Analysis of Motivational Climate, Emotional Intelligence, and Healthy Habits in Physical Education Teachers of the Future Using Structural Equations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Design
2.2. Measures
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Han, C.; Farruggia, S.; Solomon, B. Latent profiling university students’ learning strategies use and effects on academic performance and retention. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2018, 37, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaha, M.; Hawi, N. Relationships among smartphone addiction, stress, academic performance, and satisfaction with life. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 57, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerin, J.; Webb, H.; Zimmer-Gembeck, M. Resisting the temptation of food: Regulating overeating and associations with emotion regulation, mindfulness, and eating pathology. Aust. J. Psychol. 2018, 70, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetinkaya, S.; Sert, H. Sakarya University students’ fat phobia levels and attitudes towards obese individuals and their correlation with healthy lifestyle behaviours: Knowledge, attitude and practice (KAP) study. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2018, 68, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beydoun, M.; Powell, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Food Prices Are Associated with Dietary Quality, Fast Food Consumption, and Body Mass Index among US Children and Adolescents. J. Nutr. 2010, 141, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ifland, J.; Preuss, H.; Marcus, M.; Rourke, K.; Taylor, W.; Burau, K.; Manso, G. Refined food addiction: A classic substance use disorder. Med. Hypotheses 2009, 72, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirkarimi, K.; Mansourian, M.; Kabir, M.; Ozouni-Davaji, R.; Eri, M.; Hosseini, S.; Charkazi, A. Fast food consumption behaviors in high-school students based on the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB). Int. J. Pediatr. 2016, 4, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, F.; Macchi, C.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.; Casini, A. Mediterranean diet and health status: An updated meta-analysis and a proposal for a literature-based adherence score. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 2769–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastorini, C.; Milionis, H.; Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D.; Goudevenos, J.; Panagiotakos, D. The effect of Mediterranean diet on metabolic syndrome and its components: A meta-analysis of 50 studies and 534,906 individuals. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1299–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muros, J.; Cofre-Bolados, C.; Arriscado, D.; Zurita, F.; Knox, E. Mediterranean diet adherence is associated with lifestyle, physical fitness, and mental wellness among 10-y-olds in Chile. Nutrition 2017, 35, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godos, J.; Marventano, S.; Mistretta, A.; Galvano, F.; Grosso, G. Dietary sources of polyphenols in the Mediterranean healthy Eating, Aging and Lifestyle (MEAL) study cohort. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maselli, M.; Ward, P.; Gobbi, E.; Carraro, A. Promoting Physical Activity Among University Students: A Systematic Review of Controlled Trials. Am. J. Health Promot. 