Samothraki in Transition: A Report on a Real-World Lab to Promote the Sustainability of a Greek Island
Abstract
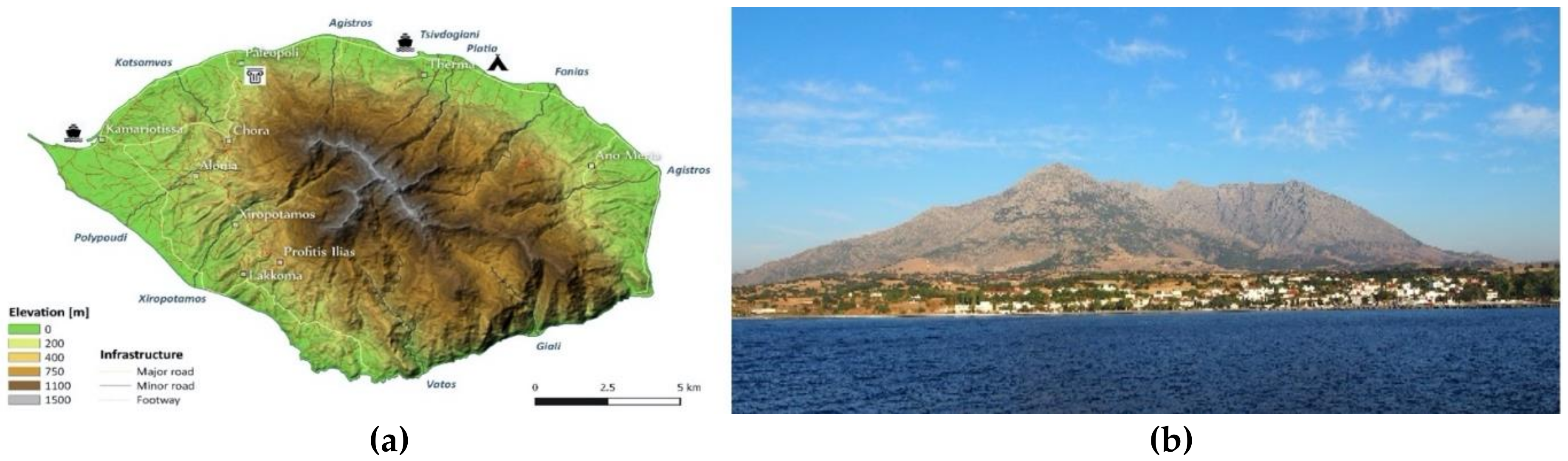
1. Introduction
2. Heuristics and Methods
3. Results
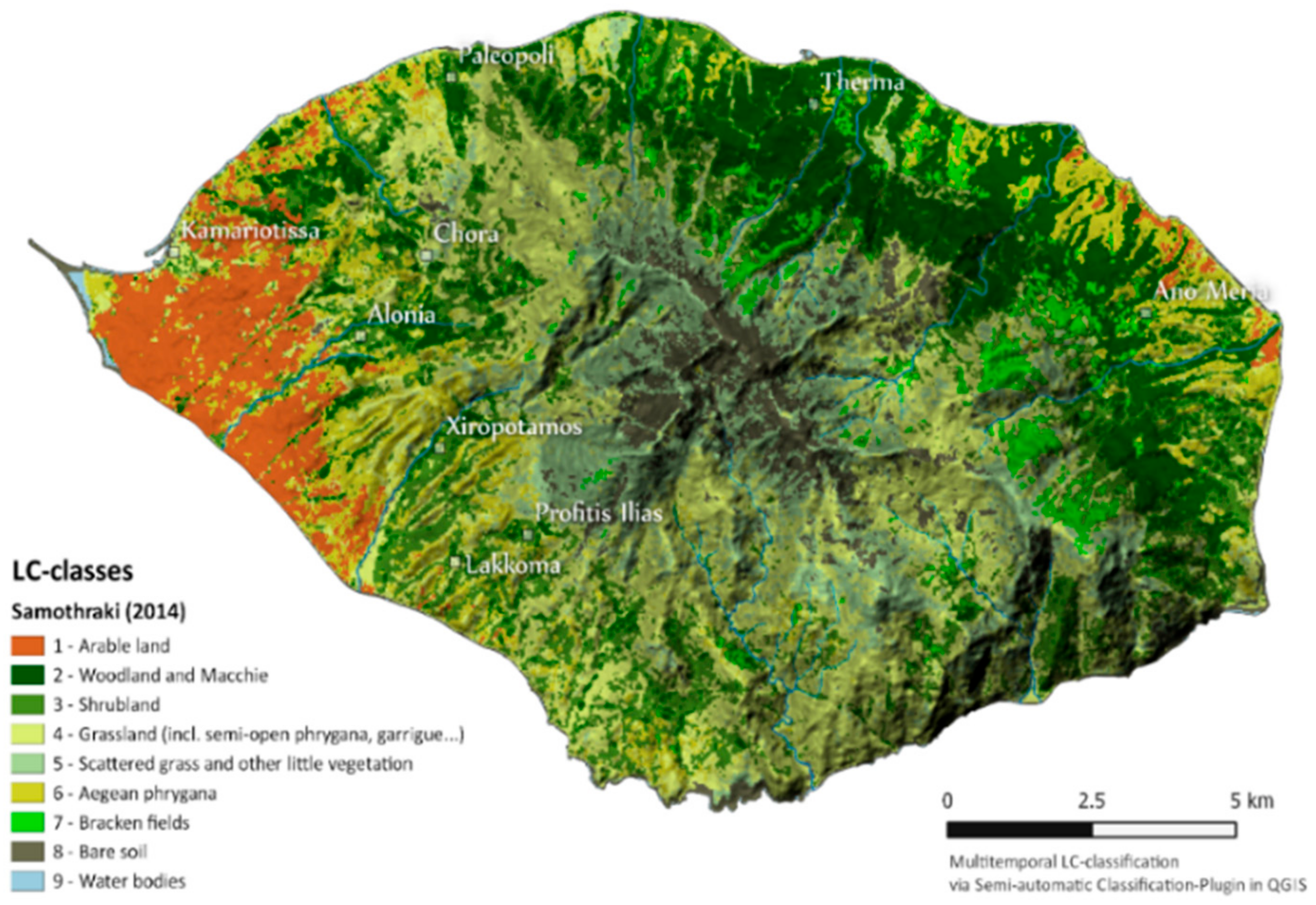
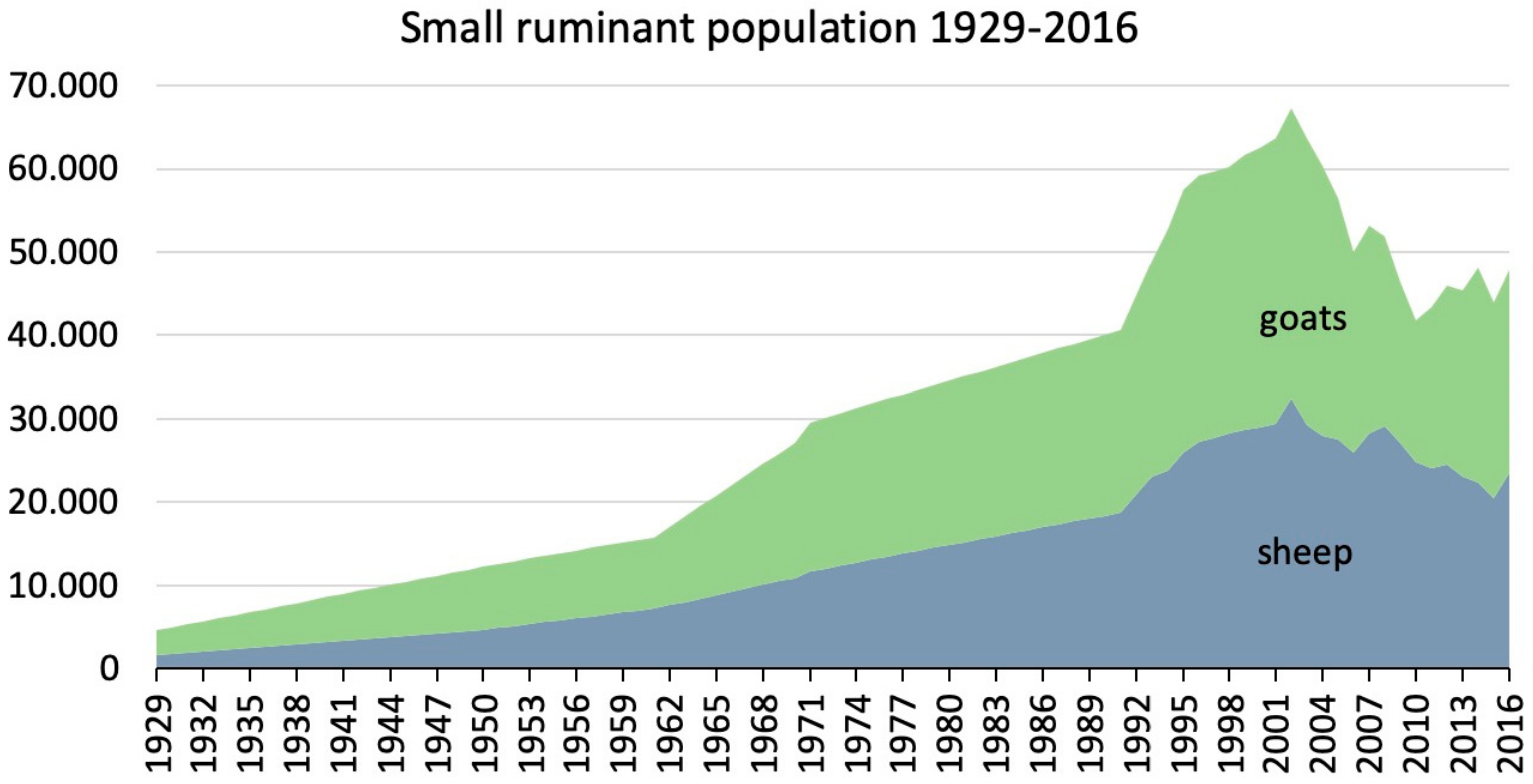
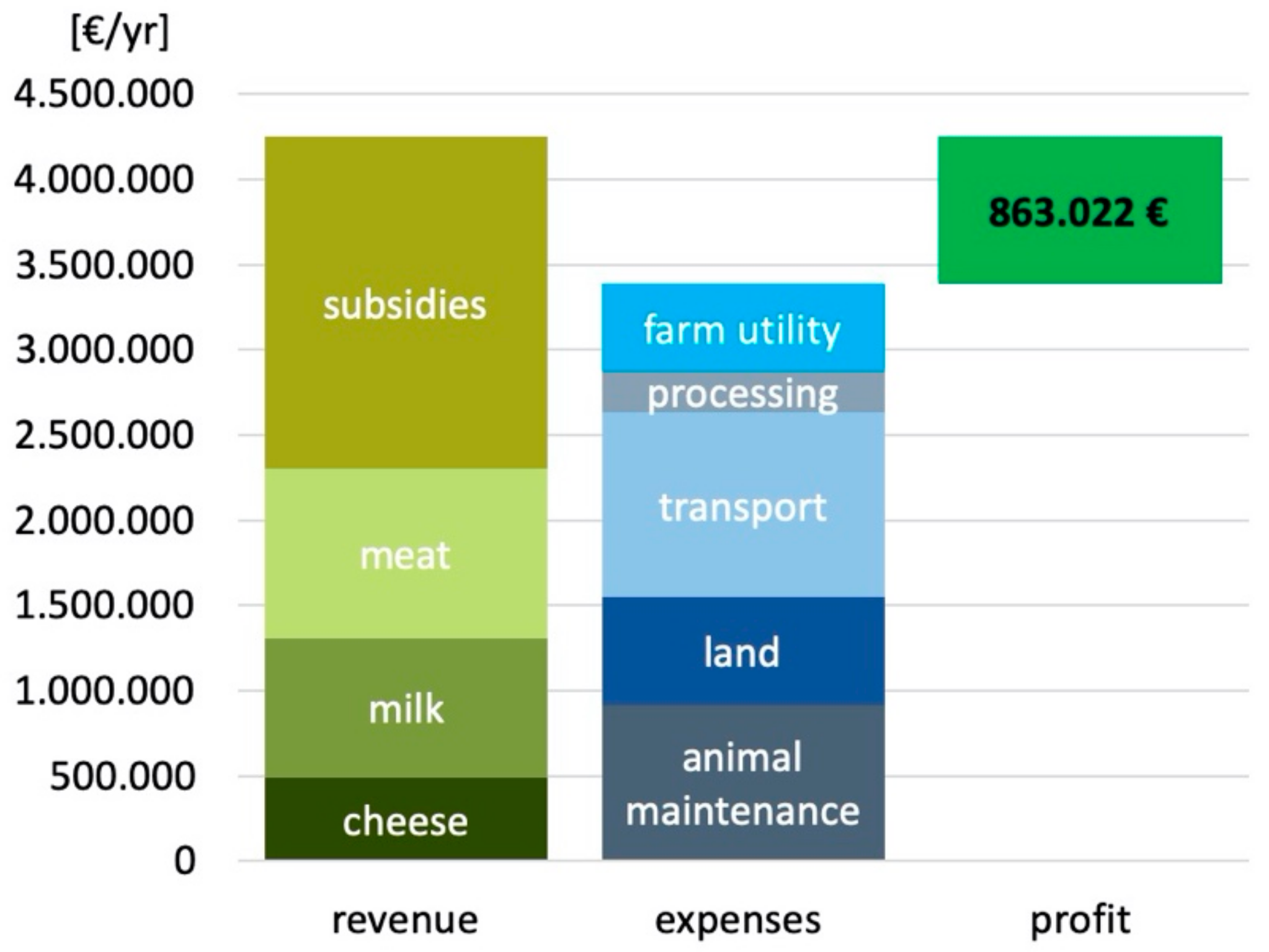
3.1. The Terrestrial Ecosystem and the Agricultural Sector (Livestock Herding)
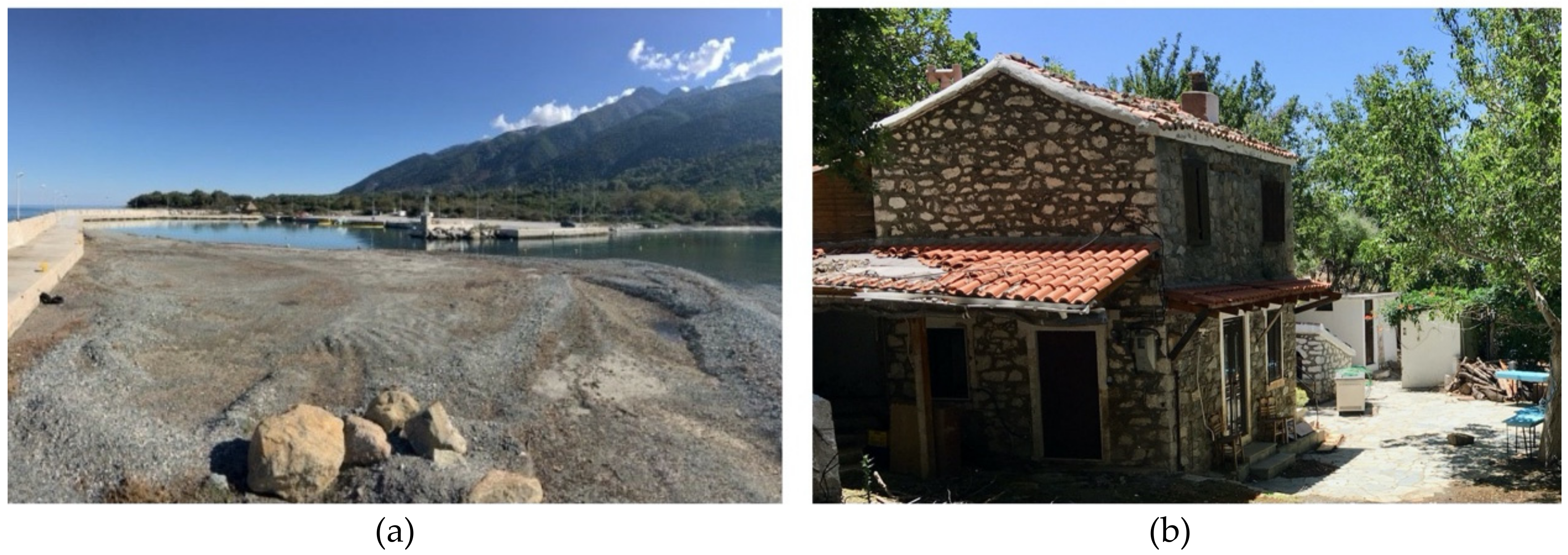
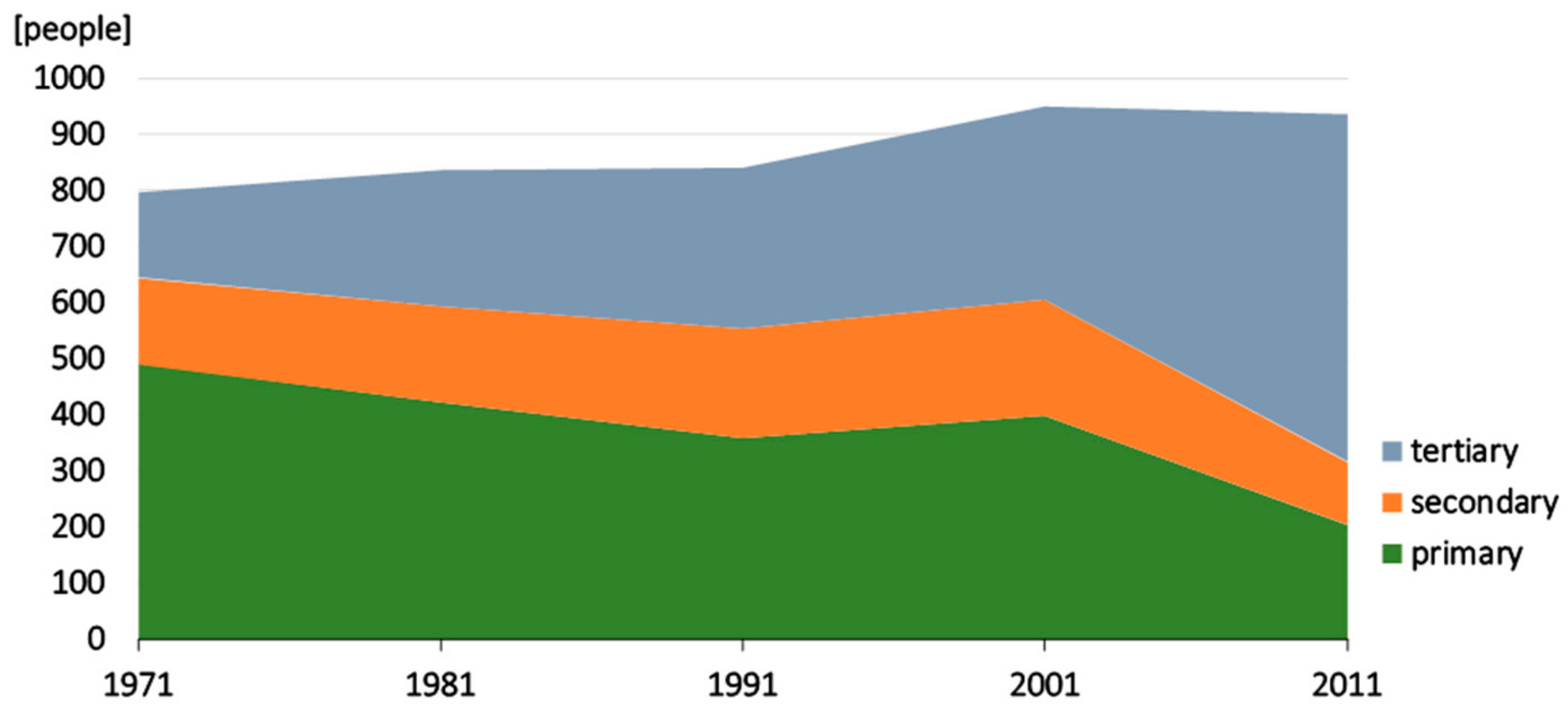
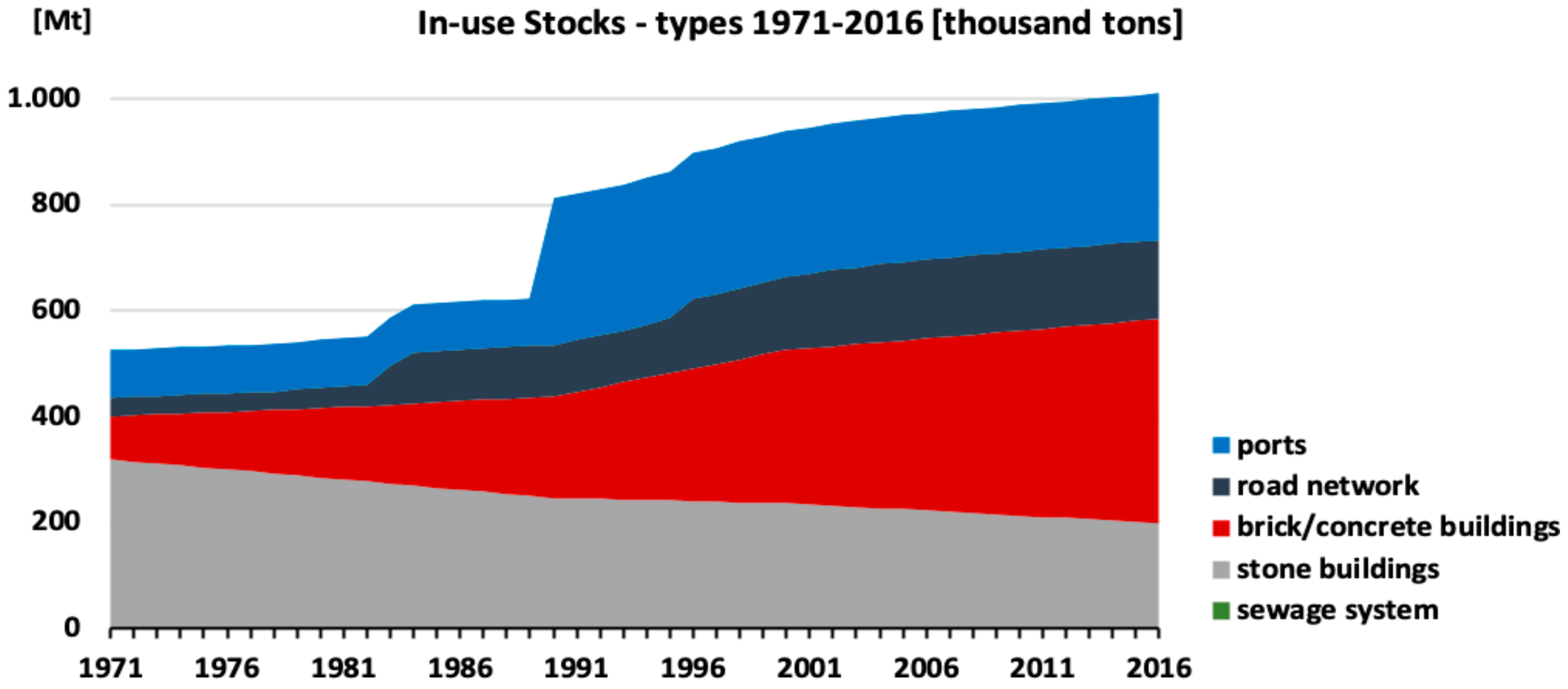
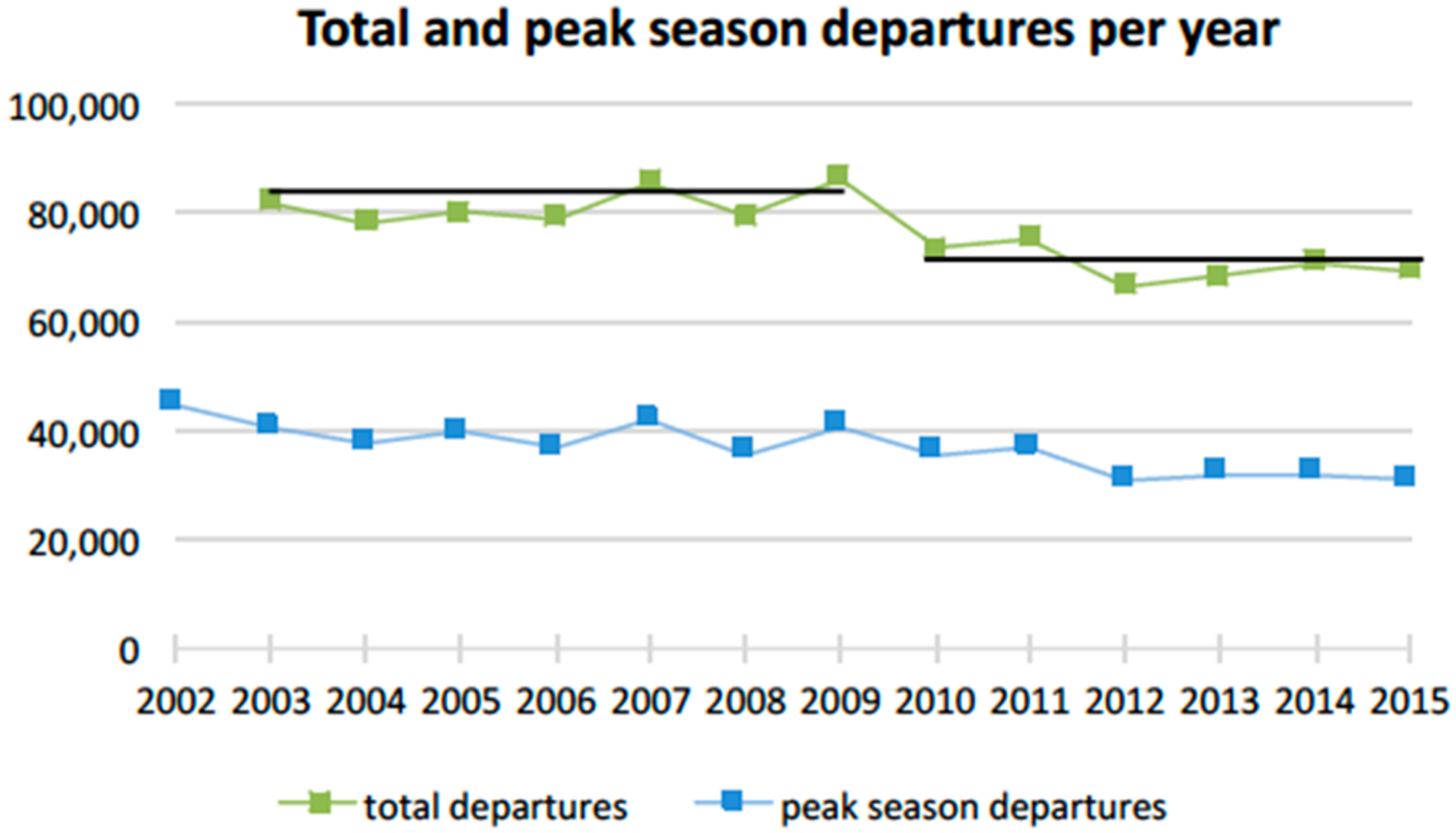
3.2. Tourism Dynamics and its Impacts on Infrastructure and Income
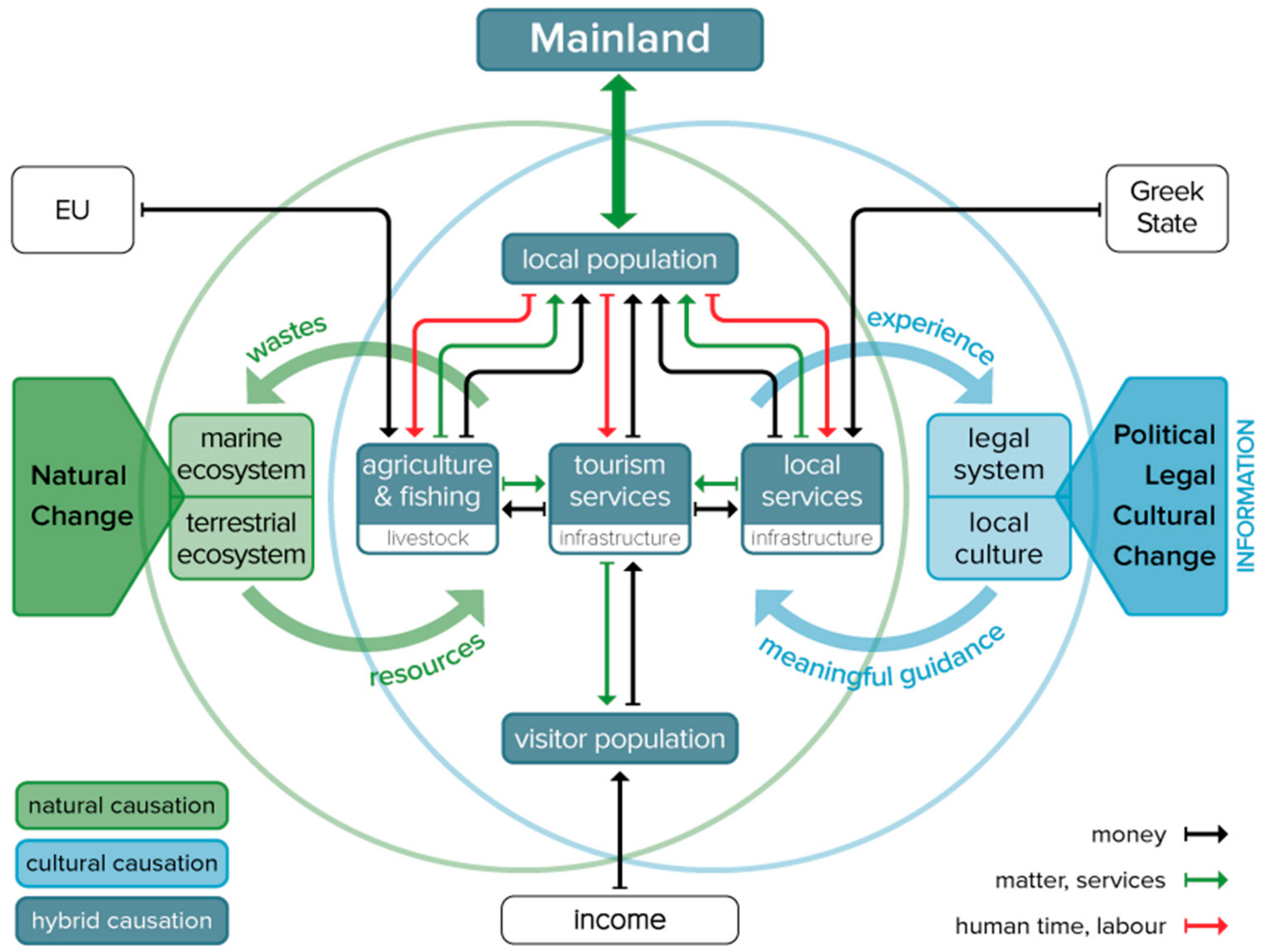
4. Discussion: On the Chances for a Sustainable Future of the Island, and the Role of Science to Support It
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biel, B.; Tan, K. Flora of Samothraki; Goulandris Natural History Museum: Athens, Greece, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Heiling, C. Spuren Historischer Ressourcennutzung anhand Dendrologischer Befunde: Eichenwälder auf der Insel Samothraki. Master’s Thesis, University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences Vienna, Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Löw, M. Spatial Patterns of Land Cover Dynamics on Samothraki Island: Applying Remote Sensing on Complex Mediterranean Pastures. Master’s Thesis, Alpen Adria University, Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bremmer, J.N. Initiation into the Mysteries of the Ancient World. In Münchner Vorlesungen zu antiken Welten; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kolodny, E. Samothrace sur