Talent Goes Social: Online Corporate Networking and Business Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background and Hypothesis Development
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Empirical Method
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Michaels, E.; Handfield-Jones, H.; Axelrod, B. The War for Talent; Harvard Business Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Clement, J. Worldwide Digital Population as of JULY 2020. 2020. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/617136/digital-population-worldwide/ (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Korzynski, P.; Rook, C.; Treacy, E.F.; de Vries, M.K. The impact of self-esteem, conscientiousness and pseudo-personality on technostress. Internet Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPrete, T.A. Horizontal and Vertical Mobility in Organizations. Adm. Sci. Q. 1987, 32, 422–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewman, S.; Konda, S.L. Careers and Organizational Labor Markets: Demographic Models of Organizational Behavior. Am. J. Sociol. 1983, 88, 637–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, P. The New Deal at Work: Managing the Market-Driven Workforce; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Paniagua, J.; Korzynski, P. Online Corporate Social Networking. In Encyclopedia of Creativity, Invention, Innovation and Entrepreneurship; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Korzynski, P. How does online social networking help leaders communicate? Evidence from the Fortune 500. Asia Pac. J. Hum. Resour. 2014, 52, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barden, J.Q.; Mitchell, W. Disentangling the Influences of Leaders’ Relational Embeddedness on Interorganizational Exchange. Acad. Manag. J. 2007, 50, 1440–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blass, E. Talent Management: Maximising Talent for Business Performance; Chartered Management Institute, Public Affairs Department: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Farley, C. HR’s role in talent management and driving business results. Employ. Relat. Today 2005, 32, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J.B.; Wright, P.M. On becoming a strategic partner: The role of human resources in gaining competitive advantage. Hum. Resour. Manag. 1998, 37, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Drazin, R. Overcoming Resource Constraints on Product Innovation by Recruiting Talent From Rivals: A Study of the Mutual Fund Industry, 1986–1994. Acad. Manag. J. 2002, 45, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Story, J.S.; Castanheira, F. The Impact of CSR Practices on Organizational Attractiveness: HRM Implications. Acad. Manag. Proc. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, E.S.; Lien, L.B. Investments in Recessions. Acad. Manag. Proc. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarique, I.; Schuler, R.S. Global talent management: Literature review, integrative framework, and suggestions for further research. J. World Bus. 2010, 45, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, P.; Singh, H.; Singh, J.; Useem, M. The India Way: Lessons for the U.S. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 2010, 24, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asur, S.; Huberman, B.A. Predicting the future with social media. In Proceedings of the Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology (WI-IAT), 2010 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference, Toronto, ON, Canada, 31 August–3 September 2010; pp. 492–499. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Varian, H. Predicting the present with google trends. Econ. Rec. 2012, 88, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettredge, M.; Gerdes, J.; Karuga, G. Using web-based search data to predict macroeconomic statistics. Commun. ACM 2005, 48, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, J.; Sapena, J. Business performance and social media: Love or hate? Bus. Horiz. 2014, 57, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzynski, P.; Paniagua, J. Score a tweet and post a goal: Social media recipes for sports stars. Bus. Horiz. 2016, 59, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzynski, P.; Paniagua, J.; Rodriguez-Montemayor, E. Employee creativity in a digital era: The mediating role of social media. Manag. Decis. 2019, 58, 1100–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, J.; Rivelles, R.; Sapena, J. Social Determinants of Success: Social Media, Corporate Governance and Revenue. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ariss, A.; Cascio, W.F.; Paauwe, J. Talent management: Current theories and future research directions. J. World Bus. 2014, 49, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collings, D.G.; Mellahi, K. Commentary on:“Talent—Innate or acquired? Theoretical considerations and their implications for talent management”. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2013, 23, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensley, M.D.; Carland, J.W.; Ensley, R.L.; Carland, J.C. The theoretical basis and dimensionality of the talent management system. Acad. Strateg. Manag. J. 2010, 9, 9–42. [Google Scholar]
- Kehinde, J. Talent Management: Effect on Organization Performances. J. Manag. Res. 2012, 4, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaiman, V.; Collings, D.G. Talent management: Advancing the field. Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 2013, 24, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collings, D.G.; Mellahi, K. Strategic talent management: A review and research agenda. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 2009, 19, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzynski, P.; Mazurek, G.; Haenlein, M. Leveraging employees as spokespeople in your HR strategy: How company-related employee posts on social media can help firms to attract new talent. Eur. Manag. J. 2020, 38, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-L.; Liu, C.-C.; Lee, Y.-D. Effect of commitment and trust towards micro-blogs on consumer behavioral intention: A relationship marketing perspective. Int. J. Electron. Businessm. 2010, 8, 292. [Google Scholar]
