Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer on Soil CO2 Emission Depends on Crop Rotation Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
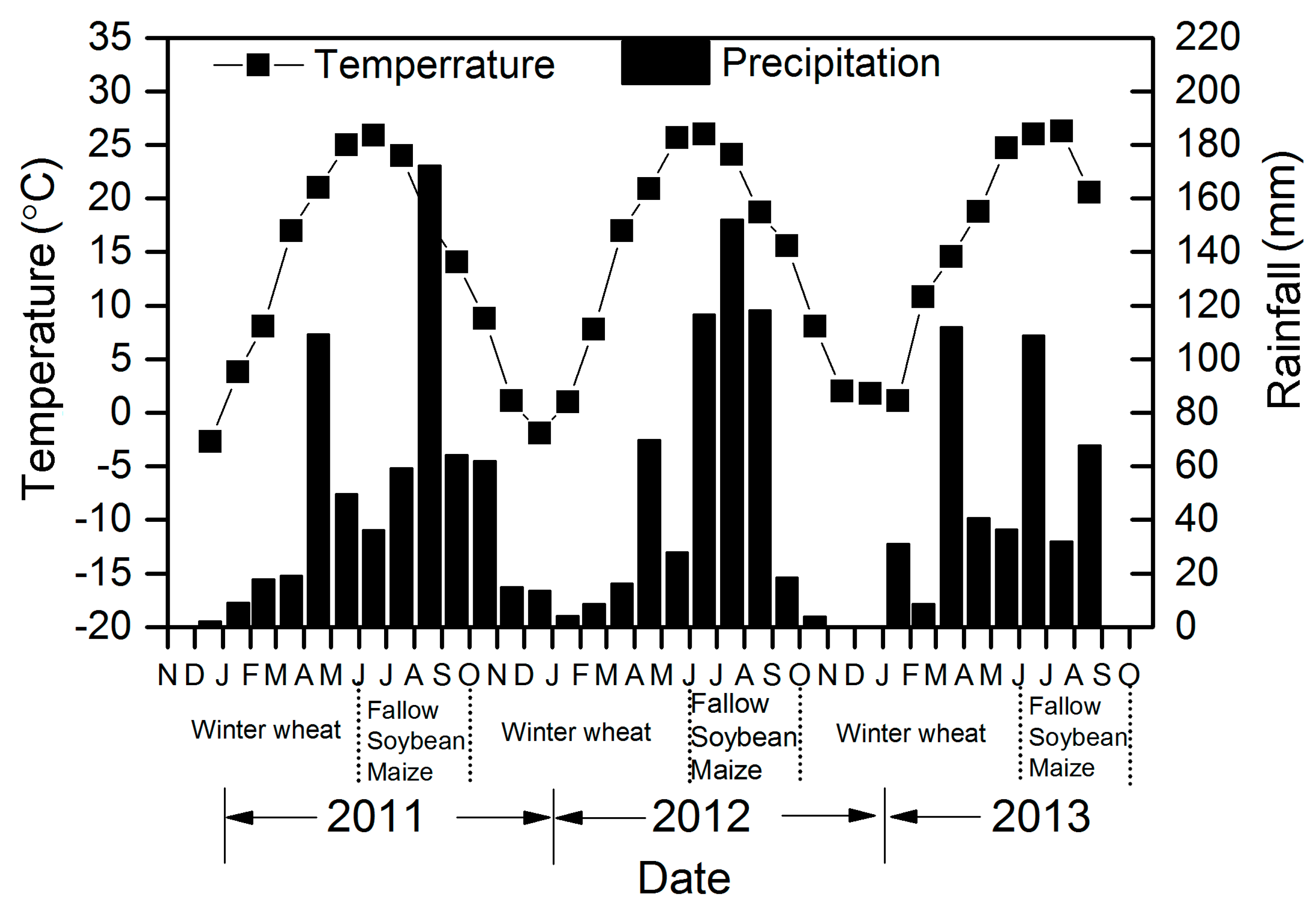
2.1. Site Description
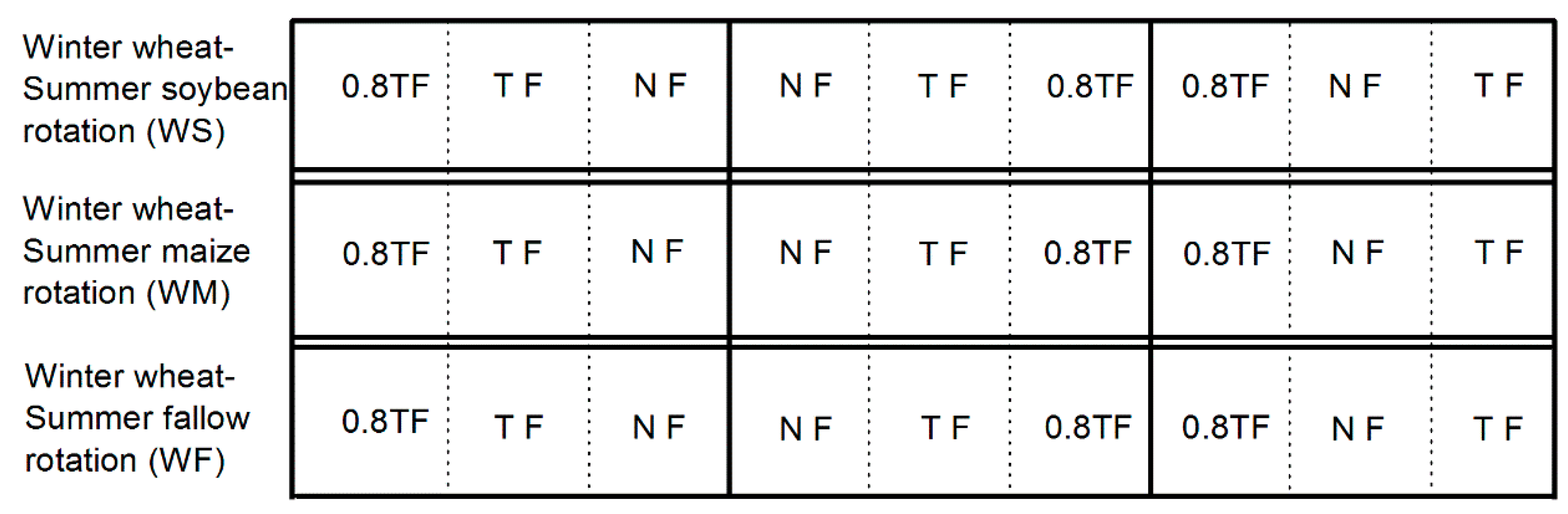
2.2. Experimental Design and Management
2.3. Soil CO2 Emission Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
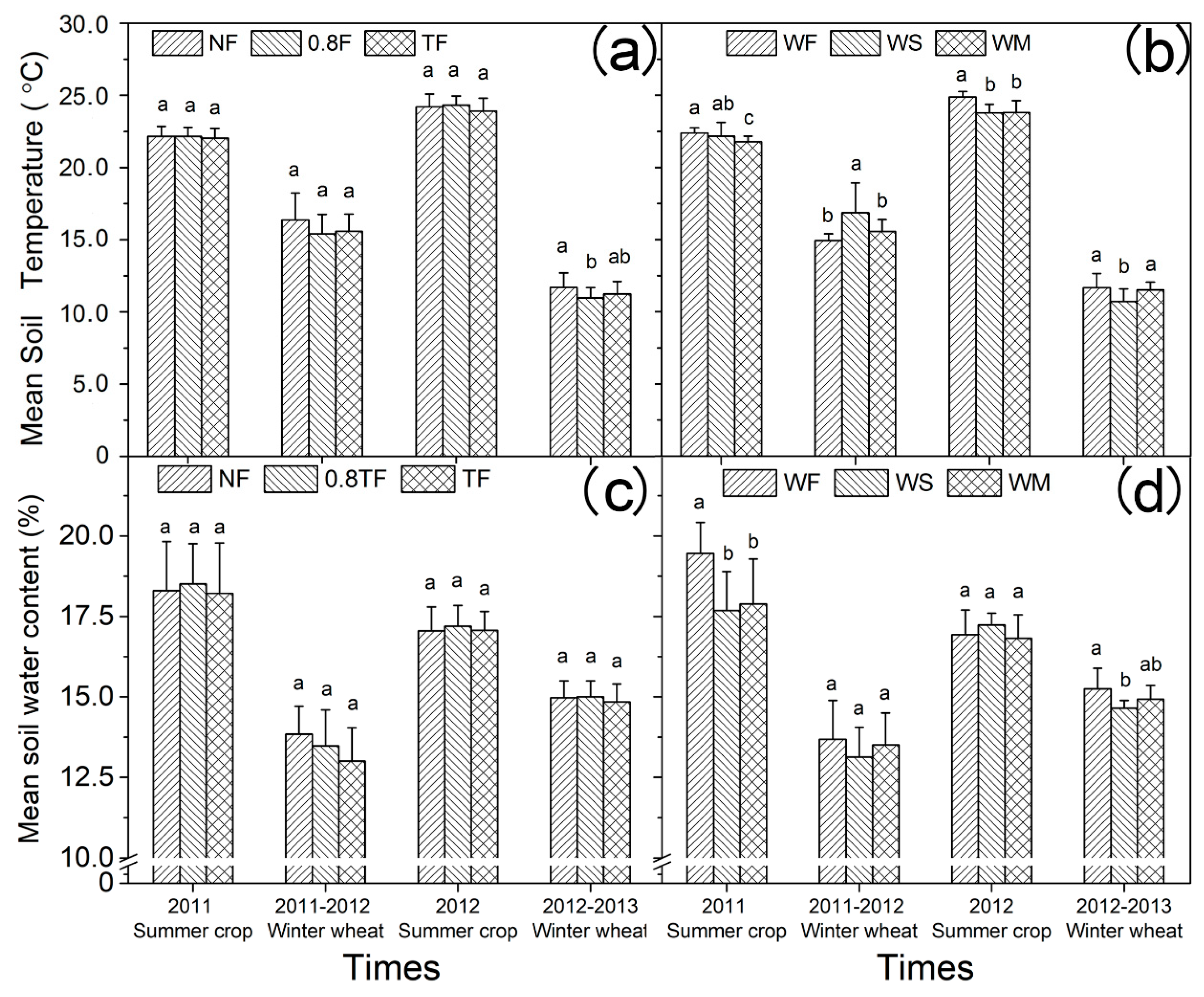
3.1. Soil Temperature and Moisture Content
3.2. Soil Organic Carbon (SOC)
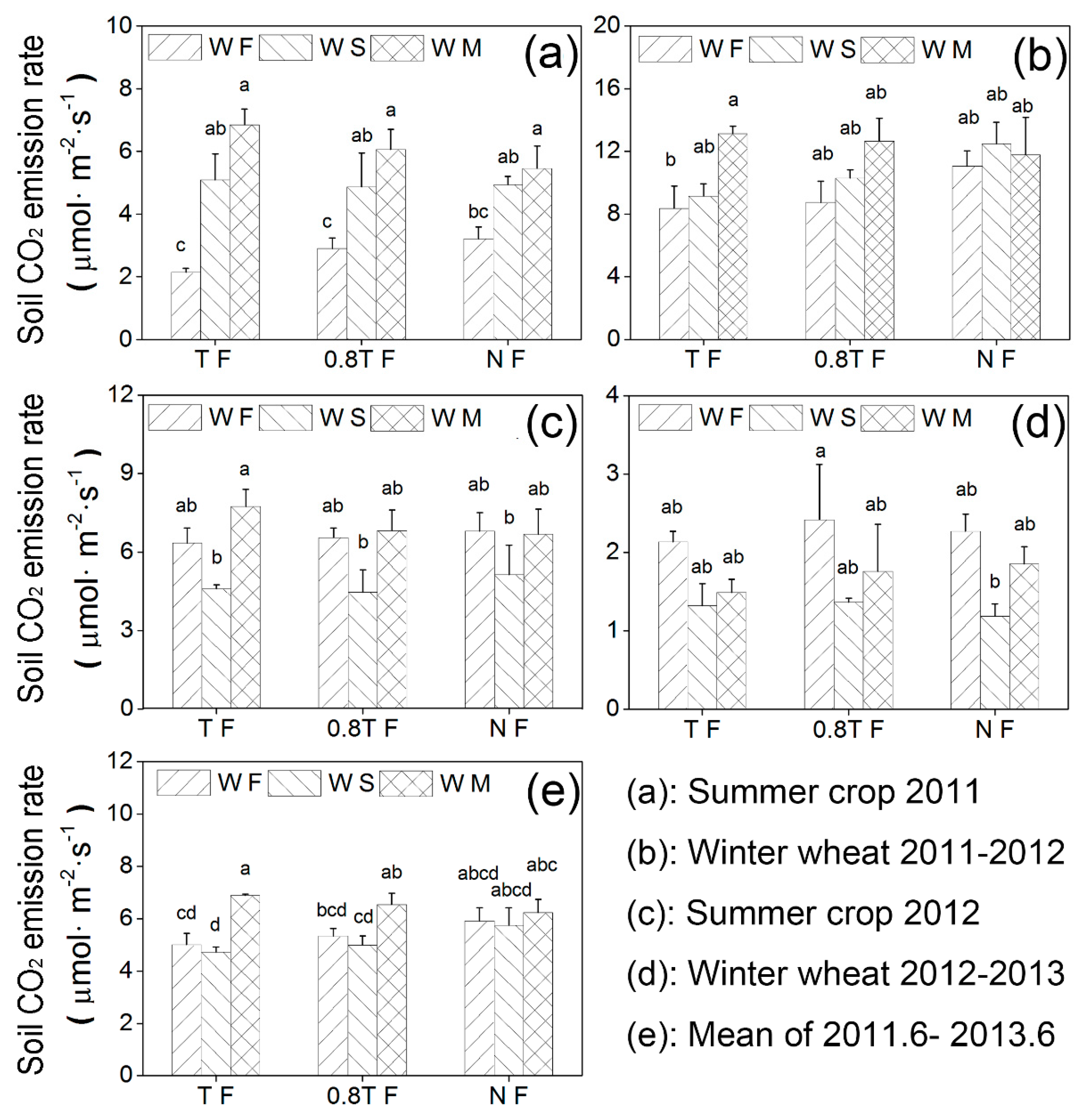
3.3. Soil CO2 Emission
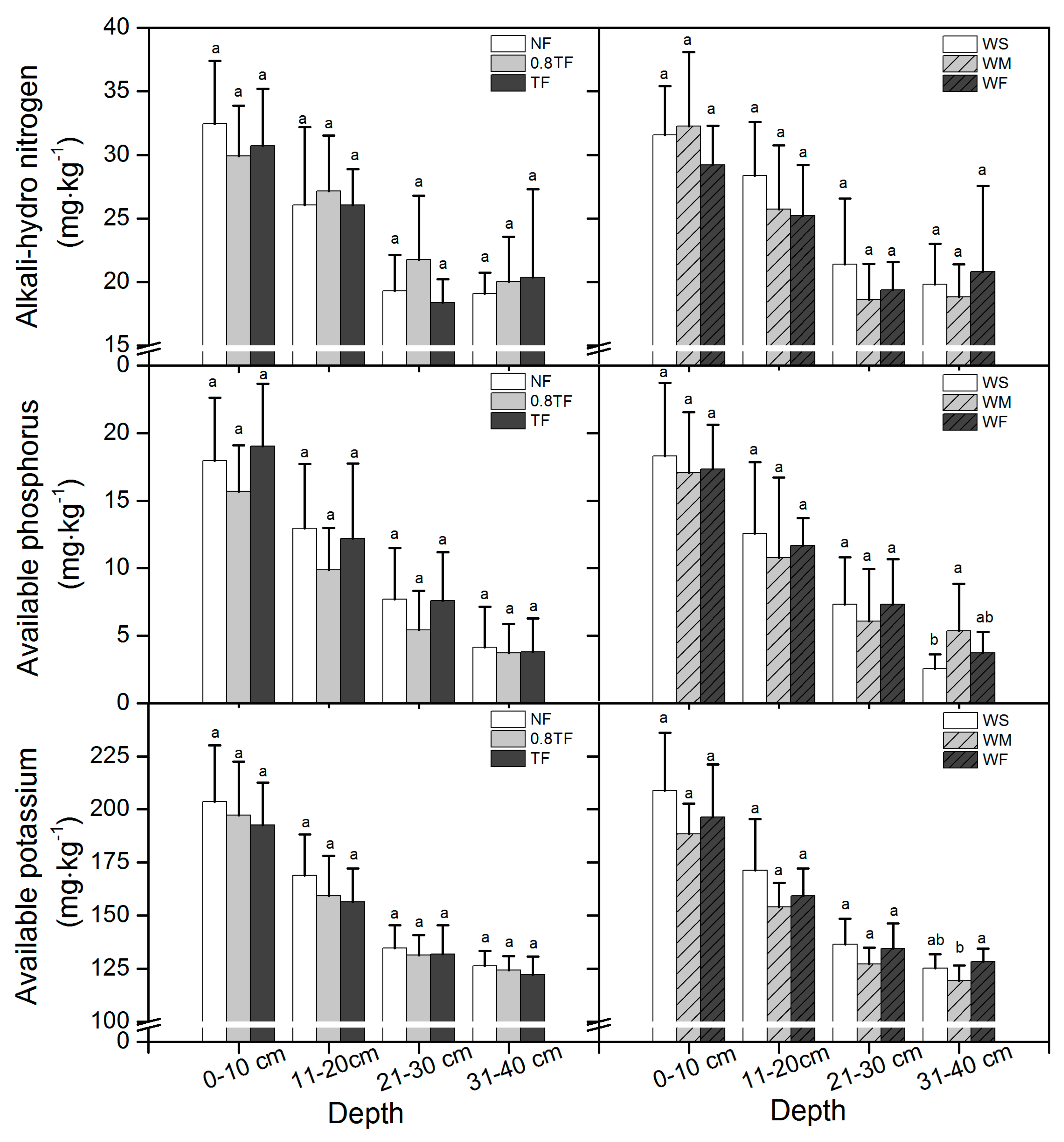
3.4. Soil Nutrients
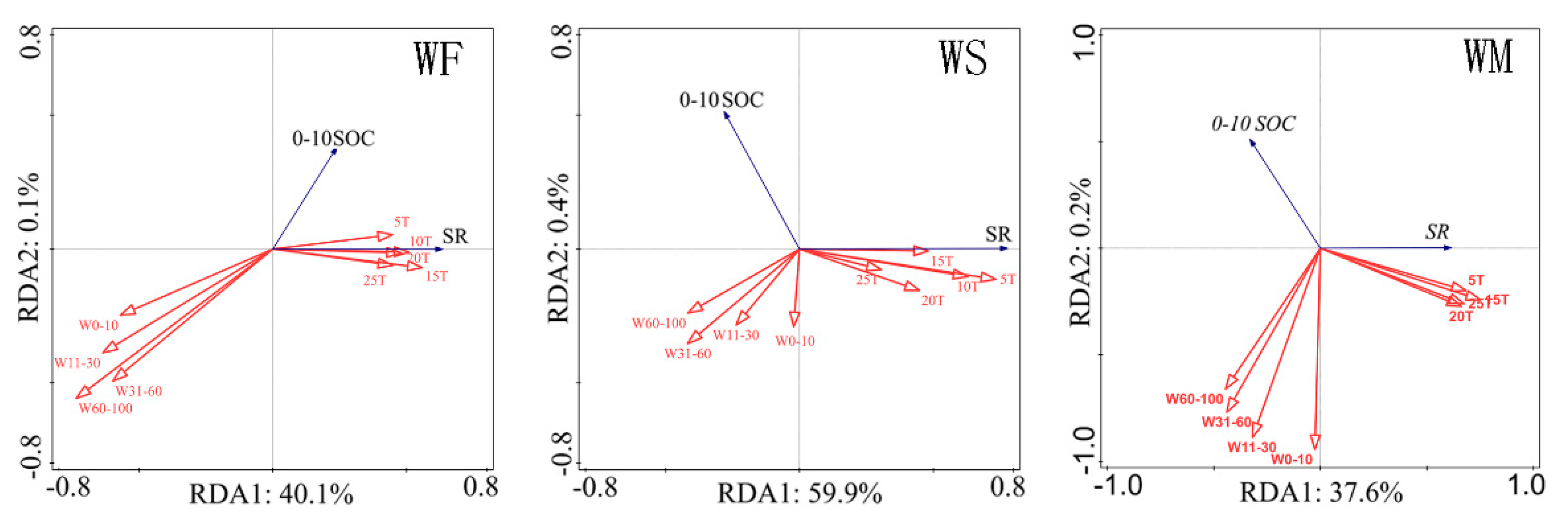
3.5. Relationship between Soil Organic Carbon and CO2 Emission and Treatment Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect on Soil Temperature, Soil Moisture, SOC, and Soil CO2 Emission in the Rotation Mode
4.2. Influence of N Fertilizer on Soil Organic Carbon (SOC), Soil Temperature, Soil Moisture, and Soil CO2 Emissions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Mohamed, I.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.S.; Li, Z.G.; Chen, F. Soil CO2 emissions and drivers in rice-Wheat rotation fields subjected to different long-term fertilization practices. Clean-Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, N.J.; Hu, Y.X.; Bloemertz, L.; He, J.; Li, H.W.; Greenwood, P. Conservation tillage and sustainable intensification of agriculture: Regional vs. global benefit analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 216, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.J.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y.D.; Deng, J.; Zhao, F.Z.; Yang, G.H.; Han, X.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Differential soil microbial community responses to the linkage of soil organic carbon fractions with respiration across land-use changes. