Sustainable Production of Sweet Sorghum as a Bioenergy Crop Using Biosolids Taking into Account Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.3. Field Treatments and Experimental Design
2.4. CO2 Emission Determination and Carbon Footprint Calculation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Weather and Soil Conditions
3.2. Sorghum Biomass Yield
3.3. Carbon Footprint of Sorghum Per Area and Per Mg of Biomass
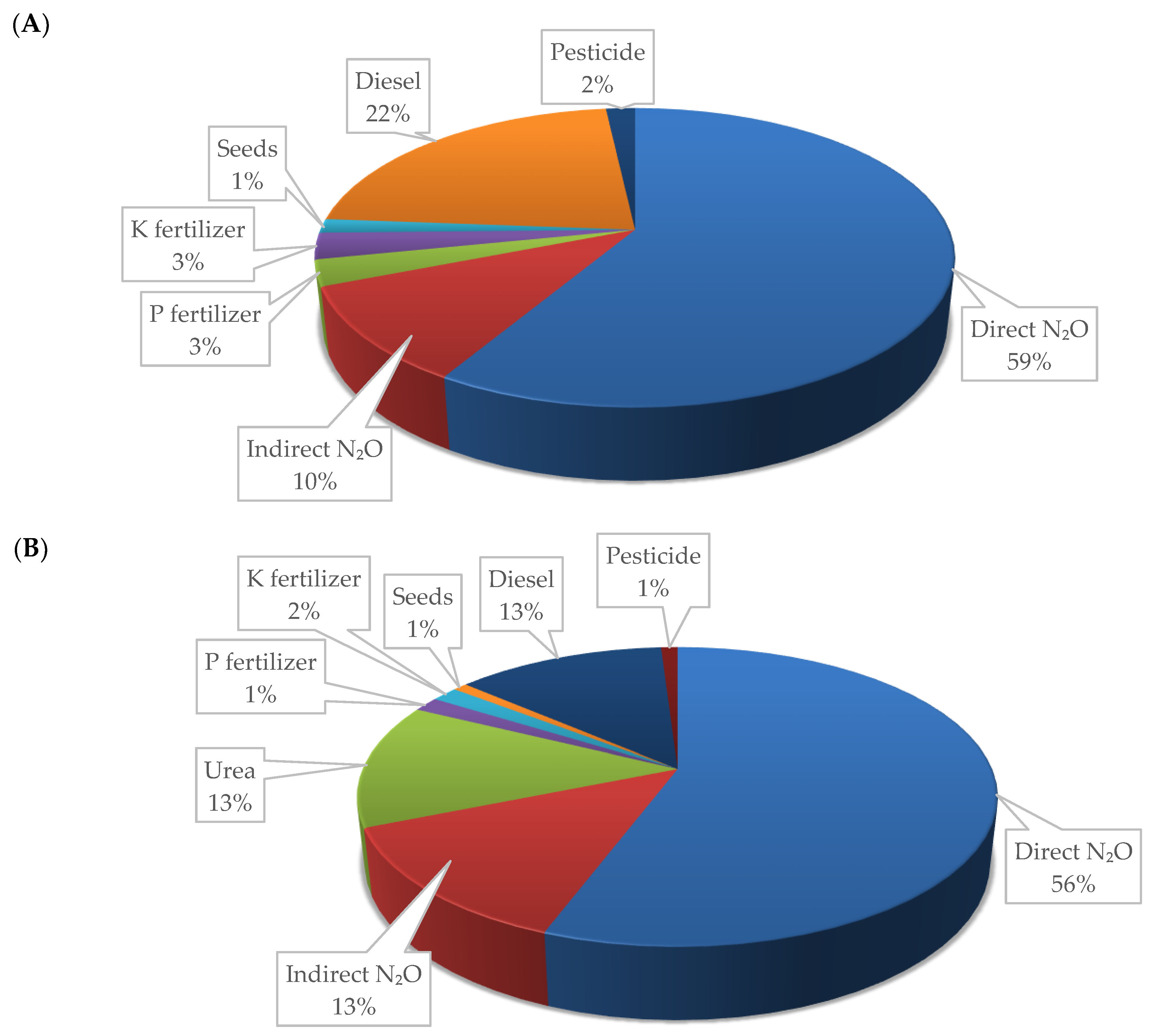
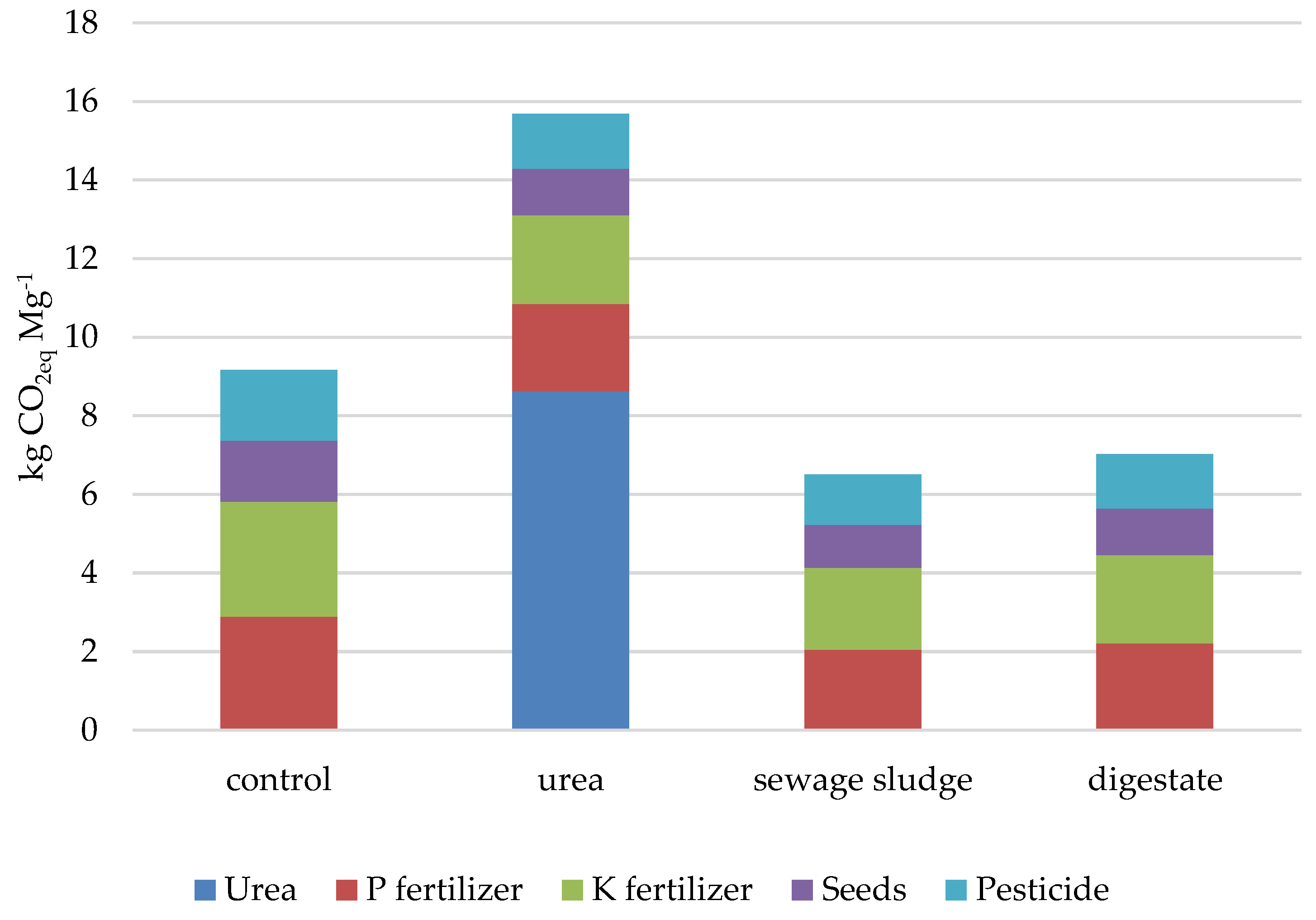
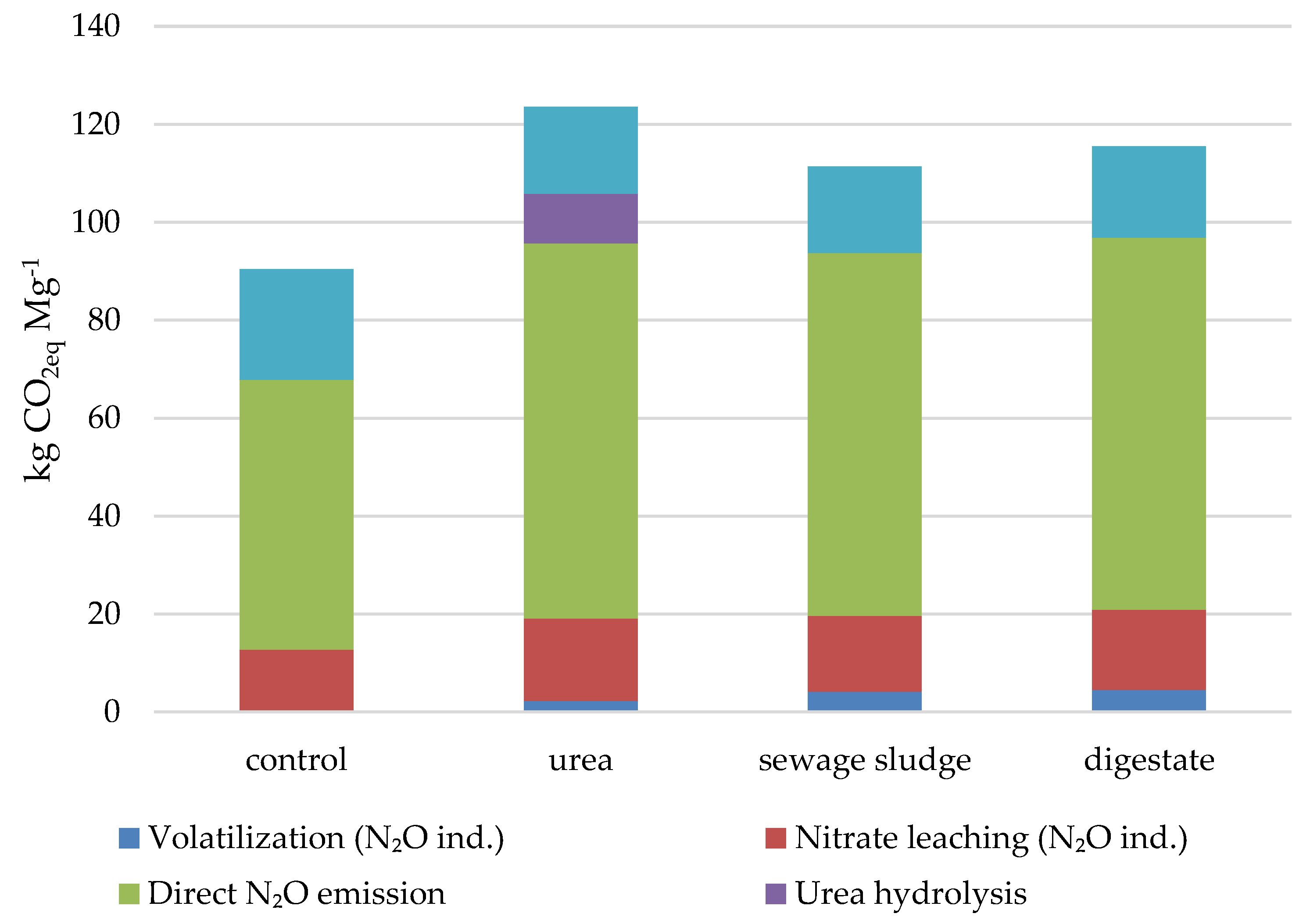
3.4. Structure of Inputs Share of Carbon Footprint
3.5. External and On-Site Emissions
4. Discussion
4.1. Biomass Yield
4.2. Carbon Footprint
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Usman, M.; Ibrahim, F.; Oyetola, S.O. Sustainable agriculture in relation to problems of soil degradation and how to amend such soils for optimum crop production in Nigeria. Int. J. Res. Agric. Food Sci. 2018, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Brodt, S.; Six, J.; Feenstra, G.; Ingels, C.; Campbell, D. Sustainable Agriculture. Nat. Educ. Knowl. 2011, 3, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Vergé, X.P.C.; De Kimpe, C.; Desjardins, R.L. Agricultural production, greenhouse gas emissions and mitigation potential. Agric. Meteorol. 2007, 142, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, L.