- Kietzmann, J.H.; Hermkens, K.; McCarthy, I.P.; Silvestre, B.S. Social media? Get serious! Understanding the functional building blocks of social media. Bus. Horiz. 2011, 54, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, P. Managing a hotel’s image on TripAdvisor. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2010, 19, 754–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieseler, C.; Fleck, M.; Meckel, M. Corporate social responsibility in the blogosphere. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 91, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapp, A.; Trainor, K.J.; Agnihotri, R. Performance implications of customer-linking capabilities: Examining the complementary role of customer orientation and CRM technology. J. Bus. Res. 2010, 63, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainor, K.J.; Andzulis, J.M.; Rapp, A.; Agnihotri, R. Social media technology usage and customer relationship performance: A capabilities-based examination of social CRM. J. Bus. Res. 2014, 67, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, L.; Gensler, S.; Leeflang, P.S.H. Popularity of Brand Posts on Brand Fan Pages: An Investigation of the Effects of Social Media Marketing. J. Interact. Mark. 2012, 26, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S. Follower Numbers on Twitter Do Matter (Just Not In The Way That You Think). 2012. Available online: http://www.mediabistro.com/alltwitter/followers_b25105 (accessed on 21 August 2014).
- Duan, Y.; Jiang, L.; Qin, T.; Zhou, M.; Shum, H.-Y. An empirical study on learning to rank of tweets. In Proceedings of the 23rd Internattional Conference on Computational Linguistics (Coling 2010), Beijing, China, 23–27 August 2010; pp. 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, H.; Lee, C.; Park, H.; Moon, S. What is Twitter, a social network or a news media? In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on World Wide Web, Raleigh, NC, USA, 26–30 April 2010; pp. 591–600. [Google Scholar]
- Paniagua, J.; Korzynski, P.; Mas-Tur, A. Crossing borders with social media: Online social networks and FDI. Eur. Manag. J. 2017, 35, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, J.; Korzynski, P. Social Media Crowdsourcing. In Encyclopedia of Creativity, Invention, Innovation and Entrepreneurship; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Prpić, J.; Shukla, P.P.; Kietzmann, J.H.; McCarthy, I.P. How to work a crowd: Developing crowd capital through crowdsourcing. Bus. Horiz. 2015, 58, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, G. The duality of collaboration: Inducements and opportunities in the formation of interfirm linkages. Strateg. Manag. J. 2000, 21, 317–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.; Rae, A. Building a personal brand through social networking. J. Bus. Strategy 2011, 32, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollier-Malaterre, A.; Rothbard, N.P.; Berg, J.M. When Worlds Collide in Cyberspace: How Boundary Work in Online Social Networks Impacts Professional Relationships. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2013, 38, 645–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, A.; Shiri, A. Sociability and social interaction on social networking websites. Libr. Rev. 2009, 58, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskorski, M.J. A Social Strategy: How We Profit from Social Media; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, R.; Rohm, A.; Crittenden, V.L. We’re all connected: The power of the social media ecosystem. Bus. Horiz. 