Safety Evaluation of Absorbent Hygiene Pads: A Review on Assessment Framework and Test Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Disposable Absorbent Hygiene Pads
2.1. Types of Disposable Absorbent Hygiene Pads
2.2. Layer Construction of Absorbent Hygiene Pads
2.3. Regulatory Classifications
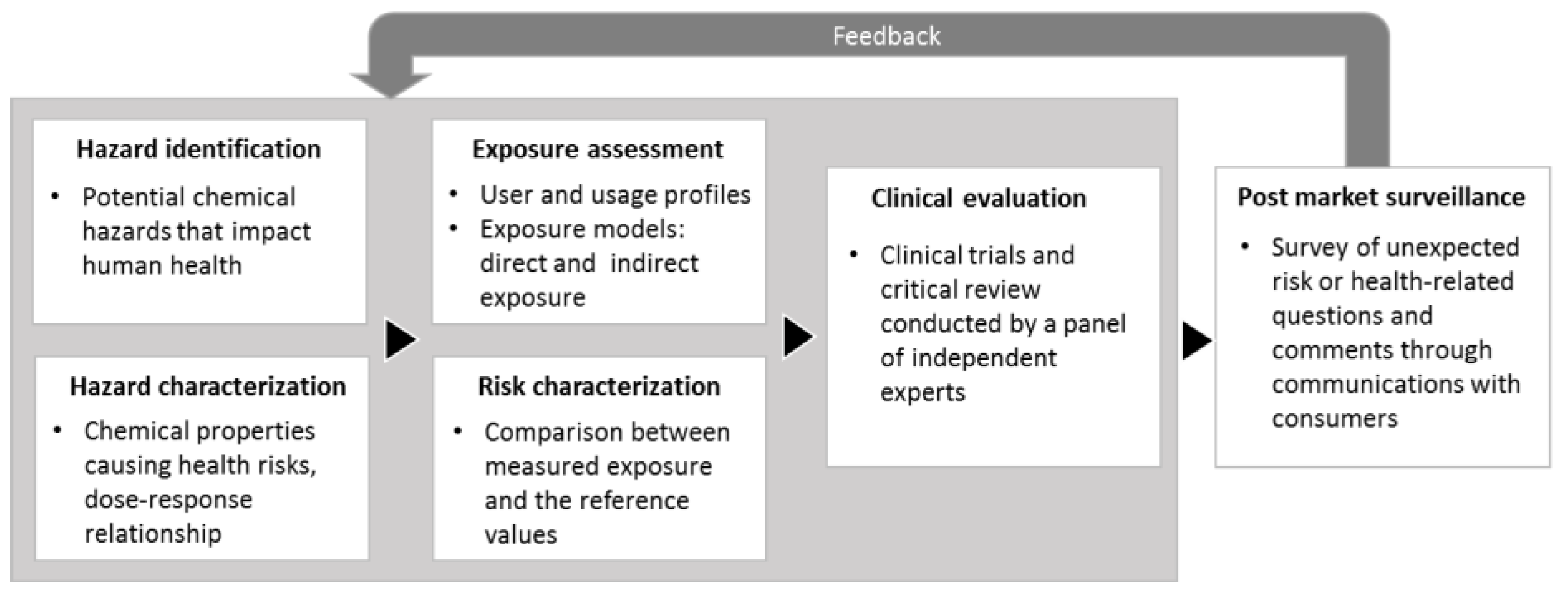
3. Safety Assessment Framework of Absorbent Hygiene Pads
3.1. Hazard Identification and Characterization
3.2. Exposure Assessment and Risk Characterization
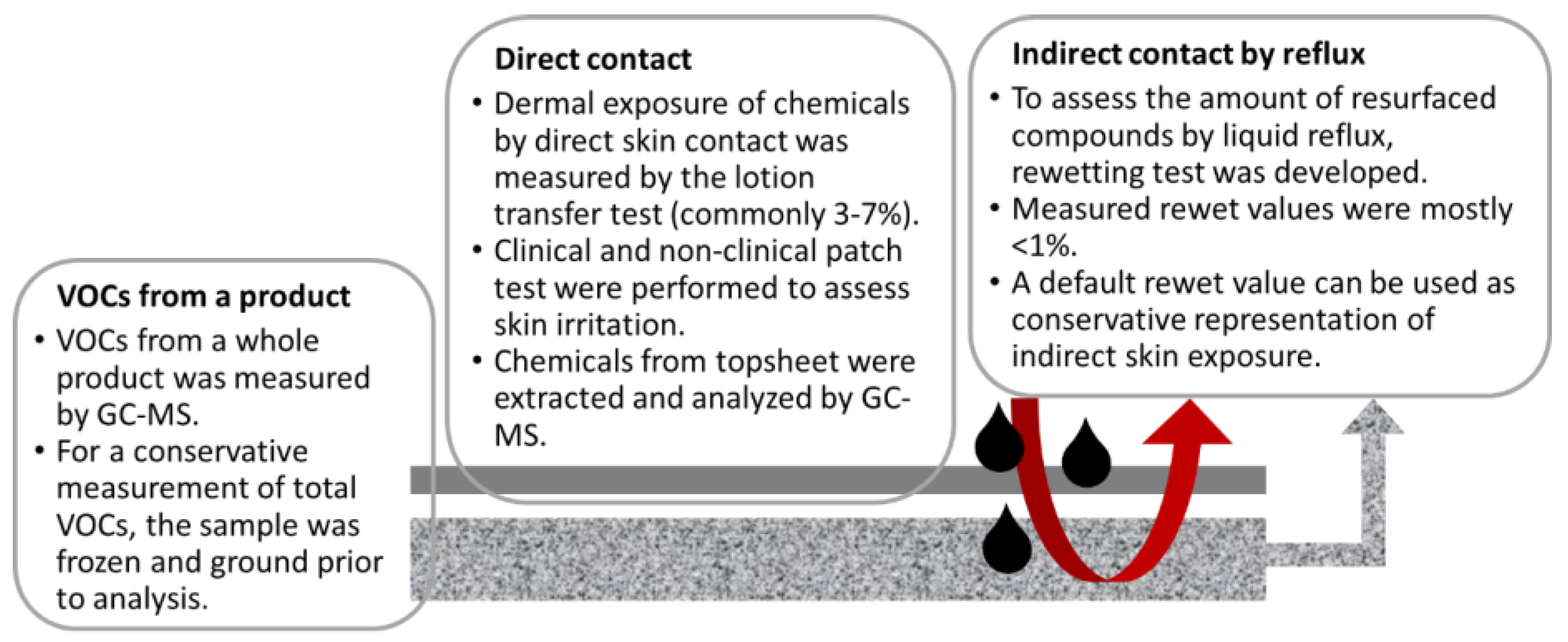
3.2.1. Exposure Model
3.2.2. Exposure by the Direct Skin Contact
3.2.3. Indirect Exposure by Reflux
3.2.4. Risk Characterization
3.3. Clinical Evaluation of Product Safety In-Use
3.4. Post-Market Surveillance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Counts, J.; Weisbrod, A.; Yin, S. Common diaper ingredient questions: Modern disposable diaper materials are safe and extensively tested. Clin. Pediatr. 2017, 56, 23S–27S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Kenneally, D.; Odio, M.; Hatzopoulos, I. Modern diaper performance: Construction, materials, and safety review. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55 (Suppl. 1), 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Purdon, M.; Kirsch, T.; Helbich, H.; Kerr, K.; Li, L.; Zhou, S. Exposure factor considerations for safety evaluation of modern disposable diapers. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosemund, K.; Schlatter, H.; Ochsenhirt, J.L.; Krause, E.L.; Marsman, D.S.; Erasala, G.N. Safety evaluation of superabsorbent baby diapers. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2009, 53, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, S.; Katagiri, R.; Minobe, Y.; Kuribara, I.; Wada, T.; Wada, M.; Imai, S. Investigation of the amount of transdermal exposure of newborn babies to phthalates in paper diapers and certification of the safety of paper diapers. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koda, K.; Goto, H.; Shintani, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Meshitsuka, G. Oxidative cleavage of lignin aromatics during chlorine bleaching of kraft pulp. J. Wood Sci. 2001, 47, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Iwasaki, K.; Minobe, Y.; Wada, M.; Imai, S.; Ishii, S. Proposal of a flow scheme for the chemical-form-based quantitative analysis of chlorine compounds in pulp for sanitary products and verification of safety. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 91, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US FDA. Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff- Menstrual Tampons and Pads: Information for Premarket Notification Submissions 510(k). 2017. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/MedicalDevices/ucm071781.htm (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). Available online: http://www.mfds.go.kr/brd/m_543/list.do (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Code of Federal Regulations. CFR 884.5425: Scented or Scented Deodorized Menstrual Pad. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/retrieveECFR?gp=1&SID=df43bf980a5782408f10c44a86b616bf&ty=HTML&h=L&mc=true&r=SECTION&n=se21.8.884_15425 (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Code of Federal Regulations. CFR 884.5435: Unscented Menstrual Pad. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/retrieveECFR?gp=1&SID=df43bf980a5782408f10c44a86b616bf&ty=HTML&h=L&mc=true&r=SECTION&n=se21.8.884_15435 (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Standardization Administration of China. GB 15979-2002: Hygienic Standard for Disposable Sanitary Products; Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 8939-2008: SANITARY Absorbent Pads (Including Pantiliner); Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Woeller, K.E.; Hochwalt, A.E. Safety assessment of sanitary pads with a polymeric foam absorbent core. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 73, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Disposables and Nonwovnes Association (EDANA). Nonwovens Standard Procedures 2015. Available online: https://www.edana.org/docs/default-source/default-document-library/toc-cover-preamble.pdf?sfvrsn=1 (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- European Disposables and Nonwovens Association (EDANA). Fact Sheet Health & Hygiene Benefits of Absorbent Hygiene Products & Personal Care Wet Wipes. Available online: https://www.edana.org/docs/default-source/default-document-library/fact-sheet---health-hygiene-benefits-of-absorbent-hygiene-products-personal-care-wet-wipes.pdf?sfvrsn=2 (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Farage, M.A.; Bjerke, D.L.; Mahony, C.; Blackburn, K.L.; Gerberick, G.F. Quantitative risk assessment for the induction of allergic contact dermatitis: Uncertainty factors for mucosal exposures. Contact Dermat. 2003, 49, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felter, S.P.; Carr, A.N.; Zhu, T.; Kirsch, T.; Niu, G. Safety evaluation for ingredients used in baby care products: Consideration of diaper rash. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 90, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felter, S.P.; Robinson, M.K.; Basketter, D.A.; Gerberick, G.F. A review of the scientific basis for uncertainty factors for use in quantitative risk assessment for the induction of allergic contact dermatitis. Contact Dermat. 2002, 47, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerberick, G.F.; Robinson, M.K.; Felter, S.P.; White, I.R.; Basketter, D.A. Understanding fragrance allergy using an exposure-based risk assessment approach. Contact Dermat. 2001, 45, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, S.; Katagiri, R.; Kataoka, T.; Wada, M.; Imai, S.; Yamasaki, K. Risk assessment study of dioxins in sanitary napkins produced in Japan. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 70, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroes, R.; Kleiner, J.; Renwick, A. The threshold of toxicological concern concept in risk assessment. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 86, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meek, M.E.; Boobis, A.R.; Crofton, K.M.; Heinemeyer, G.; Raaij, M.V.; Vickers, C. Risk assessment of combined exposure to multiple chemicals: A WHO/IPCS framework. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Lee, B.M.; Liu, T.Y.; Yuhui, Q.; Krause, E.; Marsman, D.S.; Felter, S. Safety evaluation of disposable baby diapers using principles of quantitative risk assessment. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2009, 72, 1262–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.K.; Gerberick, G.F.; Ryan, C.A.; McNamee, P.; White, I.R.; Basketter, D.A. The importance of exposure estimation in the assessment of skin sensitization risk. Contact Dermat. 2000, 42, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, M.; Birnbaum, L.S.; Denison, M.; De Vito, M.; Farland, W.; Feeley, M.; Fiedler, H.; Hakansson, H.; Hanberg, A.; Haws, L.; et al. The 2005 World Health Organization reevaluation of human and Mammalian toxic equivalency factors for dioxins and dioxin-like compounds. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 93, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Repon, M.R.; Islam, M.T.; Mamun, M.A.A. Ecological risk assessment and health safety speculation during color fastness properties enhancement of natural dyed cotton through metallic mordants. Fash. Text. 2017, 4, 24:1–24:17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farage, M.A.; Stadler, A.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H.I. Safety evaluation of modern feminine hygiene pads: Two decades of use. Female Patient 2004, 29, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Farage, M.A. A behind-the-scenes look at the safety assessment of feminine hygiene pads. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1092, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Helmes, C.T.; White, J.C.; Zhou, S. Safety of disposable diaper materials: Extensive evaluations validate use. Clin. Pediatr. 2014, 53, 17s–19s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin, F.; Spraker, M.; Aly, R.; Leyden, J.; Raynor, W.; Landin, W. Effects of breathable disposable diapers: Reduced prevalence of candida and common diaper dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2001, 18, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberta, L.; Sweeney, S.M.; Wiss, K. Diaper dye dermatitis. Pediatrics 2005, 116, e450–e452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, R.L. Clinical tests with improved disposable diapers. Pediatrician 1987, 14 (Suppl. 1), 34–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Campbell, R.L.; Seymour, J.L.; Stone, L.C.; Milligan, M.C. Clinical studies with disposable diapers containing absorbent gelling materials: Evaluation of effects on infant skin condition. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1987, 17, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.A.; Leyden, J.J.; Grove, G.L.; Raynor, W.J. Comparison of disposable diapers with fluff absorbent and fluff plus absorbent polymers: Effects on skin hydration, skin ph, and diaper dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 1989, 6, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odio, M.; Friedlander, S.F. Diaper dermatitis and advances in diaper technology. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2000, 12, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odio, M.R.; O’Connor, R.J.; Sarbaugh, F.; Baldwin, S. Continuous topical administration of a petrolatum formulation by a novel disposable diaper. 2. Effect on skin condition. Dermatology 2000, 200, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odio, M.R.; O’Connor, R.J.; Sarbaugh, F.; Baldwin, S. Continuous topical administration of a petrolatum formulation by a novel disposable diaper. 1. Effect on skin surface microtopography. Dermatology 2000, 200, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šmajgl, D.; Obhođaš, J. Occurrence of tin in disposable baby diapers. X-Ray Spectrom. 2015, 44, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.A.; Dallas, M.J. Diaper performance: Maintenance of healthy skin. Pediatr. Dermatol. 1990, 7, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farage, M.A.; Gilpin, D.A.; Enane, N.A.; Baldwin, S. Development of a new test for mechanical irritation: Behind the knee as a test site. Skin Res. Technol. 2001, 7, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Guidance on Selecting Age Groups for Monitoring and Assessing Childhood Exposures to Environmental Contaminants. 630-P-03-003F; November 2005. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/guidance-selecting-age-groups-monitoring-and-assessing-childhood-exposures-environmental (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Child-Specific Exposure Scenarios Examples (Final Report). EPA/600/R-14-217F; 2014. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/risk/recordisplay.cfm?deid=262211 (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Exposure Factors Handbook 2011 Edition (Final Report). EPA/600/R-09/052F; 2011. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/risk/recordisplay.cfm?deid=236252 (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. WHO Growth Standards are Recommended for Use in the U.S. for Infants and Children 0 to 2 Years of Age. 2010. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/who_charts.htm#The%20WHO%20growth%20charts (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Boniol, M.; Verriest, J.P.; Pedeux, R.; Dore, J.F. Proportion of skin surface area of children and young adults from 2 to 18 years old. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, S.; Rothe, H.; Page, L.; O’Connor, R.; Farahmand, S.; Toner, F.; Marsh, R.; Wehmeyer, K.; Zhou, S. An in vitro skin penetration model for compromised skin: Estimating penetration of polyethylene glycol 14c-peg-7 phosphate. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 28, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farage, M.A. Enhancement of visual scoring of skin irritant reactions using cross-polarized light and parallel-polarized light. Contact Dermat. 2008, 58, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farage, M.A.; Segarra, V.S.; Bramante, M.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H.I. Dermatological testing of an emollient-treated menstrual pad with a novel foam absorbent core. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2008, 27, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farage, M.A. Evaluating lotion transfer from products to skin using the behind-the-knee test. Skin Res. Technol. 2010, 16, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke-Baier, P.; Johannigmann, J.; Levin, R.J.; Wagner, G. Evaluation of vaginal and perineal area during the use of external sanitary protection throughout the menstrual cycle. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 1994, 73, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farage, M.A.; Berardesca, E.; Maibach, H. Skin moisturization and frictional effects of an emollient-treated menstrual pad with a foam core. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2009, 28, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, P.; Marsman, D.S.; Felter, S.P. Dermal safety evaluation: Use of disposable diaper products in the elderly. In Textbook of Aging Skin; Farage, M.A., Miller, K.W., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 857–868. ISBN 978-3-540-89656-2. [Google Scholar]
- Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). 생리대. 팬티라이너 74종 VOCs 인체 위해 우려 없어. 28 December 2017. Available online: http://www.mfds.go.kr/brd/m_99/view.do?seq=40034 (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Helmes, C.T.; O’Connor, R.; Sawyer, L.; Young, S. Disposable diaper absorbency: Improvements via advanced designs. Clin. Pediatr. 2014, 53, 14S–16S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajmeri, J.R.; Ajmeri, C.J. Nonwoven personal hygiene materials and products. In Applications of Nonwovens in Technical Textiles; Chapman, R.A., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 85–102. ISBN 9781845694371. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S. Reviewing the Korean episodes of environmental chemicals in summer 2017. Korean J. Public Health 2017, 54, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academy of Science. Risk Assessment in the Federal Government: Managing the Process; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety. The SCCS’s Notes of Guidance for the Testing of Cosmetic Ingredients and Their Safety Evaluation. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_190.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- European Chemicals Agency. E.C. Guidance on Information Requirements and Chemical Safety Assessment. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/guidance-documents/guidance-on-information-requirements-and-chemical-safety-assessment (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Human Health Risk Assessment; Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Human Health Risk Assessment Toolkit: Chemical Hazards. 2010. Available online: http://www.who.int/ipcs/methods/harmonization/areas/ra_toolkit/en/ (accessed on 8 August 2018).
- Czerwinski, B.S. Adult feminine hygiene practices. Appl. Nurs. Res. 1996, 9, 93123–93129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Emission Scenario Document on Textile Finishing Industry. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/chemicalsafety/risk-assessment/emissionscenariodocuments.htm (accessed on 24 July 2018).
