A Blockchain-Based Framework for Green Logistics in Supply Chains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Green Logistics and Supply Chain Management
2.2. Blockchain Technology
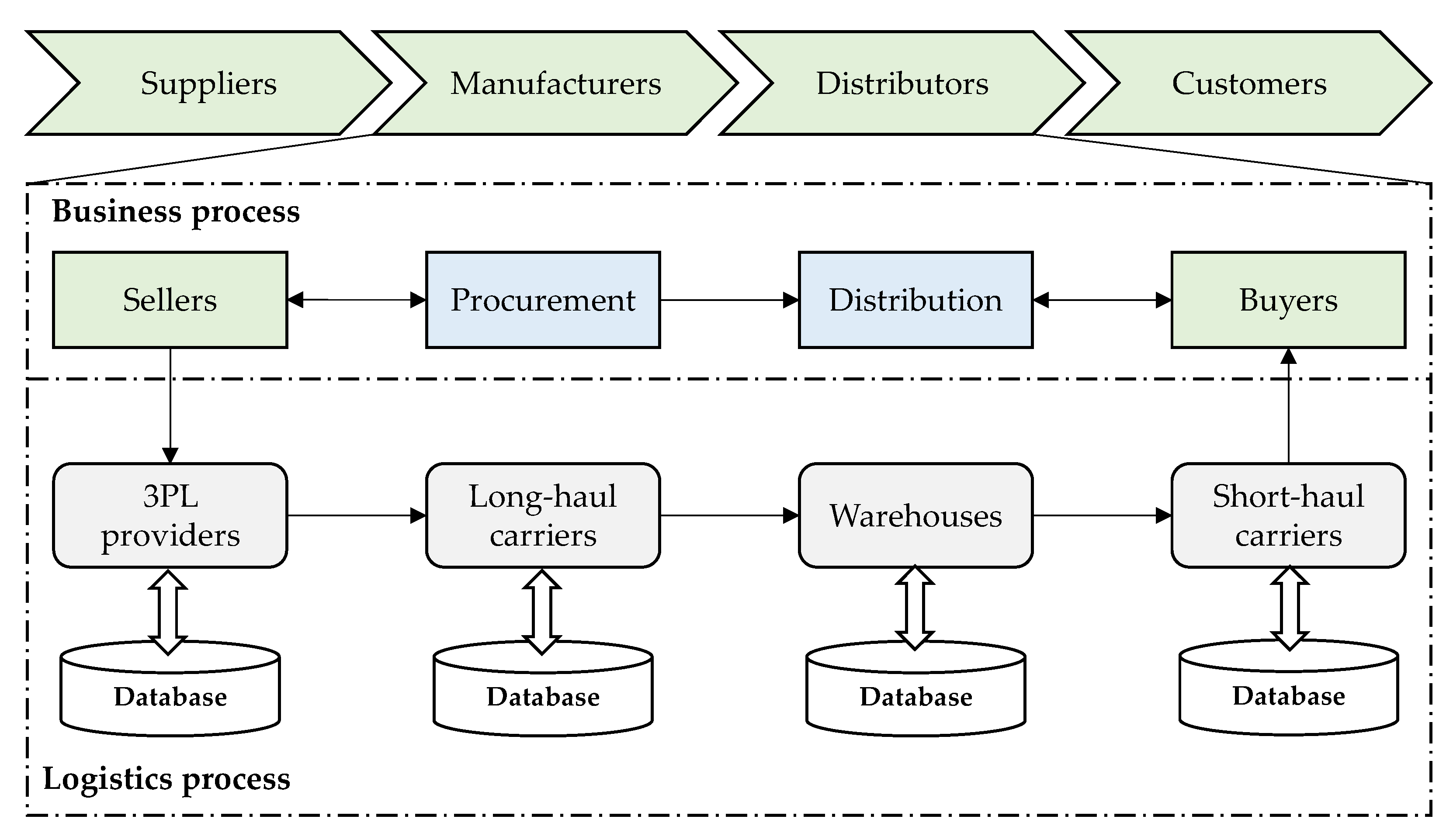
3. Logistics in Supply Chains
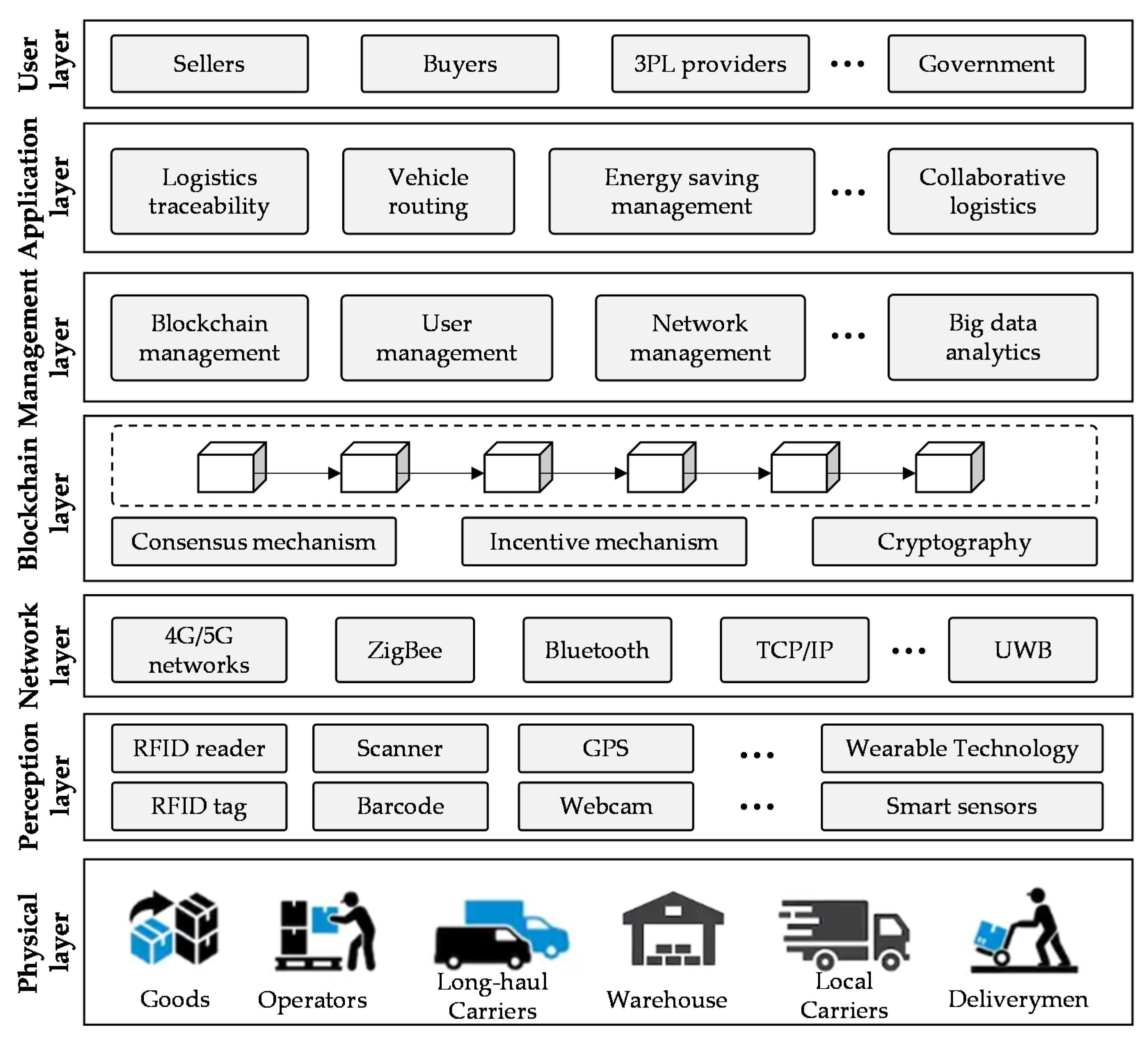
4. Blockchain-Based Framework for Green Logistics
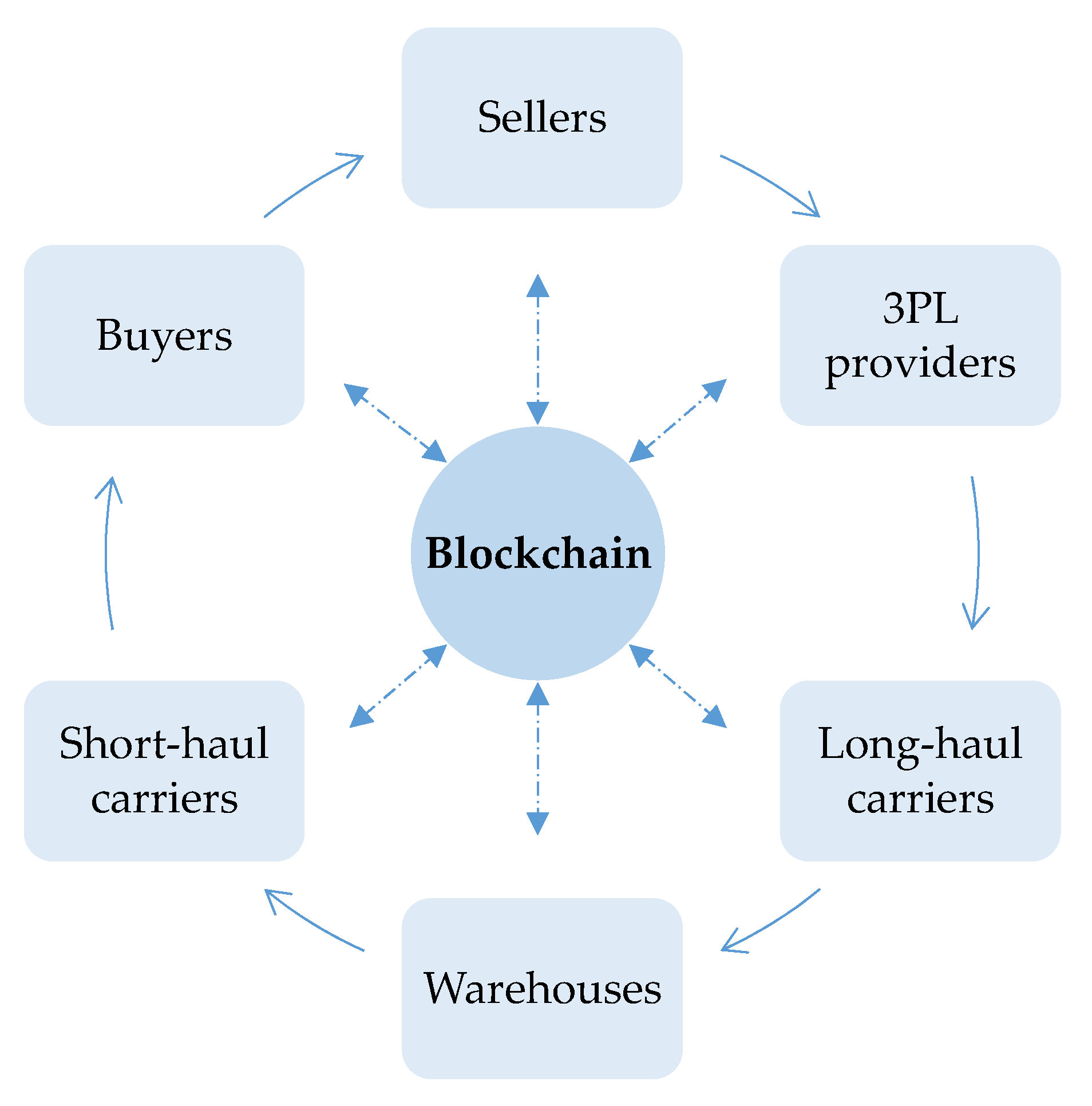
4.1. Overview of the Framework
4.2. Key Applications
5. Discussions
5.1. Benefits
5.2. Challenges
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christopher, M. Logistics & Supply Chain Management, 4th ed.; Pearson Education: Harlow, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- How Big is the Logistics Industry? Available online: https://www.freightwaves.com/news/how-big-is-the-logistics-industry (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Liu, J.; Liu, B.-L.; Lee, S.-J.; Xiao, J.-H. Contemporary Logistics in China: Collaboration and Reciprocation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, K.H.; Wong, C.W.V. Green logistics management and performance: Some empirical evidence from Chinese manufacturing exporters. Omega 2012, 40, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, D.; Garg, S.K.; Singh, R.K. Analyzing alternatives for green logistics in an Indian automotive organization: A case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinsen, U.; Bjorklund, M. Matches and gaps in the green logistics market. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. 2012, 42, 562–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, T.; Yang, H.D.; Huang, G.Q.; Zhang, Y.F.; Luo, H.; Qin, W. A case of implementing RFID-based real-time shop-floor material management for household electrical appliance manufacturers. J. Intell. Manuf. 2010, 23, 2343–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamidass, P.M. Encyclopedia of Production and Manufacturing Management || Simulation Analysis of Manufacturing and Logistics Systems; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; Chapter 881; pp. 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.H. Assessment framework for construction supply chain relationships: Development and evaluation. Int. J Proj. Manag. 2010, 28, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perboli, G.; Musso, S.; Rosano, M. Blockchain in Logistics and Supply Chain: A Lean Approach for Designing Real-World Use Cases. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 62018–62028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. Available online: https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Lee, J.; Azamfar, M.; Singh, J. A blockchain enabled Cyber-Physical System architecture for Industry 4.0 manufacturing systems. Manuf. Lett. 2019, 20, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.J.; Yan, J.Q.; Zhang, K.Z.K. Blockchain-based sharing services: What blockchain technology can contribute to smart cities. Financ. Innov. 