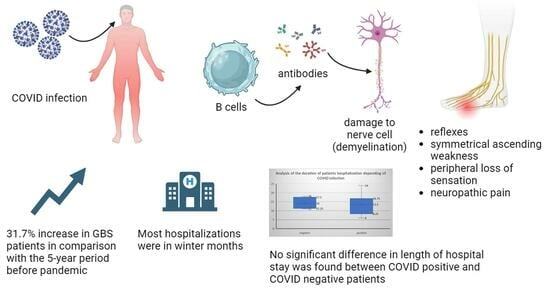
Analysis of Post-COVID-19 Guillain–Barré Syndrome over a Period of One Year in the University Hospital of Split (Croatia)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Diagnostic Criteria
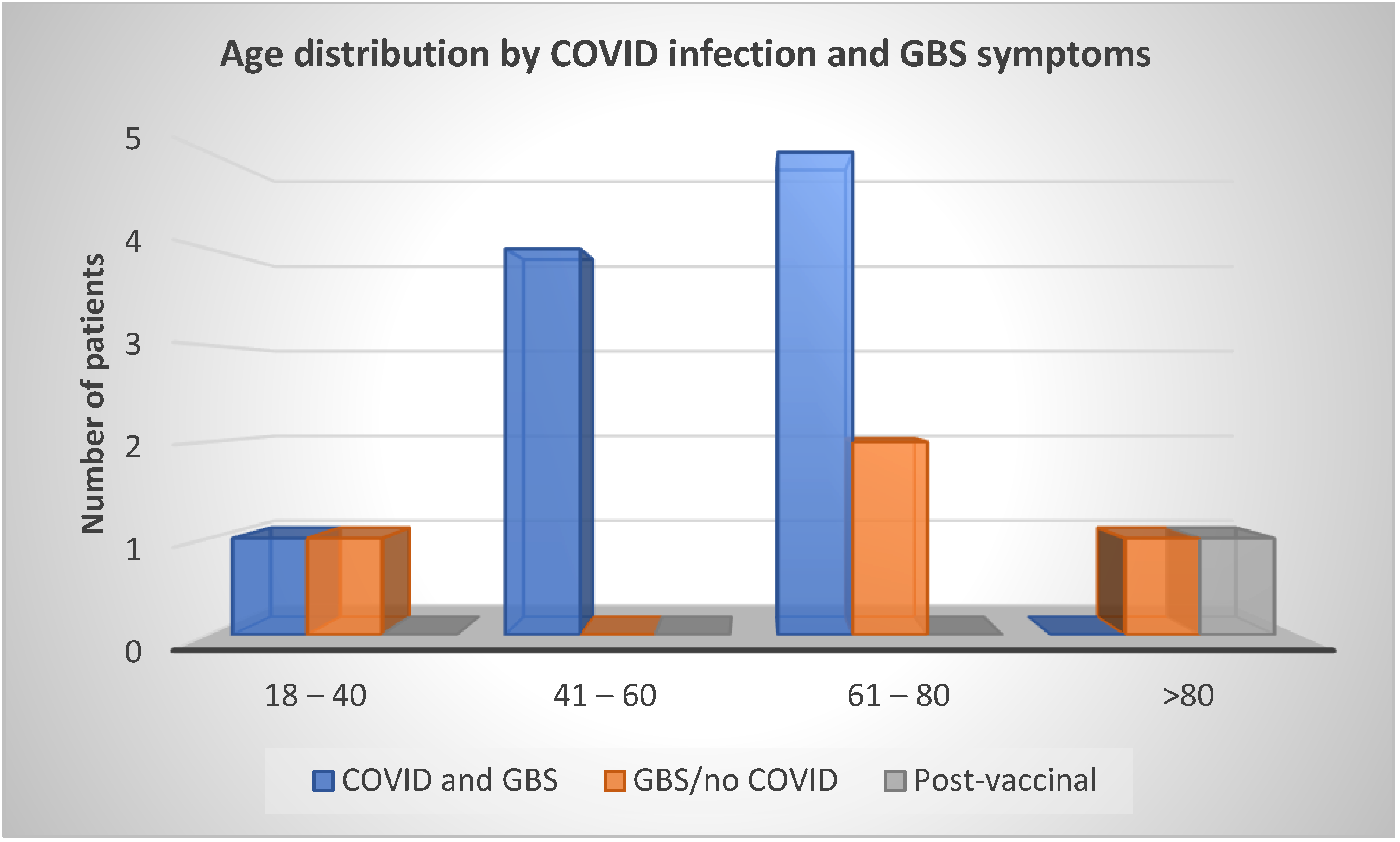
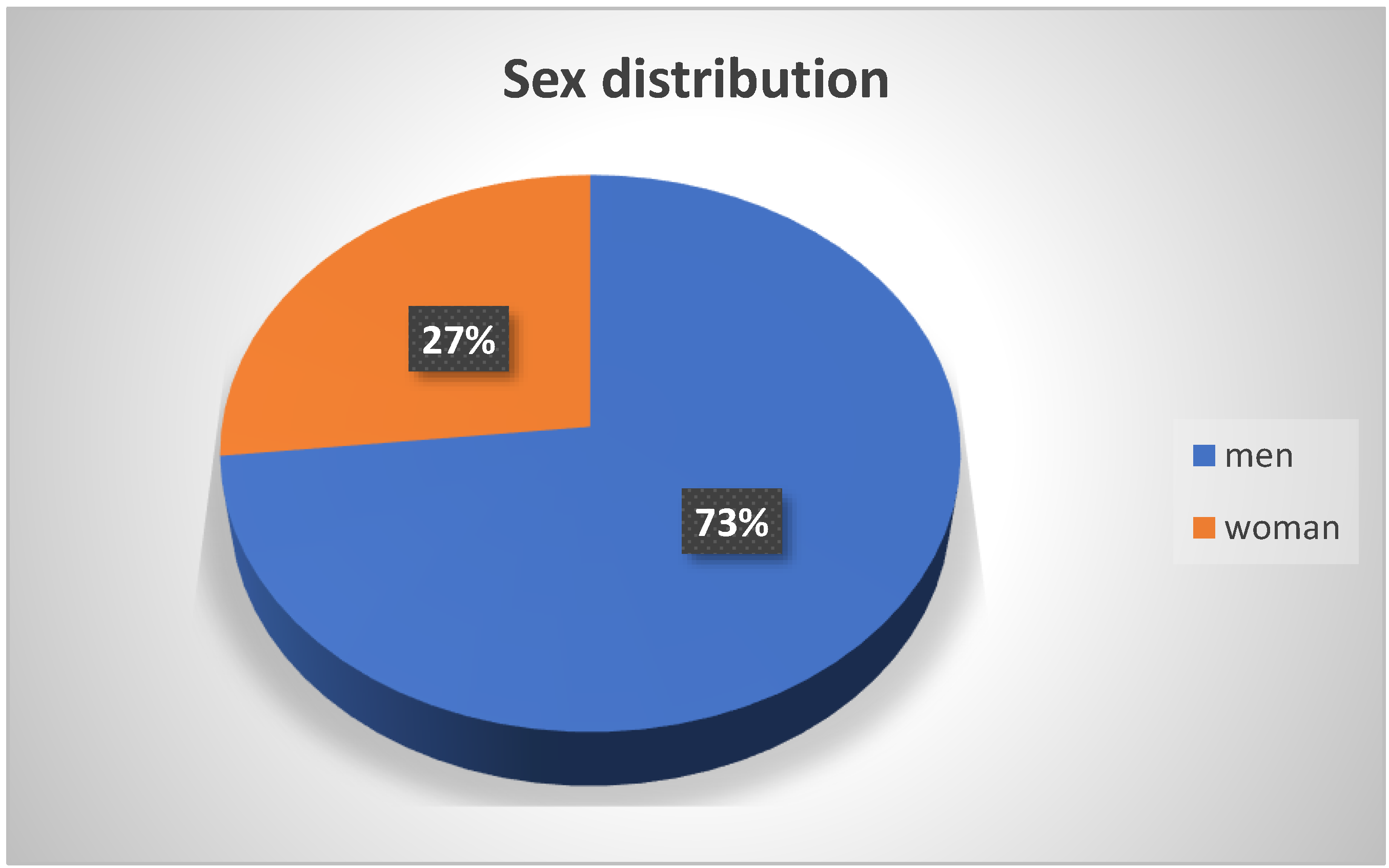
3.2. Age and Sex Distribution of Patients with Guillain–Barré Syndrome
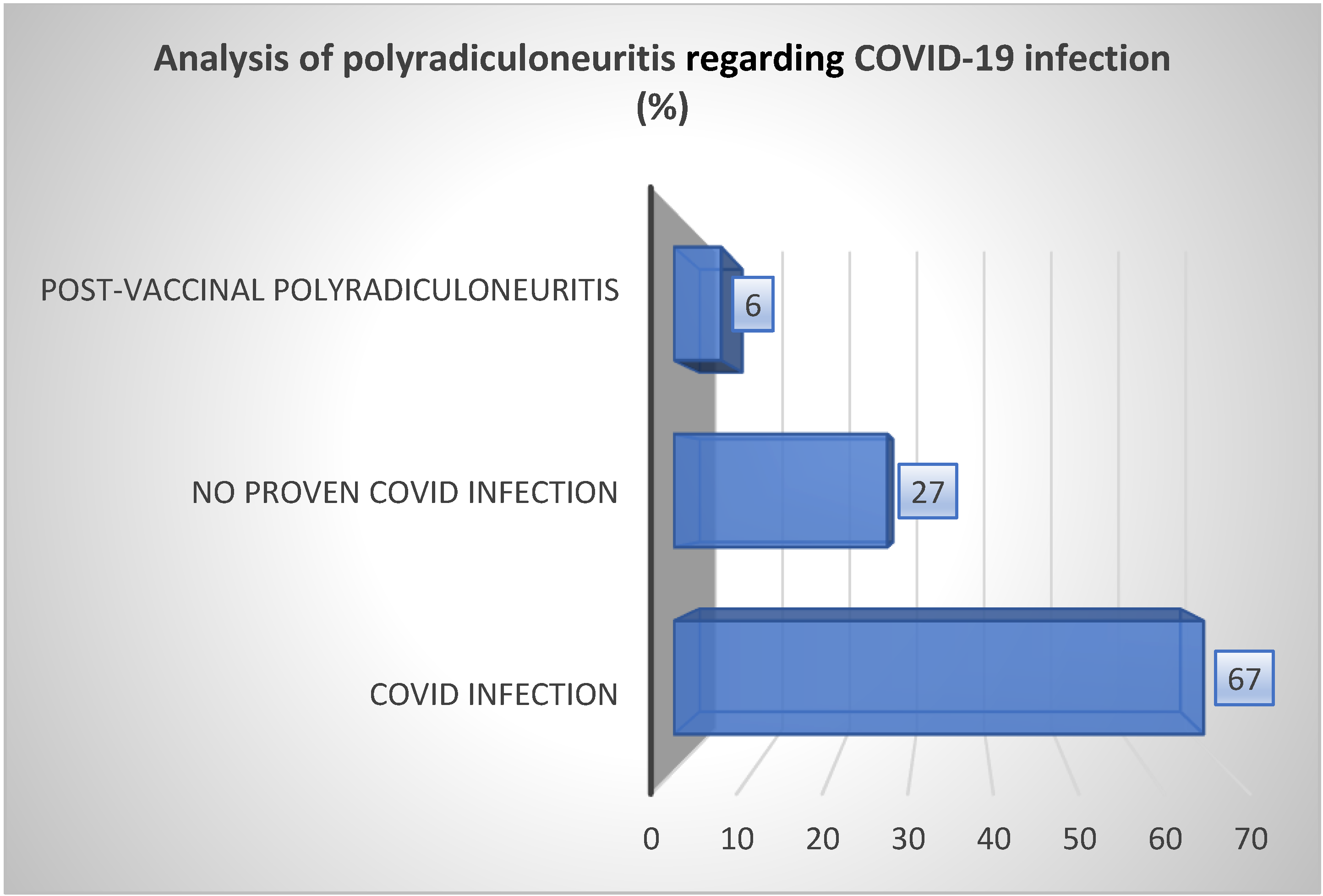
3.3. Acute Polyradiculoneuritis and COVID-19 Infection
3.4. The Time Interval between Overcoming the COVID-19 Infection and the Appearance of the First Symptoms of GBS
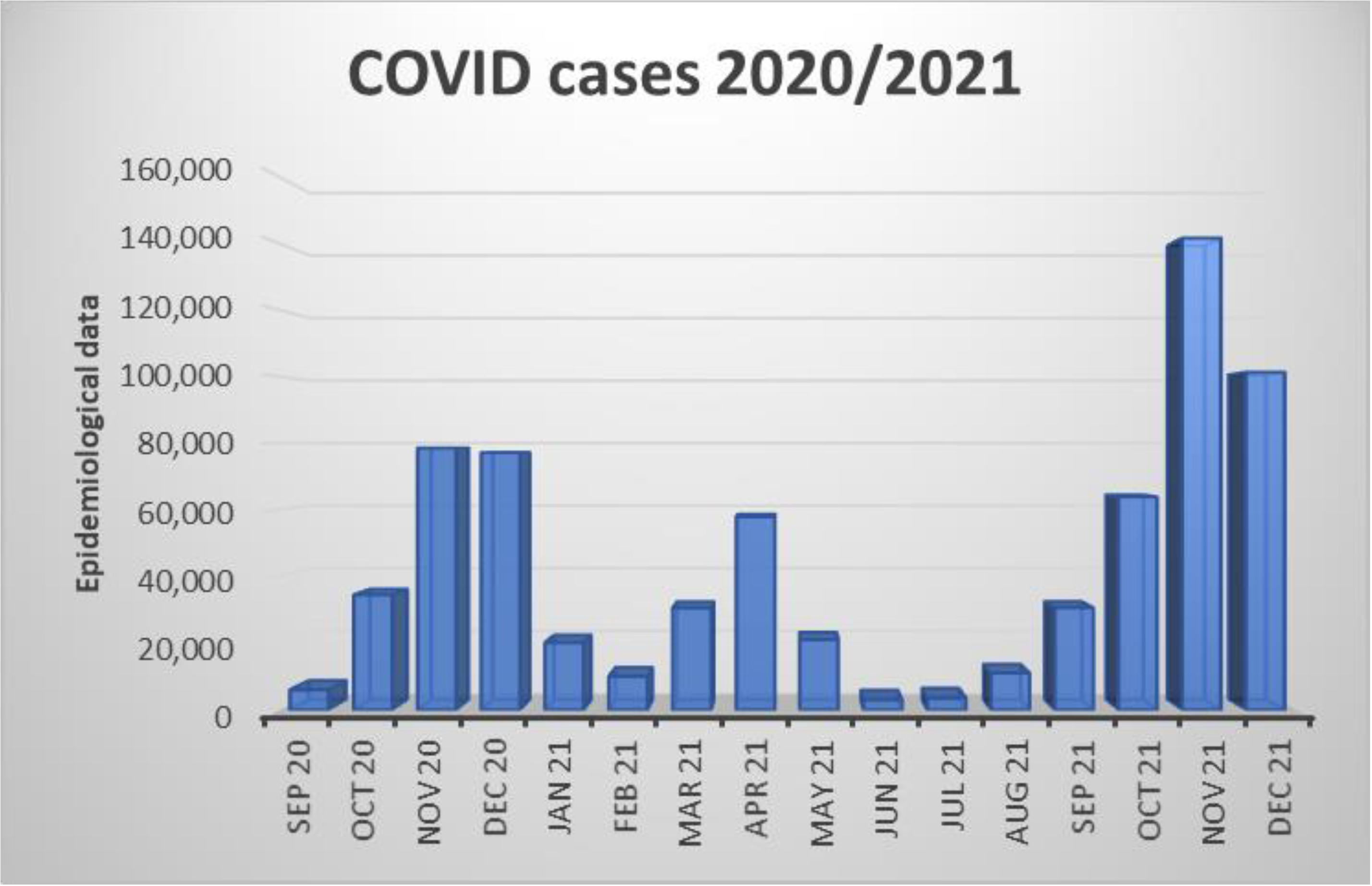
3.5. Monthly Presentation of Admissions of Patients in Addiction with Epidemiological Data of COVID-19 Infections
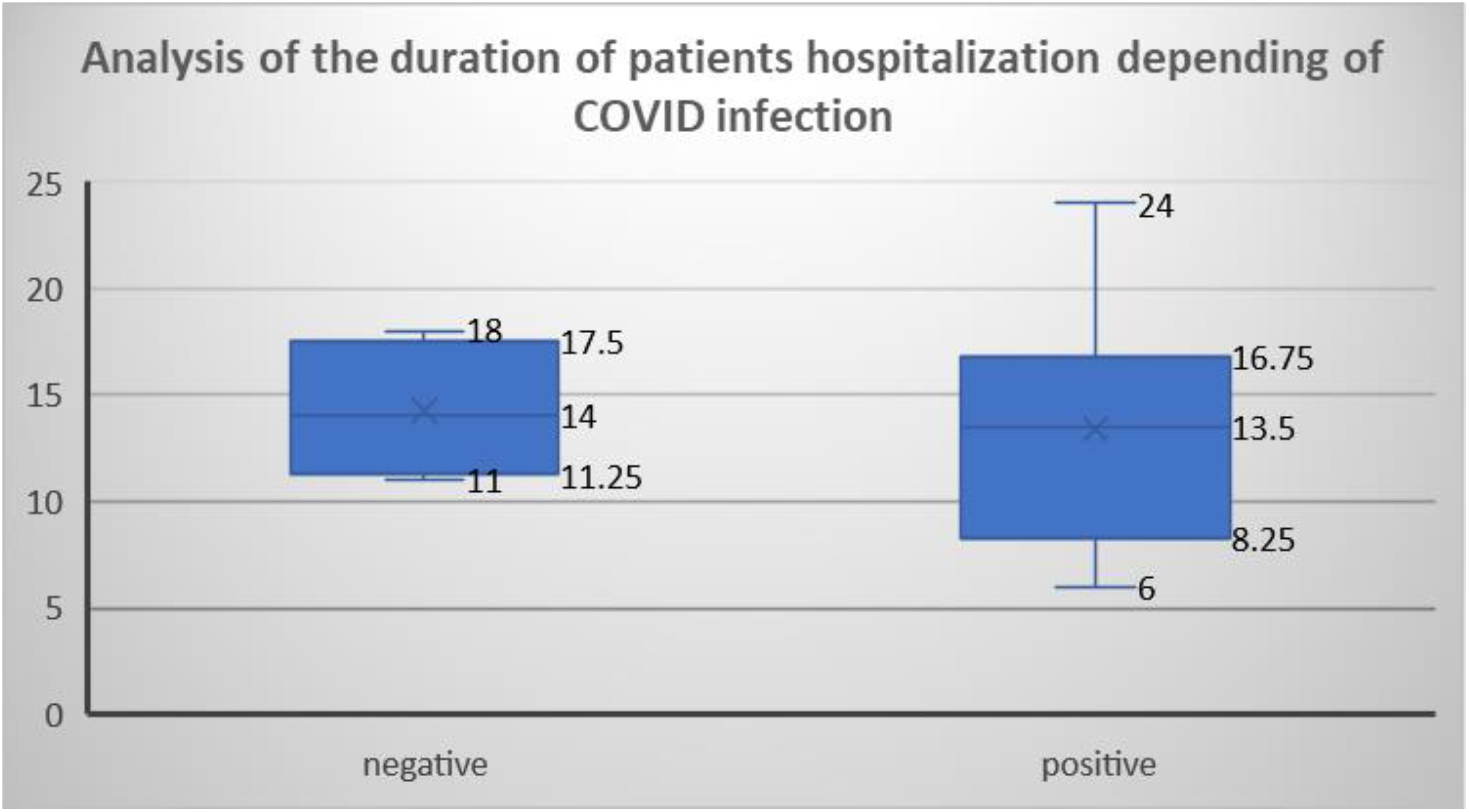
3.6. Duration and Form of Hospitalization
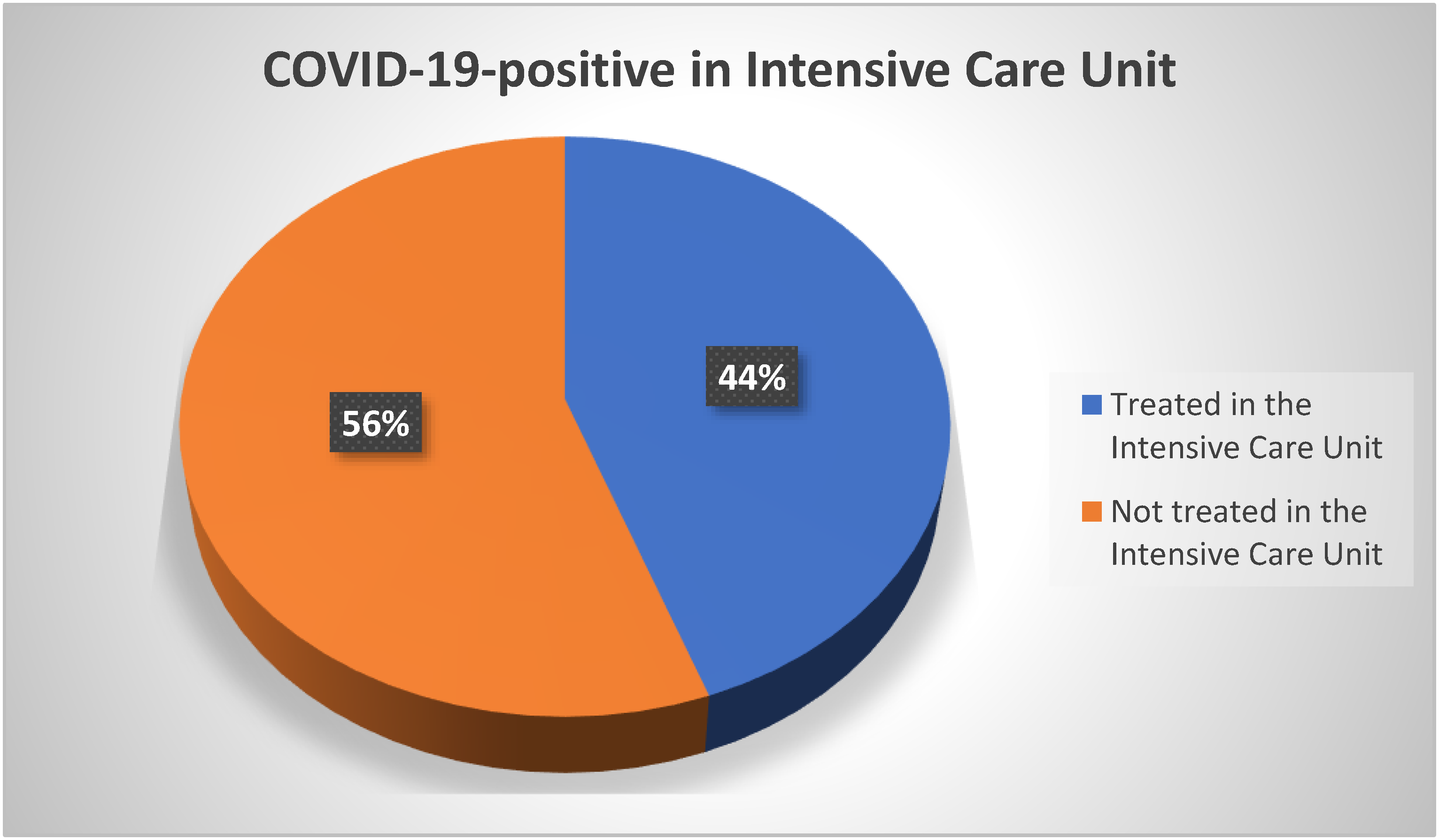
3.7. Therapy and Treatment Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Stefano, V.; Barbone, F.; Ferrante, C.; Telese, R.; Vitale, M.; Onofrj, M.; Di Muzio, A. Inflammatory Polyradiculoneuropathies: Clinical and Immunological Aspects, Current Therapies, and Future Perspectives. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2020, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaeem, Z.; Siddiqi, Z.A.; Zochodne, D.W. Autonomic Involvement in Guillain–Barré Syndrome: An Update. Clin. Auton. Res. 2019, 29, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malek, E.; Salameh, J. Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Semin. Neurol. 2019, 39, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahrizaila, N.; Yuki, N. Bickerstaff Brainstem Encephalitis and Fisher Syndrome: Anti-GQ1b Antibody Syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broers, M.C.; de Wilde, M.; Lingsma, H.F.; van der Lei, J.; Verhamme, K.M.C.; Jacobs, B.C. Epidemiology of Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy in The Netherlands. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2022, 27, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, S.A.; Ahmad, S.; Kobeissy, F.H.; Toklu, H.Z. Concomitant Guillain–Barré Syndrome and COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis of Cases. Medicina 2022, 58, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuki, N.; Susuki, K.; Koga, M.; Nishimoto, Y.; Odaka, M.; Hirata, K.; Taguchi, K.; Miyatake, T.; Furukawa, K.; Kobata, T.; et al. Carbohydrate Mimicry between Human Ganglioside GM1 and Campylobacter Jejuni Lipooligosaccharide Causes Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11404–11409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willison, H.J.; Jacobs, B.C.; van Doorn, P.A. Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Lancet 2016, 388, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrizai, L.; Lehmann, H.C.; Kuwabara, S. Guillain-Barré Syndrome. Lancet 2021, 397, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Berg, B.; Walgaard, C.; Drenthen, J.; Fokker, C.; Jacobs, B.C.; Van Doorn, P.A. Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prognosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.-L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.; Ni, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liang, W.; Ou, C.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Shan, H.; Lei, C.; Hui, D.S.C.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1708–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boban, M. Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Update on Epidemiology, Pathogenicity, Clinical Course and Treatments. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scialo, F.; Daniele, A.; Amato, F.; Pastore, L.; Matera, M.G.; Cazzola, M.; Castaldo, G.; Bianco, A. ACE2: The Major Cell Entry Receptor for SARS-CoV-2. Lung 2020, 198, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnowska, A.; Zajkowska, J.; Kułakowska, A. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 on the Nervous System. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2023, 57, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyhanian, K.; Umeton, R.P.; Mohit, B.; Davoudi, V.; Hajighasemi, F.; Ghasemi, M. SARS-CoV-2 and Nervous System: From Pathogenesis to Clinical Manifestation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 350, 577436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachou, Y.; El Idrissi, A.; Belapasov, V.; Ait Benali, S. Neuroinvasion, Neurotropic, and Neuroinflammatory Events of SARS-CoV-2: Understanding the Neurological Manifestations in COVID-19 Patients. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 41, 2657–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croatia National Institute of Public Health COVID-19 Report 2020–2022; Croatian National Institute of Public Health: Zagreb, Croatia, 2023; Available online: https://ghdx.healthdata.org/record/croatia-national-institute-public-health-covid-19-report-2020-2022 (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Fokke, C.; Van Den Berg, B.; Drenthen, J.; Walgaard, C.; Van Doorn, P.A.; Jacobs, B.C. Diagnosis of Guillain-Barré Syndrome and Validation of Brighton Criteria. Brain 2014, 137, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevots, D.R.; Sutter, R.W. Assessment of Guillain-Barre Syndrome Mortality and Morbidity in the United States: Implications for Acute Flaccid Paralysis Surveillance. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 175, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragazzi, N.L.; Kolaci, A.A.; Nekad Ghaderi, S.A.; Lochner, P.; Brigo, F.; Naldi, A.; Lanteri, P.; Garbarino, S.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Dai, H.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Guillain–Barré Syndrome and Its Underlying Causes from 1990 to 2019. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista Total Number of Cases of COVID-19 in the United States as of 17 June 2022, by Age Group. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1254477/weekly-number-of-covid-19-hospitalizations-in-the-us-by-age (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Vinciguerra, C.; Iacono, S.; Bevilacqua, L.; Landolfi, A.; Piscosquito, G.; Ginanneschi, F.; Schirò, G.; Di Stefano, V.; Brighina, F.; Barone, P.; et al. Sex Differences in Neuromuscular Disorders. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 211, 111793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luijten, L.W.G.; Leonhard, S.E.; Van Der Eijk, A.A.; Doets, A.Y.; Appeltshauser, L.; Arends, S.; Attarian, S.; Benedetti, L.; Briani, C.; Casasnovas, C.; et al. Guillain-Barré Syndrome after SARS-CoV-2 Infection in an International Prospective Cohort Study. Brain 2021, 144, 3392–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Abdulle, A.E.; Timens, W.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Navis, G.J.; Gordijn, S.J.; Bolling, M.C.; Dijkstra, G.; Voors, A.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the Pathophysiology of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Pathol. 2020, 251, 228–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalil, R.; Behroz, M.P.; Vahid, A.; Mahya, P.; Hossein, S.K.; Ali, V.; Hamid, T.; Mohammad, A. Risk Factors for COVID-19. Infez. Med. 2020, 4, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Gadi, N.; Wu, S.C.; Spihlman, A.P.; Moulton, V.R. What’s Sex Got to Do With COVID-19? Gender-Based Differences in the Host Immune Response to Coronaviruses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Population Census for 2021, Croatian Bureau of Statistics. Available online: https://dzs.gov.hr/vijesti/objavljeni-konacni-rezultati-popisa-2021/1270 (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Pelivan, A. The Incidence of Acute Inflammatory Polyradiculoneuropathy in Clinical Hospital Center Split in the Period from 2012 to 2016; School of Medicine, University of Split: Split, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aleraj Borislav Infectious Diseases in Croatia in 2012. Croat. J. Infect. 2013, 33, 127–133.
