Inclusion Complexes of Melphalan with Gemini-Conjugated β-Cyclodextrin: Physicochemical Properties and Chemotherapeutic Efficacy in In-Vitro Tumor Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
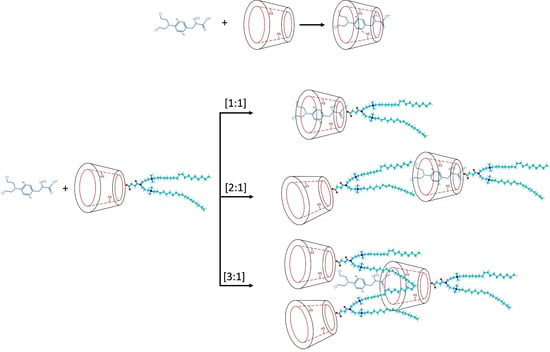
2.1. Preparation of Inclusion Complexes
2.2. Physicochemical Characterization
2.2.1. Size and Zeta Potential Measurements
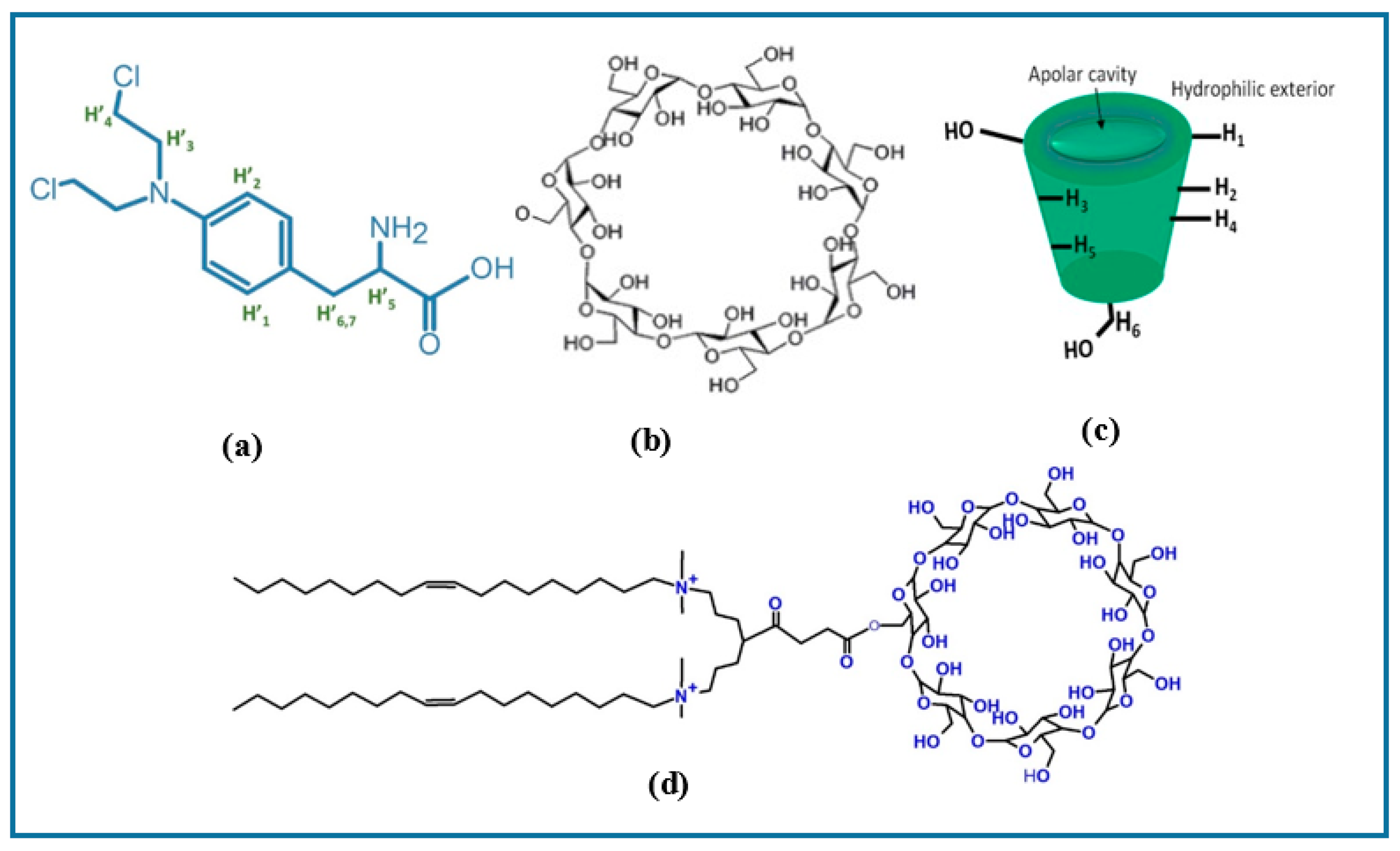
2.2.2. NMR Spectroscopy
2.3. In Vitro Evaluation
2.3.1. Determination of Half Maximal Inhibitory Concentration (IC50) in Monolayer Melanoma Cell Culture
2.3.2. In Vitro Efficiency in Spheroid Melanoma Cell
2.3.3. In Vitro Efficiency in Mel-Resistant Melanoma Cell Lines
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization
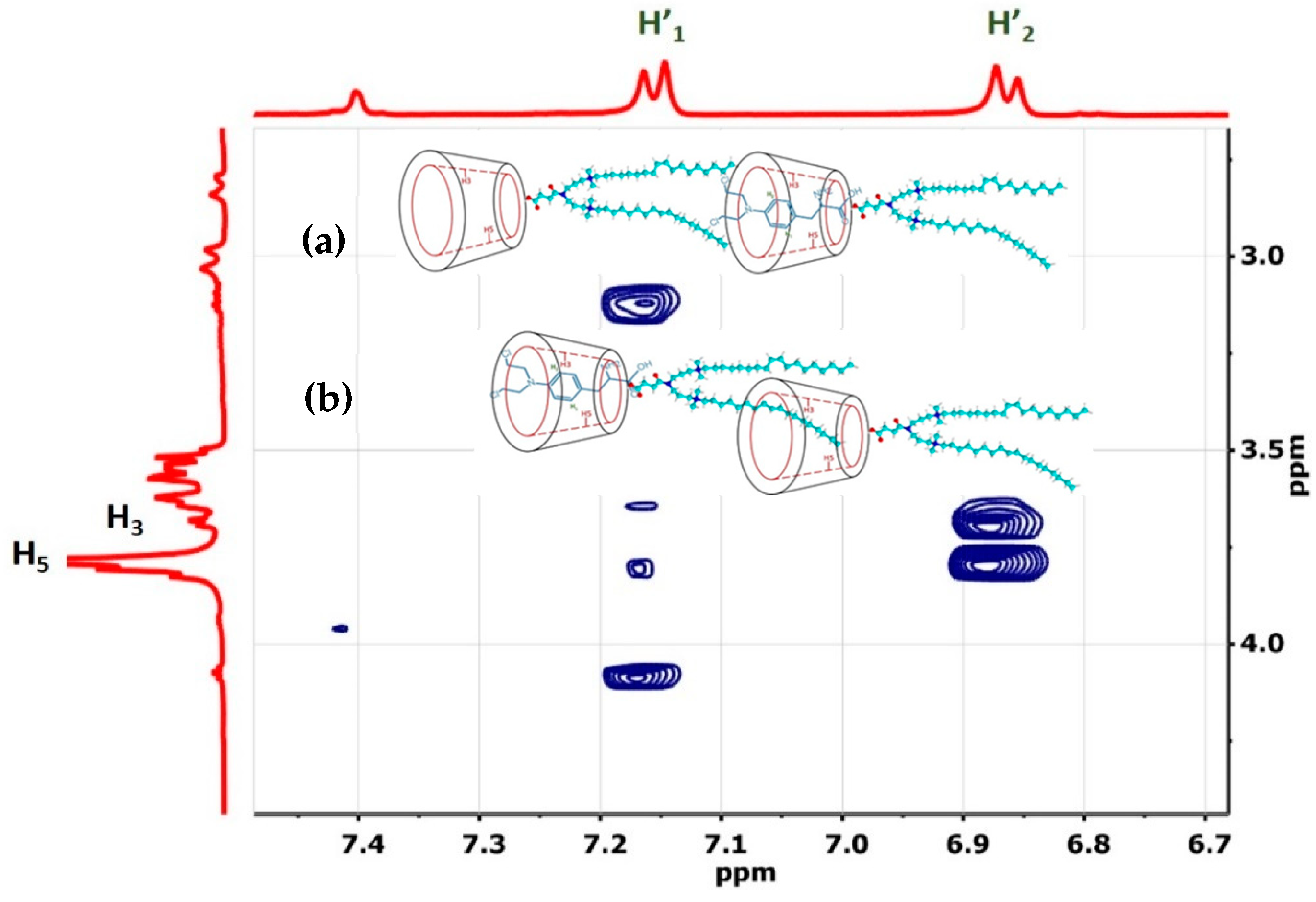