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.X.; He, D.B.; Zhao, Q.L.; Choo, K.K.R. Parking Management A blockchain-based privacy-preserving system. IEEE Consum. Electron. Mag. 2019, 8, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, S.; Kouhizadeh, M.; Sarkis, J.; Shen, L.J. Blockchain technology and its relationships to sustainable supply chain management. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 2117–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbinale, A.R.; Dimogerontakis, E.; Selimi, M.; Ali, A.; Navarro, L.; Sathiaseelan, A.; Crowcroft, J. Blockchain for economically sustainable wireless mesh networks. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020, 32, e5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vaio, A.; Varriale, L. Blockchain technology in supply chain management for sustainable performance: Evidence from the airport industry. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 102014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J.; Zhu, Q.; Lai, K.-H. An organizational theoretic review of green supply chain management literature. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 130, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahi, P.; Searcy, C. A comparative literature analysis of definitions for green and sustainable supply chain management. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 52, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimnia, B.; Sarkis, J.; Davarzani, H. Green supply chain management: A review and bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 162, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.; Anholon, R.; Quelhas, O.L.G.; Filho, W. Sustainable Practices in Logistics Systems: An Overview of Companies in Brazil. Sustainability 2019, 11, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuring, S. A review of modeling approaches for sustainable supply chain management. Decis. Support Syst. 2013, 54, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frota Neto, J.Q.; Bloemhof-Ruwaard, J.M.; van Nunen, J.A.E.E.; van Heck, E. Designing and evaluating sustainable logistics networks. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 111, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S. Network design for reverse logistics. Omega 2008, 36, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishvaee, M.S.; Torabi, S.A.; Razmi, J. Credibility-based fuzzy mathematical programming model for green logistics design under uncertainty. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2012, 62, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, D.; Khodaverdi, R.; Olfat, L.; Jafarian, A.; Diabat, A. Integrated fuzzy multi criteria decision making method and multi-objective programming approach for supplier selection and order allocation in a green supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-F.; Dong, Q.