Abstract
Hypertransaminasemia in patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) is reported to be transient. Here, we describe a child with an atypically protracted course of liver tests abnormalities and review the inherent literature. The patient was hospitalized at age 7-months for isolated hypertransaminasemia detected during a classical KD diagnosed 3 months before, and persistent since then. KD clinical evolution had been favorable, with rapid response to acetylsalicylic acid and intravenous immunoglobulins. Liver enzymes however remained persistently elevated with a fluctuating pattern (ALT > AST levels; peak of AST 186 IU/L and ALT 240 IU/L). During follow-up, the main causes of liver dysfunction had to be excluded through appropriate and extensive laboratory investigations. Transaminases values become steadily normal only 7 months after the acute presentation of KD. Conclusions: Our report shows that an atypically protracted courses of KD-related hypertransaminasemia above the previously reported temporal limits should be taken into account during the stepwise diagnostic approach to the patient’s liver dysfunction. Insidious acetylsalycilic acid-hepatotoxicity warrants consideration in the differential diagnosis.
1. Introduction
Kawasaki disease (KD) is a systemic inflammation in all the medium-sized arteries and in multiple organs and tissues during the acute febrile phase. Common gastrointestinal findings include diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, hepatitis, and gallbladder hydrops while pancreatitis and jaundice are less common. Elevations in serum aminotransferases and/or gammaglutamyl-transpeptidase (GGT) documented in about one third/one half of patients are mild to moderate [1,2,3,4,5] and are described to be transient as they improve rapidly with the resolution of acute symptoms [6]. Here, we describe the case of a KD patient with an atypically protracted course of hypertransaminasemia and focus on recovery time of abnormal liver function tests in this condition.
2. Case Report
L.S., male, was born at term after an uneventful pregnancy and vaginal delivery. He was breastfed. At age 4 months, he was hospitalized because of a 4-day-long fever resistant to paracetamol/ibuprofen. At entry, classical KD diagnosis was made (five clinical criteria in addition to fever) and he received high-dose acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) until 48 h after persistent defervescence. (i.e., 80 mg/kg/day × 5 days), subsequently switched to low-dose (3 mg/kg/day) for a total duration of 8 weeks after the onset of disease. There was no recent history of other medications or viral infection. The clinical evolution of KD was favorable, with rapid response to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and no coronary involvement. Because of persistent isolated hypertransaminasemia with normality of the remaining liver and muscular tests, at the 9th week of disease, the patient was addressed to our pediatric hepatology unit. At entry, he was aged 7 months, was anicteric, and had a liver margin palpable 2.5 cm below the costal arch, without clinical signs of severe liver disease. Spleen was not enlarged. Mental status was and remained normal overtime. After 2 further weeks of isolated liver enzymes abnormalities persistence, the main causes of KD-related and unrelated hypertransaminasemia due to infectious [including blood cultures, polymerase chain reaction studies for adenovirus, cytomegalovirus, and Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis A virus (HAV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV) screening test], autoimmune [antinuclear antibodies (ANA), anti-smooth muscle antibodies (ASMA), anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMA), anti-liver kidney microsome type 1 (LKM1), anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA), serum proteins and immunoglobulins], metabolic/genetic (including serum alpha1 antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin, glucose, ammonium and copper, and sweat test), nutritional/intestinal (serologic test for celiac disease), toxic, muscular (creatine phosphokinase, CPK) conditions were all excluded through appropriate laboratory investigations. The abdominal ultrasounds were negative for gallbladder hydrops, steatosis, and other signs except for a mild hepatomegaly.
Aminotransferase values strictly monitored during the first 3 months and nearly every 1–2 months thereafter persisted elevated with a slightly fluctuating pattern and a quite continue tendency of ALT levels > AST levels. They become steadily normal only 7 months after the diagnosis of KD.
