recent years, companies are focusing on using suppliers that meet sustainability requirements and not only considering the product efficiency itself [29]. Another approach centers in quantifying the environmental factors with computer science and, more precisely, machine learning applications when companies select a supplier [30]. Therefore, being a sustainable farm has become an added value, not only in terms of expenditure reduction, but also for being suitable for new partners. Different methodologies are being developed to identify methods of assessing sustainable value chains [31]. The last European Horizon project launched by CAP is to set into legislation the political ambition of being the world’s first climate-neutral continent by 2050 [32]. To achieve this goal, there is a planned road-map, and from this year the European Commission will launch the European Climate Pact, following its Green Deal strategy, which will be a lever to give citizens a voice and a role in designing new actions for Europe’s environmental goals. Therefore, those incentives are at political and policy levels, even though companies are also moving towards environment management policies. To face those realities, the different processes within the agriculture industry have become something much more precise. Authors such as Pedersen et al. [33] review the different applications and benefits of the new Precision Agriculture (PA) concept. In this regard, the addition of Decision Support Systems (DSS) to PA represents the combination of data for optimal decision making [34]. Nonetheless, those PA measurements have been addressed not only to the production process itself but also to the yield being produced [35].
2.1. Optimal Production and Profitability in Terms of Technology Application
According to different econometric metrics, the measurement of the Optimal Production can be translated into a production function as Equation (1), where K is the capital such as machinery (including IoT devices), L is the land and while W represents the labor. With the years and the technological advances, this K contains more and more variables, which will be disaggregated later in this Section. Where Q is the dependent output variable as shown in Equation (1). Among years, the growth on the returns to scale (which is the function that describes what happens to long-term returns as the scale of production increases) [36] was a piece of evidence on how the farms in the agricultural sector were performed, with little changes in industry or machinery [37]. Now, agriculture is also benefitting from IoT solutions and machine learning, which can be considered as a hybrid between industry improvements and globalization possibilities.
Another approach that can be considered to understand the productivity and efficiency in production in the 21st century due to the proliferation of the new technologies is the Total Factor Productivity (TFP). TFP is the part of the production that is not explained by the number of inputs used in production. It measures the residual growth in the total output of a firm, industry or national economy that cannot be explained by the accumulation of traditional inputs, such as labor and capital. As such, its level is determined by the efficiency and intensity with which inputs are used in production. TFP growth is usually measured by Solow’s residual as in Equation (2), but the productivity variable is usually attached to the labor variable in the Solow-Swan model presented by Solow [38], Swan [39], Van Beveren [40].
where t denotes time, is the elasticity of output with respect to capital, and represents total production. A refers to labor-augmenting technology or knowledge, thus represents effective labor. All factors of production are fully employed, and initial values , , and are given. The number of workers, i.e., labor, as well as the level of technology grow exogenously at rates n and g, respectively:
Moreover, in the case of our study, the demand is inelastic and therefore the Cobb-Douglas [41] function has been an interesting approach. Inelastic demand is considered because even the end of the milk quotas in 2015 mentioned in the introduction, the year after, in 2016, the European Commission launched a policy instrument for the dairy sector to reduce the quantity of milk available on the market [42]. The Cobb-Douglas function can be estimated as a linear relationship using the Equation (5), where the I respresents the Inputs and the Q is the production and the a are the model coefficients:
Once production optimizations are reached, financial profitability can be used to measure the company’s ability to keep producing benefit. The financial profitability of a company or a farm can be calculated with the Returns on Assets (ROA), which is described in Equation (6), and where the represent all the assets that the farm uses to produce the products.
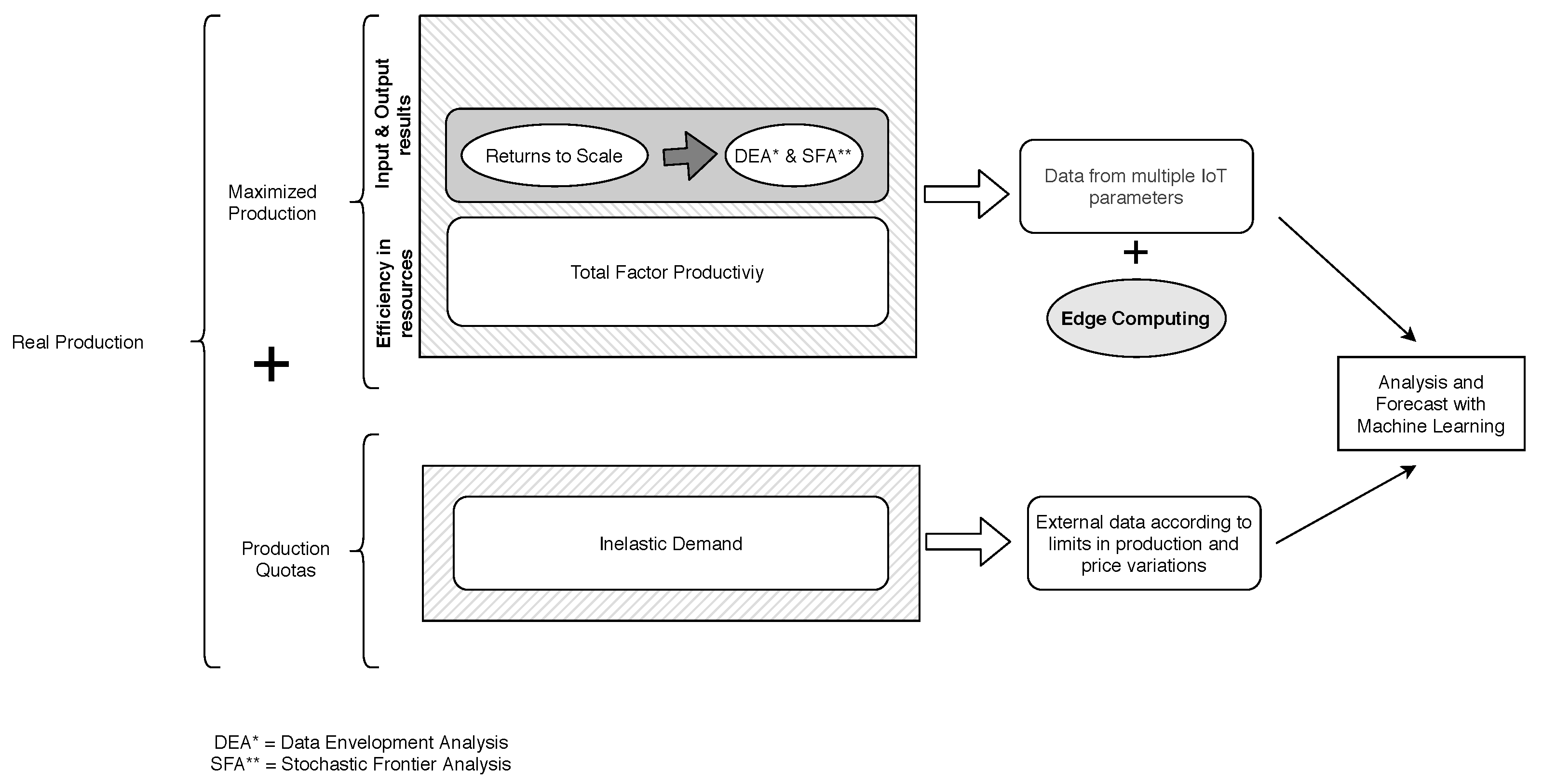
While production levels and effectiveness at production frontiers incorporate variables that are more aligned to the environment and the macroeconomic situation, when it comes to measuring profitability, any economic instability is a determining factor in the equation, as shown in studies such as Machek and Špička [43]. Another approach that could be used to forecast the Optimal Production levels are Long Short-Term Memories (LSTM), a type of artificial recurrent neural networks (RNN). This solution has been proposed in studies such as Cao et al. [44], with successful results. A summary of the different economic metrics and contributions considered regarding the production limitations is shown in Figure 2.
