Comparison of Active Nitrogen Loss in Four Pathways on a Sloped Peanut Field with Red Soil in China under Conventional Fertilization Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
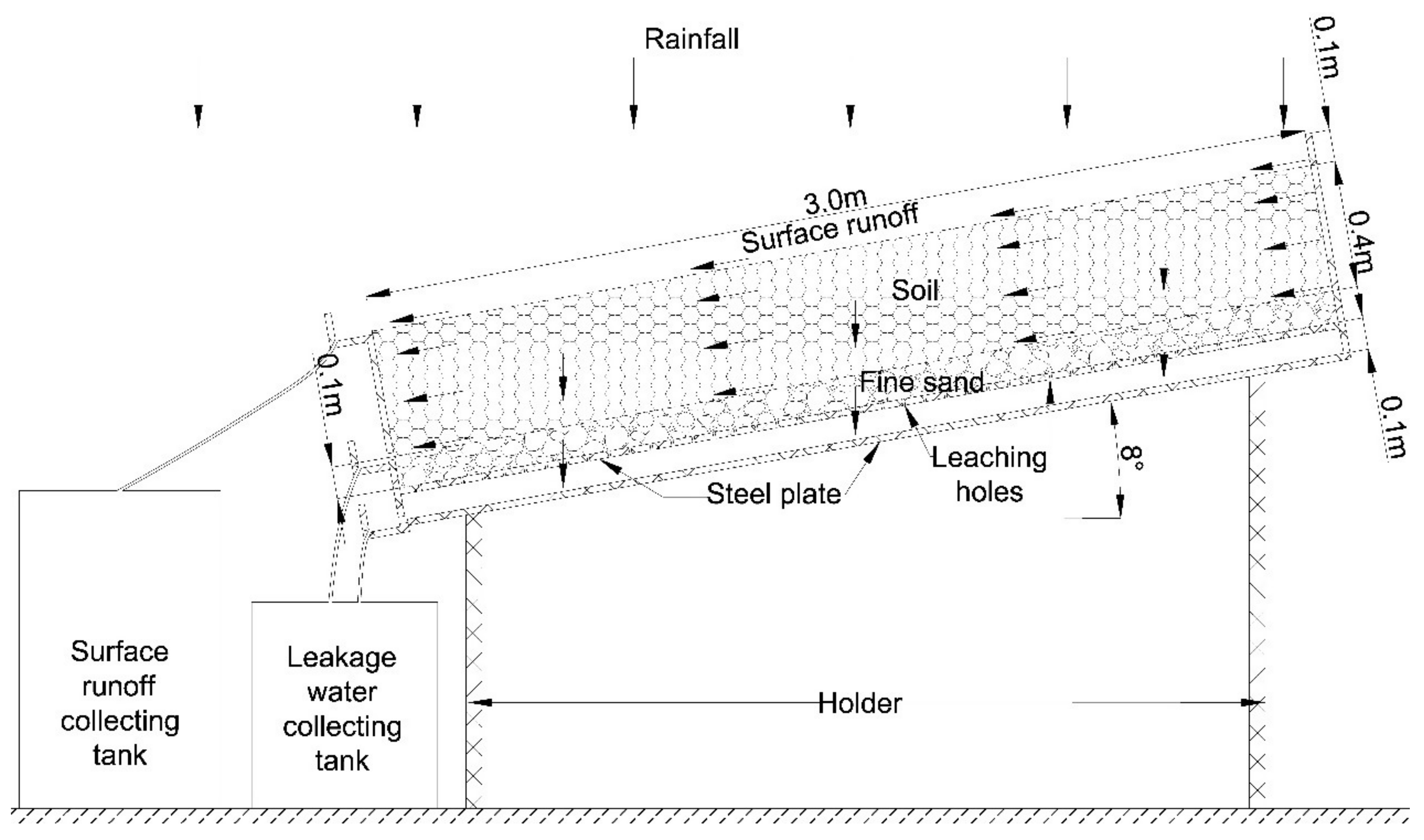
2.1. Background in Formation and Lysimeter Installation
2.2. Experimental Treatments
2.3. Sample Collection and Measurement
2.3.1. Collection and Measurement of Runoff and Leakage Water Samples
2.3.2. Measurement of Ammonia Volatilization
2.3.3. Measurement of N2O Emission
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Temporal Dynamic Change in Active Nitrogen Loss from Different Pathways
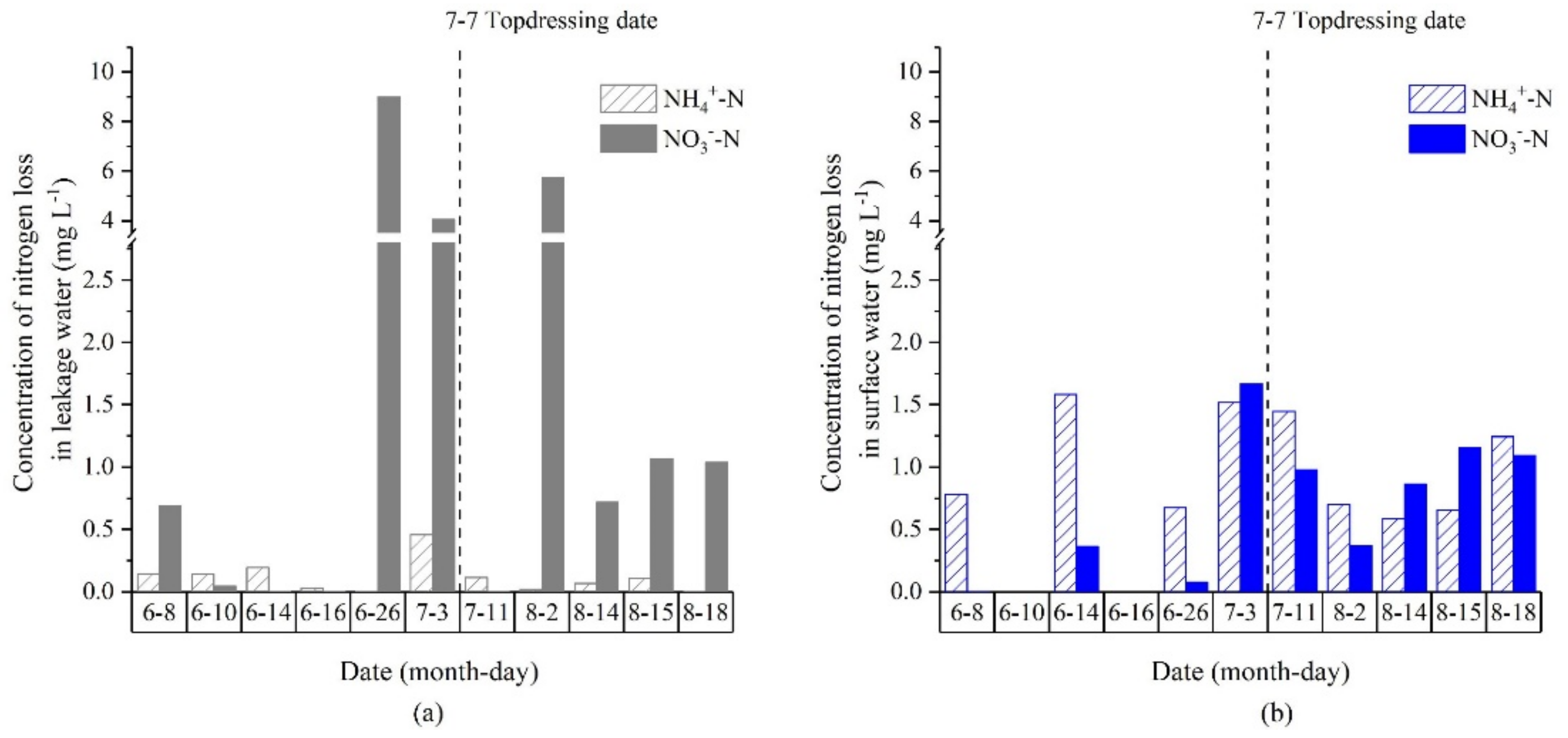
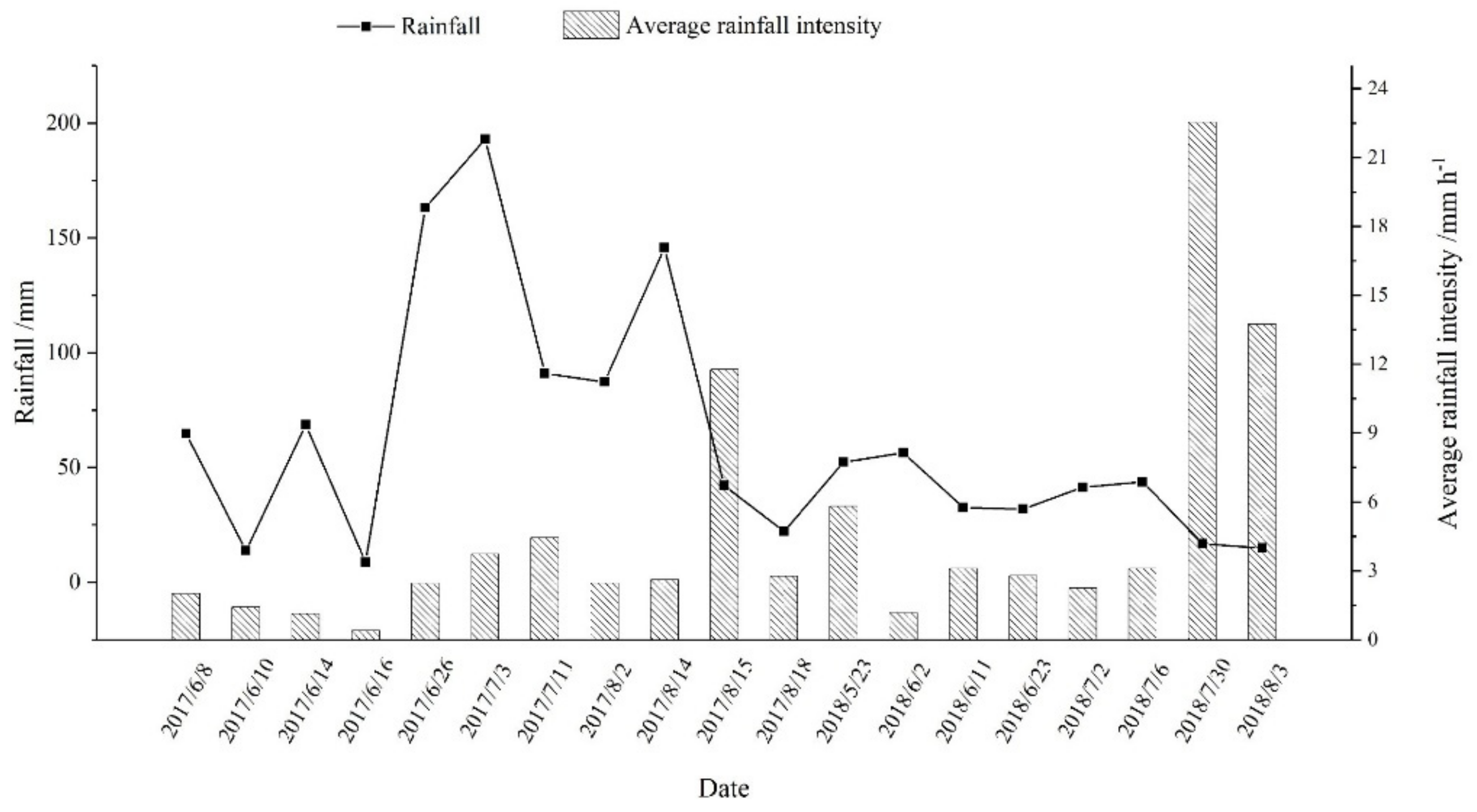
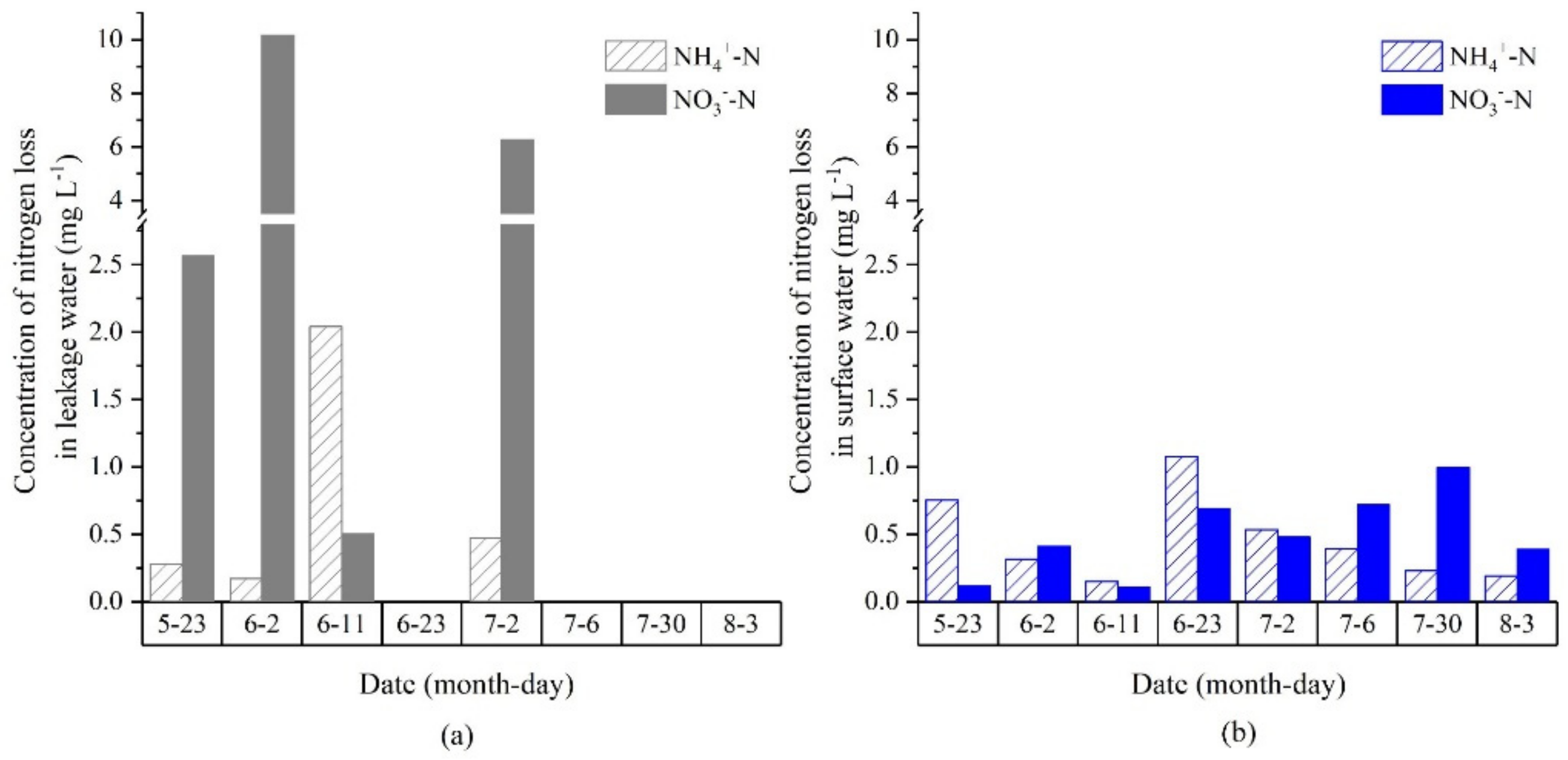
3.1.1. Loss of Active Nitrogen Concentration via Water
3.1.2. Emission Flux of Active Nitrogen via Gas
3.2. Comparison of the Loss Amount and Loss Rate of Active Nitrogen from Different Pathways
4. Discussion
4.1. The Form of Active Nitrogen Loss in Water
4.2. Potential Harm of Active Nitrogen Loss in Water
4.3. Key Pathways of Active Nitrogen Loss
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sutton, M.A.; Oenema, O.; Erisman, J.W.; Leip, A.; van Grinsven, H.; Winiwarter, W. Too much of a good thing. Nature 2011, 472, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denk, T.R.A.; Mohn, J.; Decock, C.; Lewicka-Szczebak, D.; Harris, E.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Kiese, R.; Wolf, B. The nitrogen cycle: A review of isotope effects and isotope modeling approaches. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 105, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhou, M.H.; Zhu, F.H.; Wang, T. Measurement and simulation of nitrogen leaching loss in hillslope cropland of purple soil. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2013, 21, 102–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Li, X.Y.; Jiang, Y. Response of nitrogen losses to excessive nitrogen fertilizer application in intensive greenhouse vegetable production. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera, E.; Lassaletta, L.; Sanz-Cobena, A.; Garnier, J.; Vallejo, A. The potential of organic fertilizers and water management to reduce N2O emissions in Mediterranean climate cropping systems. A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 32–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.T.; Liu, X.J.; Zou, G.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, F.S. Evaluation of nitrogen loss way in winter wheat and summer maize rotation system. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2002, 35, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, M.M.; Fan, H.; Jiang, S.S.; Jiang, J.Y. Nitrogen loss through different ways in cropland under conventional fertilization: An in-situ study of summer maize season in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 3358–3364. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.L. Research on soil nitrogen in China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2008, 45, 778–783. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.M.; Ma, Y.B.; Wang, E.L.; Liang, Q.; Jia, Y.H.; Li, T.S.; Wang, G.C. Crop productivity and nitrogen balance as influenced by nitrogen deposition and fertilizer application in North China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.J.; Zhang, H.L.; Wu, J.S.; Jiang, P.K.; Shi, W.M. Laboratory lysimeter analysis of NH3 and N2O emissions and leaching losses of nitrogen in a rice-wheat rotation system irrigated with nitrogen-rich waste water. Soil Sci. 2013, 178, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.J.; Hinton, N.J.; Cloy, J.M.; Topp, C.F.E.; Rees, R.M.; Williams, J.R.; Misselbrook, T.H.; Chadwick, D.R. How do emission rates and emission factors for nitrous oxide and ammonia vary with manure type and time of application in a Scottish farmland? Geoderma 2016, 264, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.L.; Cui, S.H.; Ju, X.T.; Cai, Z.C.; Zhu, Y.G. Impacts of reactive nitrogen on climate change in China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, S.Y.; Yao, J.W.; Liu, G.J.; Zhou, X.C. Study on ammonia loss by volatilization for urea fertilized to dry land in the tropics and subtropics. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 1999, 15, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.L.; Nie, J.; Xiao, J. Study on 15N labeled rice controlled release fertilizer in increasing nitrogen utilization efficiency. Acta Laser Biol. Sin. 2002, 11, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Cui, J.; Hu, F.; Wang, G.Q.; Ma, Y.H. N-loss through volatilization, runoff and leaching from red soil planted with digitaria ischaemum. Acta Pedol. 2007, 44, 1076–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.S.; Wang, Y.H. Quick measurement of CH4, CO2 and N2O emissions from a short-plant ecosystem. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2003, 20, 842–844. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Y.; Xu, M.G.; Wang, B.R.; Bao, Y.X.; Li, G.H.; Sun, N. Effects of long-term fertilizations on N2O emission and its relationship with soil properties in red soil of Southern China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2009, 12, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.W.; Ai, S.Y.; Zhou, X.C. Study on simulation of N fertilizer leaching loss to dry land in the tropics and subtropics. Soil Environ. Sci. 1999, 18, 314–315. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, J.W.; Zhang, J.B.; Chen, X.M.; Zhu, A.N.; Feng, J. Simulation of soil water leaching and Nitrate_N loss with Lechate in the field using HYDRUS-1D model. Rural Eco-Environ. 2004, 20, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.H.; Liu, X.J.; Ju, X.T.; Zhang, S.F. Field in situ determination of ammonia volatilization from soil: Venting method. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2002, 8, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.H.; Mei, B.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Xie, B.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Dong, H.B.; Xu, H.; Chen, G.X.; Cai, Z.C.; Yue, J.; et al. Quantification of N2O fluxes from soilplant systems may be biased by the applied gas chromatograph methodology. Plant Soil 2008, 311, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Zhang, T.L.; Zhang, B. Nutrient cycle and balance of sloping upland ecosystem on red soil. Acta Ecol. Sci. 1999, 19, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.J.; Hu, J.M.; Huang, P.F.; Wang, L.Y.; Wan, J.L. Comparative study of nitrogen and phosphorus through surface-flow and interflow on red soil farmland. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 28, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Rong, X.M.; Wang, X.X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.P.; Liu, Q.; Xie, G.X.; Song, H.X. Effects of ecology interception and film mulching on surface runoff and nitrogen loss in Upland soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 28, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.S.; Jiang, L.H.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, L.; Zheng, F.L.; Gao, X.H.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.H. In situ study on influences of different fertilization patterns on inorganic nitrogen losses through leaching and runoff: A case of field in Nansi Lake Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 3488–3496. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.A.; Yang, J.; Zheng, T.H.; Zhang, J. Sediment, runoff, nitrogen and phosphorus losses of sloping cropland of quaternary red soil in northern Jiangxi. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Su, F.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Gao, Z.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S.; Feng, Z.; Kogge, M.; Römheld, V. Ammonia volatilization from nitrogen fertilization of winter wheat-summer maize rotation system in the North China Plain. Chin. Environ. Sci. 2007, 27, 409–413. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.X.; Liu, Y.; Jin, H.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Guo, T.C.; He, D.X. Effects of nitrogen application patterns on ammonia volatilization, summer maize yield and nitrogen use efficiency in sandy loam fluvo-aquic soil. J. Maize Sci. 2015, 23, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; Volume 4: Agriculture, Forestry, and Other Land Use; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies: Hayama, Japan, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.L.; Chen, X.P.; Cui, Z.L.; Yue, S.C.; Zhang, F.S. Estimated reactive nitrogen losses for intensive maize production in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 197, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.H.; Han, S.H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Wang, M.X. Re-quantifying the emission factors based on field measurements and estimating the direct N2O emission from Chinese croplands. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2004, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwman, A.F. Factors regulating nitrous oxide and nitric oxide emission. In Global Estimates of Gaseous Emissions of NH3, NO and N2O from Agricultural Land; Bouwman, A.F., Boumans, L.J.M., Batjes, N.H., Eds.; FAO/IFA: Rome, Italy, 2001; pp. 11–16. [Google Scholar]
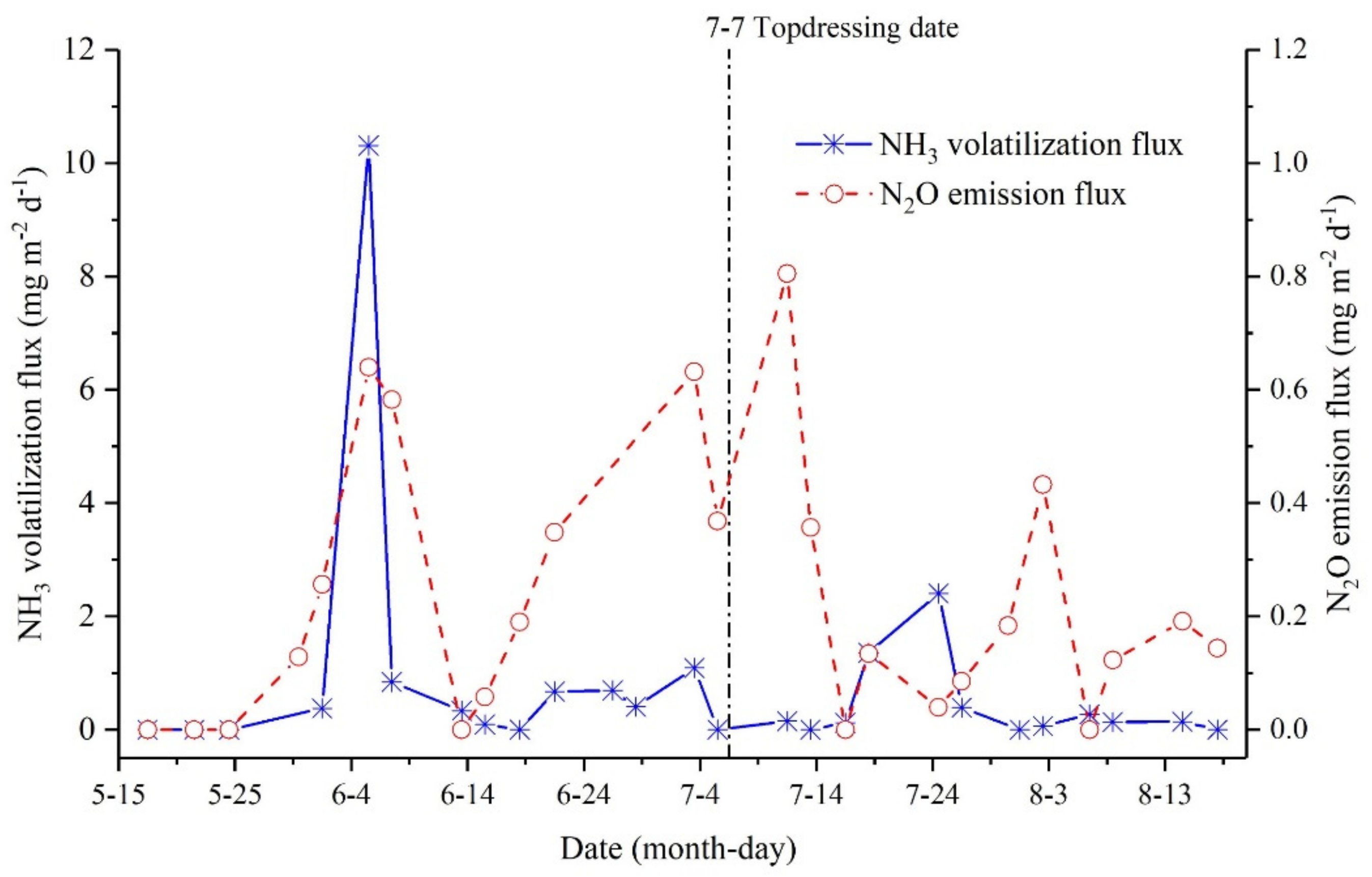
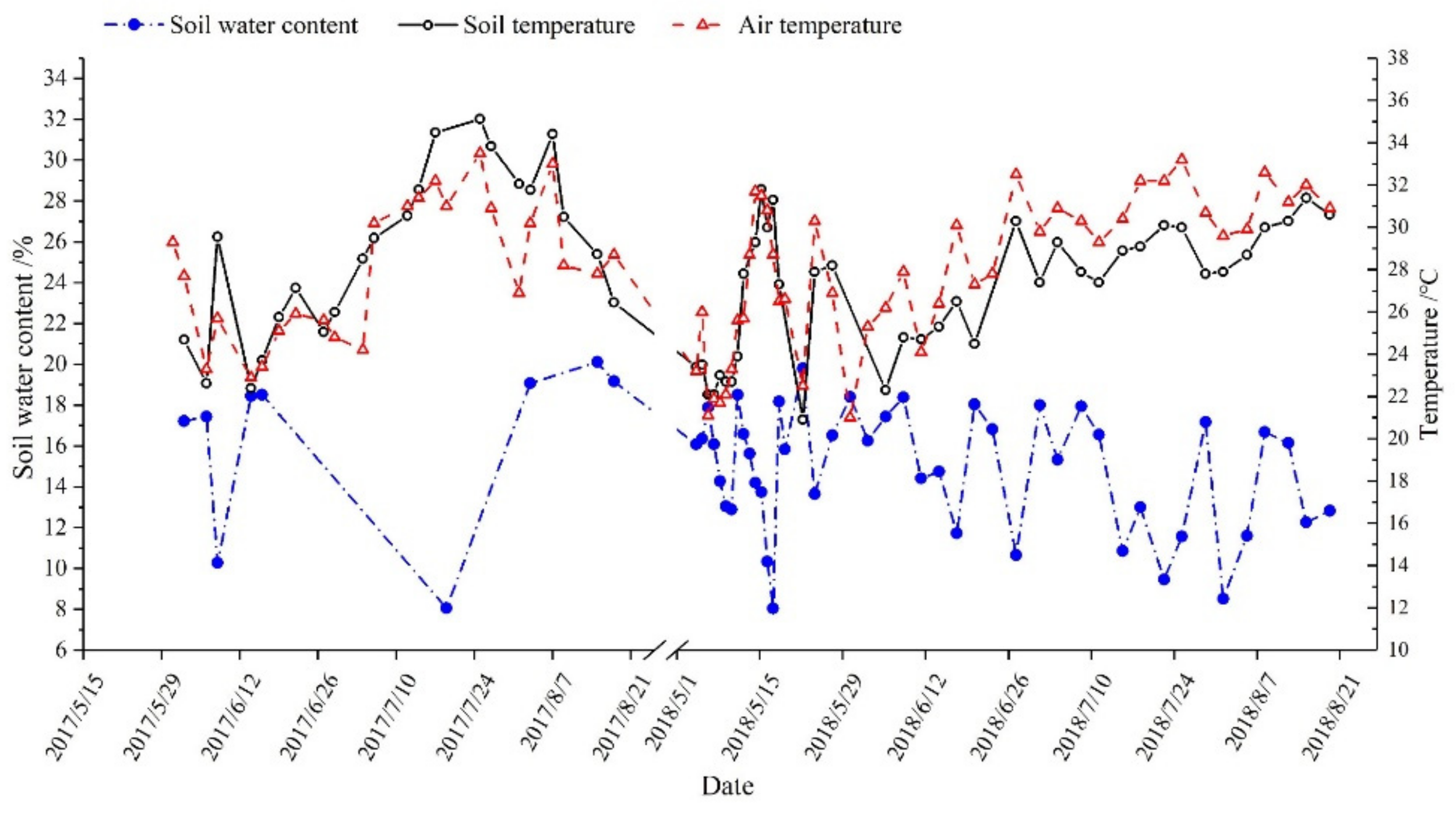
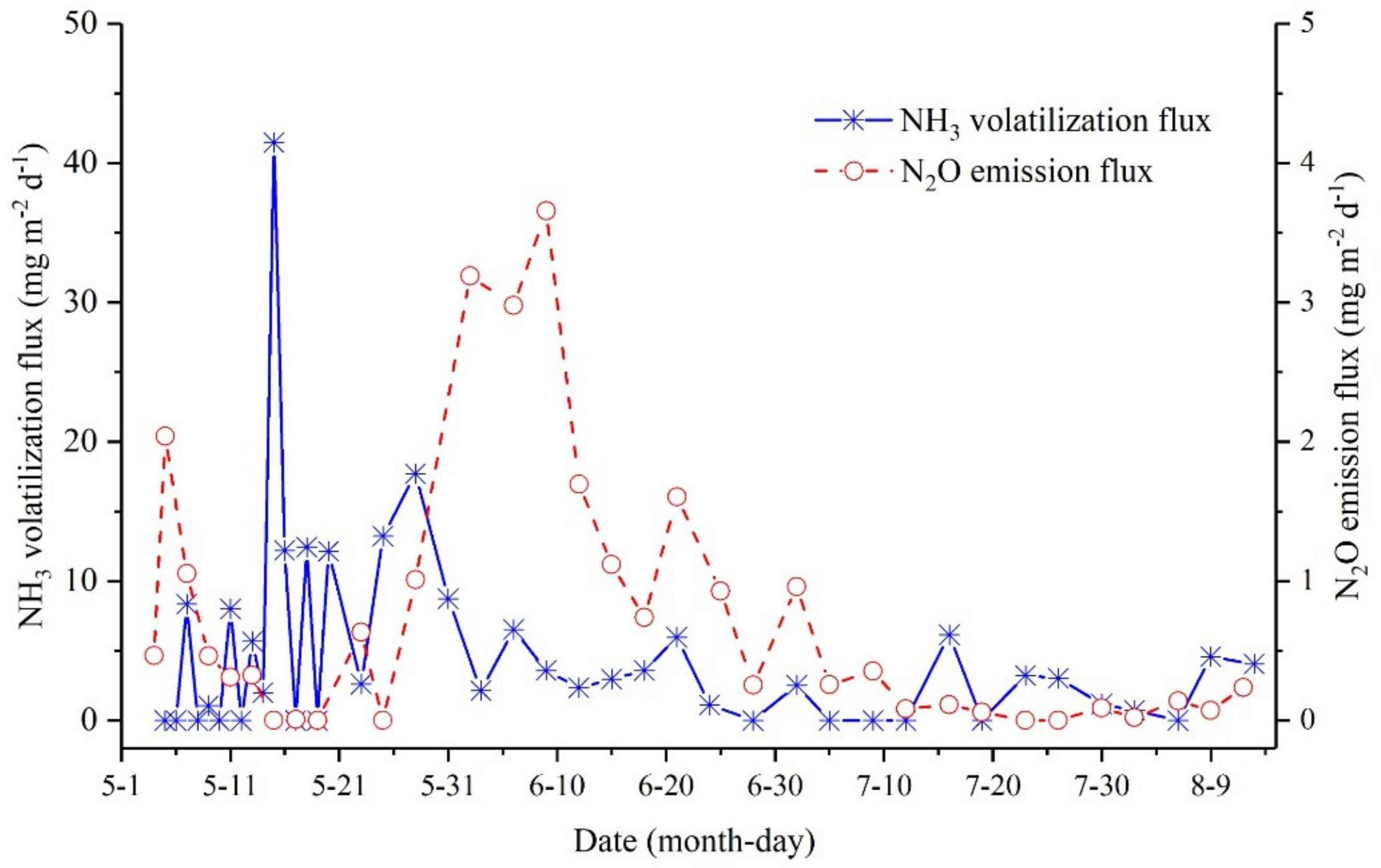
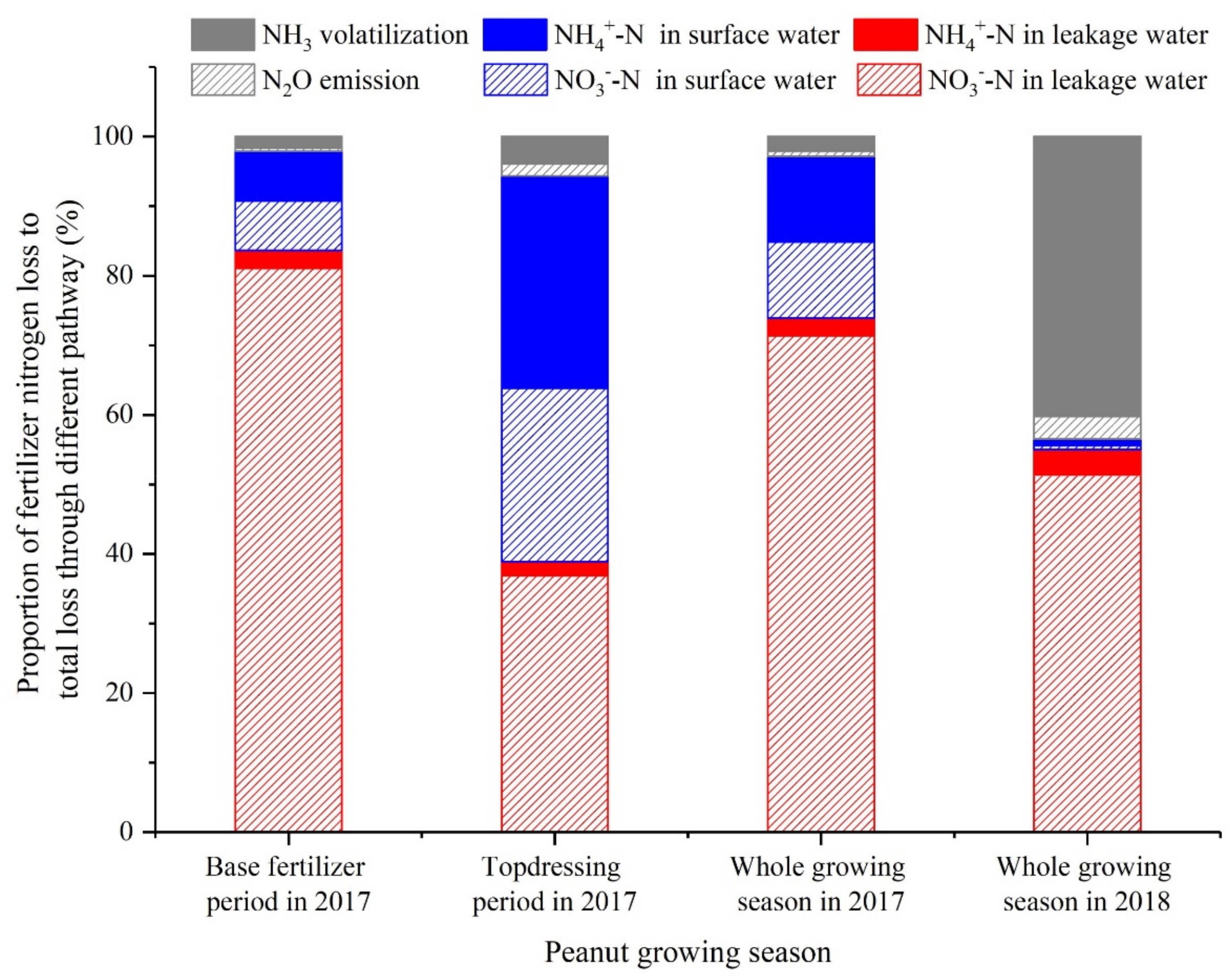
| Nitrogen Loss Concentration | 2017 | 2018 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rainfall | Rainfall Intensity | Rainfall | Rainfall Intensity | |
| NH4+-N in leakage water | 0.436 | −0.041 | 0.431 | −0.444 |
| NO3−-N in leakage water | 0.616 * | 0.404 | 0.736 * | −0.672 |
| NH4+-N in runoff water | 0.413 | 0.273 | 0.301 | −0.310 |
| NO3−-N in runoff water | 0.393 | 0.893 ** | −0.404 | 0.120 |
| Nitrogen Emission Flux | 2017 | 2018 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Temperature | Soil Moisture | Air Temperature | Soil Temperature | Soil Moisture | Air Temperature | |
| NH3-N volatilization | −0.224 | −0.076 | −0.034 | 0.112 | 0.027 | −0.011 |
