Analyzing Sustainability Literature in Maritime Studies with Text Mining
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Sets Used
2.1. Data Collection
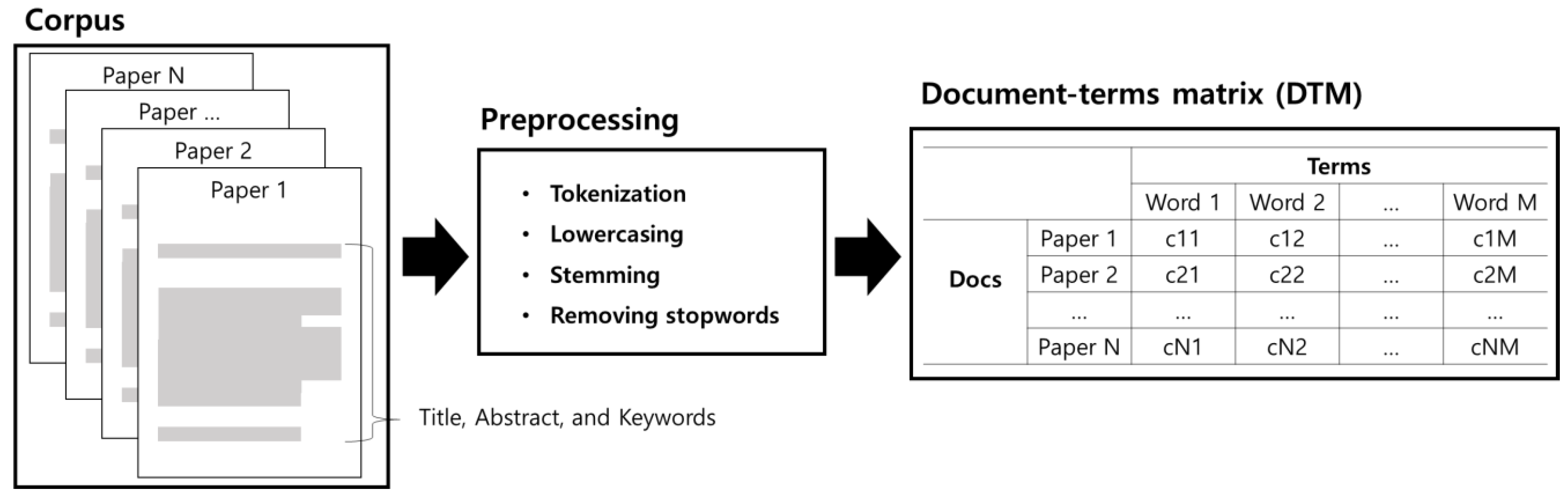
2.2. Pre-Processing
2.3. Formation of the Document Terms Matrix
3. Method: Topic Modeling
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Topics on Port Issues in Sustainability
4.2. Topics on Shipping Issues in Sustainability
4.3. Topics on Maritime Logistics Issue in Sustainability
4.4. Supportive Analysis
4.4.1. Co-Occurrence Analysis
4.4.2. Co-Authorship: Country, Affiliation, and Authors
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



| Journal | No. of Papers | SCI/SSCI/SCIE | Publication Cycle | Publish Company |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maritime Policy & Management | 17 | SSCI | Bimonthly | Taylor & Francis |
| Transportation Research Part D-Transport and Environment | 16 | SSCI, SCIE | Bimonthly | Elsevier |
| Sustainability | 14 | SSCI, SCIE | Monthly | MDPI |
| Marine Policy | 11 | SSCI | Monthly | Elsevier |
| International Journal of Shipping and Transport Logistics | 10 | SSCI | Quarterly | Inderscience Publishers |
| International Journal of Sustainable Transportation | 10 | SSCI | Bimonthly | Taylor & Francis |
| Transportation Research Part E-Logistics and Transportation Review | 8 | SSCI, SCIE | Monthly | Elsevier |
| Ocean & Coastal Management | 7 | SCIE | Semimonthly | Elsevier |
| Journal of Transport Geography | 6 | SSCI | Bimonthly | Elsevier |
| Marine Pollution Bulletin | 4 | SCI, SCIE | Monthly | Elsevier |
| Energy Policy | 3 | SSCI, SCIE | Monthly | Elsevier |
| Transport | 3 | SCIE | Quarterly | Taylor & Francis |
| Transportation Research Part A-Policy and Practice | 3 | SCI, SSCI, SCIE | Monthly | Elsevier |
| Transportation Research Record | 3 | SCI | Irregular | National Academy of Sciences |
| Business Strategy and The Environment | 2 | SSCI | Bimonthly | US National Research Council |
| Computers & Industrial Engineering | 2 | SCIE | Monthly | Elsevier |
| International Journal of Logistics-Research and Applications | 2 | SSCI | Bimonthly | Taylor & Francis |
| Promet-Traffic & Transportation | 2 | SCIE | Bimonthly | Sveuciliste u Zagrebu |
| Transport Reviews | 2 | SSCI | Bimonthly | Taylor & Francis |
| Transportation Planning and Technology | 2 | SCIE | Bimonthly | Taylor & Francis |
| Other 28 journals | 28 | - | - | - |
| Total | 155 | - | - | - |
References
- Lin, B.; Lin, C.Y. Compliance with international emission regulations: Reducing the air pollution from merchant vessels. Mar. Policy 2006, 30, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations General Assembly. Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development: Our Common Future: Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Asgari, N.; Hassani, A.; Jones, D.; Nguye, H.H. Sustainability ranking of the UK major ports: Methodology and case study. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2015, 78, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Sun, C.; Weng, J. Liner shipping fleet deployment with sustainable collaborative transportation. Sustainability 2016, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjortnaes, T.; Wiegmans, B.; Negenborn, R.R.; Zuidwijk, R.A.; Klijnhout, R. Minimizing cost of empty container repositioning in port hinterlands, while taking repair operations into account. J. Transp. Geogr. 2017, 58, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannone, F. The private and social cost efficiency of port hinterland container distribution through a regional logistics system. Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2012, 46, 1424–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searcy, T. Bridging islands and calming seas: A material flow management approach to sustainable sea transportation for Fiji’s lower southern Lau islands. Mar. Policy 2017, 83, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Navarro, M.Á. Environmental factors and intermodal freight transportation: Analysis of the decision bases in the case of Spanish motorways of the Sea. Sustainability 2014, 6, 1544–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzannatos, E.; Papadimitriou, S.; Koliousis, I. A Techno-Economic Analysis of Oil vs. Natural Gas Operation for Greek Island Ferries. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2015, 9, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, P.; Pilcher, N. Exploring the viability of an emission tax policy for ships at berth in Taiwanese ports. Int. J. Shipp. 