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- EEA. Trends and Projections in Europe 2018. Tracking Progress towards Europe’s Climate and Energy Targets; European Environment Agency report 16/2018; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, C.; Paulino, L.; Monreal, C.; Zagal, E. Greenhouse Gas (CO2 AND N2O) Emissions from Soils: A Review. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 70, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, S.; Havlík, P.; Soussana, J.F.; Levesque, A.; Valin, H.; Wollenberg, E.; Kleinwechter, U.; Fricko, O.; Gusti, M.; Herrero, M.; et al. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions in agriculture without compromising food security? Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 105004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosulski, T.; Rutkowska, B.; Szczepaniak, J.; Szulc, W.; Skowrońska, M. Impact of reduced tillage on CO2 emission from soil under maize cultivation. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 180, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storlien, J.O.; Hons, F.M.; Wight, J.P.; Heilman, J.L. Carbon Dioxide and nitrous oxide emissions impacted by bioenergy sorghum management. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1694–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, C.; Helming, K.; Nendel, C. Do greenhouse gas emission calculations from energy crop cultivation reflect actual agricultural management practices? —A review of carbon footprint calculators. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza-Bonilla, D.; Nogué-Serra, I.; Raffaillac, D.; Cantero-Martínez, C.; Justes, É. Carbon footprint of cropping systems with grain legumes and cover crops: A case-study in SW France. Agric. Syst. 2018, 167, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, G.S.; Das, A.; Lal, R.; Babu, S.; Meena, R.S.; Saha, P.; Singh, R.; Datta, M. Energy budget and carbon footprint in a no-till and mulch based rice–mustard cropping system. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 191, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, J.F.F.P.; De Haan, J.; Sukkel, W.; Schils, R.L.M. Energy use and greenhouse gas emissions in organic and conventional farming systems in the Netherlands. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2014, 68, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Parliament and Council. Directive 2009/30/EC of 23 April 2009 as Regards the Specification of Petrol, Diesel and Gas-Oil and Introducing A Mechanism to Monitor and Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions. 2009. Available online: http://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriS (accessed on 6 February 2019).