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 409, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Martínez, V.; Burow, G.; Zobeck, T.M.; Allen, V.G. Soil Microbial Communities and Function in Alternative Systems to Continuous Cotton. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; You, M.Y.; Shi, H.A.; Ding, X.L.; Qiao, Y.F.; Han, X.Z. Soil CO2 emissions from a cultivated Mollisol: Effects of organic amendments, soil temperature, and moisture. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2013, 55, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilustro, J.J.; Collins, B.; Duncan, L.; Crawford, C. Moisture and soil texture effects on soil CO2 efflux components in southeastern mixed pine forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 204, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Andrews, J.A. Soil respiration and the global carbon cycle. Biogeochemistry 2000, 48, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ali, M.; Zheng, X.Q.; He, Q.; Yang, X.H.; Huo, W.; Liang, F.C.; Wang, S.M. Diurnal dynamics of soil respiration and the influencing factors for three land-cover types in the hinterland of the Taklimakan Desert, China. J. Arid Land 2017, 9, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, Q.F.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.W.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Wen, X.X.; Liao, Y.C. Plastic-film mulching and urea types affect soil CO2 emissions and grain yield in spring maize on the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanveer, S.K.; Wen, X.X.; Lu, X.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Liao, Y.C. Tillage, Mulch and N Fertilizer Affect Emissions of CO2 under the Rain Fed Condition. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M.; Lenssen, A.; Caesar-Tonthat, T.; Waddell, J. Tillage and crop rotation effects on dryland soil and residue carbon and nitrogen. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M. A Global Meta-Analysis on the Impact of Management Practices on Net Global Warming Potential and Greenhouse Gas Intensity from Cropland Soils. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.T.; Liang, C.; Hamel, C.; Cutforth, H.; Wang, H. Strategies for reducing the carbon footprint of field crops for semiarid areas. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 31, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Fan, M.S.; Vitousek, P.; Zhao, M.; Ma, W.Q.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, W.J.; Yan, X.Y.; Yang, J.C.; et al. Producing more grain with lower environmental costs. Nature 2014, 514, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.L.; Dou, Z.X.; Chen, X.P.; Ju, X.T.; Zhang, F.S. Managing Agricultural Nutrients for Food Security in China: Past, Present, and Future. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.Z.; Luo, Q.S.; Deng, H.B.; Yan, Y. Opportunities and challenges of sustainable agricultural development in China. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 363, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norse, D.; Ju, X.T. Environmental costs of China’s food security. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 209, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.X.; Stewart, B.A.; Zhang, F.S. Long-term experiments for sustainable nutrient management in China. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 31, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Zhang, F.S. Nitrogen fertilizer induced greenhouse gas emissions in China. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 407–413. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.L.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S. Current Nitrogen Management Status and Measures to Improve the Intensive Wheat–Maize System in China. Ambio 2010, 39, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, S.M.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, B.R.; Li, X.Y.; Ma, Y.B. Nitrogen efficiency in long-term wheat–maize cropping systems under diverse field sites in China. Field Crop. Res. 2010, 118, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, J.H.; Ma, L.; Wang, F.H.; Sisák, I.; Cushman, G.; Zhang, F.S. Nitrogen flow and use efficiency in production and utilization of wheat, rice, and maize in China. Agric. Syst. 2008, 99, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitmore, A.P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Glendining, M.J.; Dailey, A.G.; Coleman, K.; Powlson, D.S. Nutrient Management in Support of Environmental and Agricultural Sustainability. Sustainability 2012, 4, 2513–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brankatschk, G.; Finkbeiner, M. Crop rotations and crop residues are relevant parameters for agricultural carbon footprints. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2017, 37, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, K.B.; Longing, S.D.; West, C.P. Soil Microbial Communities in Corn Fields Treated with Atoxigenic Aspergillus flavus. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Bonilla, D.; Arrúe, J.L.; Cantero-Martínez, C.; Fanlo, R.; Iglesias, A.; Álvaro-Fuentes, J. Carbon management in dryland agricultural systems. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 1319–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.J.; Liu, N.N.; Wang, W.Y.; Akhtar, K.; Li, N.; Ren, G.X.; Feng, Y.Z.; Yang, G.H. Soil respiration from fields under three crop rotation treatments and three straw retention treatments. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariko, S.; Nishimura, N.; Mo, W.H.; Matsui, Y.; Kibe, T.; Koizumi, H. Winter CO2 flux from soil and snow surfaces in a cool-temperate deciduous forest, Japan. Ecol. Res. 2000, 15, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.Y.; Akhtar, K.; Ren, G.X.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Yuan, L.Y. Impact of straw management on seasonal soil carbon dioxide emissions, soil water content, and temperature in a semi-arid region of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Moorman, T.B.; Novak, J.M.; Parkin, T.B.; Karlen, D.L.; Turco, R.F.; Konopka, A.E. Field-Scale Variability of Soil Properties in Central Iowa Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.S.; Olsen, S.R. Test of an Ascorbic Acid Method for Determining Phosphorus in Water and NaHCO3 Extracts from Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1965, 29, 677–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.J.; Sun, P.S.; Kang, D.; Zhao, F.Z.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H. Responsiveness of soil nitrogen fractions and bacterial communities to afforestation in the Loess Hilly Region (LHR) of China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cutforth, H.; Chai, Q.; Gan, Y.T. Farming tactics to reduce the carbon footprint of crop cultivation in semiarid areas. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2016, 36, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Wang, K.; Meng, S.X.; Zheng, X.H.; Zhou, Z.X.; Han, S.H.; Chen, D.L.; Yang, Z.P. Effects of irrigation, fertilization and crop straw management on nitrous oxide and nitric oxide emissions from a wheat-maize rotation field in northern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.Z.; Sun, J.; Ren, C.J.; Kang, D.; Deng, J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Land use change influences soil C, N, and P stoichiometry under ’Grain-to-Green Program’ in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10195. [Google Scholar]
- Halvorson, A.D.; Schlegel, A.J. Crop Rotation Effect on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Stocks under Limited Irrigation. Agron. J. 2012, 104, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M.; Caesar-TonThat, T.; Lenssen, A.W.; Barsotti, J.L. Dryland Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions Affected by Cropping Sequence and Nitrogen Fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 1741–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.Z.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Ren, C.J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Doughty, R.; Deng, J. Understory Plants Regulate Soil Respiration through Changes in Soil Enzyme Activity and Microbial C, N, and P Stoichiometry Following Afforestation. Forests 2018, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duiker, S.W.; Lal, R. Carbon budget study using CO2 flux measurements from a no till system in central Ohio. Soil Tillage Res. 2000, 54, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, J.K.; Hofmockel, K.S. Soil microbiomes and climate change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, B.; Charles, P. West, and Veronica Acosta-Martinez, Assessing the role of interseeding alfalfa into grass on improving pasture soil health in semi-arid Texas High Plains. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 147, 103399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, K.B.; West, C.P.; Acosta-Martinez, V.; Cotton, J.; Cano, A. Soil health indicators as affected by diverse forage species and mixtures in semi-arid pastures. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 132, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.Z.; Yang, G.H.; Han, X.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Stratification of Carbon Fractions and Carbon Management Index in Deep Soil Affected by the Grain-to-Green Program in China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Hu, C.S.; Ming, H.; Oenema, O.; Schaefer, D.A.; Dong, W.X.; Zhang, Y.M.; Li, X.X. Methane, Carbon Dioxide and Nitrous Oxide Fluxes in Soil Profile under a Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation in the North China Plain. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.F.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S.; Zhang, H.L.; Schroder, J.; Römheld, V. Fertilization and Nitrogen Balance in a Wheat–Maize Rotation System in North China. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Yan, X.Y.; Wang, J.Y. The effect of chemical fertilizer on soil organic carbon renewal and CO2 emission-a pot experiment with maize. Plant Soil 2012, 353, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.X.; Yu, H.Y.; Cai, Z.C.; Han, F.X.; Xu, Z.H. Responses of soil respiration to N fertilization in a loamy soil under maize cultivation. Geoderma 2010, 155, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.D.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Wang, J.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Kuzyakov, Y. Nitrogen fertilization increases rhizodeposit incorporation into microbial biomass and reduces soil organic matter losses. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wei, T.; Wang, H.X.; Wang, M.; Meng, X.P.; Mou, S.W.; Zhang, R.; Jia, Z.K.; Han, Q.F. Effects of straw mulch on soil water and winter wheat production in dryland farming. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10725. [Google Scholar]
- Ghimire, R.; Adhikari, K.R.; Chen, Z.S.; Shah, S.C.; Dahal, K.R. Soil organic carbon sequestration as affected by tillage, crop residue, and nitrogen application in rice-wheat rotation system. Paddy Water Environ. 2012, 10, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, D.; Liu, N.; Ren, C.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Li, N.; Ren, G.; Feng, Y.; Yang, G. Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer on Soil CO2 Emission Depends on Crop Rotation Strategy. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135271
Kong D, Liu N, Ren C, Li H, Wang W, Li N, Ren G, Feng Y, Yang G. Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer on Soil CO2 Emission Depends on Crop Rotation Strategy. Sustainability. 2020; 12(13):5271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135271
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, Dejie, Nana Liu, Chengjie Ren, Huiying Li, Weiyu Wang, Na Li, Guangxin Ren, Yongzhong Feng, and Gaihe Yang. 2020. "Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer on Soil CO2 Emission Depends on Crop Rotation Strategy" Sustainability 12, no. 13: 5271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135271
APA StyleKong, D., Liu, N., Ren, C., Li, H., Wang, W., Li, N., Ren, G., Feng, Y., & Yang, G. (2020). Effect of Nitrogen Fertilizer on Soil CO2 Emission Depends on Crop Rotation Strategy. Sustainability, 12(13), 5271. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135271