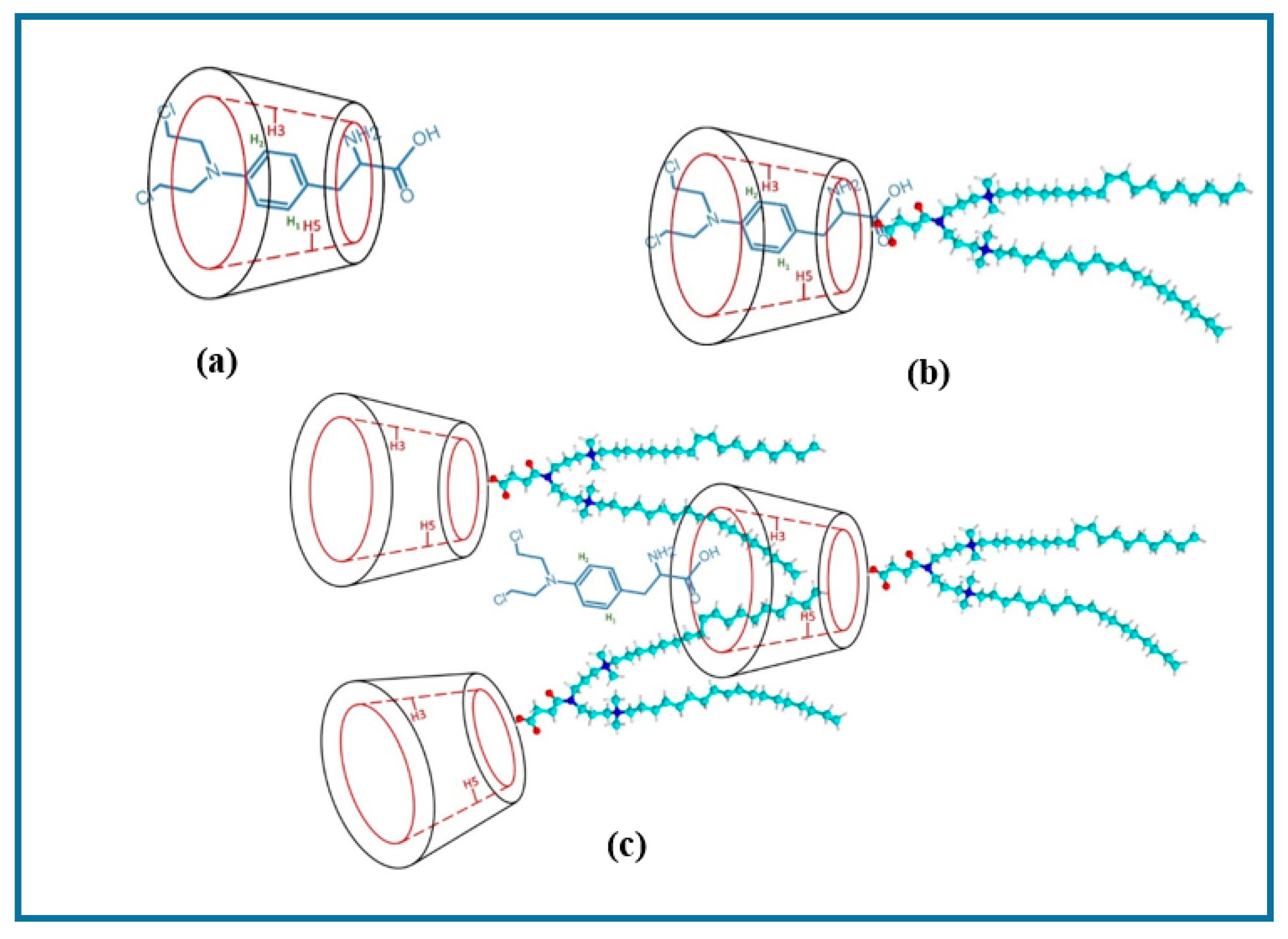
3.1.1. H NMR and 1D/2D ROESY
3.1.2. Size and Zeta Potential
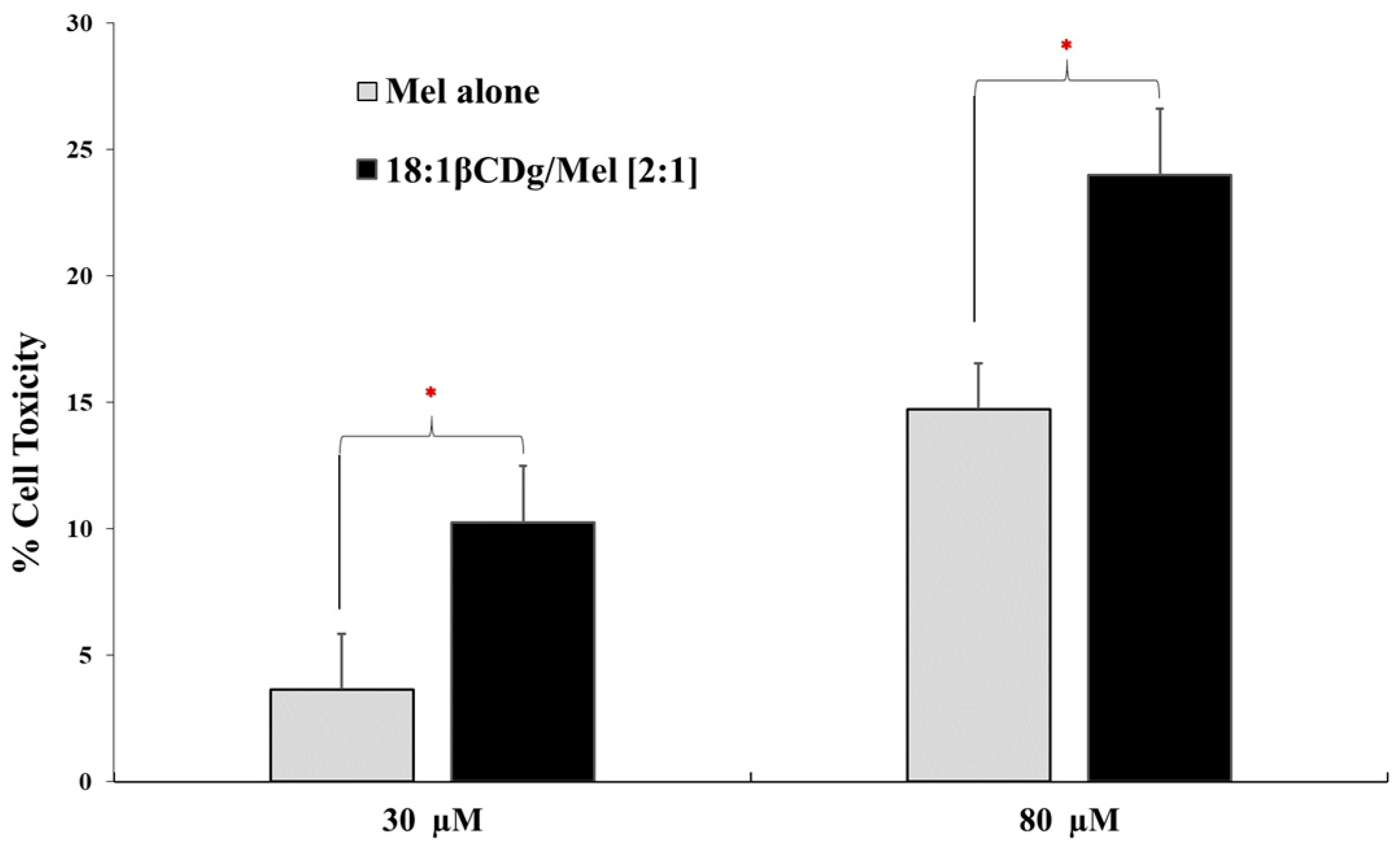
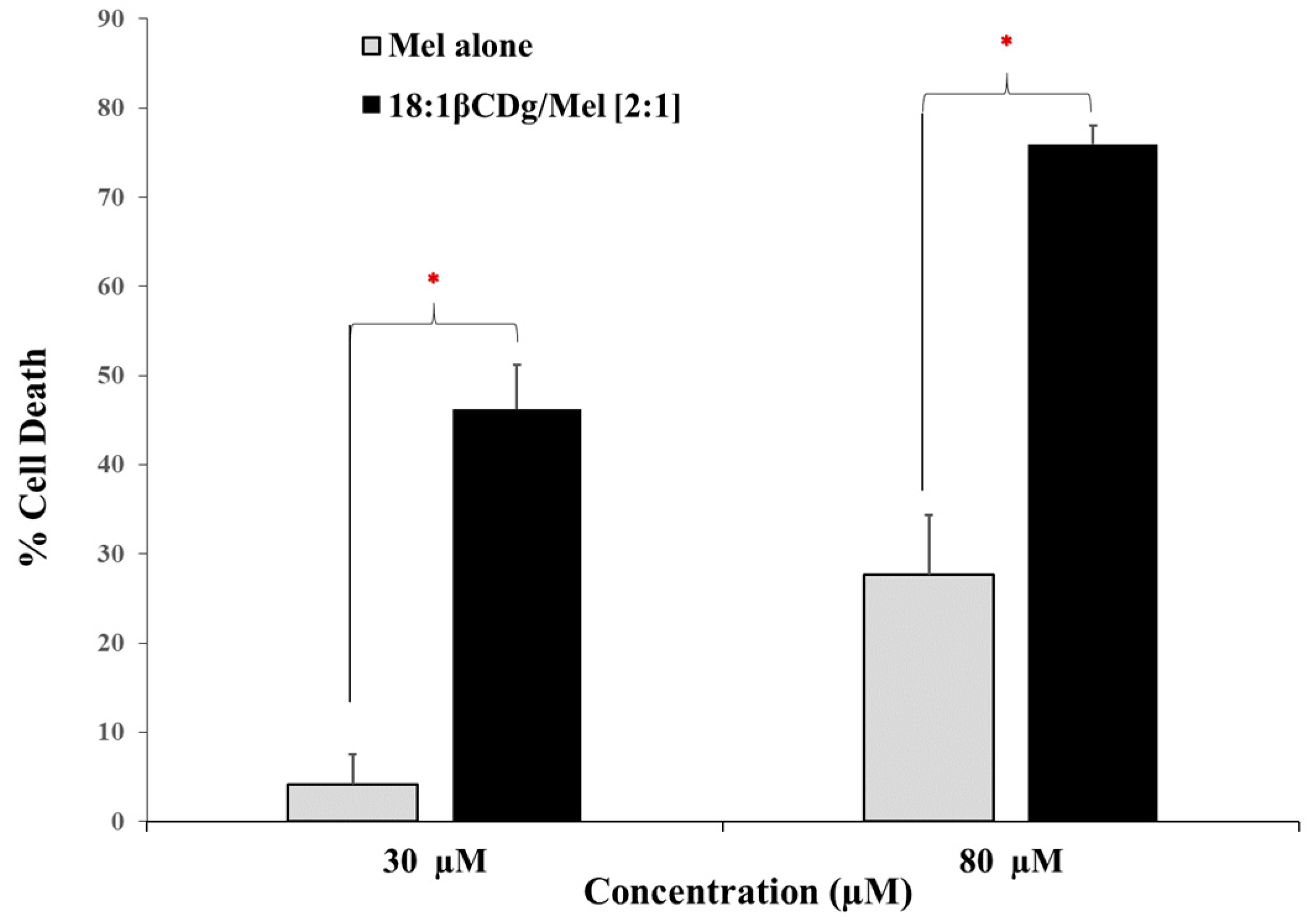
3.2. In Vitro Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pilgrim, W.; Hayes, R.; Hanson, D.W.; Zhang, B.; Boudreau, B.; Leonfellner, S. Skin Cancer (Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Malignant Melanoma): New Cases, Treatment Practice, and Health Care Costs in New Brunswick, Canada, 2002–2010. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2014, 18, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Skin Cancers. WHO, 2016. Available online: http://www.who.int/uv/faq/skincancer/en/index1.html (accessed on 26 February 2018).
- Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: The 7th Edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual and the Future of TNM. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, R.L.; Haydu, L.; Saw, R.P.; Quinn, M.J.; Shannon, K.; Spillane, A.J.; Thompson, J.F. In-transit melanoma metastases: Incidence, prognosis, and the role of lymphadenectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershenwald, J.E.; Giacco, G.G.; Lee, J.E. Cutaneous Melanoma. In 60 Years of Survival Outcomes at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 153–165. [Google Scholar]
- Testori, A.; Verhoef, C.; Kroon, H.M.; Pennacchioli, E.; Faries, M.B.; Eggermont, A.M.; Thompson, J.F. Treatment of melanoma metastases in a limb by isolated limb perfusion and isolated limb infusion. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 104, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zar, T.; Graeber, C.; Perazella, M.A. Reviews: Recognition, Treatment, and Prevention of Propylene Glycol Toxicity. Semin. Dial. 2007, 20, 217–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajazuddin; Alexander, A.; Amarji, B.; Kanaujia, P. Synthesis, characterization and in vitro studies of pegylated melphalan conjugates. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrode, C.; Weber, V.; David, E.; Vidal, A.; Auzeloux, P.; Communal, Y.; Chezal, J.M. Quaternary ammonium-melphalan conjugate for anticancer therapy of chondrosarcoma: In vitro and in vivo preclinical studies. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajpoot, P.; Bali, V.; Pathak, K. Anticancer efficacy, tissue distribution and blood pharmacokinetics of surface modified nanocarrier containing melphalan. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 426, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vodovozova, E.L.; Kuznetsova, N.R.; Kadykov, V.A.; Khutsyan, S.S.; Gaenko, G.P.; Molotkovsky, Y.G. Liposomes as nanocarriers of lipid-conjugated antitumor drugs melphalan and methotrexate. Nanotechnol. Russ. 2008, 3, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Wang, X.; Nie, S.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D.M. Therapeutic Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery in Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Sriwastawa, B.; Bhati, L.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Bannerjee, S.K. Drug delivery systems: An updated review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challa, R.; Ahuja, A.; Ali, J.; Khar, R.K. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery: An updated review. Aaps Pharmscitech 2005, 6, E329–E357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szejtli, J. Introduction and General Overview of Cyclodextrin Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Jarho, P.; Masson, M.; Järvinen, T. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Duchene, D. Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 329, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Valle, E.M. Cyclodextrins and their uses: A review. Process. Biochem. 2004, 39, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, D.R.; Tomaszewski, K.; Damle, B.; Schlamm, H.T. Review of the basic and clinical pharmacology of sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin (SBECD). J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 3291–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, P.X. Cyclodextrin-based supramolecular systems for drug delivery: Recent progress and future perspective. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1215–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilajwar, S.V.; Pednekar, P.P.; Jadhav, K.R.; Gupta, G.J.; Kadam, V.J. Cyclodextrin-based nanosponges: A propitious platform for enhancing drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallas, F.; Darcy, R. Amphiphilic Cyclodextrins—Advances in Synthesis and Supramolecular Chemistry. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 2008, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, F.; Ostacolo, L.; Mazzaglia, A.; Villari, V.; Zaccaria, D.; Sciortino, M.T. The intracellular effects of non-ionic amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanoparticles in the delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilensoy, E.; Hincal, A.A. Recent advances and future directions in amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanoparticles. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, S.; Donohue, R.; Ravoo, B.; Darcy, R.; O’Driscoll, C. Cationic cyclodextrin amphiphiles as gene delivery vectors. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2004, 14, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, D.; Chitanda, J.M.; Balogh, R.; Yang, P.; Singh, J.; Das, U.; El-Aneed, A.; Dimmock, J.; Verrall, R.; Badea, I. Design and evaluation of cyclodextrin-based delivery systems to incorporate poorly soluble curcumin analogs for the treatment of melanoma. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 81, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poorghorban, M.; Karoyo, A.H.; Grochulski, P.; Verrall, R.E.; Wilson, L.D.; Badea, I. A 1H NMR Study of Host/Guest Supramolecular Complexes of a Curcumin Analogue with β-Cyclodextrin and a β-Cyclodextrin-Conjugated Gemini Surfactant. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 2993–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poorghorban, M.; Das, U.; AlAidi, O.; Chitanda, J.M.; Michel, D.; Dimmock, J.; Verrall, R.; Grochulski, P.; Badea, I. Characterization of the host–guest complex of a curcumin analog with β-cyclodextrin and β-cyclodextrin–gemini surfactant and evaluation of its anticancer activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 503–515. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, D.; Mohammed-Saeid, W.; Getson, H.; Roy, C.; Poorghorban, M.; Chitanda, J.M.; Verrall, R.; Badea, I. Evaluation of β-cyclodextrin-modified gemini surfactant-based delivery systems in melanoma models. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 6703–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkuru, M.; Chitanda, J.M.; Verrall, R.E.; El-Aneed, A.; El-Aneed, A. Multi-stage tandem mass spectrometric analysis of novel β-cyclodextrin-substituted and novel bis-pyridinium gemini surfactants designed as nanomedical drug delivery agents. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 28, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Bharti, N.; Madan, J.; Hiremath, S. Characterization of cyclodextrin inclusion complexes—A review. J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 171–183. [Google Scholar]