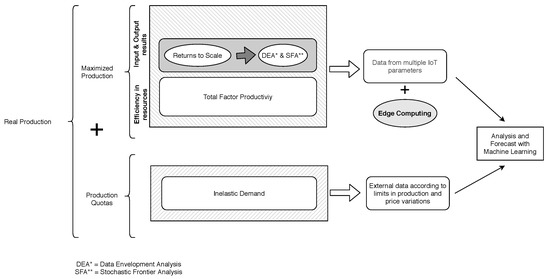
Figure 2.
Diagram with different economic metrics for performance and efficiency evaluation.
2.2. Environmental Performance
In the mid-nineties, authors such as Schmidheiny and Timberlake [45] started examining the terms and concepts of the eco-efficiency. The eco-efficiency is the ability to produce more goods and services with less environmental impact and less consumption of natural resources [46]. The eco-efficiency ratio is normally measured as the ratio of the added value of what has been produced (e.g., GDP) and the added environmental impacts of the product or service produced (typically using the emissions). In the context of eco-efficiency, the OECD [47] sets different metrics to evaluate the environmental progress at different levels. Those environmental indicators conformed types of policies and indicators which can be conceptualized as a ratio, expressed as an indicator of economic value divided by an indicator of environmental impact. To evaluate those measures, IoT sensors are a key instrument to monitor the different environmental conditions and evolution. In the last 20 years, and aligned with the concept of eco-efficiency, different authors such as Tiwari et al. [48] developed a system using multi-criteria decision-making techniques to achieve economic-environmental efficiency including sustainability and economic environmental criteria. Likewise, Simar and Wilson [15] demonstrated that environmental efficiency was negatively related to farm size, age of farmers and crop subsidies, and positively to crop rotation. They also introduced the variability of meteorological conditions (levels of temperature and precipitation) to capture the effect of production uncertainty on environmental efficiency, founding that it has a significant impact. Lansink and Wall [22] presented an overview regarding the evaluation of frontier models and their environmental efficiency. Currently, there are different ways to consider environment measurement, such as non-parametric DEA and SFA, which are models that have been widely used for measuring economic and environmental efficiency [49]. Particularly DEA has become increasingly popular in the analysis of productive efficiency, as demonstrated by Reinhard et al. [50], which is the basis for the model proposed by Simar and Wilson [15].
The following Section depicts some of the principal approaches where IoT and EC technologies have been applied in the field of Precision Agriculture and Smart Farming. One of these solutions is the Edge-IoT platform that has been used in the mixed dairy farm scenario of the case study analyzed in this work.
3. Industrial Internet of Things and Edge Computing Technologies in Smart Farming Scenarios
IoT provides multiple solutions to each of its application areas. Some of the most important functionalities are: multiple-communication-protocol management, data processing, real-time information and response, big data storage, security and data privacy [17]. However, the application of these features brings with it a series of challenges that must be addressed: data source heterogeneity, security, privacy, latency, real-time response, use of shared computing resources, etc. [51]. Although the application of IoT data ingestion layers makes it possible to tackle the problem of heterogeneity, other issues need to be solved. One of them is the large amount of data that hundreds, thousands or even millions of devices can transfer to an IoT platform. In this sense, to reduce the data traffic between the IoT layer and the cloud, solutions such as the Edge Computing paradigm arise. The Edge Computing paradigm allows the reduction of congestion due to the demand of computing, network or cloud storage resources [18]. With this strategy, the computing and service infrastructures are closer to the data sources, and also to the end-users, by migrating the filtering, processing or storage of data from the cloud to the Edge of the network [52].
Moreover, there is a wide variety of scenarios in which solutions based on IoT and Edge Computing are applied. Among the most relevant applications there are Industry 4.0 [26], smart energy [53] or, in the case of this work, Smart Farming [12], among many others. Besides, although there are scenarios in which Edge Computing is applied to a single environment as an ad-hoc system, there are also advancements aimed at providing edge functionalities as a platform (Edge as a Platform). In this way, the reproducibility of the solution increases. On the other hand, there are reference architectures whose guidelines can be followed to design and implement systems and platforms based on Edge Computing [26].
Precision Agriculture considers only the variability of crop data. However, Smart Farming provides a more comprehensive analysis, predictions and recommendations, as well as task automation, taking into account historical and real-time information about crops, machinery, livestock or humans [54]. There are specific use cases where IoT and Edge Computing are applied to intelligent agriculture, such as the work of Agrawal et al. [55], which measure the quantity and quality of the grain in the silos; Cambra et al. [56], which control the irrigation with bicarbonate for precision hydroponic agriculture; Chien and Chen [57], which use RFID sensors and egg detectors to process locally and in the cloud the behavior and welfare of hens; ElMasry et al. [58], which analyze multi-spectral images to control crop quality; Jia et al. [59], which apply neural networks, SVM (Support Vector Machines) and electronic smell techniques for the rapid detection and recognition of moldy apples; as well as the work of Potamitis et al. [60], which propose an insect surveillance system in open fields using vibroacoustic sensors.
