Pulvinar Sign, Stroke and Their Relationship with Fabry Disease: A Systematic Review and Metanalysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol
2.2. Eligibility Criteria and Study Selection
2.3. Database and Search Strategy
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Bias Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. The Pulvinar, the Pulvinar Sign, and Pathophisiology
4.2. Prevalence of the Pulvinar Sign in Fabry Disease
4.3. Pulvinar Sign and Correlation with Disease
4.3.1. Stroke
4.3.2. Renal Failure
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bokhari, S.R.A.; Zulfiqar, H.; Hariz, A. Fabry Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fabry Disease. Available online: https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/fabry-disease/#:~:text=Fabry%20disease%20is%20a%20rare,known%20as%20lysosomal%20storage%20disorders (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Chan, B.; Adam, D.N. A Review of Fabry Disease. Ski. Ther. Lett. 2018, 23, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, M.; Mauhin, W.; Belmatoug, N.; Garnotel, R.; Bedreddine, N.; Catros, F.; Ancellin, S.; Lidove, O.; Gaches, F. When and How to Diagnose Fabry Disease in Clinical Pratice. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 360, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffmann, R.; Waldek, S.; Benigni, A.; Auray-Blais, C. Biomarkers of Fabry Disease Nephropathy. CJASN 2010, 5, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocozza, S.; Russo, C.; Pisani, A.; Olivo, G.; Riccio, E.; Cervo, A.; Pontillo, G.; Feriozzi, S.; Veroux, M.; Battaglia, Y.; et al. Redefining the Pulvinar Sign in Fabry Disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2017, 38, 2264–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodny, E.; Fellgiebel, A.; Hilz, M.J.; Sims, K.; Caruso, P.; Phan, T.G.; Politei, J.; Manara, R.; Burlina, A. Cerebrovascular involvement in Fabry disease: Current status of knowledge. Stroke 2015, 46, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutchfield, K.E.; Patronas, N.J.; Dambrosia, J.M.; Frei, K.P.; Banerjee, T.K.; Barton, N.W.; Schiffmann, R. Quantitative analysis of cerebral vasculopathy in patients with Fabry disease. Neurology 1998, 50, 1746–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, L.; Manara, R.; Valentine, A.R.; Kendall, B.; Burlina, A.P. Magnetic resonance imaging changes in Fabry disease. Acta Paediatr. Suppl. 2006, 95, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlina, A.P.; Manara, R.; Caillaud, C.; Laissy, J.-P.; Severino, M.; Klein, I.; Burlina, A.; Lidove, O. The pulvinar sign: Frequency and clinical correlations in Fabry disease. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadda, L.; Floris, G.; Polizzi, L.; Meleddu, L.; Ercoli, T.; Garofalo, P.; Saba, L.; Muroni, A.; Defazio, G. Pulvinar sign in a case of anti-CV2 encephalitis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 393, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandel, J.-P.; Knight, R. Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 153, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamache, P.-L.; Gagnon, M.-M.; Savard, M.; Émond, F. Pulvinar sign in a case of anti-HU paraneoplastic encephalitis. Neuroradiol. J. 2016, 29, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cocozza, S.; Russo, C.; Pontillo, G.; Pisani, A.; Brunetti, A. Neuroimaging in Fabry disease: Current knowledge and future directions. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MOOSE Reporting Guidelines for Meta-analyses of Observational Studies|Guidelines|JAMA Surgery|JAMA Network. Available online: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamasurgery/article-abstract/2778476 (accessed on 11 July 2021).
