Oleosome Delivery Systems: Enhancing Stability and Therapeutic Potential of Natural Products and Xenobiotics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structure and Composition of Oleosomes
3. Different Extraction Methods for Natural Plant-Derived Oleosomes
3.1. Organic-Solvent (Hexane) Extraction
3.2. Aqueous Extraction
3.3. Mechanical Pressing/Twin-Screw Extrusion
3.4. Assisted Extractions (Enzyme- or Ultrasound-Aided)
3.5. Method Selection and Application Relevance
| Method | Typical Procedure | Advantages | Drawbacks | Representative Yields | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic-solvent extraction (hexane) | Flake → mill → counter-current hexane wash → desolventize | Very high lipid recovery; uses existing oil-mill infrastructure | Large solvent use; volatile organic-compound emissions; energy-intensive recovery; and membranes are stripped (no intact oleosomes) | >97% of total seed oil; ≈0% intact oleosomes | [6,20] |
| Aqueous extraction | Water/mild buffer (pH 7–9); wet grind or 50–150 MPa HPH; wash–cream centrifugation | Preserves droplet integrity; solvent-free; yields oil-in-water emulsions | High water and centrifuge throughput demands; requires effluent valorization | 80–96% intact oleosomes (soybean, rapeseed, and flaxseed) | [6,20,21] |
| Mechanical pressing/twin-screw extrusion | Low-moisture pressing/extrusion; cream separation | Continuous; 40–60% lower energy than solvent routes; minimal wastewater | Shear-induced disruption; 10–30% residual oil in press cake unless re-pressed | ~60–90% oleosome recovery (rapeseed at pilot scale) | [6,21] |
| Assisted extractions (enzyme- or ultrasound-aided) | Cell-wall-degrading enzymes and/or 20–40 kHz ultrasound before mild homogenization | Higher yields at lower shear, shorter processing times, reduced water demand, good preservation of membrane proteins | Enzyme cost; potential over-hydrolysis; ultrasound scale-up | Enzymes up to ~93% (sunflower/peanut); enzyme + ultrasound: ~85–90% recovery | [6,8,21] |
4. Seed-Derived Oleosomes
5. Nut- and Fruit-Derived Oleosomes
6. Xenobiotic Encapsulation in Oleosomes
7. Administration Routes of Oleosome-Based Formulations
8. Therapeutic Applications of Oleosome Systems
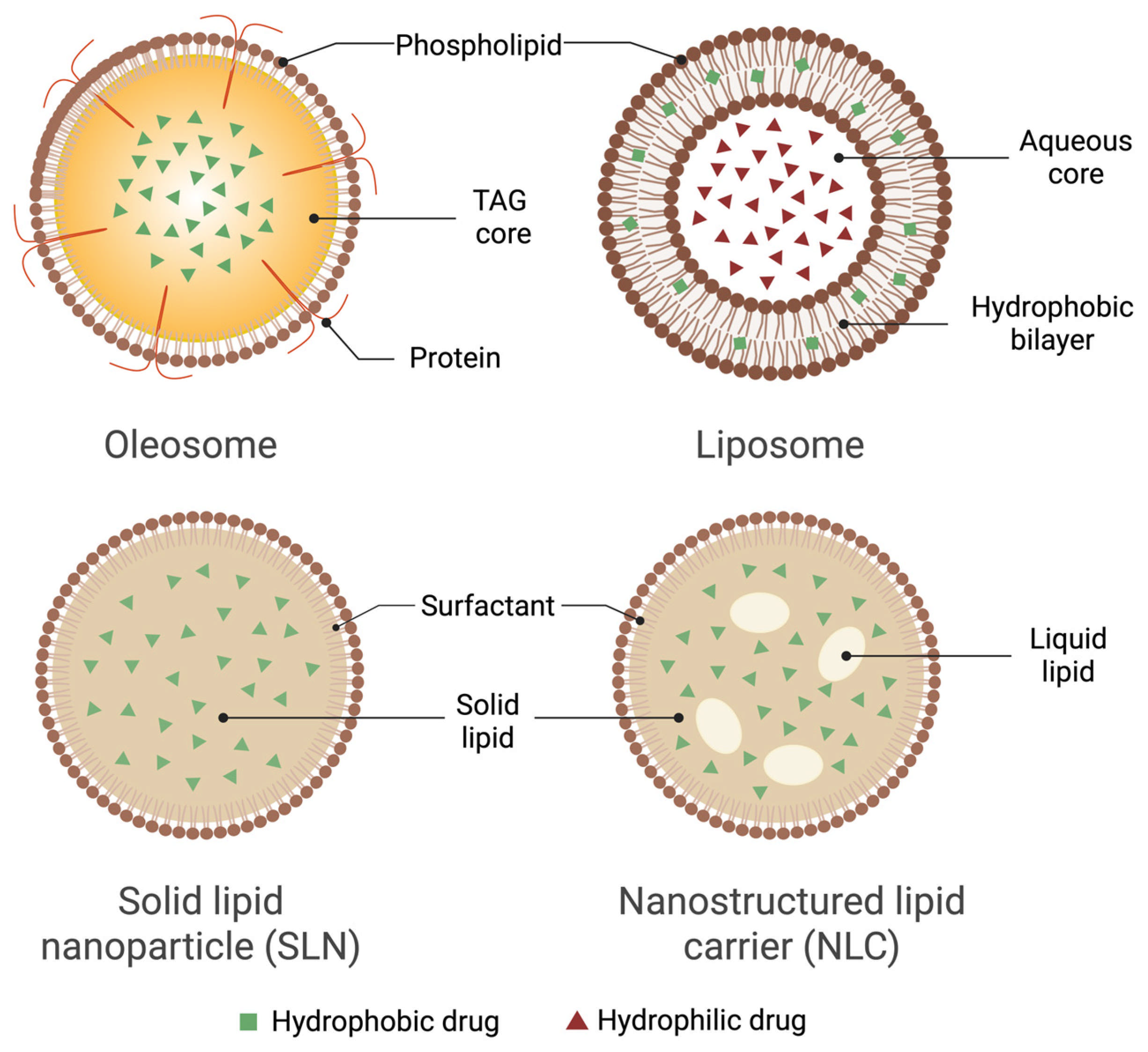
9. Comparison of Oleosomes and Other Lipid Nanocarriers
10. ADMET Advantages of Natural Oleosomes
10.1. Absorption
10.2. Distribution
10.3. Metabolism
10.4. Excretion
10.5. Toxicity
11. Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs) for Oleosomes
12. Current Limitations of Oleosome Carriers
13. Oleosomes for Topical and Systemic Delivery
14. Oleosome as a Potential for Lymph-Directed Delivery
15. Discussion
16. Research Gaps
17. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| CBD | Cannabidiol |
| CFR | Code of Federal Regulations |
| CRISPR | Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat |
| CQA | Critical quality attribute |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| GRAS | Generally recognized as safe |
| HPH | High-pressure homogenization |
| ICH | International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use |
| NLC | Nanostructured-lipid carrier |
| PDI | Polydispersity index |
| pKa | Acid dissociation constant |
| SLN | Solid lipid nanoparticle |
| SPF | Sun protection factor |
| TAG | Triacylglycerol |
