Abstract
Traditional sausage in the Republic of Kosovo has been produced for centuries as a traditional method of preserving the nutritional value of meat. In sausage fermentation, natural microbiota such as lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and Micrococcaceae usually participate; these are not only critical for ensuring product safety and flavor development but also represent significant biotechnological potential. The purpose of this study was to analyze traditional fermented sausage, in terms of production practices and hygiene, throughout the production and storage phases. Samples in three stages of production and maturation were analyzed for microbiota, pH, and water activity level. Our results show that the main changes in the bacterial populations from 0 to 7 days of storage included increases in the total numbers of viable mesophilic aerobic bacteria (LAB) and Micrococcaceae (MC). However, the Enterobacteriaceae and coliforms (EC) count showed a significant decrease (p < 0.05) in 1.60 ± 1.62 lg cfu/g by day 14. In conclusion, the number of EC in the traditional sausage was decreased during storage, while LAB and MC were stable, data that indicate the safety and quality of this product. No differences regarding the production practices and storage of traditional sausage were observed, based on the data from the butchers who participated in this study.
1. Introduction
Sausage is one of the oldest fermented foods that human hands have processed [1]. Historical records from ancient Mesopotamia, Greece, and Rome document sausage-making as a method for meat preservation [2]. Traditionally, sausages were produced by combining ground meat with salt, fat, and spices, and then encasing the mixture in natural casings and fermenting or drying it to extend its shelf life [3]. Over the centuries, various cultures have developed distinctive variations influenced by local ingredients, climate, and culinary customs. This artisanal knowledge has been transmitted across generations and continues to underpin many traditional sausage production methods, including those still practiced in Kosovo today [4]. This meat product is typically made from beef and pork [5], and in some cases, buffalo meat [6]; certain varieties can also be made using chicken meat [7]. Additionally, the flavor and preparation can vary depending on the seasoning ingredients used (e.g., garlic, onions, peppers and wine), which are incorporated in different ways [8]. The production practices and the variety of meats involved have an impact on the nutritional composition of the sausage [9]. The production process of traditional sausages depends on natural complex microbiota, which induce significant changes in the characteristics of these products, as discussed in a review by Milicevic et al. (2014) [10]. In the fermentation phase of traditional sausage, there usually is a dominance of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS), which can effect a reduction in the pH of the product, leading to reductions in pathogenic and spoilage-favoring microorganisms [5,10,11,12,13]. In an experimental study, it was shown that LAB are active throughout all phases of the production and maturation/storage of this product; there was a dominance of the genera Lactobacillus (76.96%) and Staphylococcus (6.44%) on day 0, while on day 12 of maturation there was a decrease in Lactobacillus of 63.03% and an increase in Staphylococcus of 22.29% [14]. Due to the release of free amino acids in the proteolytic and lipolytic activity of the microbial community in traditional sausage, we have the consequent production of volatile organic components, leading to the increase in these components in the maturation phase [14]. All of these changes in the microbial community, and production components such as aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, and sulfur-containing components, contribute to the development of the organoleptic characteristics and safety factors of the final product [15]. Yeast can also play an important role in sausage fermentation and its organoleptic characteristics. In particular, species such as Debaryomyces hansenii and Yarrowia lipolytica contribute to the development of aroma and flavor through the production of esters, alcohols, and sulfur-containing compounds. They exhibit lipolytic activity, breaking down fats into free fatty acids that serve as precursors to volatile compounds. Furthermore, they contribute to surface deacidification, pigment stability, and the prevention of lipid oxidation, which enhance the appearance factors and shelf life of the product [16,17,18,19]. LAB are widely distributed as inhabitants of the intestinal tract in animals, and they have very significant applications in the food industry [20,21]. They are Gram-positive, non-spore-forming, generally non-motile, catalase-negative microorganisms that grow under anaerobic or microaerophilic conditions. They are known for their fermentative metabolism, primarily converting sugars into lactic acid, which contributes to the acidification and preservation of fermented foods, and are also known for their probiotic properties. LABs are naturally present in raw meat and are dominant during sausage fermentation due to their acid tolerance and fast growth in low-oxygen environments [22,23]. The LAB group includes genera such as Lactobacillus [24], Leuconostoc, Pediococcus, and Lactococcus [25]. This group of bacteria is known to produce antibacterial compounds such as bacteriocins, which are very important for microbial stability in the fermenting consortia involved in sausage-making [26,27]. These bacteriocins serve for food preservation due to the microbiological and technological advantages they possess. They are ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial peptides or proteins that act by forming pores in the membranes that surround closely related or foodborne pathogens, including Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Clostridium spp., and other Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria [28]. Thus, the activity of bacteriocins is usually lethal to the bacterium [29,30]. Examples of these bacteriocins are nisin, leucocin, and pediocin [31]. Nisin, produced by Lactococcus lactis, is effective against Gram-positive pathogens such as Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, and Clostridium botulinum [32]. Leucocin A, produced by Leuconostoc carnosum DH25, also inhibits Listeria monocitogenes, more strongly than do factors like pH and water activity (aw) [33]. Pediocin, from Pediococcus spp., has potent antilisterial activity and is often used in meat preservation [34]. Bacteriocin production enhances the microbial safety of fermented sausages and supports natural preservation without chemical additives.
Using high-throughput sequencing, researchers have identified complex consortia of bacteria in traditional urutan sausage. An analysis showed that Bacillota was the most abundant phylum, and at the genus level, the mixture was dominated by Latilactobacillus, Macrococcoides, Lactococcus, and Weissella. The genera that were positively correlated to the pH, water activity (aW), and acidity of fermented urutan were Staphylococcus, Lactococcus, Mammalicoccus, Macrococcoides, and Citrobacter [35]. While traditional culture-based methods provide quantitative insight into the dominant microbial groups, metagenomic studies have offered a more comprehensive view of microbial succession and diversity during sausage fermentation. They are important microorganisms in the food industry, used as starter cultures to produce a larger variety of fermented foods based on lactic fermentation [22]. In meat fermentation, the main function of LAB is to ensure a rapid drop of pH, which favors product safety by suppressing the growth of pathogens, and ensures product stability and shelf life by preventing undesirable changes that may cause different biochemical interactions that, in turn, cause altered sensory properties in matured products [36,37,38]. Besides these antibacterial agents from LAB, in a recent review, extract and essential oils from plants have been used for meat products preservation [39]. Beyond the presence of lactic acid bacteria, there are also other bacteria present, such as Micrococcaceae, Staphlylococcaceae, and Enterococcaceae, which develop during the ripening/fermentation stage. Among them is coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS), which is a group of bacteria that could contribute to the safety and quality of traditional sausage [40]. Many studies have shown the effects of CNS bacteria on proteolytic and lipolytic degradation and flavor development during the fermentation and maturation of traditional sausage [41,42]. In a recent study, Liu et al. 2023 [13] found that a combination of Lactobacillus fermentum YZU-06 and Staphylococcus saprophyticus CGMCC 3475 improved the quality and flavor development of fermented sausage. Staphylococcus xylosus, which is commonly used as a starter organism in traditional sausage fermentation [43], plays an important role in biotechnological aspects such as biofilm formation and cell aggregation [44].