Nevertheless, Edge-IoT-based solutions usually consist of integral platforms. In this sense, Khan et al. [61] presented a multi-layer architecture formed by a Perception Layer or Perception Layer (i.e., data ingestion), a Network Layer or Network Layer, a middleware layer (i.e., service management), an application layer and a business layer (i.e., system-wide management). One of its main shortcomings is that it does not take into account aspects such as security. Therefore, it may not be the best option for data management and applications for value chain traceability. Jones et al. [62] proposed a framework aimed at building intelligent agricultural systems. However, in their work they do not present an implementation in a specific case study. On the other hand, Ryu et al. [63] proposed a complete solution for the implementation of a connected farm, using an IoT Service Server to create virtual IoT devices and a middleware management module installed on the physical devices. Kamilaris et al. [64] proposed a multilevel framework composed of a low level (i.e., IoT and communication devices), an intermediate level (i.e., data management and analysis) and a higher level (i.e., the application), which were tested in two scenarios (livestock and crops). Other authors such as Popović et al. [65] also proposed multilayer platforms, while Suma et al. [66] introduced a basic IoT-Edge architecture to facilitate access to intelligent agriculture in developing countries. Finally, Park et al. [67] proposed a scalable framework for data analysis in which the edge nodes pre-process and analyze the private data collected before sending the results to a remote server, to estimate and predict the total crop yield.
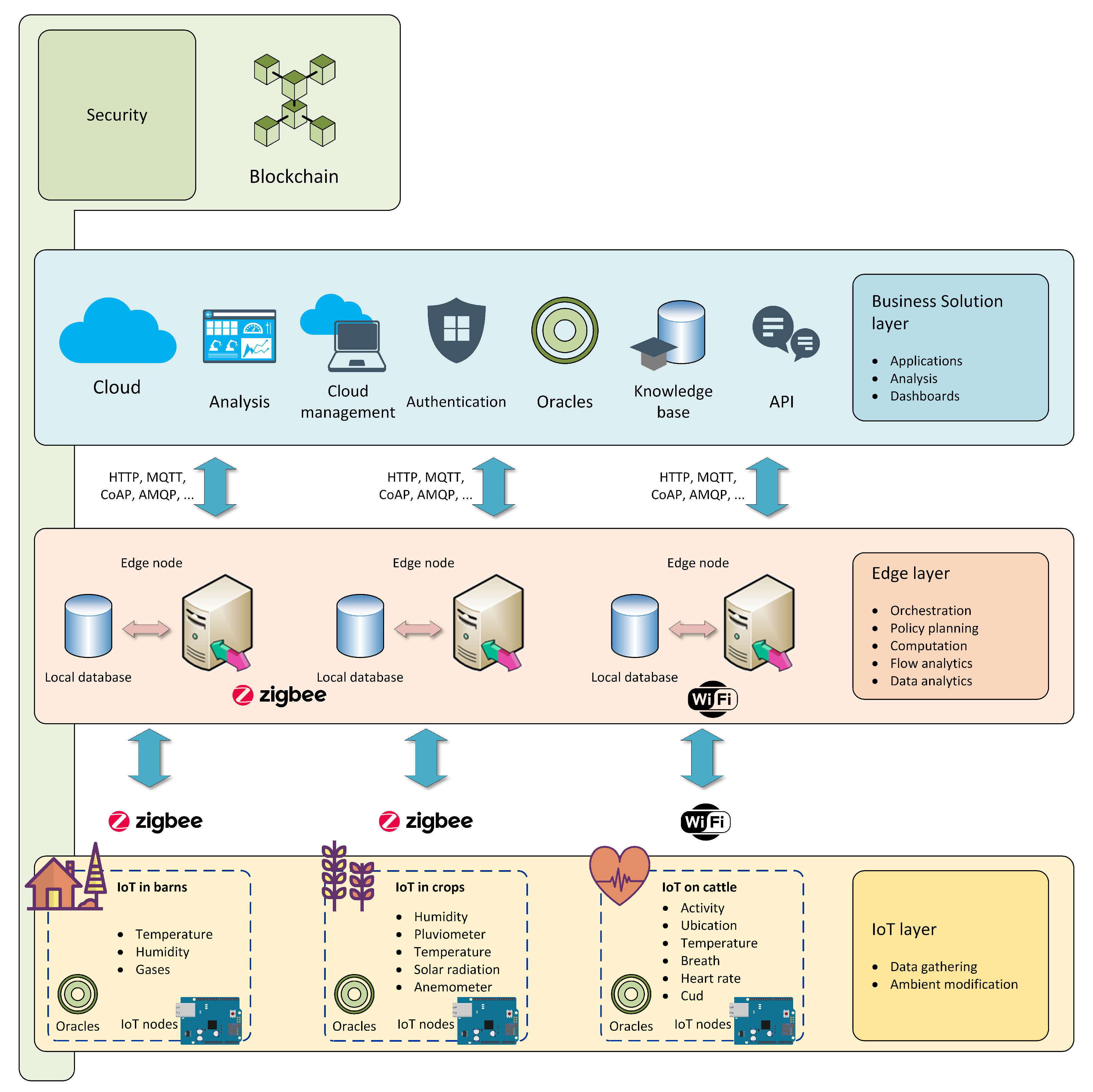
Likewise, there are different Reference Architectures within the scope of Edge Computing applied in industrial environments or Industry 4.0. One of them is the Global Edge Computing Architecture (GECA) presented by Sittón-Candanedo et al. [26], an Edge-IoT platform on which this work is based. GECA introduces Edge Computing functionalities that reduce the use of computational, storage and network resources in the Cloud. Moreover, it includes blockchain technologies that provide security and warrant the integrity and traceability of data. This architecture, in turn, was the result of analyzing four of the most important reference architectures in the field of Edge-IoT in Industry 4.0: FAR-Edge [68], INTEL-SAP [69], Edge Computing Consortium architecture [70], and the Industrial Internet Reference Architecture (IIRA) [71]. GECA is structured in three layers: the IoT layer (IoT Layer), the Edge Layer and the Business Solution Layer.
The mentioned architecture was utilized to implement the SmartDairyTracer platform (see Figure 3) trained at the traceability of agro-industry processes. The first stage of the SmartDairyTracer platform was deployed and tested in a real scenario by Alonso et al. [12], which validated the benefits of the Edge Computing, reducing the data traffic by 46.72%, which can be translated into a potential reduction of costs. The experimentation presented in Alonso et al. [12] shown that it was possible to decrease the costs associated with data transfer between the IoT layer and the remote cloud by introducing design rules from a reference architecture, such as GECA, into an agro-industrial platform designed for the monitoring, traceability and optimization of resources and processes performed in the value chain in a mixed dairy scenario. In addition, the introduction of the Edge nodes improved the reliability of communications with the cloud by reducing the number of values missing from the database. In the next Section, the profitability and environmental performance of the SmartDairyTracer are analyzed for the same mixed dairy farm scenario.
