Smooth Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Using Back Propagation Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
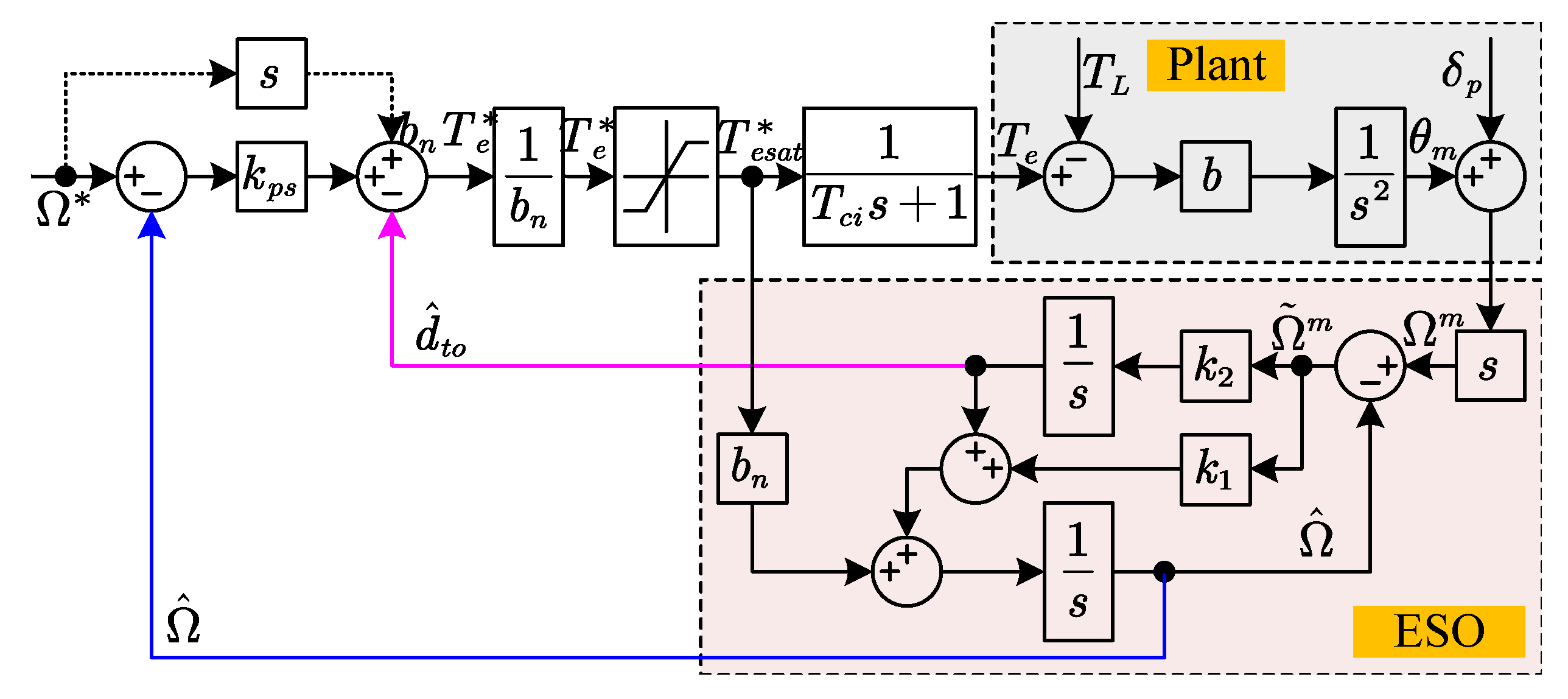
2.1. ESO-Based ADR Controller
2.1.1. Modelling of PMSM Mechanical Dynamics
2.1.2. Speed Controller Design
2.1.3. Speed and Disturbance Observation
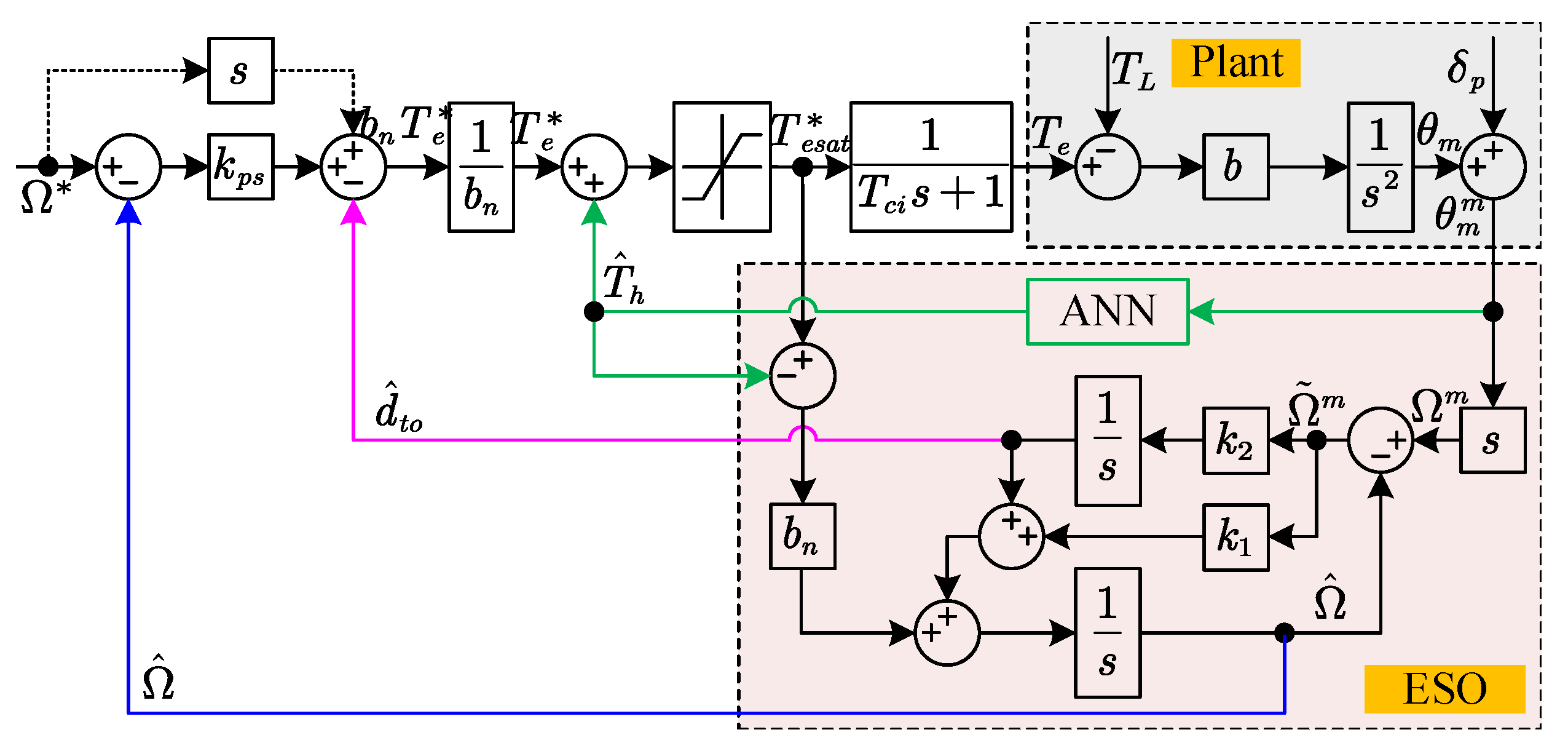
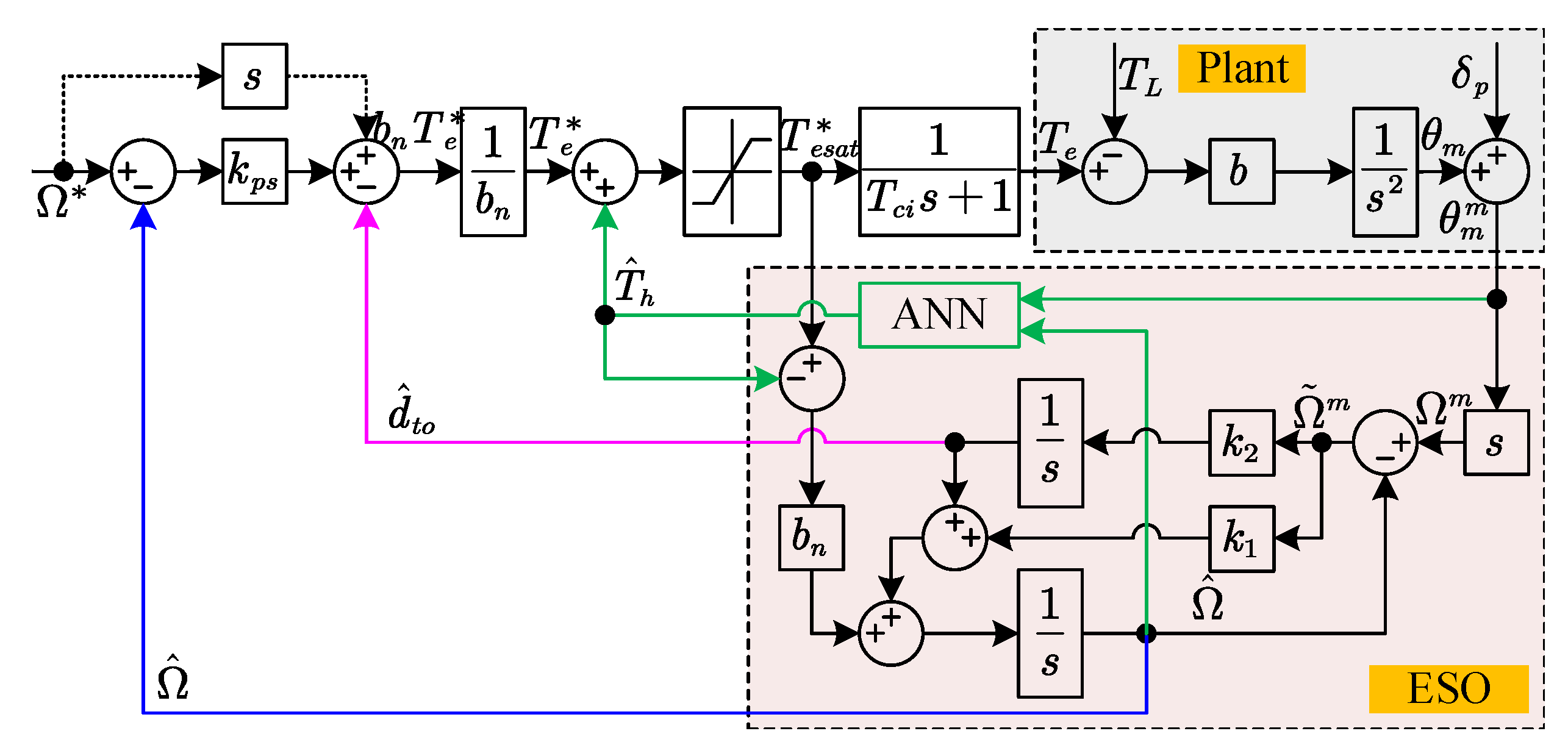
2.2. Torque Ripple Suppression Using Neural Network
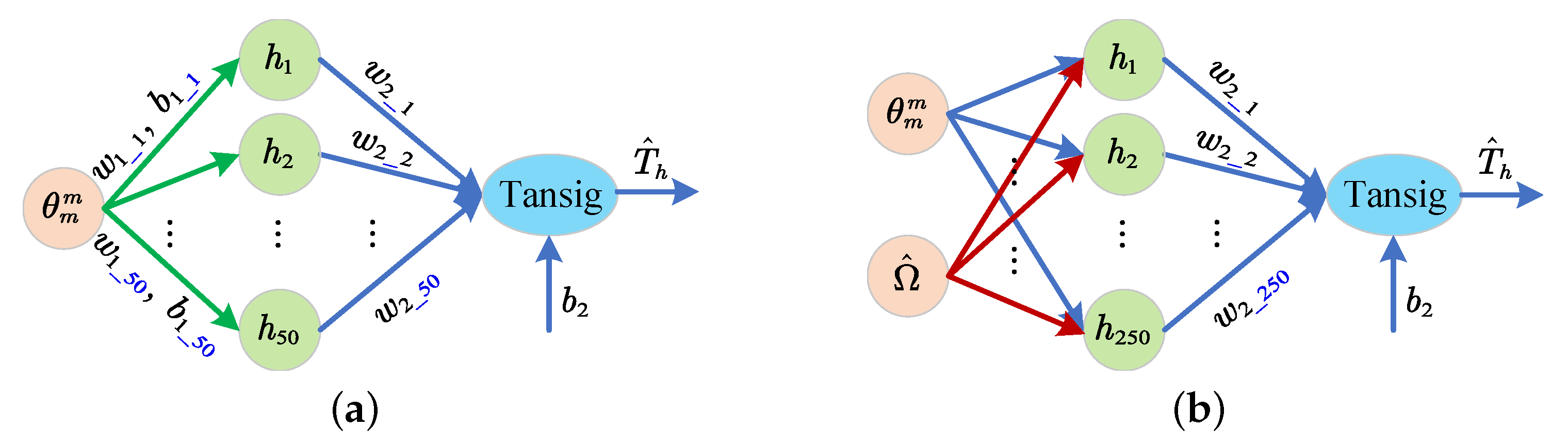
2.2.1. Structure of the Neural Network
2.2.2. Training Algorithm of Neural Network
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Test Bench Setup
3.2. Experimental Verification
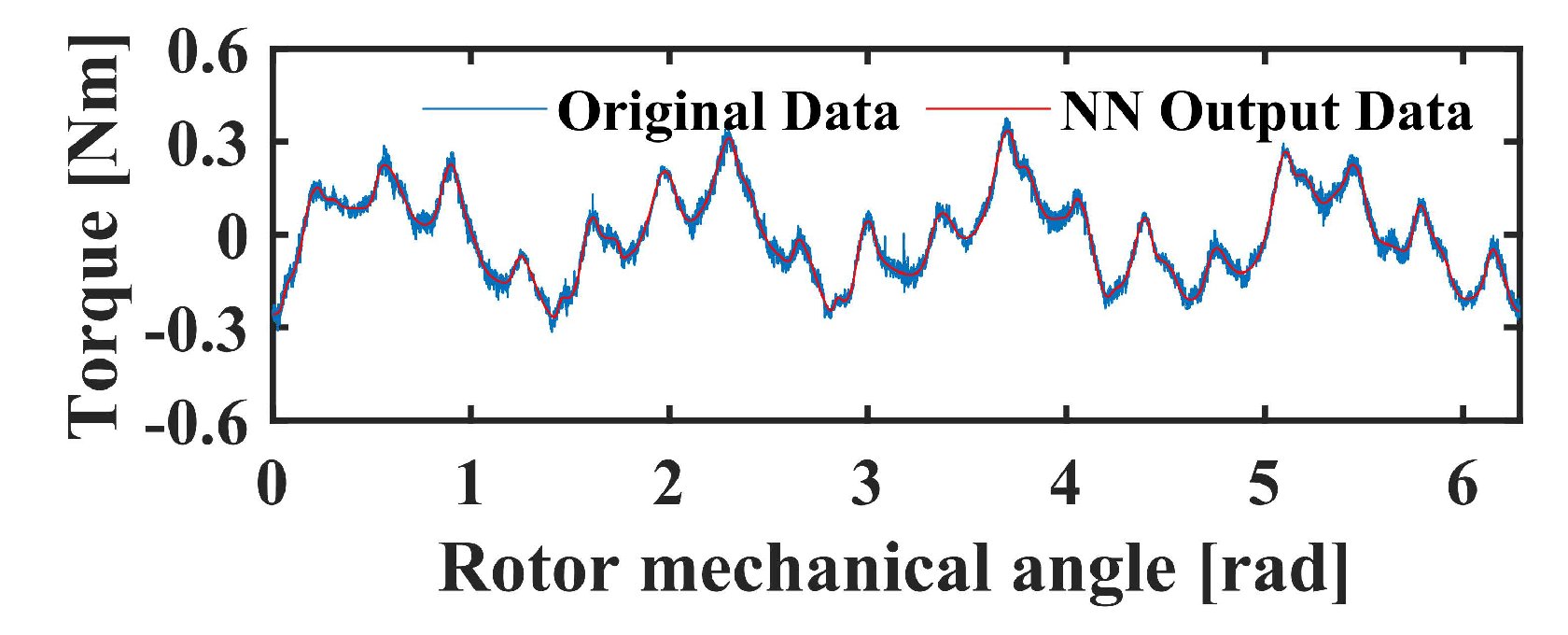
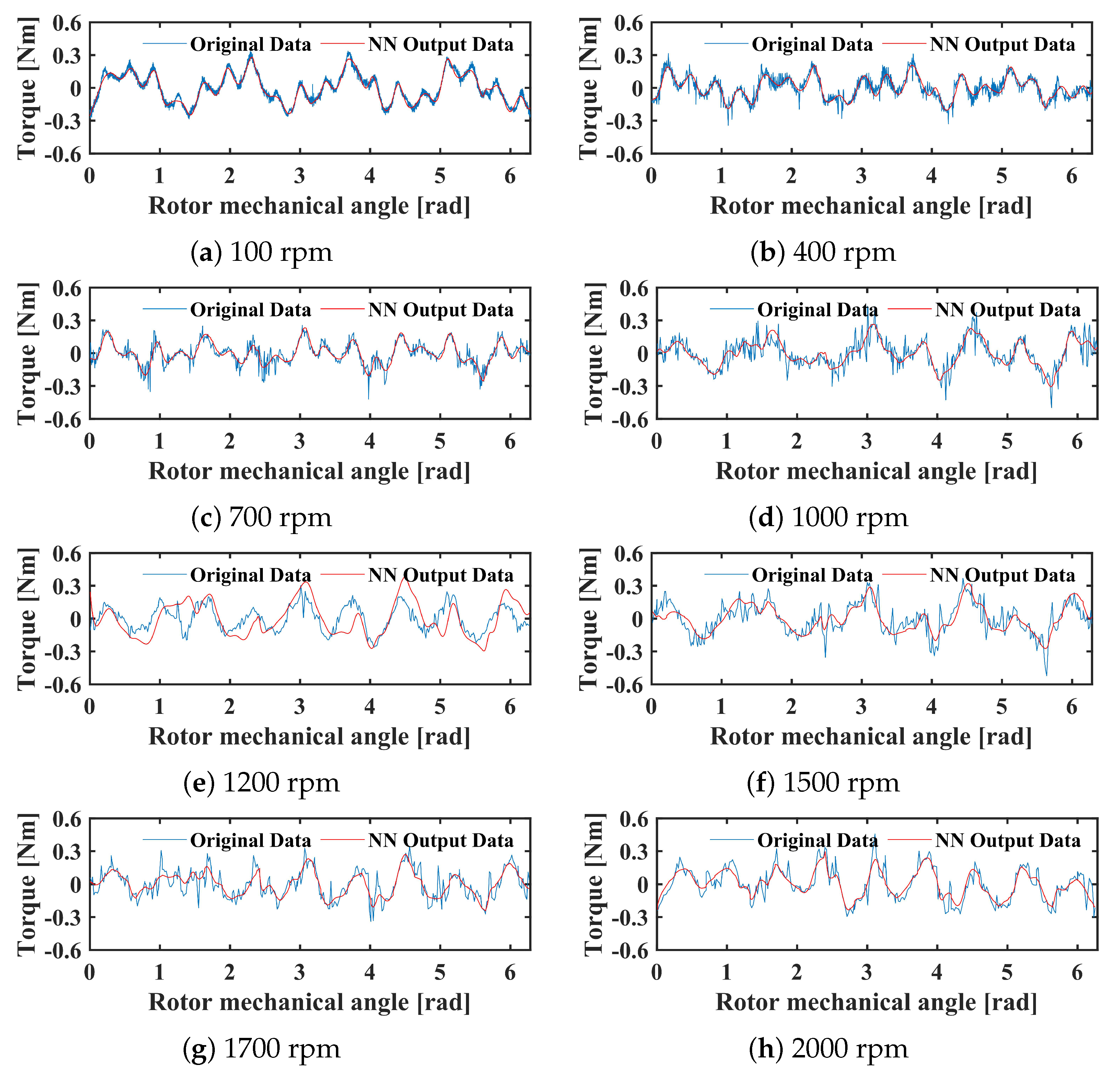
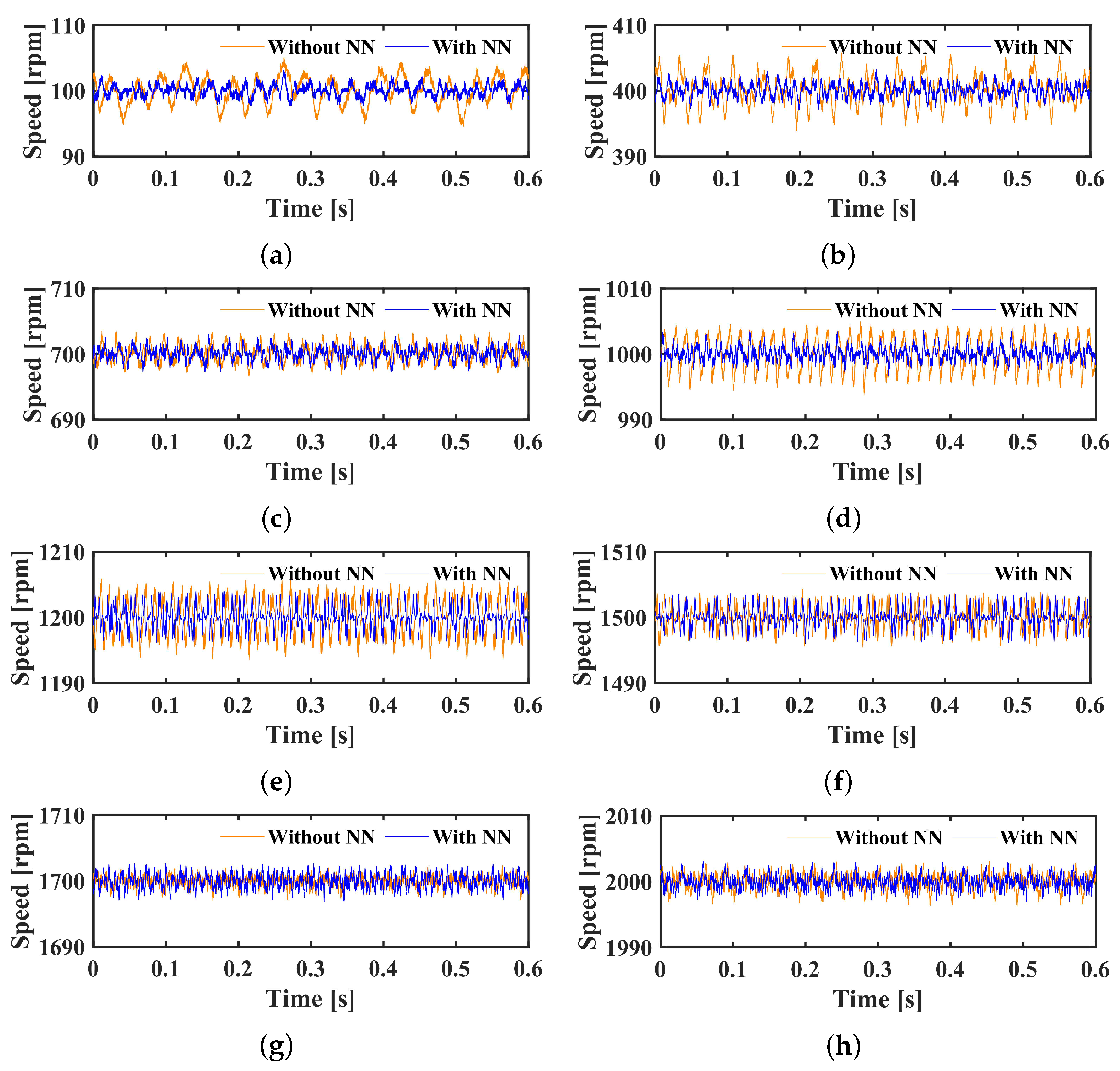
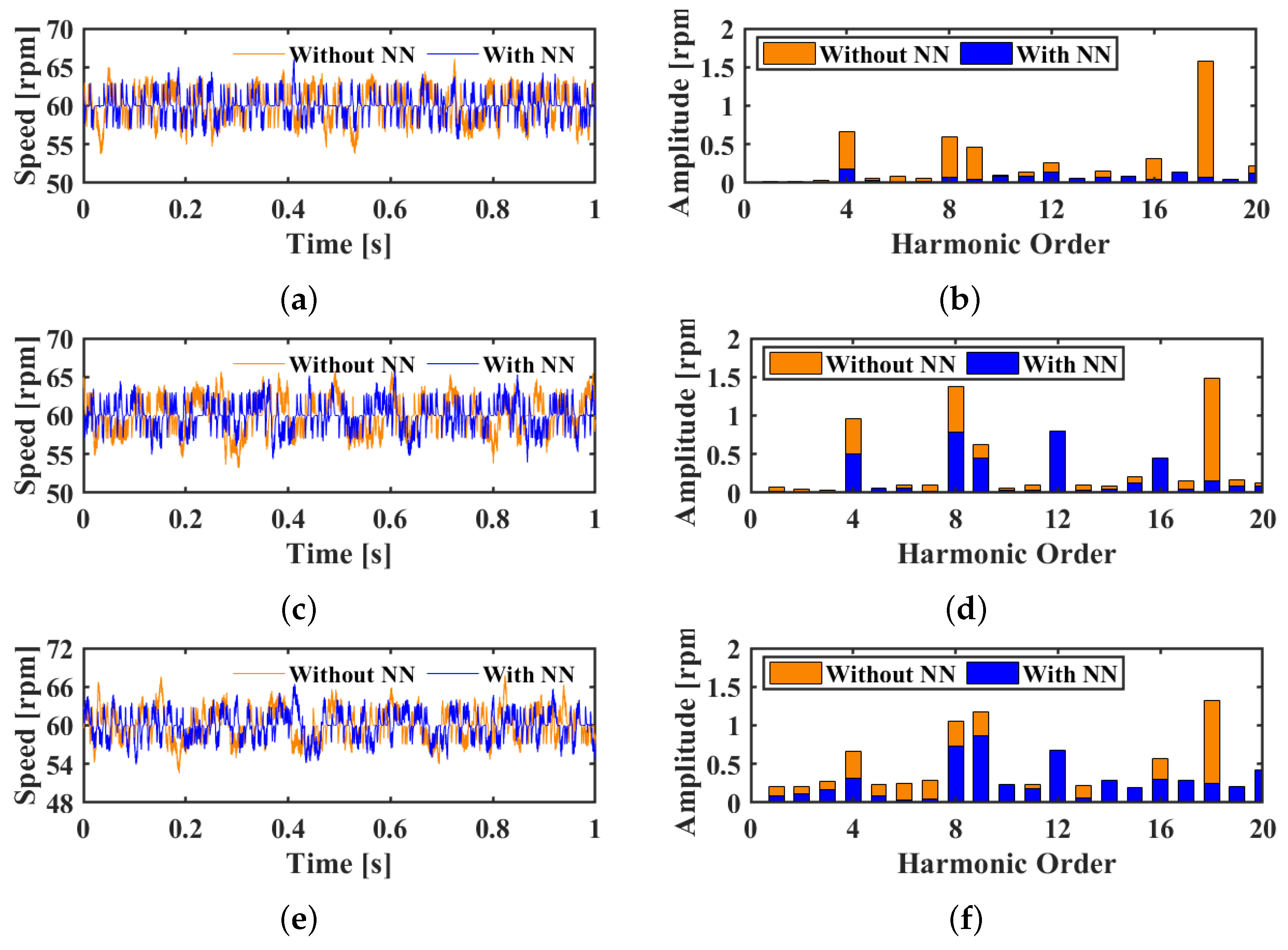
3.2.1. Performance of the NN-ESO-ADRC with Single Input
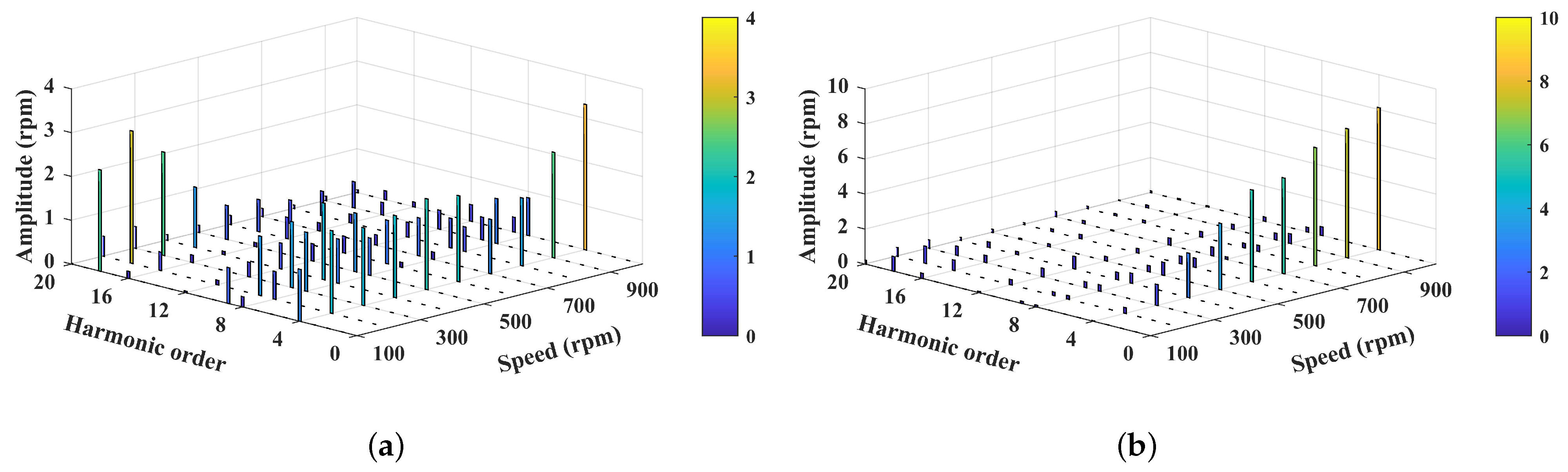
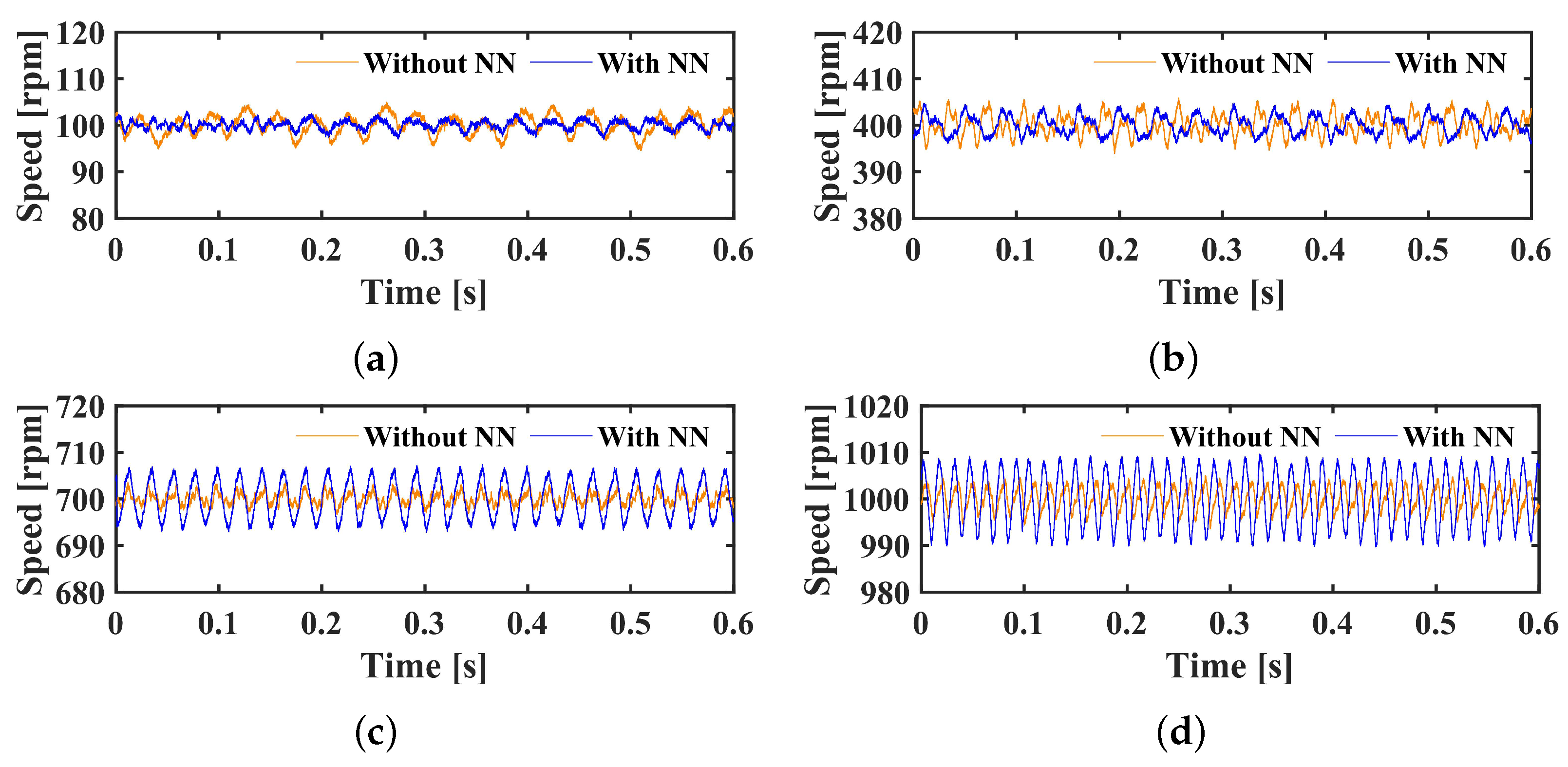
3.2.2. Performance of the NN-ESO-ADRC with Double Inputs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, S.; Kirtley, J.L.; Lee, C.H.T. Critical Review of Direct-Drive Electrical Machine Systems for Electric and Hybrid Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2022, 37, 2657–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, R. Comprehensive Analysis and Reduction of