| N2O-N emission | 0.006 | 0.418 * | −0.143 | −0.686 ** | 0.520 ** | −0.656 ** |
| Treatments | Peanut Growing Season | N Leaching Loss | N Runoff Loss | N2O-N Emission Loss | NH3-N Volatilization Loss | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4+-N | NO3−-N | Subtotal | NH4+-N | NO3−-N | Subtotal | |||||
| FT | 2017 | Base fertilizer period | 1.52 ± 0.50 | 23.30 ± 4.98 | 24.82 ± 5.40 | 3.48 ± 1.13 | 2.21 ± 0.64 | 5.69 ± 1.77 | 0.17 ± 0.09 | 3.48 ± 0.97 |
| Topdressing period | 0.46 ± 0.27 | 4.31 ± 0.66 | 4.77 ± 0.88 | 2.61 ± 0.75 | 1.98 ± 0.65 | 4.59 ± 1.26 | 0.12 ± 0.06 | 1.38 ± 0.38 | ||
| Whole growing season | 1.98 ± 0.77 | 27.61 ± 5.63 | 29.59 ± 6.28 | 6.09 ± 0.74 | 4.19 ± 0.94 | 10.28 ± 1.67 | 0.29 ± 0.15 | 4.86 ± 1.34 | ||
| 2018 | Whole growing season | 0.60 ± 0.14 | 7.89 ± 3.48 | 8.49 ± 3.38 | 0.27 ± 0.19 | 0.11 ± 0.06 | 0.38 ± 0.04 | 0.41 ± 0.08 | 13.19 ± 2.04 | |
| CK | 2017 | Base fertilizer period | 1.02 ± 0.33 | 7.82 ± 2.56 | 8.84 ± 2.72 | 2.11 ± 1.14 | 0.86 ± 0.56 | 2.97 ± 1.55 | 0.09 ± 0.04 | 3.16 ± 0.39 |
| Topdressing period | 0.35 ± 0.11 | 2.34 ± 0.46 | 2.69 ± 0.55 | 0.98 ± 0.22 | 0.65 ± 0.29 | 1.63 ± 0.14 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 1.17 ± 0.55 | ||
| Whole growing season | 1.37 ± 0.43 | 10.16 ± 3.01 | 11.53 ± 3.26 | 3.09 ± 0.96 | 1.51 ± 0.85 | 4.60 ± 1.56 | 0.12 ± 0.05 | 4.33 ± 0.95 | ||
| 2018 | Whole growing season | 0.29 ± 0.04 | 3.60 ± 0.24 | 3.89 ± 0.28 | 0.19 ± 0.06 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.02 | 9.83 ± 0.31 | |
