An Improved Hybrid Highway Traffic Flow Prediction Model Based on Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise
2.2. Improved Permutation Entropy (PE)
2.2.1. Permutation Entropy
2.2.2. Improved Weighted Permutation Entropy
2.2.3. Least-Squares Support Vector Machine (LSSVM) Model
2.2.4. Parameter Optimization for LSSVM
3. Highway Traffic Flow Forecasting Model
3.1. The Proposed Highway Traffic Flow Prediction Model
3.2. Performance Criteria
4. Experimental Verification
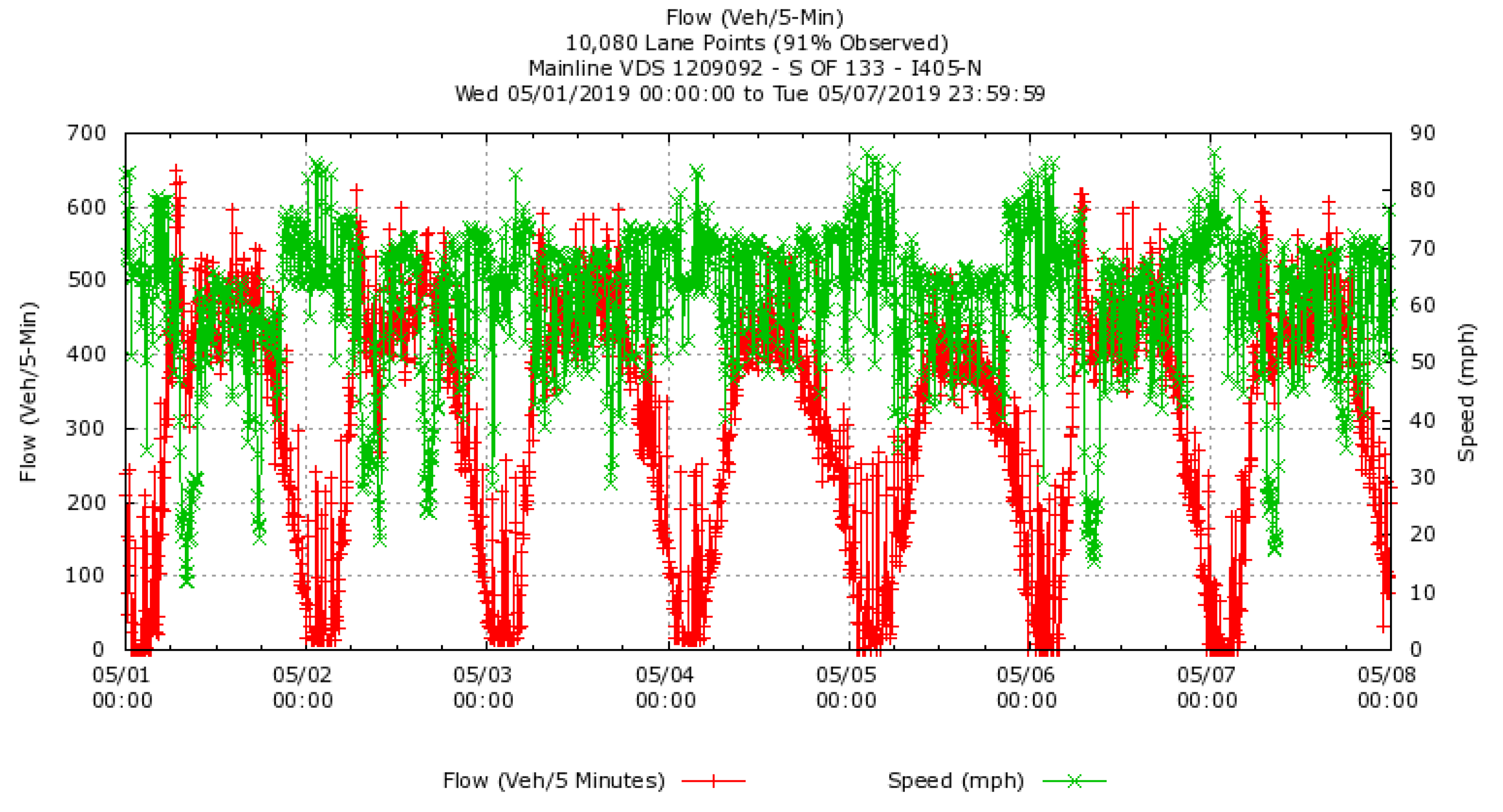
4.1. Experimental Data Description
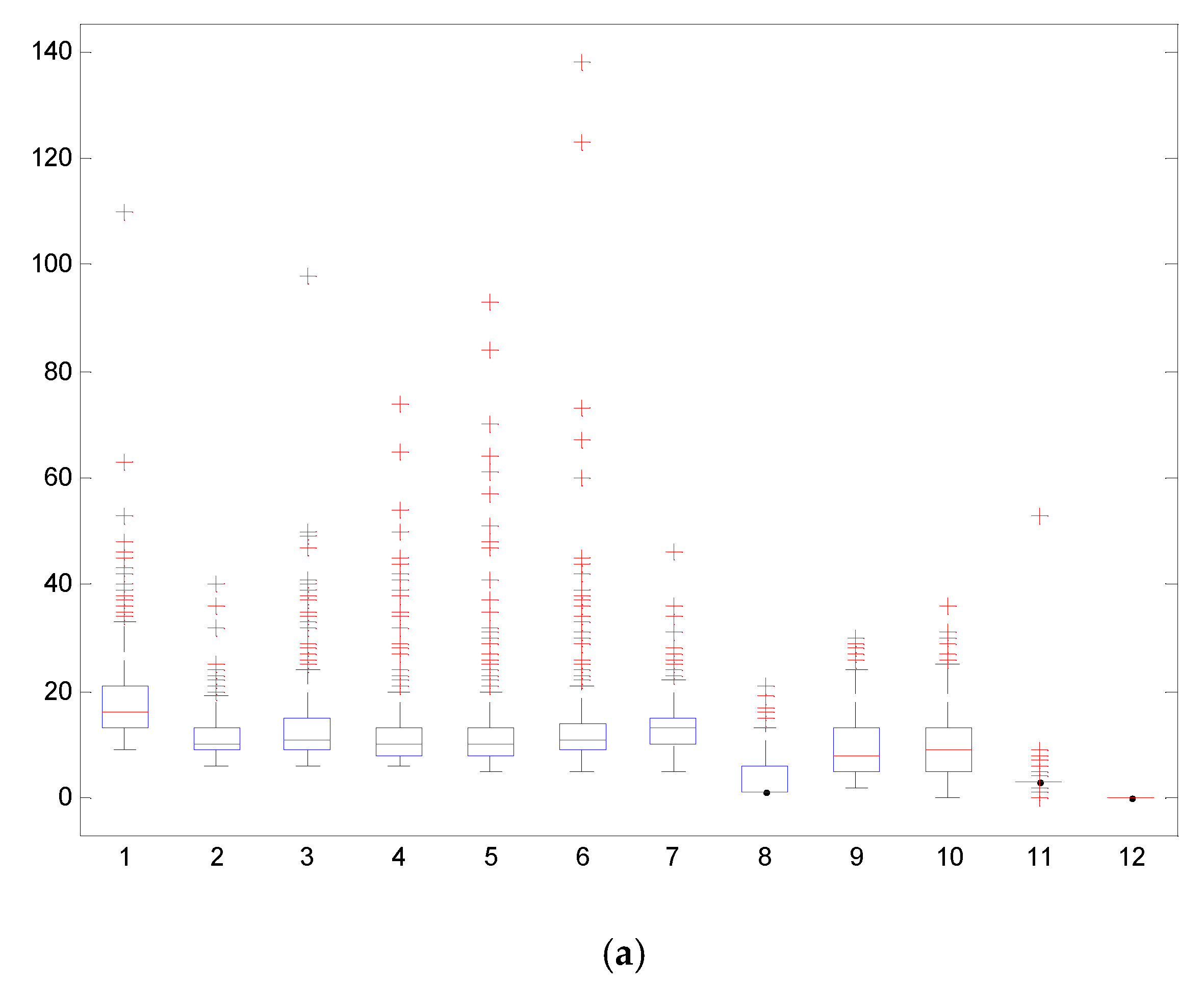
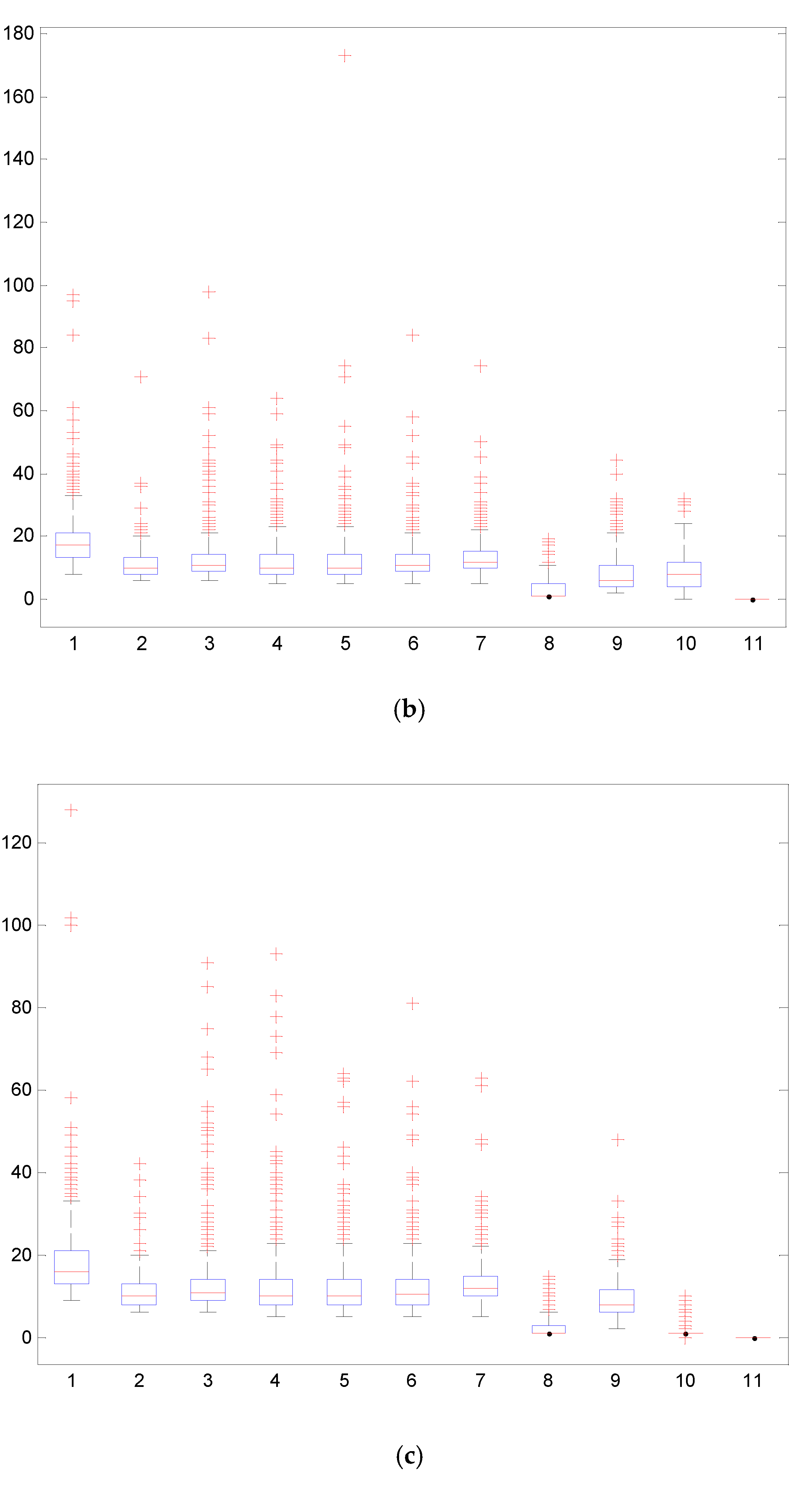
4.2. Traffic Flow Time-Series Decomposition and Reconstruction with the CEEMDAN-IWPE Method
4.3. Highway Traffic Flow Forecasting Results and Analysis
4.3.1. Highway Traffic Flow Forecasting
4.3.2. Comparison Models
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.; Kabuka, M.R. Combining weather condition data to predict traffic flow: A GRU-based deep learning approach. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 12, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djenouri, Y.; Belhadi, A.; Lin, J.C.W.; Cano, A. Adapted K-Nearest Neighbors for Detecting Anomalies on Spatio-Temporal Traffic Flow. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 10015–10027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.X.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, D.; Fu, J. Equilibrium between Road Traffic Congestion and Low-Carbon Economy: A Case Study from Beijing, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.B.; Han, G.J.; Wang, X.; Guizani, M.; Fan, K.G.; Shu, L. A Node Location Algorithm Based on Node Movement Prediction in Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 3166–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Ye, E. Lane density optimisation of automated vehicles for highway congestion control. Transp. B 2019, 7, 1096–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.C.; Huang, J.L. How to Mitigate Traffic Congestion Based on Improved Ant Colony Algorithm: A Case Study of a Congested Old Area of a Metropolis. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesiani, F.; Moreira-Matias, L.; Faizrahnemoon, M. On Learning from Inaccurate and Incomplete Traffic Flow Data. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 3698–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, M.; Kashmiri, F.A.; Naeem, H.; Yan, H.M.; Qi, X.; Rizvi, S.M.A.; Wang, T.S.; Lu, H.P. An Assessment of Age and Gender Characteristics of Mixed Traffic with Autonomous and Manual Vehicles: A Cellular Automata Approach. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Luca, S.; Di Pace, R.; Memoli, S.; Pariota, L. Sustainable Traffic Management in an Urban Area: An Integrated Framework for Real-Time Traffic Control and Route Guidance Design. Sustainability 2020, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, M. Evaluation of Traffic Assignment Models through Simulation. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.M. Modeling and Forecasting Vehicular Traffic Flow as a Seasonal Stochastic Time Series Process; University of Virginia: Charlottesville, VA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Jomnonkwao, S.; Uttra, S.; Ratanavaraha, V. Forecasting Road Traffic Deaths in Thailand: Applications of Time-Series, Curve Estimation, Multiple Linear Regression, and Path Analysis Models. Sustainability 2020, 12, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okutani, I.; Stephanedes, Y.J. Dynamic Prediction of Traffic Volume Through Kalman Filtering Theory. Transp. Res. B-Meth. 1984, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, A.; Sarvi, M.; Bagloee, S.A. Short-term traffic flow prediction based on faded memory Kalman Filter fusing data from connected vehicles and Bluetooth sensors. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2020, 102, 102025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.R.; Zhang, Z.C.; Yang, J.J.; Yu, Y.D.; Zhou, T.; Qin, J. A noise-immune Kalman filter for short-term traffic flow forecasting. Phys. A 2019, 536, 122601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, C.; Kockelman, K.M. Chaos theory and transportation systems—Instructive example. Stat. Methods Saf. Data Anal. Eval. 2004, 1897, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adewumi, A.; Kagamba, J.; Alochukwu, A. Application of Chaos Theory in the Prediction of Motorised Traffic Flows on Urban Networks. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 5656734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Neto, M.; Jeong, Y.S.; Jeong, M.K.; Han, L.D. Online-SVR for short-term traffic flow prediction under typical and atypical traffic conditions. Expert Syst Appl. 2009, 36, 6164–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, L.; Tsekeris, T.; Stathopoulos, A. Adaptive hybrid fuzzy rule-based system approach for modeling and predicting urban traffic flow. Transp. Res. C-Emerg. Techonol. 2008, 16, 554–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, H.; Sankar, S.; Daraghmi, Y.A.; Tiwari, P.; Rattagan, E.; Mohanty, M.; Puthal, D.; Prasad, M. Accurate Traffic Flow Prediction in Heterogeneous Vehicular Networks in an Intelligent Transport System Using a Supervised Non-Parametric Classifier. Sensors 2018, 18, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratsas, C.; Koupidis, K.; Salanova, J.M.; Giannakopoulos, K.; Kaloudis, A.; Aifadopoulou, G. A Comparison of Machine Learning Methods for the Prediction of Traffic Speed in Urban Places. Sustainability 2020, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.R.; Chen, Q.; Cai, W.H.; Xu, X.M.; Zhou, T.; Qin, J. SVRGSA: A hybrid learning based model for short-term traffic flow forecasting. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 13, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P.; Zhao, L.N.; Li, S.Q.; Wen, X.Y.; Xiong, Y. Short Term Traffic Flow Prediction of Urban Road Using Time Varying Filtering Based Empirical Mode Decomposition. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Huang, C.; Cao, J.D.; Lu, J.Q.; Huang, W.; Guo, J.H.; Wei, Y. Short-Term Traffic Flow Prediction Based on Least Square Support Vector Machine with Hybrid Optimization Algorithm. Neural Process. Lett. 2019, 50, 2305–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.B.; Cai, X.W.; Liang, J.; Liu, Q.C. Ensemble Learning Multiple LSSVR With Improved Harmony Search Algorithm for Short-Term Traffic Flow Forecasting. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 9347–9357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackenzie, J.; Roddick, J.F.; Zito, R. An Evaluation of HTM and LSTM for Short-Term Arterial Traffic Flow Prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, J. Vulnerability Assessment for Cascading Failure in the Highway Traffic System. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena-Oreja, J.; Gozalvez, J. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Deep Learning-Based Techniques for Traffic Prediction. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 91188–91212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Zheng, S.; Long, S.R.; Wu, M.C.; Shih, H.H.; Quanan, Z.; Yen, N.-C.; Tung, C.C.; Liu, H.H. The Empirical Mode Decomposition and the Hilbert Spectrum for Nonlinear and Non-Stationary Time Series Analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 1998, 454, 903–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.E.; Wu, M.L.C.; Long, S.R.; Shen, S.S.P.; Qu, W.D.; Gloersen, P.; Fan, K.L. A confidence limit for the empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectral analysis. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2003, 459, 2317–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition: A Noise-Assisted Data Analysis Method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2011, 1, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-R.; Shieh, J.-S.; Huang, N.E. Complementary Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition: A Novel Noise Enhanced Data Analysis Method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2011, 2, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jombo, G.; Shu, L. Adaptive Multiscale Weighted Permutation Entropy for Rolling Bearing Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 87529–87540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suykens, J.A.K.; Vandewalle, J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process. Lett. 1999, 9, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V.N. Support Vector Networks. Machine Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tashi, Q.; Abdulkadir, S.J.; Rais, H.M.; Mirjalili, S.; Alhussian, H.; Ragab, M.G.; Alqushaibi, A. Binary Multi-Objective Grey Wolf Optimizer for Feature Selection in Classification. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 106247–106263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caltrans Performance Measurement System. Available online: http://pems.dot.ca.gov/ (accessed on 8 May 2020).



