Self-Micellizing Technology Improves the Properties of Ezetimibe and Increases Its Effect on Hyperlipidemic Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Formulations
EZ Raw Material (EZ-RM) and Physical Mixture (PM)
Self-Micellizing Solid Dispersion with Kolliphor® RH40 (MS-K)
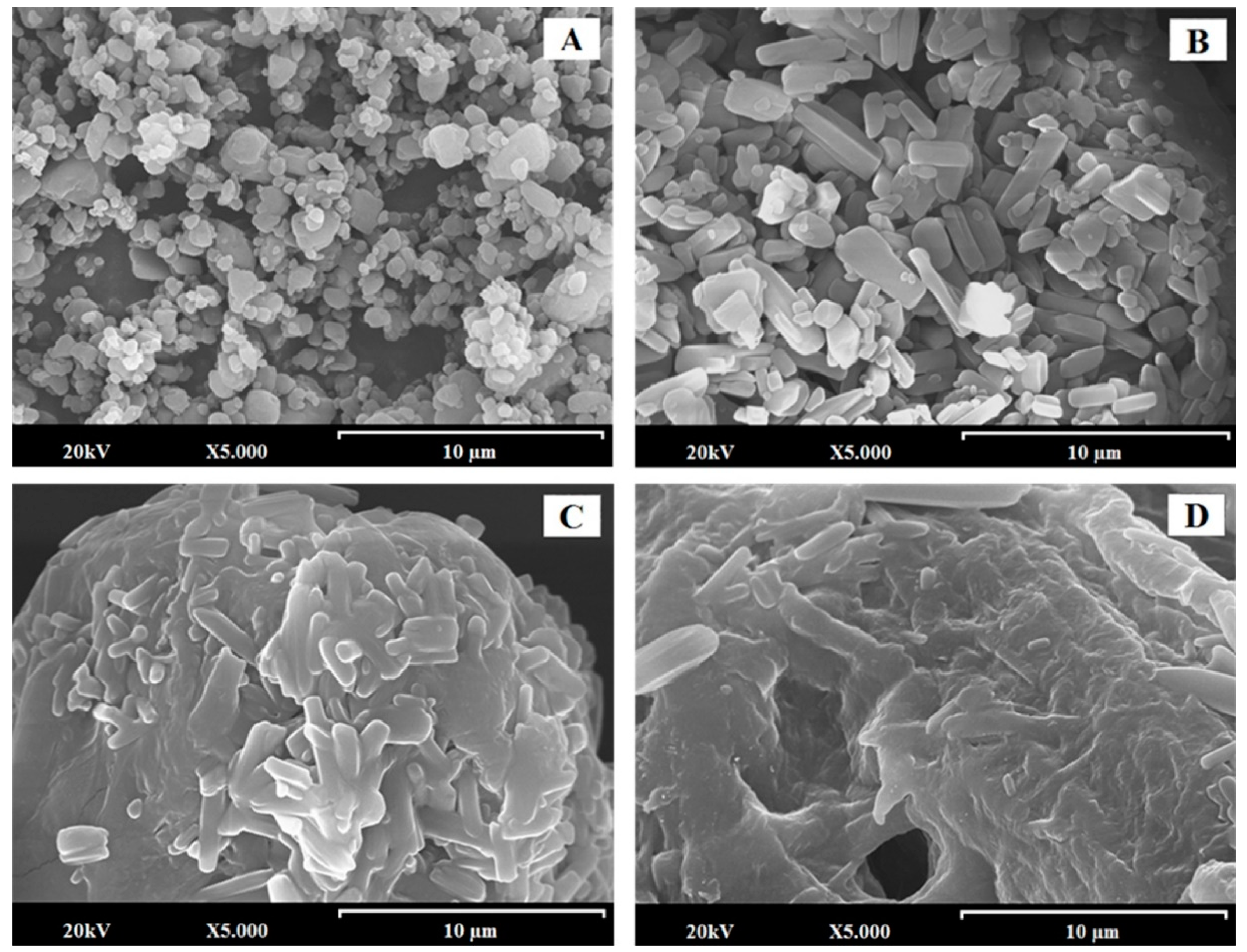