2018, 32, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, C.; Janssen, I.; Barquera, S.; Bautista-Arredondo, S.; González, M.; González, C. Occupational and leisure time physical inactivity and the risk of type II diabetes and hypertension among Mexican adults: A prospective cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Zhou, D.; Ma, Z. Effect of aerobic exercises on students’ physical health indicators. Sci. Sports 2018, 33, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Um, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, H.; Oh, S.; Lee, C.; Joh, H. Association between Physical Activity Levels and Physical Symptoms or Illness among University Students in Korea. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2016, 37, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Estrategia Mundial Sobre Régimen Alimentario, Actividad Física y Salud; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lubans, D.; Richards, J.; Hillman, C.; Faulkner, G.; Beauchamp, M.; Nilsson, M.; Biddle, S. Physical activity for cognitive and mental health in youth: A systematic review of mechanisms. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20161642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Centeio, E.; Garn, A.; Martin, J.; Kulik, N.; Somers, C.; McCaughtry, N. Parental social support, perceived competence and enjoyment in school physical activity. J. Sport Health Sci. 2018, 7, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaguer, I.; Duda, J.; Castillo, I. Motivational Antecedents of Well-Being and Health Related Behaviors in Adolescents. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 59, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usán-Supervía, P.; Murillo-Lorente, V.; Merino-Orozco, A.; Salavera-Bordas, C. Behavioral relationship between motivation and physical self-concept in drug use among adolescent athletes. Retos-Nuevas Tendencias en Educacion Fisica Deporte y Recreacion 2018, 33, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls, J.G. The Competitive Ethos and Democratic Education; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, T.; Zhang, T. Motivational processes in Sport Education programs among high school students: A systematic review. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2018, 24, 372–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, T.; Hill, A.; Hall, H.; Jowett, G. Relationships between the coach-created motivational climate and athlete engagement in youth sport. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2015, 37, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, K.; Gucciardi, D. Antisocial and prosocial behavior in sport: The role of motivational climate, basic psychological needs, and moral disengagement. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2015, 37, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Olmedo-Moreno, E.; Padial-Ruz, R.; Castro-Sánchez, M. An Exploratory Model of Psychosocial Factors and Healthy Habits in University Students of Physical Education Depending on Gender. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliff, H.; Huertas, J. Classroom motivational climate: In search of nuances. Revista de Psicología 2015, 11, 61–74. [Google Scholar]
- González-Valero, G.; Ubago-Jiménez, J.L.; Ramírez-Granizo, I.A.; Puertas-Molero, P. Association between Motivational Climate, Adherence to Mediterranean Diet, and Levels of Physical Activity in Physical Education Students. Behav. Sci. 2019, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Murcia, J.; Sicilia, A.; Sáenz-López, P.; González-Cutre, D.; Almagro, B.; Conde, C. Motivational analysis comparing three contexts of physical activity. Revista Internacional de Medicina y Ciencias de la Actividad Física y del Deporte 2014, 14, 665–685. [Google Scholar]
