Inflammatory Biomarker Profiles in Very Preterm Infants within the Context of Preeclampsia, Chorioamnionitis, and Clinically Diagnosed Postnatal Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stoll, B.J.; Hansen, N.I.; Bell, E.F.; Walsh, M.C.; Carlo, W.A.; Shankaran, S.; Laptook, A.R.; Sánchez, P.J.; Van Meurs, K.P.; Wyckoff, M.; et al. Trends in care practices, morbidity, and mortality of extremely preterm neonates, 1993–2012. JAMA 2015, 314, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.; Weitkamp, J.H.; Wynn, J.L. Why are preterm newborns at increased risk of infection? Arch. Dis. Child. Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018, 103, F391-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.M.; Beachy, J.C. Neonatal complications following preterm birth. BJOG 2003, 110, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moster, D.; Lie, R.T.; Markestad, T. Long-term medical and social consequences of preterm birth. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmatz, M.; Srinivasan, L.; Grundmeier, R.W.; Elci, O.U.; Weiss, S.L.; Masino, A.J.; Tremoglie, M.; Ostapenko, S.; Harris, M.C. Surviving sepsis in a referral neonatal intensive care unit: Association between time to antibiotic administration and in-hospital outcomes. J. Pediatr. 2020, 217, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Claud, E.C. Connection between gut microbiome and brain development in preterm infants. Dev. Psychobiol. 2019, 61, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, C.; Panero, A.; Osborn, J.F.; Simonetti, A.F.; Pacifico, L. Diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: A clinical and laboratory challenge. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproston, N.R.; Ashworth, J.J. Role of C-reactive protein at sites of inflammation and infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichberger, J.; Resch, E.; Resch, B. Diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: The role of inflammatory markers. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 840288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitkamp, J.H.; Guthrie, S.O.; Wong, H.R.; Moldawer, L.L.; Baker, H.V.; Wynn, J.L. Histological chorioamnionitis shapes the neonatal transcriptomic immune response. Early Hum. Dev. 2016, 98, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, P.