Acquired Zinc Deficiency in Preterm Infant Post-Surgery for Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) on Prolonged Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)
Abstract
1. Introduction
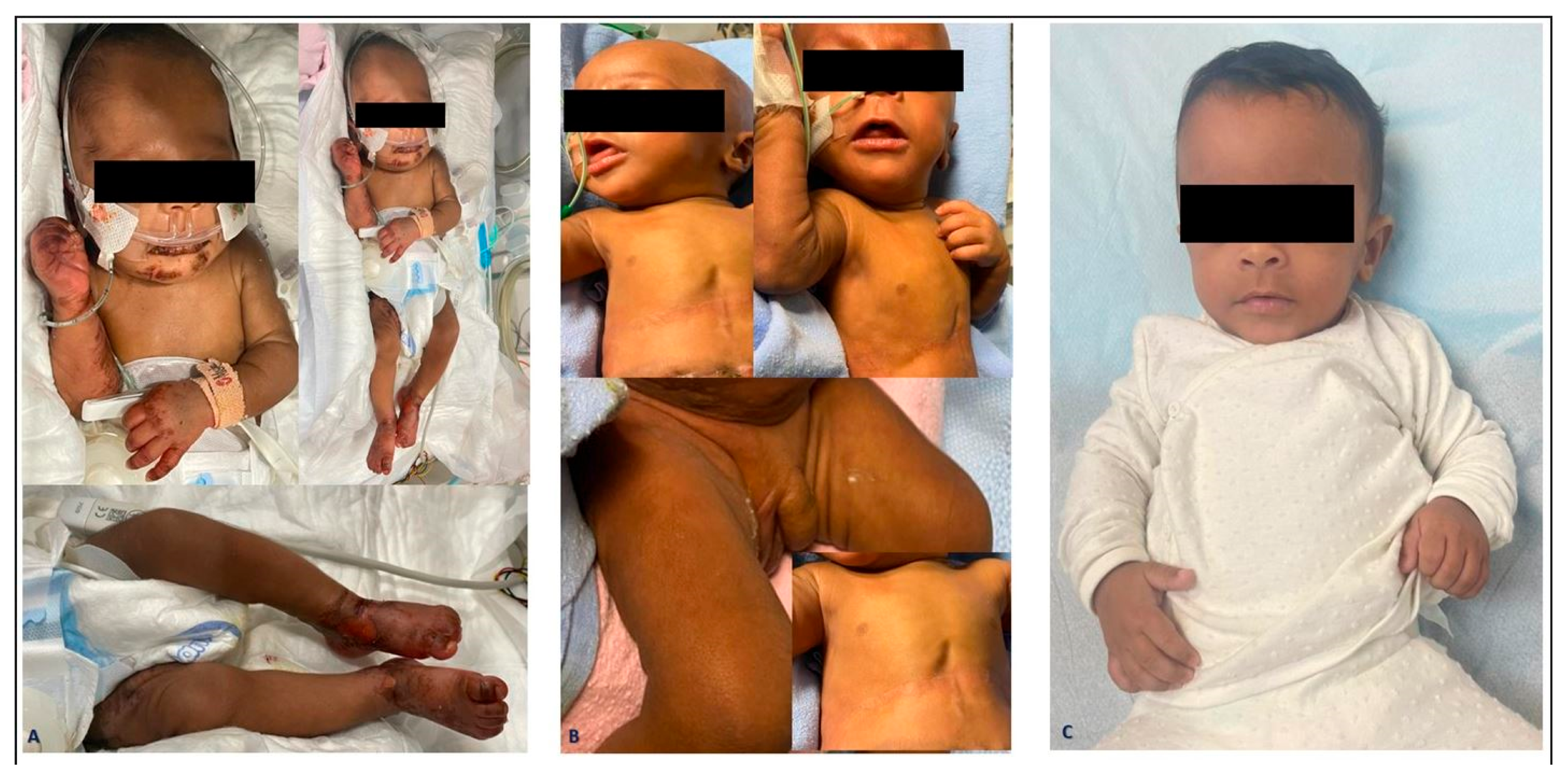
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lassi, Z.S.; Kurji, J.; de Oliveira, C.S.; Moin, A.; Bhutta, Z.A. Zinc supplementation for the promotion of growth and prevention of infections in infants less than six months of age. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, CD010205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perks, P.; Huynh, E.; Kaluza, K.; Boullata, J.I. Advances in trace element supplementation for parenteral nutrition. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.S. Impact of the discovery of human zinc deficiency on health. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khafaji, Z.; Brito, S.; Bin, B. Zinc and zinc transporters in dermatology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glutsch, V.; Hamm, H.; Goebeler, M. Zinc and skin: An update. JDDG J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2019, 17, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, Y.; Kinoshita, M.; Shimada, S.; Kawamura, T. Zinc and skin disorders. Nutrients 2018, 10, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, G.; De Laet, C.; Smits, G.; Salik, D.; Deprez, G.; Vilain, C.; Perlot, P.; Vicinanza, A. Acquired Zinc Deficiency Mimicking Acrodermatitis Enteropathica in a Breast-Fed Premature Infant. Pediatr. Rep. 2021, 13, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambe, T.; Fukue, K.; Ishida, R.; Miyazaki, S. Overview of inherited zinc deficiency in infants and children. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2015, 61, S44–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penny, M.E. Zinc supplementation in public health. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 62 (Suppl. 1), 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesan, S.; Kaliyadan, F. Acrodermatitis Enteropathica. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441835/ (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Yang, W.L.; Hsu, C.K.; Chao, S.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Lee, J.Y.Y. Transient zinc deficiency syndrome in a breast-fed infant due to decreased zinc in breast milk (type II hypozincemia of infancy): A case report and review of the literature. Dermatol. Sin. 2012, 30, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrin, G.; Berni Canani, R.; Di Chiara, M.; Pietravalle, A.; Aleandri, V.; Conte, F.; De Curtis, M. Zinc in early life: A key element in the fetus and preterm neonate. Nutrients 2015, 7, 10427–10446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carducci, B.; Keats, E.C.; Bhutta, Z.A. Zinc supplementation for improving pregnancy and infant outcome. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD000230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.J.; Jones, L.J.; Osborn, D.A. Zinc supplementation of parenteral nutrition in newborn infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2017, CD012561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawrysz, Z.; Woźniacka, A. Zinc: An undervalued microelement in research and treatment. Adv. Dermatol. Allergol./Postępy Dermatol. I Alergol. 2023, 40, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauriti, G.; Zani, A.; Aufieri, R.; Cananzi, M.; Chiesa, P.L.; Eaton, S.; Pierro, A. Incidence, prevention, and treatment of parenteral nutrition–associated cholestasis and intestinal failure–associated liver disease in infants and children: A systematic review. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Dato, F.; Iorio, R.; Spagnuolo, M.I. IFALD in children: What’s new? A narrative review. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 928371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafirovska, M.; Zafirovski, A.; Rotovnik Kozjek, N. Current insights regarding intestinal failure-associated liver disease (IFALD): A narrative review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, R.T.; Sokol, R.J. New insights into intestinal failure–associated liver disease in children. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1486–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huff, K.A.; Breckler, F.; Cruse, W.; Szeszycki, E.; Vanderpool, C. Pediatric smoflipid therapy: Patient response and safety concerns. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 45, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, B.P.; Duggan, C. Prevention and treatment of intestinal failure–associated liver disease in children. In Seminars in Liver Disease; Thieme Medical Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Volume 32, pp. 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Puder, M.; Valim, C.; Meisel, J.A.; Le, H.D.; De Meijer, V.E.; Robinson, E.M.; Zhou, J.; Duggan, C.; Gura, K.M. Parenteral fish oil improves outcomes in patients with parenteral nutrition-associated liver injury. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlana, D. Parenteral Nutrition Overview. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boullata, J.I.; Gilbert, K.; Sacks, G.; Labossiere, R.J.; Crill, C.; Goday, P. American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. ASPEN clinical guidelines: Parenteral nutrition ordering, order review, compounding, labeling, and dispensing. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 334–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeel, F.; Newkirk, M.; Sellers, A.; Shores, D.R. Postoperative feeding guidelines improve outcomes in surgical infants. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ESPGHAN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition in Children. Available online: https://espghan.info/published-guidelines/ (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- Hartman, C.; Shamir, R.; Simchowitz, V.; Lohner, S.; Cai, W.; Decsi, T.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Complications. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2418–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domellöf, M.; Szitanyi, P.; Simchowitz, V.; Franz, A.; Mimouni, F.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Iron and trace minerals. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2354–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhamid, N.; Wahby, A.; Kandil, M.E. Zinc status in infants and children with cholestatic liver diseases and its effect on growth. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; Irfan, S.M.; Kakar, J.; Zeeshan, R. Effect of iron chelator desferrioxamine on serum zinc levels in patients with beta thalassemia major. Malays. J. Pathol. 2015, 37, 35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tapiero, H.; Tew, K.D. Trace elements in human physiology and pathology: Zinc and metallothioneins. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, S.A.; Soghier, L.; Hatfield, J.; Lapinski, J.; Barfield, W.D. Zinc Deficiency Dermatitis in Cholestatic Extremely Premature Infants after a Nationwide Shortage of Injectable Zinc—Washington, DC, December 2012. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 136. [Google Scholar]
