Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Strategy for Permanent Magnet-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor Based on Adaptive Sliding Mode Observer
Abstract
1. Introduction
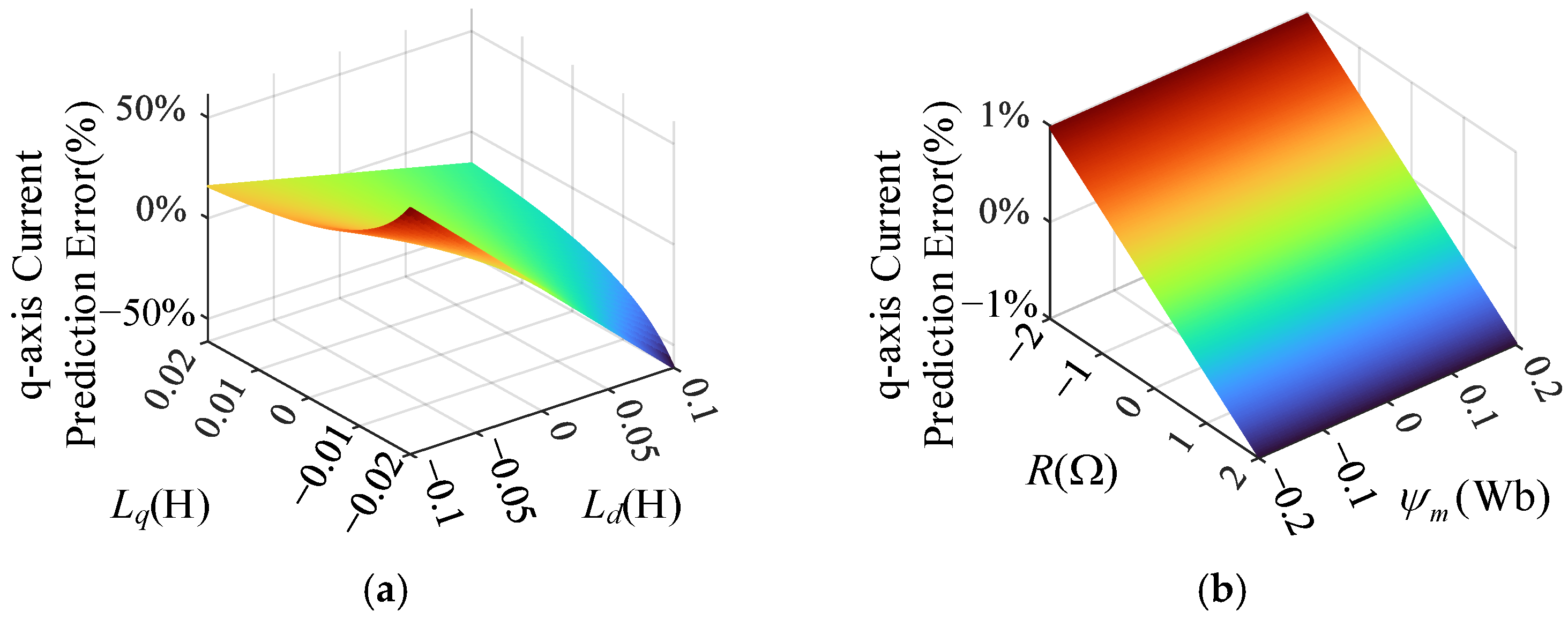
2. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis of Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Strategy
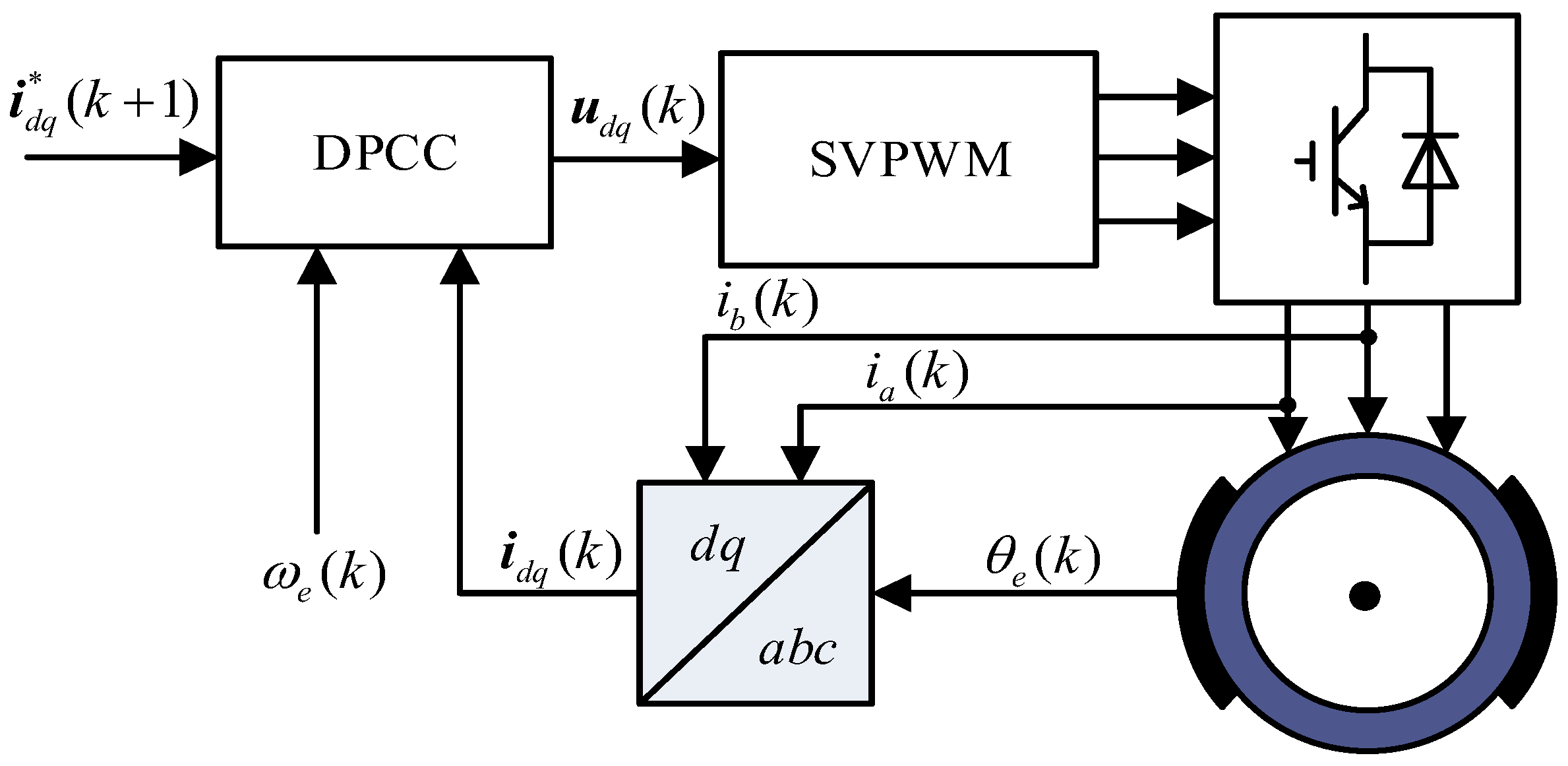
3. Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Strategy Based on Adaptive Sliding Mode Observer
3.1. Principle Analysis of the Proposed Control Strategy
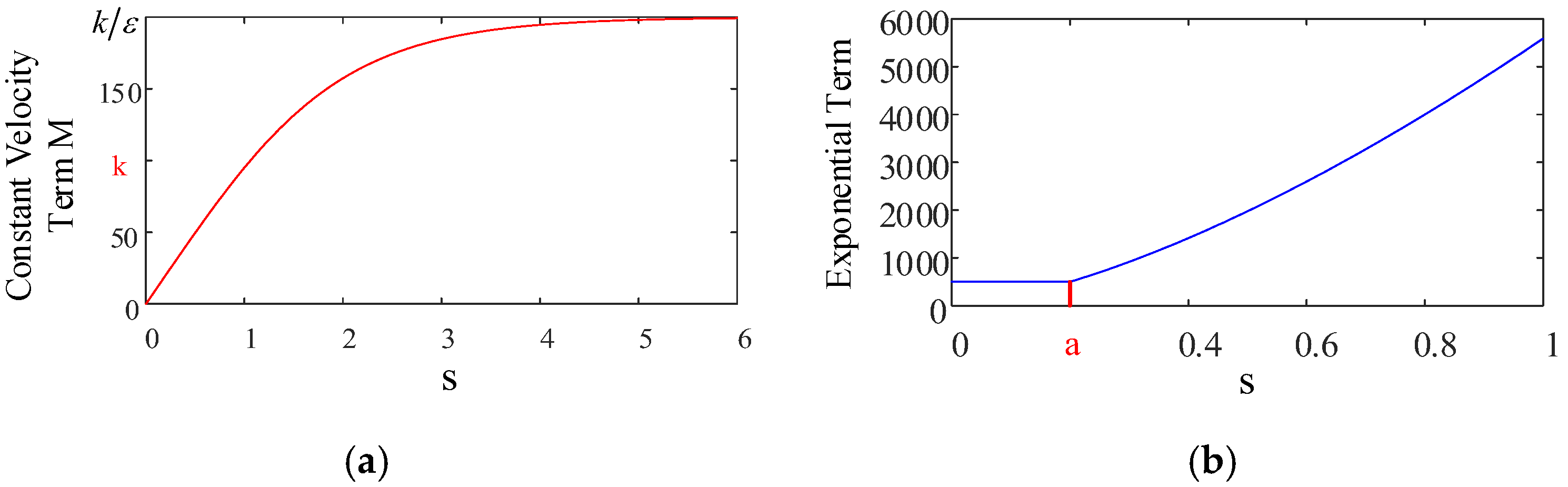
3.2. Stability Analysis and Parameter Design
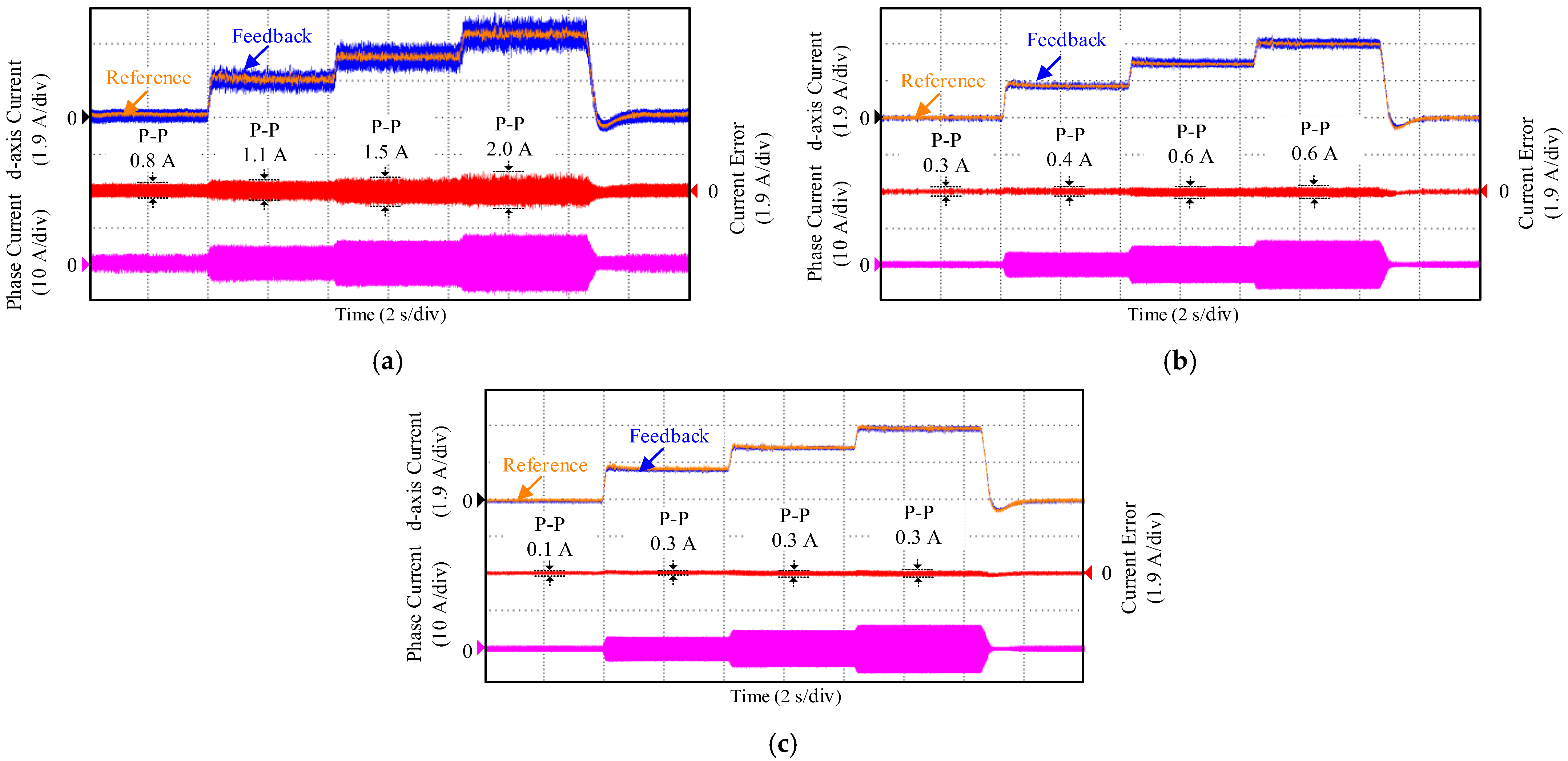
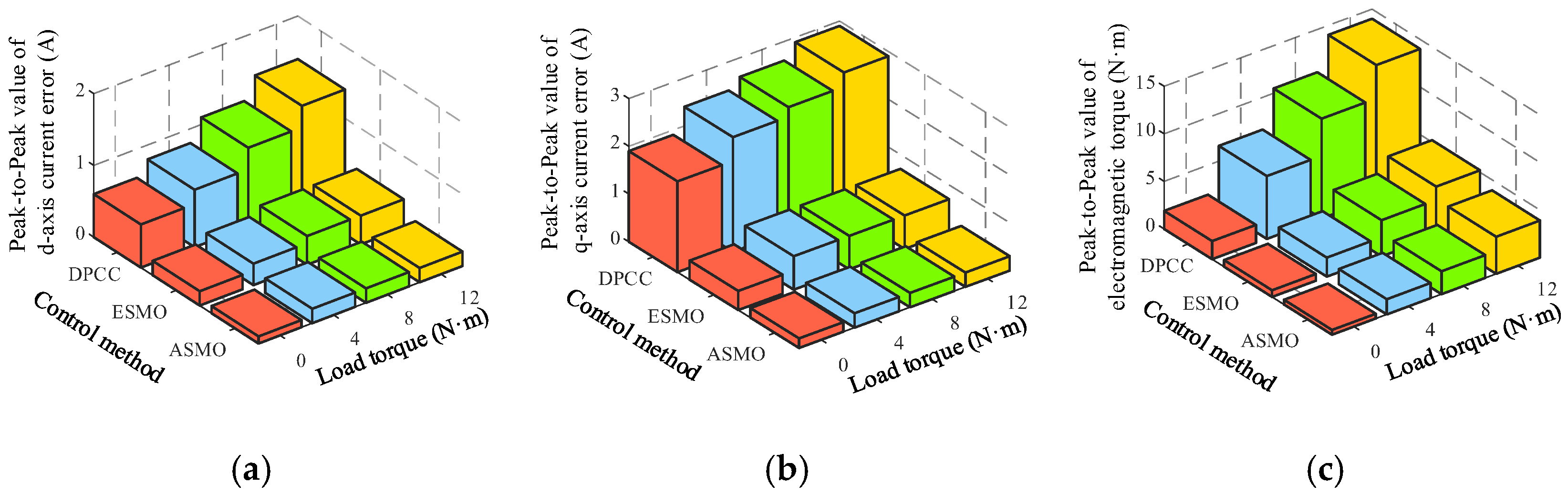
4. Experimental Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| PI | Proportional–integral |
| MPC | Model predictive control |
| DPCC | Deadbeat predictive current control |
| ESMO | Exponential sliding mode observer |
| ASMO | Adaptive sliding mode observer |
| ud, uq, id, iq | d-axis and q-axis voltages and currents |
| Ψm | Nominal values of permanent magnet flux linkage |
| R | Nominal values of stator resistance |
| Ld, Lq | Nominal values of d-axis and q-axis inductances |
| Ψm0 | Actual values of permanent magnet flux linkage |
| R0 | Actual values of stator resistance |
| Ld0, Lq0 | Actual values of d-axis and q-axis inductances |
| fd, fq | d-axis and q-axis parameter disturbances |
| Fd, Fq | Rates of change in parameter disturbance |
| Udsmo, Uqsmo | Sliding mode observation functions |
| gd, gq | Sliding mode parameters |
| k1, λ | Exponential reaching rate parameters |
| M | Adaptive factor |
References