Neckar. Des. Migrants grecs dans l’agglomeration de Stuttgard; Institute de Recherches Mediterraneennes: Aix-en-Provence, France, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Skoulikidis, N.; Lampou, A.; Karaouzas, I.; Gritzalis, K.; Lazaridou, M.; Zogaris, S. Stream ecological assessment on an Aegean island: Insights from an exploratory application on Samothraki (Greece). Fres. Envrion. Bull. 2014, 23, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Petridis, P.; Hickisch, R.; Klimek, M.; Fischer, R.; Fuchs, N.; Kostakiotis, G.; Wendland, M.; Zipperer, M.; Fischer-Kowalski, M. Exploring Local Opportunities and Barriers for a Sustainability Transition on a Greek Island; Social Ecology Working Paper 142; Institute for Social Ecology, Alpen Adria University: Vienna, Austria, 2013; Available online: https://www.aau.at/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/working-paper-142-web.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Fischer-Kowalski, M.; Xenidis, L.; Singh, S.J.; Pallua, I. Transforming the Greek Island of Samothraki into a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. An Experience in Transdisciplinarity. Gaia-Ecol. Perspect. Sci. Soc. 2011, 20, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greek National MAB Committee. Samothraki Biosphere Reserve Nomination Form: Final Official Document; Unesco MAB Programme: Athens, Greece, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Krütli, P.; Pohl, C.; Stauffacher, M. Sustainability Learning Labs in Small Island Developing States: A Case Study of the Seychelles. Gaia-Ecol. Perspect. Sci. Soc. 2018, 27, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäpke, N.; Bergmann, M.; Stelzer, F.; Lang, D.J. Labs