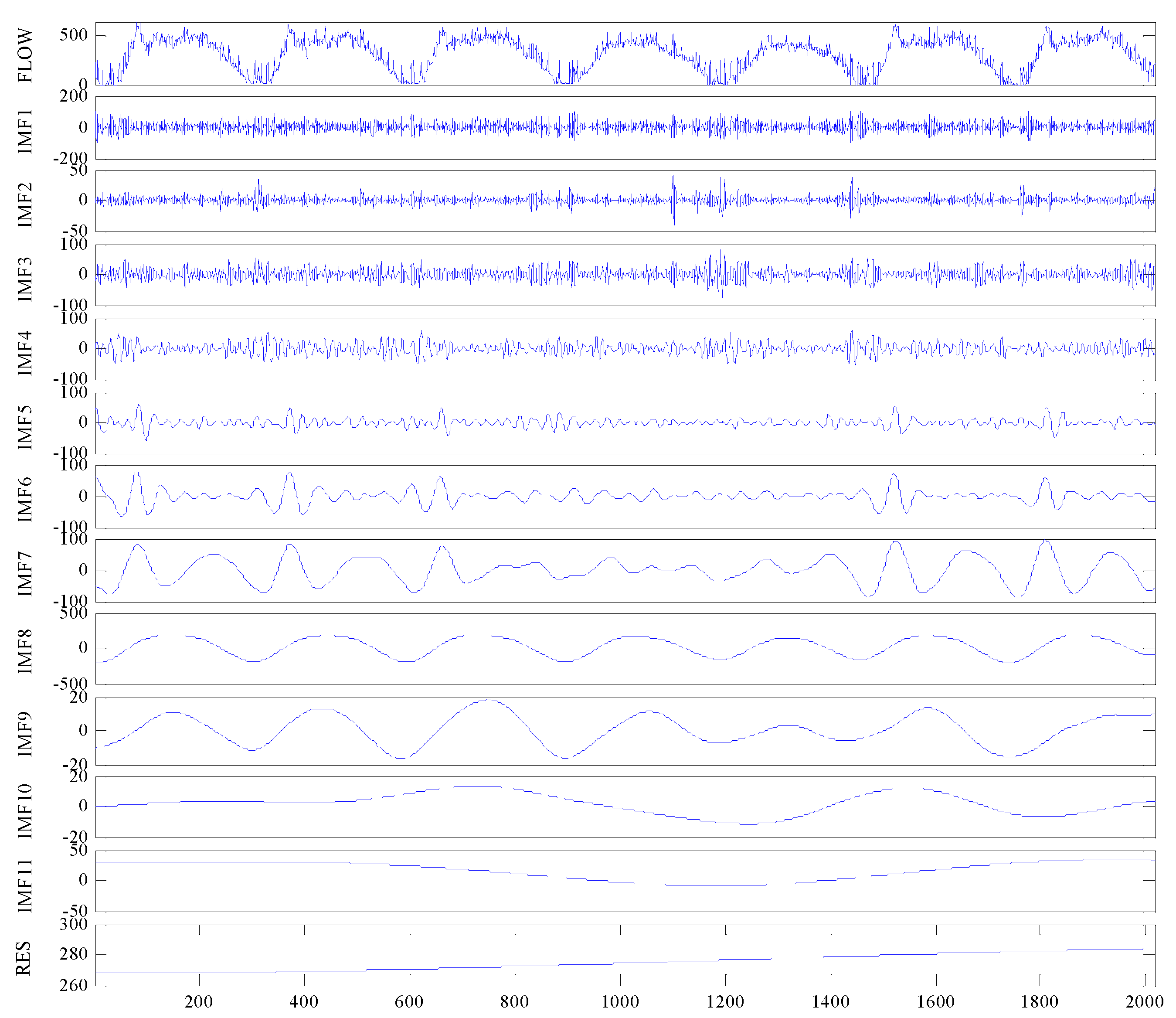
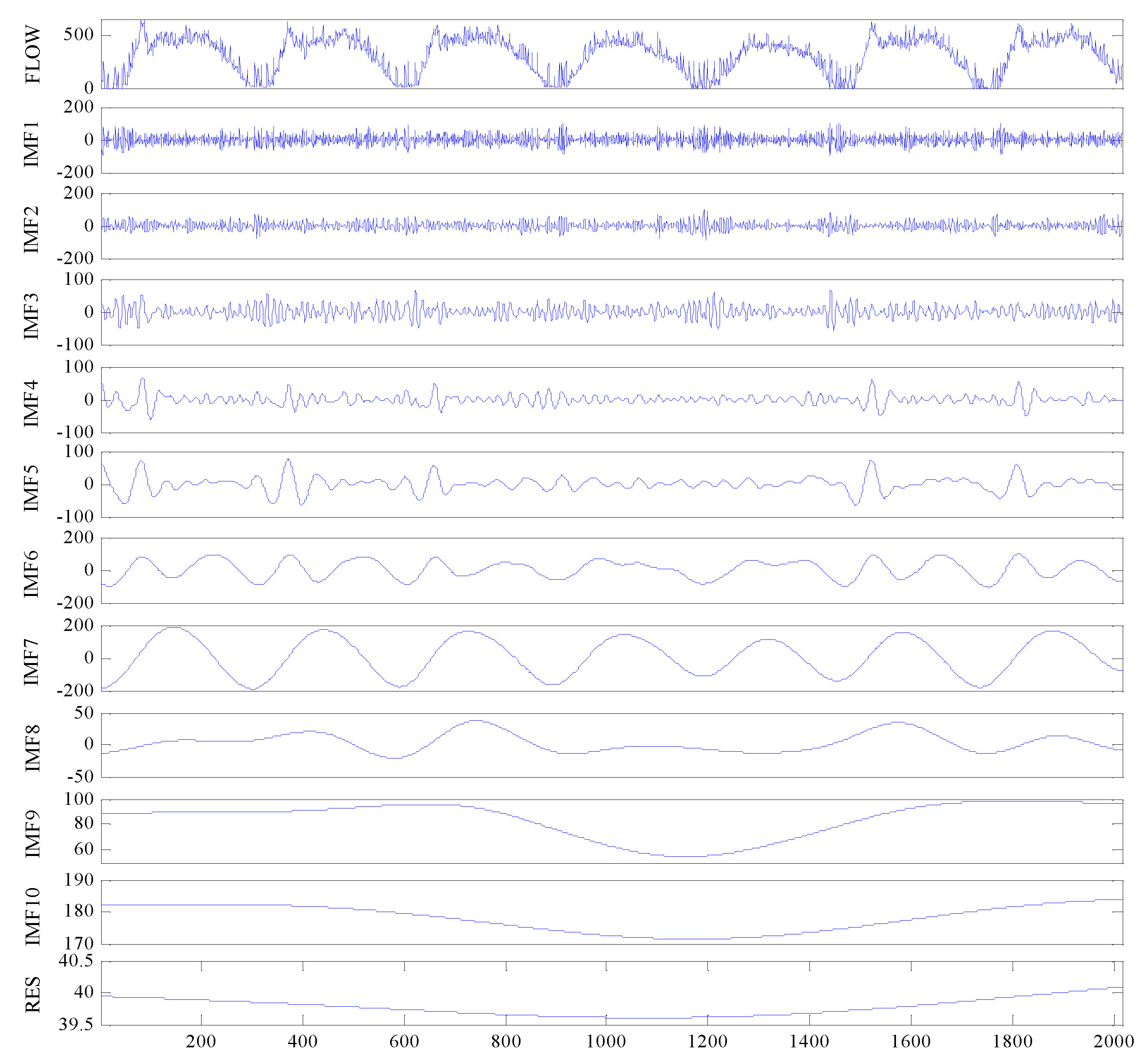
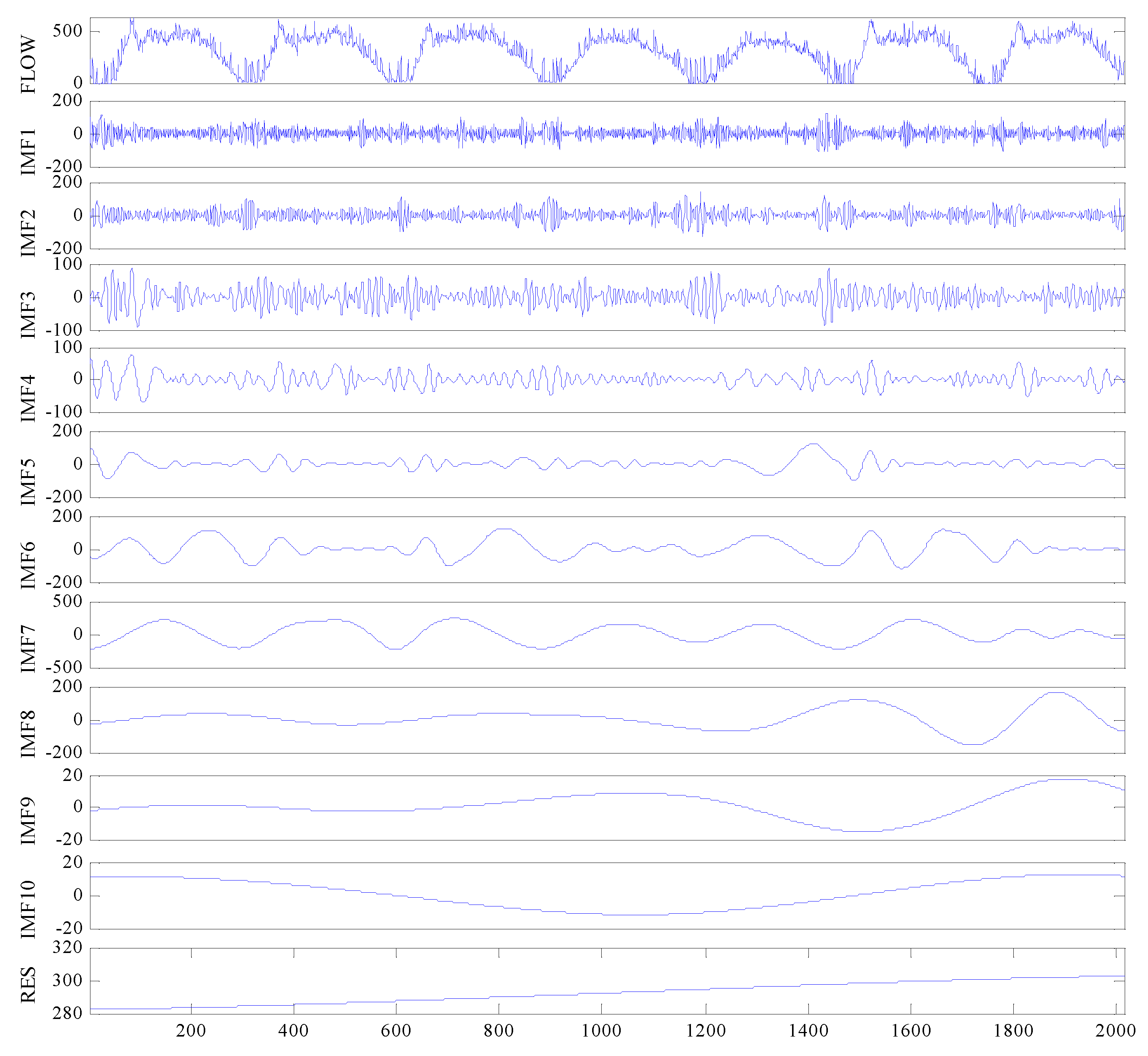
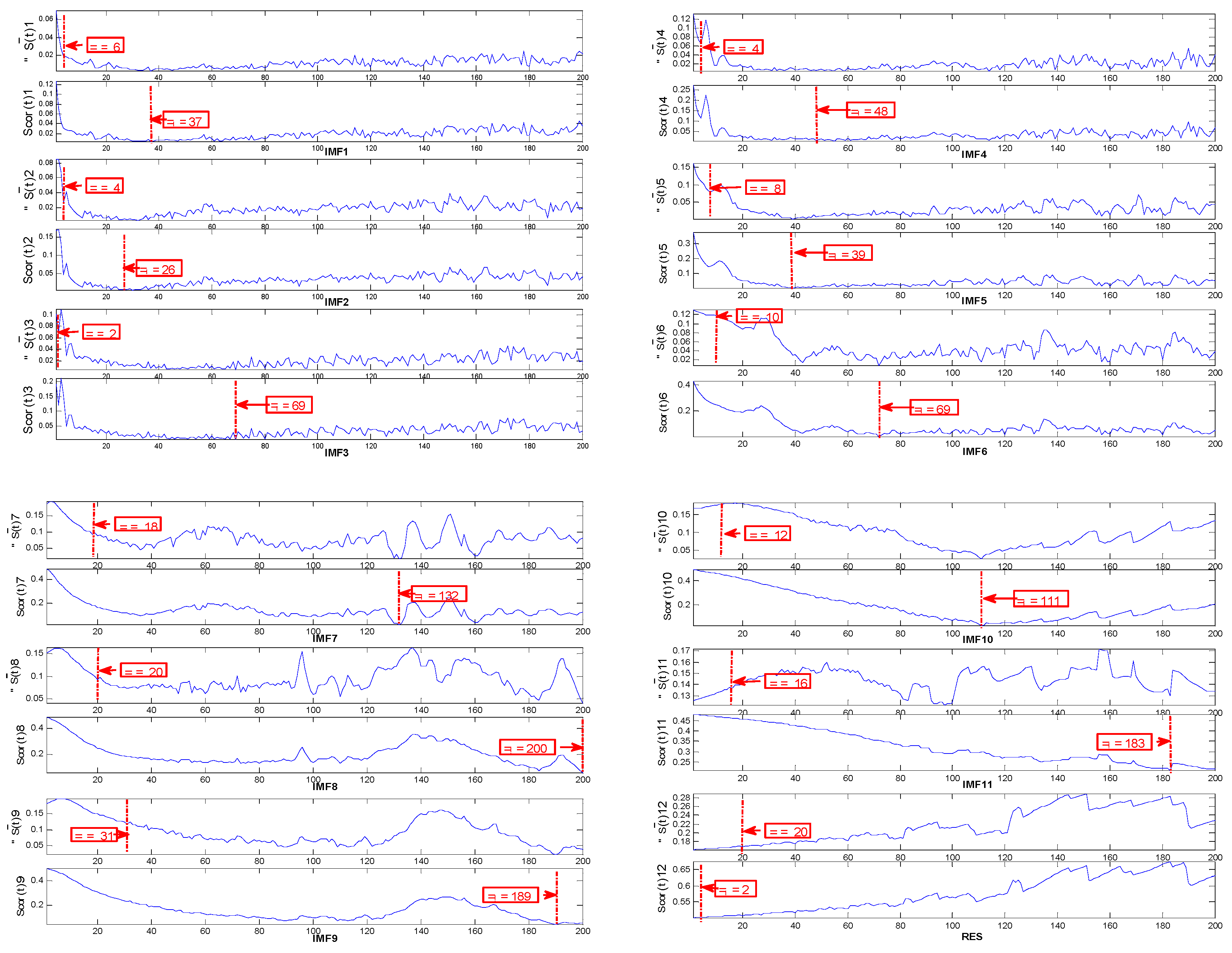
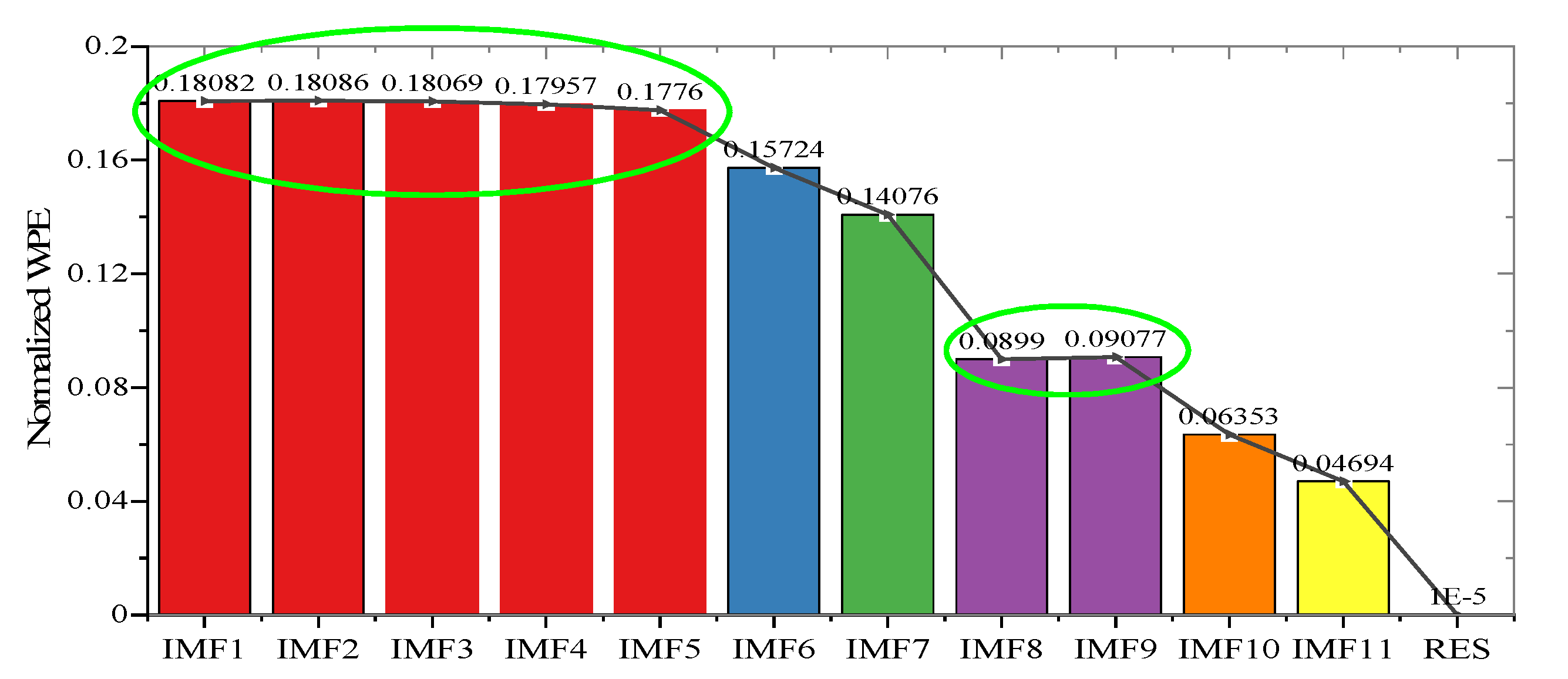


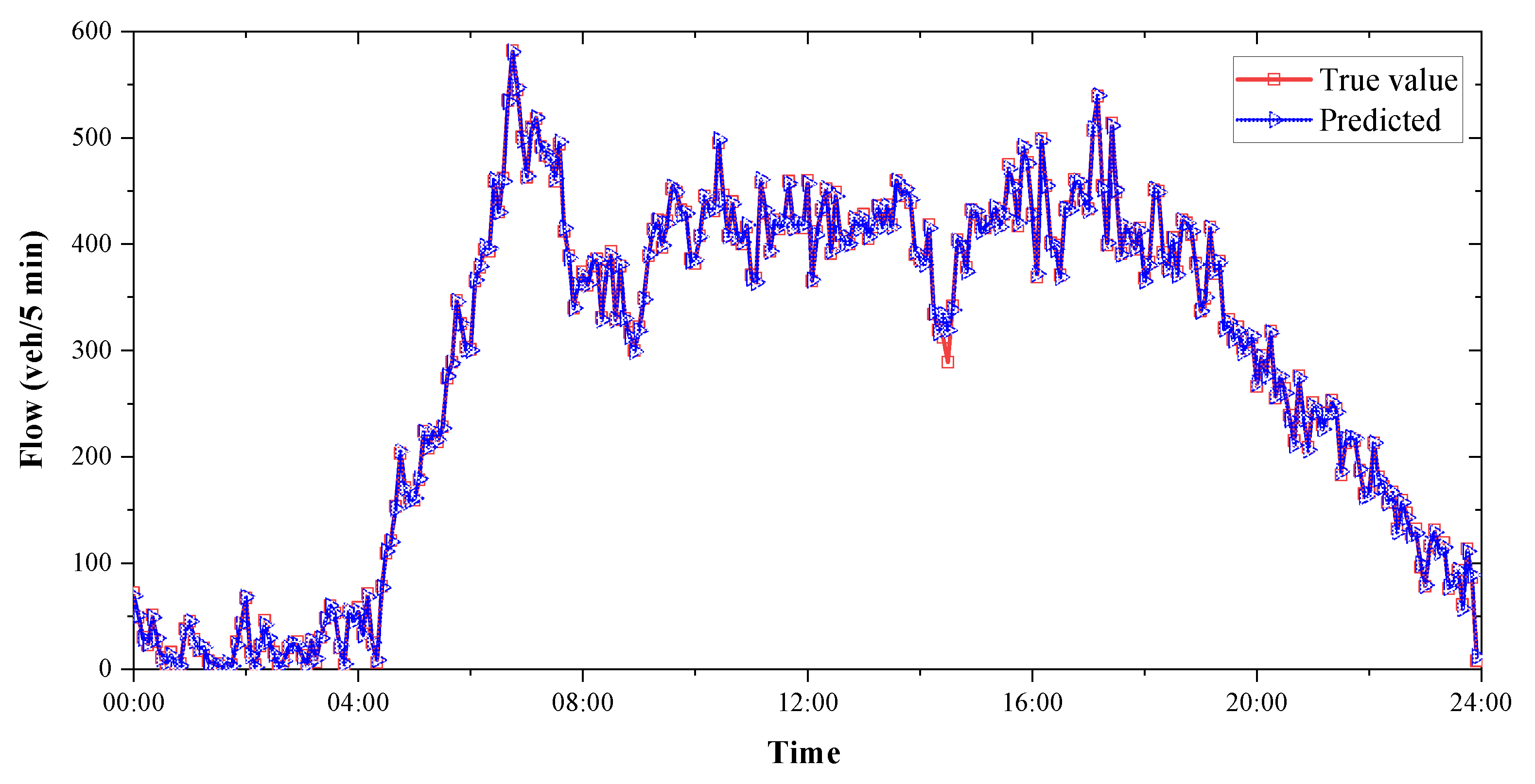
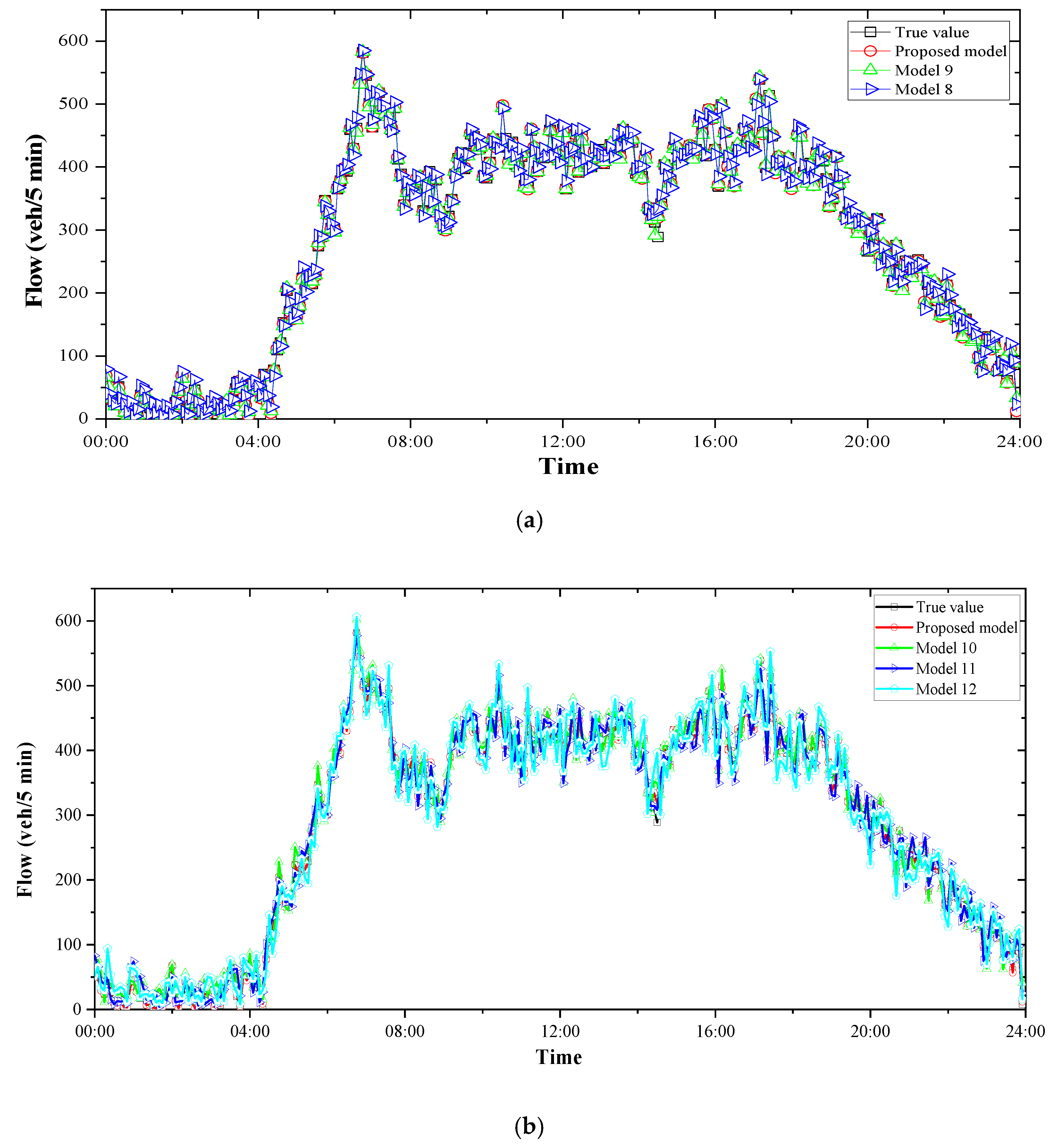
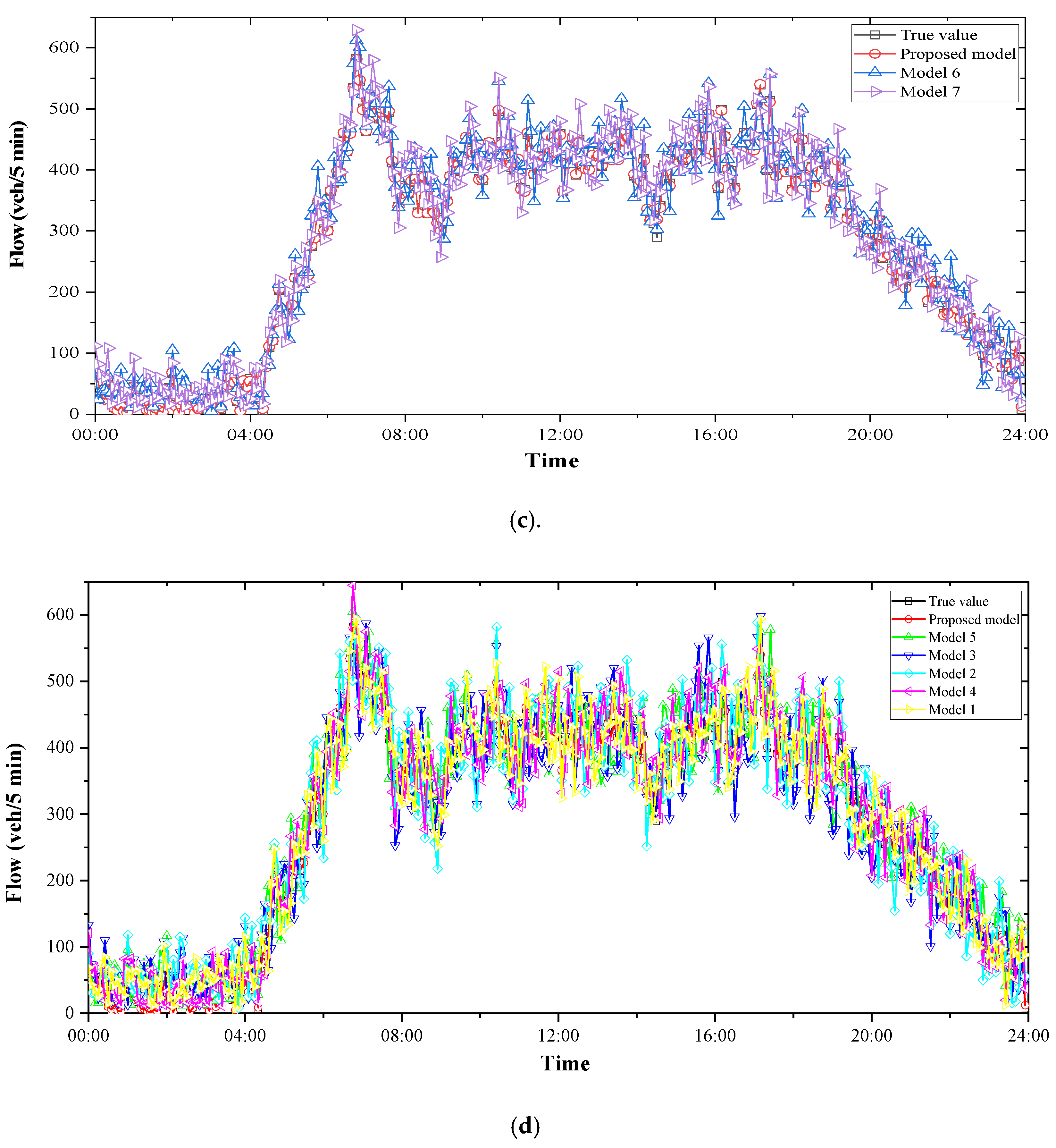
| Component | τ | d | PE | IWPE Value | Normalized IWPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMF1 | 6 | 7 | 1.31962 | 1.18967 | 0.18082 |
| IMF2 | 4 | 8 | 1.30611 | 1.18989 | 0.18086 |
| IMF3 | 2 | 37 | 1.31503 | 1.18881 | 0.18069 |
| IMF4 | 4 | 13 | 1.31713 | 1.18144 | 0.17957 |
| IMF5 | 8 | 6 | 1.27613 | 1.16850 | 0.17760 |
| IMF6 | 10 | 8 | 1.02311 | 1.03449 | 0.15724 |
| IMF7 | 18 | 9 | 0.88203 | 0.92609 | 0.14076 |