- Wang, K.; Wang, G.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Xu, D. ESO-Based Robust Hybrid Flux Observer with Active Flux Error Estimation for Position Sensorless PMa-SynRM Drives. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Xiang, R.; Wang, G.; Li, C.; Bi, G.; Zhao, N.; Xu, D. Hybrid Pseudorandom Signal Injection for Position Sensorless SynRM Drives with Acoustic Noise Reduction. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 8, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, S.; Li, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Xu, D. Acoustic Noise Reduction Using Half-Period-Switching Pseudorandom Sinusoidal Injection with External Tangent Demodulation for Sensorless PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedryczka, C.; Mysinski, M.; Szelag, W. Development and Analysis of Six-Phase Synchronous Reluctance Motor for Increased Fault Tolerance Capabilities. Energies 2024, 17, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryabeigi, E.; Vaez-Zadeh, S. A Combined Control for Fast and Smooth Performance of IPM Motor Drives Over Wide Operating Conditions. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2018, 33, 1384–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, J.; An, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, H. Control Strategy of Biaxial Variable Gain Cross-Coupled Permanent Magnet Synchronous Linear Motor Based on MPC-MRAS. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 4733–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.-H.; Bang, T.-K.; Lee, H.-K.; Kim, K.-H.; Shin, S.-H.; Choi, J.-Y. Electromagnetic Characteristic Analysis of High-Speed Motors with Rare-Earth and Ferrite Permanent Magnets Considering Current Harmonics. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 57, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbi, S.F.; Halloran, M.; LeDrew, T.; Matchem, A.; Rahman, M.A. Modeling and V/F control of a Hysteresis Interior Permanent Magnet Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 52, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebeiro, R.S.; Uddin, M.N. Performance Analysis of an FLC-Based Online Adaptation of Both Hysteresis and PI Controllers for IPMSM Drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2012, 48, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-B. Closed-Loop Estimation of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Parameters by PI Controller Gain Tuning. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Song, Z.; Zhao, H.; Dai, B. Current Harmonic Suppression for Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Chebyshev Filter and PI Controller. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2020, 57, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jing, L.; Wu, X.; Xu, W.; Liu, J.; Lyu, G.; Fan, Z. A Deadbeat PI Controller with Modified Feedforward for PMSM Under Low Carrier Ratio. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 63463–63474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarsembayev, B.; Suleimenov, K.; Do, T.D. High Order Disturbance Observer Based PI-PI Control System with Tracking Anti-Windup Technique for Improvement of Transient Performance of PMSM. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 66323–66334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, M. An Improved Inertia Disturbance Suppression Method for PMSM Based on Disturbance Observer and Two-Degree-of-Freedom PI Controller. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 38, 3590–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, X.; Xiao, D.; Wang, Z.; Mao, Y.; He, M. Online Switching Strategy Between Dual Three-Phase PMSM and Open-Winding PMSM. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 10, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, J. Speed Regulation Method Using Genetic Algorithm for Dual Three-phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2023, 7, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-H.; Nie, J.; Wei, H.-L.; Chen, L.; Li, X.-H.; Lv, M.-Y. Switched PI Control Based MRAS for Sensorless Control of PMSM Drives Using Fuzzy-Logic-Controller. IEEE Open J. Power Electron. 2022, 3, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, H.; Lin, H.; Yu, F.; Yang, Y. A Novel Finite-Set Sliding-Mode Model-Free Predictive Current Control for PMSM Drives Without DC-Link Voltage Sensor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 39, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bai, H.; Cheng, M. Improved Model Predictive Current Control with Series Structure for PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 12437–12446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Gong, C.; Li, W.; Liu, J. Novel Compensation Strategy for Calculation Delay of Finite Control Set Model Predictive Current Control in PMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 5816–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Yin, Z.; Li, L.; Li, T.; Liu, J. Gaussian Noise Suppression in Deadbeat Predictive Current Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors Based on Augmented Fading Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 38, 1410–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Peng, F.; Dong, J.; Zhang, H. An Improved Deadbeat Predictive Current Control with Online Parameter Identification for Surface-Mounted PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 10145–10155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Xie, Y. Predictive Trajectory Control Strategy for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Drives Based on Deadbeat Predictive Flux Linkage Control Method. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 38, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, H.; Liu, B.; Wu, T.; Wang, C.; Huang, S. Improved Deadbeat Predictive Current Control of PMSM Based on a Resistance Adaptive Position Observer. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2023, 10, 5215–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Shao, K.; Liu, Y. Switching Active Disturbance Rejection Based Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 13920–13932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Zou, Z.; Chen, J. Deadbeat Predictive Current Control-Based Fault-Tolerant Scheme for Dual Three-Phase PMSM Drives. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 9, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, W.; Mu, C.; Liu, Y. Improved Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Combined Sliding Mode Strategy for PMSM Drive System. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 67, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Zhang, C.; Ba, X.; Guo, Y. Improved Deadbeat Predictive Current Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Using a Novel Stator Current and Disturbance Observer. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 142815–142826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoro, S.; Husain, I. Robust Deadbeat Finite-Set Predictive Current Control with Torque Oscillation and Noise Reduction for PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 58, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Hu, Q.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Z. A Modified Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for Improving Dynamic Performance of PMSM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 14173–14185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, S.; Huang, D. An Improved Model-Free Active Disturbance Rejection Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Method of PMSM Based on Data-Driven. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 9606–9616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, J.G.; Guo, Y. Improved Deadbeat Predictive Current Control to Enhance the Performance of the Drive System of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2021, 31, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Zou, J. Integral Sliding Mode Control Based Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for PMSM Drives with Disturbance Rejection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 37, 2845–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, G.; Liu, J.; Gao, X.; Tian, W.; Li, L.; Kennel, R. Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for SPMSM at Low Switching Frequency with Moving Horizon Estimator. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2019, 9, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Bai, H. Sliding-Mode-Based Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for PMSM Drives. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2022, 11, 962–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Fang, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Enhanced Deadbeat Predictive Current Control for PMSM Drives Using Iterative Sliding Mode Observer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 13866–13876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