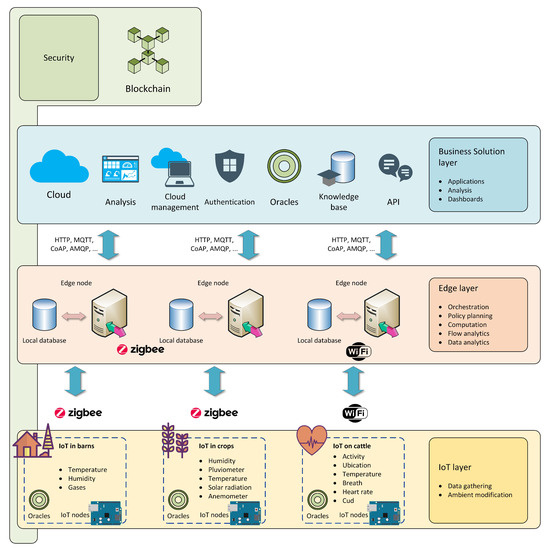
Figure 3.
SmartDairyTracer platform based on GECA and implemented in the analyzed mixed-farm scenario.
4. Profitability and Environmental Performance of an Edge-IoT Platform in a Smart Farming Scenario
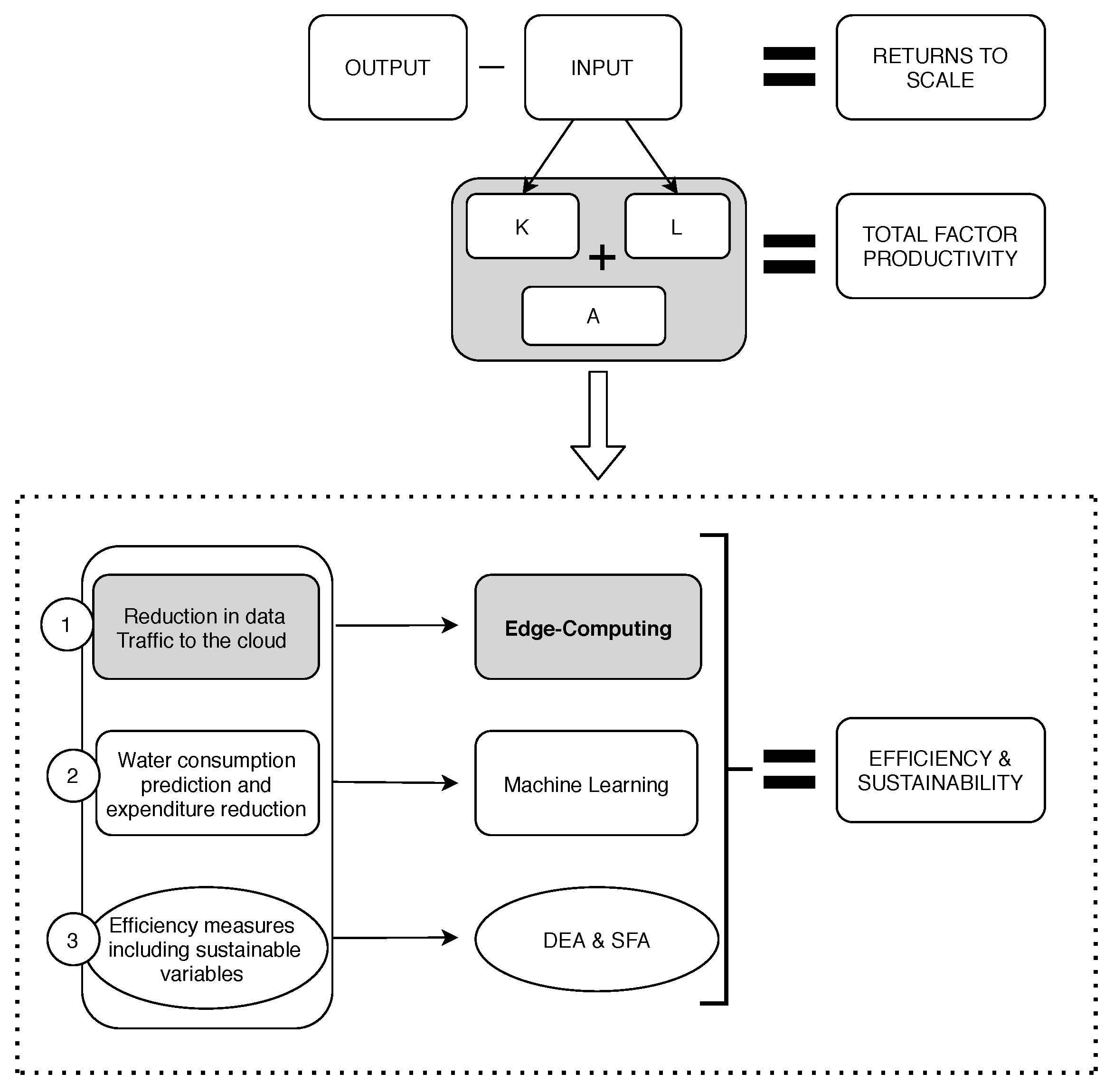
This research aims to implement and deploy a real scenario for making farms more profitable and sustainable through the application of IoT and Edge Computing. The proposed solution takes into account some of the most important variables from the Environmental Performance Index [72] and how to reduce its consumption with and Edge-IoT platform. The methods proposed to achieve and evaluate this goal are presented in Figure 4. Some of those methods will be applied in Section 5. Three direct effects are considered in the research with the proposed methodology. Different sensors have been placed in the farm, and other variables have been used as inputs to track the information (Table 1).
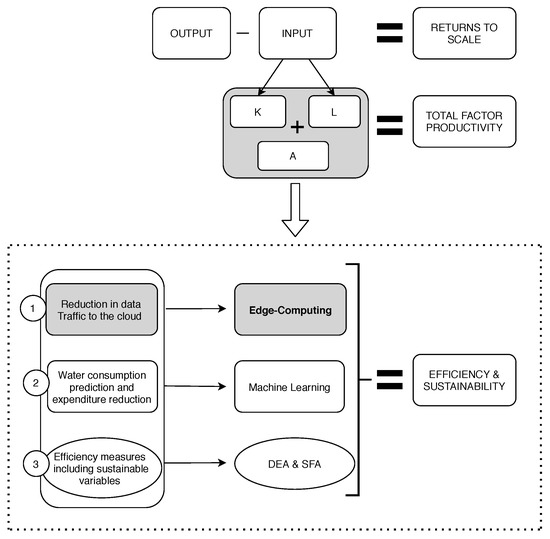
Figure 4.
Diagram of the methodology proposed.

Table 1.
Attributes on which the analysis of monitoring and efficiency will be performed.