2016, 8, 705–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-L.; Lu, C.; Chang, C.-C. The influence of organisational green climate on employees’ green behaviours: Evidence from the Eco Port of Kaohsiung. Int. J. Shipp. Transp. Logist. 2017, 9, 696–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, J.R.M.; Lee, P.M.; Lucas, H.C. A resource-based view of competitive advantage at the Port of Singapore. J. Strateg. Inf. Syst. 2005, 14, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winebrake, J.J.; Corbett, J.J.; Meyer, P.E. Energy use and emissions from marine vessels: A total fuel life cycle approach. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winebrake, J.J.; Corbett, J.J.; Wang, C.; Farrell, A.E.; Woods, P. Optimal fleetwide emissions reductions for passenger ferries: An application of a mixed-integer nonlinear programming model for the new york–new jersey harbor. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2005, 55, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, A.; Ng, A.K.Y.; McEvoy, D.; Mullett, J. Implications of climate change for shipping: Ports and supply chains. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2018, 9, e508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norlund, E.K.; Gribkovskaia, I. Reducing emissions through speed optimization in supply vessel operations. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2013, 23, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaraftis, H.N.; Kontovas, C.A. Ship speed optimization: Concepts, models and combined speed-routing scenarios. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2014, 44, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yan, X.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, X.; Lin, X.; Negenborn, R.R. Dynamic optimization of ship energy efficiency considering time-varying environmental factors. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Pacino, D.; Kontovas, C.A.; Psaraftis, H.N. A multiple ship routing and speed optimization problem under time, cost and environmental objectives. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 52, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.J.; Wang, H.; Winebrake, J.J. The effectiveness and costs of speed reductions on emissions from international shipping. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2009, 14, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.J.; Wang, H.; Winebrake, J.J. Impacts of speed reductions on vessel-based emissions for international shipping. In Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 88th Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 11–15 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Lun, V.; Lagoudis, I.N.; Lee, P.T.W. Container transportation: Resilience and sustainability. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 61, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciaro, M. Real option analysis for environmental compliance: LNG and emission control areas. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 28, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eise Fokkema, J.; Buijs, P.; Vis, I.F.A. An investment appraisal method to compare LNG-fueled and conventional vessels. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 56, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, J.J.; Winebrake, J.J. Emissions Tradeoffs among Alternative Marine Fuels: Total Fuel Cycle Analysis of Residual Oil, Marine Gas Oil, and Marine Diesel Oil. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2008, 58, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinas, O.; Stefanakos, C.N. Cost assessment of environmental regulation and options for marine operators. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2012, 25, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinas, O.; Stefanakos, C.N. Selecting technologies towards compliance with MARPOL Annex VI: The perspective of operators. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 28, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Animah, I.; Addy-Lamptey, A.; Korsah, F.; Sackey, J.S. Compliance with MARPOL Annex VI regulation 14 by ships in the Gulf of Guinea sub-region: Issues, challenges and opportunities. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 441–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, S.A.; Lee, H.; Aluko, O. Multi-objective decision support to enhance environmental sustainability in maritime shipping: A review and future directions. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2015, 78, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sislian, L.; Jaegler, A.; Cariou, P. A literature review on port sustainability and ocean’s carrier network problem. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2016, 19, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarzani, H.; Fahimnia, B.; Bell, M.; Sarkis, J. Greening ports and maritime logistics: A review. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2016, 48, 473–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.J.; Fu, P.W.; Wu, C.C. Popular Research Topics in Marketing Journals, 1995–2014. J. Interact. Mark. 2017, 40, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaquinto, R.; Banerjee, A. Topic Modeling on Health Journals with Regularized Variational Inference. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 20–22. [Google Scholar]
- Torget, A.J.; Yang, T.; Mihalcea, R. Topic modeling on historical newspapers. In Proceedings of the 5th ACL-HLT Work. Lang. Technol. Cult. Herit. Soc. Sci. Humanit; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 96–104. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, K.D. Using structural topic modeling to identify latent topics and trends in aviation incident reports. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 87, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Battisti, F.; Ferrara, A.; Salini, S. A decade of research in statistics: A topic model approach. Scientometrics 2015, 103, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Qiang, M.; Lin, P. A topic modeling based bibliometric exploration of hydropower research. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Yin, Y. Discovering themes and trends in transportation research using topic modeling. Transp. Res. Part C 2017, 77, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Lee, W.S.; Sohn, S.Y. Analyzing research trends in personal information privacy using topic modeling. Comput. Secur. 2017, 67, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortenson, M.J.; Vidgen, R. A computational literature review of the technology acceptance model. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2016, 36, 1248–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welbers, K.; Van Atteveldt, W.; Benoit, K. Text Analysis in R. Commun. Methods Meas. 2017, 11, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Jordan, M.I.; Ng, A.Y. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Blei, D. Probabilistic topic models. Commun. ACM 2012, 55, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton Michael, A.; Raftery, A.E. Approximate Bayesian Inference with the Weighted Likelihood Bootstrap. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1994, 56, 3–48. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, T.L.; Steyvers, M. Finding scientific topics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 5228–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vaio, A.; Varriale, L. Management innovation for environmental sustainability in seaports: Managerial accounting instruments and training for competitive green ports beyond the regulations. Sustainability 2018, 10, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengpeng, W.; Di, Z.; Xinping, Y.; Zaili, Y. A novel model for the quantitative evaluation of green port development: A case study of major ports in China. Transp. Res. Part D J. 2017, 61, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergqvist, R.; Egels-Zandén, N. Green port dues—The case of hinterland transport. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2012, 5, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes-Dabban, H.; van Tatenhove, J.P.M.; van Koppen, K.C.S.A.; Termeer, K.J.A.M. Institutionalizing environmental reform with sense-making: West and Central Africa ports and the ‘green port’ phenomenon. Mar. Policy 2017, 86, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirn, T.; Jim Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.J. Green performance criteria for sustainable ports in Asia. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2013, 43, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.S.L.; Notteboom, T. The Greening of Ports: A Comparison of Port Management Tools Used by Leading Ports in Asia and Europe. Transp. Rev. 2014, 34, 169–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, T.A.; Chuang, C.C. Social construction of port sustainability indicators: A case study of Keelung Port. Marit. Policy Manag. 2015, 42, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.S.L.; Gu, Y. Port hinterland intermodal container flow optimisation with green concerns: A literature review and research agenda. Int. J. Shipp. Transp. Logist. 