- Mura, P. Analytical techniques for characterization of cyclodextrin complexes in aqueous solution: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 101, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiras, A.; Carvalho, R.A.; Ribeiro, L.; Torres-Labandeira, J.J.; Veiga, F.J. Solid-state characterization and dissolution profiles of the inclusion complexes of omeprazole with native and chemically modified β-cyclodextrin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Araujo, D.R.; Tsuneda, S.S.; Cereda, C.M.; Carvalho, F.D.G.; Preté, P.S.; Fernandes, S.A.; De F.A. Braga, A. Development and pharmacological evaluation of ropivacaine-2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 33, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, D.; Williamson, M.P. The nuclear Overhauser effect in structural and conformational analysis, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, S. One Dimensional and Two Dimensional NMR Spectra by Modern Pulse Techniques. Angew. Chem. 1992, 104, 108–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoyo, A.H.; Wilson, L.D. Preparation and Characterization of a Polymer-Based “Molecular Accordion”. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3066–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, H.-J.; Hacket, F.; Rüdiger, V.; Ikeda, H. NMR Studies of Cyclodextrins and Cyclodextrin Complexes. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1755–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.D.; Siddall, S.R.; Verrall, R.E. A spectral displacement study of the binding constants of cyclodextrin–hydrocarbon and –fluorocarbon surfactant inclusion complexes. Can. J. Chem. 1997, 75, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasikuttan, A.C.; Mohanty, J.; Nau, W.M.; Pal, H. Efficient Fluorescence Enhancement and Cooperative Binding of an Organic Dye in a Supra-biomolecular Host–Protein Assembly. Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 4198–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed-Saeid, W.; Michel, D.; Badea, I.; El-Aneed, A.; Mohammed-Saeid, W.; El-Aneed, A. Rapid and Simple Flow Injection Analysis-Tandem Mass Spectrometric (FIA-MS/MS) Method for the Quantification of Melphalan in Lipid-Based Drug Delivery System. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 31, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, T.; Connors, A. Phase-solubility techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 1965, 4, 117–210. [Google Scholar]
- Zhengyu, J. Cyclodextrins: Preparation and Application in Industry; World Scientific: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gaumet, M.; Vargas, A.; Gurny, R.; Delie, F. Nanoparticles for drug delivery: The need for precision in reporting particle size parameters. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 69, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decuzzi, P.; Godin, B.; Tanaka, T.; Lee, S.-Y.; Chiappini, C.; Liu, X.; Ferrari, M. Size and shape effects in the biodistribution of intravascularly injected particles. J. Control. Release 2010, 141, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhand, C.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Beuerman, R.W.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Dwivedi, N.; Ramakrishna, S. Role of size of drug delivery carriers for pulmonary and intravenous administration with emphasis on cancer therapeutics and lung-targeted drug delivery. Rsc Adv. 2014, 4, 32673–32689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, S.E.A.; Ropp, P.A.; Pohlhaus, P.D.; Luft, J.C.; Madden, V.J.; Napier, M.E.; DeSimone, J.M. The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11613–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E. The role of surface charge in cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of medical nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5577–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, S.A.; Riley, C.M. The hydrolysis of l-phenylalanine mustard (melphalan). Int. J. Pharm. 