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Ren, T.; Zou, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Shen, B.; Ding, X. Chemokine CCL2 from proximal tubular epithelial cells contributes to sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2022, 323, F107–F119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Zhang, L.; Tong, Y.; Qu, Y.; Wang, H.; Mu, D. Interleukin-6 for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis with premature rupture of the membranes: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e13146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, Y.A.; Álvarez-Nemegyei, J.; Lavadores-May, A.I.; Girón-Carrillo, J.L.; Cedillo-Rivera, R.; Velazquez, J.R. Cytokine profile as diagnostic and prognostic factor in neonatal sepsis. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019, 32, 2830–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusyati, S.; Hulzebos, C.V.; Zandvoort, J.; Sauer, P.J. Levels of 25 cytokines in the first seven days of life in newborn infants. BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasci, Y.; Dilbaz, B.; Uzmez Onal, B.; Caliskan, E.; Dilbaz, S.; Doganci, L.; Han, U. The value of cord blood interleukin-6 levels for predicting chorioamnionitis, funisitis and neonatal infection in term premature rupture of membranes. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2006, 128, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroh Tam, P.Y.; Bendel, C.M. Diagnostics for neonatal sepsis: Current approaches and future directions. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrekera, B.; Colaizy, T.T.; Vasilakos, L.K.; Johnson, K.J.; Santillan, D.A.; Haskell, S.E.; Roghair, R.D. Origins of neonatal leptin deficiency in preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvoisin, G.; Fischer, C.; Maucort-Boulch, D.; Giannoni, E. Reduction in the use of diagnostic tests in infants with risk factors for early-onset neonatal sepsis does not delay antibiotic treatment. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2014, 144, w13981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ganesan, P.; Shanmugam, P.; Sattar, S.B.; Shankar, S.L. Evaluation of IL-6, CRP and hs-CRP as early markers of neonatal sepsis. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, DC13–DC17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassuna, N.A.; Elgezawy, E.; Mousa, S.O.; AbdelAziz, R.A.; Ibrahem, R.A.; Wahed, W.Y.A.; Nasif, K.A.; Hefzy, E.M. Diagnostic value of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, soluble mannose receptor, presepsin, and procalcitonin in critically ill children admitted with suspected sepsis. BMC Pediatr. 