| USD | United States dollar |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Dave, A.C.; Ye, A.; Singh, H. Structural and interfacial characteristics of oil bodies in coconuts (Cocos nucifera L.). Food Chem. 2019, 276, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palak, A.; Yadav, K.S.; Rai, V.K. Natural and multifunctional colloidal carriers: A new prospective in drug delivery. Pharmaspire 2021, 13, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Maurer, S.; Waschatko, G.; Schach, D.; Zielbauer, B.I.; Dahl, J.; Weidner, T.; Bonn, M.; Vilgis, T.A. The Role of Intact Oleosin for Stabilization and Function of Oleosomes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 13872–13883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, C.; Rabesona, H.; Novales, B.; Weber, M.; Anton, M. Walnut (Juglans regia L.) kernel oil bodies recovered by aqueous extraction for utilization as ingredient in food emulsions: Exploration of their microstructure, composition and the effects of homogenization, pH, and salt ions on their physical stability. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsena, Y.P.; Agarwal, D.; Logan, A.; Buckow, R. Oleosome extraction: Challenges, innovations, and opportunities for industrial applications. J. Food Eng. 2026, 404, 112780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plankensteiner, L.; Nikiforidis, C.V.; Vincken, J.-P.; Hennebelle, M. The oxidative stability of sunflower oleosomes depends on co-extracted phenolics and storage proteins. Food Chem. 2025, 475, 143145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah; Weiss, J.; Zhang, H. Recent advances in the composition, extraction and food applications of plant-derived oleosomes. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, H.H.; Araiza-Calahorra, A.; Rigby, N.M.; Sarkar, A. Flaxseed oleosomes: Responsiveness to physicochemical stresses, tribological shear and storage. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardar, U.S.; Bitter, J.H.; Nikiforidis, C.V. The mechanism of encapsulating curcumin into oleosomes (Lipid Droplets). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 236, 113819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Feng, W.; Chen, H.; Chu, Y.; Wong, A.; Zhu, Y.; Sinatra, G.; Bramante, F.; Carrière, F.; Stocks, M.J.; et al. Rapeseed oleosomes facilitate intestinal lymphatic delivery and oral bioavailability of cannabidiol. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 668, 124947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.-Y.; Lee, T.; Yoon, J.; Han, Z.; Rabie, H.; Lee, K.-B.; Su, W.W.; Choi, J.-W. Magnetic Oleosome as a Functional Lipophilic Drug Carrier for Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9301–9309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltabeeb, M.A.; Abdellatif, M.M.; El-Nabarawi, M.A.; Teaima, M.H.; AHamed, M.I.; Darwish, K.M.; Hassan, M.; Hamdan, A.M.; Hamed, R.R. Chitosan decorated oleosomes loaded propranolol hydrochloride hydrogel repurposed for Candida albicans-vaginal infection. Nanomedicine 2024, 19, 1369–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashique, S.; Singh, A.; Sandhu, N.K. Stability Issues, Probable Approaches for Stabilization and Associated Patents in the Pharmaceutical Field for Oleosome, A Novel Carrier for Drug Delivery. Recent. Pat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 16, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Farooq, S. Role of peanut oleosomes in the delivery of curcumin embedded in interpenetrating emulsion-filled gels made with whey protein and chitosan. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 707, 135962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassil, M. Investigation of Transfer of Bioactives from Oleosome into Cells: A Method Development; Wageningen University & Research: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Nikiforidis, C.V. Structure and functions of oleosomes (oil bodies). Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 274, 102039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo-Fani, A.; Dave, A.; Singh, H. Nature-Assembled Structures for Delivery of Bioactive Compounds and Their Potential in Functional Foods. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 564021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Guzmán, M.J.; Köllmann, N.; Zhang, L.; Boom, R.M.; Nikiforidis, C.V. Controlled oleosome extraction to produce a plant-based mayonnaise-like emulsion using solely rapeseed seeds. LWT 2020, 123, 109120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, J.-F.; Lacroux, E.; Cerny, M.; Vaca-Medina, G.; Cassen, A.; Merah, O.; Valentin, R.; Mouloungui, Z. Oil body extraction from oleo-proteaginous seeds and conservation of valuable native compounds. OCL 2023, 30, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; ten Voorde, S.; Wen, X.; Ni, Y.; Boom, R.M.; Nikiforidis, C.V. Efficiency of aqueous oleosome extraction from capsicum seeds compared to classical oil extraction. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 399, 130571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karefyllakis, D.; Jan van der Goot, A.; Nikiforidis, C.V. The behaviour of sunflower oleosomes at the interfaces. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 4639–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wen, J.; Wang, J.; Tian, R.; Yu, L.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X. The physicochemical properties and gastrointestinal fate of oleosomes from non-heated and heated soymilk. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 100, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assor, C.A.; Barouh, N.; Berton-Carabin, C.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Chardot, T.; D’andrea, S.; Fabre, J.-F.; Gohon, Y.; Lacroux, E.; Lullien-Pellerin, V. Storming through plant biodiversity to extract oleosomes for sustainable food applications. In Proceedings of the 16th GERLI Congress, Bordeaux, France, 26–29 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, P.; Wang, J.Y.; Mineroff, J.; Jagdeo, J. The potential cutaneous benefits of Carthamus tinctorius oleosomes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2023, 316, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Bitter, J.H.; Boom, R.M.; Nikiforidis, C.V. Encapsulation of cannabidiol in hemp seed oleosomes. Food Res. Int. 2024, 195, 114948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Han, M.; Fu, R.; Mei, Y.; Wen, X.; Ni, Y.; Boom, R.M.; Nikiforidis, C.V. Influence of extraction pH and homogenization on soybean oleosome emulsion stability. LWT 2024, 203, 116404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, D.; Smeriglio, A.; Denaro, M.; Zagami, R.; Tomassetti, M.; Pilolli, R.; De Angelis, E.; Monaci, L.; Mandalari, G. Understanding the Fate of Almond (Prunus dulcis (Mill.) D.A. Webb) Oleosomes during Simulated Digestion. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erinç, H.; Taştanoğlu, F.B. Utilisation of hazelnut-derived oleosomes in liquid margarine formulation: An investigation into stability and functional enhancement. Acta Aliment. 2024, 53, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkus, E.; Szustak, M.; Dąbrowski, G.; Czaplicki, S.; Kadłubowski, S.; Koziołkiewicz, M.; Konopka, I.; Gendaszewska-Darmach, E. The insulinotropic activity of oleosomes prepared from various sea buckthorn cultivars in mouse and human pancreatic β cell lines. NFS J. 2023, 31, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Albarrán, F.; Salgado-Garciglia, R.; Molina-Torres, J.; López-Gómez, R. Oleosome Oil Storage in the Mesocarp of Two Avocado Varieties. J. Oleo Sci. 2019, 68, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoop, A.A.; Ramees, P.M.; Ragavan, K.V. Coconut oleosomes as a sustainable ingredient for food emulsion systems. Sustain. Food Technol. 