- Petry, N.; Olofin, I.; Boy, E.; Donahue Angel, M.; Rohner, F. The effect of low dose iron and zinc intake on child micronutrient status and development during the first 1000 days of life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaladonis, C.A.; Safeer, L.Z.; Hanson, D.C.; Erickson-Parsons, L.; Krakowski, A.C. Zinc Deficiency in a Preterm Infant. J. Pediatr. 2022, 240, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázquez-Gomis, R.; Bosch-Gimenez, V.; Juste-Ruiz, M.; Vázquez-Gomis, C.; Izquierdo-Fos, I.; Pastor-Rosado, J. Zinc concentration in preterm newborns at term age, a prospective observational study. BMJ Paediatr. Open 2019, 3, e000527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Biochemical Variable | 1 Month Before | 2 Weeks Before | 1 Week Before | Time of Appearance of Skin Rash | 1 Week After | 2 Weeks After | 1 Month After |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Bilirubin (mmol/L) | 75 | 104 | 161 | - | 112 | 142 | 137 |
| Alkaline Phosphatase (U/L) | 315 | 94 | 57 | - | 480 | 643 | 655 |
| AST (U/L) | 75 | 148 | 115 | - | 142 | 182 | 74 |
| ALT (U/L) | 45 | 178 | 124 | - | 126 | 109 | 96 |
| GGT (U/L) | 43 | 43 | 47 | - | 70 | 51 | 77 |
| Zinc (mcg/dL) | 1.71 | 8.06 | 11.66 | - |
| Compound | per mL | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Zinc chloride | 521 µg |
| 2 | Copper chloride (dihydrate) | 53.7 µg |
| 3 | Manganese chloride (tetrahydrate) | 3.60 µg |
| 4 | Potassium iodide | 1.31 µg |
| 5 | Sodium fluoride | 126 µg |
| 6 | Sodium selenate (anhydrous) | 4.38 µg |
| 7 | Sodium | 70 µg/mL |
| 8 | Potassium | 0.31 µg/mL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Qurashi, M.; Mohammad, H.; Aga, S.S.; Mustafa, A.; Alallah, J.; Al Hindi, M.; Al Harbi, M.; Hasosah, M. Acquired Zinc Deficiency in Preterm Infant Post-Surgery for Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) on Prolonged Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN). Pediatr. Rep. 2024, 16, 551-557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16030046
Al Qurashi M, Mohammad H, Aga SS, Mustafa A, Alallah J, Al Hindi M, Al Harbi M, Hasosah M. Acquired Zinc Deficiency in Preterm Infant Post-Surgery for Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) on Prolonged Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN). Pediatric Reports. 2024; 16(3):551-557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16030046
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Qurashi, Mansour, Hadeel Mohammad, Syed Sameer Aga, Ahmed Mustafa, Jubara Alallah, Mohammed Al Hindi, Mohammed Al Harbi, and Mohammed Hasosah. 2024. "Acquired Zinc Deficiency in Preterm Infant Post-Surgery for Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) on Prolonged Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN)" Pediatric Reports 16, no. 3: 551-557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16030046
APA StyleAl Qurashi, M., Mohammad, H., Aga, S. S., Mustafa, A., Alallah, J., Al Hindi, M., Al Harbi, M., & Hasosah, M. (2024). Acquired Zinc Deficiency in Preterm Infant Post-Surgery for Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) on Prolonged Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN). Pediatric Reports, 16(3), 551-557. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric16030046








