Towards the Oral Treatment of Ileo-Colonic Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Infliximab Tablets: Development and Validation of the Production Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Lyophilization
2.4. IFX-Sugar Glass Compacts
2.5. Tablet Core Production
2.6. Tablet Coating
2.7. Resistance to Crushing and Friability Tests
2.8. Sample Preparation
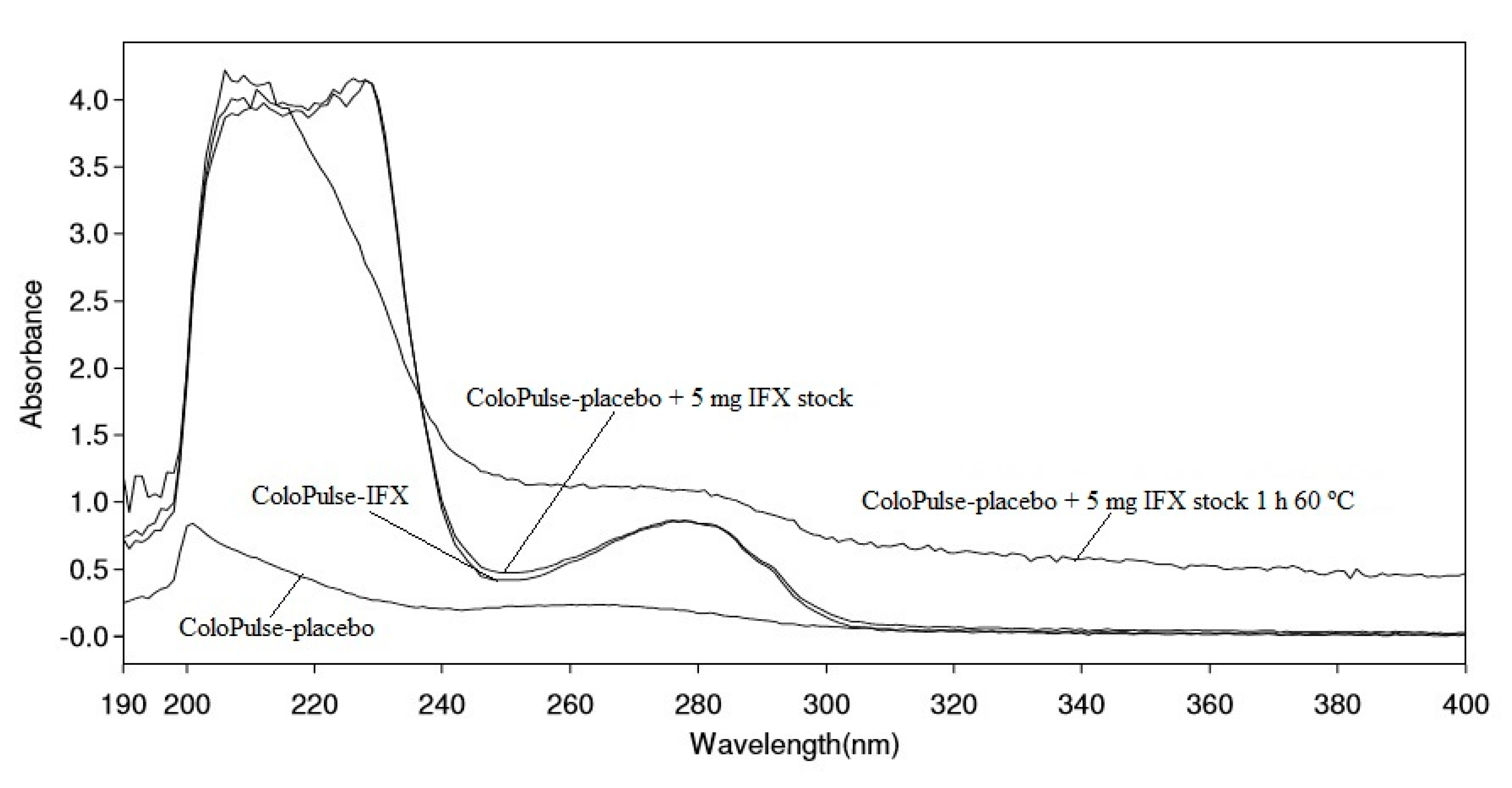
2.9. UV-VIS Spectroscopy Analysis
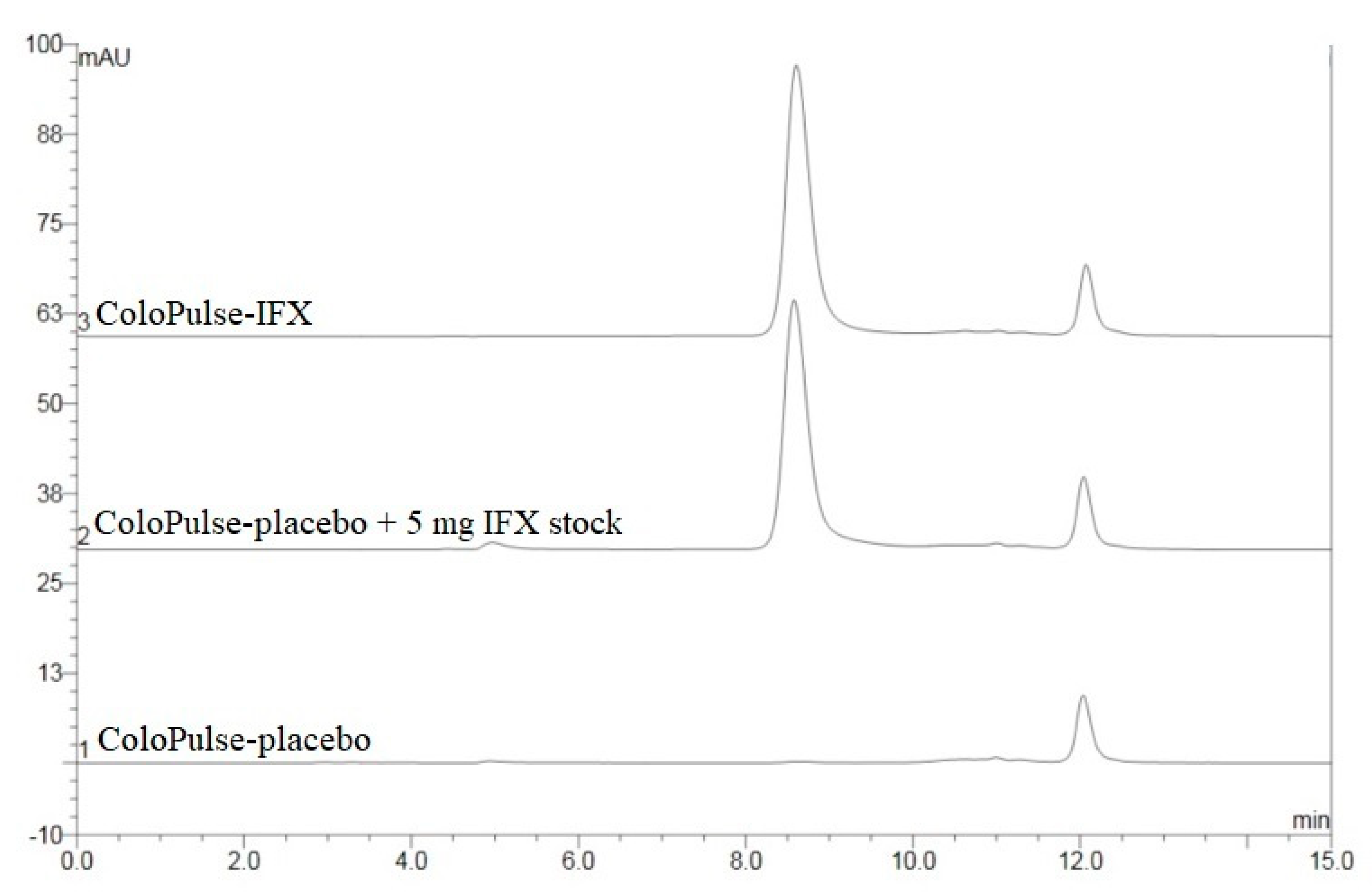
2.10. HPLC-SEC Analysis
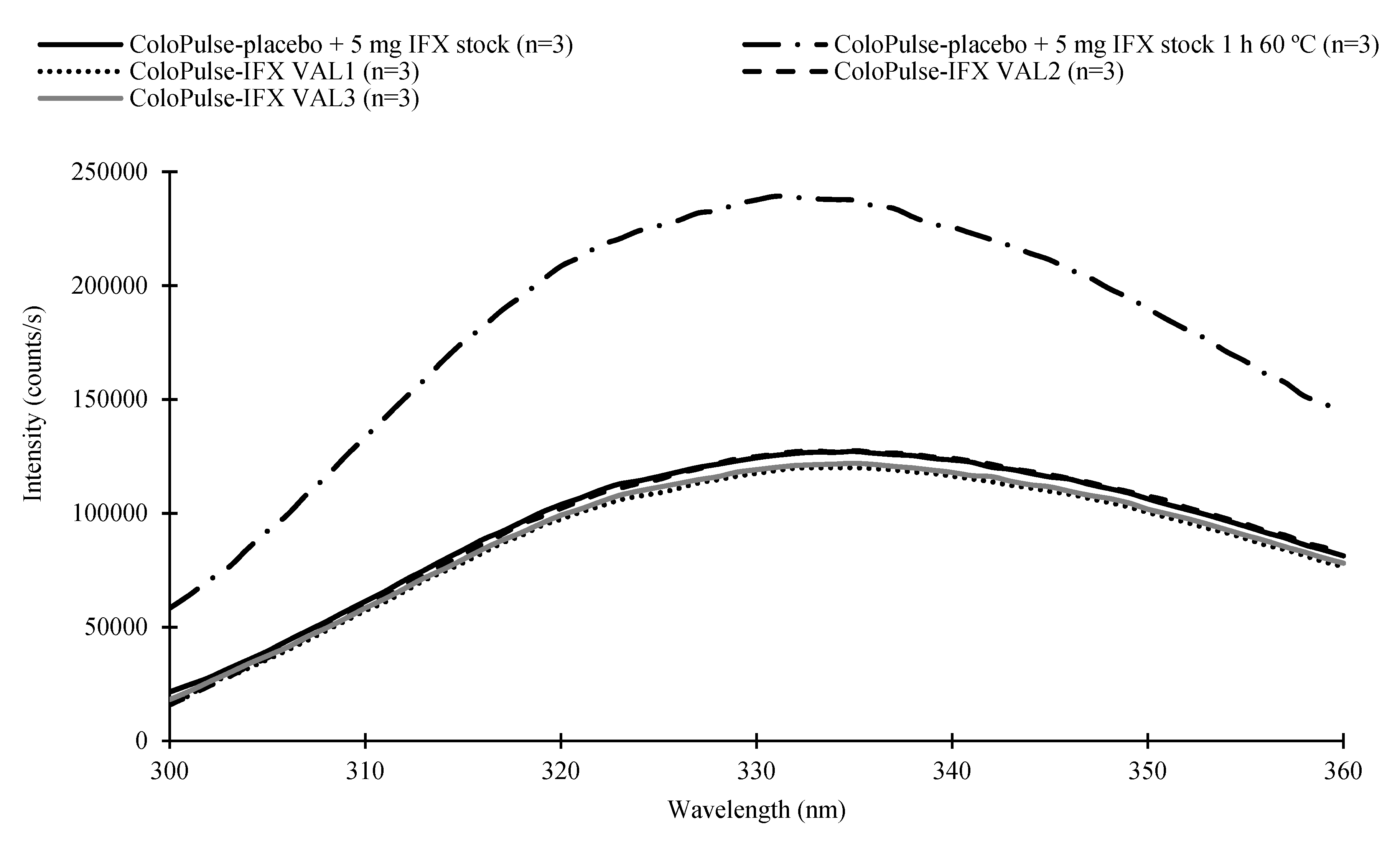
2.11. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
2.12. ELISA Analysis
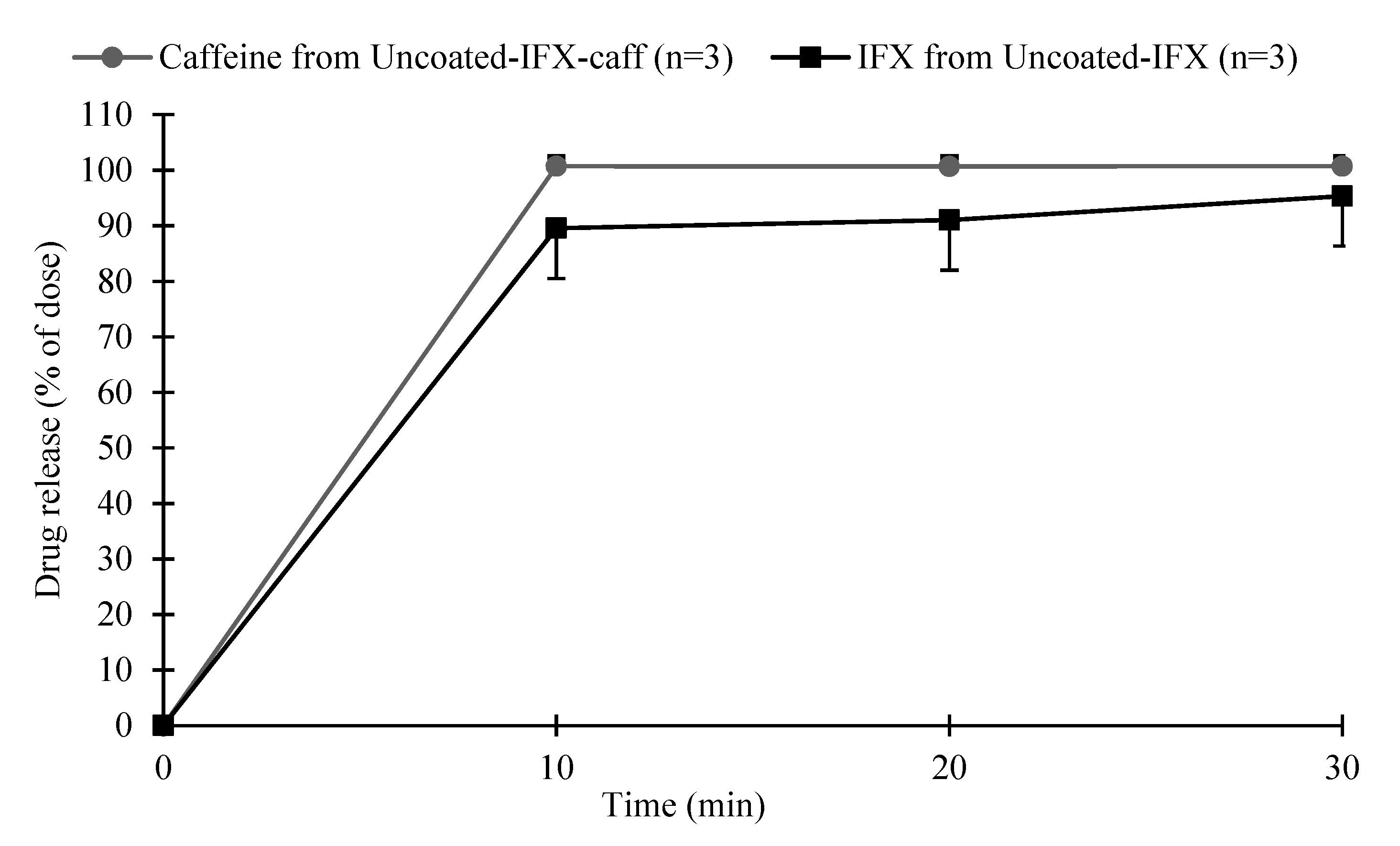
2.13. Comparison of the Infliximab and Caffeine Release Profiles
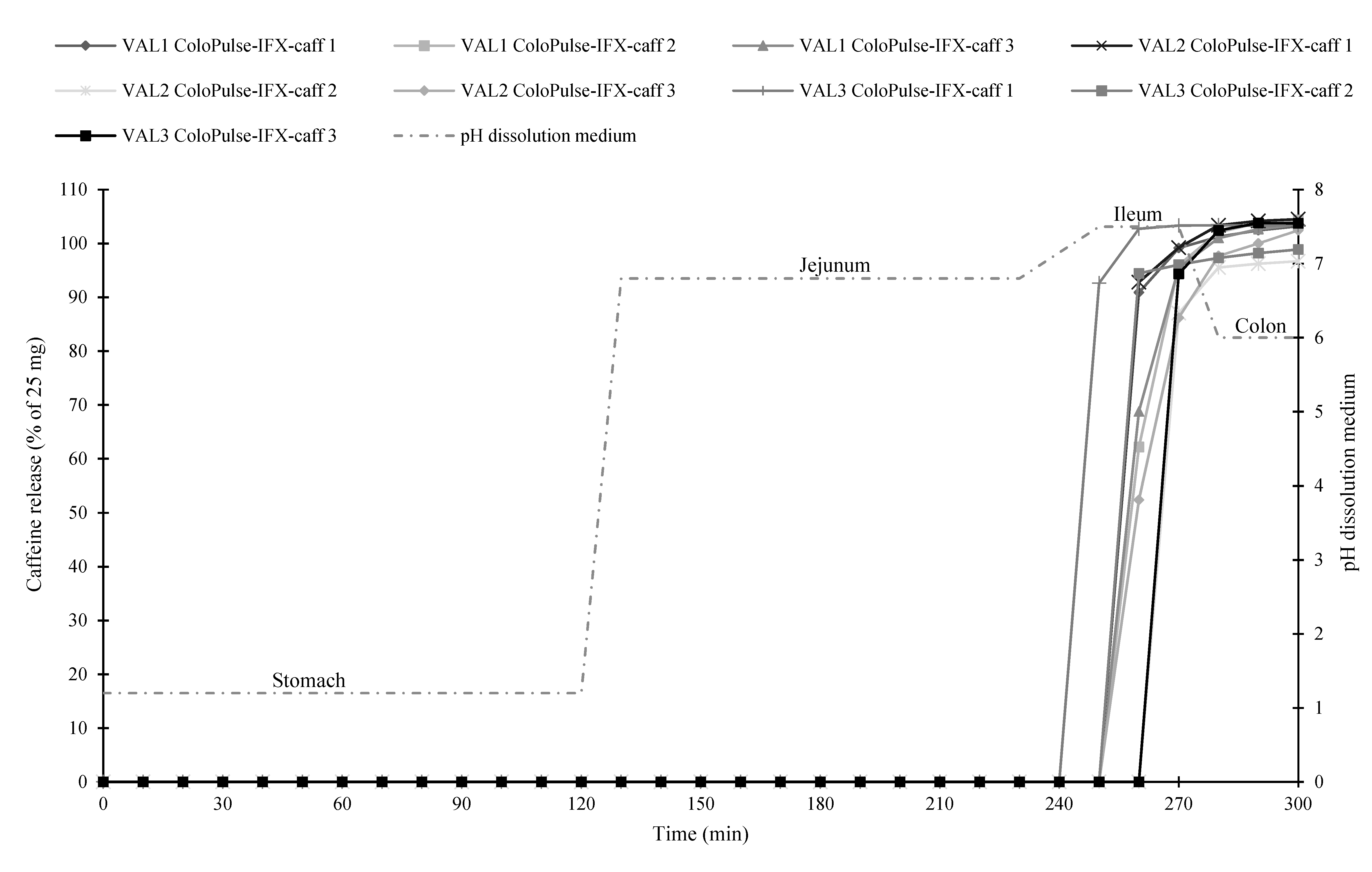
2.14. Gastrointestinal Simulation System
2.15. Preliminary Stability Study
3. Results
3.1. IFX-Sugar Glass Compacts
3.2. Resistance to Crushing and Tablet Friability
3.3. HPLC-SEC Analysis
3.4. UV-VIS Spectroscopy Analysis
3.5. Fluorescence Spectroscopy Analysis
3.6. ELISA Analysis
3.7. Comparison of the Infliximab and Caffeine Release Profiles
3.8. Gastrointestinal Simulation System
3.9. Preliminary Stability Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ungaro, R.; Mehandru, S.; Allen, P.B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Colombel, J.F. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1756–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppercorn, M.A.; Kane, S.V. Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis and Prognosis of Crohn Disease in Adults. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/clinical-manifestations-diagnosis-and-prognosis-of-crohn-disease-in-adults?search=Clinical manifestations, diagnosis and prognosis of Crohn disease in adults&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&dis (accessed on 12 May 2018).
- Spekhorst, L.M.; Imhann, F.; Festen, E.A.M.; Bodegraven, A.A.; Boer, N.K.H.; Bouma, G.; Fidder, H.H.; D’Haens, G.; Hoentjen, F.; Hommes, D.W.; et al. Cohort profile: Design and first results of the Dutch IBD Biobank: A prospective, nationwide biobank of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, C.; Cho, J.H. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2066–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vegh, Z.; Burisch, J.; Pedersen, N.; Kaimakliotis, I.; Duricova, D.; Bortlik, M.; Avnstrøm, S.; Vinding, K.K.; Olsen, J.; Nielsen, K.R.; et al. Incidence and initial disease course of inflammatory bowel diseases in 2011 in Europe and Australia: Results of the 2011 ECCO-EpiCom inception cohort. J. Crohns. Colitis 2014, 8, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, H.S.P.; Fiocchi, C.; de Souza, H.S.; Fiocchi, C.; de Souza, H.S.P.; Fiocchi, C.P.; de Souza, H.S.; Fiocchi, C. Immunopathogenesis of IBD: Current state of the art. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2015, 13, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N. Epidemiology and risk factors for IBD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F. Cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geremia, A.; Biancheri, P.; Allan, P.; Corazza, G.R.; Di Sabatino, A. Innate and adaptive immunity in inflammatory bowel disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2014, 13, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.D.; Wildenberg, M.E.; van den Brink, G.R. Mechanism of action of anti-TNF therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. J. Crohns. Colitis 2016, 10, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, S. Mechanisms of action of infliximab in inflammatory bowel disease: An anti-inflammatory multitasker. Dig. Liver Dis. 2008, 40, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peake, S.T.C.; Bernardo, D.; Mann, E.R.; Al-Hassi, H.O.; Knight, S.C.; Hart, A.L. Mechanisms of Action of Anti–tumor Necrosis Factor α Agents in Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, M.M.; Thomas, A.G.; Akobeng, A.K. Tumour necrosis factor alpha blocking agents for induction of remission in ulcerative colitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Fumery, M.; Sandborn, W.J.; Murad, M.H. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: First–and second-line pharmacotherapy for moderate-severe ulcerative colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 47, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cholapranee, A.; Hazlewood, G.S.; Kaplan, G.G.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Comparative efficacy of biologics for induction and maintenance of mucosal healing in Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis controlled trials. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1291–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbord, M.; Eliakim, R.; Bettenworth, D.; Karmiris, K.; Katsanos, K.; Kopylov, U.; Kucharzik, T.; Molnár, T.; Raine, T.; Sebastian, S.; et al. Third European evidence-based consensus on diagnosis and management of ulcerative colitis. Part 2: Current management. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stidham, R.W.; Lee, T.C.H.; Higgins, P.D.R.; Deshpande, A.R.; Sussman, D.A.; Singal, A.G.; Elmunzer, B.J.; Saini, S.D.; Vijan, S.; Waljee, A.K. Systematic review with network meta-analysis: The efficacy of anti-TNF agents for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuenzig, M.; Rezaie, A.; Seow, C.H.; Steinhart, A.H.; Griffiths, A.M.; Kaplan, G.G.; Benchimol, E.I. Budesonide for maintenance of remission in Crohn’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 1, CD002913. [Google Scholar]