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Available online: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- ECHA. Substances Restricted under REACH. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/substances-restricted-under-reach (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- International Programme on Chemical Safety. Public Health Impact of Chemicals: Knowns and Unknowns. 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/ipcs/publications/chemicals-public-health-impact/en/ (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Substance Priority List. Available online: https://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/spl/resources/index.html (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) Advanced Search. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/iris/search/index.cfm (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- European Commission. Study on the Calculation of the Benefits of Chemicals Legislation on Human Health and the Environment: Development of a System of Indicators. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/chemicals/reach/pdf/study_final_report.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- Klasmeier, J.; McLachlan, M.S. PCDD/Fs in textiles- part 1: A screening method for detection of octachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and octachlorodibenzofuran. Chemosphere 1998, 36, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eason, E.L.; Feldman, P. Contact dermatitis associated with the use of always sanitary napkins. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 1996, 154, 1173–1176. [Google Scholar]
- Nicole, W. A question for women’s health: Chemicals in feminine hygiene products and personal lubricants. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, A70–A75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Toxicology Program. Substances Listed in the Fourteenth Report on Carcinogens. Available online: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/pubhealth/roc/index-1.html#toc1 (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment. Proposition 65 List. Available online: https://oehha.ca.gov/proposition-65/about-proposition-65 (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- Christina, L.B. Methyldibromo Glutaronitrile. Int. J. Toxicol. 2017, 36, 39S–41S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterry, W.; Schmoll, M. Contact urticaria and dermatitis from self-adhesive pads. Contact Dermat. 1985, 13, 284–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, K.P.; Maibach, H.I. Factors predisposing to cutaneous irritation. Dermatol. Clin. 1990, 8, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.D.; Frowen, K.E.; Nixon, R.L. Allergic contact dermatitis from methyldibromo glutaronitrile in a sanitary pad and review of australian clinic data. Contact Dermat. 2007, 56, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaude, C.; Mohr, G.J. Indicator washcloth for detecting alkaline washing solutions to prevent dermatitis patients and babies from skin irritation. Fash. Text. 2017, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, G.; Larsen, W.G. Sanitary napkin dermatitis due to the perfume. Arch. Dermatol. 1979, 115, 363. [Google Scholar]
- DeVito, M.J.; Schecter, A. Exposure assessment to dioxins from the use of tampons and diapers. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schecter, A.J.; Papke, O.; Marquardt, S. Dioxins and dibenzofurans in american sanitary products: Tampons sanitary napkins, disposable and cloth diapers, and incontinence pads. In Proceedings of the 18th Halogenated Environmental Organic Pollutants, Stockholm, Sweden, 17–21 August 1998; Volume 36, pp. 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, H.S.; Yun, G.A. Analysis of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzo-furans in sanitary products of women. Text. Res. J. 2007, 77, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemistry Explained. Disposable Diapers. Available online: http://www.chemistryexplained.com/Di-Fa/Disposable-Diapers.html (accessed on 24 July 2018).