- Brackett, M.; Rivers, S.; Salovey, P. Emotional intelligence: Implications for personal, social, academic, and workplace success. Soc. Personal. Psychol. Compass 2011, 5, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, L.; Allen, J.; Mulvenna, C.; Russell, P. An investigation of the relationships between the teaching climate, students’ perceived life skills development and well-being within physical education. Phys. Educ. Sport Pedag. 2018, 23, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Valero, G.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Martínez-Martínez, A. Panorama motivacional y de actividad física en estudiantes: Una revisión sistemática. ESHPA 2017, 1, 41–58. [Google Scholar]
- Extremera, N.; Quintana-Orts, C.; Mérida-López, S.; Rey, L. Cyberbullying victimization, self-esteem and suicidal ideation in adolescence: Does emotional intelligence play a buffering role? Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salguero, J.; Extremera, N.; Fernández-Berrocal, P. Emotional intelligence and depression: The moderator role of gender. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2012, 53, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puertas-Molero, P.; González-Valero, G.; Sánchez-Zafra, M. Influencia de la práctica físico deportiva sobre la Inteligencia Emocional de los estudiantes: Una revisión sistemática. ESHPA 2017, 1, 10–24. [Google Scholar]
- Adilogullari, I.; Şenel, E. Examination of the relationship between general self-efficacy beliefs, emotional intelligence levels and emotional self-efficacy levels of students in school of physical education and sport. Anthropologist 2014, 18, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, M.; Duda, J.; Yin, Z. Examination of the psychometric properties of the Perceived Motivational Climate in Sport Questionnaire-2 in a sample of female athletes. J. Sports Sci. 2000, 18, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Cutre, D.; Sicilia, A.; Moreno, J. Modelo cognitivo-social de la motivación de logro en educación física. Psicothema 2008, 20, 642–651. [Google Scholar]
- Schutte, N.; Malouff, J.; Hall, L.; Haggerty, D.; Cooper, J.; Golden, C.; Dornheim, L. Development and validation of a measure of emotional intelligence. Personal. Individ. Differ. 1998, 25, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Coll, V.; Graupera-Sanz, J.; Ruiz-Pérez, L.; Palomo-Nieto, M. Inteligencia emocional en el deporte: Validación española del Schutte self Report Inventory (SSRI) en deportistas españoles. Cuadernos de Psicología del Deport 2013, 13, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, K.; Crocker, P.; Donen, R. The physical activity questionnaire for older children (PAQ-C) and adolescents (PAQ-A) manual. Coll. Kinesiol. 2004, 87, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Gómez, D.; Martínez-De Haro, V.; Pozo, T.; Welk, G.; Villagra, A.; Calle, M.; Veiga, O. Fiabilidad y validez del cuestionario de actividad física PAQ-A en adolescentes españoles. Revista Española de Salud Pública 2009, 83, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas, L.; Ngo, J.; Ortega, R.; García, A.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J. Food, youth and the Mediterranean diet in Spain. Development of KIDMED, Mediterranean Diet Quality Index in children and adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, O.; Maïano, C.; Nicol, C.; Mercier, C.S.; Vallier, J. Psycho-physiological responses of obese adolescents to an intermittent run test compared with a 20-m shuttle run. J. Sport. Sci. Med. 2016, 15, 451. [Google Scholar]