Torque Ripples in Three-Phase Four-Switch Inverter-Fed PMSM Drives Using Space Vector Pulse-Width Modulation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 5411–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtz, J.; Springob, L. Identification and Compensation of Torque Ripple in High-Precision Permanent Magnet Motor Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1996, 43, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houari, A.; Bouabdallah, A.; Djerioui, A.; Machmoum, M.; Auger, F.; Darkawi, A.; Olivier, J.-C.; Benkhoris, M.F. An Effective Compensation Technique for Speed Smoothness at Low-Speed Operation of PMSM Drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appli. 2018, 54, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abosh, A.H.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Ren, Y. Reduction of Torque and Flux Ripples in Space Vector Modulation-Based Direct Torque Control of Asymmetric Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2976–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güemes, J.A.; Iraolagoitia, A.M.; Del Hoyo, J.I.; Fernández, P. Torque Analysis in Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors: A Comparative Study. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2011, 26, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; An, Q.-T.; Duan, J.-D.; Semenov, D.; Sun, D.-Y.; Sun, L. Cancellation of Torque Ripples With FOC Strategy Under Two-Phase Failures of the Five-Phase PM Motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 5459–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Feng, G.; Mukherjee, K.; Kar, N.C. Investigations of the Influence of PMSM Parameter Variations in Optimal Stator Current Design for Torque Ripple Minimization. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Bin, H.; Gong, L.M. Current Harmonics Suppression Strategy for PMSM With Nonsinusoidal Back-EMF Based on Adaptive Linear Neuron Method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 9164–9173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, N.; Akatsu, K. Suppressing Pulsating Torques: Torque Ripple Control for Synchronous Motors. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2014, 20, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.A. Salient Pole Shoe Shapes of Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines. In Proceedings of the XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM 2010), Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, H.; Deng, Y. Torque Ripple Minimization of PMSM Based on Robust ILC Via Adaptive Sliding Mode Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 3655–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wu, J.; Lei, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J. Torque