4.1. Sensor Monitoring
The system proposed incorporate different sensors to track multiple variables in a given period. The variables considered for measuring the Environmental Performance Index (EPI) and, more precisely, the ones regarding the ecosystem vitality are those described in Table 2, were it had been marked the ones that this study affects:

Table 2.
Variables from the Environmental Performance Index—Ecosystem Vitality.
Therefore, to track the three variables mentioned in Table 2, Table 3 presents the variables that have been analyzed.

Table 3.
Tracked variables in the mixed dairy farm scenario.
Being able to trace this information, and considering that it is a mixed-farm, two main benefits are expected. On the one hand, the traceability allows saving water costs coming from both the irrigation’s and cattle’s water consumption. On the other hand, for the mixed-farms, the sensor monitoring enables to react when temperatures are inadequate and may affect the health or welfare of cows, involving a decrease in their milk production.
4.2. Reduction in Data Volume Transmitted from the IoT and Edge Layers to the Cloud
GECA’s Edge nodes filter and pre-process data from the devices in the IoT layer [26]. In addition, they are responsible for discarding values which have been repeated due to frame relaying from physical sub-layers (i.e., ZigBee, Wi-Fi) to the IoT layer. They can also perform averaging and analysis of regression data that takes place on the same Edge layer. In both cases, the amount of data and the cost of its transmission to the cloud is reduced, decreasing the costs of data traffic, as well as the need for computing and storage in the Cloud.
The experiments and results presented by Alonso et al. [12] demonstrate that applying the GECA reference architecture when building the platform for agribusiness, and providing the Edge layer to it, allows reducing the total amount of data transferred to the cloud in a mixed dairy farm scenario with the same usage and sensor conditions by 46.72% (38.86% in the uplink and 64.10% in the downlink). This reduction can be even more significant in other scenarios where, due to their characteristics, take advantage of the use of the filtering and/or pre-processing stages in the GECA architecture.
4.3. Efficiency Measures including Sustainability
SFA and DEA have been compared as measurement tools for agricultural economics for many years [49]. For example, Theodoridis and Anwar [24] conducted an experiment in Bangladesh crop farms where the SFA results are supported by the DEA results. In this study, the DEA has been selected because is a non-parametric method for estimating production frontiers and evaluating the efficiency of a sample of production units, and also because in this case, the outputs are fixed. The DEA is a frontier method that tries to optimize the efficiency measure of each unit analyzed, Charnes et al. [73] defined, in their basic DEA model, the objective function Decision Making Units (DMU). While in our case the outputs O are crops production, multiplied by their respective weights and divided by the inputs I, that is, water consumption, the seeds and the data storage costs and multiplied by their respective weights. The efficiency score is under the constrains , no efficiency score exceeds 1 as in Equation (7) and where the output values have to be positive:
To make predictions on the efficiency regarding resources availability, the tracking of the IoT has been analysed, comparing both the initial costs and the costs after the IoT implementation. The variation per year is expressed in number of sales, and not in monetary terms due to the previously mentioned quotas and prices issues.
5. Experimentation and Initial Results
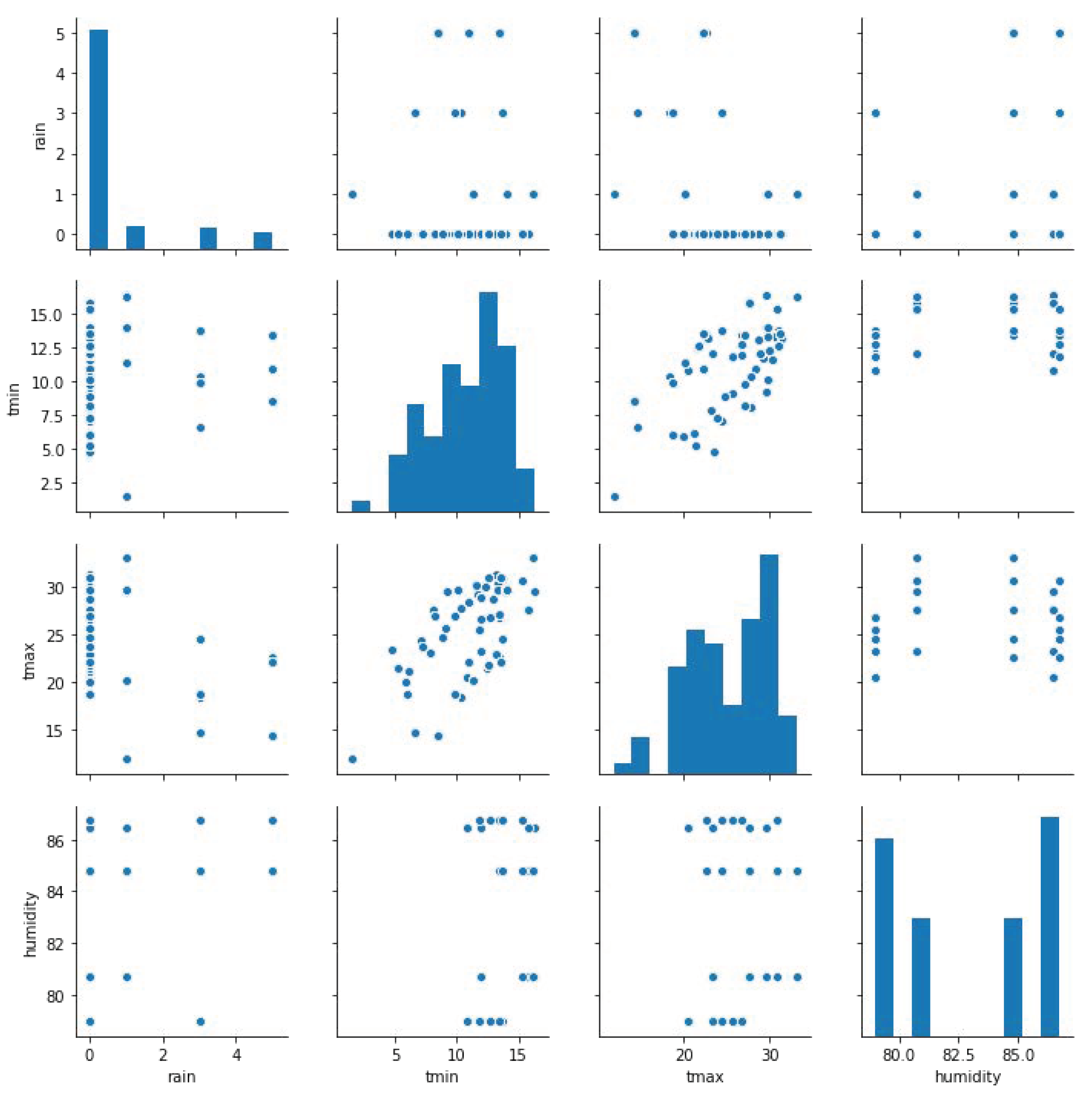
The purpose of this research is to enable the monitoring of the meteorological conditions through wireless agro-meteo weather stations to avoid uncertain situations and to measure the farm’s efficiency. The experiments conducted are divided into two parts. The first one is related to the monitoring of the meteorological conditions, performed through the IoT and Edge Computing platform. The second one concerns the measurement of the efficiency through the DEA. To accomplish the first part, three different quantities (rain, temperature and air humidity) have been considered among those gathered by the set of wireless agro-meteo weather stations installed in the farm [12]. The data collected from these stations is transferred to the cloud, taking into account daily average measures. Figure 5 presents an overview of the values tracked in the conducted experiment.
