Sliding Mode Controller Tuning Using Nature-Inspired Optimization for Induction Motor: EV Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of Induction Motor
2.2. Induction Motor Model
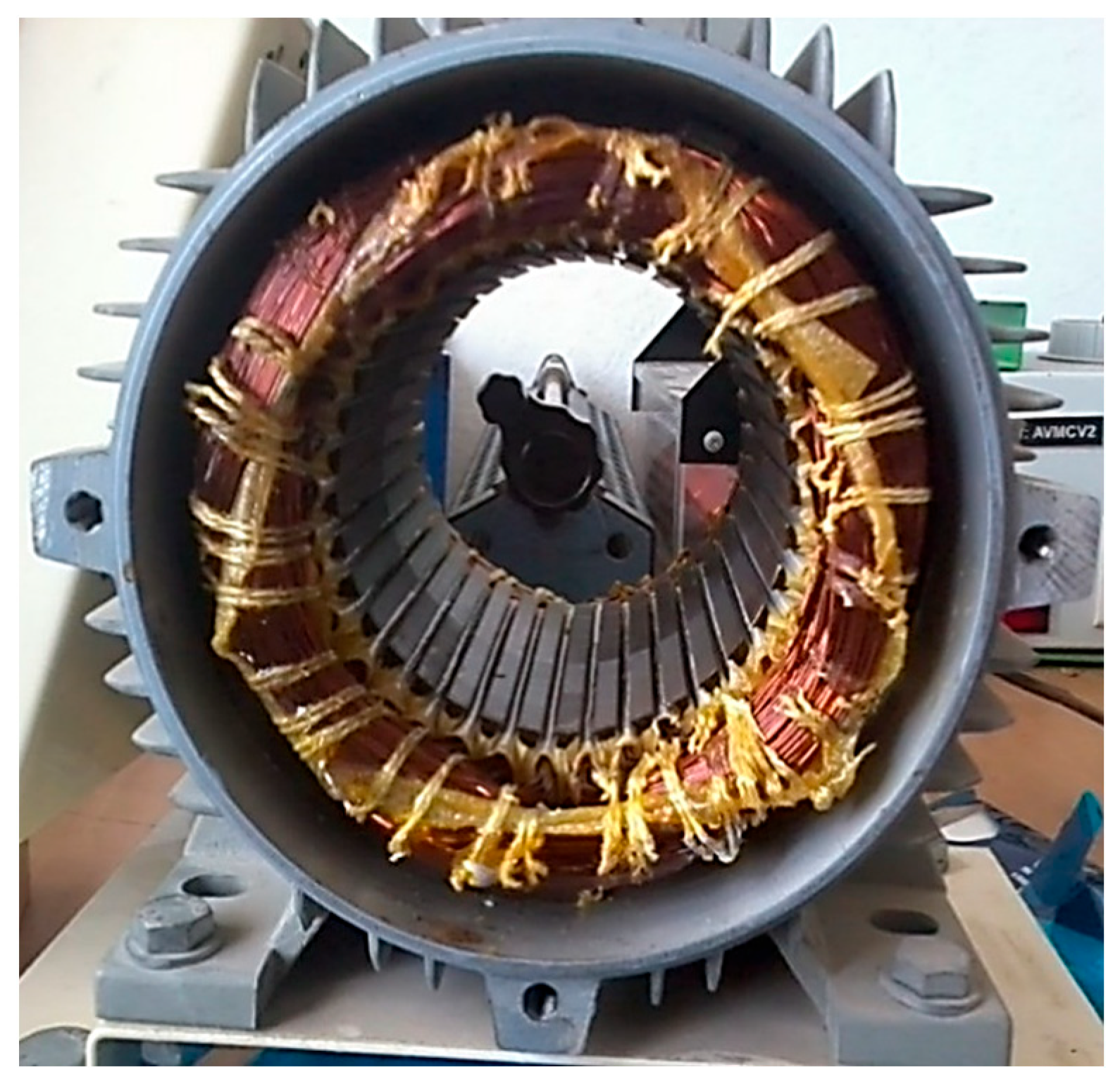
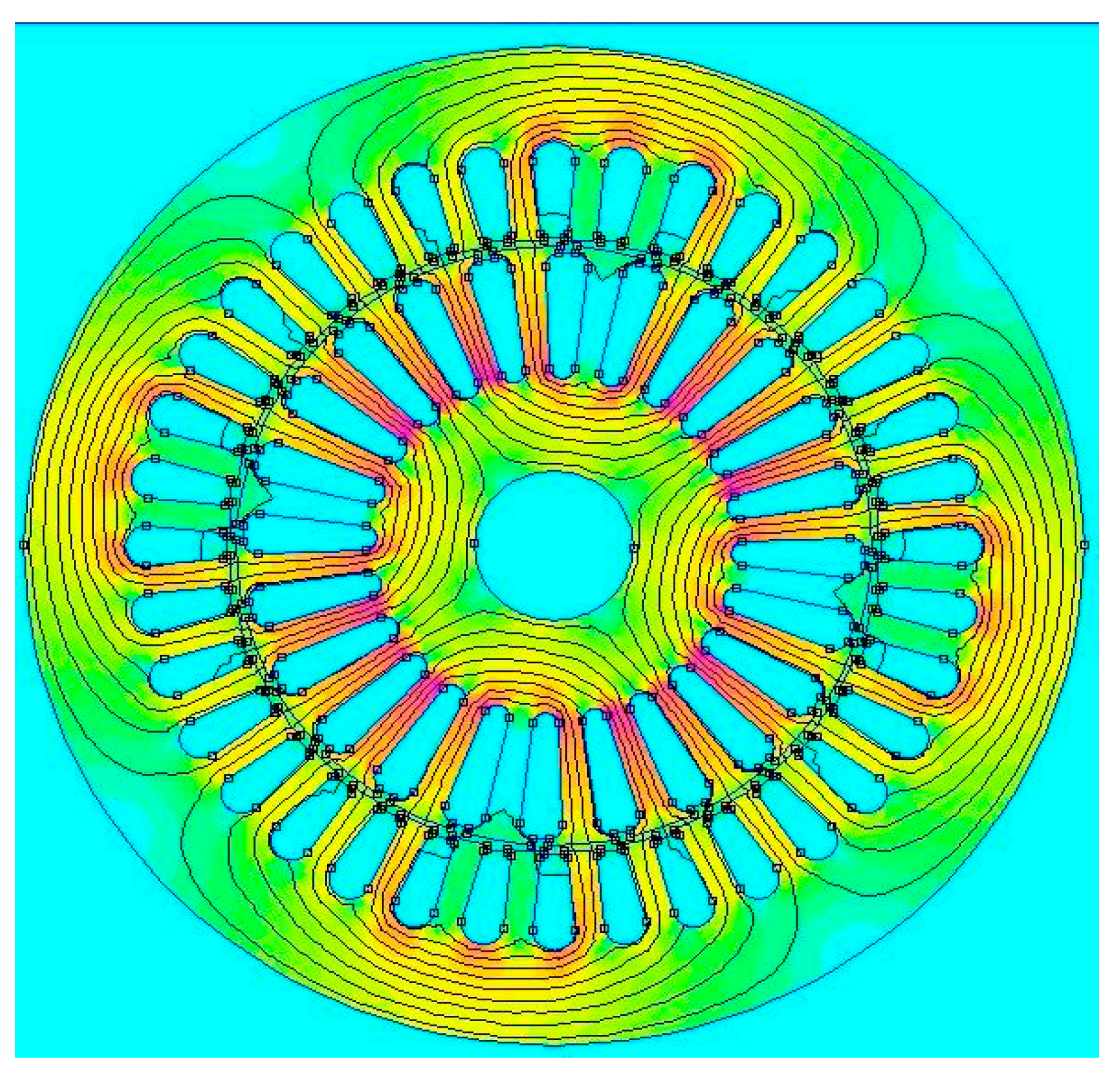
2.3. Optimizing Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor Parameters Through FEMM and MATLAB
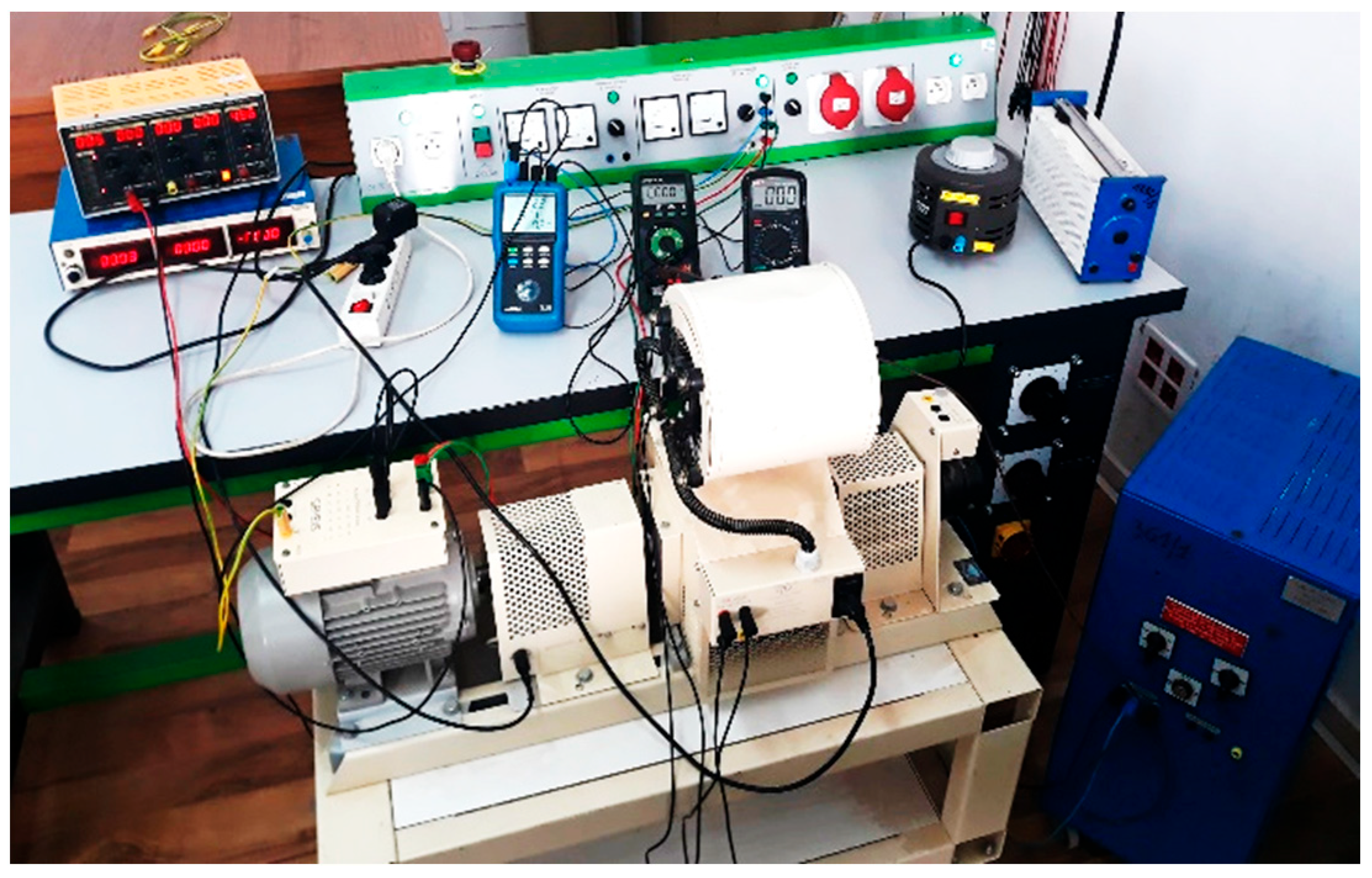
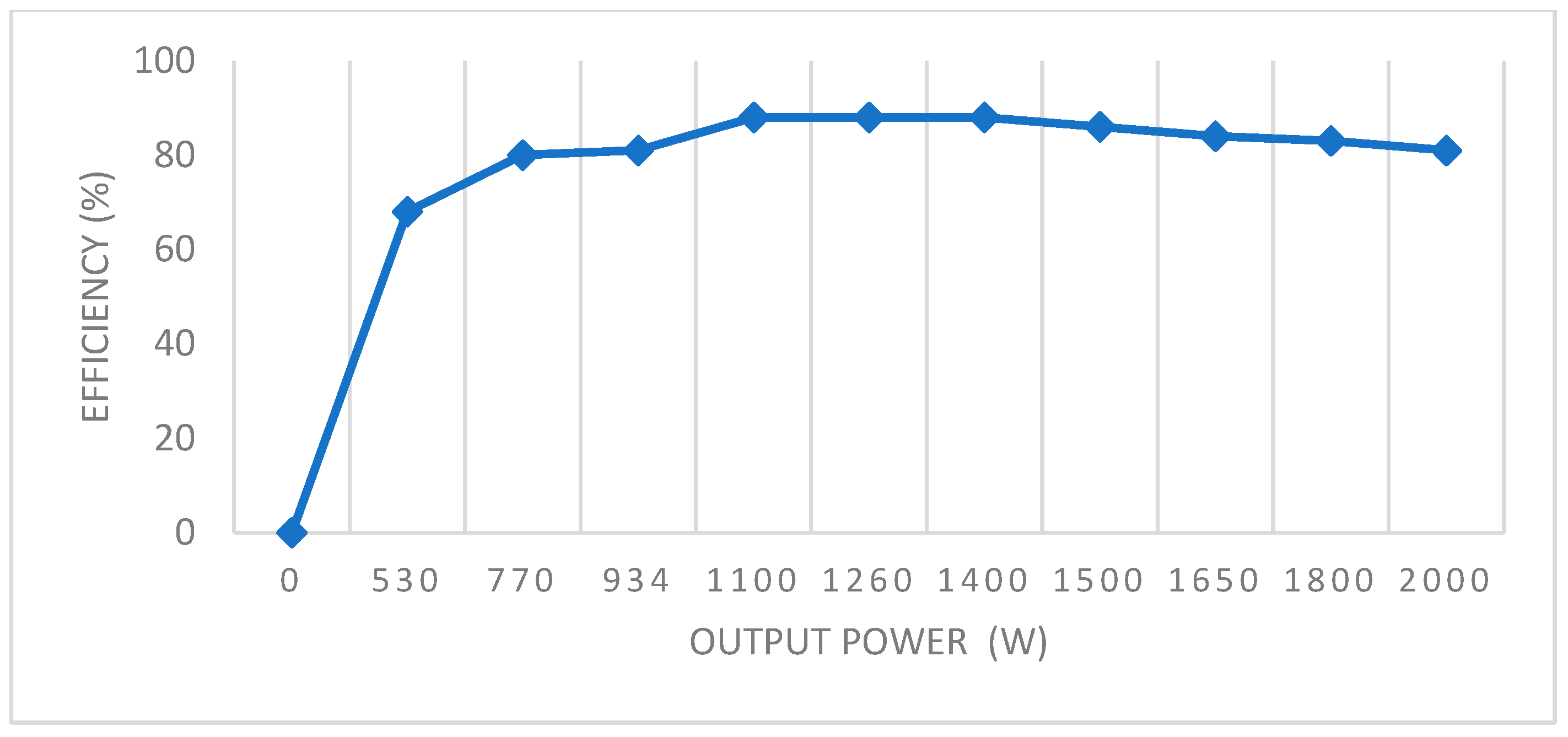