- Earls, A.O.; Axford, I.P.; Braybrook, J.H. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry determination of the migration of phthalate plasticisers from polyvinyl chloride toys and childcare articles. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 983, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU Scientific Committee on Toxicity, Ecotoxicity and the Environment. Phthalate Migration from Soft PVC Toys and Child-Care ArticlesOpinion Expressed at the CSTEE Third Plenary Meeting, Brussels, 24 April 1998. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/health/ph_risk/committees/sct/documents/out12_en.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Japan Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Phthalate Esters, Review of Amendment by Public Comment, etc. 2015. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/shingi/2010/02/dl/s0222-6g.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Risk & Policy Analysts Limited (RPA). Risk Assessment Studies on Targeted Consumer Applications of Certain Organotin Compounds. September 2005. Available online: File:///C:/Users/%EC%82%AC%EC%9A%A9%EC%9E%90/Downloads/organotins_3rd_report_16_sept_2005_en.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Hise, R.G.; Wright, B.T.; Swanson, S.E. Formation of chlorinated dioxins and furans from lignin and lignin model compounds. Chemosphere 1990, 20, 1723–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klasmeier, J.; Mühlebach, A.; McLachlan, M.S. PCDD/Fs in textiles- Part II: Transfer from clothing to human skin. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimber, I.; Dearman, R.J.; Basketter, D.A.; Ryan, C.A.; Gerberick, G.F.; McNamee, P.M.; Lalko, J.; Api, A.M. Dose metrics in the acquisition of skin sensitization: Thresholds and importance of dose per unit area. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 52, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Part 1: Guidance Document on Characterizing and Communicating Uncertainty in Exposure Assessment. 2008. Available online: http://www.who.int/ipcs/methods/harmonization/areas/exposure/en/ (accessed on 8 August 2018).
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment. March 2005. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2013-09/documents/cancer_guidelines_final_3-25-05.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- US Environmental Protection Agency. A Review of the Reference Dose and Reference Concentration Processes. December 2002. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2014-12/documents/rfd-final.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Guidelines for Exposure Assessment, Risk Assessment Forum. EPA/600/Z-92/001; 1992. Available online: https://cfpub.epa.gov/ncea/risk/recordisplay.cfm?deid=15263 (accessed on 7 August 2018).
- Eriksson, L.; Jaworska, J.; Worth, A.P.; Cronin, M.T.; McDowell, R.M.; Gramatica, P. Methods for reliability and uncertainty assessment and for applicability evaluations of classification- and regression-based QSARS. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1361–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, A.T.; Rehder, P.A.; Helm, K. Evaluations of diapers containing absorbent gelling material with conventional disposable diapers in newborn infants. Am. J. Dis. Child. 1990, 144, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, J.L.; Keswick, B.H.; Hanifin, J.M.; Jordan, W.P.; Milligan, M.C. Clinical effects of diaper types on the skin of normal infants and infants with atopic dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1987, 17, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, J.L.; Keswick, B.H.; Milligan, M.C.; Jordan, W.P.; Hanifin, J.M. Clinical and microbial effects of cloth, cellulose core, and cellulose core/absorbent gel diapers in atopic dermatitis. Pediatrician 1987, 14 (Suppl. 1), 39–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Campbell, R.L.; Bartlett, A.V.; Sarbaugh, F.C.; Pickering, L.K. Effects of diaper types on diaper dermatitis associated with diarrhea and antibiotic use in children in day-care centers. Pediatr. Dermatol. 1988, 5, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubiak, M.; Kressner, B.; Raynor, W.; Davis, J.; Syverson, R.E. Comparison of stool containment in cloth and single-use diapers using a simulated infant feces. Pediatrics 1993, 91, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van, R.; Wun, C.; Morrow, A.L.; Pickering, L.K. The effect of diaper type and overclothing on fecal contamination in day-care centers. JAMA 1991, 265, 1840–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM. F2808-17: Standard Test Method for Performing behind-the-Knee (BTK) Test for Evaluating Skin Irritation Response to Products and Materials that Come into Repeated or Extended Contact with Skin. 2010. Available online: https://compass.astm.org/EDIT/html_annot.cgi?F2808+17 (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- Xuemin, W.; Sato, N.; Chao, Y.; Na, L.; Fujimura, T.; Takagi, Y.; Nojiri, H.; Kitahara, T.; Takema, Y. Cutaneous and sensory effects of two types of sanitary pads with different surfaces in the Shanghai, Chinese population. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seenivasan, P.; Priya, K.C. A cross sectional study on awareness about menstrual hygiene among rural women. Stanley Med. J. 2015, 2, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- South Korea to Risk Assess Hundreds of Sanitary Pads. Available online: https://chemicalwatch.com/58514/south-korea-to-risk-assess-hundreds-of-sanitary-pads (accessed on 29 August 2018).
