MTC-BEV: Semantic-Guided Temporal and Cross-Modal BEV Feature Fusion for 3D Object Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a location-aware, cross-modal bidirectional feature fusion mechanism to enhance geometric consistency and fine-grained representation in multi-modal fusion.
- We design a temporal fusion module that aligns and aggregates historical features, improving spatio-temporal modeling and robustness in dynamic environments.
- We introduce a segmentation-guided BEV feature enhancement module that projects semantic masks into the BEV space and reweights features to emphasize key object regions, thereby improving detection accuracy.
2. Related Work
2.1. Camera-Based 3D Target Detection
2.2. Three-Dimensional Target Detection Based on LiDAR
2.3. Multi-Modal Fusion for 3D Target Detection
3. Methodology
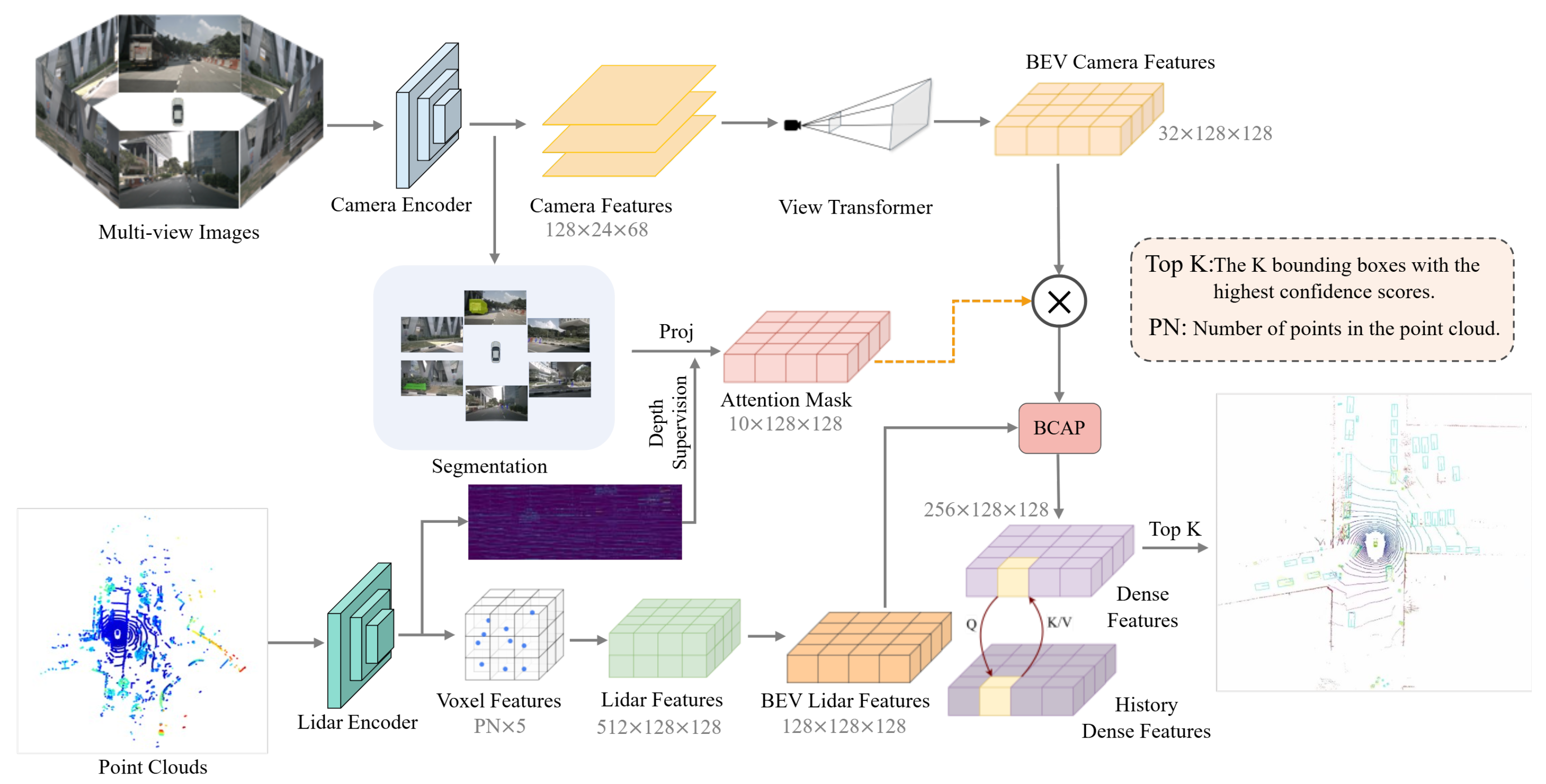
3.1. Overview
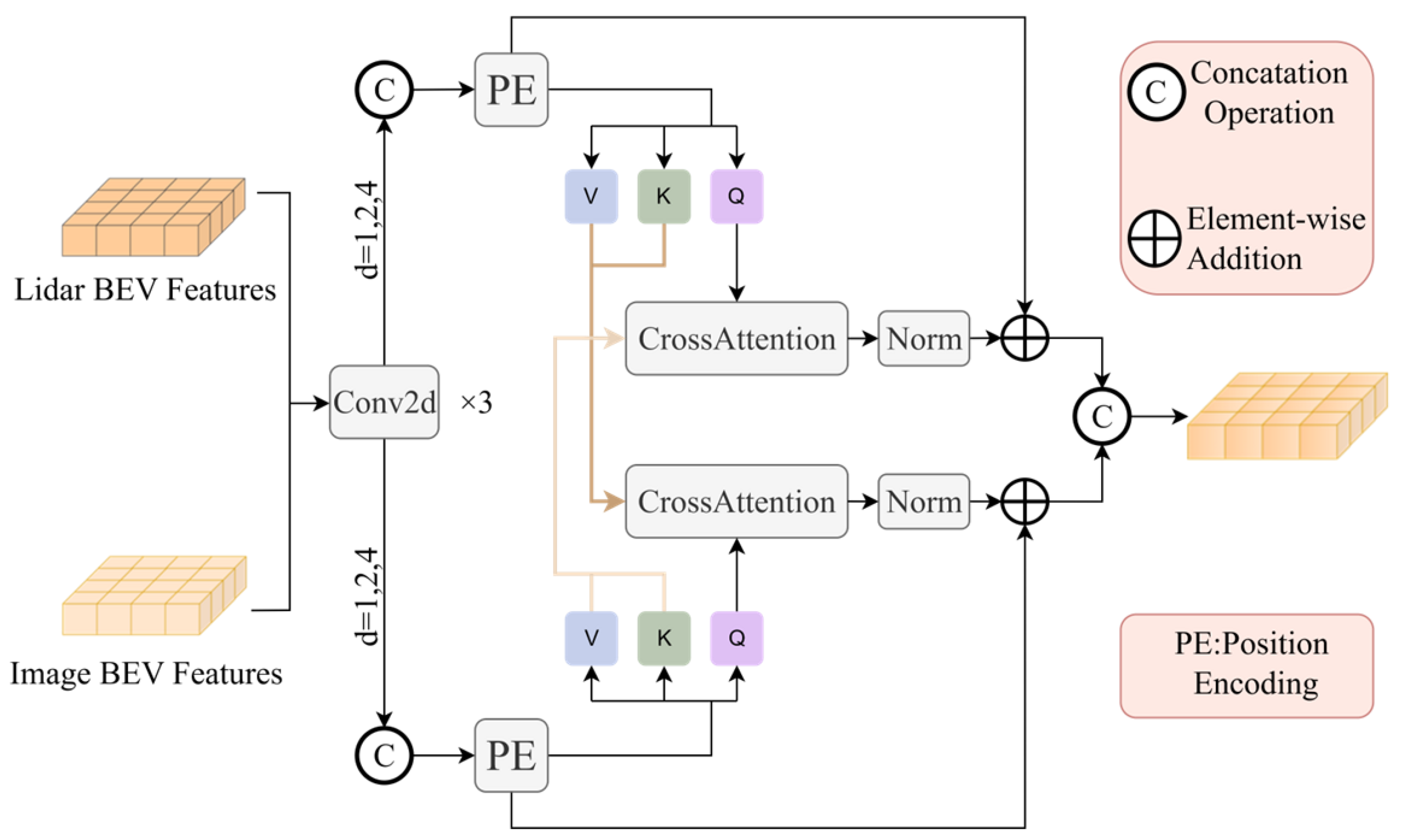
3.2. BCAP Module
3.3. TTFusion Module
3.3.1. Temporal Alignment with Motion Compensation
3.3.2. Multi-Head Temporal Attention Fusion
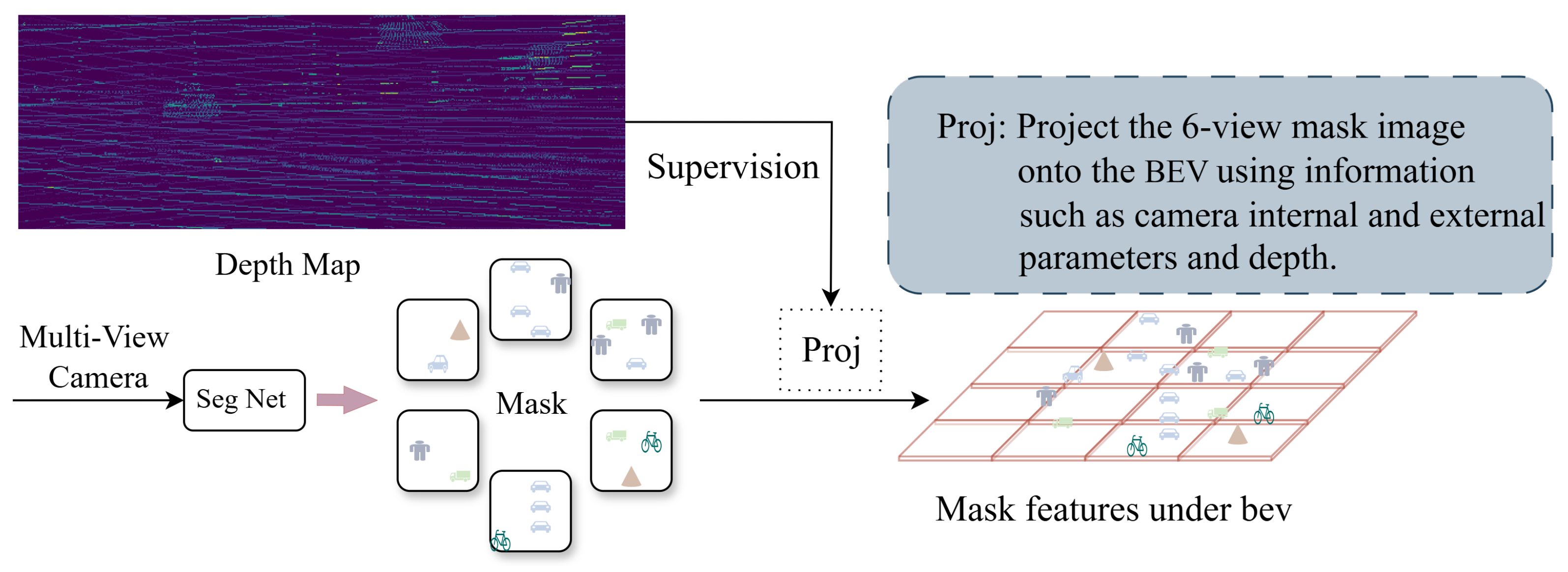
3.4. Segmentation-Guided BEV Feature Enhancement
3.4.1. Depth-Aware BEV Projection with Segmentation Masks
3.4.2. BEV Mask Generation and Feature Enhancement
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Experimental Details