-L.; Peng, Z.-M.; Khan, S.; Tarasov, A. The Green Logistics Impact on International Trade: Evidence from Developed and Developing Countries. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, R.; Mansouri, S.A.; Aktas, E. The relationship between green supply chain management and performance: A meta-analysis of empirical evidences in Asian emerging economies. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, A.I.; Musolino, G.; Rindone, C.; Vitetta, A. Sustainable mobility and energy resources: A quantitative assessment of transport services with electrical vehicles. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 113, 109236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musolino, G.; Polimeni, A.; Vitetta, A. Freight vehicle routing with reliable link travel times: A method based on network fundamental diagram. Transp. Lett. 2018, 10, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbihi, A.; Eglese, R.W. Combinatorial optimization and Green Logistics. Ann. Oper. Res. 2009, 175, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.-B.; Chou, Y.-H.; Hu, C.-C. An integrated logistics operational model for green-supply chain management. Transp. Res. Part E 2005, 41, 287–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.Q.; Xu, S.X.; Zhong, R.; Cheng, M.; Kang, K. Sequential auction based parking space sharing and pricing mechanism in the era of sharing economy. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2019, 119, 1734–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, D.; Wicher, P.; Lenort, R.; Dolejšová, V.; Staš, D.; Giurgiu, I. Sustainable Logistics Management in the 21st Century Requires Wholeness Systems Thinking. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Shuai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, H.; He, Z. Synergy Degree Evaluation Based on Synergetics for Sustainable Logistics Enterprises. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casino, F.; Dasaklis, T.K.; Patsakis, C. A systematic literature review of blockchain-based applications: Current status, classification and open issues. Telemat. Inform. 2019, 36, 55–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ouyang, L.; Yuan, Y.; Ni, X.; Han, X.; Wang, F.-Y. Blockchain-Enabled Smart Contracts: Architecture, Applications, and Future Trends. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2019, 49, 2266–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wen, J.T. The IoT electric business model: Using blockchain technology for the internet of things. Peer Peer Netw. Appl. 2017, 10, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notheisen, B.; Cholewa, J.B.; Shanmugam, A.P. Trading Real-World Assets on Blockchain An Application of Trust-Free Transaction Systems in the Market for Lemons. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2017, 59, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Wang, H.; Jin, D.; Li, M.; Jiang, W. Healthcare Data Gateways: Found Healthcare Intelligence on Blockchain with Novel Privacy Risk Control. J. Med. Syst. 2016, 40, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panarello, A.; Tapas, N.; Merlino, G.; Longo, F.; Puliafito, A. Blockchain and IoT Integration: A Systematic Survey. Sensors 2018, 18, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, S.; Yao, Y. Blockchain Enabled Industrial Internet of Things Technology. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2019, 6, 1442–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Lin, Q.; Wen, S. Blockchain-Enabled Data Collection and Sharing for Industrial IoT With Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE T. Ind. Inform. 2019, 15, 3516–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, J.J.; Haughton, J.; Kraft, M. Blockchain technology in the chemical industry: Machine-to-machine electricity market. Appl. Energy 2017, 195, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, R.; Stevenson, M.; Aitken, J. Blockchain technology: Implications for operations and supply chain management. Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 24, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.M.; Telles, R.; Bonilla, S.H. Blockchain and supply chain management integration: A systematic review of the literature. Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 25, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pournader, M.; Shi, Y.Y.; Seuring, S.; Koh, S.C.L. Blockchain applications in supply chains, transport and logistics: A systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2020, 58, 2063–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Han, J.H.; Beynon-Davies, P. Understanding blockchain technology for future supply chains: A systematic literature review and research agenda. Supply Chain Manag. 2019, 24, 62–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshetri, N. 1 Blockchain’s roles in meeting key supply chain management objectives. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 39, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, M.M.; Wamba, S.F. Blockchain adoption challenges in supply chain: An empirical investigation of the main drivers in India and the USA. Int. J. Inform. Manag. 2019, 46, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Zhong, R.Y.; Farooque, M.; Kang, K.; Venkatesh, V.G. Blockchain-based life cycle assessment: An implementation framework and system architecture. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 152, 104512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.G.; Kang, K.; Wang, B.; Zhong, R.Y.; Zhang, A. System architecture for blockchain based transparency of supply chain social sustainability. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2020, 63, 101896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijan, E.; Aksentijevic, S.; Ivanic, K.; Jardas, M. Blockchain Technology Implementation in Logistics. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.G.; Zhu, J.M. Operation Mechanisms for Intelligent Logistics System: A Blockchain Perspective. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 144202–144213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Operations Management of Logistics and Supply Chain: Issues and Directions. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2014, 2014, 701938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wang, F.Y. Blockchain and Cryptocurrencies: Mode Techniques, and Applications. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 48, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.K. Green supply-chain management: A state-of-the-art literature review. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2007, 9, 53–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liang, Y.C.; Li, W.D.; Cai, X.T. Big Data enabled Intelligent Immune System for energy efficient manufacturing management. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 507–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Lu, S.H. Economies of Product Diversity in Collaborative Logistics. J. Bus. Logist. 2017, 38, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Oyedele, L.O.; Qadir, J.; Munir, K.; Ajayi, S.O.; Akinade, O.O.; Owolabi, H.A.; Alaka, H.A.; Pasha, M. Big Data in the construction industry: A review of present status, opportunities, and future trends. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2016, 30, 500–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, B.Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Kang, K.; Costa, F. A Blockchain-Based Framework for Green Logistics in Supply Chains. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114656
Tan BQ, Wang F, Liu J, Kang K, Costa F. A Blockchain-Based Framework for Green Logistics in Supply Chains. Sustainability. 2020; 12(11):4656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114656
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Bing Qing, Fangfang Wang, Jia Liu, Kai Kang, and Federica Costa. 2020. "A Blockchain-Based Framework for Green Logistics in Supply Chains" Sustainability 12, no. 11: 4656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114656
APA StyleTan, B. Q., Wang, F., Liu, J., Kang, K., & Costa, F. (2020). A Blockchain-Based Framework for Green Logistics in Supply Chains. Sustainability, 12(11), 4656. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12114656