2025, 3, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelalim, L.R.; Elnaggar, Y.S.R.; Abdallah, O.Y. Oleosomes Encapsulating Sildenafil Citrate as Potential Topical Nanotherapy for Palmar Plantar Erythrodysesthesia with High Ex vivo Permeation and Deposition. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhalmoushy, P.M.; Elsheikh, M.A.; Matar, N.A.; El-Hadidy, W.F.; Kamel, M.A.; Omran, G.A.; Elnaggar, Y.S.R. Elaboration of novel gel-core oleosomes encapsulating phytoconstituent for targeted topical delivery in a vitiligo-induced mouse model: Focus on antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 80, 104119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). PubChem Compound Summary. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Knox, C.; Wilson, M.; Klinger, C.M.; Franklin, M.; Oler, E.; Wilson, A.; Pon, A.; Cox, J.; Chin, N.E.L.; Strawbridge, S.A.; et al. DrugBank 6.0: The DrugBank Knowledgebase for 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1265–D1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Chu, G.; Cai, W.; Li, Y.; Lan, X.; Li, J.; Du, L.; Yang, J. Beneficial Effects of Oleosomes Fused with Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 1 on Wound Healing via the Promotion of Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Capuano, E.; Bitter, J.H.; Boom, R.M.; Nikiforidis, C.V. Controlled in vitro release of CBD from oleosomes via modulation of their membrane density. Food Funct. 2025, 16, 6369–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardar, U.S.; Konings, G.; Yang, J.; Sagis, L.M.C.; Bitter, J.H.; Nikiforidis, C.V. Modifying the interfacial dynamics of oleosome (lipid droplet) membrane using curcumin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 678, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Liu, J.; Ukwatta, R.H.; Xue, F.; Xiong, X.; Li, C. Artificial oil bodies: A review on composition, properties, biotechnological applications, and improvement methods. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, N.; Awasthi, R.; Sharma, B.; Kharkwal, H.; Kulkarni, G.T. Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers for Bioactive Delivery. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazuli, Z.; Hartati, R.; Rowa, C.R.; Asyarie, S.; Satrialdi. The Potential Application of Nanocarriers in Delivering Topical Antioxidants. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, N.; Valizadeh, H.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Structure, Preparation and Application. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- zur Mühlen, A.; Schwarz, C.; Mehnert, W. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—Drug release and release mechanism. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 45, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Thuy, V.N.; Van, T.V.; Dao, A.H.; Lee, B.-J. Nanostructured lipid carriers and their potential applications for versatile drug delivery via oral administration. OpenNano 2022, 8, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.G.; de Godoi, K.R.R.; Gigante, M.L.; Pavie Cardoso, L.; Paula Badan Ribeiro, A. Developed and characterization of nanostructured lipid carriers containing food-grade interesterified lipid phase for food application. Food Res. Int. 2022, 155, 111119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardo, D.; Kiselev, M.A. Methods of Liposomes Preparation: Formation and Control Factors of Versatile Nanocarriers for Biomedical and Nanomedicine Application. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Song, H.; Li, S.; Guan, X. Selection strategy for encapsulation of hydrophilic and hydrophobic ingredients with food-grade materials: A systematic review and analysis. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Silva, C.; Alemán, A.; Montero, M.P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Storage Stability and Antioxidant Properties of Vegetable and Marine Lecithin Liposomes Loaded with Sea Cucumber (Holothuria forskali) and Musky Octopus (Eledone moschata) Protein Hydrolysates. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2025, 18, 4826–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Srivastav, P.P. Encapsulation of Centella asiatica leaf extract in liposome: Study on structural stability, degradation kinetics and fate of bioactive compounds during storage. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boafo, G.F.; Magar, K.T.; Ekpo, M.D.; Qian, W.; Tan, S.; Chen, C. The Role of Cryoprotective Agents in Liposome Stabilization and Preservation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Lim, H.; Park, H.; Yu, J.; An, J.; Yoo, H.Y.; Lee, T. Recent Progress of Lipid Nanoparticles-Based Lipophilic Drug Delivery: Focus on Surface Modifications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, J.M.; P, A.; M, R.J.; Dara, P.K.; Renuka, V.; Anandan, R. Liposome mediated encapsulation and role of chitosan on modulating liposomal stability to deliver potential bioactives—A review. Food Hydrocoll. Health 2023, 4, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Woo, Y.; Oh, B.; Yoo, D.; Kwon, H.K.; Park, C.; Cho, H.-Y.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, T. Microfluidic Fabrication of Oleosin-Coated Liposomes as Anticancer Drug Carriers with Enhanced Sustained Drug Release. Materials 2024, 17, 5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Y.; Tariq, M.; Wang, M.; Yu, X.; Liang, H.; Yuan, Q. Preparation and characterization of bionics Oleosomes with high loading efficiency: The enhancement of hydrophobic space and the effect of cholesterol. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, B.A.; Vietor, H.M.; Scott, D.W.; Lee, H.; Hashemipour, S.; Im, W.; Wittenberg, N.J.; Glover, K.J. Physicochemical Properties of Seed Oil Blends and Their Potential for the Creation of Synthetic Oleosomes with Modulated Polarities. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 43193–43202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, J.V.; Holtz, R.; In Yang, S. In vitro examination of an oleosome-based sun protection product on the influence of UVB-induced inflammation markers in human epidermal skin equivalent tissue model. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 179, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Li, K.; Meng, Z. Recent trends in oleosomes: Extraction methods, structural characterization, and novel applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 151, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (US FDA). Applications for FDA Approval to Market a New Drug; Title 21 CFR 2025, Part 314; FDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (US FDA). Current Good Manufacturing Practice in Manufacturing, Processing, Packing, or Holding of Drugs; General; Title 21 CFR 2025, Part 210; FDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (US FDA). Current Good Manufacturing Practice for Finished Pharmaceuticals; Title 21 CFR 2025, Part 211; FDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (US FDA). About the GRAS Notification Program. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/generally-recognized-safe-gras/about-gras-notification-program (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Authorisation of Medicines—Centralised Authorisation Procedure. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/about-us/what-we-do/authorisation-medicines (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Guideline on the Requirements for Quality Documentation Concerning Biological Investigational Medicinal Products in Clinical Trials—Revision 2; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH); U.S. Food and Drug Administration (US FDA). S6(R1) Preclinical Safety Evaluation of Biotechnology-Derived Pharmaceuticals; FDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH); U.S. Food and Drug Administration (US FDA). S8 Immunotoxicity Studies for Human Pharmaceuticals; FDA: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]


| Seed (Species) | Size (µm) | Fat Content (wt%) | Major FA (wt%) | Protein (wt%) | Oleosome-Associated Proteins | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum) | 0.4–2 | ≈6 | α-Linolenic (53) | ≈1 | Oleosin, Caleosin, Steroleosin, Albumins/Globulins | [9] |
| Rapeseed (Brassica napus) | 0.8–5 | ~70 | Oleic (60–65) | ≈2 | Oleosin, Caleosin, Steroleosin | [11] |
| Sunflower (Helianthus annuus) | 0.4–10 | ≈75–96.2 | Linoleic (55) | ≈3 | Oleosin, Caleosin, Steroleosin, Helianthinin, Albumins | [22] |
| Soybean (Glycine max) | 0.2–2 | ≈44.6–49.3 | Linoleic (54) | ≈3 | Oleosin, Caleosin, Steroleosin, Glycinin, β-conglycinin | [23,27] |
| Chia (Salvia hispanica) | 0.5–2 | ≈70–75 | α-Linolenic (60) | ≈1 | Oleosin, Caleosin, Steroleosin | [8,24] |
| Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius) | 0.5–2.5 | ≈75 | Linoleic (70) | ≈2 | Oleosin, Caleosin, Steroleosin | [20,25] |
| Hemp (Cannabis sativa) | 0.5–3 | ≈8.13–8.40 | Linoleic (55) | ≈2 | Oleosin, Caleosin, Steroleosin | [26] |
| Seed (Species) | Size (µm) | Distinctive Feature | Lipid/Protein (wt%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coconut (Cocos nucifera) | ~1–30 | Medium-chain FA-rich core, prominent ~14 kDa oleosin, ζ ≈ −13 mV to −33 mV | 93/5 | [1] |
| Walnut (Juglans regia) | 5.1 ± 0.3 | Highly unsaturated core, strong negative ζ near neutral pH | n.d. | [4] |
| Peanut (Arachis hypogaea) | 0.4–2 | Allergenic oleosins reinforce gels | 65/3 | [15] |
| Capsicum (Capsicum annuum) | 1–3 | Up-cycling of spice waste, low exergy loss | 67/4 | [21] |
| Almond (Prunus dulcis) | 0.2–2 | Uniform phospholipid shell slows lipolysis | 55/<3 | [28] |
| Hazelnut (Corylus avellana) | 3–11 | High-oleic core, high lubricity | 83/2.5 | [29] |
| Sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) | 0.5–20 | Palmitoleic-rich TAG, insulinotropic | n.d. | [30] |
| Avocado (Persea americana) | ~12–41.5 | Mesocarp stores oil in oleosomes, Hass ~60% oleic | n.d. | [31] |
| Compound | Molecular Formula | MW (g mol−1) | log P | pKa | Formulation Strategy | Oleosome Source | EE (%) | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curcumin | C21H20O6 | 368.40 | 3.20 | 9.08 (Acidic) | pH-shift diffusion | Rapeseed seed oleosomes | 97.5 | 4.5-fold photostability | [10] |
| CBD | C21H30O2 | 314.50 | 6.50 | 9.13 (Acidic) | Native loading in hemp-seed oleosomes; ratio-dependent | Hemp-seed oleosomes | >90 | Slow in vitro release (gradual lipid digestion); supports sustained availability | [11,26] |