2013, 5, 257–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rødseth, K.L.; Wangsness, P.B.; Schøyen, H. How do economies of density in container handling operations affect ships’ time and emissions in port? Evidence from Norwegian container terminals. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 59, 385–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; McNabola, A.; Misstear, B.; Caulfield, B. An evaluation of the impact of the Dublin Port Tunnel and HGV management strategy on air pollution emissions. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 52, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berechman, J.; Tseng, P.H. Estimating the environmental costs of port related emissions: The case of Kaohsiung. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2012, 17, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhong, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z. A carbon emission evaluation for an integrated logistics system-a case study of the port of shenzhen. Sustainability 2017, 9, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.T.; Park, H.K.; Lee, S.; Kim, E. Have Emission Control Areas (ECAs) harmed port efficiency in Europe? Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 58, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wallace, S.W. Scrubber: A potentially overestimated compliance method for the Emission Control Areas: The importance of involving a ship’s sailing pattern in the evaluation. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 55, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, L.F. Toward a smart sustainable development of port cities/areas: The role of the “Historic Urban Landscape” approach. Sustainability 2013, 5, 4329–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.H.; Maltz, A.; Dooley, K. The link between economic and environmental performance of the top 10 U.S. ports. Marit. Policy Manag. 2017, 44, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acciaro, M.; Vanelslander, T.; Sys, C.; Ferrari, C.; Roumboutsos, A.; Giuliano, G.; Lam, J.S.L.; Kapros, S. Environmental sustainability in seaports: A framework for successful innovation. Marit. Policy Manag. 2014, 41, 480–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Navarro, M.Á.; Tortosa-Edo, V.; Llorens-Monzonís, J. Environmental management systems and local community perceptions: The case of petrochemical complexes located in ports. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 2015, 24, 236–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Shyu, W.H.; Li, C.H.; Ding, J.F. Environmental risk perceptions of port residents: An empirical study on east side of Keelung Port. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2016, 24, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooldridge, C.F.; McMullen, C.; Howe, V. Environmental management of ports and harbours—Implementation of policy through scientific monitoring. Mar. Policy 1999, 23, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.H.; Choi, A.Y.; Ji, J.; Zhang, D. Environmental efficiency analysis of Chinese container ports with CO2emissions: An inseparable input-output SBM model. J. Transp. Geogr. 2017, 65, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Nam, H. A Study on Green Shipping in Major Countries: In the View of Shipyards, Shipping Companies, Ports, and Policies. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2017, 33, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.C.E.; Lai, K.H.; Venus Lun, Y.H.; Wong, C.W.Y. Green shipping management. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2013, 55, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.T.; Danao, D. Green shipping practices of shipping firms. Sustainability 2017, 9, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuisan, L.; van Leeuwen, J.; van Koppen, C.S.A. Greening international shipping through private governance: A case study of the Clean Shipping Project. Mar. Policy 2012, 36, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, Y.H.V.; Lai, K.H.; Cheng, T.C.E. An evaluation of green shipping networks to minimize external cost in the Pearl River Delta region. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2013, 80, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaefthimiou, S.; Maragkogianni, A.; Andriosopoulos, K. Evaluation of cruise ships emissions in the Mediterranean basin: The case of Greek ports. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2016, 10, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.; Osman, A.S.S.; Hussin, H.; George, A.R. Protecting the Malacca and Singapore Straits from Ships’ Atmospheric Emissions through the Implementation of MARPOL Annex VI. Int. J. Mar. Coast. Law 2017, 32, 95–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullinane, K.; Tseng, P.H.; Wilmsmeier, G. Estimation of container ship emissions at berth in Taiwan. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2016, 10, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolphin, M.J.; Melcer, M. Estimation of ship dry air emissions. Nav. Eng. J. 2008, 120, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Lützen, M. Fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making method for technology selection for emissions reduction from shipping under uncertainties. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2015, 40, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.S.; Van Wee, B. Toward a Better Methodology for Assessing CO2 Emissions for Intermodal and Truck-only Freight Systems: A European Case Study. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2014, 8, 177–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sys, C.; Vanelslander, T.; Adriaenssens, M.; Van Rillaer, I. International emission regulation in sea transport: Economic feasibility and impact. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2014, 45, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clott, C.B.; Hartman, B.C. Clean trucks in California ports: Modelling emissions policy. Int. J. Shipp. Transp. Logist. 2013, 5, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimenc, M. Overview and comparative analysis of emission calculators for inland shipping. Int. J. Sustain. Transp. 2016, 10, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernndez Soto, J.L.; Garay Seijo, R.; Fraguela Formoso, J.A.; Gregorio Iglesias, G.; Carral Couce, L. Alternative sources of energy in shipping. J. Navig. 2010, 63, 435–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuttall, P.; Newell, A.; Prasad, B.; Veitayaki, J.; Holland, E. A review of sustainable sea-transport for Oceania: Providing context for renewable energy shipping for the Pacific. Mar. Policy 2014, 43, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehmatulla, N.; Smith, T. Barriers to energy efficiency in shipping: A triangulated approach to investigate the principal agent problem. Energy Policy 2015, 84, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmola, O.P. North European companies and major Eurasian countries–future outlook on logistics flows and their sustainability. Int. J. Shipp. Transp. Logist. 2011, 3, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Cahoon, S.; Chen, S.L. Quality management for seaports integrated in supply chains. Int. J. Shipp. Transp. Logist. 2012, 4, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Sung, C.Y. Service quality improvement strategies for liner-carrier-based global logistics companies. Int. J. Shipp. Transp. Logist. 2016, 8, 456–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallidis, I.; Dekker, R.; Vlachos, D. The impact of greening on supply chain design and cost: A case for a developing region. J. Transp. Geogr. 2012, 22, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.S.L. Designing a sustainable maritime supply chain: A hybrid QFD-ANP approach. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2015, 78, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, A.; Accorsi, R.; Baruffaldi, G.; Manzini, R. Designing sustainable cold chains for long-range food distribution: Energy-effective corridors on the Silk Road Belt. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Chen, H.; Long, R.; Lu, H.; Long, Q. A Co-Word Analysis of Organizational Constraints for Maintaining Sustainability. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, M. Representing Scientific Knowledge: The Role of Uncertainty; Springer, 2017; Available online: https://www.springer.com/la/book/9783319625416 (accessed on 29 September 2018).





| 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | Total | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 93 | 99 | 02 | 04 | 05 | 06 | 07 | 08 | 09 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | ||
| Port issue in sustainability | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 7 | 11 | 16 | 72 | ||
| Shipping issue in sustainability | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 2 | 7 | 8 | 13 | 16 | 70 | |||
| Maritime logistics issue in sustainability | 1 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 13 | |||||||||||
