Predicting Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Patients with Heart Failure and Optimizing Their Dosing Strategies Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
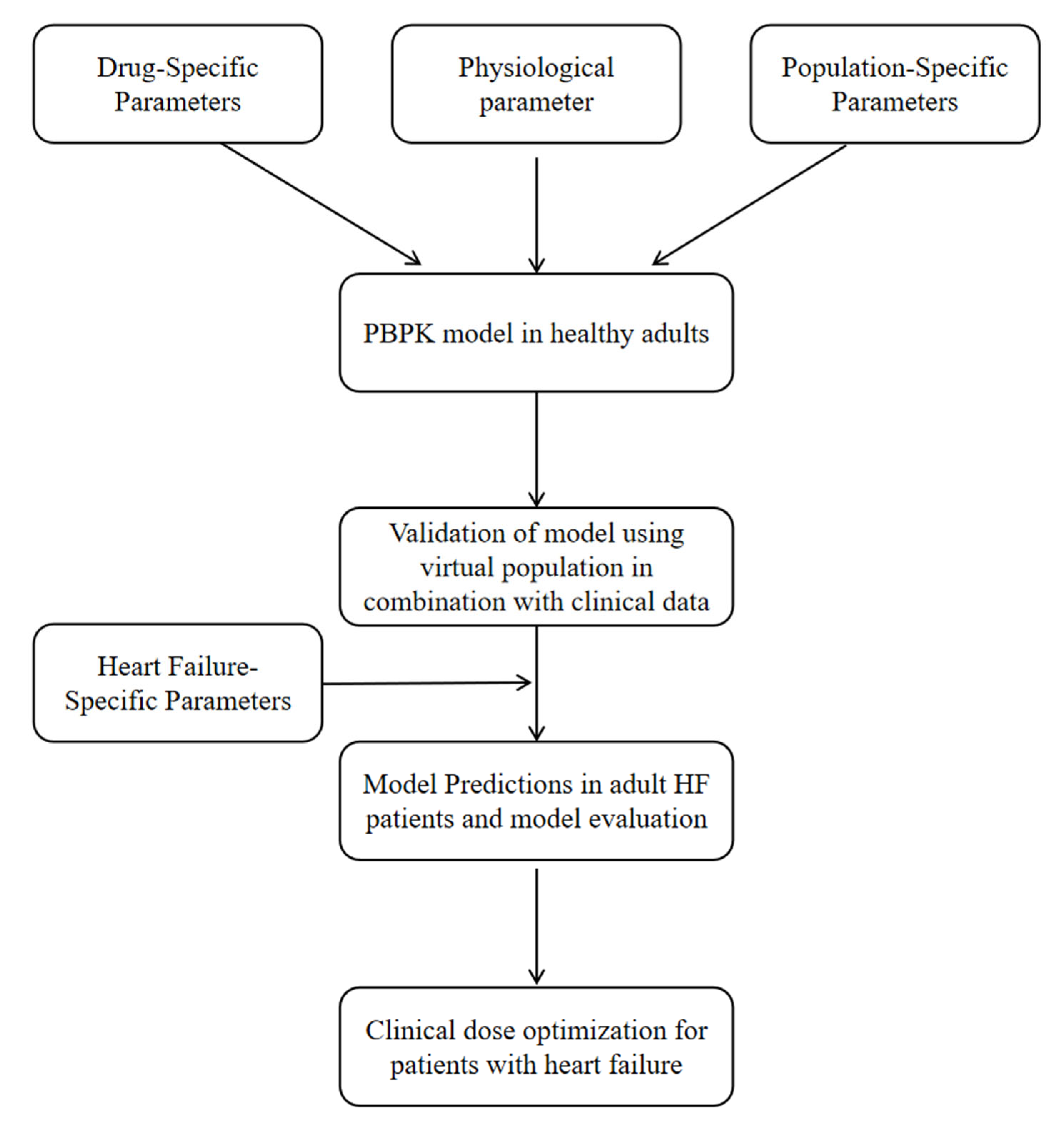
2.1. General Workflow
2.2. Model Development
2.3. Model Development in HF Patients
2.4. Criterion of the Developed PBPK Model
3. Results
3.1. Drug Data Set
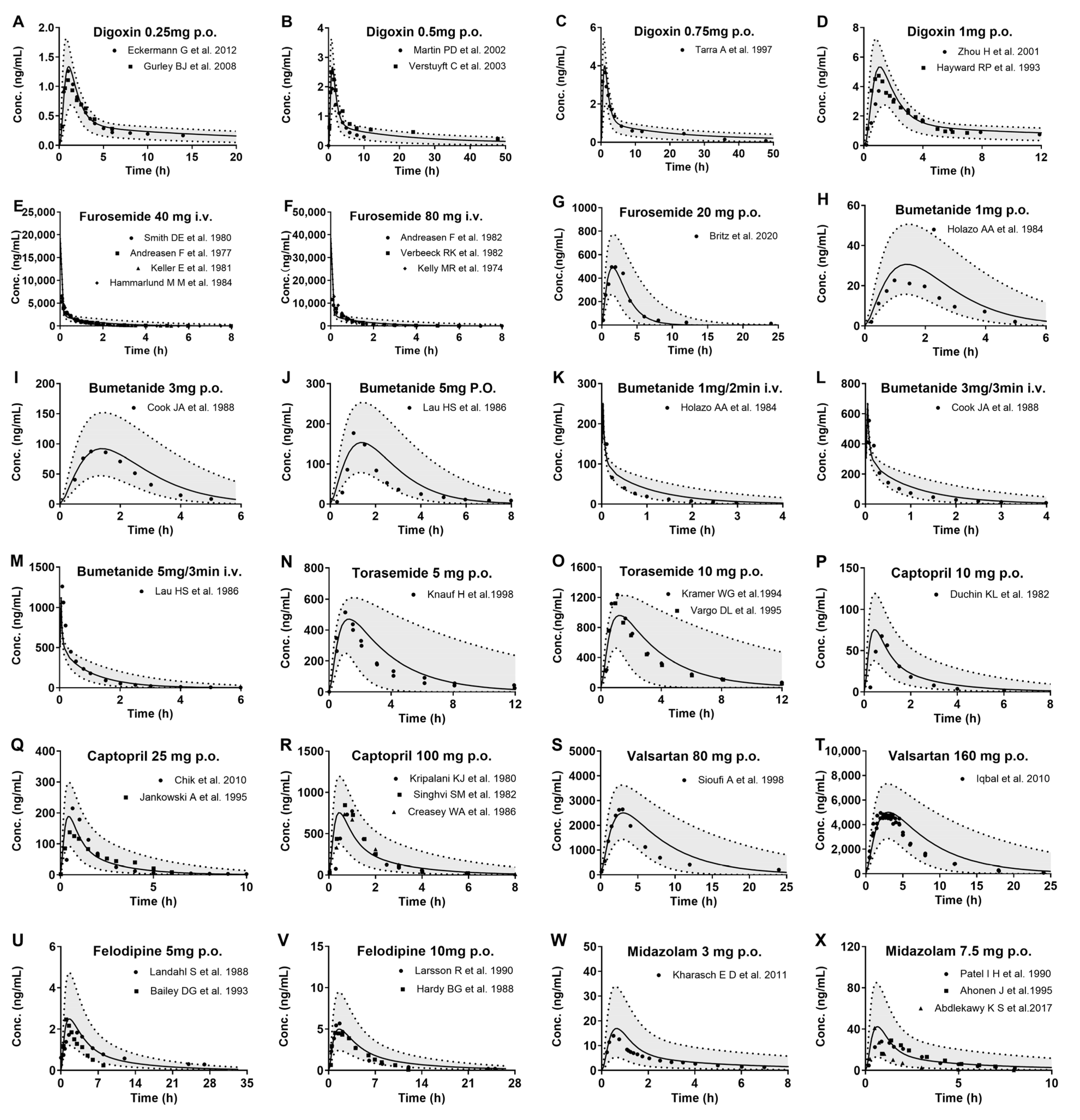
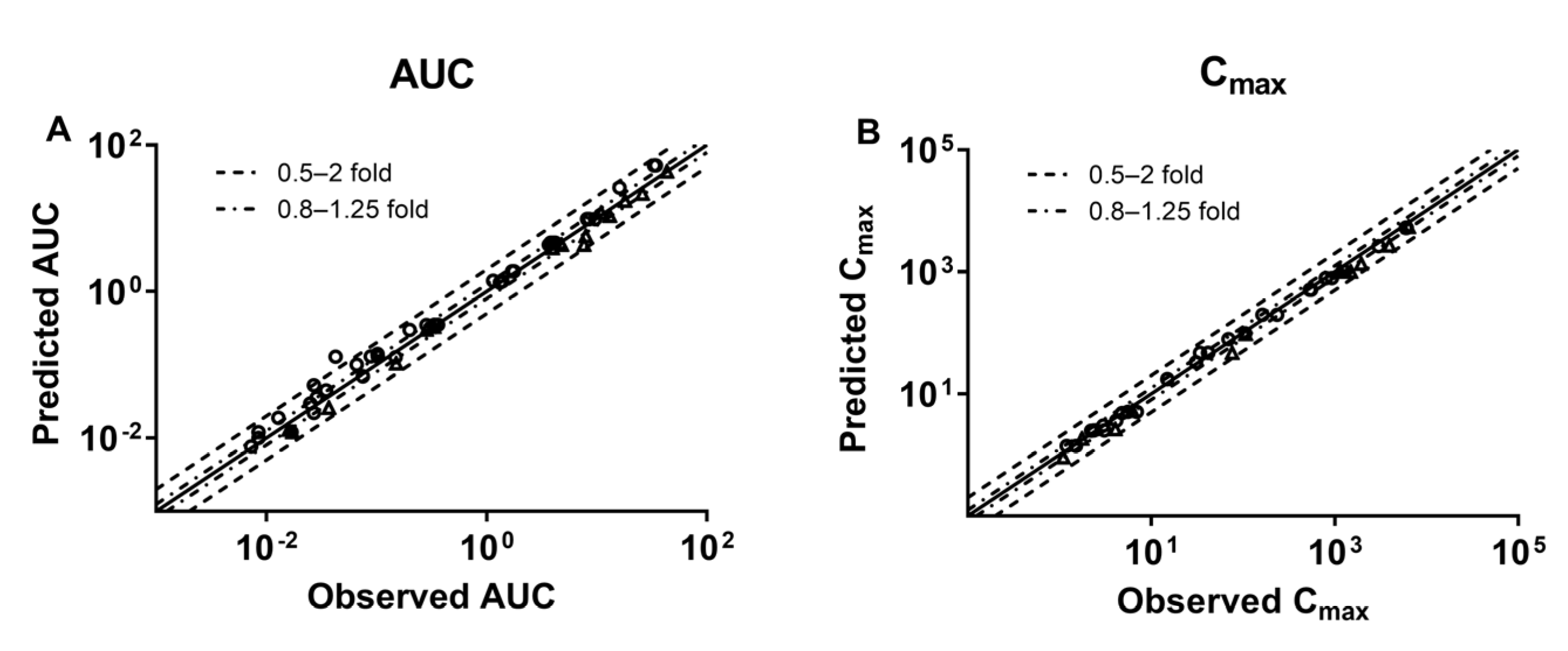
3.2. Development of PBPK Model and Validation in Healthy Subjects
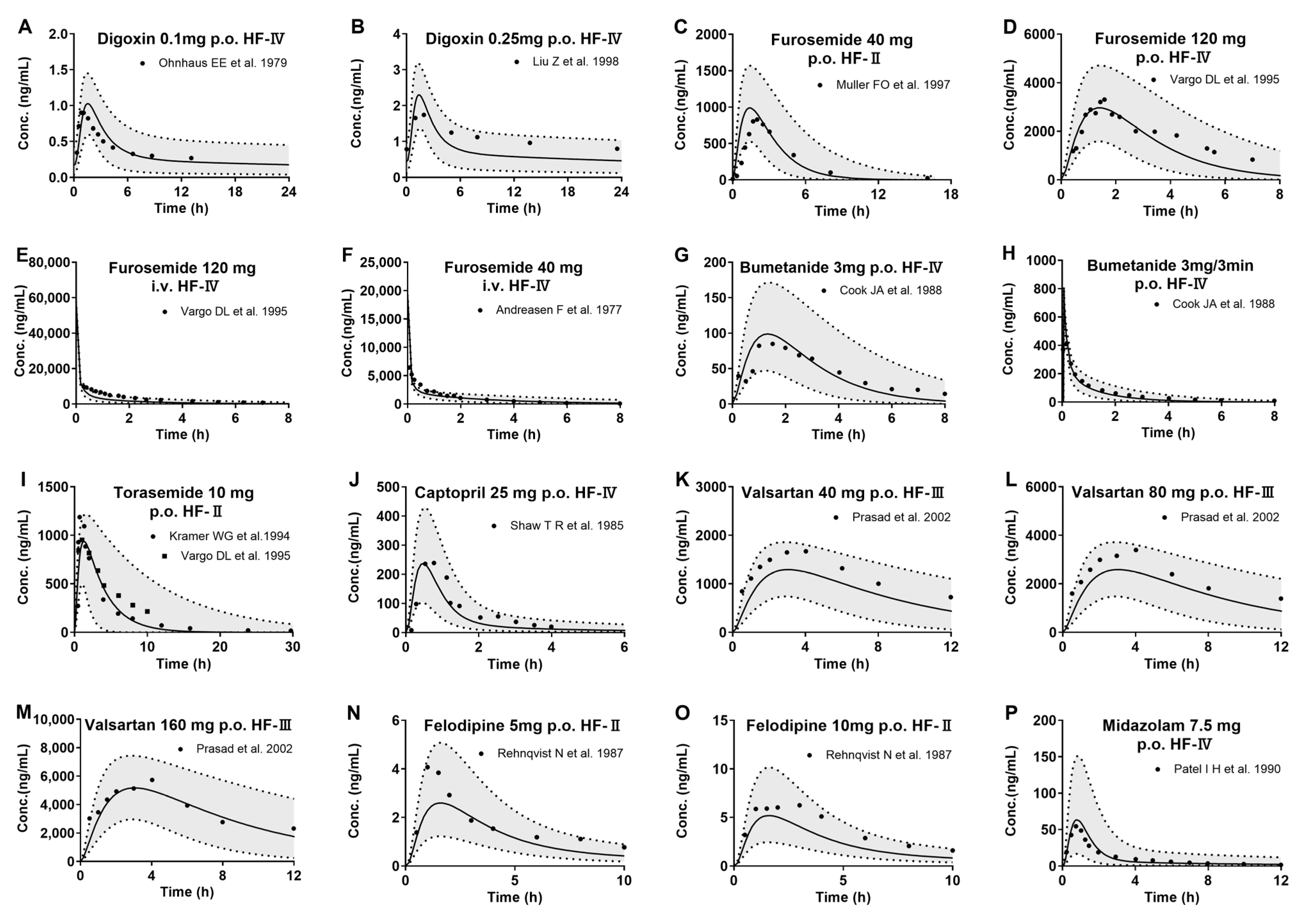
3.3. Development of PBPK Model and Validation in HF Patients
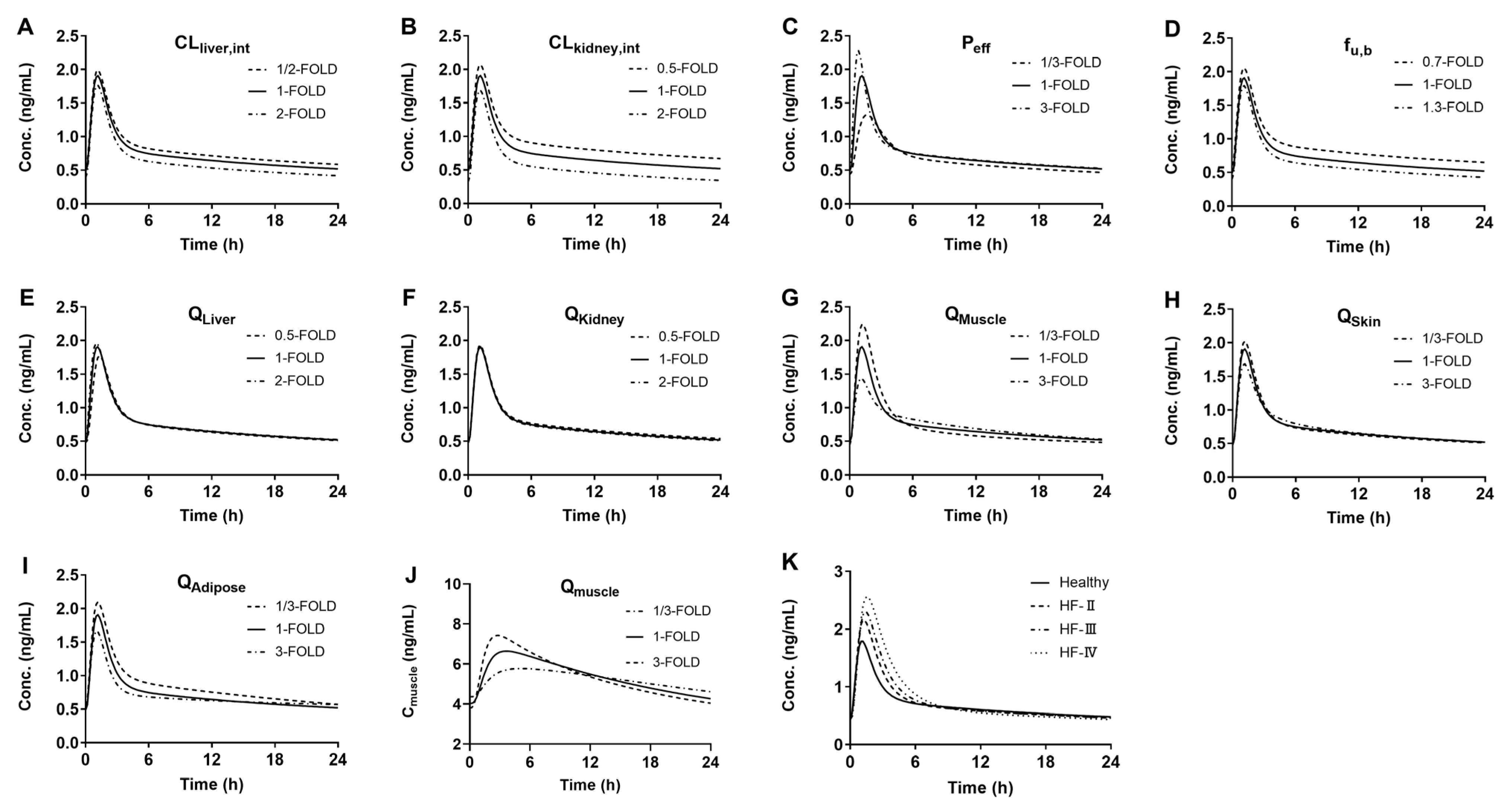
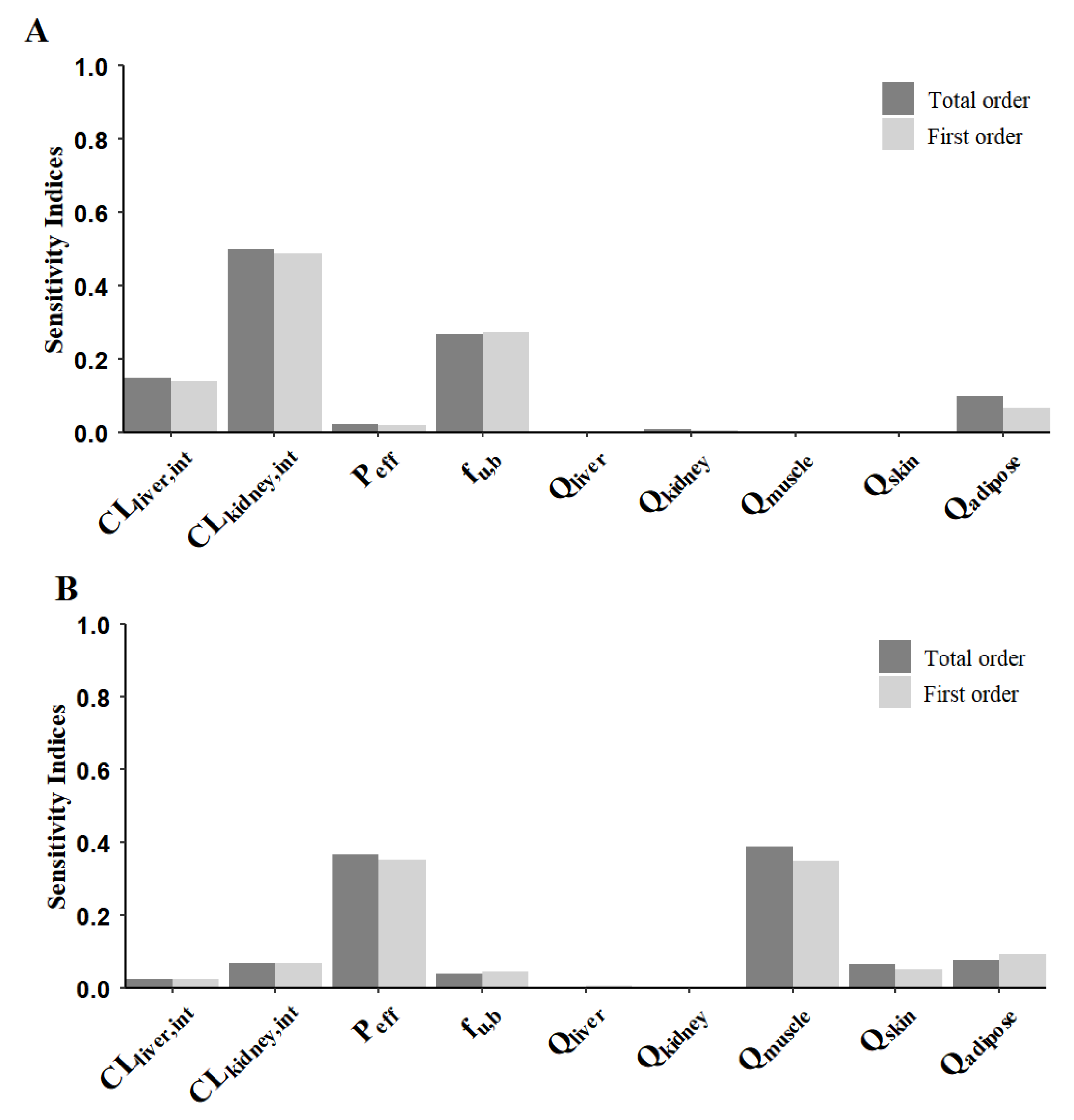
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis of Model Parameters
3.5. Virtual Simulation for Dose Optimization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HF | Heart failure |
| PBPK | Physiologically based pharmacokinetic |
| AUC | Area under the concentration-time curve |
| Cmax | Maximum plasma concentration |
| GSA | Global sensitivity analysis |
| NYHA | New York Heart Association |
| AUCR | The ratio of AUC in HF patients to that in healthy subjects |
| CmaxR | The ratio of Cmax in HF patients to that in healthy subjects |
References
- New York Heart Association. Nomenclature and Criteria for Diagnosis of Diseases of the Heart and Great Vessels; Little, Brown: Boston, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Leithe, M.E.; Margorien, R.D.; Hermiller, J.B.; Unverferth, D.V.; Leier, C.V. Relationship between central hemodynamics and regional blood flow in normal subjects and in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation 1984, 69, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, G.W.; Armstrong, P.W. Congestive heart failure. Cmaj 1988, 138, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandek, A.; Bauditz, J.; Swidsinski, A.; Buhner, S.; Weber-Eibel, J.; von Haehling, S.; Schroedl, W.; Karhausen, T.; Doehner, W.; Rauchhaus, M.; et al. Altered intestinal function in patients with chronic heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 1561–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, I.H.; Soni, P.P.; Fukuda, E.K.; Smith, D.F.; Leier, C.V.; Boudoulas, H. The pharmacokinetics of midazolam in patients with congestive heart failure. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1990, 29, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, W.G. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of torasemide in congestive heart failure. Cardiology 1994, 84 (Suppl. S2), 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sager, J.E.; Yu, J.; Ragueneau-Majlessi, I.; Isoherranen, N. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic (PBPK) Modeling and Simulation Approaches: A Systematic Review of Published Models, Applications, and Model Verification. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 1823–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Lu, C. PBPK modeling and simulation in drug research and development. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, T.; Rowland, M. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling 2: Predicting the tissue distribution of acids, very weak bases, neutrals and zwitterions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1238–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruark, C.D.; Hack, C.E.; Robinson, P.J.; Mahle, D.A.; Gearhart, J.M. Predicting passive and active tissue:plasma partition coefficients: Interindividual and interspecies variability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.F.; Ali, S.; Khalid, S.; Khalid, R.; Majeed, A.; Imran, I.; Saeed, H.; Usman, M.; Ali, M.; Alali, A.S.; et al. Development and evaluation of physiologically based pharmacokinetic drug-disease models for predicting captopril pharmacokinetics in chronic diseases. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, M.F.; Khalil, F.; Laer, S. Predicting Stereoselective Disposition of Carvedilol in Adult and Pediatric Chronic Heart Failure Patients by Incorporating Pathophysiological Changes in Organ Blood Flows-A Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Approach. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2016, 44, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckermann, G.; Lahu, G.; Nassr, N.; Bethke, T.D. Absence of pharmacokinetic interaction between roflumilast and digoxin in healthy adults. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 52, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurley, B.J.; Swain, A.; Williams, D.K.; Barone, G.; Battu, S.K. Gauging the clinical significance of P-glycoprotein-mediated herb-drug interactions: Comparative effects of St. John’s wort, Echinacea, clarithromycin, and rifampin on digoxin pharmacokinetics. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.D.; Kemp, J.; Dane, A.L.; Warwick, M.J.; Schneck, D.W. No effect of rosuvastatin on the pharmacokinetics of digoxin in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 42, 1352–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verstuyft, C.; Strabach, S.; El-Morabet, H.; Kerb, R.; Brinkmann, U.; Dubert, L.; Jaillon, P.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Trugnan, G.; Becquemont, L. Dipyridamole enhances digoxin bioavailability via P-glycoprotein inhibition. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 73, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarral, A.; Francheteau, P.; Guerret, M. Effects of terbinafine on the pharmacokinetics of digoxin in healthy volunteers. Pharmacotherapy 1997, 17, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Horowitz, A.; Ledford, P.C.; Hubert, M.; Appel-Dingemanse, S.; Osborne, S.; McLeod, J.F. The effects of tegaserod (HTF 919) on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of digoxin in healthy subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 41, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, R.P.; Greenwood, H.; Hamer, J. Comparison of digoxin and medigoxin in normal subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1978, 6, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.E.; Gee, W.L.; Brater, D.C.; Lin, E.T.; Benet, L.Z. Preliminary evaluation of furosemide-probenecid interaction in humans. J. Pharm. Sci. 1980, 69, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, F.; Mikkelsen, E. Distribution, elimination and effect of furosemide in normal subjects and in patients with heart failure. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1977, 12, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, E.; Hoppe-Seyler, G.; Mumm, R.; Schollmeyer, P. Influence of hepatic cirrhosis and end-stage renal disease on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of furosemide. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1981, 20, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarlund, M.M.; Paalzow, L.K.; Odlind, B. Pharmacokinetics of furosemide in man after intravenous and oral administration. Application of moment analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1984, 26, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, F.; Christensen, C.K.; Jacobsen, F.K.; Jansen, J.; Mogensen, C.E.; Pedersen, O.L. The individual variation in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of furosemide in young normal male subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 12, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeeck, R.K.; Patwardhan, R.V.; Villeneuve, J.P.; Wilkinson, G.R.; Branch, R.A. Furosemide disposition in cirrhosis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1982, 31, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.R.; Cutler, R.E.; Forrey, A.W.; Kimpel, B.M. Pharmacokinetics of orally administered furosemide. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1974, 15, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britz, H.; Hanke, N.; Taub, M.E.; Wang, T.; Prasad, B.; Fernandez, É.; Stopfer, P.; Nock, V.; Lehr, T. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models of Probenecid and Furosemide to Predict Transporter Mediated Drug-Drug Interactions. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holazo, A.A.; Colburn, W.A.; Gustafson, J.H.; Young, R.L.; Parsonnet, M. Pharmacokinetics of bumetanide following intravenous, intramuscular, and oral administrations to normal subjects. J. Pharm. Sci. 1984, 73, 1108–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.A.; Smith, D.E.; Cornish, L.A.; Tankanow, R.M.; Nicklas, J.M.; Hyneck, M.L. Kinetics, dynamics, and bioavailability of bumetanide in healthy subjects and patients with congestive heart failure. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1988, 44, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.S.; Hyneck, M.L.; Berardi, R.R.; Swartz, R.D.; Smith, D.E. Kinetics, dynamics, and bioavailability of bumetanide in healthy subjects and patients with chronic renal failure. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1986, 39, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauf, H.; Mutschler, E. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of torasemide. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1998, 34, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, D.L.; Kramer, W.G.; Black, P.K.; Smith, W.B.; Serpas, T.; Brater, D.C. Bioavailability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of torsemide and furosemide in patients with congestive heart failure. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1995, 57, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchin, K.L.; Singhvi, S.M.; Willard, D.A.; Migdalof, B.H.; McKinstry, D.N. Captopril kinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1982, 31, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chik, Z.; Basu, R.C.; Pendek, R.; Lee, T.C.; Mohamed, Z. A bioequivalence comparison of two formulations of rifampicin (300- vs 150-mg capsules): An open-label, randomized, two-treatment, two-way crossover study in healthy volunteers. Clin. Ther. 2010, 32, 1822–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowski, A.; Skorek, A.; Krzyśko, K.; Zarzycki, P.K.; Ochocka, R.J.; Lamparczyk, H. Captopril: Determination in blood and pharmacokinetics after single oral dose. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1995, 13, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kripalani, K.J.; McKinstry, D.N.; Singhvi, S.M.; Willard, D.A.; Vukovich, R.A.; Migdalof, B.H. Disposition of captopril in normal subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1980, 27, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhvi, S.M.; McKinstry, D.N.; Shaw, J.M.; Willard, D.A.; Migdalof, B.H. Effect of food on the bioavailability of captopril in healthy subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1982, 22, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creasey, W.A.; Funke, P.T.; McKinstry, D.N.; Sugerman, A.A. Pharmacokinetics of captopril in elderly healthy male volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1986, 26, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sioufi, A.; Marfil, F.; Jaouen, A.; Cardot, J.M.; Godbillon, J.; Ezzet, F.; Lloyd, P. The effect of age on the pharmacokinetics of valsartan. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1998, 19, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.; Khuroo, A.; Batolar, L.S.; Tandon, M.; Monif, T.; Sharma, P.L. Pharmacokinetics and bioequivalence study of three oral formulations of valsartan 160 mg: A single-dose, randomized, open-label, three-period crossover comparison in healthy Indian male volunteers. Clin. Ther. 2010, 32, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landahl, S.; Edgar, B.; Gabrielsson, M.; Larsson, M.; Lernfelt, B.; Lundborg, P.; Regårdh, C.G. Pharmacokinetics and blood pressure effects of felodipine in elderly hypertensive patients. A comparison with young healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1988, 14, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, D.G.; Arnold, J.M.; Munoz, C.; Spence, J.D. Grapefruit juice--felodipine interaction: Mechanism, predictability, and effect of naringin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1993, 53, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, R.; Karlberg, B.E.; Gelin, A.; Aberg, J.; Regårdh, C.G. Acute and steady-state pharmacokinetics and antihypertensive effects of felodipine in patients with normal and impaired renal function. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1990, 30, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, B.G.; Bartle, W.R.; Myers, M.; Bailey, D.G.; Edgar, B. Effect of indomethacin on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of felodipine. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1988, 26, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharasch, E.D.; Francis, A.; London, A.; Frey, K.; Kim, T.; Blood, J. Sensitivity of intravenous and oral alfentanil and pupillary miosis as minimal and noninvasive probes for hepatic and first-pass CYP3A induction. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 90, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahonen, J.; Olkkola, K.T.; Neuvonen, P.J. Effect of itraconazole and terbinafine on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 40, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdlekawy, K.S.; Donia, A.M.; Elbarbry, F. Effects of Grapefruit and Pomegranate Juices on the Pharmacokinetic Properties of Dapoxetine and Midazolam in Healthy Subjects. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 42, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnhaus, E.E.; Vozeh, S.; Nuesch, E. Absorption of digoxin in severe right heart failure. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1979, 15, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhu, T.; Yang, H.; Yu, S. Clinical study on chronopharmacokinetics of digoxin in patients with congestive heart failure. Curr. Med. Sci. 1998, 18, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.O.; Middle, M.V.; Schall, R.; Terblanché, J.; Hundt, H.K.; Groenewoud, G. An evaluation of the interaction of meloxicam with frusemide in patients with compensated chronic cardiac failure. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 44, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, T.R.; Duncan, F.M.; Williams, B.C.; Crichton, E.; Thomson, S.A.; Davis, J.R.; Rademaker, M.; Edwards, C.R. Plasma free captopril concentrations during short and long term treatment with oral captopril for heart failure. Br. Heart J. 1985, 54, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.P.; Yeh, C.M.; Gurrieri, P.; Glazer, R.; McLeod, J. Pharmacokinetics of multiple doses of valsartan in patients with heart failure. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2002, 40, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehnqvist, N.; Billing, E.; Moberg, L.; Lundman, T.; Olsson, G. Pharmacokinetics of felodipine and effect on digoxin plasma levels in patients with heart failure. Drugs 1987, 34 (Suppl. S3), 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Gao, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, X. Quantitatively Predicting Effects of Exercise on Pharmacokinetics of Drugs Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2024, 52, 1271–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhoff, S.; Yeo, K.R.; Barter, Z.; Jamei, M.; Turner, D.B.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Application of permeability-limited physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models: Part I-digoxin pharmacokinetics incorporating P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 3145–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsumi, K.; Kotegawa, T.; Kuranari, M.; Otani, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Matsuki, S.; Nakano, S. The effect of erythromycin and clarithromycin on the pharmacokinetics of intravenous digoxin in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 42, 1159–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.Q.; Zhao, K.J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.D. Simultaneously predict pharmacokinetic interaction of rifampicin with oral versus intravenous substrates of cytochrome P450 3A/P-glycoprotein to healthy human using a semi-physiologically based pharmacokinetic model involving both enzyme and transporter turnover. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 134, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, I.; Shehab, N.; Kegler, S.R.; Laskar, S.R.; Budnitz, D.S. Emergency department visits and hospitalizations for digoxin toxicity: United States, 2005 to 2010. Circ. Heart Fail. 2014, 7, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordog, G.J.; Benaron, S.; Bhasin, V.; Wasserberger, J.; Balasubramanium, S. Serum digoxin levels and mortality in 5,100 patients. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1987, 16, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, C.W.; Jessup, M.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Drazner, M.H.; Fonarow, G.C.; Geraci, S.A.; Horwich, T.; Januzzi, J.L.; et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation 2013, 128, e240–e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moj, D.; Hanke, N.; Britz, H.; Frechen, S.; Kanacher, T.; Wendl, T.; Haefeli, W.E.; Lehr, T. Clarithromycin, Midazolam, and Digoxin: Application of PBPK Modeling to Gain New Insights into Drug-Drug Interactions and Co-medication Regimens. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, U. Pharmacokinetics and drug metabolism in the elderly. Drug Metab. Rev. 2009, 41, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotreau, M.M.; von Moltke, L.L.; Greenblatt, D.J. The influence of age and sex on the clearance of cytochrome P450 3A substrates. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 33–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K. Sex-related differences in drug disposition in man. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1984, 9, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Y.; Zhao, Y.S. Sex-dependent differences in cytochrome P450 3A activity as assessed by midazolam disposition in humans: A meta-analysis. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2010, 38, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, R.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, J.; Fan, R.; Chen, P.; Yin, N.; Qin, H. Evaluation value of ultrasound on gastrointestinal function in patients with acute heart failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1475920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edginton, A.N.; Willmann, S. Physiology-based simulations of a pathological condition: Prediction of pharmacokinetics in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2008, 47, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.X.; Amidon, G.L. A compartmental absorption and transit model for estimating oral drug absorption. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 186, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.; Houston, J.B.; Galetin, A. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling of intestinal first-pass metabolism of CYP3A substrates with high intestinal extraction. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2011, 39, 1633–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalese, M.J.; Salvatore, D.J. Role of Digoxin in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 30, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lainscak, M.; Vitale, C.; Seferovic, P.; Spoletini, I.; Cvan Trobec, K.; Rosano, G.M. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cardiovascular drugs in chronic heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 224, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, D.; Choudhary, S.; Vora, A.; Ghose, T.; Mantri, R.R.; Modi, N.; Sawhney, J.; Singhal, A.; Kumar, A.; Edakutty, R.; et al. Loop Diuretics Unique Mechanism of Action. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2024, 72, 14–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponto, L.L.; Schoenwald, R.D. Furosemide (frusemide). A pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic review (Part I). Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1990, 18, 381–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapa, R.; Li, C.Y.; Basit, A.; Thakur, A.; Ladumor, M.K.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Selen, A.; Prasad, B. Contribution of Uptake and Efflux Transporters to Oral Pharmacokinetics of Furosemide. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 32939–32950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, M.D.; Abduljalil, K.; Cryan, J.F.; Boylan, G.B.; Griffin, B.T. Application of a physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model for the prediction of bumetanide plasma and brain concentrations in the neonate. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2018, 39, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brogden, R.N.; Todd, P.A.; Sorkin, E.M. Captopril. An update of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic use in hypertension and congestive heart failure. Drugs 1988, 36, 540–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, M.C.; Foster, C.; Brunner, H.R.; Liu, L. A systematic comparison of the properties of clinically used angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists. Pharmacol. Rev. 2013, 65, 809–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedinak, K.C.; Lopez, L.M. Felodipine: A new dihydropyridine calcium-channel antagonist. Dicp 1991, 25, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, F.; Nimavardi, A.; Mudunuru, J.; Tompson, D.; Bloomer, J.; Turner, D.B.; Taskar, K.S. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling for development and applications of a virtual celiac disease population using felodipine as a model drug. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2023, 12, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.M.; Sun, B.B.; Wang, Z.J.; Zheng, X.K.; Zhao, K.J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Liu, P.H.; Zhu, L.; Xu, R.J.; et al. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling for prediction of vonoprazan pharmacokinetics and its inhibition on gastric acid secretion following intravenous/oral administration to rats, dogs and humans. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 852–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, X. Prediction of Cyclosporin-Mediated Drug Interaction Using Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model Characterizing Interplay of Drug Transporters and Enzymes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.H.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, Y.B. Torsemide Pharmacometrics in Healthy Adult Populations Including CYP2C9 Genetic Polymorphisms and Various Patient Groups through Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, S.; Perrier, J.; Dunn, C.; Khadra, I.; Davidson, S.; Ainousah, B.; Wilson, C.G.; Halbert, G. Small scale design of experiment investigation of equilibrium solubility in simulated fasted and fed intestinal fluid. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 150, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhr, L.M.; Marok, F.Z.; Mees, M.; Mahfoud, F.; Selzer, D.; Lehr, T. A Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Model of the CYP3A4 Substrate Felodipine for Drug-Drug Interaction Modeling. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlender, J.F.; Meyer, M.; Thelen, K.; Krauss, M.; Willmann, S.; Eissing, T.; Jaehde, U. Development of a Whole-Body Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Approach to Assess the Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Elderly Individuals. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 55, 1573–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, A.; Cascais, A.C.; Funk, C.; Lavé, T. Prediction of pharmacokinetic profile of valsartan in human based on in vitro uptake transport data. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2009, 36, 585–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.M.; Jaipal, A.; Kumar, A.; Malik, R.; Charde, S.Y. Determination of pK(a) of felodipine using UV-Visible spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 115, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, N.; Frechen, S.; Moj, D.; Britz, H.; Eissing, T.; Wendl, T.; Lehr, T. PBPK Models for CYP3A4 and P-gp DDI Prediction: A Modeling Network of Rifampicin, Itraconazole, Clarithromycin, Midazolam, Alfentanil, and Digoxin. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2018, 7, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, S.; Brater, D.C.; Pound, D.; Green, P.K.; Kramer, W.G.; Rudy, D. Bioavailability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of torsemide in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1993, 54, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flesch, G.; Müller, P.; Lloyd, P. Absolute bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of valsartan, an angiotensin II receptor antagonist, in man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 52, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland Yeo, K.; Walsky, R.L.; Jamei, M.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A.; Tucker, G.T. Prediction of time-dependent CYP3A4 drug-drug interactions by physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling: Impact of inactivation parameters and enzyme turnover. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 43, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Heart Failure Class | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood Flow (mL/min) | II Grade | III Grade | IV Grade |