- Gomollón, F.; Dignass, A.; Annese, V.; Tilg, H.; Van Assche, G.; Lindsay, J.O.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Cullen, G.J.; Daperno, M.; Kucharzik, T.; et al. 3rd European evidence-based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease 2016: Part 1: Diagnosis and medical management. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonovas, S.; Fiorino, G.; Allocca, M.; Lytras, T.; Nikolopoulos, G.K.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Biologic Therapies and Risk of Infection and Malignancy in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 1385–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, E.D.; Farida, J.P.; Siegel, C.A.; Chong, K.; Melmed, G.Y. Risk for Overall Infection with Anti-TNF and Anti-integrin Agents Used in IBD. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Meara, S.; Nanda, K.S.; Moss, A.C. Antibodies to infliximab and risk of infusion reactions in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2014, 20, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, K.S.; Cheifetz, A.S.; Moss, A.C. Impact of antibodies to infliximab on clinical outcomes and serum infliximab levels in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): A meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maser, E.A.; Villela, R.; Silverberg, M.S.; Greenberg, G.R. Association of Trough Serum Infliximab to Clinical Outcome After Scheduled Maintenance Treatment for Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornillie, F.; Shealy, D.; D’Haens, G.; Geboes, K.; Van Assche, G.; Ceuppens, J.; Wagner, C.; Schaible, T.; Plevy, S.E.; Targan, S.R.; et al. Infliximab induces potent anti-inflammatory and local immunomodulatory activity but no systemic immune suppression in patients with Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Haens, G.; Van Deventer, S.; Van Hogezand, R.; Chalmers, D.; Kothe, C.; Baert, F.; Braakman, T.; Schaible, T.; Geboes, K.; Rutgeerts, P. Endoscopic and histological healing with infliximab anti–tumor necrosis factor antibodies in Crohn’s disease: A European multicenter trial. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Arena, V.; Stigliano, E.; Boninsegna, A.; Bibbò, S.; Poscia, A.; Alfieri, S.; Rosa, F.; Amato, A.; et al. Direct effect of infliximab on intestinal mucosa sustains mucosal healing: Exploring new mechanisms of action. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T.; Rismo, R.; Gundersen, M.D.; Paulssen, E.J.; Johnsen, K.; Kvamme, J.M.; Goll, R.; Florholmen, J. Normalization of mucosal tumor necrosis factor-α: A new criterion for discontinuing infliximab therapy in ulcerative colitis. Cytokine 2016, 79, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarur, A.J.; Jain, A.; Sussman, D.A.; Barkin, J.S.; Quintero, M.A.; Princen, F.; Kirkland, R.; Deshpande, A.R.; Singh, S.; Abreu, M.T. The association of tissue anti-TNF drug levels with serological and endoscopic disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease: The ATLAS study. Gut 2015, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, C.; Ierardi, E.; Burattini, O.; De Francesco, V.; Zullo, A.; Stoppino, G.; Panella, C.; Morini, S. Tumour necrosis factor alpha down-regulation parallels inflammatory regression in ulcerative colitis patients treated with infliximab. Dig. Liver Dis. 2007, 39, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Zúñiga, V.; Boix, J.; Mañosa, M.; Lezcano, C.; Cabré, E.; Moreno de Vega, V.; Domènech, E. Local injection of infliximab in symptomatic isolated mucosal lesions: A novel scenario for endoscopic therapy? Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendel, J.; Karstensen, J.G.; Vilmann, P. Serial intralesional injections of infliximab in small bowel Crohn’s strictures are feasible and might lower inflammation. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2014, 2, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancone, L.; Cretella, M.; Tosti, C.; Palmieri, G.; Petruzziello, C.; Geremia, A.; Calabrese, E.; Pallone, F. Local injection of infliximab in the postoperative recurrence of Crohn’s disease. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2006, 63, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, M.S.; Hartman, D.; Lemos, B.R.; Erlich, E.C.; Spence, S.; Kennedy, S.; Ptak, T.; Pruitt, R.; Vermeire, S.; Fox, B.S. AVX-470, an Orally Delivered Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor Antibody for Treatment of Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results of a First-in-Human Trial. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2016, 10, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, D.S.; Tracey, D.E.; Lemos, B.R.; Erlich, E.C.; Burton, R.E.; Keane, D.M.; Patel, R.; Kim, S.; Bhol, K.C.; Harris, M.S.; et al. Effects of AVX-470, an Oral, Locally Acting Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor Antibody, on Tissue Biomarkers in Patients with Active Ulcerative Colitis. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2016, 10, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugent, S.G.; Kumar, D.; Rampton, D.S.; Evans, D.F. Intestinal luminal pH in inflammatory bowel disease: Possible determinants and implications for therapy with aminosalicylates and other drugs. Gut 2001, 48, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.F.; Pye, G.; Bramley, R.; Clark, A.G.; Dyson, T.J.; Hardcastle, J.D. Measurement of gastrointestinal pH profiles in normal ambulant human subjects. Gut 1988, 29, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, J.M.; Schellekens, R.C.A.; Van Rieke, H.M.; Wanke, C.; Iordanov, V.; Stellaard, F.; Wutzke, K.D.; Dijkstra, G.; Van Der Zee, M.