- Runeman, B. Skin interaction with absorbent hygiene products. Clin. Dermatol. 2008, 26, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rademaker, M. Allergic contact dermatitis to a sanitary pad. Aust. J. Dermatol. 2004, 45, 234–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scranton, A. CChem Fatale: Potential Health Effects of Toxic Chemicals in Feminine Care Products. Missoula, MT: Women’s Voices for the Earth (November 2013). Available online: http://goo.gl/BgIwdu (accessed on 10 August 2018).
- Women’s Voices for the Earth. ‘Product Testing Results: Always Pads. 2014. Available online: http://www.womensvoices.org/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/Always-fact-sheet-FINAL.pdf (accessed on 6 August 2018).
- H.R. 2332 (112th Congress): Robin Danielson Act. Available online: https://www.congress.gov/bill/115th-congress/house-bill/2379?q=%7B%22search%22%3A%5B%22robin+danielson%22%5D%7D&r=1 (accessed on 22 August 2018).

| Pad Type | Baby Diaper | Feminine Hygiene Pad | Adult Incontinence Diaper | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User profile | Age | 0–36 months 1 | 14–49 years 3 | NA |
| Body weight | TWA body weight 10.2 kg 1 | 50–60 kg 3 | 60 kg 6 | |
| Typical application | Frequency | 4.7 diapers/day 2 | 5–7.5 pads/day 4 7 days/month 5 | 2–5 pads/day 6 |
| Length of use | 36 months | 35 years | NA | |
| Product | Regulation | Restriction | |
|---|---|---|---|
| US [10,11] | Baby diaper | Not available | Manufacturers are recommended to identify new formulations and bleaching process. |
| Menstrual pad and adult diaper | FDA Class I Medical Device (guidance) | ||
| China [12,13] | Baby diapers | GB 15979-2002 (mandatory) | Manufacturers should provide microbial and toxicological indicators. |
| Sanitary pads | GB 15979-2002 (mandatory) GB/T 8939-2008 (guidance) | ||
| Korea [9] | Baby and adult diapers | MFDS Sanitary Products (mandatory) | There are restrictions on chemicals and heavy metals for baby 1 and adult diapers. 2 |
| Menstrual pad | MFDS Quasi-Drugs (mandatory) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, J.; Kwon, H.; Kim, J. Safety Evaluation of Absorbent Hygiene Pads: A Review on Assessment Framework and Test Methods. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114146
Bae J, Kwon H, Kim J. Safety Evaluation of Absorbent Hygiene Pads: A Review on Assessment Framework and Test Methods. Sustainability. 2018; 10(11):4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114146
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Jihyun, Hoonjeong Kwon, and Jooyoun Kim. 2018. "Safety Evaluation of Absorbent Hygiene Pads: A Review on Assessment Framework and Test Methods" Sustainability 10, no. 11: 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114146
APA StyleBae, J., Kwon, H., & Kim, J. (2018). Safety Evaluation of Absorbent Hygiene Pads: A Review on Assessment Framework and Test Methods. Sustainability, 10(11), 4146. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10114146





