Application of MALDI-TOF Protein Profiles for Rapid Detection of Streptococcus agalactiae Highly Virulent Strains: ST1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Preparation for MALDI-TOF
2.2. MTPP Library
2.3. Manual Visualization of Mass Peaks
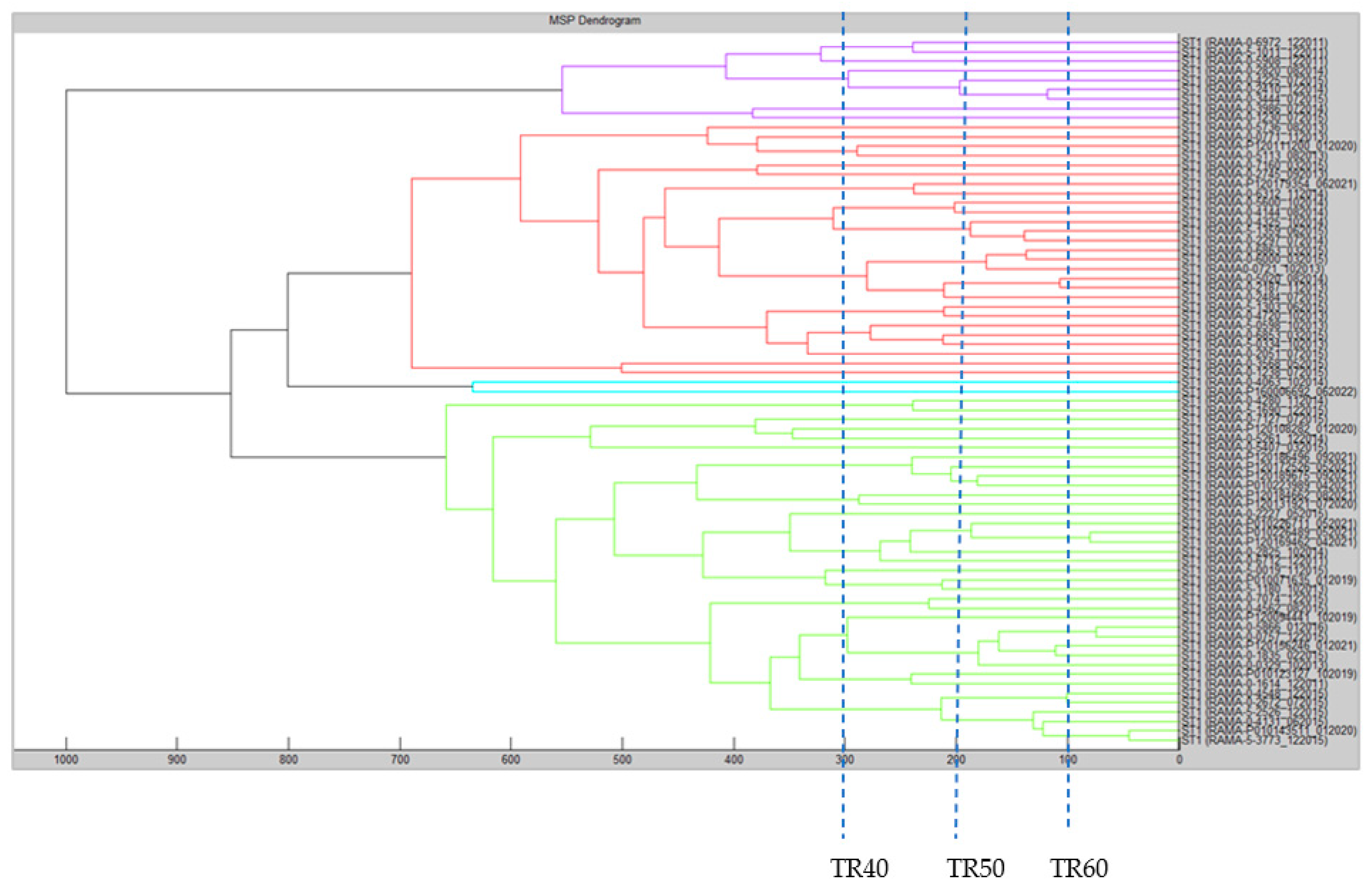
2.4. MTPP Dendrogram
2.5. TR and TS Groups
2.6. Evaluation of the Automatic Identification of ST1
3. Results
3.1. Manual Mass Peak Identification of ST1
3.2. Automatic Prediction of ST1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GBS | Group B Streptococcus, Streptococcus agalactiae |
| ST | Sequence Type |
| CC | Clonal Complex |
| MALDI | Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization |
| TOF | Time-of-Flight |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| MTPP | MALDI-TOF Protein Profile |
| PP | Protein Profile |
| S/N | Signal/Noise |
| TR | Training |
| TS | Testing |
| MLST | Multi-locus sequence type |
| CLSI | Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute |
| S | Sensitivity |
| SP | Specificity |
| AC | Accuracy |
| P | Peak presented |
| N | No peak presented |
References
- Raabe, V.N.; Shane, A.L. Group B Streptococcus agalactiae. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onruang, K.; Rattawongjirakul, P.; Pongchaikul, P.; Santanirand, P. Using the bca gene coupled with a tetracycline and macrolide susceptibility profile to identify the highly virulent ST283 Streptococcus agalactiae strains in Thailand. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, L.M.; Huband, M.D.; Charbon, S.; Castanheira, M.; Mendes, R.E. High rates of nonsusceptibility to common oral antibiotics in Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates from the United States (2019–2021). Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2024, 11, ofae470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristram, S.; Jacobs, M.R.; Appelbaum, P.C. Antimicrobial resistance in Haemophilus influenzae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 368–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Amini, C.; Bagheri, P.; Salehi, Z.; Goudarzi, M. Unveiling the genetic landscape of Streptococcus agalactiae bacteremia: Emergence of hypervirulent CC1 strains and new CC283 strains in Tehran, Iran. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubria, M.B.; Vega, L.A.; Shropshire, W.C.; Sanson, M.A.; Shah, B.J.; Regmi, S.; Rench, M.; Baker, C.J.; Flores, A.R. Population genomics reveals distinct temporal association with the emergence of ST1 serotype V group B Streptococcus and macrolide resistance in North America. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0071421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.; Bohnsack, J.F.; Takahashi, S.; Oliver, K.A.; Chan, M.-S.; Kunst, F.; Glaser, P.; Rusniok, C.; Crook, D.W.M.; Harding, R.M.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing system for group B Streptococcus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2530–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchiya, M.; Urushibara, N.; Aung, M.S.; Shimada, S.; Nakamura, M.; Ito, M.; Habadera, S.; Kobayashi, N. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from pregnant women in Japan, 2017–2021. IJID Reg. 2022, 4, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Jin, Y.; Han, X.; Jiang, X.; Miao, B.; Meng, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, H.; Feng, J.; et al. Genomic characterization and resistance features of Streptococcus agalactiae isolated from non-pregnant adults in Shandong, China. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 38, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kassel, M.N.; de Boer, G.; Teeri, S.A.F.; Jamrozy, D.; Bentley, S.D.; Brouwer, M.C.; van der Ende, A.; van de Beek, D.; Bijlsma, M.W. Molecular epidemiology and mortality of group B streptococcal meningitis and infant sepsis in the Netherlands: A 30-year nationwide surveillance study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e32–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, Y.; Rahav, G.; Nissan, I.; Treygerman, O.; Prajgrod, G.; Attia, B.Z.; Raz, R.; Valenci, G.Z.; Tekes-Manova, D.; Maor, Y. Group B Streptococcus virulence factors associated with different clinical syndromes: Asymptomatic carriage in pregnant women and early-onset disease in the newborn. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1093288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Li, M.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, K.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, L. Strain-level genomic analysis of serotype, genotype and virulence gene composition of group B Streptococcus. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1396762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat, A.J.; Budimir, A.; Nashev, D.; Sá-Leão, R.; van Dijl, J.M.; Laurent, F.; Grundmann, H.; Friedrich, A.W.; ESCMID Study Group of Epidemiological Markers (ESGEM). Overview of molecular typing methods for outbreak detection and epidemiological surveillance. Eurosurveillance 2013, 18, 20380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, E.-J.; Jeong, S.H. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry technology as a tool for the rapid diagnosis of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candela, A.; Arroyo, M.J.; Sánchez-Molleda, Á.; Méndez, G.; Quiroga, L.; Ruiz, A.; Cercenado, E.; Marín, M.; Muñoz, P.; Mancera, L.; et al. Rapid and reproducible MALDI-TOF-based method for the detection of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium using classifying algorithms. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-M.; Kim, I.; Chung, S.H.; Chung, Y.; Han, M.; Kim, J.-S. Rapid discrimination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by MALDI-TOF MS. Pathogens 2019, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauget, M.; Valot, B.; Bertrand, X.; Hocquet, D. Can MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry reasonably type bacteria? Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Gao, K.; Chen, G.; Zhong, H.; Li, Z.; Guan, X.; Deng, Q.; Xie, Y.; Ji, W.; McIver, D.J.; et al. Rapid classification of multilocus sequence subtype for Group B Streptococcus based on MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and statistical models. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas-Chanoine, M.-H.; Bertrand, X.; Madec, J.-Y. Escherichia coli ST131, an intriguing clonal group. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 543–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, O.; Tanaka, S.; Nagasawa, Z.; Hanaki, H.; Shobuike, T.; Miyamoto, H. Development of a novel matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrum (MALDI-TOF-MS)-based typing method to identify methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones. J. Hosp. Infect. 2015, 90, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrolier, N.; Sauget, M.; Bertrand, X.; Hocquet, D. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry identifies Pseudomonas aeruginosa high-risk clones. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, H.; Woolfitt, A.R.; Carvalho, M.G.; Pavlopoulos, A.; Teixeira, L.M.; Satten, G.A.; Barr, J.R. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry as a tool for differentiation of invasive and noninvasive Streptococcus pyogenes isolates. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 53, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, C.; Botelho, J.; Grosso, F.; Silva, L.; Lopes, J.; Peixe, L. Unsuitability of MALDI-TOF MS to discriminate Acinetobacter baumannii clones under routine experimental conditions. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrazeg, M.; Diene, S.M.; Drissi, M.; Kempf, M.; Richet, H.; Landraud, L.; Rolain, J.-M. Biotyping of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates from France and Algeria using MALDI-TOF MS. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, S.; Ferroni, A.; Lotz, A.; Jolley, K.A.; Guérin, P.; Leto, J.; Dauphin, B.; Jamet, A.; Maiden, M.C.; Nassif, X.; et al. Ribosomal proteins as biomarkers for bacterial identification by mass spectrometry in the clinical microbiology laboratory. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 94, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbuddhe, S.B.; Maier, T.; Schwarz, G.; Kostrzewa, M.; Hof, H.; Domann, E.; Chakraborty, T.; Hain, T. Rapid identification and typing of Listeria species by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5402–5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson, V.; Resman, F.; Kostrzewa, M.; Nilson, B.; Riesbeck, K. Identification of Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates by use of matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunne, E.M.; Ong, E.K.; Moser, R.J.; Siba, P.M.; Phuanukoonnon, S.; Greenhill, A.R.; Robins-Browne, R.M.; Mulholland, E.K.; Satzke, C. Multilocus sequence typing of Streptococcus pneumoniae by use of mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3756–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, S.; Matsumura, Y.; Ito, Y.; Fujisawa, T.; Chang, B.; Suga, S.; Kato, K.; Yunoki, T.; Hotta, G.; Noguchi, T.; et al. Development and evaluation of MALDI-TOF MS-based serotyping for Streptococcus pneumoniae. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wayne, P. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute CLSI M58. In Methods for the Identification of Cultured Organisms Using Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry, 1st ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rothen, J.; Sapugahawatte, D.N.; Li, C.; Lo, N.; Vogel, G.; Foucault, F.; Pflüger, V.; Pothier, J.F.; Blom, J.; Daubenberger, C.; et al. A simple, rapid typing method for Streptococcus agalactiae based on ribosomal subunit proteins by MALDI-TOF MS. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothen, J.; Pothier, J.F.; Foucault, F.; Blom, J.; Nanayakkara, D.; Li, C.; Ip, M.; Tanner, M.; Vogel, G.; Pflüger, V.; et al. Subspecies typing of Streptococcus agalactiae based on ribosomal subunit protein mass variation by MALDI-TOF MS. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Gao, K.; Zhong, H.; Xie, Y.; Liang, B.; Ji, W.; Liu, H. Automated classification of group B Streptococcus into different clonal complexes using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1355448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Belkum, A.; Tassios, P.; Dijkshoorn, L.; Haeggman, S.; Cookson, B.; Fry, N.; Fussing, V.; Green, J.; Feil, E.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; et al. Guidelines for the validation and application of typing methods for use in bacterial epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2007, 13, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartigue, M.-F.; HérY-Arnaud, G.; Haguenoer, E.; Domelier, A.-S.; Schmit, P.-O.; van der Mee-Marquet, N.; Lanotte, P.; Mereghetti, L.; Kostrzewa, M.; Quentin, R. Identification of Streptococcus agalactiae isolates from various phylogenetic lineages by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 2284–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lartigue, M.-F.; Kostrzewa, M.; Salloum, M.; Haguenoer, E.; Héry-Arnaud, G.; Domelier, A.-S.; Stumpf, S.; Quentin, R. Rapid detection of “highly virulent” Group B Streptococcus ST-17 and emerging ST-1 clones by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 86, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normand, A.-C.; Cassagne, C.; Ranque, S.; L’ollivier, C.; Fourquet, P.; Roesems, S.; Hendrickx, M.; Piarroux, R. Assessment of various parameters to improve MALDI-TOF MS reference spectra libraries constructed for the routine identification of filamentous fungi. BMC Microbiol. 2013, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yi, J.; Han, G.; Qiao, L. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical analysis and research. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2022, 2, 385–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Detail | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Bacterial growth conditions | 18–24 h at 35 °C on sheep blood |
| Protocol guideline | CLSI M58-Ed1 |
| Standard reference | MLST, whole genome sequencing (WGS) |
| Protein extraction | Standard tube ethanol/formic acid extraction |
| Matrix | HCCA |
| Target plate | Stainless |
| m/z range | 2000–20,000 |
| Internal mass control | Bacterial test standard (Bruker) |
| Instrument | MALDI-TOF MS Sirius |
| Program running | AutoXecute Run Editor. Version 3.4.150.0 |
| Program analysis | With flexAnalysis software version 3.4 |