- European Parliament and Council. Directive 2009/28/EC of 23 April 2009 on the Promotion of the Use of Energy from Renewable Sources. 2009. Available online: http://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2009:140:0016:0062:EN:PDF (accessed on 12 January 2019).
- Hennecke, A.M.; Faist, M.; Reinhardt, J.; Junquera, V.; Neeft, J.; Fehrenbach, H. Biofuel greenhouse gas calculations under the European Renewable Energy Directive–A comparison of the BioGrace tool vs. the tool of the Roundtable on Sustainable Biofuels. Appl. Energy 2013, 102, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BioGrace Software. Available online: http://www.biograce.net (accessed on 23 February 2019).
- IPCC. Chapter 11: N2O Emissions from Managed Soils, and CO2 Emissions from Lime and Urea Application. In IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES): Kanagawa, Japan, 2006; pp. 11.1–11.54. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Sui, P.; Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Whalen, J.K.; Chen, Y. Global warming potential from maize and maize-soybean as affected by nitrogen fertilizer and cropping practices in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2018, 225, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, G.G.T.; Ryan, M.R.; Richard, T.L. Energy Use and Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Crop Production Using the Farm Energy Analysis Tool. Bioscience 2013, 63, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartocci, P.; Fantozzi, P.; Fantozzi, F. Environmental impact of Sagrantino and Grechetto grapes cultivation for wine and vinegar production in central Italy. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 140, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COM. Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council Laying Down Rules on the Making Available on the Market of CE Marked Fertilising Products and Amending Regulations (EC) No 1; 157 final, 17.3.2016 2016/0084 (COD); COM: Brussels, Belgium, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kołodziej, B.; Antonkiewicz, J.; Stachyra, M.; Bielińska, E.J.; Wiśniewski, J.; Luchowska, K.; Kwiatkowski, C. Use of sewage sludge in bioenergy production—A case study on the effects on sorghum biomass production. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 69, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Janssens, T.K.S.; Ruijs, R.; Kim, S.Y.; de Boer, W.; Termorshuizen, A.; van der Putten, W.H.; Bodelier, P.L.E. Effects of bio-based residue amendments on greenhouse gas emission from agricultural soil are stronger than effects of soil type with different microbial community composition. Gcb Bioenergy 2017, 9, 1707–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maucieri, C.; Nicoletto, C.; Caruso, C.; Sambo, P.; Borin, M. Effects of digestate solid fraction fertilisation on yield and soil carbon dioxide emission in a horticulture succession. Ital. J. Agron. 2017, 12, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendooven, L.; Fernández-Luqueño, F.; Paredes-López, O.; Hernández, G.; Pampillón-González, L.; Franco-Hernández, O.; Luna-Guido, M.; Ruíz-Valdiviezo, V.M. Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Growth of Wheat Cultivated in Soil Amended with Digestate from Biogas Production. Pedosphere 2017, 27, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juárez-Rodríguez, J.; Fernández-Luqueño, F.; Conde, E.; Reyes-Varela, V.; Cervantes-Santiago, F.; Botello-Alvarez, E.; Cárdenas-Manríquez, M.; Dendooven, L. Greenhouse gas emissions from an alkaline saline soil cultivated with maize (Zea mays L.) and amended with anaerobically digested cow manure: A greenhouse experiment. J. Plant Nutr. 2012, 35, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, J.J.; Jones, D.L.; Edwards-Jones, G.; Williams, A.P. Replacing inorganic fertilizer with anaerobic digestate may maintain agricultural productivity at less environmental cost. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzolla, D.; Bol, R.; Gigliotti, G.; Sawamoto, T.; López, A.L.; Cardenas, L.; Chadwick, D. Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from soils amended with digestate derived from anaerobic treatment of food waste. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 26, 2422–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.; Kretschmer, B.; Baldock, D.; Menadue, H.; Nanni, S.; Tucker, G. Space for Energy Crops—Assessing the Potential Contribution to Europe’s Energy Future; Report Produced for BirdLife Europe; European Environmental Bureau and Transport & Environ: Brussels, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brentrup, F.; Palliere, C. Energy efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions in European nitrogen fertilizer production and use. Fertil. Eur. 2008, 639, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Chmielewska, J.; Sowiński, J.; Foszczyńska, B.; Szydełko-Rabska, E.; Kawa-Rygielska, J. Production of bioethanol from sweet sorghum juices with varying content of mineral compounds. Przem. Chem. 2014, 93, 999–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, S.C.; Parton, W.J.; Del Grosso, S.J.; Keough, C.; Marx, E.; Adler, P.R.; Delucia, E.H. Impact of second-generation biofuel agriculture on greenhouse-gas emissions in the corn-growing regions of the US. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubicki, A.; Dubicka, M.; Szymanowski, M. Klimat Wrocławia. In Środowisko Wrocławia-Informator; Smolnicki, K., Szykasiuk, M., Eds.; Dolnośląska Fundacja Ekorozwoju: Wrocław, Poland, 2002; pp. 9–20. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Szczepaniak, W. Metody Instrumentalne w Analizie Chemicznej; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2005. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Sowiński, J.; Szydełko-Rabska, E. Comparison of sorghum type yielding in Polish conditions. Ann. Univ. Mariae Curie-Skłodowska Lub. Pol. Sect. E 2013, LXVIII, 30–40. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Hybrid Characteristic. Available online: https://www.gabonakutato.hu/en/our-seeds/sorghum/silage-sorghum/rona-1 (accessed on 13 January 2019).
- Hybrid Characteristic. Available online: https://www.caussade-nasiona.pl/sorgo-trawa-sudanska/ (accessed on 17 January 2019).
- Hybrid Characteristic. Available online: https://www.benelux.saaten-union.com/index.cfm?m=varieties&p=325,1683,html (accessed on 17 January 2019).
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). Chapter 3. Mobile combustion. In Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES): Kanagawa, Japan, 2006; Volume 2, Energy; Available online: https://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/vol2.html (accessed on 23 February 2019).