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; et al. Gastrointestinal pH and transit time profiling in healthy volunteers using the IntelliCap system confirms ileo-colonic release of ColoPulse tablets. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, E.L.; Fadda, H.M.; Basit, A.W. Gut instincts: Explorations in intestinal physiology and drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, J.M.; Schellekens, R.C.A.; van Rieke, H.M.; Stellaard, F.; Wutzke, K.D.; Buurman, D.J.; Dijkstra, G.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Frijlink, H.W.; Kosterink, J.G.W. ColoPulse tablets perform comparably in healthy volunteers and Crohn’s patients and show no influence of food and time of food intake on bioavailability. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, M.J.M.; Schellekens, R.C.A.; Wutzke, K.D.; Dijkstra, G.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Frijlink, H.W.; Kosterink, J.G.W.; Stellaard, F. A non-invasive, low-cost study design to determine the release profile of colon drug delivery systems: A feasibility study. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 2070–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellekens, R.C.A.; Stellaard, F.; Olsder, G.G.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Frijlink, H.W.; Kosterink, J.G.W. Oral ileocolonic drug delivery by the colopulse-system: A bioavailability study in healthy volunteers. J. Control. Release 2010, 146, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schellekens, R.C.A.; Olsder, G.G.; Langenberg, S.M.C.H.; Boer, T.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Frijlink, H.W.; Kosterink, J.G.W.; Stellaard, F. Proof-of-concept study on the suitability of 13C-urea as a marker substance for assessment of in vivo behaviour of oral colon-targeted dosage forms. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maurer, J.M.; Hofmana, S.; Schellekens, R.C.A.; Tonnis, W.F.; Dubois, A.O.T.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Hinrichs, W.L.J.; Kosterink, J.G.W.; Frijlink, H.W. Development and potential application of an oral ColoPulse infliximab tablet with colon specific release: A feasibility study. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 505, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, R.M.; Domingo, R.; Sandhu, J. Oral Delivery of Antibodies. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1997, 32, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jasion, V.S.; Burnett, B.P. Survival and digestibility of orally-administered immunoglobulin preparations containing IgG through the gastrointestinal tract in humans. Nutr. J. 2015, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Waaij, L.A.; Kroese, F.G.; Visser, A.; Nelis, G.F.; Westerveld, B.D.; Jansen, P.L.; Hunter, J.O. Immunoglobulin coating of faecal bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2004, 16, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yadav, V.; Varum, F.; Bravo, R.; Furrer, E.; Basit, A.W. Gastrointestinal stability of therapeutic anti-TNF α IgG1 monoclonal antibodies. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 502, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Volpatti, D.; Gulisano, E.; Spanghero, M. Short note: Infliximab recovery in a simulated intestinal fluid of the upper intestine tract. Hum. Antibodies 2019, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensink, M.A.; Frijlink, H.W.; van der Voort Maarschalk, K.; Hinrichs, W.L.J. How sugars protect proteins in the solid state and during drying (review): Mechanisms of stabilization in relation to stress conditions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 114, 288–295. [Google Scholar]
- Hinrichs, W.L.J.; Sanders, N.N.; De Smedt, S.C.; Demeester, J.; Frijlink, H.W. Inulin is a promising cryo- and lyoprotectant for PEGylated lipoplexes. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 465–479. [Google Scholar]
- Bubník, Z.; Kadlec, P. Sucrose solubility. In Sucrose: Properties and Applications; Mathlouthi, M., Reiser, P., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 101–125. ISBN 978-1-4615-2676-6. [Google Scholar]
- Tonnis, W.F.; Mensink, M.A.; de Jager, A.; van der Voort Maarschalk, K.; Frijlink, H.W.; Hinrichs, W.L.J. Size and Molecular Flexibility of Sugars Determine the Storage Stability of Freeze-Dried Proteins. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products Q1A(R2). Available online: https://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quality/Q1A_R2/Step4/Q1A_R2__Guideline.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2018).
- Ph. Eur. Appendix XVII G. Friability. Available online: https://www-pharmacopoeia-com.proxy-ub.rug.nl/bp-2018/appendices/appendix-17/appendix-xvii-g--friability.html?date=2018-07-01 (accessed on 29 May 2019).
- Ph. Eur. Appendix XII C. Consistency of Formulated Preparations. Available online: https://www-pharmacopoeia-com.proxy-ub.rug.nl/bp-2019/appendices/appendix-12/appendix-xii-c--consistency-of-formulated-preparations.html?date=2019-04-01&text=uniformity+of+content (accessed on 29 May 2019).