in the Real World: Advancing Transdisciplinary Research and Sustainability Transformation. Gaia-Ecol. Perspect. Sci. Soc. 2018, 27, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes, P.J.; Chertow, M. An Island Approach to Industrial Ecology: Towards Sustainability in the Island Context. Envrion. Plan. Manag. 2004, 47, 201–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.J.; Grünbühel, C.M.; Schandl, H.; Schulz, N. Social Metabolism and Labour in a Local Context: Changing Environmental Relations on Trinket Island. Pop. Envrion. 2001, 23, 71–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.J.; Schandl, H. Socio-Economic Metabolism in the Nicobar Islands. Empirical Research in Society-Nature Interactions. In Exploitation and Overexploitation in Societies Past and Present. IUAES-Intercongress 2001 Goettingen; Benzing, B., Herrmann, B., Eds.; LIT Publishing House: Münster, Germany, 2003; pp. 169–184. [Google Scholar]
- Okoli, A. Socioeconomic Metabolism of Biomass in Jamaica in the Context of Trade and National Food Security: A Time Series Biophysical Analysis (1961–2013). Ph.D. Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas-Hope, E. Migration, small farming and food security in the Caribbean: Jamaica and St. Vincent and the Grenadines. Int. Migr. 2017, 55, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizos, T.; Plieninger, T.; Schaich, H. ‘Instead of 40 Sheep there are 400’: Traditional Grazing Practices and Landscape Change in Western Lesvos, Greece. Landsc. Res. 2013, 38, 476–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haberl, H.; Wiedenhofer, D.; Pauliuk, S.; Krausmann, F.; Müller, D.B.; Fischer-Kowalski, M. Contributions of sociometabolic research to sustainability science. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krausmann, F. Social Metabolism. In The Routledge Handbook of Ecological Economics: Nature and Society; Spash, C.L., Ed.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2017; pp. 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Kowalski, M.; Petridis, P. Can Socioecological Research Help to Create a Realistic Perspective for a Sustainable Samothraki? Sustain. Med. 2016, 73, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, J. Collapse. In How Societies Choose to Fail or Succeed; Viking: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Petridis, P.; Fischer-Kowalski, M. Island Sustainability: The Case of Samothraki. In Social Ecology Society-Nature Relations across Time and Space; Haberl, H., Fischer-Kowalski, M., Krausmann, F., Winiwarter, V., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 543–554. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrom, E. Governing the Commons. The Evolution of Institutions for Collective Action; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen, P. The DPSIR Framework. UNEP Headquarters Nairobi 2004. Available online: https://wwz.ifremer.fr/dce/content/download/69291/.../DPSIR.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- Fischer-Kowalski, M.; Petridis, P. Fifth Summer School on Aquatic and Social Ecology on Samothraki, Greece; Social Ecology Working Paper 178; Institute for Social Ecology, Alpen Adria University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2019; Available online: https://www.aau.at/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/working-paper-178-web.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Summer University of Samothraki 2016; UNESCO, Global Water Partnership, Mediterranean Information Office for Environment, Culture and Sustainable Development; Institute of Social Ecology, Hellenic Centre for Marine Research. Integrated Management Approaches for Biosphere Reserves and other Designated Areas, 9–22 July 2016. Sustain. Mediterr. 2016, 73, 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- 6th Summer School on ‘Aquatic and Social Ecology’ on Samothraki, Greece; Working Paper Social Ecology; Petridis, P., Fischer-Kowalski, M., Eds.; Institute for Social Ecology Vienna, University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2020; In Preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Δημοσιοποίηση Ποσών Επιδότησης (ΕΓΤΕ/ΕΓΤAA). Available online: https://transpay.opekepe.gr/ (accessed on 12 January 2018).
- Baierl, C. Analysis of the EU-Common Agricultural Policy Subsidies on the Greek Island of Samothraki. Master’s Thesis, Alpen Adria University, Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, N.A. Sozial-ökologische Effekte der EU-Agrarsubventionen; AV Akademikerverlag: Saarland, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schwaiger, N. Exploring Sustainable Tourism on Samothraki: Current State and Perspectives. Master’s Thesis, Alpen Adria University, Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fetzel, T.; Petridis, P.; Noll, D.; Singh, S.J.; Fischer-Kowalski, M. Reaching a socio-ecological tipping point: Overgrazing on the Greek island of Samothraki and the role of European agricultural policies. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, D.; Lauk, C.; Gaube, V.; Wiedenhofer, D. Caught in a deadlock: Small ruminant farming on the Greek island of Samothrace. The importance of regional contexts for effective EU agricultural policies. Sustainability 2020, 12, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noll, D.; Wiedenhofer, D.; Miatto, A.; Singh, S.J. The expansion of the built environment, waste generation and EU recycling targets on Samothraki, Greece: An island’s dilemma. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 150, 104405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, E.; Skoulikidis, N. Hydrometereological and Hydrochemical analysis of the Fonias River Basin. In Fifth Summer School on Aquatic and Social Ecology on Samothraki, Greece; Social Ecology Working Paper 178; Fischer-Kowalski, M., Petridis, P., Eds.; Institute for Social Ecology: Alpen Adria University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2019; pp. 22–34. [Google Scholar]
- Skoulikidis, N.; Lampou, A.; Katopodis, G. Water Metabolism and Water Management. In Samothraki as a Biosphere Reserve (SamoMAB); Report to the Austrian Academy of Sciences; Dominik, N., Ed.; University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2018; pp. 5–36. ISBN 978. [Google Scholar]
- Panagopoulos, Y.; Dimitriou, E.; Skoulikidis, N. Vulnerability of a Northeast Mediterranean Island to Soil Loss. Can Grazing Management Mitigate Erosion? Water 2019, 11, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Work less- earn more. Available online: www.happygoats.eu/#/ (accessed on 15 December 2019).