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). Cropland. In IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Agriculture, Forestry and Other Land Use; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES): Kanagawa, Japan, 2006; Volume 4, Available online: http://www.ipcc-nggip.iges.or.jp/public/2006gl/vol4.h (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- ISO. ISO/TS 14067: Greenhouse Gases e Carbon Footprint of Products e Requirements and Guidelines for Quantification and Communication; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- BioGrace List of Standard Values, Version 4. Available online: http://www.biograce.net/content/ghgcalculationtools/standardvalues (accessed on 11 January 2019).
- Nielsen, S.; Bruun, S.; Bekiaris, G.; Gómez-Muñoz, B.; Larsen, J.D.; Jensen, L.S.; Scheutz, C. Nitrogen mineralisation and greenhouse gas emission from the soil application of sludge from reed bed mineralisation systems. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, T.O.; Marland, G. A synthesis of carbon sequestration, carbon emissions, and net carbon flux in agriculture: Comparing tillage practices in the United States. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 91, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Zahediasl, S. Normality tests for statistical analysis: A guide for non-statisticians. Int. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazderu, K.; Hodoval, J.; Urban, J.; Pulkrabek, J.; Pacuta, V.; Adamcik, J. The influence of sweet sorghum crop stand arrangement on biomass and biogas production. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 60, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, B.; Rosen, C.J.; Lamb, J.A.; Venterea, R.T. Corn response to nitrogen management under fully-irrigated vs. water-stressed conditions. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowiński, J.; Głąb, L. The effect of nitrogen fertilization management on yield and nitrate contents in sorghum biomass and bagasse. Field Crops Res. 2018, 227, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdeniz, H.; Yilmaz, I.; Bozkurt, M.A.; Keskin, B. The effects of sewage sludge and nitrogen applications on grain sorghum grown (Sorghum vulgare L.) in Van-Turkey. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Verdi, L.; Kuikman, P.J.; Orlandini, S.; Mancini, M.; Napoli, M.; Dalla Marta, A. Does the use of digestate to replace mineral fertilizers have less emissions of N2O and NH3? Agric. Meteorol. 2019, 269–270, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formowitz, B.; Fritz, M. Biogas Diegstate as Organic Fertilizer in Different Crop Rotations. In Proceedings of the 18th European Biomass Conference and Exibition, Lyon, France, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Jaša, S.; Badalíková, B.; Červinka, J. Influence of Digestate on Physical Properties of Soil in Zd Budišov. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2019, 67, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurnjak, I.; Ryckaert, B.; Tack, F.M.G.; Ghekiere, G.; Meers, E.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Michels, E. Fertilizer performance of liquid fraction of digestate as synthetic nitrogen substitute in silage maize cultivation for three consecutive years. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styles, D.; Jones, M.B. Energy crops in Ireland: Quantifying the potential life-cycle greenhouse gas reductions of energy-crop electricity. Biomass Bioenergy 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czubaszek, R.; Wysocka-Czubaszek, A. Emissions of carbon dioxide and methane from fields fertilized with digestate from an agricultural biogas plant. Int. Agrophysics 2018, 32, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baral, K.R.; Labouriau, R.; Olesen, J.E.; Petersen, S.O. Nitrous oxide emissions and nitrogen use efficiency of manure and digestates applied to spring barley. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 239, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storlien, J.O. The Carbon Footprint of Bioenergy Sorghum Production in Central Texas: Production Implications on Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Carbon Cycling, and Life Cycle Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters/Chemical Elements with Limit Value for Organic Fertilizer and Organic Soil Improver | Unit | Digestate | Sewage Sludge | Methods |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.6 | 7.4 | PN-EN 12176:2004 | |
| DM (1) | % | 2.8 | 42 | PN-EN 12880:2004 |
| Organic compounds | % DM | 71 | 31.5 | PN-EN 12879:2004 |
| Total nitrogen (N) | 8 | 1.29 | KJ-I-5.4-179 | |
| Ammonia nitrogen N-NH4 | 2 | <0.10 | PN-EN 14671:2007 | |
| Total phosphorus (P) | 0.54 | 1.63 | PN-EN ISO 1185:2009 | |
| Calcium (Ca) | 2.99 | 4.11 | ||
| Magnesium (Mg) | 1.02 | 0.60 | ||
| Potassium (K) | mg kg −1 DM | 1280 | n.a. (2) | PN-EN ISO 1185:2009; PN-EN 13657:2006 |
| Copper (Cu), 200 (3) | 49.6 | 239 | PN-EN ISO 1185:2009 | |
| Zinc (Zn) | 170 | 777 | ||
| Lead (Pb), 120 (3) | 6.13 | 94 | ||
| Cadmium (Cd), 3 (3) | 2.78 | 0.71 | ||
| Chromium (Cr) | 11.2 | 32.9 | ||
| Nickel (Ni), 50 (3) | 11.6 | 24.7 | ||
| Mercury (Hg), 1 (3) | 0.050 | 0.540 | KJ-I-5.4-36 | |
| Salmonella bacteria: | PB/BB/7/F:20.03.2014 | |||
| no Salmonella species in 25 g sample (3) | 0 | 0 |
| Rule | Description |
|---|---|
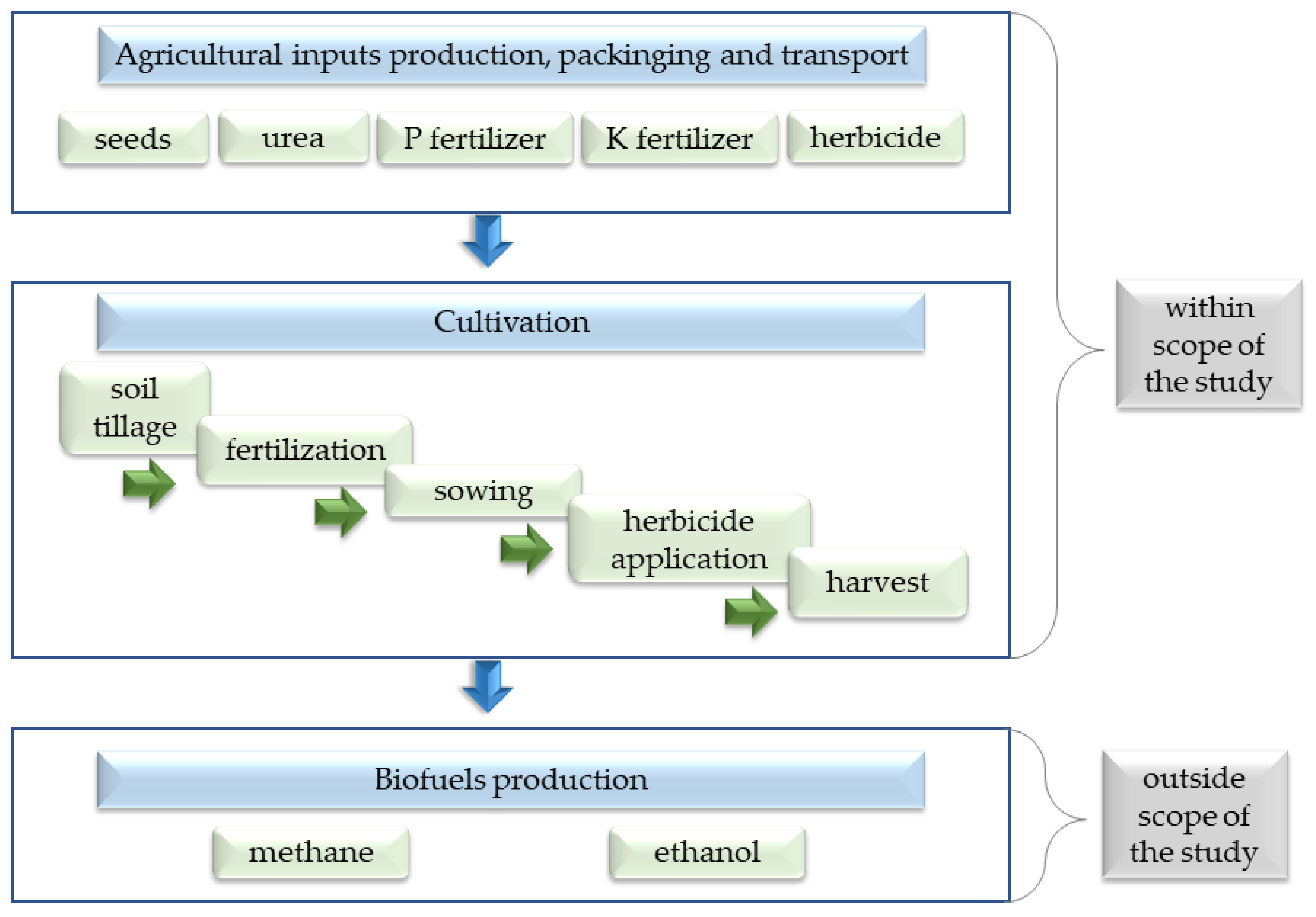
| Scope of the study | Calculate the GHG emissions during sweet sorghum production for biofuels (methane and bioethanol) production. |
| System boundary | Farm stage—including external and on-farm greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Functional unit | 1 ton of sorghum biomass. |
| Time reference | One growing season (as an average of three seasons). |
| Data collection—cultivation | The following agricultural operations were included: soil tillage, sowing, fertilization, herbicide application, and harvest. |
| Carbon footprint calculation: | |
| Calculator | BioGrace Excel GHG calculation tool [17] |
| Methods | IPCC 2006 [18,40,41] |
| Norm | ISO14067 [42] |
| Description of Emission Factor | Unit | Default Value | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emission factor for N2O emissions from N inputs | kg N2O–N kg−1 N input | 0.01 | [18] |
| FracGASF fraction of synthetic fertilizer N that volatilizes as NH3 and NOx, kg N volatilized | % | 10 | |
| FracGASM fraction of applied organic N fertilizer materials that volatilizes as NH3 and NOx, kg N volatilized | 20 | ||
| Emission factor for N2O emissions from atmospheric deposition of N on soils and water surfaces | 1 | ||
| FracLEACH-(H) fraction of all N added to/mineralized in managed soils in regions where leaching/runoff occurs that is lost through leaching and runoff, | 30 | ||
| Emission factor for N2O emissions from N leaching and runoff | 0.75 | ||
| Energy factor for urea production | 20 | ||
| Fuel density (diesel) | kg m−3 | 832 | [17] |
| LHV (diesel) (1) | MJ kg−1 | 43.1 | |
| Emission factor for combustion of Diesel: CO2 diesel | kg TJ−1 | 74100 | [40] |
| Emission factor for combustion of Diesel: CH4 diesel | 4.15 | ||
| Emission factor for combustion of Diesel: N2O diesel | 28.6 | ||
| Energy factor for mesotrione | MJ kg−1 a.i. (2) | 691 | [31] |
| Energy factor for tetrabulazine and atriazine | 208 | ||
| Energy factor for metolachlor and metazachlor | 388 | ||
| Energy factor for pesticide | kg CO2eq MJ−1 | 0.069 | |