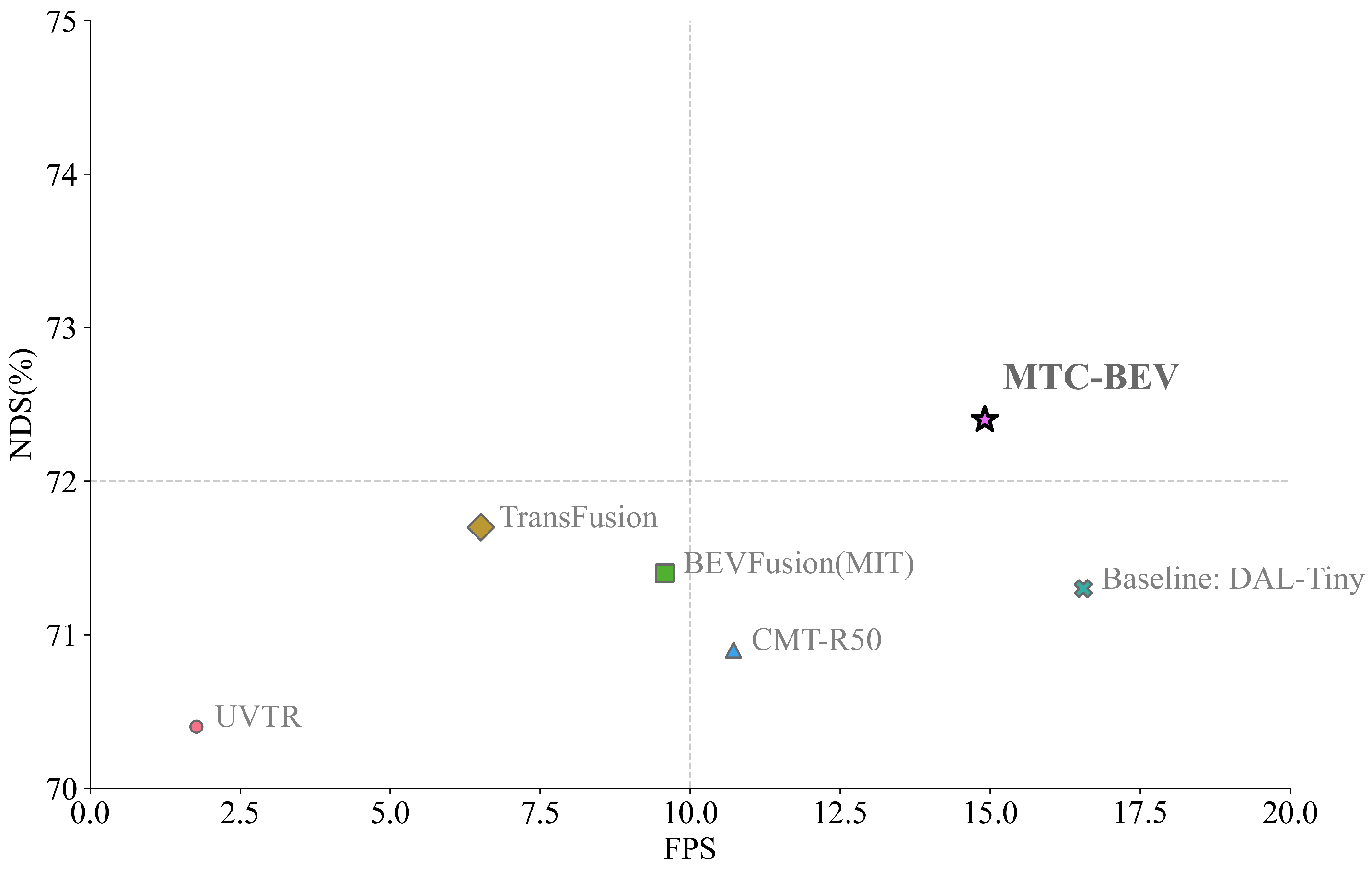
4.4. Comparison with Other Methods
| Method | Modality | CB | Voxel Size (m) | NDS | mAP | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PETRv2 [21] | C | R50 | - | 0.456 | 0.349 | 18.90 |
| BEVDepth [22] | C | R50 | - | 0.475 | 0.351 | 15.68 |
| StreamPETR [23] | C | R50 | - | 0.546 | 0.449 | 31.70 |
| CenterPoint [14] | L | - | (0.075, 0.075, 0.2) | 0.648 | 0.564 | 31.21 |
| FSTR-L [24] | L | - | (0.075, 0.075, 0.2) | 0.703 | 0.655 | 8.92 |
| DSVT-Pillar [25] | L | - | (0.3, 0.3, 8.0) | 0.711 | 0.664 | 9.43 |
| UVTR [26] | L+C | R101-DCN | (0.075, 0.075, 0.075) | 0.704 | 0.663 | 1.77 |
| TransFusion [27] | L+C | R50 | (0.075, 0.075, 0.2) | 0.717 | 0.689 | 6.51 |
| BEVFusion (MIT) [16] | L+C | Swin-T | (0.075, 0.075, 0.2) | 0.714 | 0.685 | 9.58 |
| DAL-Tiny [20] | L+C | R18 | (0.1, 0.1, 0.2) | 0.713 | 0.674 | 16.55 |
| CMT [28] | L+C | R50 | (0.1, 0.1, 0.2) | 0.709 | 0.679 | 10.72 |
| Ours | L+C | R18 | (0.1, 0.1, 0.2) | 0.724 | 0.684 | 14.91 |
4.5. Ablation Study
4.6. Effect of Historical Frame Number
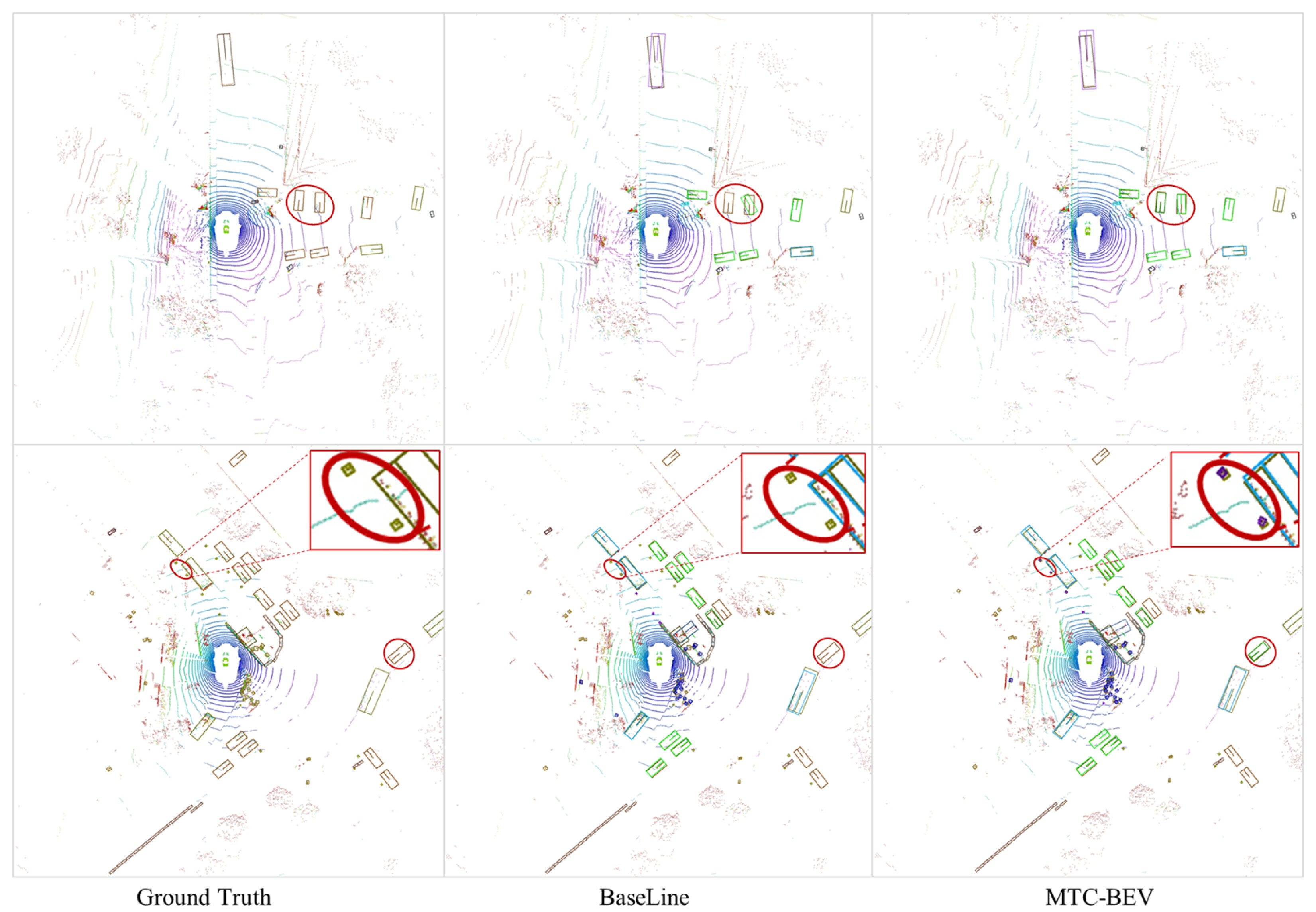
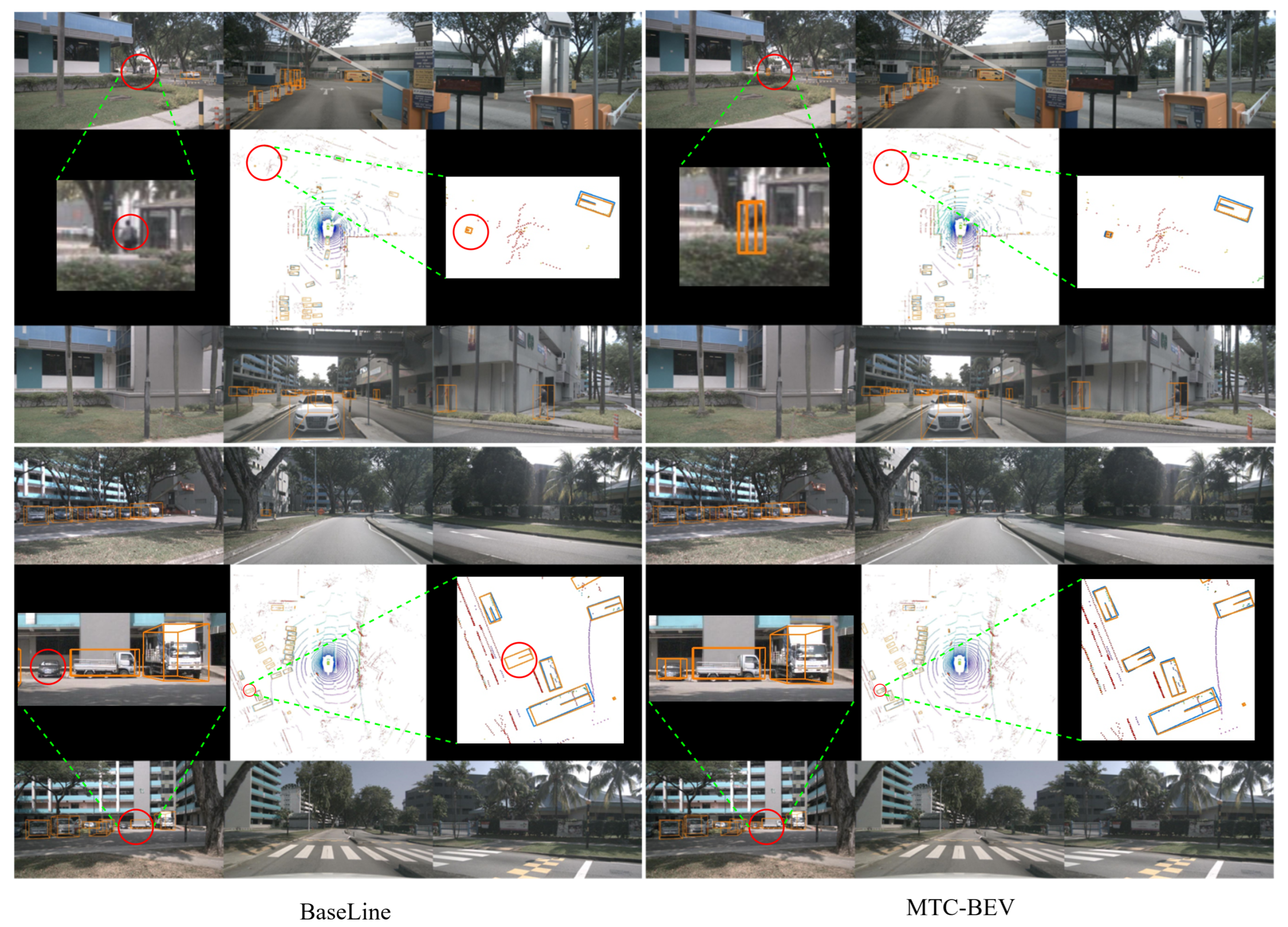
4.7. Qualitative Results
5. Discussion
5.1. Results Analysis
5.2. Limitations
5.3. Potential Improvements
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MTC-BEV | Semantic-Guided Temporal and Cross-Modal BEV Feature Fusion |