1985, 24, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-M.J.; Zhang, L. Nanoparticle-based combination therapy toward overcoming drug resistance in cancer. Biochem. Pharm. 2012, 83, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

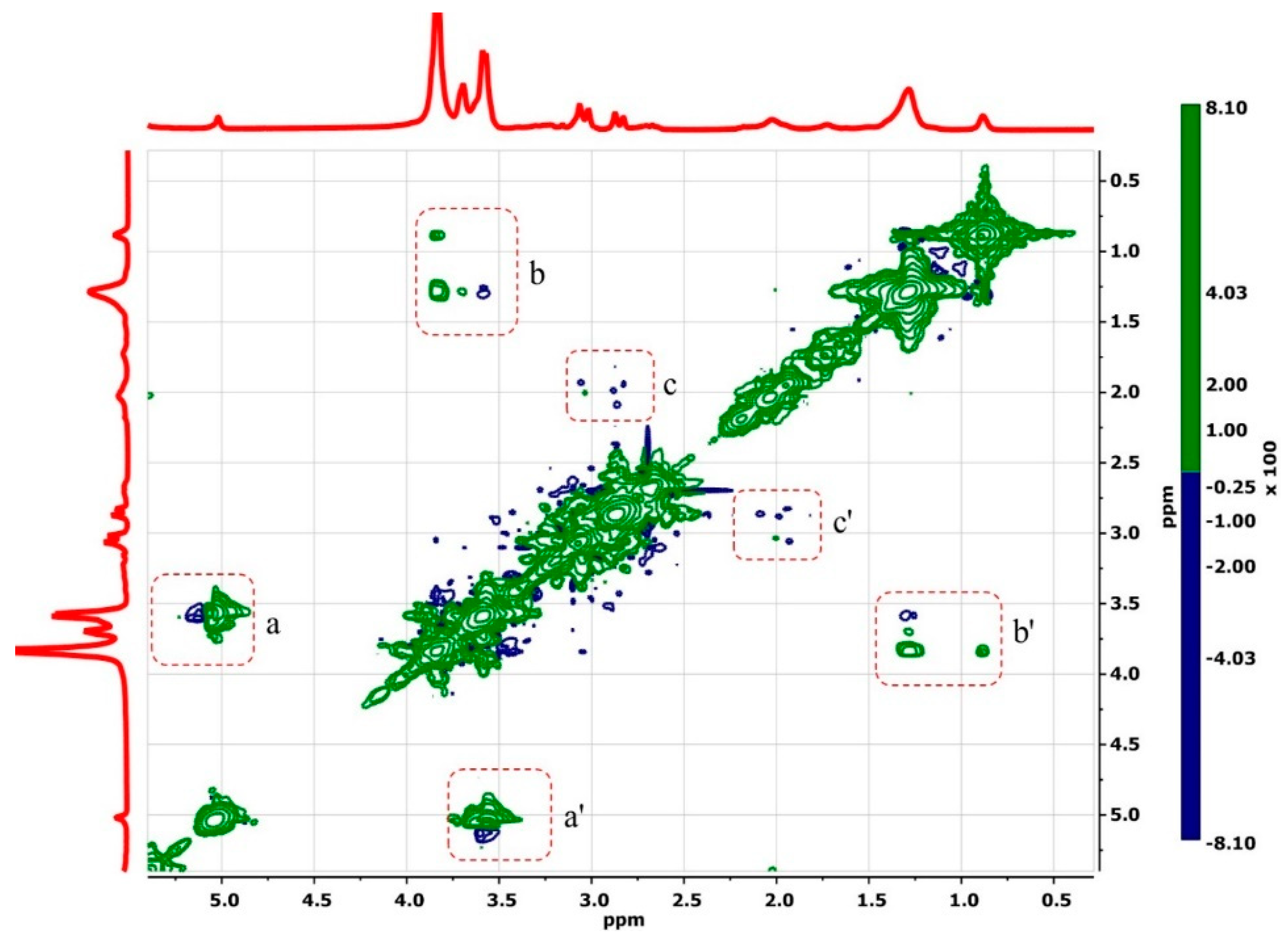
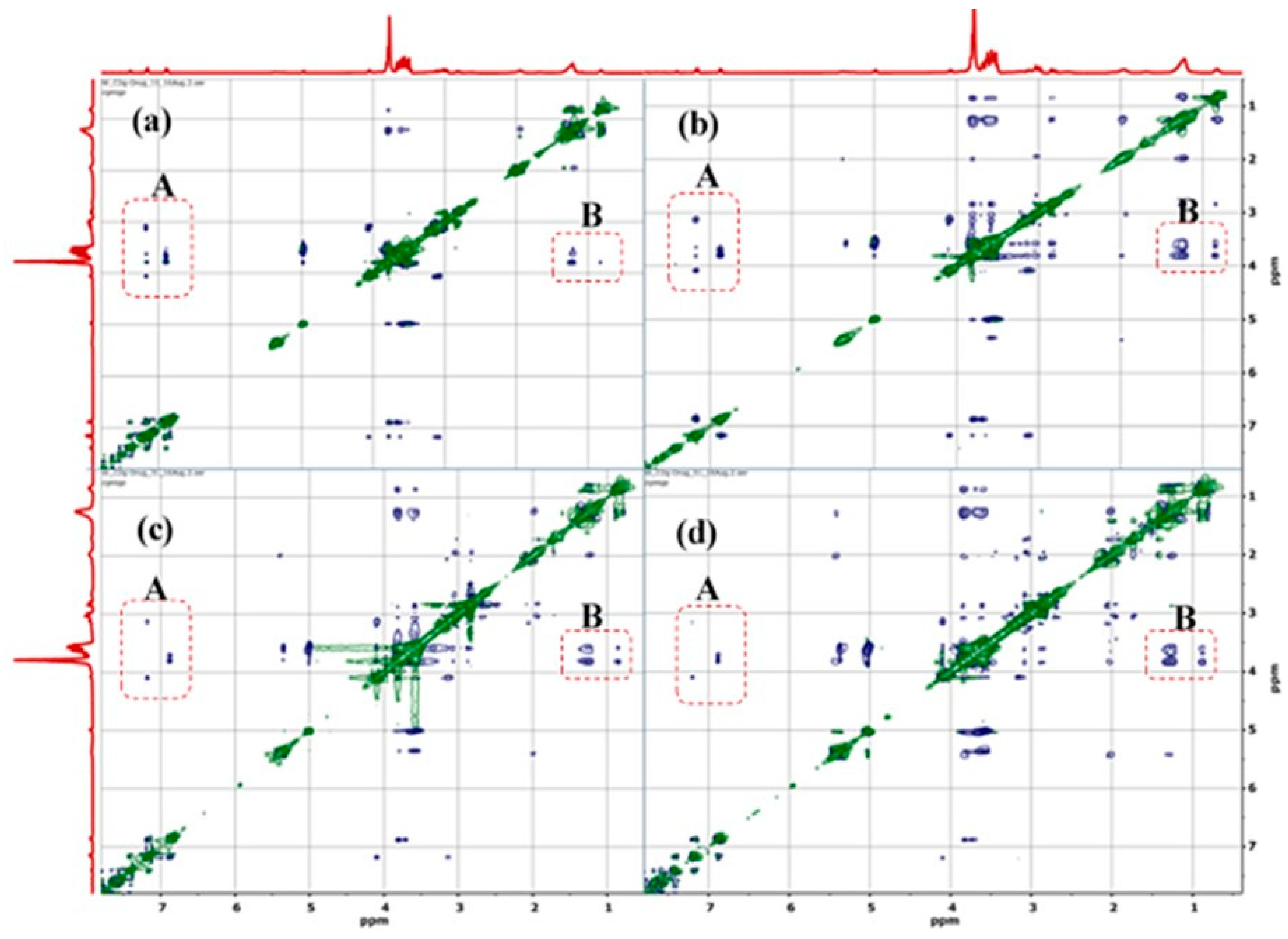
| Host:Guest | Ratio | 1H Nuclei | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 | ||
| βCD | -- | 4.98 | 3.56 | 3.87 | 3.49 | 3.77 | 3.76 |
| βCD:Mel | 2:1 | 4.97 (−0.01) | 3.57 (0.01) | 3.85 (−0.02) | 3.48 (−0.01) | 3.70 (−0.07) | 3.78 * (0.02) |
| 18:1βCDg | -- | 5.02 (0.04) | * | 3.84 (−0.03) | 3.59 * (0.10) | 3.69 (−0.08) | 3.83 (0.07) |
| 18:1βCDg:Mel | 1:1 | 4.97 (−0.01) | 3.57 (0.01) | 3.80 (−0.07) | 3.50 (0.01) | 3.61 (−0.16) | 3.77 (0.01) |
| 18:1βCDg:Mel | 2:1 | 4.98 (0.00) | 3.57 (0.01) | 3.81 (−0.06) | 3.52 (0.03) | 3.62 (−0.15) | 3.79 (0.03) |
| 18:1βCDg:Mel | 3:1 | 4.99 (0.01) | 3.57 (0.01) | 3.81 (−0.06) | 3.52 (0.03) | 3.63 (−0.14) | 3.79 (0.03) |
| 18:1βCDg:Mel | 5:1 | 5.01 (0.03) | 3.60 * (0.04) | 3.83 (−0.04) | 3.55 * (0.06) | 3.67 (−0.10) | 3.82 (0.06) |
| Componenta | Size nm ± SD | PDI | Zeta Potential mV ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mel (1 mM) | -- | -- | -- |
| βCD (2 mM) | -- | -- | -- |
| 18:1βCDg (2 mM) | 170 ± 17 | 0.329 ± 0.047 | +14 ± 3 |
| βCD-Mel (2:1 mole ratio) | -- | -- | -- |
| 18:1βCDg-Mel (2:1 mole ratio) | 160 ± 15 | 0.430 ± 0.04 | +46 ± 2 |
| Treatment | IC50 | |
|---|---|---|
| [A] | Mel | 98 ± 1 µM |
| [B] | 18:1βCDg | 89 ± 2 µM |
| [C] | 18:1βCDg-Mel [2:1 molar ratio] | 27 ± 1 µM |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohammed-Saeid, W.; Karoyo, A.H.; Verrall, R.E.; Wilson, L.D.; Badea, I. Inclusion Complexes of Melphalan with Gemini-Conjugated β-Cyclodextrin: Physicochemical Properties and Chemotherapeutic Efficacy in In-Vitro Tumor Models. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090427
Mohammed-Saeid W, Karoyo AH, Verrall RE, Wilson LD, Badea I. Inclusion Complexes of Melphalan with Gemini-Conjugated β-Cyclodextrin: Physicochemical Properties and Chemotherapeutic Efficacy in In-Vitro Tumor Models. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(9):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090427
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohammed-Saeid, Waleed, Abdalla H Karoyo, Ronald E Verrall, Lee D Wilson, and Ildiko Badea. 2019. "Inclusion Complexes of Melphalan with Gemini-Conjugated β-Cyclodextrin: Physicochemical Properties and Chemotherapeutic Efficacy in In-Vitro Tumor Models" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 9: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090427
APA StyleMohammed-Saeid, W., Karoyo, A. H., Verrall, R. E., Wilson, L. D., & Badea, I. (2019). Inclusion Complexes of Melphalan with Gemini-Conjugated β-Cyclodextrin: Physicochemical Properties and Chemotherapeutic Efficacy in In-Vitro Tumor Models. Pharmaceutics, 11(9), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090427