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Liver involvement in KD is commonly subclinical and self-limiting. In a large retrospective study of 240 patients with KD patients, approximately one third had hypertransaminasemia with only mildly elevated aminotransferases values, i.e., less than twice the upper limit of normal. Only a few presented with a picture of clinical hepatitis with jaundice and aminotransferase elevations of more than 10-fold [2].
The natural recovery time of liver function tests in KD has been rarely studied. As summarized in Table 1, it has been reported only in one series where it appears to be 7 days (median), ranging from 2 days to 99 days [6], and in one case report where aminotransferases recovered after 4 months from onset [7]. Another series describes only an early tendency to recovery in the first/second week of illness [8].

Table 1.
Natural recovery time of liver enzymes abnormalities in Kawasaki disease.
The much longer duration of liver abnormalities with a slow decrease of aminotransferase values at considerable distance from initial diagnosis of KD observed in our patient suggests that hypertransaminasemia may occasionally be more protracted than previously thought.
Hepatobiliary enzymes elevations in KD may reflect a number of underlying manifestations ranging from asymptomatic increase in liver enzymes to severe cholestatic hepatitis, acute acalculous cholecystitis, or hydrops of the gallbladder [10]. Though hepatic disease per se is not a significant cause of morbidity or mortality in KD patients, monitoring of abnormal liver function is important because it may mirror the severity of ongoing systemic inflammation, which has been reported to affect in some manner the efficacy of IVIG treatment. Early recognition of liver function tests abnormalities may help to intercept an IVIG resistant disease, a condition which tends to be more prevalent in those who develop coronary artery abnormalities [11]. High AST levels and abnormal ultrasonographic biliary findings moreover have been considered risk factors for coronary artery abnormality and/or recurrent KD if they are present during the first episode [7,10,12].
KD is a childhood systemic vasculitis which still remains without a well-defined etiology. The epidemiology and clinical presentation suggest a possible underlying viral/bacterial infection or an abnormal immunologic response to an infection in genetically predisposed children; autoimmune disease is a possibility as well [13,14]. After exhaustive investigation, we were not able to find any of the above-mentioned causative triggers of KD in our patient and therefore we are not aware if the agent triggering KD was also hepatotropic and responsible for both the vasculitis and this atypically prolonged liver involvement. Alternatively, the liver involvement was due to a concomitantly associated but unrelated liver insult deriving by another cause. Considering that, the prolonged course of the liver test abnormalities of our patient required to exclude the entire series of the most frequent liver infections, autoimmune, metabolic, or toxic causes [15].
Pathologic findings of the liver described in KD patients with hepatic presentation or in autopsies encompass a variety of sinusoids and portal areas lesions, and/or swelling of Kupffer cells, fatty degeneration, and severe congestion. Regarding the latter, therefore, postulated mechanisms underlying liver function tests abnormalities in these patients suggest to include also congestive heart failure secondary to myocarditis, drug induced liver injury (so called DILI), and/or a combination of the above [2]. As shown in Figure 1, in our patient, the temporal relationship between ASA treatment and the highest aminotransferases values might indeed imply also a DILI mechanism.
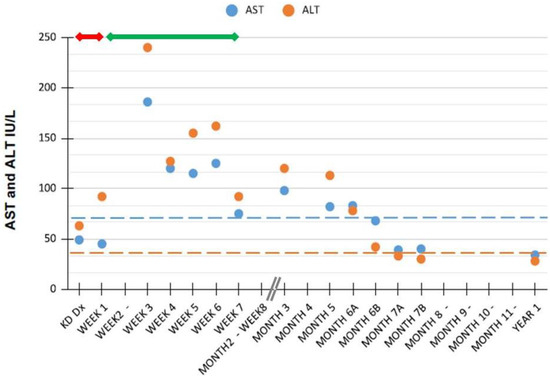
Figure 1.