Ripple Reduction of SRM Drive Using Improved Direct Torque Control with Sliding Mode Controller and Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 9334–9345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Lee, C.H.T. Different Active Disturbance Rejection Controllers Based on the Same Order GPI Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 10969–10983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Gaeta, A.; Formentini, A.; Zanchetta, P. A Fractional Delay Variable Frequency Repetitive Control for Torque Ripple Reduction in PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 5553–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Formentini, A.; Odhano, S.A.; Zanchetta, P. Torque Ripple Reduction of PMSMs Using a Novel Angle-Based Repetitive Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 2689–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Zhang, P.; Jatskevich, J.; Zhang, C. Torque Ripple Reduction of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives Based on Novel Speed Harmonic Control at Low-Speed Operation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 70, 7683–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Lai, C.; Kar, N.C. A Closed-Loop Fuzzy-Logic-Based Current Controller for PMSM Torque Ripple Minimization Using the Magnitude of Speed Harmonic as the Feedback Control Signal. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2642–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Jatskevich, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S. Torque Ripple Reduction Method for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Drives With Novel Harmonic Current Control. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2502–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.; Feng, G.; Mukherjee, K.; Loukanov, V.; Kar, N.C. Torque Ripple Modeling and Minimization for Interior PMSM Considering Magnetic Saturation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 2417–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Lai, C.; Tan, X.; Wang, B.; Kar, N.C. Optimal Current Modeling and Identification for Fast and Efficient Torque Ripple Minimization of PMSM Using Theoretical and Experimental Models. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 11806–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, P.H.; Flieller, D.; Nguyen, N.K.; Mercklé, J.; Sturtzer, G. Torque Ripple Minimization in Non-Sinusoidal Synchronous Reluctance Motors Based on Artificial Neural Networks. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2016, 140, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieller, D.; Nguyen, N.K.; Wira, P.; Sturtzer, G.; Abdeslam, D.O.; Merckle, J. A Self-Learning Solution