| The acceptable mass peak of each ST for data analysis | Within in run not exceeding 0.05% |
| Between runs not exceeding 0.5% | |
| s/n ratio > 5 is valuable | |
| The acceptable minimum random mass PP/isolate | Concordance of at least 20 PPs/isolate |
| Selected the criteria for mass peaks for data analysis | Maximum mass peaks generated |
| Program automatic prediction | MBT compass explorer version 4.4.100 |
| Interpretation criteria/decision criteria | The top three matches 3/3; top two matches 2/2; two of three matches 2/3 |
| Training isolates the ST of interest for the new library | At least 30 isolates |
| Testing isolates ST | At least 30 isolates for the ST of interest and other STs up to 100 isolates for evaluation of sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy |
| Sequence Type | Number of Isolates | Proportions | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40:60 | 50:50 | 60:40 | |||||
| ST1 | 75 | 30 | 45 | 37 | 38 | 44 | 31 |
| ST283 | 81 | 30 | 51 | 40 | 41 | 49 | 32 |
| ST19 | 22 | 9 | 13 | 11 | 11 | 13 | 9 |
| ST17 | 18 | 7 | 11 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 9 |
| ST23 | 16 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 6 |
| ST12 | 10 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 4 |
| ST485 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 3 |
| ST103 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| ST314 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| ST889 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| ST861 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| ST651 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| ST652 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| ST28 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| ST41 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| ST196 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ST249 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ST335 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ST1626 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ST14 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| ST509 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| ST739 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| ST751 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| ST1167 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| ST361 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Total | 277 | 111 | 166 | 137 | 140 | 166 | 111 |
| Prediction ST1 Automatically Match | Training: Testing by MALDI-TOF MS | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40:60 | 50:50 | 60:40 | |||||||
| 3/3 | Top 2 | 2/3 | 3/3 | Top 2 | 2/3 | 3/3 | Top 2 | 2/3 | |
| Sensitivity (%) | 73.3 | 88.9 | 97.8 | 71.1 | 76.3 | 94.7 | 83.9 | 90.3 | 96.8 |
| Specificity (%) | 100.0 | 97.5 | 96.7 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 99.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 98.8 |
| Accuracy (%) | 92.8 | 95.2 | 97.0 | 91.4 | 93.6 | 97.9 | 95.5 | 97.3 | 98.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onruang, K.; Rattawongjirakul, P.; Santanirand, P. Application of MALDI-TOF Protein Profiles for Rapid Detection of Streptococcus agalactiae Highly Virulent Strains: ST1. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16090199
Onruang K, Rattawongjirakul P, Santanirand P. Application of MALDI-TOF Protein Profiles for Rapid Detection of Streptococcus agalactiae Highly Virulent Strains: ST1. Microbiology Research. 2025; 16(9):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16090199
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnruang, Kwanchai, Panan Rattawongjirakul, and Pitak Santanirand. 2025. "Application of MALDI-TOF Protein Profiles for Rapid Detection of Streptococcus agalactiae Highly Virulent Strains: ST1" Microbiology Research 16, no. 9: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16090199
APA StyleOnruang, K., Rattawongjirakul, P., & Santanirand, P. (2025). Application of MALDI-TOF Protein Profiles for Rapid Detection of Streptococcus agalactiae Highly Virulent Strains: ST1. Microbiology Research, 16(9), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/microbiolres16090199