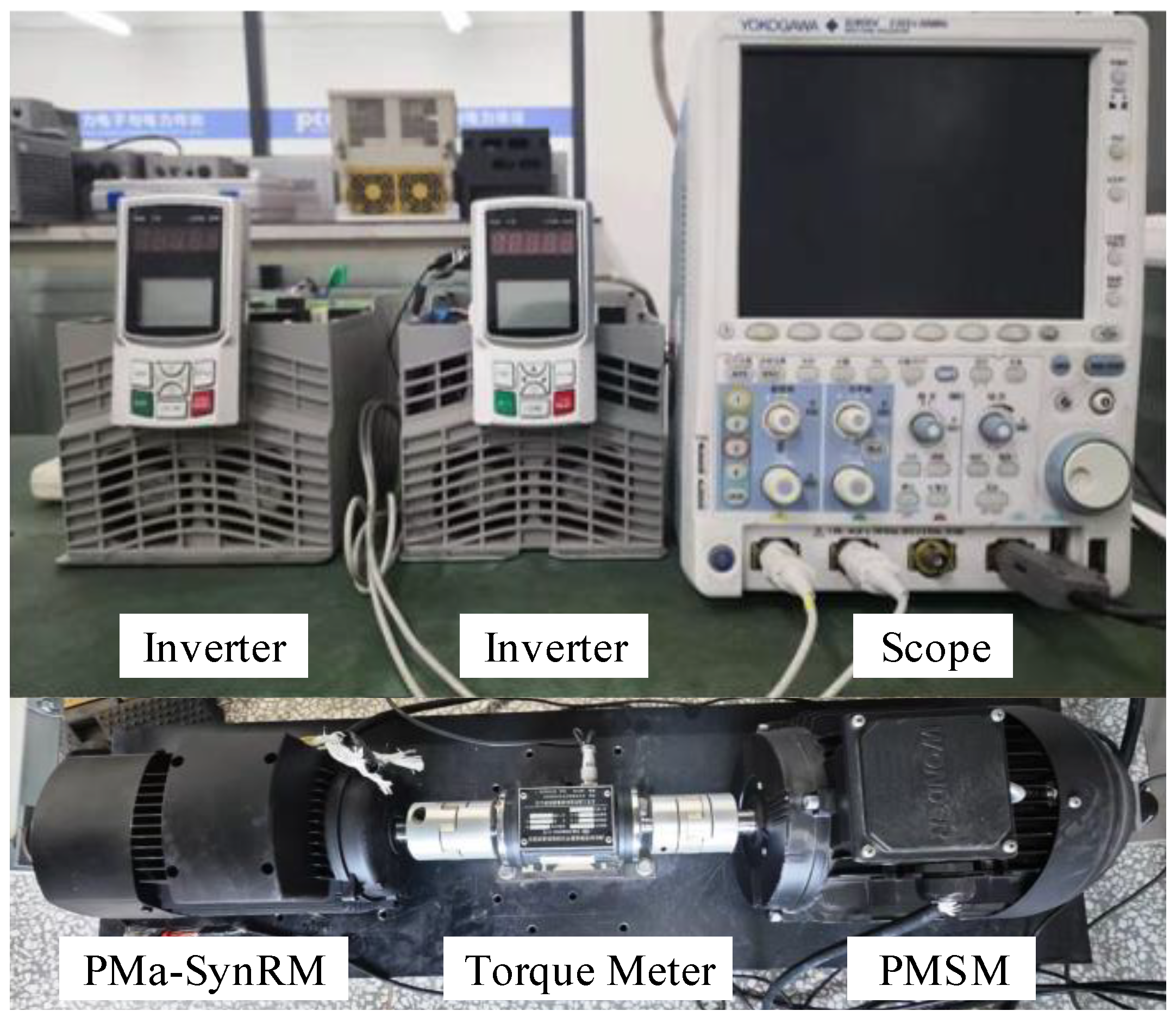









| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated power (kW) | 2.2 | Pole pairs | 3 |
| Rated current (A) | 4.8 | Stator resistance (Ω) | 3.0 |
| Rated speed (r/min) | 1500 | D-axis inductance (mH) | 154 |
| Flux linkage (Wb) | 0.21 | Q-axis inductance (mH) | 45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, B.; Zhang, G.; Wang, G.; Xu, D. Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Strategy for Permanent Magnet-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor Based on Adaptive Sliding Mode Observer. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16040202
Gao B, Zhang G, Wang G, Xu D. Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Strategy for Permanent Magnet-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor Based on Adaptive Sliding Mode Observer. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(4):202. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16040202
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Bo, Guoqiang Zhang, Gaolin Wang, and Dianguo Xu. 2025. "Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Strategy for Permanent Magnet-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor Based on Adaptive Sliding Mode Observer" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 4: 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16040202
APA StyleGao, B., Zhang, G., Wang, G., & Xu, D. (2025). Deadbeat Predictive Current Control Strategy for Permanent Magnet-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Motor Based on Adaptive Sliding Mode Observer. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(4), 202. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16040202







