Assessment of Ventilation Efficiency in School Classrooms Based on Indoor–Outdoor Particulate Matter and Carbon Dioxide Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CO2-Based Method
2.2. PM-Based Method
3. Results and Discussion
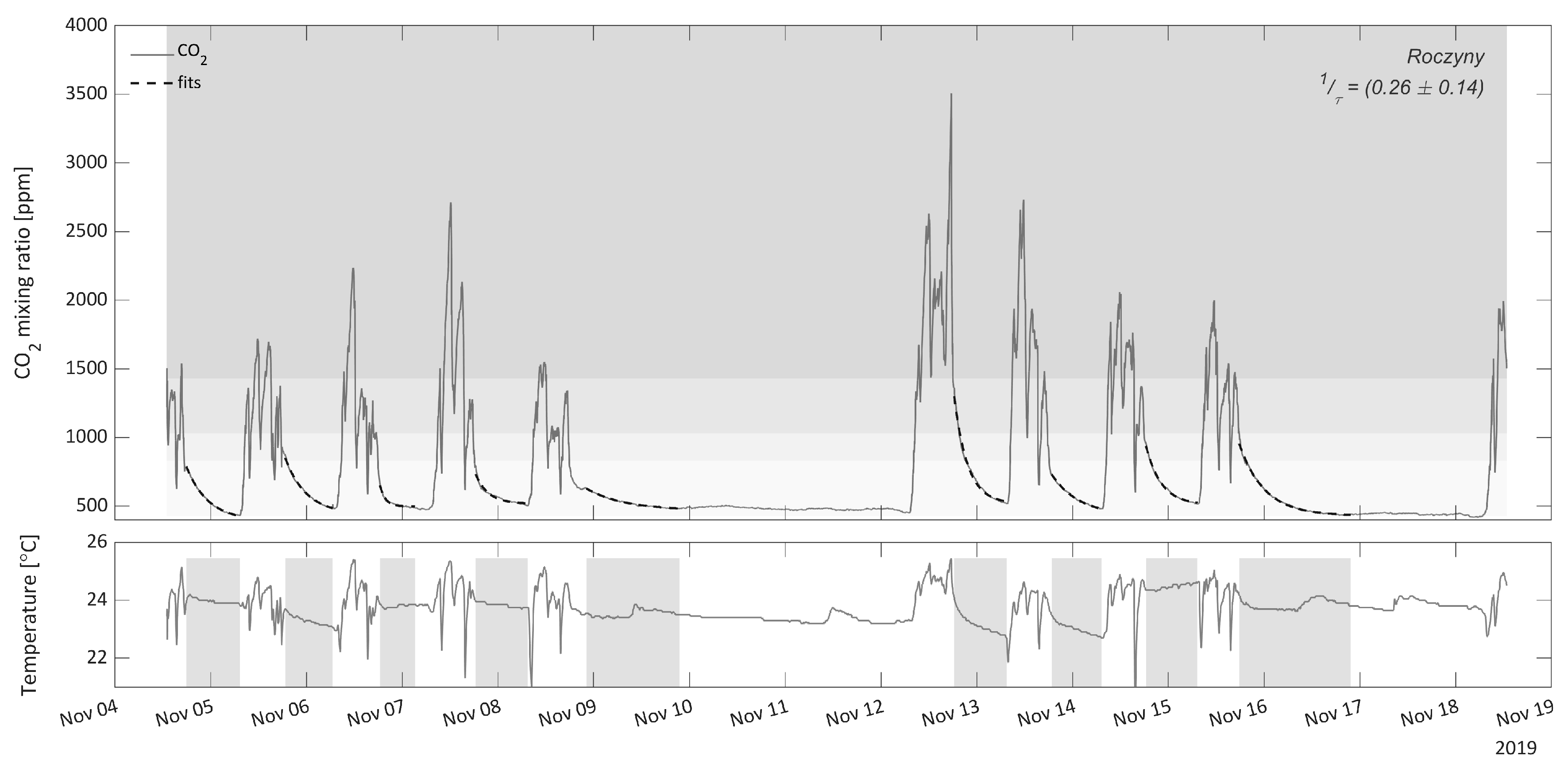
3.1. CO2
3.2. PM
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Błaszczyk, E.; Rogula-Kozłowska, W.; Klejnowski, K.; Kubiesa, P.; Fulara, I.; Mielżyńska-Švach, D. Indoor Air Quality in Urban and Rural Kindergartens: Short-Term Studies in Silesia, Poland. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2017, 10, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainka, A.; Zajusz-Zubek, E.; Kaczmarek, K. PM10 Composition in Urban & Rural Nursery Schools in Upper Silesia, Poland: A Trace Elements Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 61, 98–118. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, S.D.; Podstawczyńska, A. Improved Method for Characterising Temporal Variability in Urban Air Quality Part II: Particulate Matter and Precursors in Central Poland. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 219, 117040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, L.; Ayoko, G.A.; Bae, G.N.; Buonanno, G.; Chao, C.Y.H.; Clifford, S.; Fu, S.C.; Hänninen, O.; He, C.; Isaxon, C.; et al. Airborne Particles in Indoor Environment of Homes, Schools, Offices and Aged Care Facilities: The Main Routes of Exposure. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Regional Office for Europe. Health Aspects of Air Pollution with Particulate Matter, Ozone and Nitrogen Dioxide; WHO Regional Office for Europe: Bonn, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kozielska, B.; Mainka, A.; Żak, M.; Kaleta, D.; Mucha, W. Indoor Air Quality in Residential Buildings in Upper Silesia, Poland. Build. Environ. 2020, 177, 106914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozielska, B.; Brągoszewska, E.; Kaleta, D. Investigation of Indoor Air Quality in Offices and Residential Homes in an Urban Area of Poland. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahyuddin, N.; Awbi, H.B. A Review of CO2 Measurement Procedures in Ventilation Research. Int. J. Vent. 2012, 10, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish, U.; Mendell, M.J.; Shekhar, K.; Hotchi, T.; Sullivan, D.; Streufert, S.; Fisk, W.J. Is CO2 an Indoor Pollutant? Direct Effects of Low-to-Moderate CO2 Concentrations on Human Decision-Making Performance. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1671–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CEN (European Committee for Standardization). Ventilation for Non-Residential Buildings - Performance Requirements for Ventilation and Room Conditioning Systems. Ital. Stand. 2005, 1, 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Kameishi, K.; Onishi, S.; Ito, K. Field-Based Study on the Energy-Saving Effects of CO2 Demand Controlled Ventilation in an Office with Application of Energy Recovery Ventilators. Energy Build. 2014, 68, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Cohen, M.; Stabat, P.; Marchio, D. CO2 Tracer Gas Concentration Decay Method for Measuring Air Change Rate. Build. Environ. 2015, 84, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloszewski, P.; Zuber, A. Lumped Parameter Models for the Interpretation of Environmental Tracer Data. In Manual on Mathematical Models in Isotope Hydrogeology, TECDOC-910; IAEA, Ed.; International Atomic Energy Agency Publishing Section: Vienna, Austria, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Geyh, M. Volume IV Groundwater: Saturated and Unsaturated Zone. In Environmental Isotopes in the Hydrological Cycle Principles and Applicationst; Mook, W.G., Ed.; International Atomic Energy Agency Publishing Section: Paris, France, 2000; pp. 308–424. [Google Scholar]
- Zuber, A.; Maloszewschi, P.; Campana, P.E.; Harrington, G.A.; Tezcan, L.; Konikow, K.L. Volume VI Modelling. In Environmental Isotopes in the Hydrological Cycle Principles and Applicationst; Mook, W.G., Yurtsever, Y., Eds.; International Atomic Energy Agency Publishing Section: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 488–570. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, B. Review of Relationship between Indoor and Outdoor Particles: I/O Ratio, Infiltration Factor and Penetration Factor. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wargocki, P.; Lian, Z.; Thyregod, C. Effects of Exposure to Carbon Dioxide and Bioeffluents on Perceived Air Quality, Self-Assessed Acute Health Symptoms, and Cognitive Performance. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niachou, K.; Hassid, S.; Santamouris, M.; Livada, I. Experimental Performance Investigation of Natural, Mechanical and Hybrid Ventilation in Urban Environment. Build. Environ. 2008, IV, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| N° | Measurement Period | Location | Ventilation System | Air Purification System | Declared Classroom Occupancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 04.11.2019–18.11.2019 | Roczyny | natural | in the classroom | 25 |
