Food Security during the Pandemic and the Importance of the Bioeconomy in the New Era
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. A Brief Overview of SARS-CoV-2 Health Implications
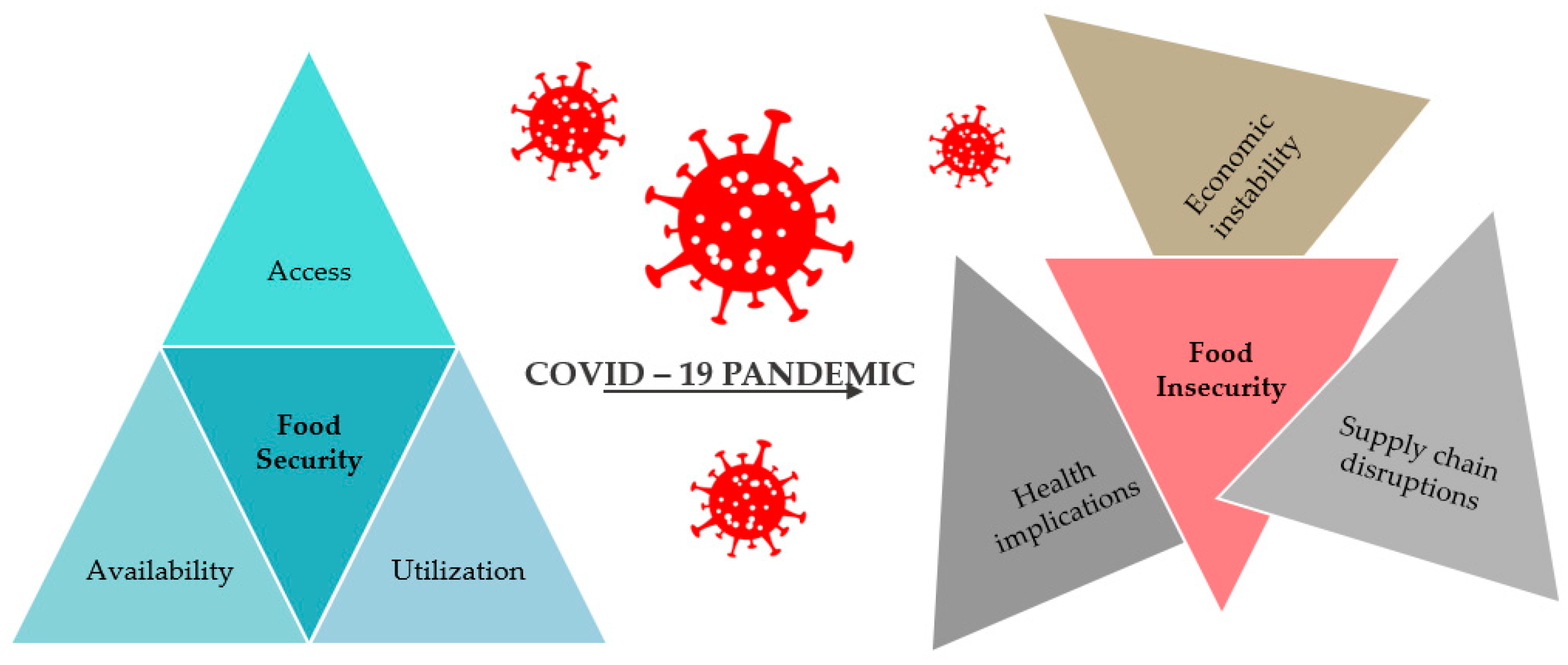
3. Food Security and Insecurity
4. The Importance of Nutritional Behavior during a Pandemic
5. Bioeconomy Concept Importance in Pandemic
6. Food Banks Concept
7. Conclusions and Future Trends
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Letko, M.; Seifert, S.N.; Olival, K.J.; Plowright, R.K.; Munster, V.J. Bat-borne virus diversity, spillover and emergence. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghani, M.; Bliemer, M.C.; Goerlandt, F.; Li, J. The scientific literature on Coronaviruses, COVID-19 and its associated safety-related research dimensions: A scientometric analysis and scoping review. Saf. Sci. 2020, 129, 104806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizou, M.; Galanakis, I.M.; Aldawoud, T.M.; Galanakis, C.M. Safety of foods, food supply chain and environment within the COVID-19 pandemic. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jribi, S.; Ismail, H.B.; Doggui, D.; Debbabi, H. COVID-19 virus outbreak lockdown: What impacts on household food wastage? Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 3939–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, R. Innovations in agriculture and food supply in response to the COVID-19 pandemic. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1095–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, J.E. Food supply chains during the COVID-19 pandemic. Can. J. Agric. Econ. 2020, 68, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torero, M. Without food, there can be no exit from the pandemic. Nature 2020, 580, 588–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.H.; Strych, U.; Hotez, P.J.; Bottazzi, M.E. The SARS-CoV-2 vaccine pipeline: An overview. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2020, 7, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, D. An overview of coronaviruses including the SARS-2 coronavirus—Molecular biology, epidemiology and clinical implications. Curr. Med. Res. Pract. 2020, 10, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.W.; Kok, K.H.; Zhu, Z.; Chu, H.; To, K.K.W.; Yuan, S.; Yuen, K.Y. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronaviridae Study Group of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. The species severe acute respiratory syndrome related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 8 December 2020).
- Acter, T.; Uddin, N.; Das, J.; Akhter, A.; Choudhury, T.R.; Kim, S. Evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: A global health emergency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Alharbi, O.M. COVID-19: Disease, management, treatment, and social impact. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Taylor, E.W.; Bennett, K.; Saad, R.; Rayman, M.P. Association between regional selenium status and reported outcome of COVID-19 cases in China. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shereen, M.A.; Khan, S.; Kazmi, A.; Bashir, N.; Siddique, R. COVID-19 infection: Origin, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 24, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, D.; Qi, X.; Nielsen-Saines, K.; Musso, D.; Pomar, L.; Favre, G. Real estimates of mortality following COVID-19 infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Aziz, T.M.; Stockand, J.D. Recent progress and challenges in drug development against COVID-19 coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)—An update on the status. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 83, 104327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, C.; Alsafi, Z.; O’Neill, N.; Khan, M.; Kerwan, A.; Al-Jabir, A.; Iosifidis, C.; Agha, R. World Health Organization declares global emergency: A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Int. J. Surg. 2020, 76, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation (WHO). Draft Landscape of COVID-19 Candidate Vaccines. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-candidate-vaccines (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanakis, C.M. The food systems in the era of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic crisis. Foods 2020, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segneanu, A.; Grozescu, I.; Cepan, C.; Cziple, F.; Lazar, V. Food security into a circular economy. J. Food Sci. Nut. 2018, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations World Food Programme. COVID-19 Will Double Number of People Facing Food Crises Unless Swift Action Is Taken. Available online: https://www.wfp.org/news/covid-19-will-double-number-people-facing-food-crises-unless-swift-action-taken (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO Rome). Trade Reforms and Food Security: Conceptualizing the Linkages. 2003. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-y4671e.pdf (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- Udmale, P.; Pal, I.; Szabo, S.; Pramanik, M.; Large, A. Global food security in the context of COVID-19: A scenario-based exploratory analysis. Prog. Disaster Sci. 2020, 7, 100120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naja, F.; Hamadeh, R. Nutrition amid the COVID-19 pandemic: A multi-level framework for action. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crew, S. Food Safety Risk during the Pandemic. JFST 2020, 34, 14–17. Available online: https://ifst.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/fsat.3402_4.x (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Turner, C.; Aggarwal, A.; Walls, H.; Herforth, A.; Drewnowski, A.; Coates, J.; Kalamatianou, S.; Kadiyala, S. Concepts and critical perspectives for food environment research: A global framework with implications for action in low-and middle-income countries. Glob. Food Sec. 2018, 18, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, I.G.; Suharoschi, R.; Vodnar, D.C.; Pop, C.R.; Socaci, S.A.; Vulturar, R.; Istrati, M.; Moroșan, I.; Farcas, A.C.; Kerezsi, A.D.; et al. Iron supplementation influence on the gut microbiota and probiotic intake effect in iron deficiency—A literature-based review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle-Bayer, L.; Aldaco, R.; Bala, A.; Puig, R.; Laso, J.; Margallo, M.; Vázquez-Rowe, I.; Maria Antó, J.; Fullana-i-Palmera, P. Environmental and nutritional impacts of dietary changes in Spain during the COVID-19 lockdown. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 748, 141410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracale, R.; Vaccaro, C.M. Changes in food choice following restrictive measures due to Covid-19. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1423–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, A.V.; Sciomer, S.; Cocchi, C.; Maffei, S.; Gallina, S. Quarantine during COVID-19 outbreak: Changes in diet and physical activity increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handu, D.; Moloney, L.; Rozga, M.; Cheng, F.W. Malnutrition care during the COVID-19 pandemic: Considerations for registered dietitian nutritionists. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.H.; Je, Y.S.; Baek, J.; Chung, M.-H.; Kwon, H.Y.; Lee, J.-S. Nutritional status of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 100, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Haleem, A.; Javaid, M. Analysing COVID-19 pandemic through cases, deaths, and recoveries. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 10, 450–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiles, J.L.; Rivas-García, L.; Varela-López, A.; Llopis, J.; Battino, M.; Sánchez-González, C. Do nutrients and other bioactive molecules from foods have anything to say in the treatment against COVID-19? Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh-Hesary, F.; Akbari, H. The powerful immune system against powerful COVID-19: A hypothesis. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 140, 109762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop, O.L.; Salanță, L.C.; Pop, C.R.; Coldea, T.; Socaci, S.A.; Suharoschi, R.; Vodnar, D.C. Prebiotics and Dairy Applications. In Dietary Fiber: Properties, Recovery, and Applications; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 247–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, A.S. Bioavailability of minerals in legumes. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaconeasa, Z.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Coman, C.; Leopold, L.; Mesaros, A.; Pop, O.; Rugină, D.; Ştefan, R.; Tăbăran, F.; Tripon, S.; et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticles and its cytotoxicity human lung cancer cells. Rom. Bio. Lett. 2015, 20, 10679–10687. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, N. Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida Brasiel, P.G. The key role of zinc in elderly immunity: A possible approach in the COVID-19 crisis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 38, 65–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, A.; Noor, S.; Tippairote, T.; Dadar, M.; Menzel, A.; Bjørklund, G. Individual risk management strategy and potential therapeutic options for the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 215, 108409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Lipinski, B. Selenium supplementation in the prevention of coronavirus infections (COVID-19). Med. Hypotheses 2020, 143, 109878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoor, H.; Feehan, J.; Al Dhaheri, A.S.; Ali, H.I.; Platat, C.; Ismail, L.C.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Stojanovska, L. Immune-boosting role of vitamins D, C, E, zinc, selenium and omega-3 fatty acids: Could they help against COVID-19? Maturitas 2021, 143, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haryanto, B.; Suksmasari, T.; Wintergerst, E.; Maggini, S. Multivitamin supplementation supports immune function and ameliorates conditions triggered by reduced air quality. Vitam. Miner. 2015, 3, 1000128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggini, S.; Pierre, A.; Calder, P.C. Immune function and micronutrient requirements change over the life course. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, B.P.; Park, J.S. Carotenoid action on the immune response. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Mach, N. Role of vitamin D in the hygiene hypothesis: The interplay between vitamin D, vitamin D receptors, gut microbiota, and immune response. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojadoost, B.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Yitbarek, A.; Laursen, A.; Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Alkie, T.N.; Barjesteh, N.; Quinteiro-Filho, W.M.; Smith, T.K.; Sharif, S. Dietary selenium supplementation enhances antiviral immunity in chickens challenged with low pathogenic avian influenza virus subtype H9N2. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2019, 207, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Zhu, G. Psychological interventions for people affected by the COVID-19 epidemic. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, G.; Parmigiani, B.; Amerio, A.; Aguglia, A.; Sher, L.; Amore, M. The psychological impact of COVID-19 on the mental health in the general population. QJM Int. J. Med. 2020, 113, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teigiserova, D.A.; Hamelin, L.; Thomsen, M. Towards transparent valorization of food surplus, waste and loss: Clarifying definitions, food waste hierarchy, and role in the circular economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 136033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, D.A.; Gómez-García, R.; Vilas-Boas, A.A.; Madureira, A.R.; Pintado, M.M. Management of fruit industrial by-products—A case study on circular economy approach. Molecules 2020, 25, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farcas, A.C.; Socaci, S.A.; Diaconeasa, Z.M. Introductory Chapter: From Waste to New Resources. In Food Preservation and Waste Exploitation; Socaci, S.A., Farcas, A.C., Aussenac, T., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, J. The significance of biomass in a circular economy. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, T.M.; Xiong, X.; Tsang, D.C.; Iris, K.; Poon, C.S. Sustainable food waste management towards circular bioeconomy: Policy review, limitations and opportunities. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socaci, S.A.; Farcas, A.C.; Vodnar, D.C.; Tofana, M. Food Wastes as Valuable Sources of Bioactive Molecules. In Superfood and Functional Food—The Development of Superfoods and Their Roles as Medicine; Shiomi, N., Ed.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2017; pp. 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulos, S.; Burger, M.J.; Dufourmont, J. Urban circular policies and employment through greenfield FDI. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.; Honkasalo, A.; Seppala, J. Circular economy: The concept and its limitations. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 143, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetherill, M.S.; White, K.C.; Seligman, H. Charitable food as prevention: Food bank leadership perspectives on food banks as agents in population health. Community Dev. 2019, 50, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loopstra, R.; Lambie-Mumford, H.; Fledderjohann, J. Food bank operational characteristics and rates of food bank use across Britain. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mook, L.; Murdock, A.; Gundersen, C. Food banking and food insecurity in high-income countries. Voluntas 2020, 31, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banca Pentru Alimente Bucuresti. Available online: http://bancapentrualimente.ro (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Barker, M.; Russell, J. Feeding the food insecure in Britain: Learning from the 2020 COVID-19 crisis. Food Secur. 2020, 12, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.; Smith, D.; Cummins, S. Understanding the health and wellbeing challenges of the food banking system: A qualitative study of food bank users, providers and referrers in London. Soc. Sci. Med. 2018, 211, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulker, C.E.; Trapp, G.S.; Scott, J.A.; Pollard, C.M. Global supermarkets’ corporate social responsibility commitments to public health: A content analysis. Glob. Health 2018, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Banks Federatioan (FEBA). Available online: https://www.eurofoodbank.org (accessed on 15 August 2020).



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farcas, A.C.; Galanakis, C.M.; Socaciu, C.; Pop, O.L.; Tibulca, D.; Paucean, A.; Jimborean, M.A.; Fogarasi, M.; Salanta, L.C.; Tofana, M.; et al. Food Security during the Pandemic and the Importance of the Bioeconomy in the New Era. Sustainability 2021, 13, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010150
Farcas AC, Galanakis CM, Socaciu C, Pop OL, Tibulca D, Paucean A, Jimborean MA, Fogarasi M, Salanta LC, Tofana M, et al. Food Security during the Pandemic and the Importance of the Bioeconomy in the New Era. Sustainability. 2021; 13(1):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010150
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarcas, Anca C., Charis M. Galanakis, Carmen Socaciu, Oana L. Pop, Dorin Tibulca, Adriana Paucean, Mirela A. Jimborean, Melinda Fogarasi, Liana C. Salanta, Maria Tofana, and et al. 2021. "Food Security during the Pandemic and the Importance of the Bioeconomy in the New Era" Sustainability 13, no. 1: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010150
APA StyleFarcas, A. C., Galanakis, C. M., Socaciu, C., Pop, O. L., Tibulca, D., Paucean, A., Jimborean, M. A., Fogarasi, M., Salanta, L. C., Tofana, M., & Socaci, S. A. (2021). Food Security during the Pandemic and the Importance of the Bioeconomy in the New Era. Sustainability, 13(1), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13010150