Aminotransferases values after diagnosis of Kawasaki disease in our patient. Horizontal dashed lines indicate ALT and AST upper normal values for age [16]; the horizontal continuous red and green lines indicate treatment duration with acetylsalicylic acid at high and low doses, respectively. Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; Dx, diagnosis; KD, Kawasaki disease.
Hepatotoxicity of ASA through mitochondrial dysfunction, higher hepatic fatty acid supply, and microvesicular steatosis could explain at least in part the dose dependent and usually transient and asymptomatic hepatic dysfunction seen in KD [17,18]. As liver failure is generally observed mainly when ASA is used at medium-high dosage, aminotransferase level monitoring is mandatorily recommended to either reduce dosage or stop ASA treatment. In connection with chickenpox and flu, the risky possibility of Reye’s syndrome should be seriously considered although, at low dosage of ASA, the occurrence of this syndrome is reported to be rare [19,20]. In our case, the modest transaminase peak observed during aspirin treatment along with the other clinical and laboratory data make improbable a Reye’s syndrome like related hepatotoxicity in addition to the usual KD-related transient hypertransaminasemia. Still, an atypically prolonged idiosyncratic ASA hepatotoxicity remains an open question.
In spite of these premises, it is worth of note that ASA frequency of use and doses (ranging 10–30 mg/kg/day) are reported having been not significantly different in 381 KD patients (mean age 25.3 months) divided in three groups allocated into children with ALT level ≥40 IU/L on admission, ≥40 IU/L at some point after admission, or ALT levels consistently <40 IU/L throughout hospitalization [9]. Still, these authors considered an arbitrary upper normal value of transaminases, which is not appropriate during the first year of life. (Table 1)
In conclusion, our report shows the possibility of facing an atypically protracted course of KD-related hypertransaminasemia above the hitherto reported temporal limits. Due to the likely uncommonness of the event here described, those infectious/immune causes which could have acutely triggered both conditions still need to be investigated in first instance. Should hypertransaminasemia persist, pending specific markers of KD-related liver dysfunction, a stepwise approach with careful evaluation of the cost–benefit ratio in the use of additional diagnostic resources is anyway warranted to search for an underlying KD-unrelated persistent/chronic hepatopathy [15]. Because ASA doses recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American Heart Association to attain an anti-inflammatory effect during the acute phase of KD are fairly high, reaching up to 80–100 mg/kg per day, high dose-ASA-related DILI risk remains a possible insidious confounder in KD. The question of whether the benefits of high dose ASA warrants its continued use in KD however is not likely to get an answer presently since all prospective studies that have demonstrated the effectiveness of IVIG in treating KD also employed moderate to high doses of aspirin [21].
Author Contributions
P.P., M.L. and L.N. followed the patient at entry and during follow-up, performed the study, and co-wrote the first draft of the paper; A.G.E.D.A., R.C., M.C.R., M.A.S. and N.B. retrieved the existing literature; P.V. supervised the study and is the guarantor. All contributed to the ongoing writing and approved the present version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study, due to the nature of the article and being case report. This study was carried out in accordance with the Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
No additional data sets are associated with this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tremoulet, A.H.; Jain, S.; Chandrasekar, D.; Sun, X.; Sato, Y.; Burns, J.C. Evolution of Laboratory Values in Patients with Kawasaki Disease. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eladawy, M.; Dominguez, S.R.; Anderson, M.S.; Glodé, M.P. Abnormal liver panel in acute Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCrindle, B.W.; Rowley, A.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Burns, J.C.; Bolger, A.F.; Gewitz, M.; Pahl, E. Diagnosis, Treatment, and Long-Term Management of Kawasaki Disease: A Scientific Statement for Health Professionals From the American Heart Association [published correction appears in Circulation. 2019, 140, e181–e184]. Circulation 2017, 135, e927–e999. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Makino, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Yashiro, M.; Ae, R.; Tsuboi, S.; Aoyama, Y.; Yanagawa, H. Descriptive epidemiology of Kawasaki disease in Japan, 2011-2012: From the results of the 22nd nationwide survey. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stasiak, A.; Smolewska, E. Retrospective study of the course, treatment and long-term follow-up of Kawasaki disease: A single-center experience from Poland. Rheumatol. Int. 2019, 39, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jang, M.; Oh, M.S.; Oh, S.C.; Kang, K.S. Distribution of Diseases Causing Liver Function Test Abnormality in Children and Natural Recovery Time of the Abnormal Liver Function. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 1784–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, I.M.; Beran, E.; Dapunt, O.E. Kawasaki disease and hepatobiliary involvement: Report of two cases. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2016, 42, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tomita, Y.; Fukaya, T.; Yamaura, Y.; Tsujiguchi, R.; Muratani, H.; Shimaya, M. Implications of hepatic dysfunction in Kawasaki disease: Time-related changes in aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, total bilirubin, and C-reactive protein levels. Pediatr. Investig. 2019, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohani, P.; Imanzadeh, F.; Sayyari, A.; Aghdam, M.K.; Shiari, R. Persistent elevation of aspartate aminotransferase in a child after incomplete Kawasaki disease: A case report and literature review. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.-M.; Du, Z.-D.; Fu, P.-P. Clinical features of recurrent Kawasaki disease and its risk factors. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 172, 1641–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yin, W.; Wang, R.; Sun, D.; He, X.; Ding, Y. The prognostic role of abnormal liver function in IVIG unresponsiveness in Kawasaki disease: A meta-analysis. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 65, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, D.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, E.Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Yang, H.R. Hepatobiliary risk factors for clinical outcome of Kawasaki disease in children. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, A.; Ikeda, K.; Hamaoka, K. Aetiological Significance of Infectious Stimuli in Kawasaki Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosencrantz, R.A.; Huang, T.; Sonke, P.Y.; Tewari, D.; Chander, P.N. Autoimmune sclerosing cholangitis: An atypical association with Kawasaki disease. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2253–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajro, P.; Maddaluno, S.; Veropalumbo, C. Persistent hypertransaminasemia in asymptomatic children: A stepwise approach. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2740–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colantonio, D.A.; Kyriakopoulou, L.; Chan, M.K.; Daly, C.H.; Brinc, D.; Venner, A.A.; Pasic, M.D.; Armbruster, D.; Adeli, K. Closing the Gaps in Pediatric Laboratory Reference Intervals: A CALIPER Database of 40 Biochemical Markers in a Healthy and Multiethnic Population of Children. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 854–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aithal, G.P.; Day, C.P. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug–Induced Hepatotoxicity. Clin. Liver Dis. 2007, 11, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammadov, G.; Liu, H.H.; Chen, W.X.; Fan, G.Z.; Li, R.X.; Liu, F.F.; Samadli, S.; Wang, J.J.; Wu, Y.F.; Luo, H.H.; et al. Hepatic dysfunction secondary to Kawasaki disease: Characteristics, etiology and predictive role in coronary artery abnormalities. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchesi, A.; De Jacobis, I.T.; Rigante, D.; Rimini, A.; Malorni, W.; Corsello, G.; Bossi, G.; Buonuomo, S.; Cardinale, F.; Cortis, E.; et al. Kawasaki disease: Guidelines of the Italian Society of Pediatrics, part I—definition, epidemiology, etiopathogenesis, clinical expression and management of the acute phase. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marchesi, A.; De Jacobis, I.T.; Rigante, D.; Rimini, A.; Malorni, W.; Corsello, G.; Villani, A. Kawasaki disease: Guidelines of Italian Society of Pediatrics, part II—treatment of resistant forms and cardiovascular complications, follow-up, lifestyle and prevention of cardiovascular risks. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2018, 44, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sundel, R. Kawasaki Disease: Initial Treatment and Prognosis. 2020. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/kawasaki-disease-initial-treatment-and-prognosis. (accessed on 30 June 2021).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).