Kosovo has an ancient tradition centered on the production and consumption of traditional products such as meat-based products [45], milk products [46,47,48,49], cereal-based products [50], fermented vegetable products, and wine. For meat products such as beef- and chicken-based processed meat products, we have relevant information about the incidence of adulteration [51], as well as a microbial assessment of ground beef from fast food outlets in Prishtina [52], but very limited information about the microbial quality of traditional sausage. This traditional sausage is usually made from beef meat, mainly beef horn (neck) combined with beef fat, and some mixed ingredients, without the addition of starter cultures. Due to its characteristics such as water activity (aw) and pH, fresh sausage is prone to rancidity, and when produced using traditional methods in our country, it has a shelf life of 10–14 days. It is stored at +4 °C and cooked beforehand. Despite the long-standing tradition of sausage-making in Kosovo, there is a notable lack of scientific literature and systematic studies on the microbial quality of traditionally produced sausages. The relevant research regarding the quality and safety of traditional sausage could be used as a reference study in the case of standardization and certification of this traditional product in the future. This study takes a first step in that direction by analyzing the microbiological changes during the production and storage of traditionally fermented sausage in Kosovo.
The hypotheses for this study were as follows: (i) that those traditional fermented sausages produced without starter cultures in Kosovo harbor dynamic microbial communities dominated by LAB and Micrococcaceae, which evolve during fermentation and storage in a way that promotes product safety; (ii) that microbial succession, in combination with changes in pH and water activity, reduces spoilage and pathogenic bacteria (e.g., Enterobacteriaceae and coliforms), thereby contributing to the hygienic quality of the product; and (iii) that the production practices and storage practices associated with traditional sausage vary, and the three local butchers use different methods of production and storage conditions. To test these hypotheses, we collected traditional sausage samples from three local butcher shops and monitored microbial counts (total number of colonies, lactic acid bacteria, Micrococcaceae, Enterobacteriaceae, and coliforms) and physicochemical parameters (pH and water activity) at three stages of production and maturation: day 0 (pre-fermentation), day 7 (post-fermentation), and day 14 (end of storage). The present work aimed to evaluate the microbiological properties and production practices associated with the different stages of production and the storage of traditional Kosovar sausage. The importance of this research on these groups of bacteria lies in their crucial role in determining both the quality and safety of the traditional sausage. In particular, lactic acid bacteria and micrococci, or a mixture of these two groups, have been demonstrated as playing a role in fermentation, which is essential in traditional sausage production, and this fact is widely recognized in the meat processing industry [10].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Collection
Samples were collected in March and April 2024 from three butchers who produce traditional sausage and other meat products, in the region of Prishtina, Kosovo. These butchers were selected based on the following criteria: (i) they had a long-standing tradition of producing fermented sausages using artisanal methods, (ii) they produced sausages without the addition of starter cultures and commercial additives, and (iii) they used consistent, repeatable processes in sausage preparation. All shops operated under similar hygienic standards and had local customer bases. The traditional sausages were composed of locally sourced beef meat, including rib and neck cuts, mixed with beef fat. No commercial starter cultures or curing agents were added, in line with traditional preparation methods.
The traditional sausage was analyzed in three different stages of production and storage, specifically, on day 0 (before the drying process), day 7 (after drying/fermentation), and day 14 (after two weeks of storage) at a temperature of +4 °C, two samples per stage and 2 repetitions (n = 2). During the sample collection, we gained detailed information from traditional sausage producers about the ingredients/preparation methods of traditional sausage. This type of traditional meat product was manufactured by traditional methods without adding any starter culture. All samples were transferred to the sterile plastic pouches and kept refrigerated until analysis in the laboratory.
2.2. Production Practices
Traditional sausage in Kosovo has been produced in homes, and it is also made commercially, both on a small scale and on a large scale. The production diagram of the traditional sausage of the Prishtina region is given for the first time in this study (Figure 1).
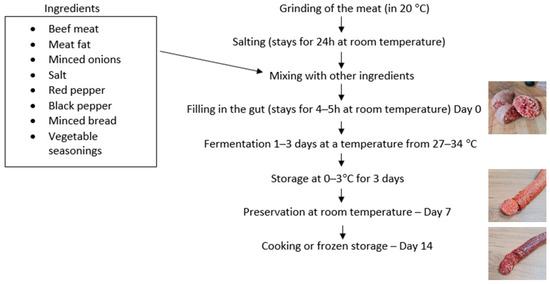
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the production process used by traditional sausage producers. The arrows represent the sequential processing steps, while also indicating the addition of specific ingredients.
The knowledge associated with the traditional preparation method is generally passed on from one generation to another and may differ between producers as to any detail in the production practice. From all sampling points, those preparing the sausage declared the use of beef rib meat in the sausage production. In the described method, as given by the three butchers, they mainly use beef meat, a combination of neck and rib meat and fat. The ground meat, salted (NaCl) for 24 h at room temperature, is then mixed with minced onions, red and black pepper, and vegetable seasonings, and some minced bread is added at the end. The ingredients used in the sausage preparation, such as the beef meat, onions, and bread, were not subjected to any disinfection or pasteurization procedures before processing. The whole mixture is then filled into the gut casings and is kept for 4–5 h at room temperature. The fermentation stage lasts 1–3 days, and the sausages are usually placed in special rooms for fermentation at a moderate temperature, starting at 27 °C on the first day and then rising to reach 34 °C by the end of 3rd day of fermentation. The fermented sausage is then put in storage at 0–3 °C for 3 days, after which it can later be preserved at room temperature. The environmental temperatures involved in the sausage production and storage ranged from 0 °C during refrigeration to 34 °C during fermentation.
2.3. Microbial Cultivation
The 20 g samples of the sausage taken severally on day 0, day 7 and day 14 were each mixed with 180 mL sterile Ringer’s Solution 0.9% and homogenized for approximately 90 s using a Stomacher Lab Blender 400 (VWR). Homogenized and diluted in Buffered Peptone Water-BPW (typical formula: pancreatic digest of casein 1.0 g/L, sodium chloride 4.3 g/L, sodium phosphate monobasic anhydrous 5.77 g/L, and potassium phosphate dibasic 3.56 g/L; final pH 7.0 ± 0.2 at 25 °C), samples were plated for bacterial enumeration according to the pour plate method. Briefly, 1 mL aliquots of the diluted samples were inoculated directly into the molten media [46,49]. Microbial analysis was performed by culturing in certain media, and samples were weighed on an analytical scale. For all media, distilled water was used, in accordance with the manufacturer’s prescription; samples were mixed in the magnetic stirrer hot plate and then sterilized in an autoclave in 121 °C, for 15 min at a pressure of 1.5 atm. The media were then cooled at 45–50 °C and aseptically distributed into Petri dishes. All groups of microorganisms were cultivated in aerobic conditions. The same procedures were repeated at each stage of the sausage production and storage.
Total number of colonies (TNC) was based on samples cultured on Plate Count Agar (Liofilchem, Roseto degli Abruzzi (TE), Italy), also called “standard medium”; the total number of aerobic bacteria within a sample was measured and counted after 72 h of incubation at 30 °C. The typical formula for PCA in g/L was as follows: enzymatic digest of casein 5.0 g; yeast extract 2.5 g; glucose 1.0 g; agar 15.0 g; and final pH 7.0 ± 0.2 at 25 °C, according to ISO 4833-1:2013 [53].
Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) were cultivated on de Man, Rogosa, and Shape agar (MRSA; Biolife, Milan, Italy) and counted after 72 h at 37 °C. The typical formula for MRSA in g/mL/L was as follows: Pepton 10.0 g; beef extract 10.0 g; yeast extract 5.0 g; glucose 20.0 g; dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2.0 g; sodium acetate 5.0 g; diammonium citrate 2.0 g; magnesium sulphate 0.2 g; manganous sulphate 0.05 g; agar 15.0 g; tween 80 1.0 mL; and final pH 6.4 ± 0.2 at 20–25 °C.