3. Experimental Validation of the IM Model
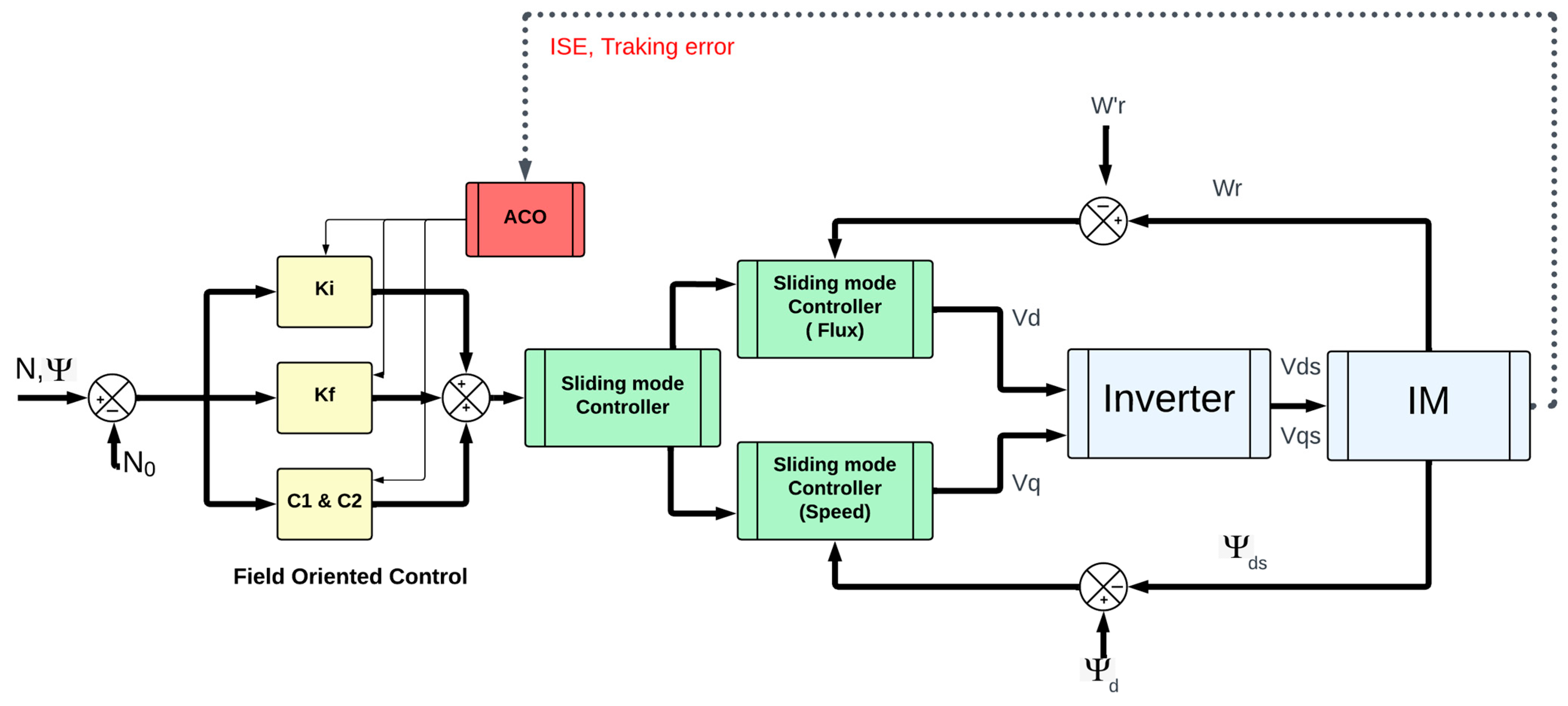
4. Control and Regulation (Closed Loop) Based on Speed and Flux Using Sliding Mode
4.1. Sliding Mode Control
4.2. Flux Regulation
4.3. Speed Regulation
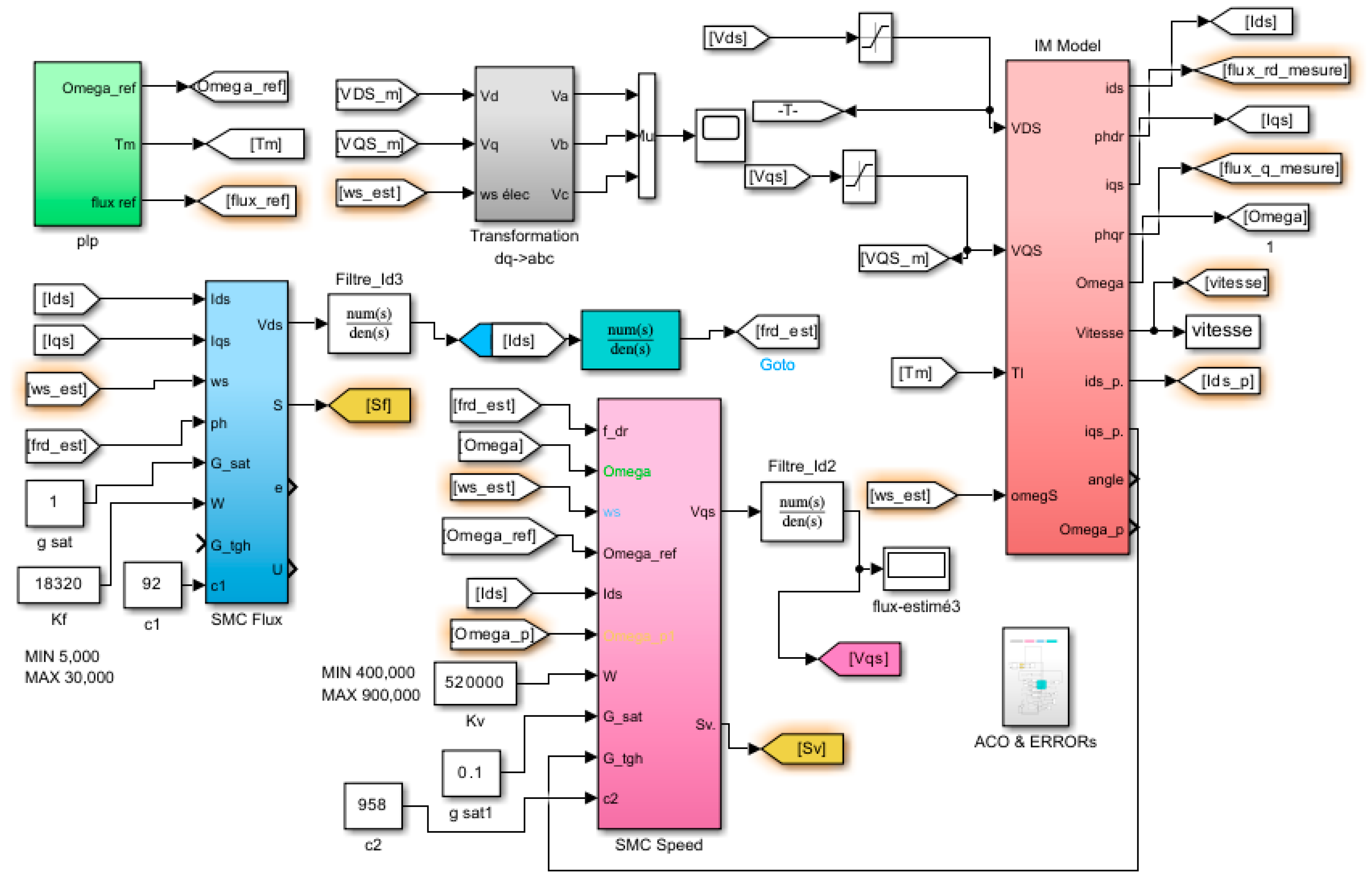
5. Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) for Enhancing Sliding Mode Field-Oriented Control
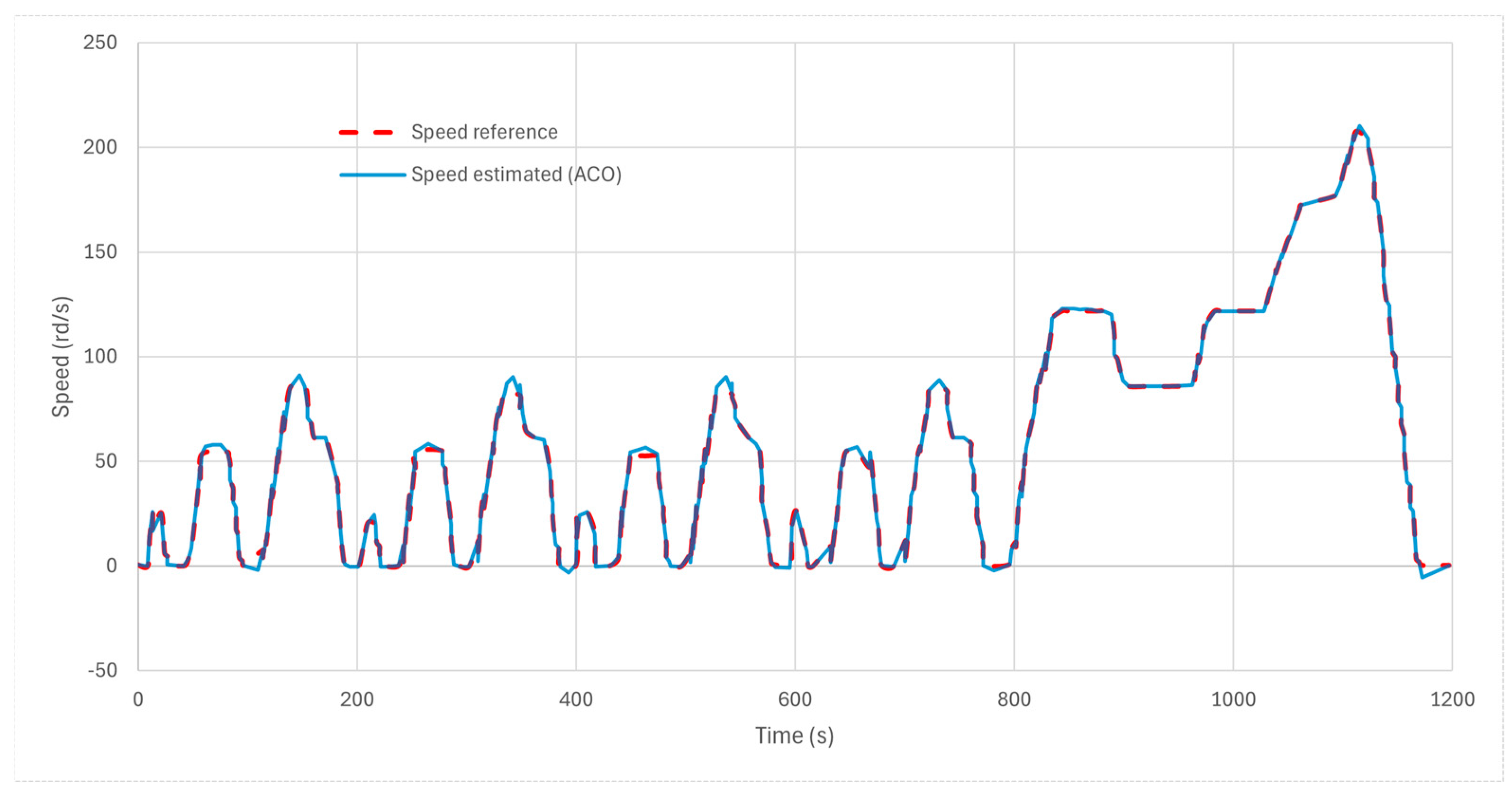
6. New European Driving Cycle
- Urban Driving Cycle (UDC): This segment simulates city driving conditions with low speeds and frequent stops, consisting of four repeated cycles, each lasting 195 s, totaling approximately 780 s.
- Extra-Urban Driving Cycle (EUDC): Following the UDC, this segment represents higher-speed driving conditions typical of suburban or highway scenarios, lasting about 400 s, with vehicle speeds reaching up to 120 km/h.