2021, 21, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermick, J.; Gallagher, K.; denDekker, A.; Kunkel, S.; Lukacs, N.; Schaller, M. Chorioamnionitis exposure remodels the unique histone modification landscape of neonatal monocytes and alters the expression of immune pathway genes. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 82–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, E.; Hancock, D.G.; Wells, C.; Richmond, P.; Simmer, K.; Burgner, D.; Strunk, T.; Currie, A.J. Exposure to chorioamnionitis alters the monocyte transcriptional response to the neonatal pathogen Staphylococcus epidermidis. Immunol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 96, 792–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, B.W.; Kallapur, S.G.; Moss, T.J.; Nitsos, I.; Newnham, J.P.; Jobe, A.H. Intra-amniotic LPS modulation of TLR signaling in lung and blood monocytes of fetal sheep. Innate Immun. 2009, 15, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szarka, A.; Rigó, J., Jr.; Lázár, L.; Beko, G.; Molvarec, A. Circulating cytokines, chemokines and adhesion molecules in normal pregnancy and preeclampsia determined by multiplex suspension array. BMC Immunol. 2010, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; Liu, L.; Chen, J. Combined use of serum MCP-1/IL-10 ratio and uterine artery Doppler index significantly improves the prediction of preeclampsia. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 473, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Shi, J.L.; Chen, M.; Zheng, Z.M.; Li, M.Q.; Shao, J. CCL2: An important cytokine in normal and pathological pregnancies: A review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1053457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, D.H.; Yang, Q.; Kathiresan, S.; Cupples, L.A.; Massaro, J.M.; Keaney, J.F., Jr.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; O’Donnell, C.J.; et al. CCL2 polymorphisms are associated with serum monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 levels and myocardial infarction in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 2005, 112, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agachan, B.; Attar, R.; Isbilen, E.; Aydogan, H.Y.; Sozen, S.; Gurdol, F.; Isbir, T. Association of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 and CC chemokine receptor 2 gene variants with preeclampsia. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2010, 30, 673–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, R.; Yang, L.; Wang, Y.; Mao, B.; Xu, X.; Yu, J. Meta-analysis of cardiovascular risk factors in offspring of preeclampsia pregnancies. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, R.A.; McCowan, L.M.; Dekker, G.A.; Poston, L.; Chan, E.H.; Stewart, A.W.; Black, M.A.; Taylor, R.S.; Walker, J.J.; Baker, P.N.; et al. Clinical risk prediction for pre-eclampsia in nulliparous women: Development of model in international prospective cohort. BMJ 2011, 342, d1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliodromiti, Z.; Anastasiadis, A.; Varras, M.; Pappa, K.I.; Siristatidis, C.; Bakoulas, V.; Mastorakos, G.; Vrachnis, N. Monocyte function in the fetus and the preterm neonate: Immaturity combined with functional impairment. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 753752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Aranguren, L.C.; Prada, C.E.; Riaño-Medina, C.E.; Lopez, M. Endothelial dysfunction and preeclampsia: Role of oxidative stress. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E.; Eves, D.; Menon, P.J.; Alnafisee, S.; Mooney, E.E.; Downey, P.; Culliton, M.; Murphy, J.F.A.; Vavasseur, C.; Molloy, E.J. Histological chorioamnionitis is predicted by early infant C-reactive protein in preterm infants and correlates with neonatal outcomes. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichberger, J.; Resch, B. Reliability of interleukin-6 alone and in combination for diagnosis of early onset neonatal sepsis: Systematic review. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 840778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I.H.; Demirel, F.G.; Uras, N.; Oguz, S.S.; Erdeve, O.; Biyikli, Z.; Dilmen, U. What are the cut-off levels for IL-6 and CRP in neonatal sepsis? J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2010, 24, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenebe, C.U.; Hesse, F.; Blohm, M.E.; Jung, R.; Kunzmann, S.; Singer, D. Diagnostic accuracy of interleukin-6 for early-onset sepsis in preterm neonates. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021, 34, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessema, B.; Lippmann, N.; Willenberg, A.; Knüpfer, M.; Sack, U.; König, B. The diagnostic performance of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein for early identification of neonatal sepsis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Castell, J.V.; Andus, T. Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem. J. 1990, 265, 621–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küster, H.; Weiss, M.; Willeitner, A.E.; Detlefsen, S.; Jeremias, I.; Zbojan, J.; Geiger, R.; Lipowsky, G.; Simbruner, G. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-6 for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis 2 days before clinical manifestation. Lancet 1998, 352, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
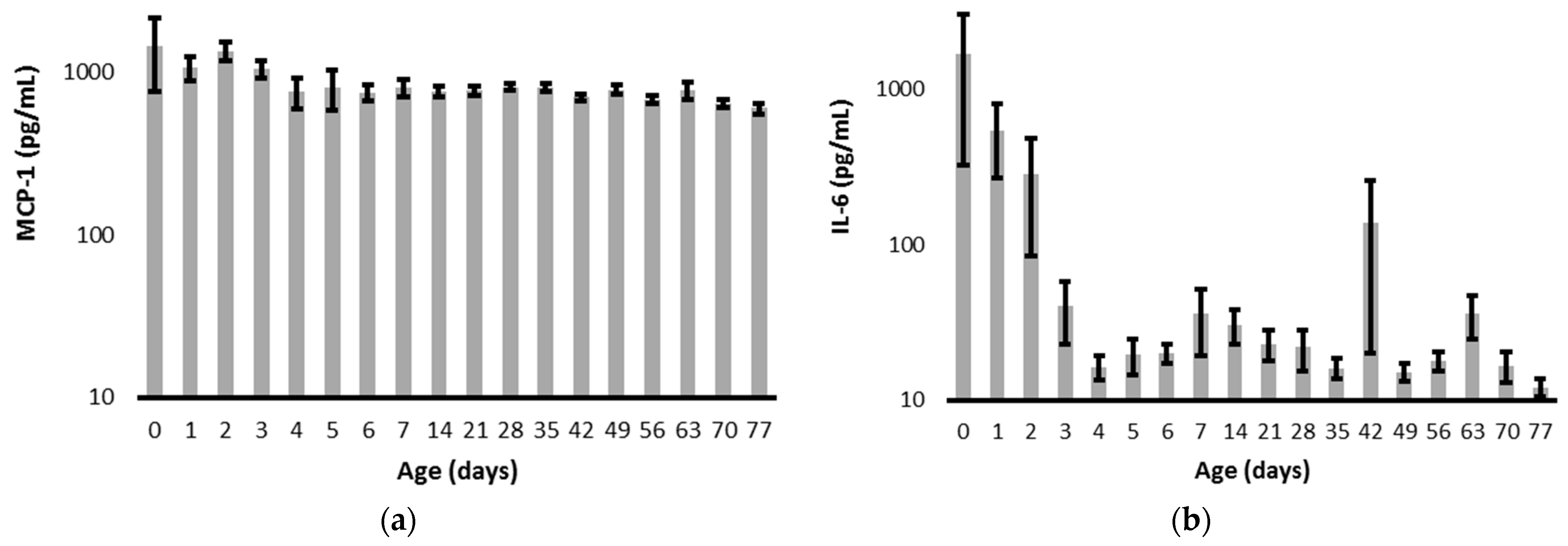
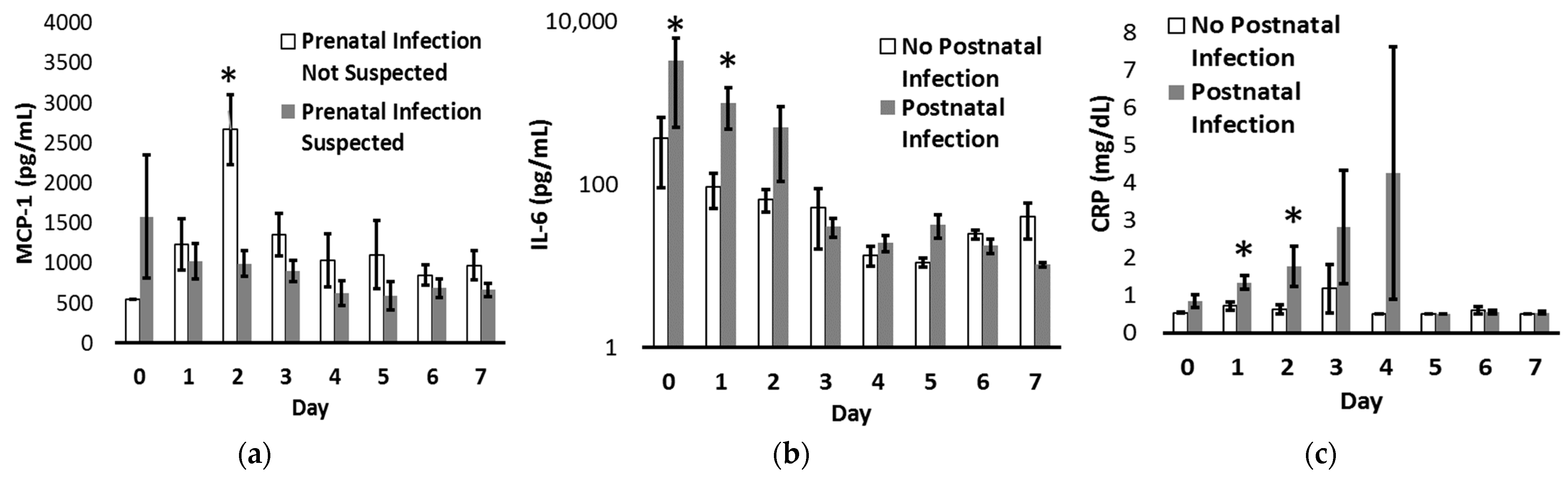
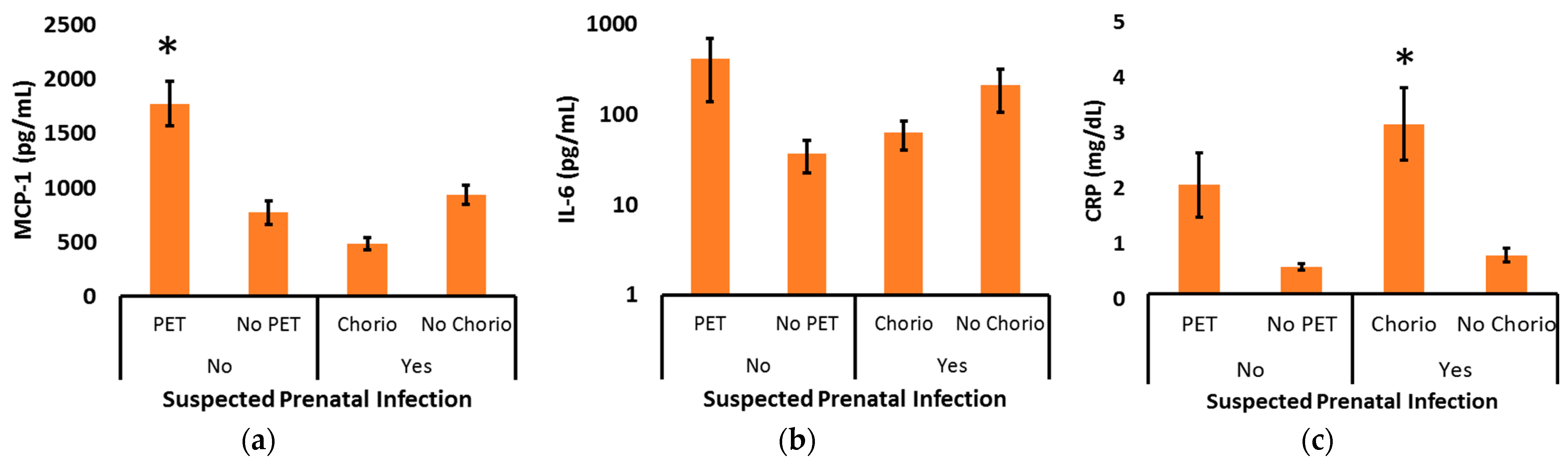
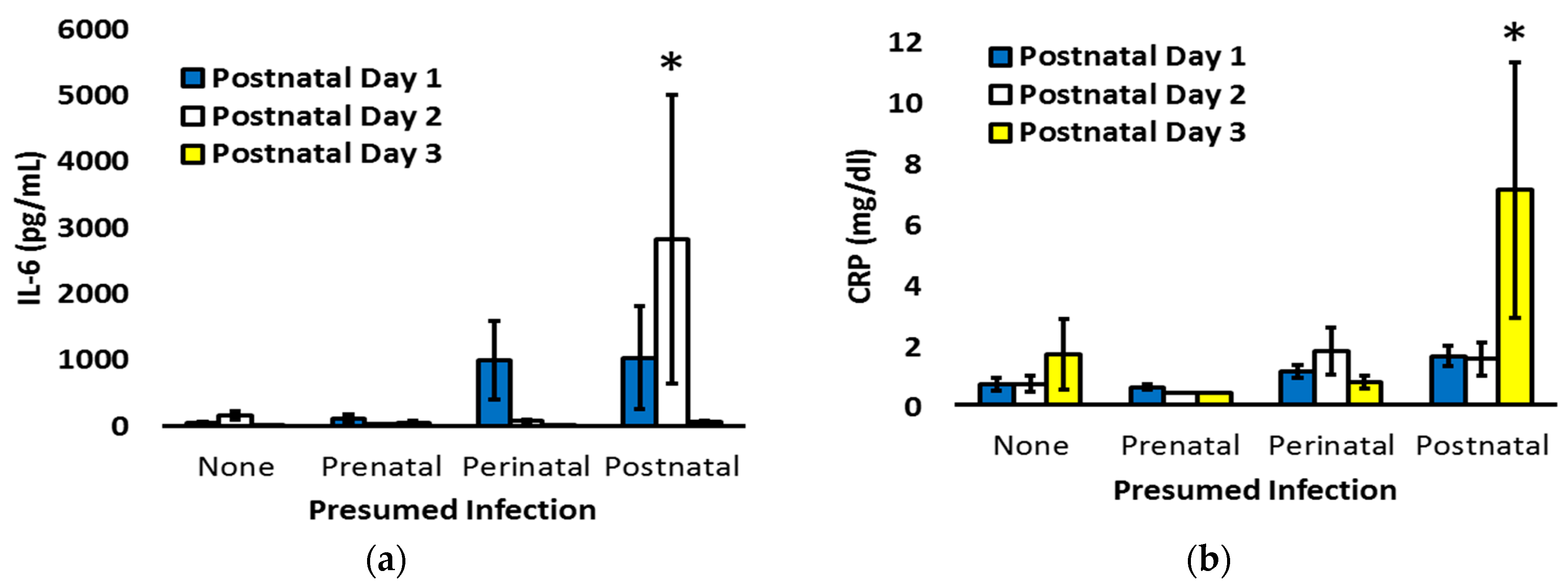
| All Infants N = 142 | 22–25 Weeks N = 29 | 26–29 Weeks N = 51 | 30–32 Weeks N = 62 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gestational Age (weeks) | 29.4 (26.6, 31.3) | 24.3 (23.2, 25.1) | 28.0 (27.1, 29.1) | 31.8 (31.0, 32.0) | <0.01 |
| Birth Weight (g) | 1186 (883, 1610) | 624 (554, 757) | 1075 (966, 1223) | 1655 (1370, 1914) | <0.01 |
| Male Sex | 75 (53%) | 17 (59%) | 22 (43%) | 36 (58%) | 0.22 |
| Prenatal Infection Suspected | 90 (63%) | 27 (93%) | 33 (65%) | 30 (48%) | <0.01 |
| Preterm Labor | 83 (53%) | 27 (93%) | 30 (59%) | 26 (42%) | <0.01 |
| Clinical Chorioamnionitis | 9 (6%) | 4 (14%) | 3 (6%) | 2 (3%) | 0.15 |
| Fetal Distress | 7 (5%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (6%) | 4 (6%) | 0.39 |
| Prenatal Infection Not Suspected | 52 (37%) | 2 (7%) | 18 (35%) | 32 (52%) | <0.01 |
| Preeclampsia | 29 (20%) | 1 (3%) | 9 (18%) | 19 (31%) | <0.01 |
| Abnormal Placenta | 12 (8%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (10%) | 7 (11%) | 0.18 |
| Cervical Insufficiency | 4 (3%) | 1 (3%) | 1 (2%) | 2 (3%) | 0.90 |
| Maternal Morbidity | 7 (5%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (6%) | 4 (6%) | 0.39 |
| Postnatal Infection Diagnosed | 63 (44%) | 21 (72%) | 26 (51%) | 16 (26%) | <0.01 |
| MCP-1 (pg/mL) | IL-6 (pg/mL) | CRP (mg/dL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Female | 938 ± 99 | 213 ± 123 | 1.1 ± 0.2 |
| Male | 1159 ± 112 p = 0.16 | 331 ± 151 p = 0.57 | 1.0 ± 0.1 p = 0.73 | |
| Mode of Delivery | Vaginal | 821 ± 92 | 206 ± 149 | 1.3 ± 0.3 |
| Cesarean | 1189 ± 105 p = 0.02 | 320 ± 134 p = 0.60 | 0.9 ± 0.1 p = 0.11 | |
| Preterm Labor | Yes | 792 ± 74 | 363 ± 165 | 1.2 ± 0.2 |
| No | 1487 ± 147 p = 0.000007 | 157 ± 49 p = 0.32 | 0.7 ± 0.1 p = 0.04 | |