For enumeration of Micrococcaceae (MC), we used Manitol Salt Agar (MSA; Liofilchem, Roseto degli Abruzzi (TE), Italy), and counted after 72 h of incubation at 30 °C. The typical formula for MSA in g/L was as follows: pancreatic digest of casein 5.0 g; peptic digest of animal tissue 5.0 g; D-Mannitol 10.0 g; sodium chloride 75.0 g; phenol red 0.025 g; agar 15.0 g; and final pH 7.4 ± 0.2 at 25 °C.
Enterobacteriaceae and coliforms (EC) were cultured on MacConkey agar (MCA; Biolife, Milan, Italy) and were counted after 48 h of incubation at 37 °C. For MSA, the typical formula in g/L was as follows: gelatin peptone 17.0 g; peptones 3.0 g; lactose 10.0 g; bile salts 1.5 g; sodium chloride 5.0 g; neutral red 0.003 g; crystal violet 0.001 g; agar 13.5 g; and a final pH at 25 °C of 7.1 ± 02.
2.4. pH and Water Activity Analysis
The pH was measured using a pH-meter Basic 20 (Criston Instrument, Barcelona, Spain). For pH determination, 10 g of the sausage sample was homogenized with 90 mL of distilled water in a sterile blender to create a 1:10 (w/v) suspension. The pH of the resulting homogenate was measured using a calibrated pH meter. Measurements were performed in duplicate for each sample [40]. The determination of water activity (aw) of the traditional sausage samples was conducted with the LabTouch-aw apparatus manufactured by Novasina, Photo X (Lachen, Switzerland). The samples were measured after processing and during ripening and storage at 17–20.2 °C.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All experimental data are presented as average ± SD. Plate counts were log-transformed before statistical analysis. The statistical significance was determined using ANOVA, while the differences between the groups were analyzed with Fisher’s LSD test. The results were considered significant if p < 0.05. Principal component analysis (PCA) [54], and the Pearson correlogram were generated using RStudio (R version 2025.05.1, Build 513) to explore variable patterns and correlations. Additional statistical visualizations, including box plots and descriptive graphs, were created with OriginPro 2021 to assess data distribution and variability.
3. Results
3.1. Microbiological Analyses
An evaluation of the microbiota present in the traditional sausage samples during production and ripening is summarized in Figure 2. The environmental temperatures involved in the sausage production and storage ranged from 0 °C during refrigeration to 34 °C during fermentation. On day 0 (pre-ripening phase), the average TNC was 7.06 ± 0.12 lg cfu/g, LAB 6.11 ± 1.01 lg cfu/g, MC 5.63 ± 0.33 lg cfu/g, and EC 5.10 ± 0.49 lg cfu/g. The main changes in bacterial populations appeared on day 7 of storage (after fermentation), including the increase in TNC to 8.88 ± 2.27 lg cfu/g, LAB 6.01 ± 1.59 lg cfu/g, and MC 5.69 ± 1.46 lg cfu/g. At this stage, there was a significant change (p < 0.05) for the EC group (2.47 ± 1.37 lg cfu/g), compared to day 0. After 14 days of sausage storage at +4 °C, the numbers of mesophilic bacteria and LAB had slight decreases to 6.68 ± 2.22 lg cfu/g and 5.99 ± 0.74 lg cfu/g, respectively, and the number of MC (5.30 ± 2.22 lg cfu/g) was approximately the same as on day 7. While EC during traditional sausage fermentation decreases up to 1.60 ± 1.62 lg cfu/g, LAB, from day 0 to day 14, did not show any significant changes.
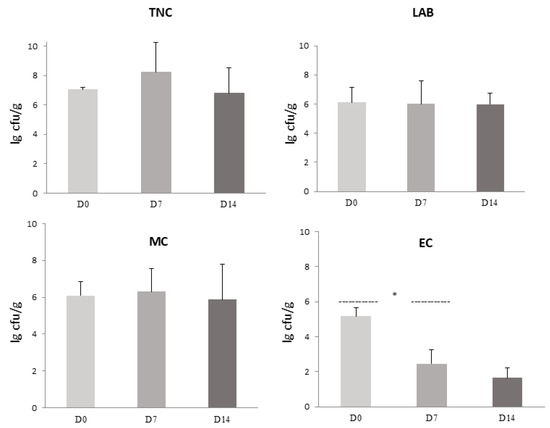
Figure 2.
Microbiological evaluation of traditional sausage during production and storage, including total number of colonies (TNC), lactic acid bacteria (LAB), Micrococcaceae (MC), and Enterobacteriaceae and coliforms (EC). Error bars indicate standard deviations. A significant decrease in Enterobacteriaceae and coliforms was observed during storage (* p < 0.05).
The evaluation of microbial changes in the three batches is shown in Figure 3. The numbers of microorganisms for the TNC, LAB, and MC groups analyzed in this study were not the same for all batches, with EC being the exception. Despite this, the average values associated with these three microbial groups did not show significant changes during the production and storage of the traditional sausage.
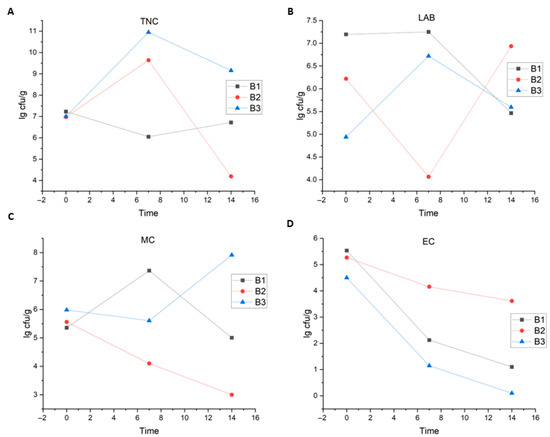
Figure 3.
Dynamics of key microbial groups during the production and storage of traditional sausage: (A) Total number of colonies (TNC; total mesophilic aerobic count), (B) Lactic acid bacteria (LAB), (C) Micrococcaceae (MC), and (D) Enterobacteriaceae and coliforms (EC). The trends are shown for three independent production batches (B1, B2, and B3) sourced from different butchers.
3.2. Physico-Chemical Parameters
Evaluations of pH and aw during the traditional sausage production and storage by the three butchers are shown in Figure 4. The pH values in all three batches during the phases analyzed in this study were approximately the same. The average pH value in the initial phase (D0) was 6.64 ± 0.03, and it was almost the same in all samples. In the final phase, the average pH value was 5.07 ± 0.13, which indicates an acidification of the product, and this may have contributed to the decrease in the EC number. Our results regarding the pH value during the production and storage of traditional sausage are in harmony with the results of other authors regarding similar products [55,56,57,58].
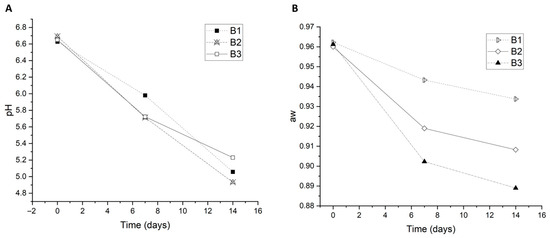
Figure 4.
Time-course changes in physicochemical parameters critical for sausage safety and quality. (A) pH values show a characteristic decline over time, with product B3 exhibiting the most pronounced acidification. (B) Water activity (aw) gradually decreases during storage, indicating a loss of moisture. Data points represent mean values from three independent samples per batch (B1, B2, and B3).
A small reduction in aw was noted from the initial phase of production to the final phase of sausage maturation and storage. On day 0, the mean of the water activity was 0.96 ± 0.01; this decreased on D7 to 0.92 ± 0.17, and on D14, the mean value was 0.91 ± 0.01. This decrease could have been the reason that EC was low in the final phase. The same trend was observed in all batches where samples were taken. These findings are in harmony with the results of other authors [55,56,57,58].