| Peanut Growing Season | Total Nitrogen Applied (kg hm−2) | N Leakage Loss Rate (%) | N Runoff Loss Rate (%) | N2O Emission Coefficient (%) | NH3 Volatilization Coefficient (%) | Total Loss Rate of Active Nitrogen in Four Pathways (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | Base fertilizer period | 103.2 | 15.52 | 2.64 | 0.08 | 0.31 | 18.55 |
| Topdressing period | 68.8 | 3.01 | 4.29 | 0.13 | 0.31 | 7.73 | |
| Whole growing season | 172.0 | 10.50 | 3.30 | 0.10 | 0.31 | 14.21 | |
| 2018 | Whole growing season | 150.0 | 3.07 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 2.24 | 5.57 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, H.; Liu, Z.; Nie, X.; Zuo, J.; Wang, L. Comparison of Active Nitrogen Loss in Four Pathways on a Sloped Peanut Field with Red Soil in China under Conventional Fertilization Conditions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11226219
Zheng H, Liu Z, Nie X, Zuo J, Wang L. Comparison of Active Nitrogen Loss in Four Pathways on a Sloped Peanut Field with Red Soil in China under Conventional Fertilization Conditions. Sustainability. 2019; 11(22):6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11226219
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Haijin, Zhao Liu, Xiaofei Nie, Jichao Zuo, and Lingyun Wang. 2019. "Comparison of Active Nitrogen Loss in Four Pathways on a Sloped Peanut Field with Red Soil in China under Conventional Fertilization Conditions" Sustainability 11, no. 22: 6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11226219
APA StyleZheng, H., Liu, Z., Nie, X., Zuo, J., & Wang, L. (2019). Comparison of Active Nitrogen Loss in Four Pathways on a Sloped Peanut Field with Red Soil in China under Conventional Fertilization Conditions. Sustainability, 11(22), 6219. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11226219