| Total | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 19 | 13 | 14 | 17 | 25 | 35 | 155 |
| Topic #1 | Topic #2 | Topic #3 | Topic #4 | Topic #5 |  |
| /green-/ | /envirntl-/ | /emiss-/ | /perform-/ | /process-/ | |
| /region-/ | /industri- | /polici-/ | /econom-/ | /citi-/ | |
| /effect-/ | /framework-/ | /pollut-/ | /evalu-/ | /urban-/ | |
| /strateg-/ | /environ- | /cost-/ | /critic-/ | /locat-/ | |
| /integr-/ | /institut-/ | /truck-/ | /intern-/ | /plan-/ | |
| Topic #6 | Topic #7 | Topic #8 | Topic #9 | Topic #10 | |
| /chain-/ | /network-/ | /improv-/ | /activ-/ | /decis-/ | |
| /suppli-/ | /industri-/ | /logist-/ | /reduc-/ | /factor-/ | |
| /compet-/ | /social-/ | /innov-/ | /energi-/ | /green-/ | |
| /collabor-/ | /trade-/ | /chang-/ | /strateg-/ | /influenc-/ | |
| /import-/ | /design-/ | /govern-/ | /prtsystem-/ | /project-/ |
| Topic #1 | Topic #2 | Topic #3 | Topic #4 | Topic #5 |  |
| /green-/ | /ship-/ | /freight-/ | /improv-/ | /estim-/ | |
| /industri-/ | /compet-/ | /perform-/ | /chain-/ | /plan-/ | |
| /econom-/ | /intern-/ | /decis-/ | /road-/ | /urban-/ | |
| /collabor-/ | /pollut-/ | /criteria-/ | /compar-/ | /citi-/ | |
| /strateg-/ | /factor-/ | /fuzzi-/ | /project-/ | /state-/ | |
| Topic #6 | Topic #7 | Topic #8 | Topic #9 | Topic #10 | |
| /emiss-/ | /envirntl-/ | /servic-/ | /energi-/ | /optim-/ | |
| /reduc-/ | /intermod-/ | /activ-/ | /compani-/ | /cost-/ | |
| /benefit-/ | /shipper-/ | /sector-/ | /resourc-/ | /network-/ | |
| /csma-/ | /reduc-/ | /govern-/ | /influenc-/ | /regul-/ | |
| /air-/ | /truck-/ | /climat-/ | /applic-/ | /empti-/ | |
| Topic #11 | Topic #12 | Topic #13 | Topic #14 | ||
| /region-/ | /technolog-/ | /rout-/ | /corridor-/ | ||
| /cost-/ | /econom-/ | /effici-/ | /motorway-/ | ||
| /govern-/ | /control-/ | /time-/ | /import-/ | ||
| /process-/ | /liner-/ | /custom-/ | /rail-/ | ||
| /environ-/ | /effect-/ | /polici-/ | /extern-/ |
| Topic #1 | Topic #2 | Topic #3 | Topic #4 | Topic #5 |  |
| /logist-/ | /region-/ | /cost-/ | /chain-/ | /green-/ | |
| /improv-/ | /custom-/ | /qualiti-/ | /suppli-/ | /integr-/ | |
| /envirntl-/ | /effect-/ | /distribut-/ | /qualiti-/ | /energi-/ | |
| /hinterland-/ | /effici-/ | /product-/ | /perform-/ | /intern-/ | |
| /econom-/ | /social-/ | /rout-/ | /influenc-/ | /program-/ | |
| Topic #6 | Topic #7 | Topic #8 | Topic #9 | ||
| /extern-/ | /servic-/ | /design-/ | /compani-/ | ||
| /polici-/ | /compet-/ | /chang-/ | /strateg-/ | ||
| /import-/ | /network-/ | /structur-/ | /growth-/ | ||
| /rail-/ | /empti-/ | /intertid-/ | /framework-/ | ||
| /scale-/ | /process-/ | /emerg-/ | /resourc-/ |
| No. | Count | Keywords | No. | Count | Keywords |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22 | sustainability | 17 | 5 | cost |
| 2 | 21 | management | 18 | 5 | operation |
| 3 | 18 | port | 19 | 4 | indicator |
| 4 | 17 | emission | 20 | 4 | carbon emission |
| 5 | 14 | impact | 21 | 4 | city |
| 6 | 14 | performance | 22 | 4 | inventory |
| 7 | 9 | model | 23 | 4 | policy |
| 8 | 9 | logistics | 24 | 4 | co2 emission |
| 9 | 8 | system | 25 | 4 | governance |
| 10 | 8 | framework | 26 | 3 | harbor |
| 11 | 7 | environmental management | 27 | 3 | environmental sustainability |
| 12 | 7 | transport | 28 | 3 | dry port |
| 13 | 6 | seaport | 29 | 3 | container transport |
| 14 | 6 | shipping | 30 | 3 | corporate social responsibility |
| 15 | 5 | supply chain management | 31 | 3 | sea |
| 16 | 5 | perspective | 32 | 3 | container terminal |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, S.-H.; Kwon, O.K.; Ruan, X.; Chhetri, P.; Lee, P.T.-W.; Shahparvari, S. Analyzing Sustainability Literature in Maritime Studies with Text Mining. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103522
Shin S-H, Kwon OK, Ruan X, Chhetri P, Lee PT-W, Shahparvari S. Analyzing Sustainability Literature in Maritime Studies with Text Mining. Sustainability. 2018; 10(10):3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103522
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Sung-Ho, Oh Kyoung Kwon, Xiao Ruan, Prem Chhetri, Paul Tae-Woo Lee, and Shahrooz Shahparvari. 2018. "Analyzing Sustainability Literature in Maritime Studies with Text Mining" Sustainability 10, no. 10: 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103522
APA StyleShin, S.-H., Kwon, O. K., Ruan, X., Chhetri, P., Lee, P. T.-W., & Shahparvari, S. (2018). Analyzing Sustainability Literature in Maritime Studies with Text Mining. Sustainability, 10(10), 3522. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10103522