- Ghisaidoobe, A.; Chung, S. Intrinsic Tryptophan Fluorescence in the Detection and Analysis of Proteins: A Focus on Förster Resonance Energy Transfer Techniques. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22518–22538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanquin MabTrack M2920 Infliximab Instruction Manual. Available online: https://www.sanquin.org/products-and-services/reagents/products/immune-reagents/biologics/m2920 (accessed on 8 April 2019).
- Schelleken, R.C.A.; Stuurman, F.E.; van der Weert, F.H.J.; Kosterink, J.G.W.; Frijlink, H.W. A novel dissolution method relevant to intestinal release behaviour and its application in the evaluation of modified release mesalazine products. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, H.J.; Hinrichs, W.L.; van Veen, B.; Somsen, G.; de Jong, G.; Frijlink, H. Investigations into the stabilisation of drugs by sugar glasses: I. Tablets prepared from stabilised alkaline phosphatase. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 249, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandroni, L.; Kohn, A.; Cosintino, R.; Marrollo, M.; Papi, C.; Monterubbianesi, R.; Tersigni, R. Local injection of infliximab in severe fistulating perianal Crohn’s disease: An open uncontrolled study. Tech. Coloproctol. 2011, 15, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asteria, C.R.; Ficari, F.; Bagnoli, S.; Milla, M.; Tonelli, F. Treatment of perianal fistulas in Crohn’s disease by local injection of antibody to TNF-alpha accounts for a favourable clinical response in selected cases: A pilot study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 41, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poggioli, G.; Laureti, S.; Pierangeli, F.; Rizzello, F.; Ugolini, F.; Gionchetti, P.; Campieri, M. Local injection of infliximab for the treatment of perianal Crohn’s disease. Dis. Colon Rectum 2005, 48, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imon Lichtiger, S. Healing of perianal fistulae by local injection of antibody to TNF. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, A621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminath, A.; Lichtiger, S. Dilation of colonic strictures by intralesional injection of infliximab in patients with Crohn’s colitis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjögren, E.; Abrahamsson, B.; Augustijns, P.; Becker, D.; Bolger, M.B.; Brewster, M.; Brouwers, J.; Flanagan, T.; Harwood, M.; Heinen, C.; et al. In vivo methods for drug absorption—Comparative physiologies, model selection, correlations with in vitro methods (IVIVC), and applications for formulation/API/excipient characterization including food effects. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 57, 99–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, A.C.; Basit, A.W.; Choudhary, R.; Piong, C.W.; Merchant, H.A. Does sex matter? The influence of gender on gastrointestinal physiology and drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, V.; Varum, F.; Bravo, R.; Furrer, E.; Bojic, D.; Basit, A.W. Inflammatory bowel disease: Exploring gut pathophysiology for novel therapeutic targets. Transl. Res. 2016, 176, 38–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Auria, G.; Peris-Bondia, F.; Džunková, M.; Mira, A.; Collado, M.C.; Latorre, A.; Moya, A. Active and secreted IgA-coated bacterial fractions from the human gut reveal an under-represented microbiota core. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, A.; Khoo, U.Y.; Forgacs, I.; Philpott-Howard, J.; Bjarnason, I. Mucosal antibodies in inflammatory bowel disease are directed against intestinal bacteria. Gut 1996, 38, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandse, J.F.; van den Brink, G.R.; Wildenberg, M.E.; van der Kleij, D.; Rispens, T.; Jansen, J.M.; Mathôt, R.A.; Ponsioen, C.Y.; Löwenberg, M.; D’Haens, G.R.A.M. Loss of Infliximab into Feces Is Associated with Lack of Response to Therapy in Patients with Severe Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espacenet pH-Controlled Pulsatile Delivery System, Methods for Preparation and Use Thereof. Available online: https://worldwide.espacenet.com/publicationDetails/originalDocument?FT=D&date=20070201&DB=EPODOC&locale=en_EP&CC=WO&NR=2007013794A1&KC=A1&ND=4 (accessed on 5 August 2019).