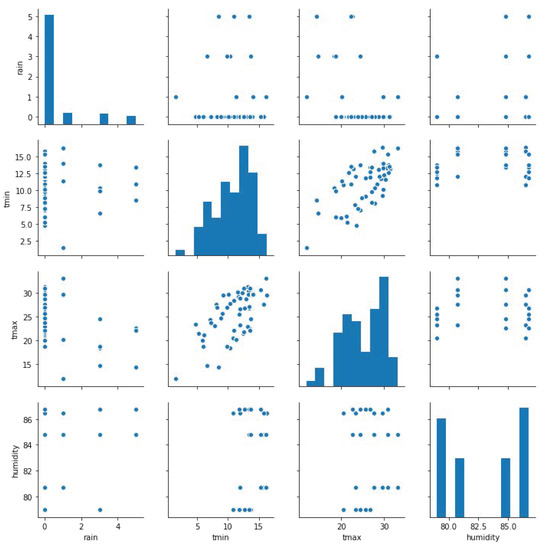
Figure 5.
Scatter plots and bar charts displaying the information captured by the sensors for data exploration.
The data transferred to the Cloud has been measured both in the previous version of the system (i.e., not using the Edge Computing platform) and the new version of the monitoring system (i.e., based on the GECA Edge-IoT platform) to compare the effect in the efficiency; considering the variations of costs as inputs for the production. Alonso et al. [12] demonstrated a reduction in data transfer costs when applying Edge Computing to filter and pre-process data using the new GECA-based platform. Other authors such as Chen et al. [74] and Guillén et al. [75], also demonstrated a reduction in data transfer to the cloud in Precision Agriculture.
To analyse the efficiency we consider the variable inputs (those that have a variation within the production process) and the technology applied in a mixed-farm:
- Seeds (kg).
- Irrigation (m).
- Data transfer between the IoT and Cloud layers (KiB) (The Data transfer between the IoT and Cloud layers has been presented in KiB, according to the International System Units [76]).
The efficiency is calculated by analysing the DEA. To carry out the DEA analysis, Table 4 presents the input and output data considered for the experiment. The descriptive statistics on production inputs and outputs are displayed per month () in Table 5. Once the descriptive statistics are examined, the analysis of the DEA is presented in Table 6. To conduct the experiment, an estimation has been made for those months in which the Edge was not available so that the two scenarios proposed can be compared. Therefore, from November until May, an estimation without Edge has been included; and from June until September, an estimation with Edge has been added. As presented in Table 6, the most efficient DMU are April and August. Being more precise, when considering the technological inputs, such as the data transferred to the Cloud, only August is the most efficient DMU. The calculation of the DMUs serves, above all, to identify if the DMUs are efficient or not, even though a variation in the decimal values is important, the great difference of the model, and where is possible to see if it is being efficient or not, which is when it is closer to 1.

Table 4.
Input and output values for the DEA analysis. February and March have been excluded due to the lack of irrigation, seeds and crops. The Data Transfer values (KiB) vary between months. The value 98 corresponded to the dates when there was an Edge layer; while the other values corresponded to the dates when there was not an Edge layer.

Table 5.
Descriptive Statistics for .

Table 6.
Technical Efficiency, Variable Returns to Scale. The results with * correspond to the efficient ones.
6. Conclusions
Almost 20 years ago, in 2002, Nuthall [77] conducted an experiment to understand how technology was affecting the farms’ profitability and performance; and, in that case, having access to a computer already meant an increase in their benefit. Several years later, Piedra-Munoz et al. [78] took different experiments and reviewed years of improvements in the application of technology and its compatibility with sustainability. This study provides the results of tracking different variables from the Environmental Performance Index with real-time sensors and the application of an Edge-Computing platform that reduces the data traffic to the Cloud. This reduction affects farms’ efficiency. Considering that technology is already a reality in the agricultural sector and that in the following years the data transferred to the Cloud is an input that will be used because it affects the output’s efficiency. This study shows that the application of vanguard techniques, such as IoT and Edge-Computing, in the long-term it can represent a competitive advantage when measuring the efficiency of the Decision Making Units. This study incorporates the data traffic to the Cloud as an input, reflecting the importance of technology when analysing the DEA production. The results are presented after analysing the DEA, showing the most efficient values in terms of efficiency of the DMU when there are variations in the data traffic to the Cloud, being a representative asset. The agri-tech paradigm is leading to large scale scenarios (i.e., farms with millions of ha with a vast number of sensors) which translates into an increase of data traffic to the Cloud. In future research lines, the authors will carry out further experiments where the efficiency of the livestocks in mixed-farms will be measured. This will be conducted in scenarios where the inputs will include all the information collected by the IoT sensors for real-time monitoring (i.e., in terms of sustainable milk production). Moreover, the authors would like to continue contributing on how to make farms more efficient and also to include Machine Learning to forecast the future levels of resources consumption. The authors will investigate the application of technologies that allow the monitoring of crops or livestock without requiring excellent connections to the network, as well as the efficiency analysis in the most inclusive way at a technological and resource level.