| IMF8 | 20 | 11 | 0.52279 | 0.59146 | 0.08990 |
| IMF9 | 31 | 7 | 0.49014 | 0.59723 | 0.09077 |
| IMF10 | 12 | 10 | 0.31855 | 0.41780 | 0.06353 |
| IMF11 | 16 | 12 | 0.16218 | 0.30883 | 0.04694 |
| RES | 20 | 1 | 0.00203 | 0.00120 | 0.00001 |
| Model | Model Instruction | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|
| proposed model | a hybrid model of CEEMDAN with IWPE for raw traffic data decomposition and GWO optimized LSSVM for prediction | CEEMDAN-IWPE-LSSVM-GWO |
| Model 1 | Least-squares support vector machine model | LSSVM |
| Model 2 | Back-propagation neural network model | BP |
| Model 3 | Support vector machine model | SVM |
| Model 4 | Autoregression moving average model | ARIMA |
| Model 5 | GWO-optimized LSSVM model | LSSVM-GWO |
| Model 6 | a hybrid model of EMD with IWPE and GWO-optimized LSSVM | EMD-IWPE-LSSVM-GWO |
| Model 7 | a hybrid model of EEMD with IWPE and GWO-optimized LSSVM | EEMD-IWPE-LSSVM-GWO |
| Model 8 | a hybrid model of CEEMDAN with IWPE and LSSVM | CEEMDAN-IWPE-LSSVM |
| Model 9 | a hybrid model of CEEMDAN with PE and GWO optimized LSSVM | CEEMDAN-PE-LSSVM-GWO |
| Model 10 | a hybrid model of CEEMDAN with IWPE and BP | CEEMDAN-IWPE-BP |
| Model 11 | a hybrid model of CEEMDAN with IWPE and SVM | CEEMDAN-IWPE-SVM |
| Model 12 | a hybrid model of CEEMDAN with IWPE and ARIMA | CEEMDAN-IWPE-ARIMA |
| Forecasting Model | MAE | RMSE | EC | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed model | 1.9167 | 2.2623 | 0.992 | 1 |
| Model 1 | 22.4542 | 28.1592 | 0.919 | 10 |
| Model 2 | 24.6958 | 32.1445 | 0.907 | 12 |