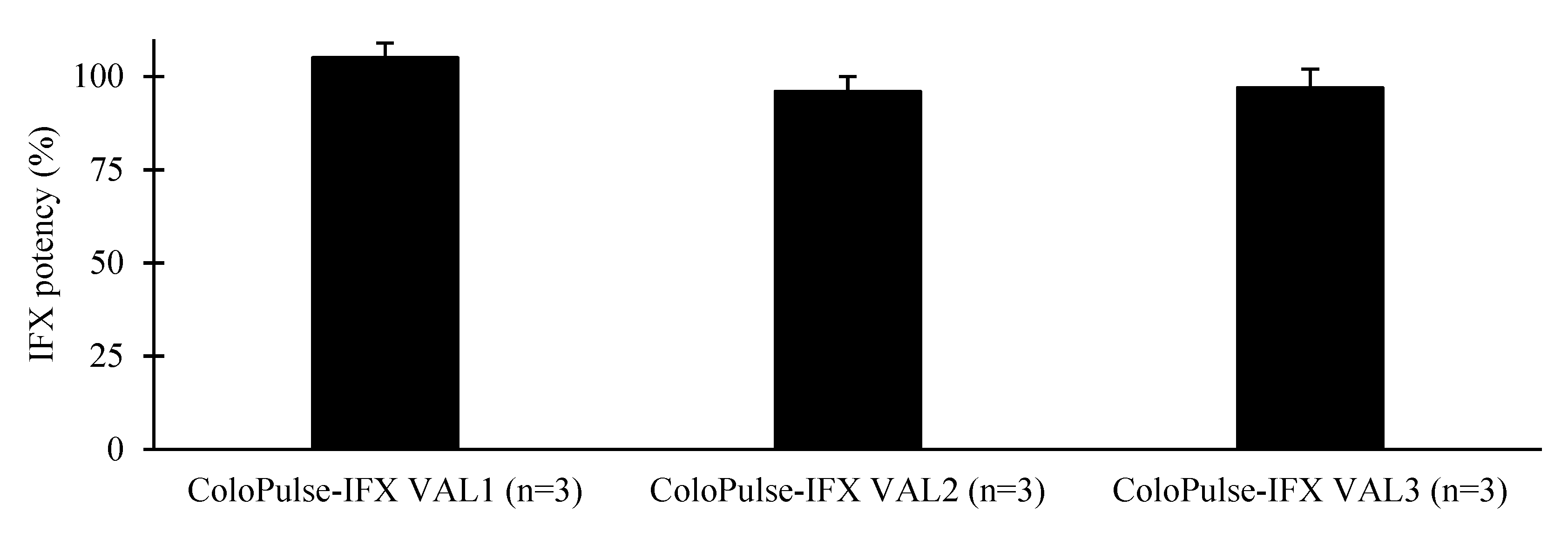
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Tablet shape | Biconvex, round, 9 mm |
| Uncoated tablet mass | 350 mg |
| Content a | 90%–110% of claim |
| IFX release a | ≥85% of the dose within 30 min in simulated ileum |
| Tertiary protein structure b | No apparent deviations compared to fresh IFX stock |
| Soluble aggregates/fragments a | No apparent deviations compared to fresh IFX stock |
| IFX potency c | 90%–110% compared to fresh IFX stock |
| Applied coating d | 11–15 mg/cm2 |
| Ileo-colonic targeting e | Initial coating disintegration in the simulated ileum |
| Components | Uncoated-IFX | Uncoated-IFX-Caff | ColoPulse-IFX | ColoPulse-IFX-Caff | ColoPulse-Placebo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFX-I a | 5 mg IFX | 5 mg IFX | 5 mg IFX | 5 mg IFX | - |
| Inulin (mg) | - | - | - | - | 55 b |
| Microcrystalline cellulose (mg) | Ad 350 | Ad 350 | Ad 350 | Ad 350 | Ad 350 |
| Silicon dioxide (mg) | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Croscarmellose sodium (mg) | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| Sodium stearyl fumarate (mg) | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Caffeine (mg) | - | 25 | - | 25 | - |
| ColoPulse (mg/cm2) c | - | - | 11–15 | 11–15 | 11–15 |
| Sugar | Processing a | Content (IFX mg/g) b | Recovery (%) b |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFX-I | Non-comp. | 87 ± 0.1 | 97 ± 0.1 |
| Non-comp. pulv. | 89 ± 2 | 99 ± 2 | |
| Comp. 1 kN | 82 ± 0.2 | 91 ± 0.2 | |
| Comp. 3 kN | 82 ± 0.7 | 91 ± 0.8 | |
| IFX-D | Non-comp. | 82 ± 0.3 | 91 ± 0.3 |
| Non-comp. pulv. | 80 ± 0.1 | 89 ± 0.1 | |
| Comp. 1 kN | 73 ± 0.3 | 81 ± 0.3 | |
| Comp. 3 kN | 69 ± 1 | 77 ± 1 | |
| IFX-T | Non-comp. | 83 ± 0.1 | 92 ± 0.1 |
| Non-comp. pulv. | 82 ± 0.3 | 91 ± 0.3 | |
| Comp. 1 kN | 82 ± 0.6 | 91 ± 0.7 | |
| Comp. 3 kN | 80 ± 1 | 89 ± 1 |
| Analysis | VAL1 | VAL2 | VAL3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFX-I (mg/g) a | 91 ± 1 | 88 ± 0.5 | 89 ± 2 |
| Uncoated-IFX (%) | 101 ± 2 | 94 ± 1 | 96 ± 3 |
| ColoPulse-IFX (%) | 96 ± 2 | 97 ± 3 | 96 ± 2 |
| Acceptance Value b | 6.9 | 8.3 | 7.3 |
| Aggregates/fragments | Not observable | Not observable | Not observable |
| IFX-I (mg IFX/g Powder) | ColoPulse-IFX (% of 5 mg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 months | 6 months | 0 months | 6 months | ||
| HPLC-SEC | HPLC-SEC | ELISA | HPLC-SEC | ELISA | HPLC-SEC |
| 91 ± 1.0 | 92 ± 0.4 | 105 ± 4 | 97 ± 2 | 98 ± 2 | 103 ± 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gareb, B.; Posthumus, S.; Beugeling, M.; Koopmans, P.; Touw, D.J.; Dijkstra, G.; Kosterink, J.G.W.; Frijlink, H.W. Towards the Oral Treatment of Ileo-Colonic Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Infliximab Tablets: Development and Validation of the Production Process. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090428
Gareb B, Posthumus S, Beugeling M, Koopmans P, Touw DJ, Dijkstra G, Kosterink JGW, Frijlink HW. Towards the Oral Treatment of Ileo-Colonic Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Infliximab Tablets: Development and Validation of the Production Process. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(9):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090428
Chicago/Turabian StyleGareb, Bahez, Silke Posthumus, Max Beugeling, Pauline Koopmans, Daan J. Touw, Gerard Dijkstra, Jos G.W. Kosterink, and Henderik W. Frijlink. 2019. "Towards the Oral Treatment of Ileo-Colonic Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Infliximab Tablets: Development and Validation of the Production Process" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 9: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090428
APA StyleGareb, B., Posthumus, S., Beugeling, M., Koopmans, P., Touw, D. J., Dijkstra, G., Kosterink, J. G. W., & Frijlink, H. W. (2019). Towards the Oral Treatment of Ileo-Colonic Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Infliximab Tablets: Development and Validation of the Production Process. Pharmaceutics, 11(9), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090428