| Sildenafil citrate | C28H38N6O11S | 666.70 | 1.90 | 9.2 (Acidic); 6.5 (Basic) | Ethanol-injection nano-oleosome | Soy-phospholipid reconstituted oleosomes | 95.6 | 4.5-fold skin deposition | [33] |
| Berberine | C20H18NO4+ | 336.40 | 3.60 | 11.73 (Basic) | Gel-core oleosome | Soy-phospholipid reconstituted oleosomes | 92.3 | Complete repigmentation (vitiligo model) | [34] |
| Carmustine | C5H9Cl2N3O2 | 214.05 | 1.53 | 13.36 (Basic) | Magnetic antibody-targeted oleosome | Engineered nano-oleosomes (olive-oil core + recombinant oleosin) | ≈88 | 70% tumor reduction | [12] |
| Propranolol | C16H21NO2 | 259.34 | 3.48 | 9.53 (Basic) | Chitosan-decorated vaginal gel | Soy-lecithin oleosomes | 79.6 | Candida biofilm eradication | [13] |
| Route | Prototype Formulation | Primary Indication | Advantage Demonstrated | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | CBD-loaded rapeseed oleosome emulsion | Epilepsy/chronic pain | ≈2-fold higher systemic exposure through lymphatic uptake | [11] |
| Intravenous | Magnetically steerable carmustine oleosome | Breast cancer | Dual antibody targeting plus magnetic-hyperthermia synergy | [12] |
| Vaginal | Propranolol chitosan-decorated oleogel | Candida albicans vaginitis | Strong mucoadhesion and biofilm disruption | [13] |
| Oral (digestive hydrogel) | Curcumin WPI–chitosan emulsion gel | Gut inflammation/inflammatory bowel disease | pH-triggered intestinal release | [15] |
| Topical (dermal) | Sildenafil nano-oleosome cream | Chemotherapy-induced hand-foot syndrome | 4.5-fold increase in cutaneous drug deposition | [33] |
| Topical (dermal) | Berberine gel-core oleosome | Vitiligo | Sustained release with accelerated repigmentation | [34] |
| Condition | Encapsulated Cargo | Key outcome | Experimental Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | Carmustine (magnetic, antibody-targeted oleosomes) | 69.7% reduction in tumor volume | MDA-MB-231 xenograft (mouse) | [12] |
| Vitiligo | Berberine (gel-core oleosomes) | Complete repigmentation | Hydroquinone-induced mouse model | [34] |
| Hand-foot syndrome | Sildenafil (nano-oleosome cream) | Marked reduction in erythema and pain | Rat skin-toxicity model | [33] |
| Vaginal candidiasis | Propranolol (chitosan-decorated oleogel) | Total fungal clearance | Immunosuppressed rat model | [13] |
| Metabolic dysfunction | Sea-buckthorn free FAs (digested oleosomes) | Increased insulin secretion | MIN6 and EndoC-βH1 β-cell lines | [30] |
| Wound healing | FGF-1 fused oleosome protein | 98% wound closure | Rat full-thickness wounds | [37] |
| Photoprotection | Oleosome-based UV-filter blend | SPF 30 using 80% less active | Human in vivo study | [25] |
| Carrier Type | Source/Origin | EE | Stability (Shelf-Life/Peroxide Value) | Ease of Production | Approximate Industrial Cost (USD/kg) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oleosomes | Natural, plant-derived droplets from seeds | 90–98% for highly lipophilic drugs such as curcumin and CBD | Phospholipid–oleosin shell plus native tocopherols gives peroxide-induction times > 120 d at 25 °C | Aqueous grinding and centrifugation; no organic solvent or >500 bar HPH | 15–20 | [7,10,11,17,21] |
| SLNs | Synthetic (hydrogenated lipids + surfactants) | 60–85% for lipophilic drugs; <25% for hydrophiles | Solid matrix slows leakage, but polymorphic transitions can expel drug on storage | Hot/cold HPH (>500 bar) + surfactant mix | 80–100 | [43,44] |
| NLCs | Synthetic blend of solid + liquid lipids | 80–95% due to imperfect crystal lattice | More stable than SLNs yet oil separation occurs above 30 °C | Same equipment as SLNs with liquid lipid step | 90–110 | [45,46] |