| BCAP | Bidirectional Cross-Modal Attention Fusion |
| BEV | Bird’s-Eye View |
| TTFusion | Temporal Fusion |
| NDS | nuScenes Detection Score |
| mAP | mean Average Precision |
| FPS | Frames Per Second |
References
- Dal’Col, L.; Oliveira, M.; Santos, V. Joint perception and prediction for autonomous driving: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.14088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Meng, S.; Wang, Y.; Chau, L.-P. A survey on occupancy perception for autonomous driving: The information fusion perspective. Inf. Fusion 2025, 114, 102671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, L. Panoptic perception for autonomous driving: A survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.15388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kundu, K.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, H.; Fidler, S.; Urtasun, R. Monocular 3D object detection for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2147–2156. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavian, A.; Anguelov, D.; Flynn, J.; Kosecka, J. 3D bounding box estimation using deep learning and geometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7074–7082. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chao, W.-L.; Garg, D.; Hariharan, B.; Campbell, M.; Weinberger, K.Q. Pseudo-LiDAR from visual depth estimation: Bridging the gap in 3D object detection for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 8445–8453. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J. PETR: Position embedding transformation for multi-view 3D object detection. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 531–548. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Ren, X.; Fu, Y. MVSFormer: Multi-view stereo by learning robust image features and temperature-based depth. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.02541. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Tuzel, O. VoxelNet: End-to-end learning for point cloud based 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4490–4499. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Mao, Y.; Li, B. SECOND: Sparsely embedded convolutional detection. Sensors 2018, 18, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Wang, X.; Li, H. PointRCNN: 3D object proposal generation and detection from point cloud. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 770–779. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Caesar, H.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Beijbom, O. PointPillars: Fast encoders for object detection from point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12697–12705. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Guo, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Li, H. PV-RCNN: Point-voxel feature set abstraction for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10529–10538. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, T.; Zhou, X.; Krahenbuhl, P. Center-based 3D object detection and tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 11784–11793. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Qi, X.; Jia, J. VoxelNext: Fully sparse VoxelNet for 3D object detection and tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 21674–21683. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, H.; Amini, A.; Yang, X.; Mao, H.; Rus, D.; Han, S. BEVFusion: Multi-task multi-sensor fusion with unified bird’s-eye view representation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.13542. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Guan, R.; Wu, T.; Man, K.L.; Yu, L.; Yue, Y. UniBEVFusion: Unified radar-vision BEV fusion for 3D object detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.14751. [Google Scholar]
- Caesar, H.; Bankiti, V.; Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Liong, V.E.; Xu, Q.; Krishnan, A.; Pan, Y.; Baldan, G.; Beijbom, O. nuScenes: A multimodal dataset for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11621–11631. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Qiu, J.; Chaurasia, A. Ultralytics YOLO (Version 8.0.0) [Computer Software]. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Huang, J.; Ye, Y.; Liang, Z.; Shan, Y.; Du, D. Detecting as labeling: Rethinking LiDAR-camera fusion in 3D object detection. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 439–455. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Jia, F.; Li, S.; Gao, A.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X. PETRv2: A Unified Framework for 3D Perception from Multi-Camera Images. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 3262–3272. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Ge, Z.; Yu, G.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z. BevDepth: Acquisition of Reliable Depth for Multi-View 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 1477–1485. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Exploring Object-Centric Temporal Modeling for Efficient Multi-View 3D Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 3621–3631. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zheng, Z.; Niu, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. Fully Sparse Transformer 3-D Detector for LiDAR Point Cloud. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5705212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shi, C.; Shi, S.; Lei, M.; Wang, S.; He, D.; Schiele, B.; Wang, L. DSVT: Dynamic Sparse Voxel Transformer with Rotated Sets. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 13520–13529. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Jia, J. Unifying voxel-based representation with transformer for 3D object detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 18442–18455. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Fu, H.; Tai, C.-L. TransFusion: Robust LiDAR-camera fusion for 3D object detection with transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1090–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Jia, F.; Li, S.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X. Cross modal transformer: Towards fast and robust 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 18268–18278. [Google Scholar]

| BCAP | TTFusion | Mask Guide | NDS | mAP | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.713 | 0.674 | 16.55 | |||
| ✓ | 0.718 | 0.677 | 16.05 | ||
| ✓ | 0.717 | 0.677 | 15.91 | ||
| ✓ | 0.716 | 0.678 | 15.64 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 0.720 | 0.679 | 15.45 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 0.721 | 0.681 | 15.19 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 0.719 | 0.678 | 15.06 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 0.724 | 0.684 | 14.91 |
| Number of Historical Frames | NDS | mAP | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.715 | 0.676 | 16.09 |
| 2 | 0.717 | 0.677 | 15.91 |
| 3 | 0.714 | 0.675 | 15.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xi, Q.; Ma, L.; Zhang, J.; Bai, H.; Wang, Z. MTC-BEV: Semantic-Guided Temporal and Cross-Modal BEV Feature Fusion for 3D Object Detection. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090493
Xi Q, Ma L, Zhang J, Bai H, Wang Z. MTC-BEV: Semantic-Guided Temporal and Cross-Modal BEV Feature Fusion for 3D Object Detection. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(9):493. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090493
Chicago/Turabian StyleXi, Qiankai, Li Ma, Jikai Zhang, Hongying Bai, and Zhixing Wang. 2025. "MTC-BEV: Semantic-Guided Temporal and Cross-Modal BEV Feature Fusion for 3D Object Detection" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 9: 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090493
APA StyleXi, Q., Ma, L., Zhang, J., Bai, H., & Wang, Z. (2025). MTC-BEV: Semantic-Guided Temporal and Cross-Modal BEV Feature Fusion for 3D Object Detection. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(9), 493. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16090493