3.3. PCA Analysis
Figure 5 presents the results of a principal component analysis (PCA) based on the covariance matrix of the microbiological and physicochemical parameters, conducted using RStudio. PCA showed significant correlation in the first two dimensions, explaining 95.7% of the total variance (Dim1: 62.6%; Dim2: 33.1%). Dim1 shows a strong positive correlation of TNC, LAB, and pH (all clustered in the positive quadrant). This triad aligns with established fermentation kinetics: LAB proliferation drives acid production, suppressing pH while dominating microbial ecology [59].
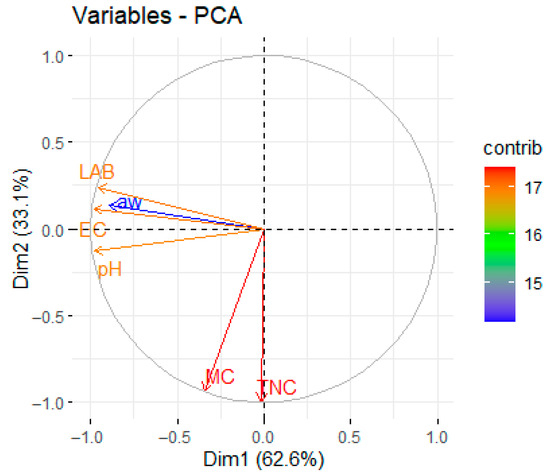
Figure 5.
Principal component analysis (PCA) plot of microbiological and physicochemical parameters of traditional sausage during production and storage.
LAB expansion explains the acidification (pH drop) and the major microbial colonization. To the contrary, aw is projected independently in Dim2′s negative quadrant, confirming its detachment from fermentation trends, with a structure primarily regulated by the substrate’s composition and storage conditions, confirming that aw is governed primarily by substrate composition (e.g., salt content) rather than microbial activity.
Dim2 also displayed an antagonistic and competitive hierarchy, clearly separating the MC and EC in the negative quadrant, opposite to the LAB. This spatial segregation validates the competitive exclusion principle [60] due to which, in LAB, metabolites (e.g., bacteriocins, organic acids) inhibit competitors.
The maximal Euclidean distance between LAB and EC mirrors previous observations in fermented meats, underscoring fermentation’s role as a biological preservative. Notably, an orthogonal projection highlights the role of EC as an independent hurdle—consistent with Leistner’s hurdle technology framework [61]—demanding targeted control strategies (e.g., humectant optimization) beyond acidification. Such predominance initiates the evidence in the orthogonal projection of aw related to fermentation variables. Orthogonality implies a lack of dependence upon a general fermentation-independent effect, reinforcing that specified selection (e.g., humectants or drying methods) is required in the control for adequate food safety outcomes. The principal component loadings obtained from the analysis are presented in Supplementary Table S1.
3.4. Pearson Correlation
Figure 6 displays the Pearson correlation matrix, visualized as a correlogram generated using RStudio (R version 2025.05.1, Build 513). A correlogram offers a fascinating glimpse into the intricate relationships between biological and environmental factors during the production and storage of traditional sausage. Researchers look at biological “players” like the TNC, LAB, MC, and EC alongside environmental “influencers” such as pH and aw. This analysis aligns with recent food microbiology research [62] and is all about uncovering how these elements might depend on each other, shaping the microbial landscape and overall product quality. The influence of pH on LAB is also noteworthy, with a correlation of 0.92 (depicted in a rich red shade), indicating a significant positive relationship in which higher pH levels may foster the growth of LAB, which is crucial for fermentation and preservation. On the flip side, the gentle negative link of −0.23 between TNC and LAB, painted in a soft blue shade, hints at microbial competition, and is consistent with antagonistic interactions documented in meat matrices. When it comes to preservation, the high correlations between EC and both pH (0.96) and aw (0.83) emphasize how crucial these environmental conditions are in controlling EC, which is key to food safety. The bold red tones reflect the strength of these connections, warning us that even small shifts in pH or aw could tip the scales on microbial safety. The strong correlations observed between LAB and EC (r = 0.99) and between TNC and MC (r = 0.94) indicate a potential synergistic growth under permissive conditions, consistent with previously reported patterns of pathogen dynamics in fermented meats [63]. Meanwhile, the faint 0.11 link between LAB and MC (pale pink) implies ecological independence, and is likely driven by niche-specific factors. These insights underscore the need to monitor environmental and microbial variables, providing a foundation for the optimization of preservation strategies aiming to enhance sausage quality and shelf life.
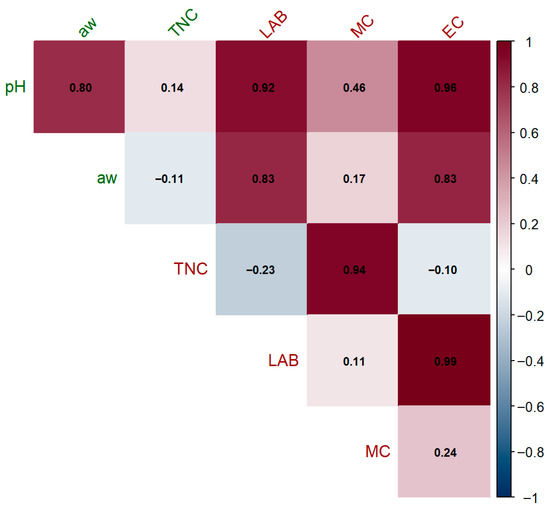
Figure 6.
Correlogram showing Pearson correlation coefficients among microbial and environmental parameters: water activity (aw), electrical conductivity (EC), lactic acid bacteria count (LAB), moisture content (MC), pH, and total number of colonies (TNC). The lower triangle displays pairwise Pearson correlation coefficients (r-values), and the color gradient indicates the strength and direction of the correlation (dark red: strong positive; dark blue: strong negative). Correlation significance was assessed using the two-tailed Pearson test in RStudio (p < 0.05).
The boxplot in Figure 7 illustrates the pH changes of sausage over 14 days, comparing measurements from day 0, day 7, and day 14. At D0, the pH is notably higher, with a median around 6.64 ± 0.03 and a narrow interquartile range (IQR), indicating minimal variability and a stable, likely fresh, state. By day 7, the pH decreases significantly (p < 0.05), with a median around 5.8 ± 0.14 and a broader IQR, suggesting increased variability and potential microbial activity or fermentation processes affecting acidity. At day 14, the pH further declines to a median of approximately 5.18 ± 0.13, with an IQR similar to day 7, reflecting continued acidification. This trend indicates a progressive decrease in pH over time, which is consistent with natural fermentation.
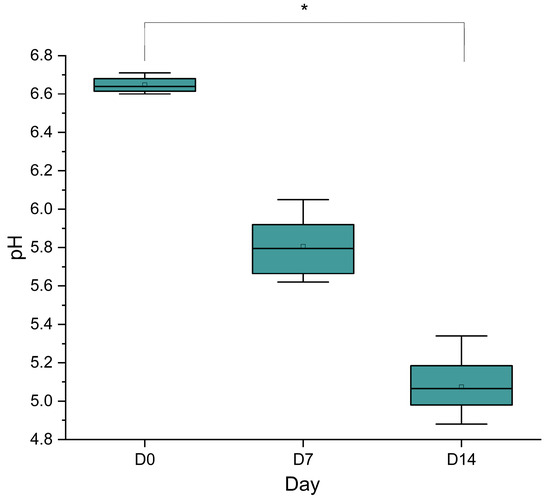
Figure 7.