- Hostert, P.; Röder, A.; Hill, J.; Udelhoven, T.; Tsiourlis, G. Retrospective studies of grazing-induced land degradation: A case study in central Crete, Greece. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 24, 4019–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjigeorgiou, I. Past, present and future of pastoralism in Greece. Pastor. Res. Policy Pract. 2011, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perevolotsky, A.; Seligman, N.G. Role of Grazing in Mediterranean Rangeland Ecosystems. BioScience 1998, 48, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallentine, J.F. Grazing Management; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jepsen, M.R.; Kuemmerle, T.; Müller, D.; Erb, K.; Verburg, P.H.; Haberl, H. Transitions in European land-management regimes between 1800 and 2010. Land Use Policy 2015, 49, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damianakos, S. The Ongoing Quest for a Model of Greek Agriculture. Sociol. Rural. 1997, 37, 190–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.; Detsis, V.; Karamesouti, M.; Kounalaki, K.; Vassiliou, P.; Salvati, L. Exploring Long-Term Impact of Grazing Management on Land Degradation in the Socio-Ecological System of Asteroussia Mountains, Greece. Land 2015, 4, 541–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Overview of CAP Reform 2014–2020—Agricultural Policy Perspectives Brief N° 5*/December 2013. DG Agriculture and Rural Development, Unit for Agricultural Policy Analysis and Perspective. 2013. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/info/sites/info/files/food-farming-fisheries/farming/documents/agri-policy-perspectives-brief-05_en.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- Pispini, M. National Proposals for the new CAP. ARC 2020 (Agricultural & Rural Convention). 2014. Available online: https://arc2020.eu/2014/06/greece-national-proposals-for-the-new-cap/ (accessed on 9 January 2020).
- Giourga, H.; Margaris, N.S.; Vokou, D. Effects of Grazing Pressure on Succession Process and Productivity of Old Fields on Mediterranean Islands. Environ. Manag. 1998, 22, 589–596. [Google Scholar]
- Hohenwarter, S.; Winkler, A.; Zilleruelo, R.; Anagnostou, C.; Lampou, A. Coastal Morphodynamics with a Focus on Anthropogenic Activities and Sustainable Coastal Areas. In Fifth Summer School on Aquatic and Social Ecology on Samothraki, Greece; Social Ecology Working Paper 178; Fischer-Kowalski, M., Petridis, P., Eds.; Institute for Social Ecology, Alpen Adria University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2019; pp. 14–21. [Google Scholar]
- Municipality of Samothraki. Operational Program 2014–2019; Municipality of Samothraki: Samothraki, Greece, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Spilanis, I.; Kizos, T.; Karampela, S.; Vayanni, H. A tourism typology for the Greek islands. In Proceedings of the Island Tourism (International Conference of Trends, Impacts and Policies on Tourism development), Crete, Greece, 15–18 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Petridis, P.; Huber, J. A Socio-metabolic Transition of Diets on a Greek Island: Evidence of “Quiet Sustainability”. In Socio-Metabolic Perspectives on the Sustainability of Local Food Systems; Fraňková, E., Haas, W., Singh, S.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 263–289. [Google Scholar]
- Petridis, P.; Fischer-Kowalski, M.; Singh, S.J.; Noll, D. The role of science in sustainability transitions: Citizen science, transformative research, and experiences from Samothraki island, Greece. Isl. Stud. J. 2017, 12, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association Sustainable Samothraki. Recommendations of the International Scientific Advisory Board to the Association Sustainable Samothraki. 2019. Available online: http://sustainable-samothraki.net/local_action/sustainable-samothraki-association/scientific-advisory-board/ (accessed on 9 January 2020).