| Gestational Cohort | 22–25 weeks | 809 ± 186 | 786 ± 457 | 1.1 ± 0.2 |
| 26–29 weeks | 1180 ± 149 | 157 ± 64 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | |
| 30–32 weeks | 1080 ± 93 p = 0.24 | 174 ± 111 p = 0.06 | 0.7 ± 0.3 p = 0.46 | |
| Prenatal Infection | Suspected | 928 ± 88 | 288 ± 126 | 0.8 ± 0.1 |
| Not Suspected | 1388 ± 146 p = 0.006 | 268 ± 170 p = 0.93 | 1.3 ± 0.3 p = 0.05 | |
| Postnatal Infection | Diagnosed | 1175 ± 140 | 518 ± 213 | 1.4 ± 0.2 |
| Not Diagnosed | 969 ± 75 p = 0.18 | 71 ± 19 p = 0.03 | 0.7 ± 0.1 p = 0.001 |
| Histopathologic Chorioamnionitis | MCP-1 (pg/mL) | IL-6 (pg/mL) | CRP (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Present (N = 51) With Funisitis (N = 23) No Funisitis (N = 28) | 796 ± 91 ** 799 ± 137 ** 792 ± 115 ** | 427 ± 201 451 ± 269 398 ± 301 | 1.32 ± 0.23 * 1.83 ± 0.47 ** 0.93 ± 0.16 |
| Not Present (N = 61) | 1406 ± 141 | 104 ± 27 | 0.82 ± 0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ewald, J.T.; Steinbrekera, B.; Bermick, J.R.; Santillan, D.A.; Colaizy, T.T.; Santillan, M.K.; Roghair, R.D. Inflammatory Biomarker Profiles in Very Preterm Infants within the Context of Preeclampsia, Chorioamnionitis, and Clinically Diagnosed Postnatal Infection. Pediatr. Rep. 2023, 15, 483-493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15030044
Ewald JT, Steinbrekera B, Bermick JR, Santillan DA, Colaizy TT, Santillan MK, Roghair RD. Inflammatory Biomarker Profiles in Very Preterm Infants within the Context of Preeclampsia, Chorioamnionitis, and Clinically Diagnosed Postnatal Infection. Pediatric Reports. 2023; 15(3):483-493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15030044
Chicago/Turabian StyleEwald, Jordan T., Baiba Steinbrekera, Jennifer R. Bermick, Donna A. Santillan, Tarah T. Colaizy, Mark K. Santillan, and Robert D. Roghair. 2023. "Inflammatory Biomarker Profiles in Very Preterm Infants within the Context of Preeclampsia, Chorioamnionitis, and Clinically Diagnosed Postnatal Infection" Pediatric Reports 15, no. 3: 483-493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15030044
APA StyleEwald, J. T., Steinbrekera, B., Bermick, J. R., Santillan, D. A., Colaizy, T. T., Santillan, M. K., & Roghair, R. D. (2023). Inflammatory Biomarker Profiles in Very Preterm Infants within the Context of Preeclampsia, Chorioamnionitis, and Clinically Diagnosed Postnatal Infection. Pediatric Reports, 15(3), 483-493. https://doi.org/10.3390/pediatric15030044