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, J.; Nakagawa, N.; Kano, K.; Saito, T.; Katayama, T.; Sawada, T.; Momosaki, K.; Nakamura, K.; Hasebe, N. Characteristics of Neurological Symptoms in Adult Japanese Patients with Fabry Disease. Intern. Med. 2021, 60, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Hsu, T.-R.; Hung, S.-C.; Yu, W.-C.; Chu, T.-H.; Yang, C.-F.; Bizjajeva, S.; Tiu, C.-M.; Niu, D.-M. A comparison of central nervous system involvement in patients with classical Fabry disease or the later-onset subtype with the IVS4 + 919G > A mutation. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazekas, F.; Enzinger, C.; Schmidt, R.; Grittner, U.; Giese, A.-K.; Hennerici, M.G.; Huber, R.; Jungehulsing, G.J.; Kaps, M.; Kessler, C.; et al. Brain magnetic resonance imaging findings fail to suspect Fabry disease in young patients with an acute cerebrovascular event. Stroke 2015, 46, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.F.; Ye, F.; Schiffmann, R.; Butman, J.A. Increased signal intensity in the pulvinar on T1-weighted images: A pathognomonic MR imaging sign of Fabry disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 24, 1096–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Takanashi, J.; Barkovich, A.J.; Dillon, W.P.; Sherr, E.H.; Hart, K.A.; Packman, S. T1 hyperintensity in the pulvinar: Key imaging feature for diagnosis of Fabry disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2003, 24, 916–921. [Google Scholar]
- Burlina, A.P.; Politei, J.; Cinque, S.; Soliani, A.; Carlier, R.Y.; Germain, D.P.; Manara, R. The pulvinar sign in Fabry patients: The first report in female patients. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 1227–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Hung, S.-C.; Hsu, T.-R.; Ko, S.-C.; Chui-Mei, T.; Huang, C.-C.; Niu, D.-M.; Lin, C.-P. Brain MR Imaging Findings of Cardiac-Type Fabry Disease with an IVS4+919G>A Mutation. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia, D.; Floriolli, D.; Han, E.; Lee, G.; Paganini-Hill, A.; Wang, S.; Zandihaghighi, S.; Kimonis, V.; Fisher, M. Prevalence of cerebral small vessel disease in a Fabry disease cohort. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2021, 29, 100815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buechner, S.; Moretti, M.; Burlina, A.P.; Cei, G.; Manara, R.; Ricci, R.; Mignani, R.; Parini, R.; Di Vito, R.; Giordano, G.P.; et al. Central nervous system involvement in Anderson-Fabry disease: A clinical and MRI retrospective study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolfs, A.; Fazekas, F.; Grittner, U.; Dichgans, M.; Martus, P.; Holzhausen, M.; Böttcher, T.; Heuschmann, P.U.; Tatlisumak, T.; Tanislav, C.; et al. Acute cerebrovascular disease in the young: The Stroke in Young Fabry Patients study. Stroke 2013, 44, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, E.E. Pulvinar: Associative role in cortical function and clinical correlations. Neurology 2015, 84, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Sharma, N.; Ud Din, M.; Bansal, V. Isolated Pulvinar/Hockey Stick Sign in Nonalcoholic Wernicke’s Encephalopathy. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e928272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, M.; Sugase, S.; Konaka, K.; Sugai, F.; Sato, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hirota, S.; Sakai, K.; Sakoda, S. The “pulvinar sign” in a case of paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis associated with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 882–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wilke, M.; Dechent, P.; Bähr, M. Sarcoidosis Manifestion Centered on the Thalamic Pulvinar Leading to Persistent Astasia. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2017, 4, 898–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, J.; Macário, M.C.; Gaspar, E.; Santana, I. Severe post-influenza (H1N1) encephalitis involving pulvinar nuclei in an adult patient. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2015212667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üçeyler, N.; Homola, G.A.; González, H.G.; Kramer, D.; Wanner, C.; Weidemann, F.; Solymosi, L.; Sommer, C. Increased Arterial Diameters in the Posterior Cerebral Circulation in Men with Fabry Disease. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, O.; Cordeiro, F.; Gago, M.F.; Miltenberger-Miltenyi, G.; Ferreira, C.; Sousa, N.; Cunha, D. Fabry Disease and the Heart: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana-Baptista, M. Stroke and Fabry disease. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Author, Year, Country | Study Type | Sample Size | Age (Years) | Prevalence of the Pulvinar Sign |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sawada, 2021, Japan [17] | Cross-sectional—Single-center | 10 Males | 53.8 | 0 |
| 2 Females | ||||
| Cocozza et al., 2017, Italy [6] | Cross-sectional— Multicenter study | 80 Males | 41 ± 13.8 | 4 |
| 53 Females | ||||
| Lee et al., 2017, Taiwan [18] | Cross-sectional study | 23 Males | 53.9 ± 7.2 | 12 |
| 14 Females | ||||
| Fazekas et al., 2015, Europe [19] | Cross-sectional study | Females | 0 | |
| Males | ||||
| Moore et al., 2003, USA [20] | Cross-sectional study | 0 Memale | 35 ± 12 | 22 |
| 94 Males | ||||
| Burlina et al., 2008, France and Italy [10] | Cross-sectional study | 16 Males | 40 | 5 |
| 20 Females | ||||
| Takanashi et al., 2003, Japan [22] | Cross-sectional study | 9 Males | 36.9 | 7 |
| 1 Female | ||||
| Burlina, 2012, Italy, Argentina and France [21] | Case Series | 4 Females | 25.25 | 2 |
| Lee et al., 2016, Taiwan [23] | Cross-sectional study | 20 Males | 59.5 ± 7.2 | 8 |
| 6 Females | ||||
| Tapia et al., 2021, USA [24] | Cross-sectional study | 8 Males | 50 ± 13.4 | 0 |
| 13 Females | ||||
| Buechner et al., 2008, Italy [25] | Cross-sectional study | 25 males | 41.94 ± 10.83 | 0 |
| 18 Females | 52.48 ± 17.50 | 2 | ||
| Rolfs, Europe [26] | Crossectional -Multicenter Study | 16 Females 11 Males | Not Reported | 0 |
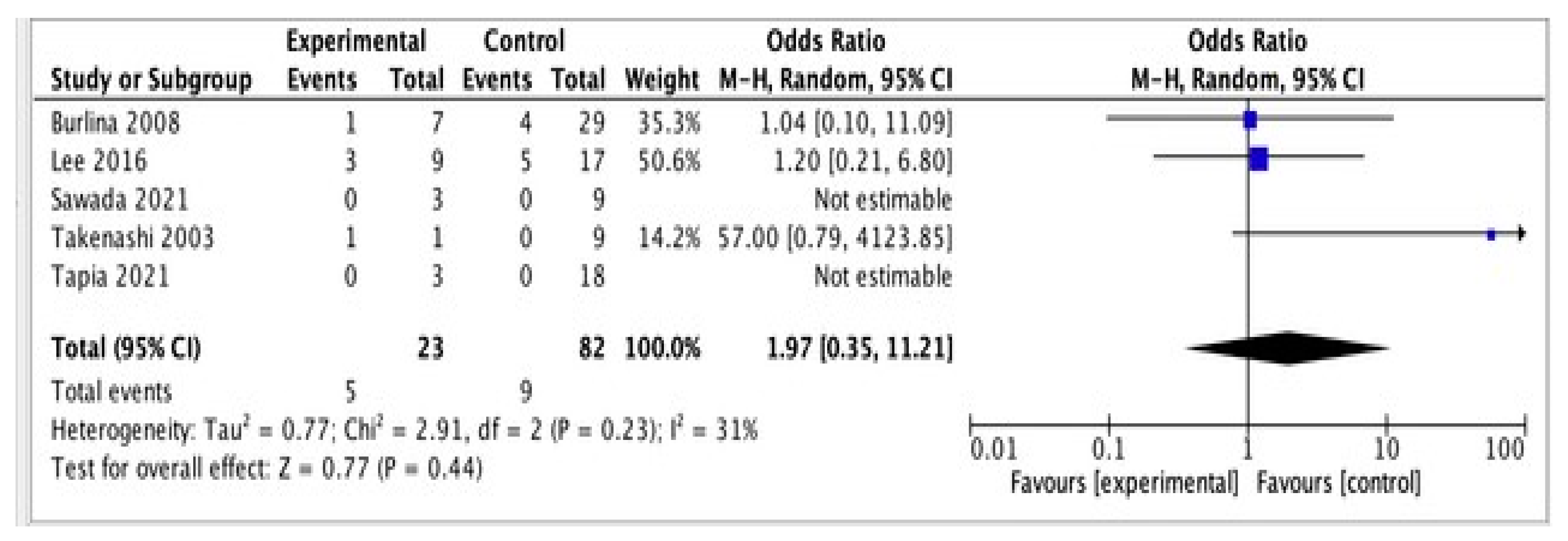
| Autor, Year | Stroke | Without Stroke |
|---|---|---|
| Burlina, 2008 [10] | 1 PS | 4 PS |
| 6 WPS | 25 WPS | |
| Lee, 2016 [23] | 3 PS | 5 PS |
| 6 WPS | 12 WPS | |
| Sawada et al., 2021 [17] | 0 PS | 0 PS |
| 3 WPS | 9 WPS | |
| Tapia et al., 2021 [24] | 0 PS | 0 PS |
| 3 WPS | 18 WPS | |
| Takenashi et al., 2003 [22] | 1 PS | 0 PS |
| 0 WPS | 9 WPS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortíz, J.F.; Solís, M.B.; Ali, S.S.; Khurana, M.; Moncayo, J.A.; Kothari, N.Y.; Alzamora, M.; Eissa-Garces, A.; Patel, G.; Monteros, G.A.; et al. Pulvinar Sign, Stroke and Their Relationship with Fabry Disease: A Systematic Review and Metanalysis. Neurol. Int. 2022, 14, 497-505. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14020041
Ortíz JF, Solís MB, Ali SS, Khurana M, Moncayo JA, Kothari NY, Alzamora M, Eissa-Garces A, Patel G, Monteros GA, et al. Pulvinar Sign, Stroke and Their Relationship with Fabry Disease: A Systematic Review and Metanalysis. Neurology International. 2022; 14(2):497-505. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14020041
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtíz, Juan Fernando, María Belén Solís, Syed Saad Ali, Mahika Khurana, Juan Andrés Moncayo, Nishel Yogesh Kothari, Mateo Alzamora, Ahmed Eissa-Garces, Ghanshyam Patel, Gustavo Andrés Monteros, and et al. 2022. "Pulvinar Sign, Stroke and Their Relationship with Fabry Disease: A Systematic Review and Metanalysis" Neurology International 14, no. 2: 497-505. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14020041
APA StyleOrtíz, J. F., Solís, M. B., Ali, S. S., Khurana, M., Moncayo, J. A., Kothari, N. Y., Alzamora, M., Eissa-Garces, A., Patel, G., Monteros, G. A., Sen, M., & Quiñonez, J. (2022). Pulvinar Sign, Stroke and Their Relationship with Fabry Disease: A Systematic Review and Metanalysis. Neurology International, 14(2), 497-505. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint14020041