7. Results
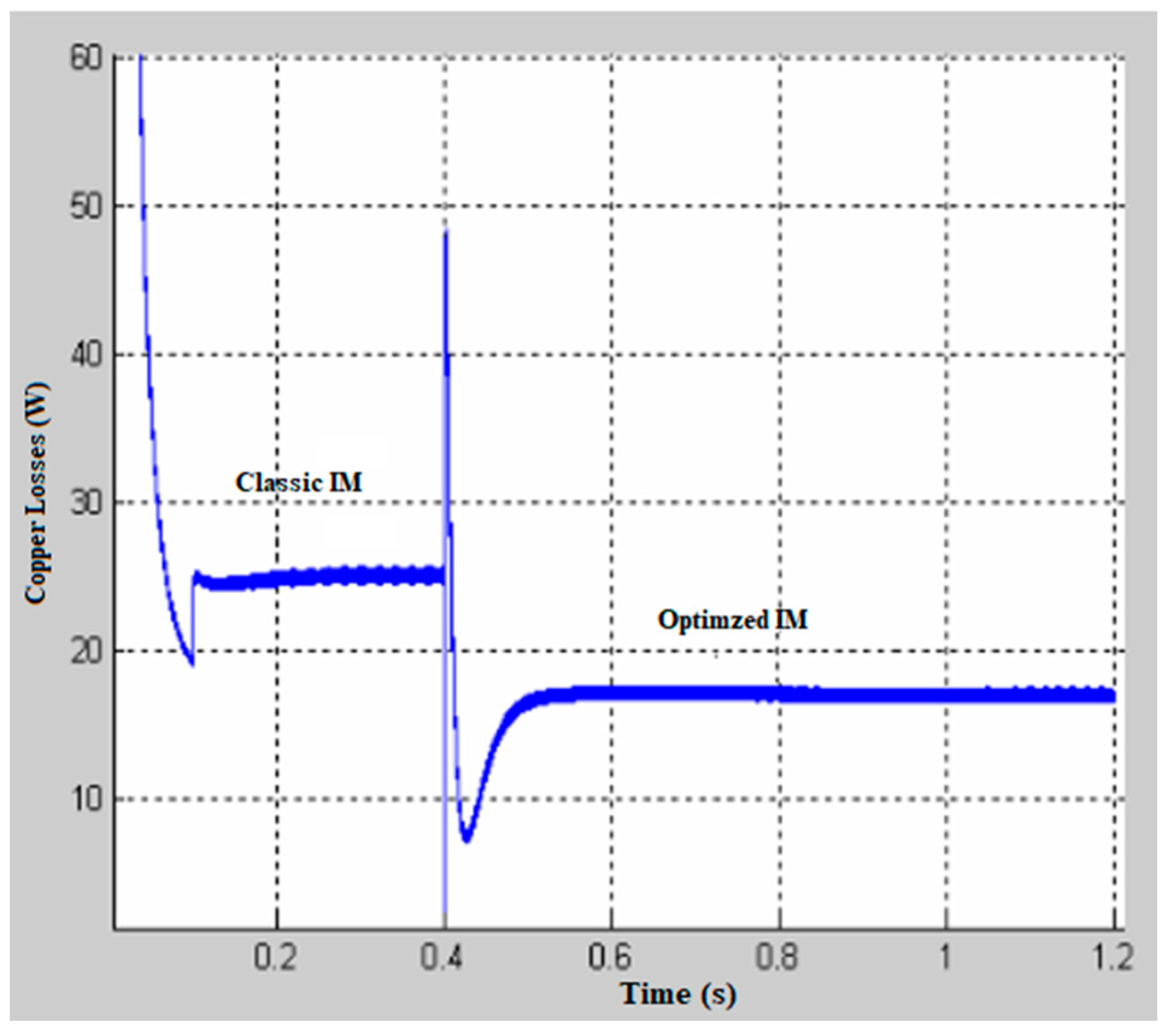
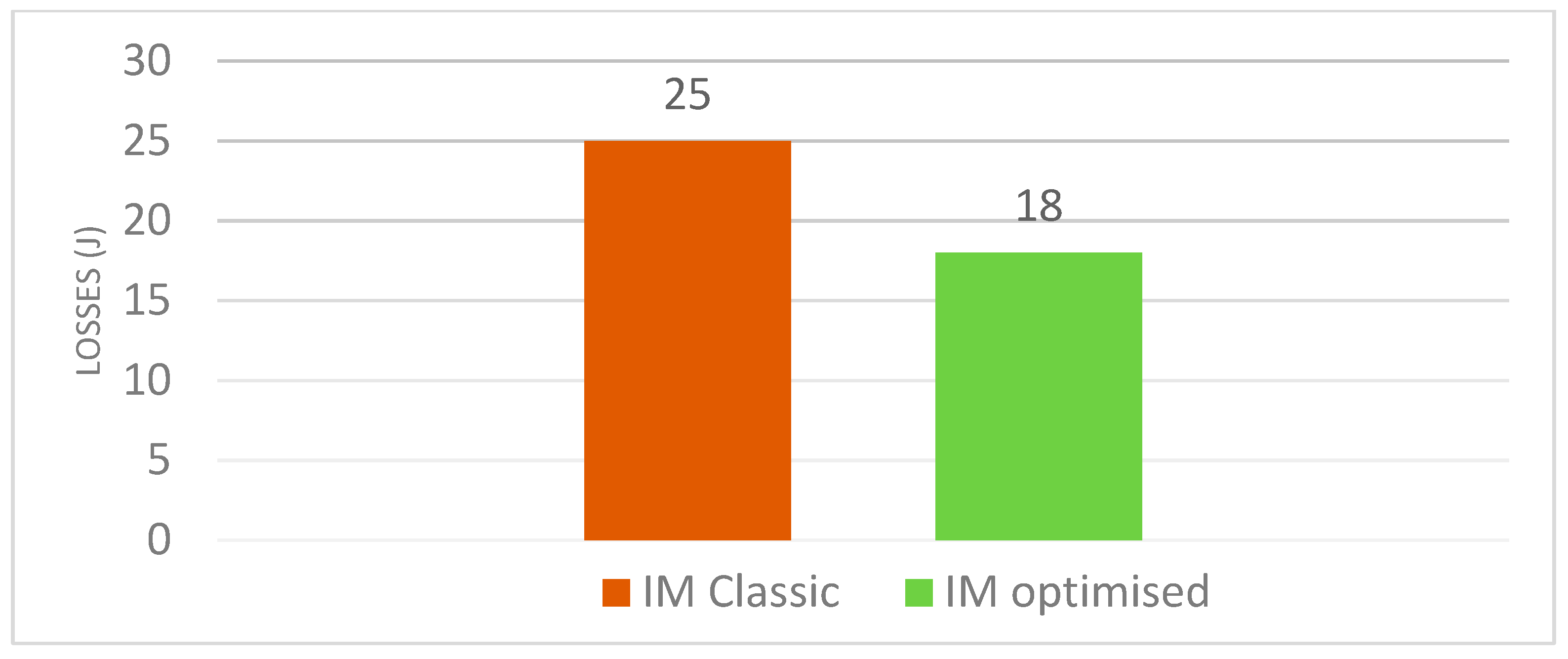
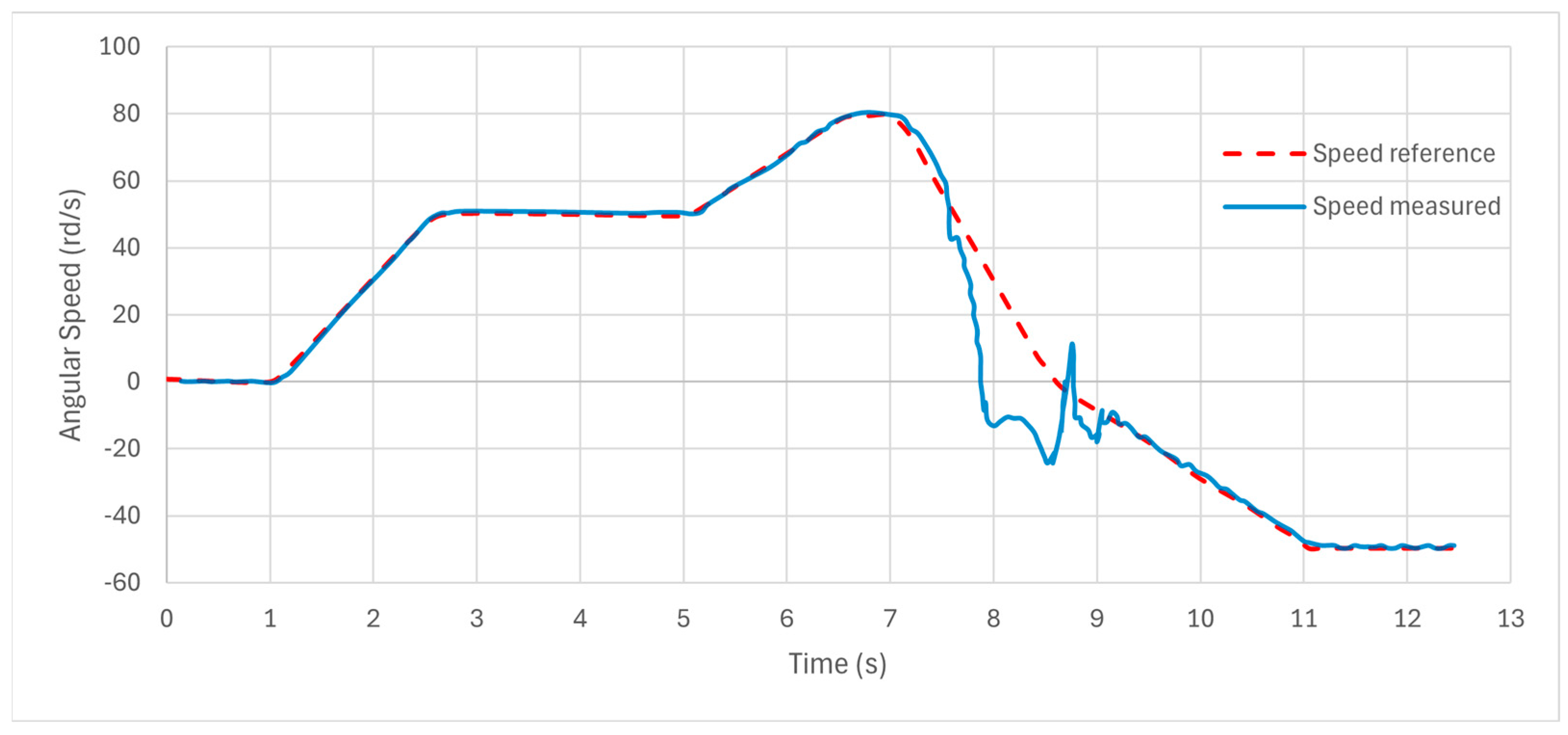
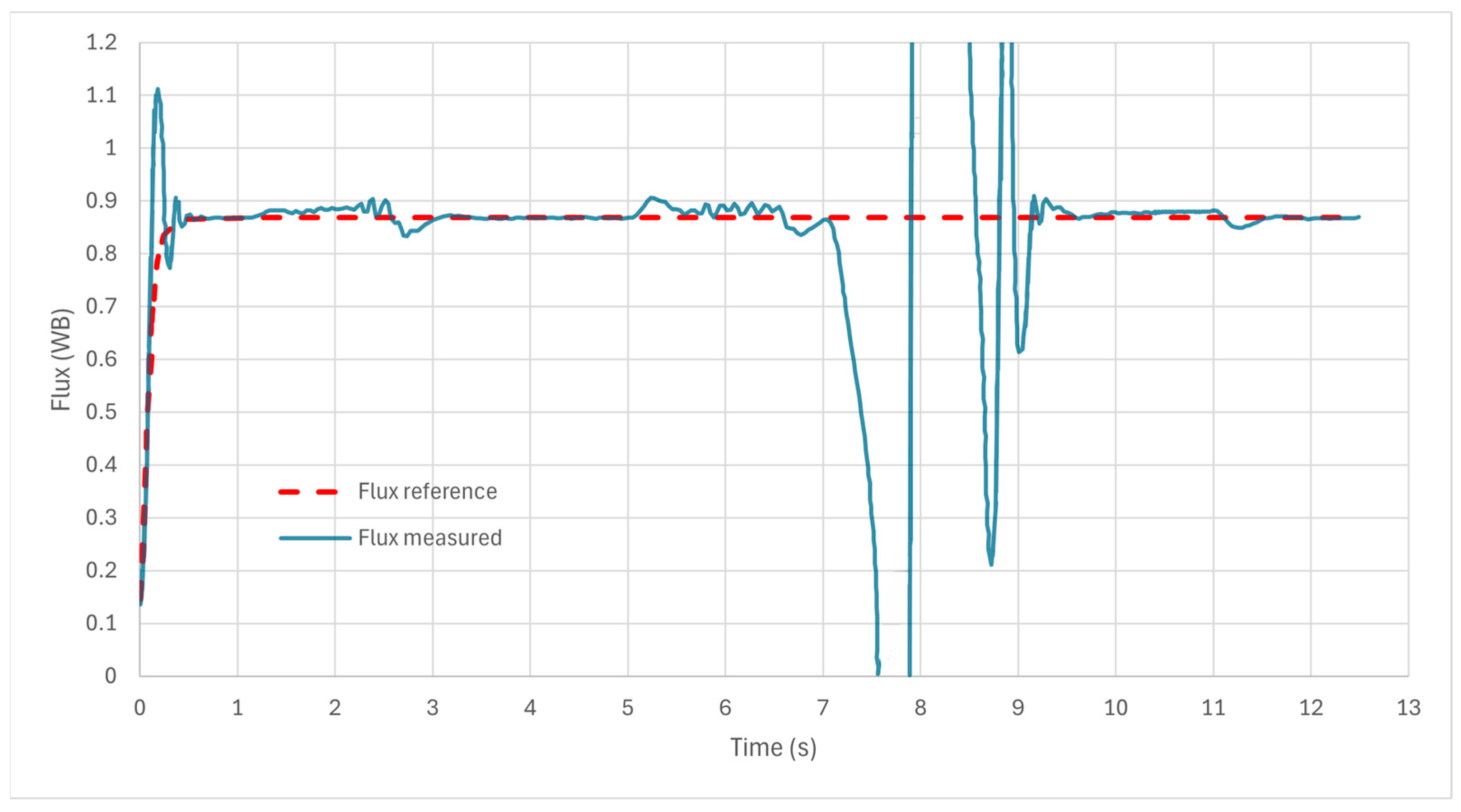
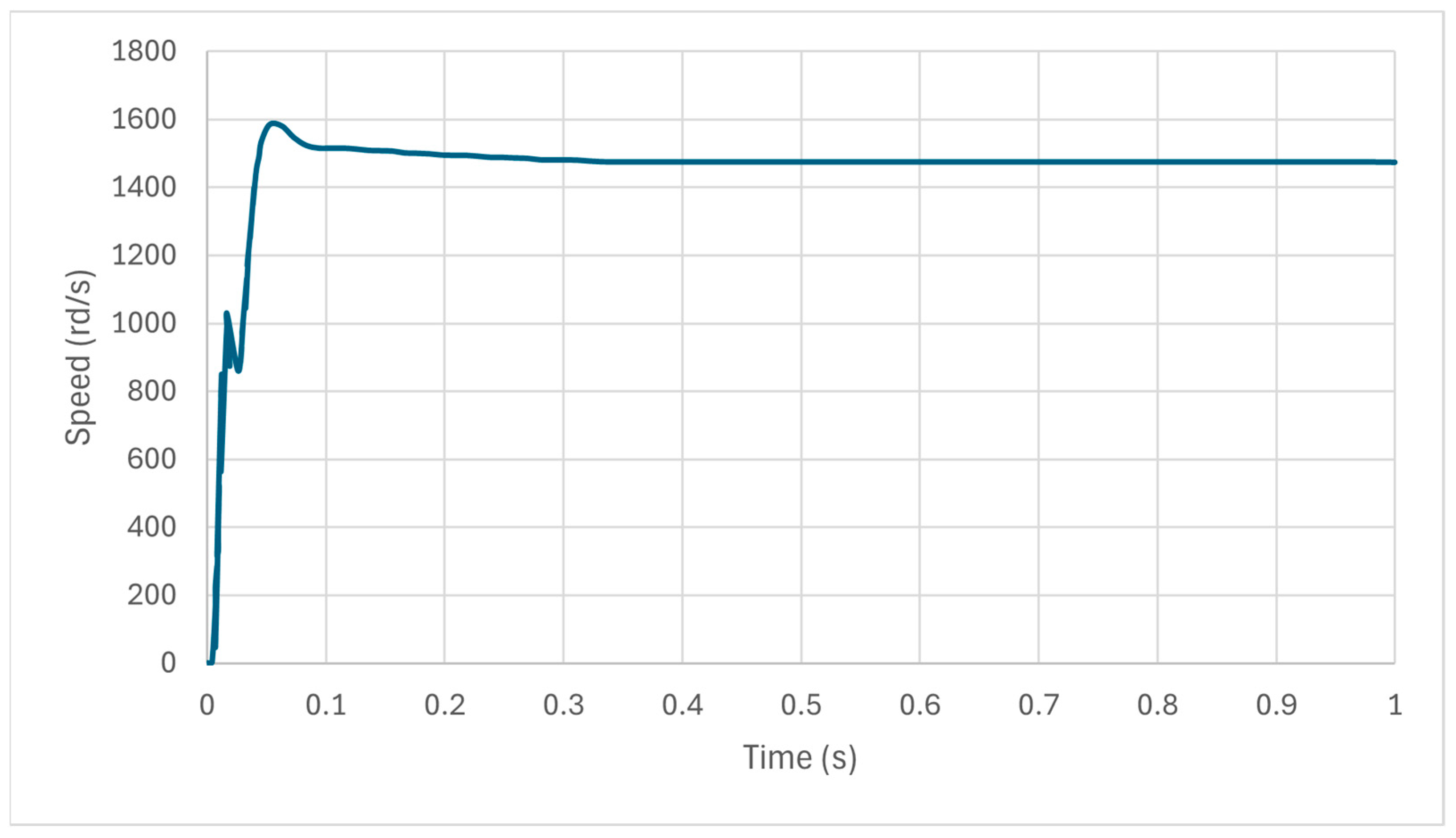
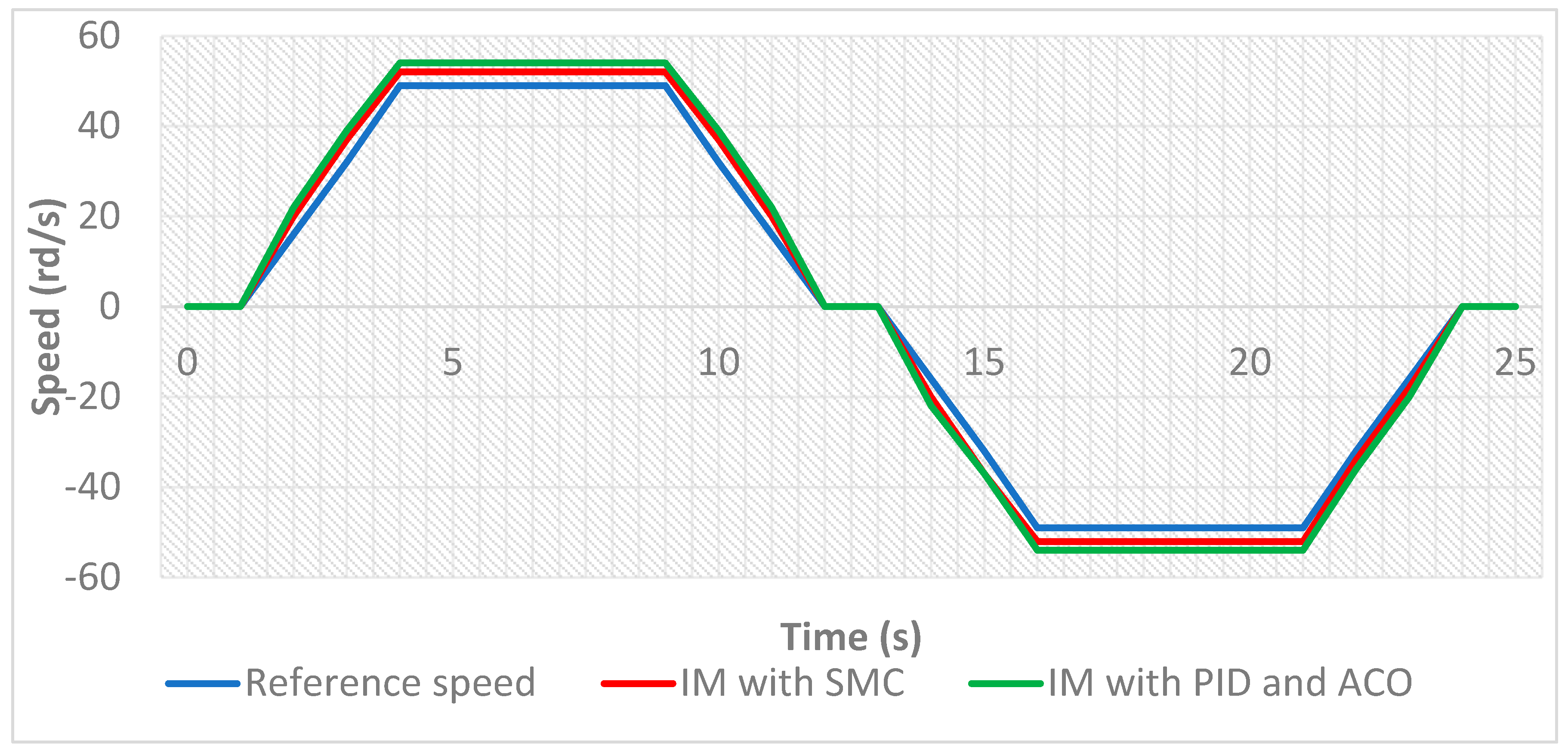
7.1. Simulation Results
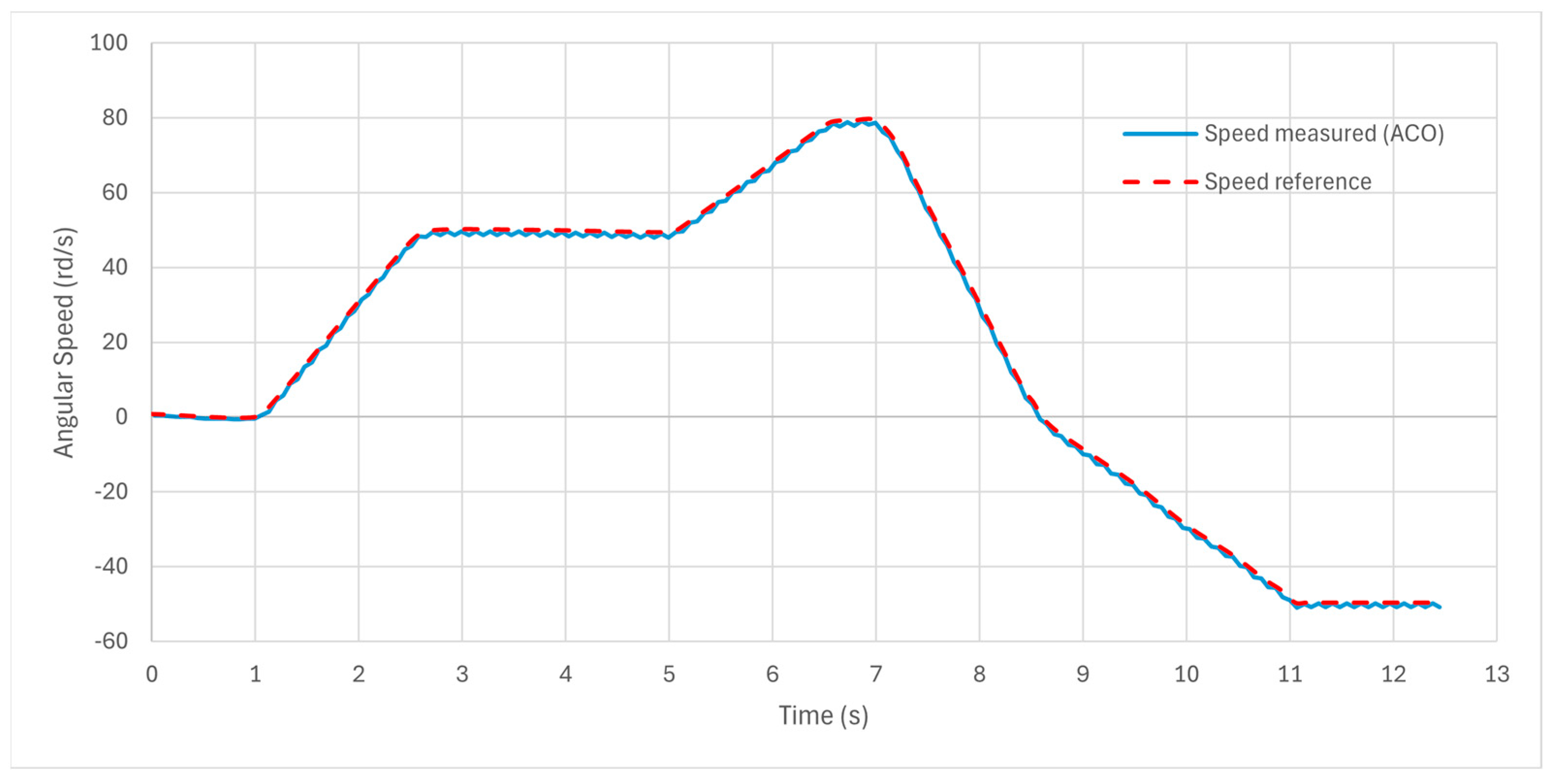
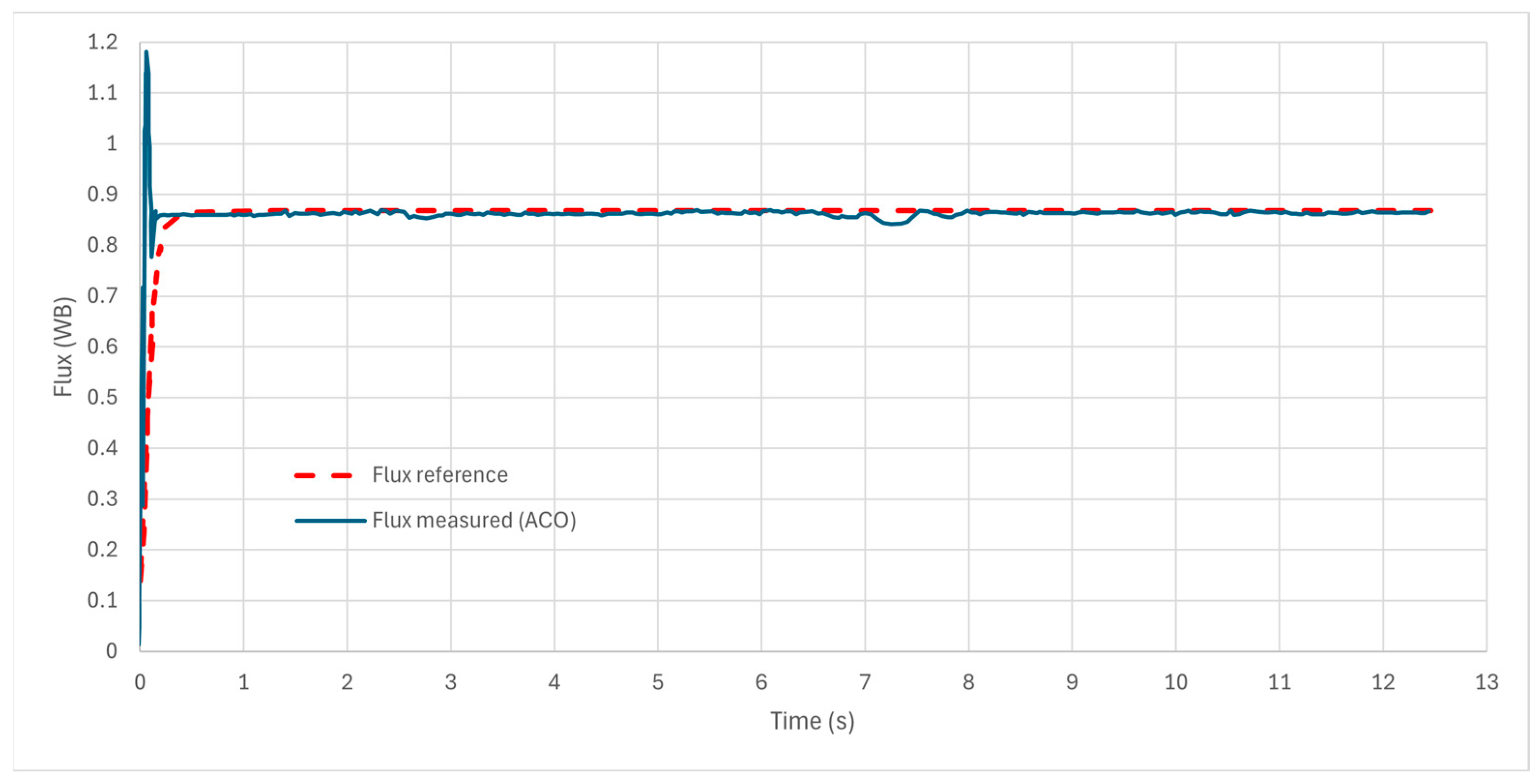
7.2. NEDC Validation
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ehsani, M.; Gao, Y.; Emadi, A. Modern Electric, Hybrid Electric, and Fuel Cell Vehicles: Fundamentals, Theory, and Design, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 105–120. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, A.M.; Tyther, B.; Leahy, P.G.; McKeogh, E.J. Electric vehicles and energy storage—A case study on Ireland. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Dearborn, MI, USA, 7–11 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.Y.; Strunz, K. Electric vehicle battery technologies—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1679–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Vetter, J.; Novak, P.; Wagner, M.R.; Veit, C.; Möller, K.-C.; Besenhard, J.O.; Winter, M.; Wohlfahrt-Mehrens, M.; Vogler, C.; Hammouche, A. Ageing mechanisms in lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 147, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janek, J.; Zeier, W.G. A solid future for battery development. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Feng, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Egardt, B. State estimation for advanced battery management: Key challenges and future trends. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 114, 109334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechmair, D.; Steidl, K. Why the Induction Motor could be the better choice for your electric vehicle program. World Electr. Veh. J. 2012, 5, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Rotor design to reduce secondary winding harmonic loss for induction motors in hybrid electric vehicle applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Milwaukee, WI, USA, 18–22 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Konuhova, M. Induction Motor Dynamics Regimes: A Comprehensive Study of Mathematical Models and Validation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Electric Motor R&D. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/vehicles/articles/electric-motor-rd (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Akhtar, M.J.; Behera, R.K. Optimal design of stator and rotor slot of induction motor for electric vehicle application. IET Electr. Syst. Transp. 2019, 9, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfoli, A.; Di Nardo, M.; Degano, M.; Gerada, C.; Chen, W. Rotor Design Optimization of Squirrel Cage Induction Motor—Part I: Problem Statement. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R. Electric Motor Drives: Modeling, Analysis, and Control; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2001; pp. 262–499. [Google Scholar]
- Holtz, J. Sensorless control of induction machines—With or without signal injection? IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.; Guldner, J.; Shi, J. Sliding Mode Control in Electro-Mechanical Systems, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 159–196. [Google Scholar]
- Hannan, M.; Lipu, M.; Hussain, A.; Mohamed, A. A review of lithium-ion battery state of charge estimation and management system in electric vehicle applications: Challenges and recommendations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 834–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, H. Adaptive sliding mode control of induction motors based on artificial intelligence optimization. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 159711–159722. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S. Evolutionary Algorithms and Neural Networks: Theory and Applications, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 15–55. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, C. Ant colony optimization: Introduction and recent trends. Phys. Life Rev. 2005, 2, 353–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigo, M.; Stützle, T. Ant Colony Optimization, 1st ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 153–204. [Google Scholar]