| 2 | 04.11.2019–18.11.2019 | Sidzina | natural | no | 19 |
| 3 | 20.11.2019–04.12.2019 | Skała | natural | in the classroom | 18 |
| 4 | 20.11.2019–04.12.2019 | Wolbrom | natural | no | 23 |
| 5 | 05.12.2019–19.12.2019 | Chocznia | mechanical | central | 25 |
| 6 | 05.12.2019–19.12.2019 | Tomice | natural | no | 30 |
| 7 | 03.01.2020–20.01.2020 | Nowy Targ | natural | no | 22 |
| 8 | 03.01.2020–20.01.2020 | Paszyn | natural | no | 16 |
| 9 | 21.01.2020–04.02.2020 | Otwock | natural | no | 22 |
| 10 | 21.01.2020–04.02.2020 | Piastów | natural | no | 22 |
| N° | Air flux (m3/h) | AER (reg) (1/h) | AER (CO2) (1/h) | AER (PM) (1/h) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500 | 3.20 | (0.26 ± 0.14) | (0.19 ± 0.03) | (0.58 ± 0.02) |
| 2 | 380 | 2.82 | (0.39 ± 0.30) | (0.34 ± 0.05) | (0.58 ± 0.03) |
| 3 | 360 | 2.21 | (0.18 ± 0.05) | (0.13 ± 0.03) | (0.44 ± 0.02) |
| 4 | 460 | 2.57 | (0.16 ± 0.03) | (0.17 ± 0.04) | (0.56 ± 0.06) |
| 5 | 500 | 2.83 | no data | (0.76 ± 0.07) | (0.63 ± 0.02) |
| 6 | 600 | 2.86 | (0.26 ± 0.17) | (0.20 ± 0.02) | (0.42 ± 0.02) |
| 7 | 440 | 2.33 | (0.35 ± 0.14) | (0.27 ± 0.06) | (0.55 ± 0.02) |
| 8 | 320 | 2.93 | (1.47 ± 0.22) 1 | (0.38 ± 0.05) | (0.61 ± 0.02) |
| 9 | 440 | 2.38 | (0.05 ± 0.01) | (0.11 ± 0.04) | (0.49 ± 0.09) |
| 10 | 440 | 2.69 | (0.65 ± 0.33) | (0.77 ± 108.48) 1 | (0.60 ± 0.16) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bartyzel, J.; Zięba, D.; Nęcki, J.; Zimnoch, M. Assessment of Ventilation Efficiency in School Classrooms Based on Indoor–Outdoor Particulate Matter and Carbon Dioxide Measurements. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145600
Bartyzel J, Zięba D, Nęcki J, Zimnoch M. Assessment of Ventilation Efficiency in School Classrooms Based on Indoor–Outdoor Particulate Matter and Carbon Dioxide Measurements. Sustainability. 2020; 12(14):5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145600
Chicago/Turabian StyleBartyzel, Jakub, Damian Zięba, Jarosław Nęcki, and Mirosław Zimnoch. 2020. "Assessment of Ventilation Efficiency in School Classrooms Based on Indoor–Outdoor Particulate Matter and Carbon Dioxide Measurements" Sustainability 12, no. 14: 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145600
APA StyleBartyzel, J., Zięba, D., Nęcki, J., & Zimnoch, M. (2020). Assessment of Ventilation Efficiency in School Classrooms Based on Indoor–Outdoor Particulate Matter and Carbon Dioxide Measurements. Sustainability, 12(14), 5600. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145600