2011, 54, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, M.R.; Rajagopalan, B. Knowledge-sharing and influence in online social networks via viral marketing. Commun. ACM 2003, 46, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahalad, C.; Hamel, G. The core competence of the corporation. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1990, 68, 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Carmeli, A.; Tishler, A. The relationships between intangible organizational elements and organizational performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2004, 25, 1257–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.W.; Dowling, G.R. Corporate reputation and sustained superior financial performance. Strateg. Manag. J. 2002, 23, 1077–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberson, Q.M.; Williamson, I.O. Justice in self-managing teams: The role of social networks in the emergence of procedural justice climates. Acad. Manag. J. 2012, 55, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain, C. Finding a Job in the Internet Age. Soc. Forces 2005, 83, 1235–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corkindale, D.; Newall, J. Advertising thresholds and wearout. Eur. J. Mark. 1978, 12, 329–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwell, G.; Oliver, P.E.; Prahl, R. Social networks and collective action: A theory of the critical mass. III. Am. J. Sociol. 1988, 94, 502–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-Y.; Lu, H.-P. Why people use social networking sites: An empirical study integrating network externalities and motivation theory. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2011, 27, 1152–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, N.; Ramanujam, V. Measurement of business performance in strategy research: A comparison of approaches. Acad. Manag. Rev. 1986, 11, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, P.E. Do not cross me: Optimizing the use of cross-sectional designs. J. Bus. Psychol. 2019, 34, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, M.; Barlow, A. Use and measurement of social media for SMEs. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2015, 22, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odoom, R.; Anning-Dorson, T.; Acheampong, G. Antecedents of social media usage and performance benefits in small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2017, 30, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufrenot, G.; Mignon, V.; Tsangarides, C. The trade-growth nexus in the developing countries: A quantile regression approach. Rev. World Econ. 2010, 146, 731–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, J.; Figueiredo, E.; Sapena, J. Quantile regression for the FDI gravity equation. J. Bus. Res. 2015, 68, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huarng, K.-H.; Yu, T.H.-K. A new quantile regression forecasting model. J. Bus. Res. 2014, 67, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Gibson, D.E.; Doty, D.H. The Effects of Flexibility in Employee Skills, Employee Behaviors, and Human Resource Practices on Firm Performance. J. Manag. 2005, 31, 622–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D.; Paquette, S. Emergency knowledge management and social media technologies: A case study of the 2010 Haitian earthquake. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2011, 31, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