- Fragiel, M.; Miró, Ò.; Llorens, P.; Jiménez, S.; Piñera, P.; Burillo, G.; Martín, A.; Martín-Sánchez, F.J.; García-Lamberechts, E.J.; Jacob, J.; et al. Incidence, Clinical, Risk Factors and Outcomes of Guillain-Barré in COVID-19. Ann. Neurol. 2021, 89, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filosto, M.; Cotti Piccinelli, S.; Gazzina, S.; Foresti, C.; Frigeni, B.; Servalli, M.C.; Sessa, M.; Cosentino, G.; Marchioni, E.; Ravaglia, S.; et al. Guillain-Barré Syndrome and COVID-19: A 1-Year Observational Multicenter Study. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 3358–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rosa Mesquita, R.; Francelino Silva Junior, L.C.; Santos Santana, F.M.; Farias de Oliveira, T.; Campos Alcântara, R.; Monteiro Arnozo, G.; Rodrigues da Silva Filho, E.; Galdino dos Santos, A.G.; Oliveira da Cunha, E.J.; Salgueiro de Aquino, S.H.; et al. Clinical Manifestations of COVID-19 in the General Population: Systematic Review. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2021, 133, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caress, J.B.; Castoro, R.J.; Simmons, Z.; Scelsa, S.N.; Lewis, R.A.; Ahlawat, A.; Narayanaswamy, P. COVID-19–Associated Guillain-Barré Syndrome: The Early Pandemic Experience. Muscle Nerve 2020, 62, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasti, A.K.; Selmi, C.; Sarmiento-Monroy, J.C.; Vega, D.A.; Anaya, J.M.; Gershwin, M.E. Guillain-Barré Syndrome: Causes, Immunopathogenic Mechanisms and Treatment. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 12, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Rmeileh, S.; Abdelhak, A.; Foschi, M.; Tumani, H.; Otto, M. Guillain–Barré Syndrome Spectrum Associated with COVID-19: An up-to-Date Systematic Review of 73 Cases. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 1133–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacono, S.; Di Stefano, V.; Alonge, P.; Vinciguerra, C.; Milella, G.; Caputo, F.; Lasorella, P.; Neto, G.; Pignolo, A.; Torrente, A.; et al. Adherence and Reactogenicity to Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 in 285 Patients with Neuropathy: A Multicentric Study. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dunkić, N.; Nazlić, M.; Dunkić, V.; Bilić, I. Analysis of Post-COVID-19 Guillain–Barré Syndrome over a Period of One Year in the University Hospital of Split (Croatia). Neurol. Int. 2023, 15, 1359-1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15040086
Dunkić N, Nazlić M, Dunkić V, Bilić I. Analysis of Post-COVID-19 Guillain–Barré Syndrome over a Period of One Year in the University Hospital of Split (Croatia). Neurology International. 2023; 15(4):1359-1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15040086
Chicago/Turabian StyleDunkić, Niko, Marija Nazlić, Valerija Dunkić, and Ivica Bilić. 2023. "Analysis of Post-COVID-19 Guillain–Barré Syndrome over a Period of One Year in the University Hospital of Split (Croatia)" Neurology International 15, no. 4: 1359-1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15040086
APA StyleDunkić, N., Nazlić, M., Dunkić, V., & Bilić, I. (2023). Analysis of Post-COVID-19 Guillain–Barré Syndrome over a Period of One Year in the University Hospital of Split (Croatia). Neurology International, 15(4), 1359-1370. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint15040086