Author Contributions
M.E.P.-P. and M.P.-H. performed the economic and sustainability analysis. R.S.A. designed and developed the platform. M.E.P.-P., M.P.-H. and R.S.A. reviewed the state of the art and conducted the case study. J.P.-D. and J.P. formalized the problem, designed the methodology and reviewed the work. All the authors contributed to the redaction of the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research has been supported by the Interreg Spain-Portugal V-A Program (PocTep) under grant 0677 DISRUPTIVE-2-E (Intensifying the activity of Digital Innovation Hubs within the PocTep region to boost the development of disruptive and last generation ICTs through cross-border cooperation.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Authors would like to give a special thanks to Rancho Guareña Hermanos Olea Losa, S.L. (Castrillo de la Guareña, Zamora, Spain) for their collaboration during the implementation and testing of the platform.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Igna, I.A.; Rincon-Aznar, A.; Venturini, F. Upstream regulation, factor demand and productivity: Cross-industry differences in OECD countries, 1975–2007. Inf. Econ. Policy 2019, 49, 100830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, B. European Agriculture: Policies, Production, and Trade; Psychology Press: Hove, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. The End of Milk Quotas; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer, S.; Sauer, J. Profitability Development and Resource Reallocation: The Case of Sugar Beet Farming in Germany. J. Agric. Econ. 2020, 71, 816–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cathagne, A.; Guyomard, H.; Levert, F. Milk quotas in the European Union: Distribution of marginal costs and quota rents. Eur. Dairy Ind. Model Work. Pap. 2006, 1, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Philippidis, G.; Waschik, R. Melitz Meets Milk: The Impact of Quota Abolition on EU Dairy Export Competitiveness. J. Agric. Econ. 2019, 70, 44–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Arendonk, J.A.; Liinamo, A.E. Dairy cattle production in Europe. Theriogenology 2003, 59, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milk and Milk Product Statistics—Statistics Explained. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Milk_and_milk_product_statistics#Milk_products (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Reardon, T.; Barrett, C.B.; Berdegué, J.A.; Swinnen, J.F. Agrifood industry transformation and small farmers in developing countries. World Dev. 2009, 37, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beus, C.E.; Dunlap, R.E. Conventional versus alternative agriculture: The paradigmatic roots of the debate. Rural Sociol. 1990, 55, 590–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweeten, L. Government commodity program impacts on farm numbers. In Size, Structure and the Changing Face of 368 American Agriculture; Westview Press: Boulder, CO, USA, 1993; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, R.S.; Sittón-Candanedo, I.; García, Ó.; Prieto, J.; Rodríguez-González, S. An intelligent Edge-IoT platform for monitoring livestock and crops in a dairy farming scenario. Ad Hoc Netw. 2020, 98, 102047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agri-Environmental Indicator—Irrigation—Statistics Explained. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Agri-environmental_indicator_-_irrigation (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Agriculture Statistics at Regional Level—Statistics Explained. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Agriculture_statistics_at_regional_level&oldid=431854 (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Simar, L.; Wilson, P.W. Estimation and inference in two-stage, semi-parametric models of production processes. J. Econom. 2007, 136, 31–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, K.; Waweru, P.; Wambua, M.; Ondula, E.; Samuel, L. Toward quantified small-scale farms in africa. IEEE Internet Comput. 2016, 20, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisinni, E.; Saifullah, A.; Han, S.; Jennehag, U.; Gidlund, M. Industrial Internet of Things: Challenges, Opportunities, and Directions. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 4724–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liang, F.; He, X.; Hatcher, W.G.; Lu, C.; Lin, J.; Yang, X. A Survey on the Edge Computing for the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 6900–6919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, R.S.; Sittón-Candanedo, I.; Casado-Vara, R.; Prieto, J.; Corchado, J.M. Deep Reinforcement Learning for the Management of Software-Defined Networks and Network Function Virtualization in an Edge-IoT Architecture. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Toosi, A.N.; Buyya, R.; Ramamohanarao, K. Hedonic Pricing of Cloud Computing Services. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Peng, M.; Zhang, K. Edge computing technologies for Internet of Things: A primer. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2018, 4, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansink, A.O.; Wall, A. Frontier models for evaluating environmental efficiency: An overview. Econ. Bus. Lett. 2014, 3, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.; Lewin, A.Y.; Seiford, L.M. Data envelopment analysis theory, methodology and applications. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1997, 48, 332–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridis, A.M.; Anwar, M.M. A comparison of DEA and SFA methods: A case study of farm households in Bangladesh. J. Dev. Areas 2011, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyckhoff, H.; Allen, K. Measuring ecological efficiency with data envelopment analysis (DEA). Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 132, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittón-Candanedo, I.; Alonso, R.S.; Corchado, J.M.; Rodríguez-González, S.; Casado-Vara, R. A review of edge computing reference architectures and a new global edge proposal. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 99, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, P.; Petersen, N.C. A procedure for ranking efficient units in data envelopment analysis. Manag. Sci. 1993, 39, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balafoutis, A.T.; Beck, B.; Fountas, S.; Tsiropoulos, Z.; Vangeyte, J.; van der Wal, T.; Soto-Embodas, I.; Gómez-Barbero, M.; Pedersen, S.M. Smart farming technologies–description, taxonomy and economic impact. In Precision Agriculture: Technology and Economic Perspectives; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 21–77. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, M.C. Environmental management and its impact on the operations function. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 1995, 15, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, P.; McIvor, R.; Chan, F. Using case-based reasoning to evaluate supplier environmental management performance. Expert Syst. Appl. 2003, 25, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handfield, R.B.; Walton, S.V.; Seegers, L.K.; Melnyk, S.A. ‘Green’value chain practices in the furniture industry. J. Oper. Manag. 1997, 15, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. European Commission Horizon 2050; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen, S.M.; Lind, K.M. (Eds.) Precision Agriculture: Technology and Economic Perspectives; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McBratney, A.; Whelan, B.; Ancev, T.; Bouma, J. Future directions of precision agriculture. Precis. Agric. 2005, 6, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Langemeier, M.R.; Small, I.M.; Joseph, L.; Fry, W.E. Risk management strategies using precision agriculture technology to manage potato late blight. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shephard, R.W. Theory of Cost and Production Functions; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Takeshima, H. Custom-hired tractor services and returns to scale in smallholder agriculture: A production function approach. Agric. Econ. 2017, 48, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solow, R.M. Technical change and the aggregate production function. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1957, 39, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, T.W. Economic growth and capital accumulation. Econ. Rec. 1956, 32, 334–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Beveren, I. Total factor productivity estimation: A practical review. J. Econ. Surv. 2012, 26, 98–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellner, A.; Kmenta, J.; Dreze, J. Specification and estimation of Cobb-Douglas production function models. Econom. J. Econom. Soc. 1966, 34, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission Policy Instruments for the Dairy Sector. 