- Dorigo, M.; Maniezzo, V.; Colorni, A. Ant system: Optimization by a colony of cooperating agents. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 1996, 26, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayoumi, E.H.E.; Soliman, H.M.; Lee, S. Ellipsoidal-Set Design of Robust and Secure Control Against Denial-of-Service Cyber Attacks in Electric-Vehicle Induction Motor Drives. Technologies 2025, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudey, S.K.; Malla, M.; Jasthi, K.; Gampa, S.R. Direct Torque Control of an Induction Motor Using Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Control Technique for Quick Response and Reduced Torque Ripple. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rtibi, W.; Yaich, M.; Hanini, W.; M’barki, L.; Ayadi, M. The Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm Application on the Speed Control of the Electrical Vehicle System Powered by the Five-Level NPC Inverter. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Innovative Research in Applied Science, Engineering and Technology (IRASET), Meknes, Morocco, 12–13 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Azab, M. A Review of Recent Trends in High-Efficiency Induction Motor Drives. Vehicles 2025, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rihar, A.; Nemec, M.; Lavrič, H.; Zajec, P.; Vončina, D.; Nedeljković, D.; Ambrožič, V.; Drobnič, K. Emerging Technologies for Advanced Power Electronics and Machine Design in Electric Drives. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamoussi, K.; El Hajjaji, A.; Ouali, M. Robust Sliding Mode Control Using Adaptive Switching Gain for Induction Motors. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2013, 10, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamoussi, K.; Chadli, M.; El Hajjaji, A.; Ouali, M. Robust Fuzzy Sliding Mode Observer for an Induction Motor. J. Electr. Eng. Theory Appl. 2010, 1, 42–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ryvkin, S.; Schmidt-Oberm, R.; Steimel, A. Sliding Mode Control Technique for an Induction Motor Drive Supplied by a Three-Level Voltage Source Inverter. Ser. Elec. Energ. 