| Energy factor for P fertilizer production | kg CO2eq kg−1 fertilizer | 0.26 | |
| Energy factor for K fertilizer production | kg CO2eq kg−1 fertilizer | 0.25 | |
| Emission factor for sorghum seeds | g CO2 eq kg−1 | 0.86 | [45] |
| Month | Taverage (°C) | Rainfall (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | Long-Term Average 1986–2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | Long-Term Average 1986–2015 | |
| May | 15.3 | 14.2 | 17.1 | 14.4 | 5.3 | 24.1 | 54.3 | 54.1 |
| June | 18.6 | 18.5 | 18.8 | 17.3 | 44.6 | 52.5 | 36.6 | 67.4 |
| July | 19.5 | 19.0 | 20.1 | 19.6 | 114.3 | 112.2 | 79.1 | 78.9 |
| August | 17.9 | 19.4 | 21.1 | 18.6 | 27.1 | 43.6 | 20.3 | 65.3 |
| September | 16.4 | 13.3 | 15.8 | 13.7 | 44.7 | 65.7 | 38.4 | 44.9 |
| Average temperature or rainfall sum in the period from May to September | 17.5 | 16.9 | 18.6 | 16.7 | 236.0 | 298.1 | 228.7 | 310.6 |
| Soil Texture | pH | NO3-N | NH4-N | Pavailable | Kavailable | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | g kg−1 | mg kg−1 | |||||
| sand: 87 | silt: 5 | clay: 8 | 6.0 | 0.79 | 0.55 | 337.5 | 154.0 |
| Sorghum Hybrid | Fertilization Treatment | Dry Matter Yield Mg ha−1 | Spatial Carbon Footprint kg CO2eq ha−1 | Yield-Scaled Carbon Footprint kg CO2eqMg−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sucrosorgo 506 | control | 17.0 | 1731 b | 88 |
| Urea | 18.9 | 2742 f | 130 | |
| sewage sludge | 23.6 | 2736 f | 111 | |
| digestate | 19.0 | 2498 def | 117 | |
| Rona 1 | control | 10.9 | 1414 a | 96 |
| Urea | 15.0 | 2528 def | 141 | |
| sewage sludge | 15.3 | 2282 cd | 126 | |
| digestate | 15.8 | 2303 cd | 125 | |
| Goliath | control | 12.2 | 1286 a | 109 |
| Urea | 17.9 | 2621 ef | 135 | |
| sewage sludge | 19.6 | 2446 cde | 118 | |
| digestate | 16.9 | 2340 cde | 120 | |
| SuperSile 20 | control | 10.5 | 1412 a | 96 |
| Urea | 13.1 | 2472 def | 147 | |
| sewage sludge | 14.8 | 2301 cd | 124 | |
| digestate | 12.6 | 2180 c | 131 | |
| Average for factors | ||||
| Hybrid * | ||||
| Sucrosorgo 506 | 19.6 c | 2427 b | 111a | |
| Rona 1 | 14.2 ab | 2132 a | 122ab | |
| Goliath | 16.6 b | 2163 ab | 120ab | |
| SuperSile 20 | 12.7 a | 2091 a | 125b | |
| Fertilization treatment ** | ||||
| control | 12.6 a | 1461 a | 97a | |
| urea | 16.2 b | 2590 c | 138c | |
| sewage sludge | 18.3 b | 2441 b | 119b | |
| digestate | 16.1 b | 2330 b | 123b | |
| Average for years *** | ||||
| 2016 | 15.3 b | 2019 a | 133b | |
| 2017 | 20.2 c | 2282 b | 114a | |
| 2018 | 11.8 a | 2265 b | 115a | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Głąb, L.; Sowiński, J. Sustainable Production of Sweet Sorghum as a Bioenergy Crop Using Biosolids Taking into Account Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113033
Głąb L, Sowiński J. Sustainable Production of Sweet Sorghum as a Bioenergy Crop Using Biosolids Taking into Account Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Sustainability. 2019; 11(11):3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113033
Chicago/Turabian StyleGłąb, Lilianna, and Józef Sowiński. 2019. "Sustainable Production of Sweet Sorghum as a Bioenergy Crop Using Biosolids Taking into Account Greenhouse Gas Emissions" Sustainability 11, no. 11: 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113033
APA StyleGłąb, L., & Sowiński, J. (2019). Sustainable Production of Sweet Sorghum as a Bioenergy Crop Using Biosolids Taking into Account Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Sustainability, 11(11), 3033. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113033