| Agricultural Sector | Tourism Sector | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicator | Methods Used | Indicator | Methods Used | |
| Drivers | system of EU-CAP subsidies, Greek variant | statistical analysis of the “transparency database” for EU-CAP subsidies for the years 2014–2016 [28], supplemented by expert interviews [29,30] | tourists: numbers, their expectations and spending tourism entrepreneur expectations | analysis of port statistics 2002–2017 survey of tourists (random sample of ferry passengers, N=1425) interviews with tourism entrepreneurs [31] |
| Pressures | excessive number of grazing animals | analysis of data from agricultural statistics and utilization of a bottom-up metabolic model for estimating the feed demand of sheep and goats [32,33] | expansion of tourist infra-structures; use of non-reusable nor degradable materials | construction history from municipal sources; dynamic bottom-up modelling of materials use, maintenance requirements and wastes [34] |
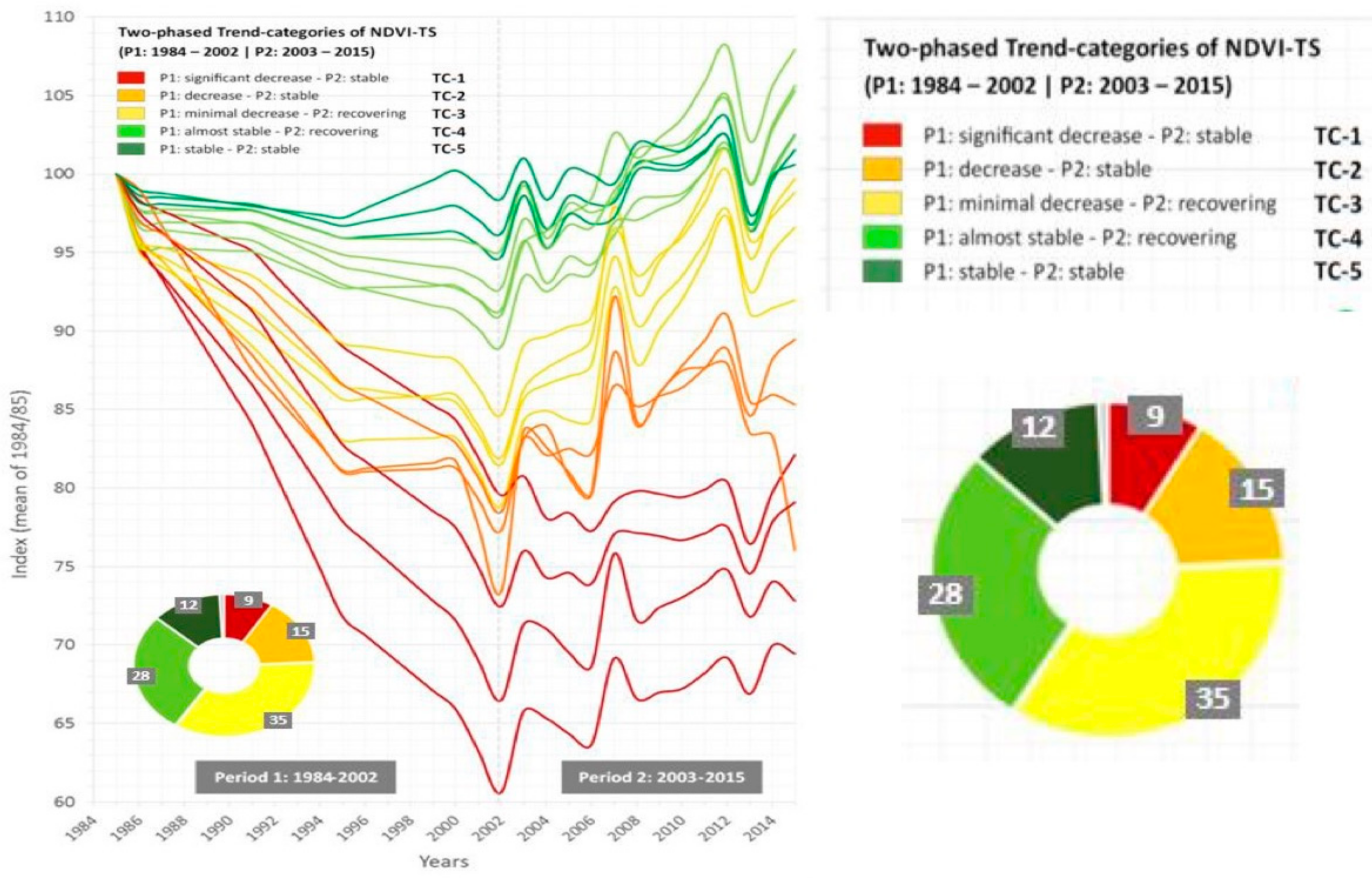
| States | vegetation cover | estimation of local NPP for different land cover classes [32]; time series analysis of remote sensing data (satellite images) of the land cover of the island (NDVI) 1984–1916 [3] analysis of spatial and age structure of mountain oak forests [2] | freshwater resources, quantity, and quality | drinking water quality of spring water; ecological quality of streams, wetlands, and lagoons; hydrometeorological analysis of the Fonias river basin; estimation of freshwater resources availability and water abstraction [6,35,36] |
| Impacts | loss of vegetation cover, erosion | remote sensing [3] erosion [37] lack of forest regeneration [2] | increase of water demand and wastewater production | documenting inadequate water supply and wastewater management [36] |
| Responses | introduction of sown bio-diverse pas-tures (SBP) improving farmers‘ business practices support for farmers cooperatives | SBP field experiments with farmers (20 fields, for 3–4 years) [27] development of a “Happy Goats App” decision support tool for farmers [38] follow-up interviews with farmers to explore their income & costs [33] olive oil and livestock cooperatives actually formed in 2018/19 | better synergies with local agriculture sector support for legal eco-camping | interviews with restaurant owners to explore / support use of local produce [27] survey of campers 2017; development of an eco-camp concept for the municipality [27] |
| Persons | Length of Stay | Daily Consumption Estimates | Summer Spending Estimate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Av. Days | Low:€/Day | High:€/Day | Low:€/Season | High:€/Season | ||
| second homeowners | 3000 | 20 | 33.7 | 41.2 | 2,022,000 | 2,472,000 |
| seasonal workers | 2000 | 23 | 16.5 | 22.2 | 759,000 | 1,021,200 |
| family visitors | 1800 | 19 | 29.8 | 37.8 | 1,019,160 | 1,292,760 |
| tourists (hotel/rented room) | 13,000 | 5 | 72.4 | 86.9 | 4,706,000 | 5,648,500 |
| tourists (camping) | 9000 | 9 | 38.1 | 45.5 | 3,086,100 | 3,685,500 |
| all tourists | 22,000 | 7 | 7,792,100 | 9,334,000 | ||
| all visitors | 28,800 | 11,592,260 | 14,119,960 | |||
| In Thousand€ | % of Overall Income | % of Active Population 2001(1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| inflow from tourism | 13,000 (2) | 49 | 21 |
| inflow from CAP subsidies | 3000 (3) | 11 | 42 |
| inflow from agricultural sales | 2300 (4) | 9 | |
| income from fishing | 4000 (5) | 15 | 9 |
| salaries from public sources | 4480 (6) | 17 | 28 |
| total | 26,780 | 100 | 100 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fischer-Kowalski, M.; Löw, M.; Noll, D.; Petridis, P.; Skoulikidis, N. Samothraki in Transition: A Report on a Real-World Lab to Promote the Sustainability of a Greek Island. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051932
Fischer-Kowalski M, Löw M, Noll D, Petridis P, Skoulikidis N. Samothraki in Transition: A Report on a Real-World Lab to Promote the Sustainability of a Greek Island. Sustainability. 2020; 12(5):1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051932
Chicago/Turabian StyleFischer-Kowalski, Marina, Markus Löw, Dominik Noll, Panos Petridis, and Nikolaos Skoulikidis. 2020. "Samothraki in Transition: A Report on a Real-World Lab to Promote the Sustainability of a Greek Island" Sustainability 12, no. 5: 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051932
APA StyleFischer-Kowalski, M., Löw, M., Noll, D., Petridis, P., & Skoulikidis, N. (2020). Samothraki in Transition: A Report on a Real-World Lab to Promote the Sustainability of a Greek Island. Sustainability, 12(5), 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051932