2008, 21, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhieb, Y.; Yaich, M.; Guermazi, A.; Ghariani, M. PID Controller Tuning using Ant Colony Optimization for Induction Motor. J. Electr. Syst. 2019, 15, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Borzabadi, A.H.; Mehne, H.H. Ant Colony Optimization for Optimal Control Problems. Sci. J. 2009, 4, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Spotvin, M.J.-Y. Ant Colony Optimization: Overview and Recent Advances. In Handbook of Metaheuristics, 3rd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 311–352. [Google Scholar]
- Kanthi Mathew, K.; Abraham, D.M.; Harish, A. Speed regulation of PMSM drive in electric vehicle applications with sliding mode controller based on harris Hawks optimization. e-Prime Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2024, 9, 100643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendjedia, M.; Tehrani, K.A.; Azzouz, Y. Design of RST and fractional order PID controllers for an induction motor drive for electric vehicle application. In Proceedings of the 7th IET International Conference on Power Electronics, Machines and Drives (PEMD 2014), Manchester, UK, 8–10 April 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzirakis, E.; Pitsas, K.; Zannikos, F.; Stournas, S. Vehicle emissions and driving cycles: Comparison of the Athens Driving Cycle (ADC) with ECE-15 and European Driving Cycle (EDC). Glob. NEST J. 2006, 8, 282–290. [Google Scholar]
- Safdari, M.; Ahmadi, R.; Sadeghzadeh, S. Numerical and experimental investigation on electric vehicles battery thermal management under New European Driving Cycle. Appl. Energy 2022, 315, 119026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawieh, H.; Tehrani, K.A.; Azzouz, Y.; Dakyo, B. A new active common-mode voltage elimination method for three-Level Neutral-Point Clamped inverters. In Proceedings of the IECON 2014—40th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Dallas, TX, USA, 29 October–1 November 2014; pp. 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

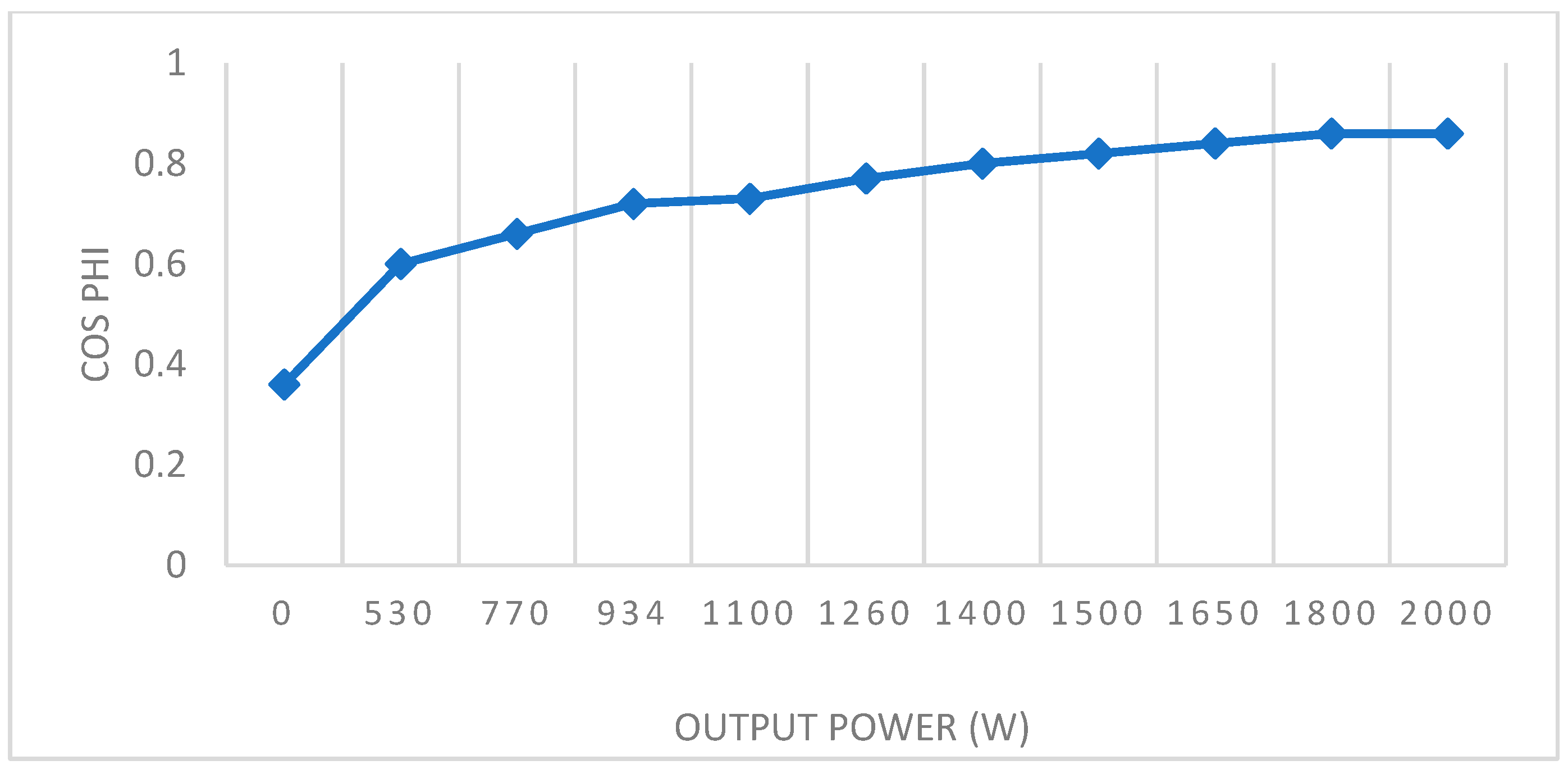