- Lager, L.; Lambert, J. A maximal multistage 20-m shuttle run test to predict. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 1982, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfell-Jones, M.; Stewart, A.; De Ridder, J. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Wellington, New Zealand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Marsh, H. Handbook of Sport Psychology; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mak, K.; Jeong, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, K. Mediating Effect of Internet Addiction on the Association between Resilience and Depression among Korean University Students: A Structural Equation Modeling. Psychiatry Investig. 2018, 15, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Respondek, L.; Seufert, T.; Stupnisky, R.; Nett, U.E. Perceived Academic Control and Academic Emotions Predict Undergraduate University Student Success: Examining Effects on Dropout Intention and Achievement. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harwood, C.; Keegan, R.; Smith, J.; Raine, A. A systematic review of the intrapersonal correlates of motivational climate perceptions in sport and physical activity. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2015, 18, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakkola, T.; Wang, C.; Soini, M.; Liukkonen, J. Students’ Perceptions of Motivational Climate and Enjoyment in Finnish Physical Education: A Latent Profile Analysis. J. Sport. Sci. Med. 2015, 14, 477–483. [Google Scholar]
- Laborde, S.; Dosseville, F.; Allen, M.S. Emotional intelligence in sport and exercise: A systematic review. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2016, 26, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajbafnezhad, H.; Ahadi, H.; Heidarie, A.; Askari, P.; Enayati, M. Difference between team and individual sports with respect to psychological skills, overall emotional intelligence and athletic success motivation in Shiraz city athletes. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2011, 11, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Chatzisarantis, N.; Lim, C. Influence of perceived motivational climate on achievement goals in physical education: A structural equation mixture modeling analysis. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2010, 32, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.; Ross, M.; Garvican-Lewis, L.; Welvaert, M.; Heikura, I.; Forbes, S.; Hawley, J. Low carbohydrate, high fat diet impairs exercise economy and negates the performance benefit from intensified training in elite race walkers. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 2785–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahia, N.; Wang, D.; Rapley, M.; Dey, R. Assessment of weight status, dietary habits and beliefs, physical activity, and nutritional knowledge among university students. Perspect. Public Health 2016, 136, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kun, B.; Demetrovics, Z. Emotional intelligence and addictions: A systematic review. Subst. Use Misuse 2010, 45, 1131–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puertas-Molero, P.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Martínez-Martínez, A.; Castro-Sánchez, M.; González-Valero, G. An Explanatory Model of Emotional Intelligence and Its Association with Stress, Burnout Syndrome, and Non-Verbal Communication in the University Teachers. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claros, E.; Sharma, M. The relationship between emotional intelligence and abuse of alcohol, marijuana, and tobacco among college students. J. Alcohol. Drug Educ. 2012, 56, 8–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, A.; Devonport, T.; Soos, I.; Karsai, I.; Leibinger, E.; Hamar, P. Emotional intelligence and emotions associated with optimal and dysfunctional athletic performance. J. Sport. Sci. Med. 2010, 9, 388. [Google Scholar]