| Liposomes | Synthetic/semi-synthetic phospholipid bilayers | 60–95% for lipophiles; ≈100% for remote-loaded amphipathic drugs | Susceptible to oxidation/hydrolysis; often lyophilized or stored ≤ 4 °C | Thin-film hydration or microfluidics; purified phospholipids required | 150–200 | [47,48,49,50,53] |
| CQA | Importance | Primary Controls and Readouts | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Droplet size and PDI | Governs uptake, skin deposition, creaming, and release | Dynamic light scattering or laser diffraction targets by route; adjust pH and shear to tighten PDI | [1] |
| Zeta potential and interfacial proteins | Drives colloidal stability across pH and salts | ζ at storage pH; sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profile of oleosin, caleosin, steroleosin | |
| Lipid profile and oxidative state | Impacts robustness and release of lipophilic actives | FA by gas chromatography, sterols, peroxide value, and secondary products | |
| Co-extracted phenolics and storage proteins | Major determinant of oxidative stability and interface behavior | Retain phenolics or add antioxidants; monitor headspace O2, peroxide value, aldehydes | [7] |
| EE and loading | Sets feasible dose and exposure | EE and loading by mass balance or ultrafiltration; pH-shift or mild co-solvent loading | [10] |
| Release and bioaccessibility | Links in vitro behavior to in vivo absorption | pH-stat lipolysis with micellar partitioning for oral; Franz diffusion for topical | [11] |
| Study | Oleosome Source/ Xenobiotic | Lymphatic Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH-stat lipolysis (in vitro) Rat in vivo pharmacokinetics | Rapeseed oleosomes/CBD | ≈68% TAG hydrolysis and 90% CBD transfer into mixed micelles 2-fold higher plasma AUC and 8–26-fold greater CBD in mesenteric lymph nodes compared with bulk oil | [11] |
| Simulated digestion + rat in vivo | Hemp seed oleosomes/CBD | Droplets remain intact in the stomach and release CBD gradually in the intestine, supporting sustained lymph uptake | [26] |
| Mechanistic review | Multiple botanical sources | Identifies 0.5–2 µm diameter and unsaturated C18 TAGs as optimal for chylomicron assembly | [18] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mallillin III, M.C.; Pajimna, R.M.B.; Zhao, S.; Salami, M.; Loebenberg, R.; Davies, N.M. Oleosome Delivery Systems: Enhancing Stability and Therapeutic Potential of Natural Products and Xenobiotics. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1303. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101303
Mallillin III MC, Pajimna RMB, Zhao S, Salami M, Loebenberg R, Davies NM. Oleosome Delivery Systems: Enhancing Stability and Therapeutic Potential of Natural Products and Xenobiotics. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(10):1303. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101303
Chicago/Turabian StyleMallillin III, Marlon C., Roi Martin B. Pajimna, Shengnan Zhao, Maryam Salami, Raimar Loebenberg, and Neal M. Davies. 2025. "Oleosome Delivery Systems: Enhancing Stability and Therapeutic Potential of Natural Products and Xenobiotics" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 10: 1303. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101303
APA StyleMallillin III, M. C., Pajimna, R. M. B., Zhao, S., Salami, M., Loebenberg, R., & Davies, N. M. (2025). Oleosome Delivery Systems: Enhancing Stability and Therapeutic Potential of Natural Products and Xenobiotics. Pharmaceutics, 17(10), 1303. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17101303