| Model 3 | 23.5438 | 29.7531 | 0.914 | 11 |
| Model 4 | 26.0764 | 31.4462 | 0.875 | 13 |
| Model 5 | 21.3694 | 26.6698 | 0.932 | 9 |
| Model 6 | 19.8924 | 24.5237 | 0.946 | 7 |
| Model 7 | 21.0938 | 25.4538 | 0.941 | 8 |
| Model 8 | 7.7882 | 9.1956 | 0.981 | 3 |
| Model 9 | 3.0799 | 4.0412 | 0.984 | 2 |
| Model 10 | 12.3194 | 14.8003 | 0.978 | 4 |
| Model 11 | 13.5625 | 15.7054 | 0.966 | 5 |
| Model 12 | 14.3958 | 18.7354 | 0.953 | 6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Chu, R.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Luan, S. An Improved Hybrid Highway Traffic Flow Prediction Model Based on Machine Learning. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8298. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208298
Wang Z, Chu R, Zhang M, Wang X, Luan S. An Improved Hybrid Highway Traffic Flow Prediction Model Based on Machine Learning. Sustainability. 2020; 12(20):8298. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208298
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhanzhong, Ruijuan Chu, Minghang Zhang, Xiaochao Wang, and Siliang Luan. 2020. "An Improved Hybrid Highway Traffic Flow Prediction Model Based on Machine Learning" Sustainability 12, no. 20: 8298. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208298
APA StyleWang, Z., Chu, R., Zhang, M., Wang, X., & Luan, S. (2020). An Improved Hybrid Highway Traffic Flow Prediction Model Based on Machine Learning. Sustainability, 12(20), 8298. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12208298