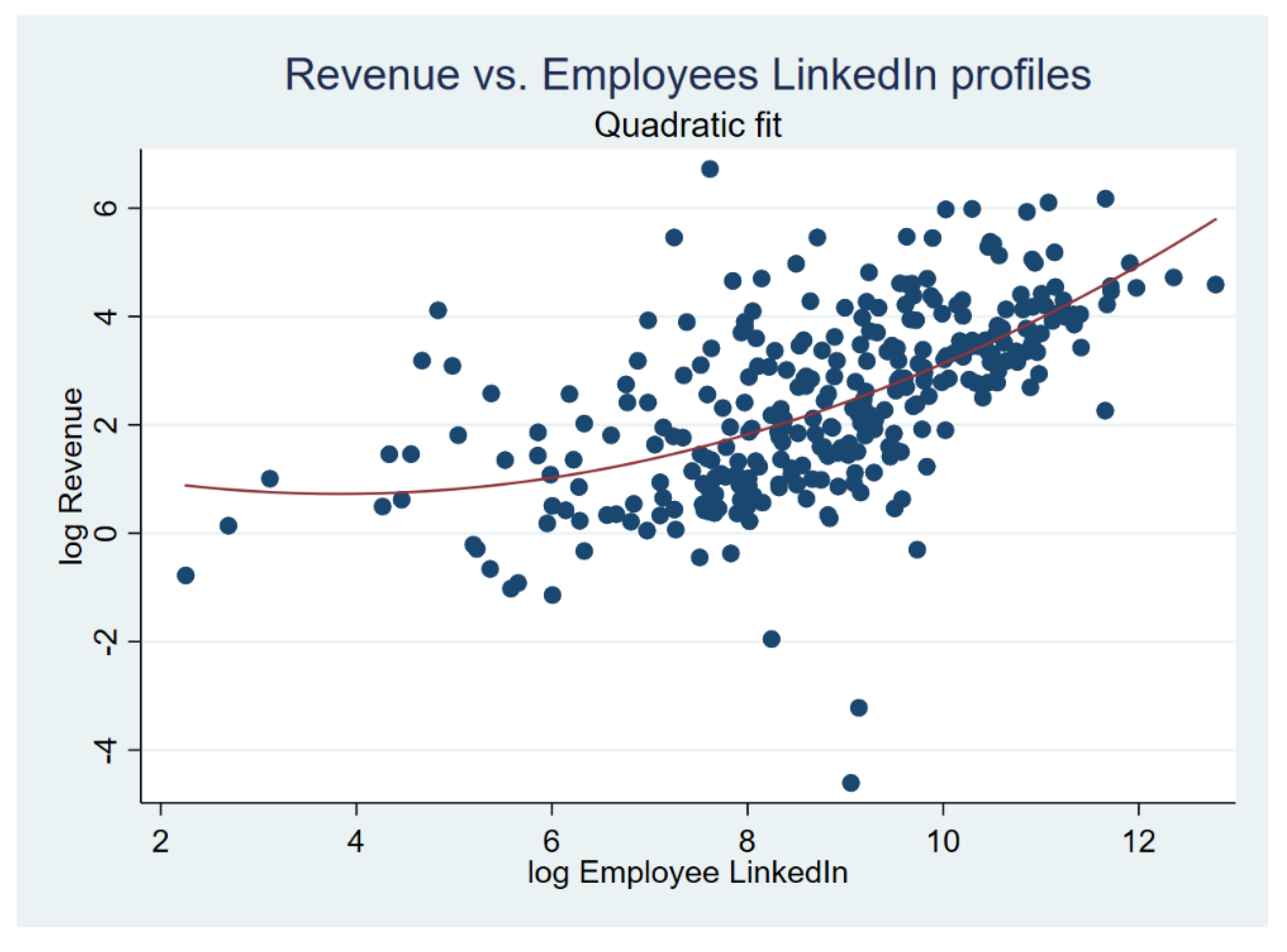
| Variable | Observations | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max | Revenue | Employees |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue | 296 | 38.795 | 81.298 | 0.01 | 829.73 | ||
| (Billion USD) | |||||||
| Employees | 296 | 19,317.25 | 34,281.01 | 9 | 357,455 | 0.556 *** | |
| (Number) | |||||||
| Skills | 296 | 559,799.4 | 829,675.7 | 8138 | 7,126,588 | 0.408 *** | 0.408 *** |
| (Number) |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Log employees | 0.503 *** | −1.132 ** |
| (0.0731) | (0.437) | |
| Log skills | 0.161 * | 1.159 |
| (0.0879) | (1.041) | |
| Log employee2 | 0.104 *** | |
| (0.0264) | ||
| Log skills2 | −0.0494 | |
| (0.0423) | ||
| s == Consumer Goods | −0.836 ** | −0.636 * |
| (0.328) | (0.338) | |
| sector == Financial | −1.562 *** | −1.343 *** |
| (0.361) | (0.383) | |
| sector == Healthcare | −1.183 *** | −1.028 ** |
| (0.425) | (0.434) | |
| sector == Industrial Goods | −1.405 *** | −1.307 *** |
| (0.365) | (0.379) | |
| sector == Services | −1.422 *** | −1.240 *** |
| (0.333) | (0.342) | |
| sector == Technology | −1.810 *** | −1.757 *** |
| (0.333) | (0.339) | |
| sector == Utilities | −0.981 * | −0.829 |
| (0.553) | (0.546) | |
| Constant (Basic materials) | −2.676 *** | −1.462 |
| (0.807) | (5.966) | |
| Observations | 296 | 296 |
| R2 | 0.394 | 0.427 |
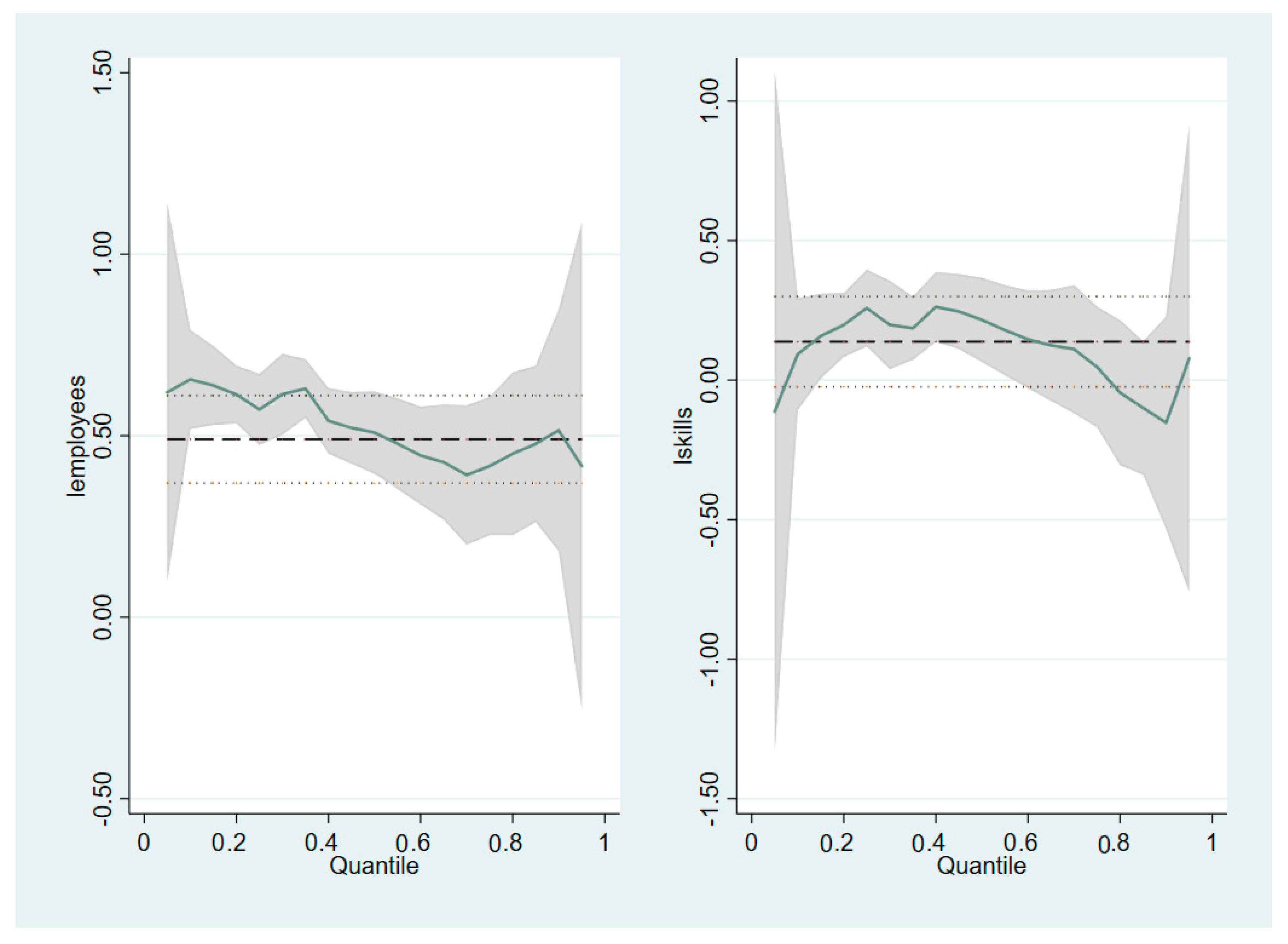
| Q(0.1) | Q(0.25) | Q(0.5) | Q(0.75) | Q(0.90) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue(billions)→ | 1.53 | 3.42 | 13 | 39 | 93 |
| Log employees | 0.655 *** | 0.572 *** | 0.509 *** | 0.416 *** | 0.515 *** |
| (0.090) | (0.053) | (0.067) | (0.096) | (0.126) | |
| Log skills | 0.0933 | 0.258 *** | 0.216 * | 0.0469 | −0.153 |
| (0.121) | (0.071) | (0.090) | (0.129) | (0.168) | |
| N | 296 | 296 | 296 | 296 | 296 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paniagua, J.; Peris-Ortiz, M.; Korzynski, P. Talent Goes Social: Online Corporate Networking and Business Performance. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8660. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208660
Paniagua J, Peris-Ortiz M, Korzynski P. Talent Goes Social: Online Corporate Networking and Business Performance. Sustainability. 2020; 12(20):8660. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208660
Chicago/Turabian StylePaniagua, Jordi, Marta Peris-Ortiz, and Pawel Korzynski. 2020. "Talent Goes Social: Online Corporate Networking and Business Performance" Sustainability 12, no. 20: 8660. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208660
APA StylePaniagua, J., Peris-Ortiz, M., & Korzynski, P. (2020). Talent Goes Social: Online Corporate Networking and Business Performance. Sustainability, 12(20), 8660. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208660