2016. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/RegData/etudes/BRIE/2018/630345/EPRS_BRI(2018)630345_EN.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Machek, O.; Špička, J. Productivity and profitability of the Czech agricultural sector after the economic crisis. WSEAS Trans. Bus. Econ. 2014, 11, 700–706. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Q.; Banerjee, R.; Gupta, S.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; Jeyachandra, B. Data driven production forecasting using machine learning. In SPE Argentina Exploration and Production of Unconventional Resources Symposium; Society of Petroleum Engineers: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidheiny, S.; Timberlake, L. Changing Course: A Global Business Perspective on Development and the Environment; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ichimura, M.; Nam, S.; Bonjour, S.; Rankine, H.; Carisma, B.; Qiu, Y.; Khrueachotikul, R. Eco-Efficiency Indicators: Measuring Resource-Use Efficiency and the Impact of Economic Activities on the Environment; ESCAP: Bangkok, Thailand, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. Eco-Efficiency; OECD: Paris, France, 2008; Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/eco-efficiency_9789264040304-en (accessed on 11 November 2020). [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, D.; Loof, R.; Paudyal, G. Environmental–economic decision-making in lowland irrigated agriculture using multi-criteria analysis techniques. Agric. Syst. 1999, 60, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalmarsson, L.; Kumbhakar, S.C.; Heshmati, A. DEA, DFA and SFA: A comparison. J. Product. Anal. 1996, 7, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, S.; Lovell, C.K.; Thijssen, G.J. Environmental efficiency with multiple environmentally detrimental variables; estimated with SFA and DEA. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2000, 121, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, R.S.; Sittón-Candanedo, I.; Rodríguez-González, S.; García, Ó.; Prieto, J. A Survey on Software-Defined Networks and Edge Computing over IoT. In Highlights of Practical Applications of Survivable Agents and Multi-Agent Systems. The PAAMS Collection; Communications in Computer and Information Science; de la Prieta, F., González-Briones, A., Pawleski, P., Calvaresi, D., Del Val, E., Lopes, F., Julian, V., Osaba, E., Sánchez-Iborra, R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 289–301. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Iborra, R.; Sánchez-Gómez, J.; Skarmeta, A. Evolving IoT networks by the confluence of MEC and LP-WAN paradigms. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 88, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittón-Candanedo, I.; Alonso, R.S.; García, Ó.; Gil, A.B.; Rodríguez-González, S. A Review on Edge Computing in Smart Energy by means of a Systematic Mapping Study. Electronics 2020, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfert, S.; Ge, L.; Verdouw, C.; Bogaardt, M.J. Big data in smart farming—A review. Agric. Syst. 2017, 153, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, H.; Prieto, J.; Ramos, C.; Corchado, J.M. Smart feeding in farming through IoT in silos. In Intelligent Systems Technologies and Applications 2016; Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Corchado, J.M., Mitra, S., Thampi, S.M., El-Alfy, E.S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 355–366. [Google Scholar]
- Cambra, C.; Sendra, S.; Lloret, J.; Lacuesta, R. Smart system for bicarbonate control in irrigation for hydroponic precision farming. Sensors 2018, 18, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.R.; Chen, Y.X. An rfid-based smart nest box: An experimental study of laying performance and behavior of individual hens. Sensors 2018, 18, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElMasry, G.; Mandour, N.; Al-Rejaie, S.; Belin, E.; Rousseau, D. Recent Applications of Multispectral Imaging in Seed Phenotyping and Quality Monitoring—An Overview. Sensors 2019, 19, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Liang, G.; Tian, H.; Sun, J.; Wan, C. Electronic nose-based technique for rapid detection and recognition of moldy apples. Sensors 2019, 19, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potamitis, I.; Rigakis, I.; Tatlas, N.A.; Potirakis, S. In-Vivo Vibroacoustic Surveillance of Trees in the Context of the IoT. Sensors 2019, 19, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.; Khan, S.U.; Zaheer, R.; Khan, S. Future internet: The internet of things architecture, possible applications and key challenges. In Proceedings of the 2012 10th International Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology, Islamabad, India, 17–19 December 2012; pp. 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.W.; Antle, J.M.; Basso, B.; Boote, K.J.; Conant, R.T.; Foster, I.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Herrero, M.; Howitt, R.E.; Janssen, S.; et al. Toward a new generation of agricultural system data, models, and knowledge products: State of agricultural systems science. Agric. Syst. 2017, 155, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, M.; Yun, J.; Miao, T.; Ahn, I.Y.; Choi, S.C.; Kim, J. Design and implementation of a connected farm for smart farming system. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE SENSORS, Busan, Korea, 1–4 November 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Kamilaris, A.; Gao, F.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X.; Ali, M.I. Agri-IoT: A semantic framework for Internet of Things-enabled smart farming applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 3rd World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Reston, VA, USA, 12–14 December 2016; pp. 442–447. [Google Scholar]
- Popović, T.; Latinović, N.; Pešić, A.; Zečević, Ž.; Krstajić, B.; Djukanović, S. Architecting an IoT-enabled platform for precision agriculture and ecological monitoring: A case study. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 140, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suma, N.; Samson, S.R.; Saranya, S.; Shanmugapriya, G.; Subhashri, R. IoT based smart agriculture monitoring system. Int. J. Recent Innov. Trends Comput. Commun. 2017, 5, 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Choi, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Min, O. A Layered Features Analysis in Smart Farm Environments. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Big Data and Internet of Thing; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Factory Automation Edge Computing Operating System Reference Implementation (FAR-EDGE). FAR-EDGE Project H2020. 2017. Available online: https://www.edge4industry.eu/2018/02/15/h2020-far-edge-project-factory-automation-meets-edge-computing-blockchain-technology/ (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- INTEL-SAP. IoT Joint Reference Architecture from Intel and SAP. Technical Report; INTEL-SAP: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Edge Computing Consortium; Alliance of Industrial Internet. Edge Computing Reference Architecture 2.0; Technical Report; Edge Computing Consortium: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, M.; Canaran, T.E.; Canaran, L. Introduction to Edge Computing in IIoT; Technical Report; Industrial Internet Consortium: Needham, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- The EPI Team. Environmental Performance Index; Yale University and Columbia University: New Haven, CT, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Charnes, A.; Cooper, W.W.; Rhodes, E. Measuring the efficiency of decision making units. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1978, 2, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, Q.; Yang, L.; Xu, J. ThriftyEdge: Resource-efficient edge computing for intelligent IoT applications. IEEE Netw. 2018, 32, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, M.A.; Llanes, A.; Imbernón, B.; Martínez-España, R.; Bueno-Crespo, A.; Cano, J.C.; Cecilia, J.M. Performance evaluation of edge-computing platforms for the prediction of low temperatures in agriculture using deep learning. J. Supercomput. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, D.B.; Tiesinga, E. The international system of units (SI). NIST Spec. Publ. 2019, 330, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Nuthall, P.L. Case studies of the interactions between farm profitability and the use of a farm computer. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2004, 42, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedra-Muñoz, L.; Galdeano-Gómez, E.; Pérez-Mesa, J.C. Is sustainability compatible with profitability? An empirical analysis on family farming activity. Sustainability 2016, 8, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).