Data are presented as box plots indicating the distribution, median, interquartile range, and variability of pH measurements at each time point. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by post hoc testing to assess differences between time points. A significant decrease in pH was observed from day 0 to day 14 (p < 0.05), indicating acidification during storage. * p < 0.05.
Figure 8 presents the boxplot of water activity (aw) measured during production and storage. At day 0, aw is highest, with a median around 0.96 ± 0.001 and a narrow interquartile range (IQR), indicating minimal variability and a fresh sample. By day 7, the median aw decreases slightly to approximately 0.92 ± 0.01, with a broader IQR, suggesting some moisture loss or drying processes, possibly due to evaporation or microbial activity altering the sausage’s matrix. At day 14, the median remains stable at around 0.91 ± 0.01, with an IQR similar to day 7, indicating that aw stabilizes after the initial decline, potentially reflecting equilibrium with the storage environment or continued drying. This pattern suggests a reduction in aw over time, which is critical for extending shelf life and inhibiting microbial proliferation.
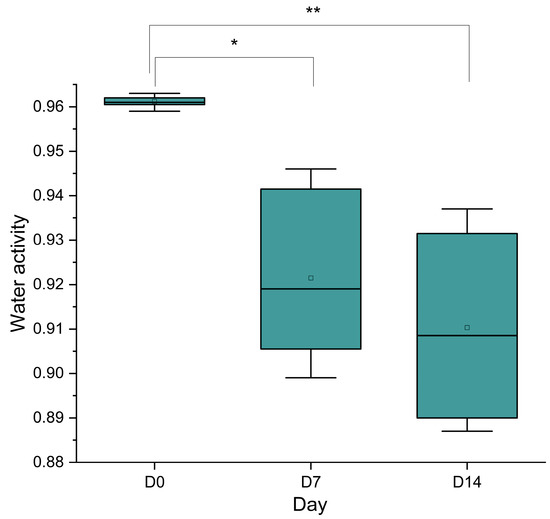
Figure 8.
Box plot showing changes in water activity (aw) in traditional sausages at three stages of production and storage: day 0 (D0), day 7 (D7), and day 14 (D14). Data are presented as box plots illustrating the arithmetic mean (small circle), the median (horizontal line inside), the interquartile range, and variability. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by post hoc comparison. A significant decrease in aw was observed from D0 to D7 (p < 0.05), and a further reduction occurred from D7 to D14 (p < 0.05). The overall reduction from D0 to D14 was highly significant (p < 0.01), reflecting the progressive drying and dehydration of the product, which is critical for improving shelf life and ensuring microbiological safety. ** p < 0.01; * p < 0.05.
4. Discussion
The objectives of this study were to understand whether the butchers selected in the study used the same techniques for the production of traditional sausage in Prishtina. Moreover, the research sought to evaluate parameters such as pH, aw, and microbial groups during the production and storage/maturation of the sausage, and to understand more about the quality and safety of this product.
The high concentrations of TNC and LAB in the three analyzed stages of production and storage of traditional sausage appeared to be in harmony with the results of other authors, who have found approximately the same numbers of these bacteria to be present in traditional sausage [6,55,56,64,65]. This could be indicated by the presence of normal flora in the raw meat and other ingredients that have been used for sausage production, and must be unique to this product. TNC increased from an initial level of 7.06 ± 0.12 to 8.88 ± 2.27 lg cfu/g during sausage production, but started to decrease on day 14 of storage [57]. A high presence of LAB was found in previous studies [5]. The increases in TNC and LAB by day 7 are likely due to favorable fermentation conditions (27–34 °C); the presence of fermentable substrates (e.g., carbohydrates from minced bread); and the lack of a starter culture, which allows spontaneous fermentation. The evaluation of this group of bacteria was almost the same in all stages and slightly decreased at the end of maturation; these findings are in harmony with those of other studies [57]. The numbers associated with this group of bacteria in the three stages of fermentation and storage could affect the increase in the acidity of the product, which could then have an impact on the reduction in the numbers of MC and EC [58,66,67]. LAB proliferation leads to acidification, as observed in the pH drop from 6.64± to 5.07± by day 14. The number of LAB ranged from 6.01 ± 1.59 lg cfu/g on day 7 to 5.99 ± 0.74 lg cfu/g on day 14. According to Dallas Santa et al. (2014) [55], the population of LAB in sausage produced with the use of different starter cultures was in the range between 6 to 7 lg cfu/g and increased from day 0 to 14. The average number of MC on day 0 was 5.63 ± 0.33 lg cfu/g, with a decrease on day 14 to 5.30 ± 2.22 lg cfu/g that can be explained by the presence of salt in the product [68]. Some studies have reported MC in the range from 2 to 7 lg cfu/g [55,69,70]. The number of EC, which is the indicator for food contamination, was higher in the first stage of production (5.10 ± 0.49 lg cfu/g), but significantly decreased after fermentation and during storage (1.60 ± 1.62 lg cfu/g). Lower EC (2.47 ± 1.37 lg cfu/g) was found in sausage immediately after heat processing. These findings are in harmony with many other results from authors who have analyzed traditional sausage, and who have also reported the decline of EC from the initial to final stage of production and storage [5,56,71]. The pH reduction inhibits acid-sensitive bacteria like EC, which explains their decline from the first phase to the end. By day 14, the decrease in TNC and slight reduction in LAB suggest that lower storage temperatures (0–4 °C), reduced water activity, and acidic conditions limit further microbial growth. Other authors have reported the decrease in total coliforms in the final product in sausage; this might confirm the competitiveness of LAB in the production of acidity during the fermentation process. One very important factor that could be affected was the aw value after fermentation [45,47]. In this study, the final pH and aw values (averages of all samples) of the traditional sausage were 5.07 ± 0.13 and 0.91 ± 0.01, respectively [55,56]. These microbial changes are beneficial from a safety standpoint, as the decline in EC reduces the risk of contamination. Additionally, the stability of LAB and MC support flavor development and preservation, while the declines in water activity and pH contribute to extended shelf life and reduced spoilage.
The results derived from the PCA and Pearson correlogram demonstrated consistency, both underscoring the strong interrelations among EC, LAB, and pH during fermentation. In the PCA biplot, these variables were grouped closely along Dim1, indicating microbial proliferation and acidification as driving forces of fermentation; similarly, the correlogram revealed robust positive correlations, supporting this association. In a parallel manner, the PCA positioning of MC and TNC in opposition to LAB mirrored the negative or weak correlations evident in the correlogram, suggesting competitive inhibition. The orthogonal placement of aw in the PCA aligned with its lower correlations in the matrix, confirming that water activity functions as an independent barrier predominantly influenced by formulation and storage conditions, rather than fermentation dynamics.
No differences regarding the production practices and storage of traditional sausage were observed, based on the data from the butchers who participated in this study. They follow a consistent, heritage-based process involving natural fermentation without starter cultures, controlled drying/fermentation phases, and almost the same ingredient combinations for sausage production and storage.
Based on our knowledge of Kosovar cuisine, sausage consumption is high and sausage occupies a very important place on consumers’ tables. However, accurate data regarding the statistics associated with the consumption of this product in Kosovo is lacking. Regarding the consumption of meat products on the global level today, concerns have increased for health reasons [72]; however, it is important to emphasize that products such as sausage or other meat-based products are a good source of protein for our diet. Another issue related to the consumption of meat products is the impact of their production on the environment [73], which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and land use. Despite all this, beef production increased in 2024, as reflected in the increase in slaughter rates and higher carcass weights [74].