- Jäger, K.; Schmidt, M.; Conzelmann, A.; Roebers, C. Cognitive and physiological effects of an acute physical activity intervention in elementary school children. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita-Ortega, F.; Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Castro-Sánchez, M.; Gutiérrez-Vela, F.; González-Valero, G. Effect of an intervention program based on active video games and motor games on health indicators in university students: A pilot study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Sánchez, M.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Chacón-Cuberos, R.; López-Gutiérrez, C.; Zafra-Sántos, E. Emotional Intelligence, Motivational Climate and Levels of Anxiety in Athletes from Different Categories of Sports: Analysis through Structural Equations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
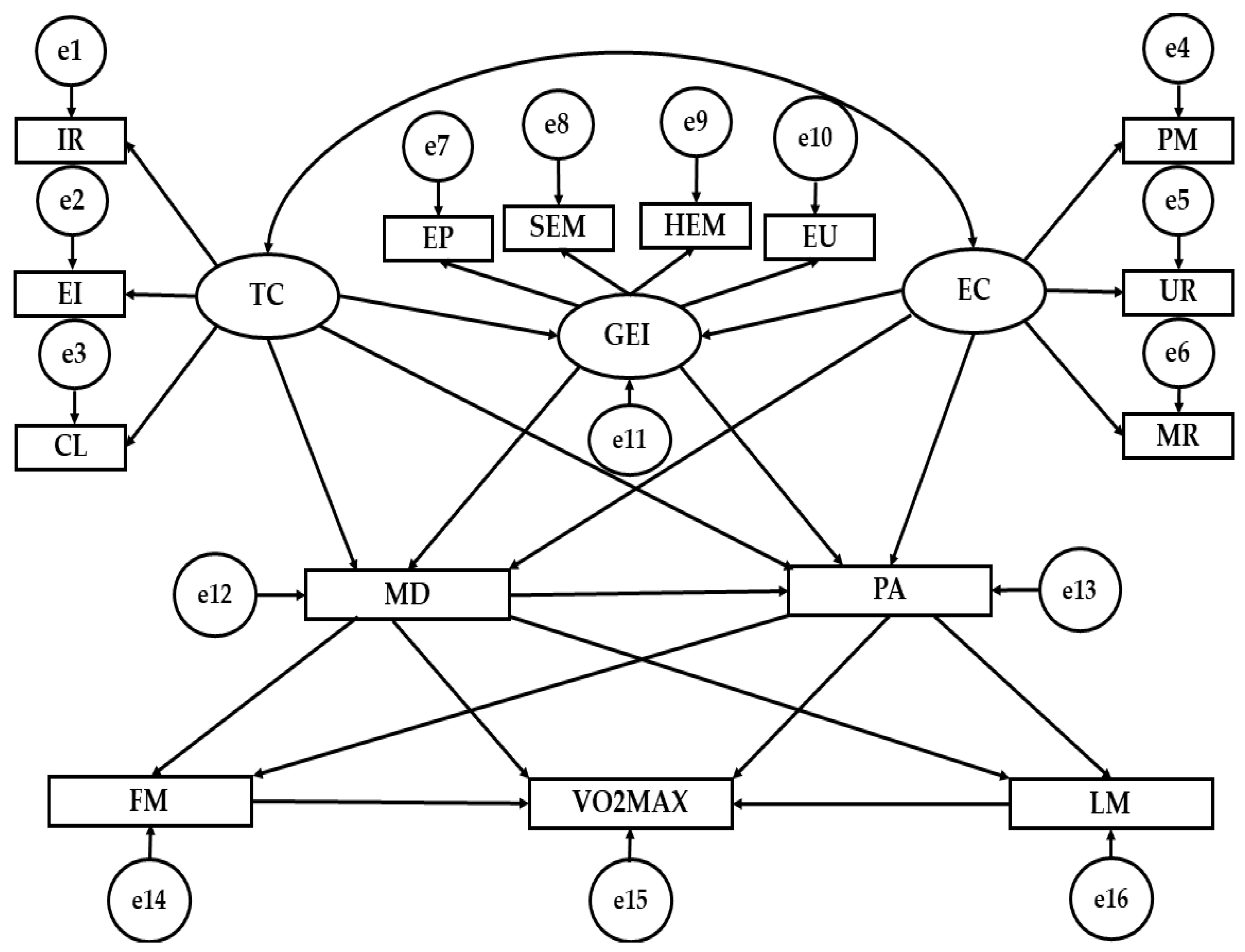

| Relationship Among Variables | Regression Weights | S.R.W | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | S.E. | C.R. | p | Estimate | |||
| GEI | ← | TC | 0.434 | 0.033 | 13.264 | *** | 0.603 |
| GEI | ← | EC | 0.075 | 0.029 | 2.539 | ** | 0.103 |
| MD | ← | TC | −0.195 | 0.219 | −0.889 | 0.374 | −0.048 |
| MD | ← | GEI | 0.795 | 0.278 | 2.863 | * | 0.141 |
| MD | ← | EC | 0.364 | 0.178 | 2.044 | * | 0.088 |
| PA | ← | EC | 2.189 | 0.568 | 3.850 | *** | 0.158 |
| PA | ← | TC | 0.947 | 0.694 | 1.364 | 0.173 | 0.069 |
| PA | ← | GEI | 4.573 | 0.893 | 5.122 | *** | 0.241 |
| PA | ← | MD | 0.693 | 0.114 | 6.064 | *** | 0.206 |
| FM | ← | MD | 0.393 | 0.100 | 3.922 | *** | 0.144 |
| LM | ← | PA | 0.205 | 0.090 | 2.277 | * | 0.084 |
| LM | ← | MD | 0.485 | 0.304 | 1.597 | 0.110 | 0.059 |
| FM | ← | PA | −0.089 | 0.030 | −2.990 | ** | −0.109 |
| EI | ← | TC | 0.827 | 0.030 | 27.380 | *** | 0.818 |
| PM | ← | EC | 1.000 | - | - | - | 0.773 |
| MR | ← | EC | 0.882 | 0.055 | 16.047 | *** | 0.583 |
| EP | ← | GEI | 1.000 | - | - | - | 0.779 |
| SEM | ← | GEI | 0.857 | 0.042 | 20.498 | *** | 0.732 |
| HEM | ← | GEI | 0.926 | 0.038 | 24.165 | *** | 0.866 |
| EU | ← | GEI | 0.905 | 0.045 | 20.317 | *** | 0.726 |
| VO2MAX | ← | MD | −23.372 | 10.341 | −2.260 | * | −0.075 |
| VO2MAX | ← | PA | 16.428 | 3.067 | 5.356 | *** | 0.176 |
| CTAP | ← | TC | 1.000 | - | - | - | 0.864 |
| CL | ← | TC | 1.037 | 0.034 | 30.112 | *** | 0.884 |
| UR | ← | EC | 1.327 | 0.065 | 20.260 | *** | 0.929 |
| VO2MAX | ← | LM | 13.257 | 1.211 | 10.950 | *** | 0.348 |
| VO2MAX | ← | FM | −27.200 | 3.668 | −7.416 | *** | −0.237 |
| EC | ↔ | TC | −0.168 | 0.018 | −9.103 | *** | −0.427 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Valero, G.; Zurita-Ortega, F.; Chacón-Cuberos, R.; Puertas-Molero, P. Analysis of Motivational Climate, Emotional Intelligence, and Healthy Habits in Physical Education Teachers of the Future Using Structural Equations. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133740
González-Valero G, Zurita-Ortega F, Chacón-Cuberos R, Puertas-Molero P. Analysis of Motivational Climate, Emotional Intelligence, and Healthy Habits in Physical Education Teachers of the Future Using Structural Equations. Sustainability. 2019; 11(13):3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133740
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Valero, Gabriel, Félix Zurita-Ortega, Ramón Chacón-Cuberos, and Pilar Puertas-Molero. 2019. "Analysis of Motivational Climate, Emotional Intelligence, and Healthy Habits in Physical Education Teachers of the Future Using Structural Equations" Sustainability 11, no. 13: 3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133740
APA StyleGonzález-Valero, G., Zurita-Ortega, F., Chacón-Cuberos, R., & Puertas-Molero, P. (2019). Analysis of Motivational Climate, Emotional Intelligence, and Healthy Habits in Physical Education Teachers of the Future Using Structural Equations. Sustainability, 11(13), 3740. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11133740