| Lung | 4399.58 | 3610.12 | 3378.28 |
| Muscle | 427.5 | 330 | 210 |
| Adipose | 148.2 | 114.4 | 72.8 |
| Skin | 171 | 132 | 84 |
| Kidney | 967.2 | 682 | 781.2 |
| Liver | 228 | 162 | 138 |
| Spleen | 60.8 | 43.2 | 36.8 |
| Stomach | 28.88 | 20.52 | 17.48 |
| Duodenum | 89.68 | 63.72 | 54.28 |
| Jejunum | 313.88 | 223.02 | 189.98 |
| Ileum | 185.44 | 131.76 | 112.24 |
| Cecum | 33.44 | 23.76 | 20.24 |
| Colon | 213.56 | 151.74 | 129.26 |
| Heart a | 240 | 240 | 240 |
| Brain a | 700 | 700 | 700 |
| ROB a | 592 | 592 | 592 |
| Drug | Dose | Subjects | AUC0-t (μg × h/mL) | Cmax (ng/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obs | Pre | Obs/Pre | Obs | Pre | Obs/Pre | |||
| digoxin | 0.1 mg a [48] | HF-IV | NR | 0.0067 | / | 1.10 | 0.93 | 1.18 |
| 0.25 mg b [49] | HF-III | 0.024 | 0.020 | 1.2 | 1.72 | 2.46 | 0.70 | |
| furosemide | 40 mg a, i.v [32] | HF-III | 7.98 | 5.78 | 1.38 | / | / | / |
| 120 mg a, i.v [21] | HF-IV | 18.02 | 17.36 | 1.04 | / | / | / | |
| 40 mg a [50] | HF-II | 3.96 | 3.92 | 1.01 | 1124 | 1057.70 | 1.06 | |
| 120 mg a [32] | HF-IV | 10.99 | 11.78 | 0.93 | NR | 3173.23 | / | |
| bumetanide | 3 mg a [29] | HF-IV | 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.85 | 107 | 96.36 | 1.11 |
| 3 mg,3 min a, i.v [29] | HF-IV | 0.33 | 0.33 | 1 | / | / | / | |
| torasemide | 10 mg b [6] | HF-II | 7.69 | 4.35 | 1.77 | 1159 | 1008.50 | 1.15 |
| 10 mg c [32] | HF-II | 4.80 | 4.35 | 1.1 | 1500 | 1008.50 | 1.49 | |
| captopril | 25 mg [51] | HF-IV | NR | 0.32 | / | NR | 248.68 | / |
| valsartan | 40 mg d [52] | HF-III | 13.12 | 10.86 | 1.21 | 1940 | 1359.91 | 1.43 |
| 80 mg d [52] | HF-III | 25.94 | 21.72 | 1.19 | 3950 | 2719.87 | 1.45 | |
| 160 mg d [52] | HF-III | 43.54 | 43.45 | 1 | 6400 | 5439.70 | 1.18 | |
| felodipine | 5 mg d [53] | HF-II | 0.016 | 0.013 | 1.23 | 4.07 | 2.65 | 1.54 |
| 10 mg d [53] | HF-II | 0.037 | 0.026 | 1.42 | 6.26 | 5.29 | 1.18 | |
| midazolam | 7.5 mg a [5] | HF-IV | 0.15 | 0.10 | 1.50 | 76 | 46.92 | 1.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, W.; Shao, Q.; Jiang, L. Predicting Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Patients with Heart Failure and Optimizing Their Dosing Strategies Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111394
Gu W, Shao Q, Jiang L. Predicting Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Patients with Heart Failure and Optimizing Their Dosing Strategies Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(11):1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111394
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Weiye, Qingxuan Shao, and Ling Jiang. 2025. "Predicting Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Patients with Heart Failure and Optimizing Their Dosing Strategies Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 11: 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111394
APA StyleGu, W., Shao, Q., & Jiang, L. (2025). Predicting Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Patients with Heart Failure and Optimizing Their Dosing Strategies Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model. Pharmaceutics, 17(11), 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17111394