Despite providing information, for the first time, regarding the numbers of relevant microbial groups and production methods for the sausage produced in Prishtina, our study has a limitation regarding the methods used for the identification of microorganisms. The culture-dependent method can provide information regarding the numbers of some microorganisms, but can exclude information on the growth in some others, ones which may not have been cultivated but are present in the sausage. Furthermore, this method cannot provide us with detailed data regarding the diversity of the microbial community in traditional sausage. This method can, though, provide us with data on the vitality of the bacterial cells that may be active in the fermentation and maturation of the product. However, culture-independent techniques such as 16s rRNA sequencing or metagenomics can provide relevant information regarding microbial dynamics and their functional contributions during the fermentation and maturation of traditional sausage [15,75].
The differences between our findings and those of previous studies can be attributed to several key variables. The absence of added starter cultures in our sausages allowed the natural microbiota from raw ingredients (meat and seasonings) to dominate fermentation, which contrasts with studies that used selected LAB or CNS strains to standardize microbial dynamics [76]. The fermentation in this study was performed under traditional room-temperature conditions (27–34 °C) without humidity or airflow control, which may have influenced microbial succession differently than in chamber-controlled processes [77]. Finally, the composition of the sausage—particularly the inclusion of onions, bread, and local vegetable seasonings—provides fermentable substrates and endogenous enzymes that are not present in standardized formulations.
5. Conclusions
Based on this study, we can conclude that the predominance of lactic acid bacteria in the initial stage of production and the subsequent stages of storage testifies to their role in the fermentation process of this traditional sausage. A relatively high number of Micrococaceae, especially after the seventh day of fermentation, participated in the natural fermentation process of the sausage. The decreased number of EC, ranging from the initial to the final phase, indicates an internal control of this traditional product that may play a role in ensuring the safety and preservation of the sausage (fermented by normal flora, without the addition of starter culture). Our findings offer valuable documentation of local practices that could influence product quality and shelf life. In the context of this study, we urge Kosovar food safety authorities to implement awareness programs for producers of traditional meat products, to promote best practices, and ensure the production of safe and high-quality products. This is needed to increase the quality of the sausage and other meat products produced by traditional methods, through improving their hygienic parameters, labeling, and packaging, which can effect increases in export and product value. Additional investigation may focus on analyzing this product for the presence of pathogens such as Salmonella Thyphimurium, Listeria monocytogenes, and Staphylococcus aureus, which pose risks to consumer health, and characterizing the full microbial community using culture-independent methods, such as 16S rRNA sequencing or metagenomics, to better understand the roles of uncultured and functionally important organisms. Further studies in the future would focus on analyzing more physicochemical parameters, including proteins, fats, moisture, dry matter, and biogenic amines. As to the biotechnological aspect of the production of the traditional sausage produced in the Prishtina region, it would be of interest to analyze the types of BAL and coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS), in order to better understand their proteolytic and lipolytic activities in this product. Furthermore, measuring volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during the fermentation and storage of sausage can provide us with more detailed information regarding the development of the aromas of this product, which affect the organoleptic characteristics of the product in question. Moreover, this study was aimed at preventing the loss of the tradition of sausage production through the promotion of this product and an increase in consumer confidence in this product.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/microbiolres16090200/s1, Table S1: PCA results table: component, Eigenvalue, variance, and cumulative percent.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.C.A. and S.S.; methodology, F.C.A., V.H. and N.D.; validation, M.A.E., R.M.G. and I.V.; formal analysis, X.B.; investigation, F.C.A. and S.S.; resources, S.S., F.C.A. and V.L.-M.; data curation, V.H.; writing—original draft preparation, S.S. and F.C.A.; writing—review and editing, F.C.A., M.A.E. and R.M.G.; visualization, F.C.A., V.H., S.S. and R.M.G.; supervision, F.C.A.; project administration, F.C.A. and S.S.; funding acquisition, F.C.A., V.H. and S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Tanja Stojanovska from the Faculty of Technology and Engineering, Veles, as well as Durim Alija, University of Tetova, Republic of North Macedonia, for their technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| TNC | Total number of colony (Viable mesophilic aerobic bacteria) |
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| MC | Micrococcaceae |
| EC | Enterobacteria and Coliforms |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| aw | Water activity |
| D0 | Day 0 |
| D7 | Day 7 |
| D14 | Day 14 |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
References
- Pearson, A.M.; Gillett, T.A. Processed Meats, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 210–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.C.; Paramithiotis, S.; Thekkangil, A.; Nethravathy, V.; Rai, A.K.; Martin, J.G.P. Food Fermentation and Its Relevance in the Human History. In Trending Topics on Fermented Foods; Martin, J.G.P., De Dea Lindner, J., Melo Pereira, G.V.d., Ray, R.C., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, K.; Rifky, M.; Nurmukhamedov, K.; Makhmayorov, J.; Abdullayev, B.; Farmanov, J.; Samadiy, M. A comparative analysis of traditional meat processing methods. E3S Web Conf. 2024, 494, 04023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo, J. Sausages: Nutrition, Safety, Processing and Quality Improvement. Foods 2021, 10, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Fontán, M.C.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Parada, A.; Franco, I.; Carballo, J. Microbiological characteristics of Androlla, a Spanish traditional pork sausage. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachindra, N.M.; Sakhare, P.Z.; Yashoda, K.P.; Rao, D.N. Microbial profile of buffalo sausage during processing and storage. Food Control 2005, 16, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.; Barbosa, J.; Vendeiro, S.; Mota, A.; Silva, F.; Monteiro, M.J.; Hogg, T.; Gibbs, P.; Teixeira, P. Chemical and microbiological characterization of alheira: A typical Portuguese fermented sausage with particular reference to factors relating to food safety. Meat Sci. 2006, 73, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos, C.; Viegas, C.; Almeida, A.M.; Guerra, M.M. Portugese traditional sausages: Different types, nutritional composition, and novel trends. J. Ethn. Foods 2016, 3, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulić, A.; Cvetnić, Ž.; Kos, I.; Vnučec, I.; Vahčić, N.; Lešić, T.; Simonović, D.; Kudumija, N.; Pleadin, J. Comparison of the Nutritional Composition of Meat Products Derived from Croatian Indigenous Pig Breeds. Foods 2024, 13, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milicevic, B.; Danilovic, B.; Zdolec, N.; Kozachinski, L.; Dobranic, V.; Savic, D. Microbiota of the fermented sausages: Influence to product quality and safety. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 20, 1061–1078. Available online: https://www.agrojournal.org/20/05-07.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Moretti, V.M.; Madonia, G.; Diaferia, C.; Mentasti, T.; Paleari, M.A.; Panseri, S.; Pirone, G.; Gandini, G. Chemical and microbiological parameters and sensory attributes of a typical Sicilian salami ripened in different conditions. Meat Sci. 2004, 66, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauriello, G.; Casaburi, A.; Blaiotta, G.; Villani, F. Isolation and technological properties of coagulase- negative staphylococci from fermented sausage of Southern Italy. Meat Sci. 2004, 67, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Ma, Y.; Chen, L.; Lu, C.; Ge, Q.; Wu, M.; Xi, J.; Yu, H. Effects of the addition of leucine on flavor and quality of sausage fermented by Lactobacillus fermentum YZU-06 and Staphylococcus saprophyticus CGMCC 3475. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1118907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Aziz, T.; Bai, R.; Zhang, X.; Shahzad, M.; Sameeh, M.Y.; Khan, A.A.; Dablool, A.S.; Zhu, Y. Dynamic change of bacterial diversity, metabolic pathways, and flavor during ripening of the Chinese fermented sausage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 990606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, J.; Sun, Z.; Fu, L. High-throughput sequencing-based characterization of the predominant microbial community associated with characteristic flavor formation in Jinhua ham. Food Microbiol. 2021, 94, 103643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrignani, F.; Lucci, L.; Vallicelli, M.; Guerzoni, E.; Gardini, F.; Lanciotti, R. Role of surface-inoculated Debaryomyces hansenii and Yarrowia lipolytica strains in dried fermented sausage manufacture. Part 1: Evaluation of their effects on microbial evolution, lipolytic and proteolytic patterns. Meat Sci. 2007, 75, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, R.; Chen, X.; Xiong, S.; Qi, B.; Li, J.; Qiao, J.; Chen, W.; Qu, C.; Wang, S. Predominant yeasts in Chinese Dong fermented pork (Nanx Wudl) and their aroma-producing properties in fermented sausage condition. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 10, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Yin, X.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. Technological properties and flavour formation potential of yeast strains isolated from traditional dry fermented sausages in Northeast China. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 15, 4112853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidari, R.; Tofalo, R. Dual Role of Yeasts and Filamentous Fungi in Fermented Sausages. Foods 2024, 13, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayivi, R.D.; Gyawali, R.; Krastanov, A.; Aljaloud, S.O.; Worku, M.; Tahergorabi, R.; Silva, R.C.d.; Ibrahim, S.A. Lactic Acid Bacteria: Food Safety and Human Health Applications. Dairy 2020, 1, 202–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anumudu, C.K.; Miri, T.; Onyeaka, H. Multifunctional Applications of Lactic Acid Bacteria: Enhancing Safety, Quality, and Nutritional Value in Foods and Fermented Beverages. Foods 2024, 13, 3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, J.S.; Oslan, S.N.H.; Mokshin, N.A.S.; Othman, R.; Amin, Z.; Dejtisakdi, W.; Prihanto, A.A.; Tan, J.S. Comprehensive Review of Strategies for Lactic Acid Bacteria Production and Metabolite Enhancement in Probiotic Cultures: Multifunctional Applications in Functional Foods. Fermentation 2025, 11, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulitz, A.; Stadie, J.; Wenning, M.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. The microbial diversity of water kefir. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 151, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigle, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresfor, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. The complex microbiota of raw milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. Bacteriocins: Developing innate immunity for food. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, M.J.; Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Aerts, M.; Vandamme, P.; Maiden, M.C.; Marchesi, J.R.; Mahenthiralingam, E. The domestication of the probiotic bacterium Lactobacillus acidophilus. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guetouache, M.; Ajazi Flutura, C.; Medjekal, S.; Guessas, B. Antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus spp. against Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 65 38. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 29, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. What’s in a name? Class distinction for bacteriocins. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumariya, R.; Garsa, A.K.; Rajput, Y.S.; Sood, S.K.; Akhtar, N.; Patel, S. Bacteriocins: Classification, synthesis, mechanism of action and resistance development in food spoilage causing bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Mu, D.; Qiao, W.; Zhu, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Xu, H.; Saris, P.; Kuipers, O.P.; Qiao, M. Co-expression of Nisin Z and Leucocin C as a Basis for Effective Protection Against Listeria monocytogenes in Pasteurized Milk. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbandi, A.; Asadi, A.; Mahdizade Ari, M.; Ohadi, E.; Talebi, M.; Halaj Zadeh, M.; Darb Emamie, A.; Ghanavati, R.; Kakanj, M. Bacteriocins: Properties and potential use as antimicrobials. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tönz, A.; Freimüller Leischtfeld, S.; Stevens, M.J.A.; Glinski-Häfeli, D.; Ladner, V.; Gantenbein-Demarchi, C.; Miescher Schwenninger, S. Growth Control of Listeria monocytogenes in Raw Sausage via Bacteriocin-Producing Leuconostoc carnosum DH25. Foods 2024, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afraei, M.; Razavi, S.H.; Nouri, M.; Jahan, F.M.; Shafiepour, M. Innovative applications of pediocin in food preservation: A natural alternative to chemical additives—A review. Microbe 2025, 8, 100452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogeswara, I.B.A.; Nursini, N.W.; Kusumawati, I.G.A.W.; Kusumaningsih, P. Metagenomic Insights into the Bacterial Diversity of Balinese Fermented Sausage (Urutan) from the Household Industry. Fermentation 2024, 10, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, F.K. Utilization of microbes to procesess and preserve meat. Meat Sci. 2000, 56, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Flavour Characteristics of Fermented Meat Products in China: A Review. Fermentation 2023, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ștefan, G.; Goran, G.V.; Predescu, C.N.; Gurău, M.R.; Bărăităreanu, S. The Behavior of Listeria monocytogenes During the Shelf Life of Wiener Sausages, as an Effect of Fermented Parsley Root Juice and Hawthorn Berry Phenolics. Foods 2025, 14, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campolina, G.A.; das Graças Cardoso, M.; Caetano, A.R.S.; Nelson, D.L.; Ramos, E.M. Essential Oil and Plant Extracts as Preservatives and Natural Antioxidants Applied to Meat and Meat Products: A Review. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2023, 61, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdolec, N.; Hadžiosmanović, M.; Kozačinski, L.; Cvrtila, Z.; Filipović, I.; Skrivanko, M.; Leskovar, K. Microbial and physicochemical succession in fermented sausages produced with bacteriocinogenic culture of Lactobacillus sakei and semi-purified bacteriocin mesenterocin Y. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaburi, A.; Villani, F.; Toldrá, F.; and Sanz, Y. Protease and esterase activity of staphylococci. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 112, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaburi, A.; Aristoy, M.C.; Cavella, S.; Monaco, R.D.; Ercolini, D.; Toldra, F.; Villani, F. Biochemical and sensory characteristics of traditional fermented sausages of Vallo di Diano (Southern Italy) as affected by the use of starter cultures. Meat Sci. 2007, 76, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; Verluyten, J.; Vuyst, L.D. Functional meat starter cultures for improved sausage fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 106, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffer, C.J.; Schaudinn, C.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. SxsA, a novel surface protein mediating cell aggregation and adhesive biofilm formation of Staphylococcus xylosus. Mol. Microbiol. 2022, 117, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashi Rasiti, B.; Kutllovci Zogaj, D.; Jaka Loxha, A.; Zeqiri, M.; Nura, A.; Ajazi, F.C. Microbiological and physico-chemical analysis of traditional meat products in Prizren region, Kosova. In Proceedings UBT 12th International Conference; Hajrizi, E., Ed.; UBT Knowledge Center: Lipjan, Kosovo, 2023; p. 254. Available online: https://knowledgecenter.ubt-uni.net/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4234&context=conference (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Ajazi, F.C.; Kurteshi, K.; Ehrman, M.A.; Gecaj, R.; Ismajli, M.; Berisha, B.; Vehapi, I. Microbiological study of traditional cheese produced in Rugova region of Kosovo. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 24, 321–325. Available online: https://journal.agrojournal.org/page/en/details.php?article_id=1068 (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Ajazi, F.C.; Ehrmann, M.; Vehapi, I.; Sylejmani, D.; Hamidi, A.; Gecaj, R.M. Bacteriocin production by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) isolated from traditional cheese. In Proceedings of the UBT International Conference; Hajrizi, E., Ed.; UBT Knowledge Center: Lipjan, Kosovo, 2019; Available online: https://knowledgecenter.ubt-uni.net/conference/2019/events/424 (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Mestani, M.; Ramadani, X.; Maloku Gjergji, T.; Mehmeti, H.; Ademi, A.; Mehmeti, I. The effect of saline concentration and storage temperature in the quality of Sharri cheese. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2017, 15, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gecaj, R.M.; Ajazi, F.C.; Bytyqi, H.; Mehmedi, B.; Çadraku, H.; Ismaili, M. Somatic Cell Number Physicochemical, and Microbiological Parameters of Raw Milk of Goats During the End of Lactation as Compared by Breeds and Number of Lactations. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 694114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavraj, S.; Hasanaj, N.; Pehlivani, K.; Daci, E.; Ajazi, F.C. Traditional cereal-based products in the Peja region. In Proceedings UBT 11th International Conference; Hajrizi, E., Ed.; UBT Knowledge Center: Lipjan, Kosovo, 2022; Available online: https://knowledgecenter.ubt-uni.net/conference/2022/all-events/358/ (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Gecaj, R.M.; Muji, S.; Ajazi, F.C.; Berisha, B.; Kryeziu, A.; Ismaili, M. Investigation of pork meat in chicken- and beef-based commercial products by ELISA and real-time PCR sold at retail in Kosovo. Czech J. Food Sci. 2021, 39, 368–375. Available online: https://cjfs.agriculturejournals.cz/artkey/cjf-202105-0004_investigation-of-pork-meat-in-chicken-and-beef-based-commercial-products-by-elisa-and-real-time-pcr-sold-at-re.php (accessed on 27 June 2025). [CrossRef]
- Kastrati, D.; Haziri, V.; Mehmeti, I.; Lajqi Makolli, V.; Nura, A.; Ajazi, F.C. Assessment of Microbiological and Physicochemical Parameters in Ground Beef from Fast Food Outlets in the Prishtina region. In Proceedings UBT 13th International Conference; Hajrizi, E., Ed.; UBT Knowledge Center: Lipjan, Kosovo, 2024; pp. 17–21. Available online: https://knowledgecenter.ubt-uni.net/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=4705&context=conference (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- ISO 4833-1:2013; Microbiology of Food and Animal Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Behbahani, B.A.; Yazdi, F.T.; Shahidi, F.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Mohebbi, M. Principal component analysis (PCA) for investigation of relationship between population dynamics of microbial pathogenesis, chemical and sensory characteristics in beef slices containing Tarragon essential oil. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 105, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Santa, O.R.; Macedo, R.E.F.; Dalla Santa, H.S.; Zanette, C.M.; Freitas, R.J.S.; Terra, N.N. Use of starter cultures isolated from native microbiota of artisanal sausage in the production of Italian sausage. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 34, 780–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simion, A.M.C.; Vizireanu, C.; Alexe, P.; Franco, I.; Carballo, J. Effect of the use of selected starter cultures on some quality, safety and sensorial properties of Dacia sausage, a traditional Romanian dry-sausage variety. Food Control 2014, 35, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dučić, M.; Barcenilla, C.; Cobo-Díaz, J.F.; López, M.; Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Prieto, M. High pressure processing at the early stages of ripening enhances the safety and quality of dry fermented sausages elaborated with or without starter culture. Food Res. Int. 2023, 163, 112162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montanari, C.; Barbieri, F.; Gardini, G.; Magnani, R.; Gottardi, D.; Gardini, F.; Tabanelli, G. Effects of Starter Cultures and Type of Casings on the Microbial Features and Volatile Profile of Fermented Sausages. Fermentation 2022, 8, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.S.; Bonilla-Luque, O.M.; Carvalho, L.; Fernandes, N.; Prieto, M.A.; Cadavez, V.; Gonzales-Barron, U. Microbiological and Physicochemical Profile of Traditionally Produced Chouriça de Carne Dry-Fermented Sausages: Towards Benchmarking of Products Against Established Quality Groups. Foods 2024, 13, 3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Liang, Z.; Fu, X.; Li, D.; Zhu, C.; Kong, Q.; Mou, H. Current challenges and development strategies of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria applied in the food industry. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2025, 24, e70038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, S.; Kumar, E.A.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Food preservation and Hurdle Technology. In Emerging Technologies for the Food Industry; Apple Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 39–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Kong, B. The potential correlation between bacterial diversity and the characteristic volatile flavour of traditional dry sausages from Northeast China. Food Microbiol. 2020, 91, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrović, T.Ž.; Tomović, V.M.; Kocić-Tanackov, S.; Marković, K.G.; Joković, N.; Radojević, I.D.; Grujović, M.Ž. Microbial Dynamics and Quality Evolution in the Spontaneous Fermentation of the Traditional Meat Product Sjenica Sheep Stelja. Fermentation 2025, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantsiou, K.; Urso, R.; Iacumin, L.; Cantoni, C.; Cattaneo, P.; Comi, G.; Cocolin, L. Culture-dependent and -independent methods to investigate the microbial ecology of Italian fermented sausages. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ed-dra, A.; Rhazi Filali, F.; El Allaoui, A.; Aboulkacem, A. Factors influencing the bacteriological quality of sausages sold in Meknes city, Morocco. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 933–938. Available online: http://ifrj.upm.edu.my/24%20(03)%202017/(5).pdf (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Tabanelli, G.; Bargossi, E.; Gardini, A.; Lanciotti, R.; Magnani, R.; Gardini, F.; Montanari, C. Physico-chemical and microbiological characterisation of Italian fermented sausages in relation to their size. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 96, 2773–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laranjo, M.; Potes, M.E.; Elias, M. Role of starter cultures on the safety of fermented meat products. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, S.; Mauriello, G.; Aponte, M.; Moschetti, G.; Villani, F. Microbial sucession during ripening of Naples-type salami, a southern Italian fermented sausage. Meat Sci. 2000, 56, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samelis, J.; Stavropoulos, S.; Kakouri, A.; Metaxopoulos, J. Quantification and characterization of microbial populations associated with naturally fermented Greek dry salami. Food Microbiol. 1994, 11, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papamanoli, E.; Kotzekidou, P.; Tzanetakis, N.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E. Characterization of Micrococcaceae isolated from dry fermented sausage. Food Microbiol. 2002, 19, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papamanoli, E.; Tzanetakis, N.; Litopoulou-Tzanetaki, E.; Kotzekidou, P. Characterization of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from a Greek Dry Fermented Sausage in Respect of Their Technological and Probiotic Properties. Meat Sci. 2003, 65, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, L.F.M.; Malhão, T.A.; da Silva Barbosa, R.; Schilithz, A.O.C.; da Silva, R.C.F.; Moreira, L.G.M.; Ferrari, G.; Machado, P.A.N.; Diogenes, M.E.L. The current and future costs of colorectal cancer attributable to red and processed meat consumption in Brazil. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2023, 23, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleinikova, Y.; Maksimovich, S.; Khadzhibayeva, I.; Zhaksylyk, A.; Alybayeva, A. Meat quality, safety, dietetics, environmental impact, and alternatives now and ten years ago: A critical review and perspective. Food Prod. Process Nutr. 2025, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Meat Market Review: Overview of Global Market Developments in 2024. Rome. 2025. Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/cd5077en (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Zeng, X.; Wei, C.; Li, D.; Cao, W.; Lin, Q. Comparative Analysis of the Microbial Community Profiles of Sichuan and Guizhou Smoke-Cured Sausages Using a High-Throughput Sequencing Approach. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essid, I.; Hassouna, M. Effect of inoculation of selected Staphylococcus xylosus and Lactobacillus plantarum strains on biochemical, microbiological and textural characteristics of a Tunisian dry fermented sausage. Food Control 2013, 32, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cava, R.; García-Parra, J.; Ladero, L. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure processing and storage temperature on food safety, microbial counts, colour and oxidative changes of a traditional dry-cured sausage. LWT 2020, 128, 109462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).