for Torque Ripple Reduction for Nonsinusoidal Permanent-Magnet Motor Drives Based on Artificial Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattavelli, P.; Tubiana, L.; Zigliotto, M. Torque-Ripple Reduction in PM Synchronous Motor Drives Using Repetitive Current Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-J.; Kwon, Y.-C.; Sul, S.-K. Torque Ripple-Minimizing Control of IPMSM With Optimized Current Trajectory. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 3852–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, E.B.; Elsheikh, A. Predicting Characteristics of Dissimilar Laser Welded Polymeric Joints Using a Multi-Layer Perceptrons Model Coupled with Archimedes Optimizer. Polymers 2023, 15, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheikh, A.H. Applications of Machine Learning in Friction Stir Welding: Prediction of Joint Properties, Real-Time Control and Tool Failure Diagnosis. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 121, 105961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A.H.; El-Said, E.M.S.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Fujii, M.; El-Tahan, H.R. Water Distillation Tower: Experimental Investigation, Economic Assessment, and Performance Prediction Using Optimized Machine-Learning Model. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 388, 135896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshaim, A.B.; Moustafa, E.B.; Bafakeeh, O.T.; Elsheikh, A.H. An Optimized Multilayer Perceptrons Model Using Grey Wolf Optimizer to Predict Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Friction Stir Processed Aluminum Alloy Reinforced by Nanoparticles. Coatings 2021, 11, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsheikh, A. Bistable Morphing Composites for Energy-Harvesting Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, W.; Xie, S.; Zhu, X.; Chen, W.-H.; Lee, C.H.T. Active Disturbance Rejection Controller for Smooth Speed Control of Electric Drives Using Adaptive Generalized Integrator Extended State Observer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 4323–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, Z.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Ombach, G. Influence of Electric Loading and Magnetic Saturation on Cogging Torque, Back-EMF and Torque Ripple of PM Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2650–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Symbol | Quantity | Symbol | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated power | 0.75 (kW) | PolePair numbers | 4 |
| Rated voltage | 220 (V) | D axis inductance | 5.7 (mH) |
| Rated speed | 3000 (rpm) | Q axis inductance | 5.7 (mH) |
| Rated torque | 2.4 (Nm) | Torque constant | 0.553 (Nm/A) |
| Current limit | 9 (A) | Motor inertia J | 1.62 () |
| Stator resistance | 1.1 (Ohm) | Motor system inertia | 4.44 () |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, C.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, H.; Hou, Q.; Lee, C.H.T. Smooth Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Using Back Propagation Neural Network. World Electr. Veh. J. 2023, 14, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj14040092
Zhao C, Zuo Y, Wang H, Hou Q, Lee CHT. Smooth Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Using Back Propagation Neural Network. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2023; 14(4):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj14040092
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Chenhao, Yuefei Zuo, Huanzhi Wang, Qiankang Hou, and Christopher H. T. Lee. 2023. "Smooth Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Using Back Propagation Neural Network" World Electric Vehicle Journal 14, no. 4: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj14040092
APA StyleZhao, C., Zuo, Y., Wang, H., Hou, Q., & Lee, C. H. T. (2023). Smooth Speed Control of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine Using Back Propagation Neural Network. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 14(4), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/wevj14040092