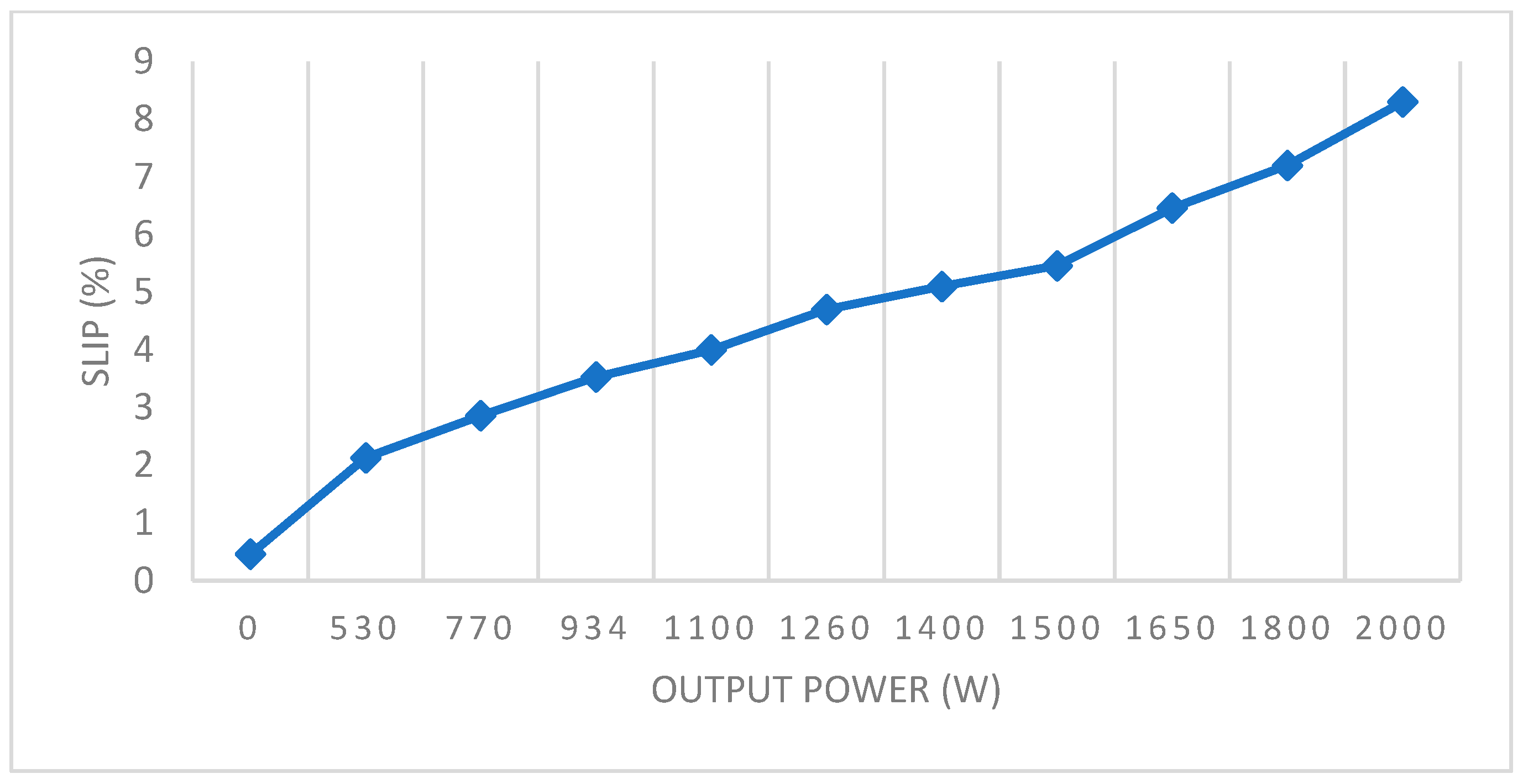

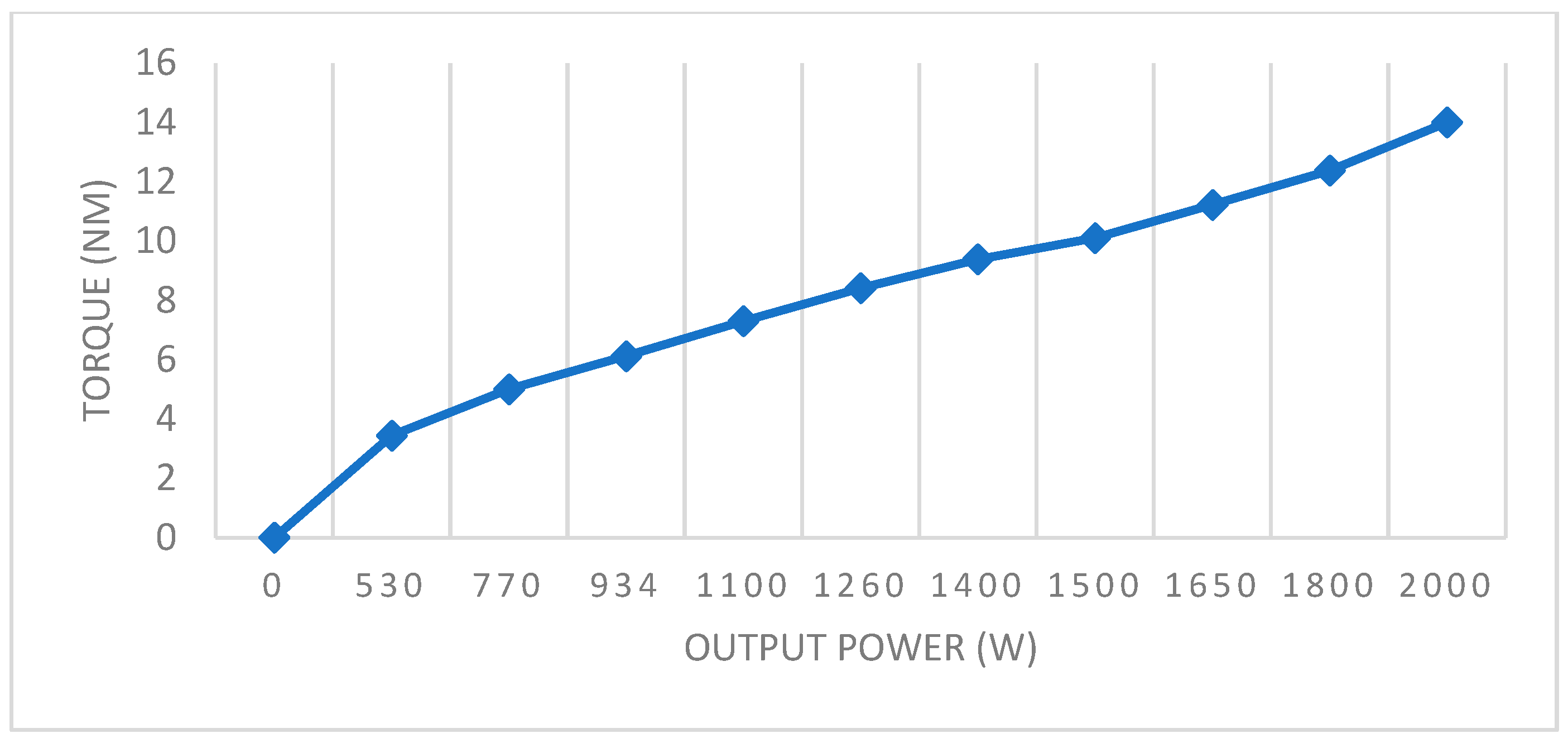
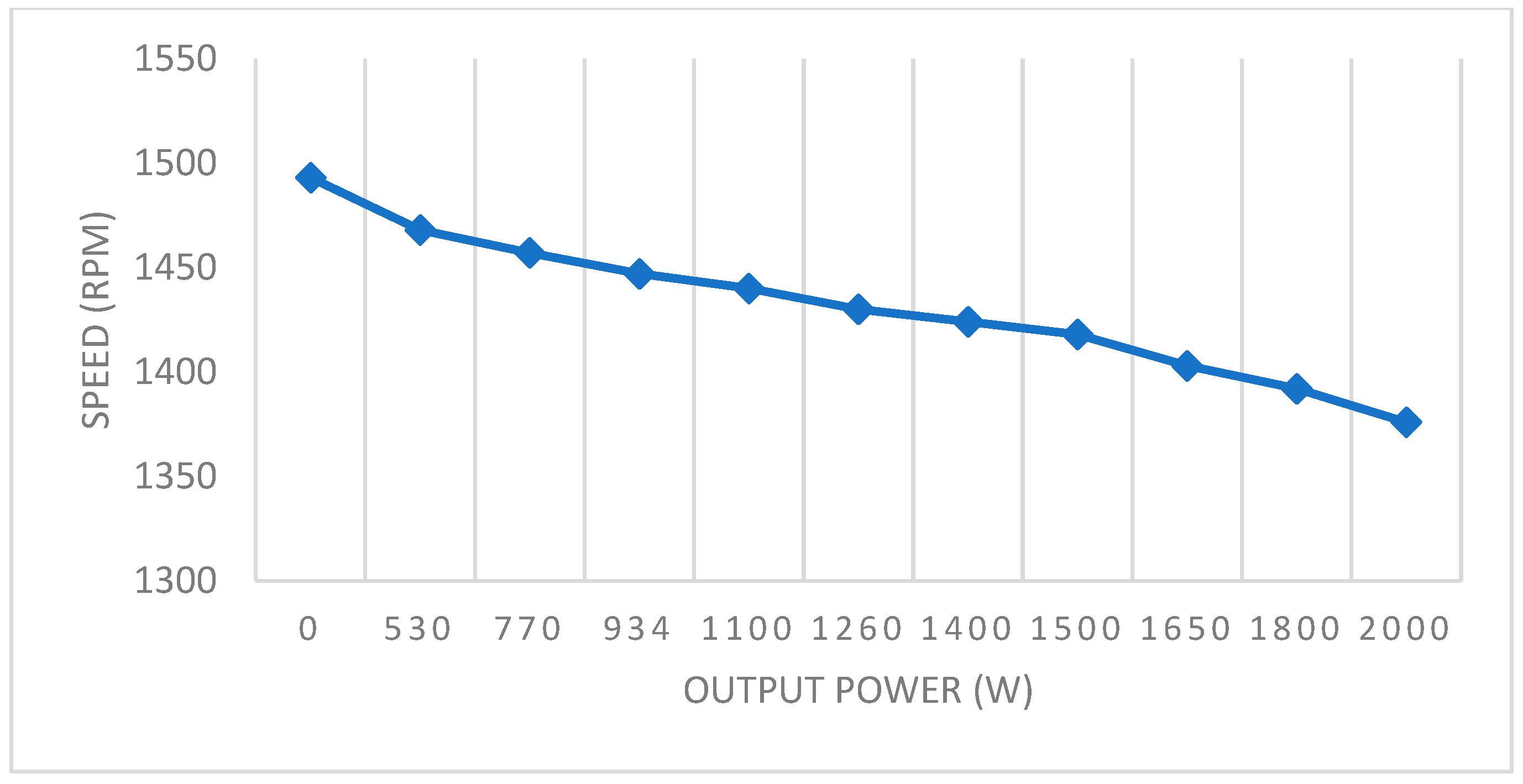

| Nominal Speed (rpm) | Rr (Ω) | Rs (Ω) | Lr (mH) | Ls (mH) | Lm (mH) | J (kg·m2) | P (pairs) | Power (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1479 | 4.2 | 5.72 | 461 | 462 | 460 | 0.015 | 2 | 1800 |
| Nominal Speed (rpm) | Rr (Ω) | Rs (Ω) | Lr (mH) | Ls (mH) | Lm (mH) | J (kg·m2) | P (pairs) | Power (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1479 | 4.2 | 5.72 | 460.04 | 462.05 | 53.1 | 0.0015 | 2 | 1800 |
| Parameters | Manual Tuning | ACO Tuning |
|---|---|---|
| 100,000 | 520,000 | |
| 3000 | 18,320 | |
| 10 | 92 | |
| 1200 | 958 | |
| ISE (Speed) | 970 | 2.535 |
| ISE (Flux) | 7.729 | 0.0314 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the World Electric Vehicle Association. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhieb, Y.; Ayadi, W.; Malik, F.H.; Ambramoli, S.; Alkhatib, F.; Ghariani, M. Sliding Mode Controller Tuning Using Nature-Inspired Optimization for Induction Motor: EV Application. World Electr. Veh. J. 2025, 16, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16100559
Dhieb Y, Ayadi W, Malik FH, Ambramoli S, Alkhatib F, Ghariani M. Sliding Mode Controller Tuning Using Nature-Inspired Optimization for Induction Motor: EV Application. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2025; 16(10):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16100559
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhieb, Youssef, Walid Ayadi, Farhan Hameed Malik, Soumya Ambramoli, Fawwaz Alkhatib, and Moez Ghariani. 2025. "Sliding Mode Controller Tuning Using Nature-Inspired Optimization for Induction Motor: EV Application" World Electric Vehicle Journal 16, no. 10: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16100559
APA StyleDhieb, Y., Ayadi, W., Malik, F. H., Ambramoli, S., Alkhatib, F., & Ghariani, M. (2025). Sliding Mode Controller Tuning Using Nature-Inspired Optimization for Induction Motor: EV Application. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 16(10), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj16100559