2.2.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM): Particle Morphology, Size, and Shape
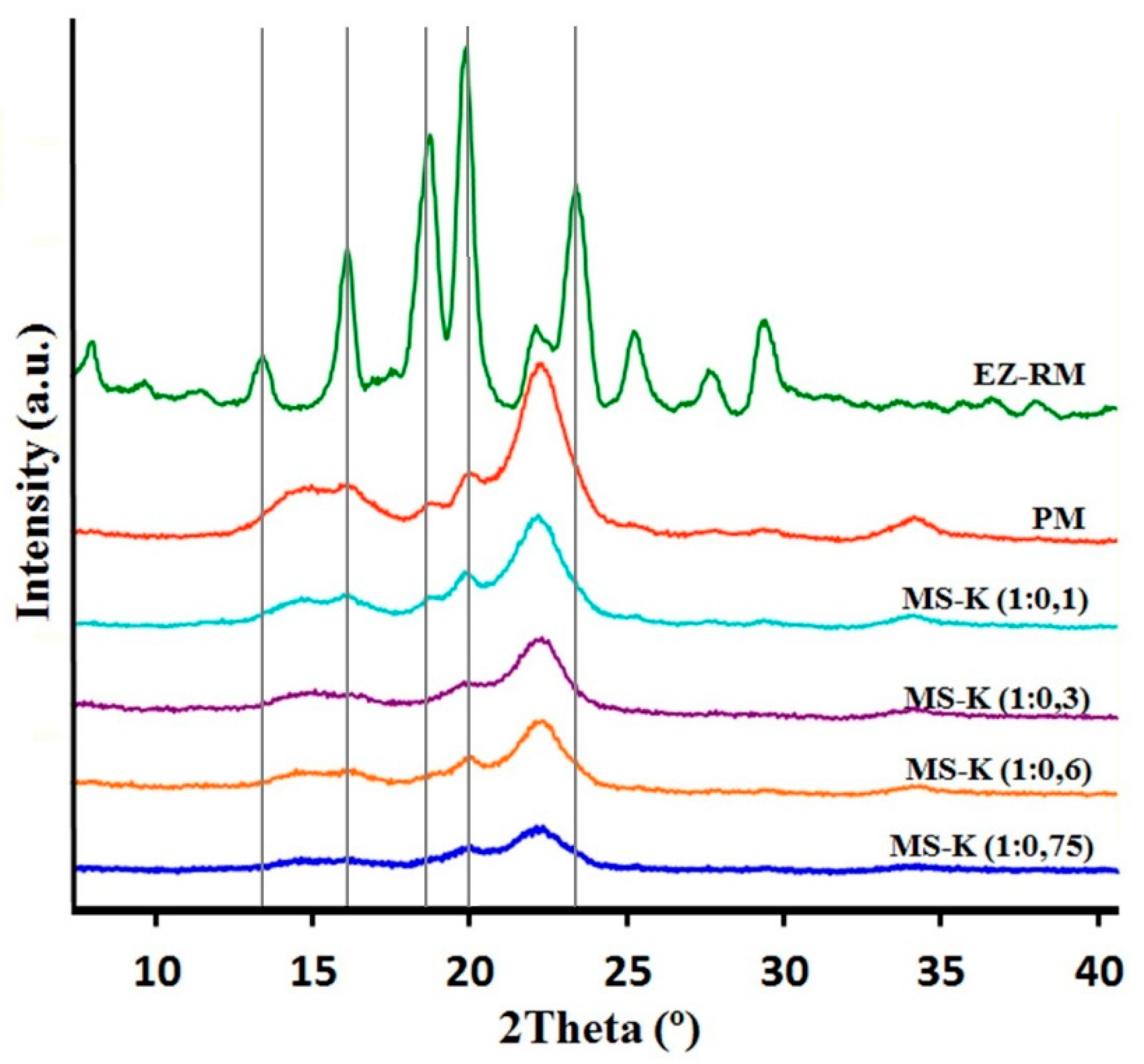
2.2.3. X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD): Structure and Crystal Size Characterization
2.2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2.5. Dissolution and Solubility Studies
2.2.6. Animal Study
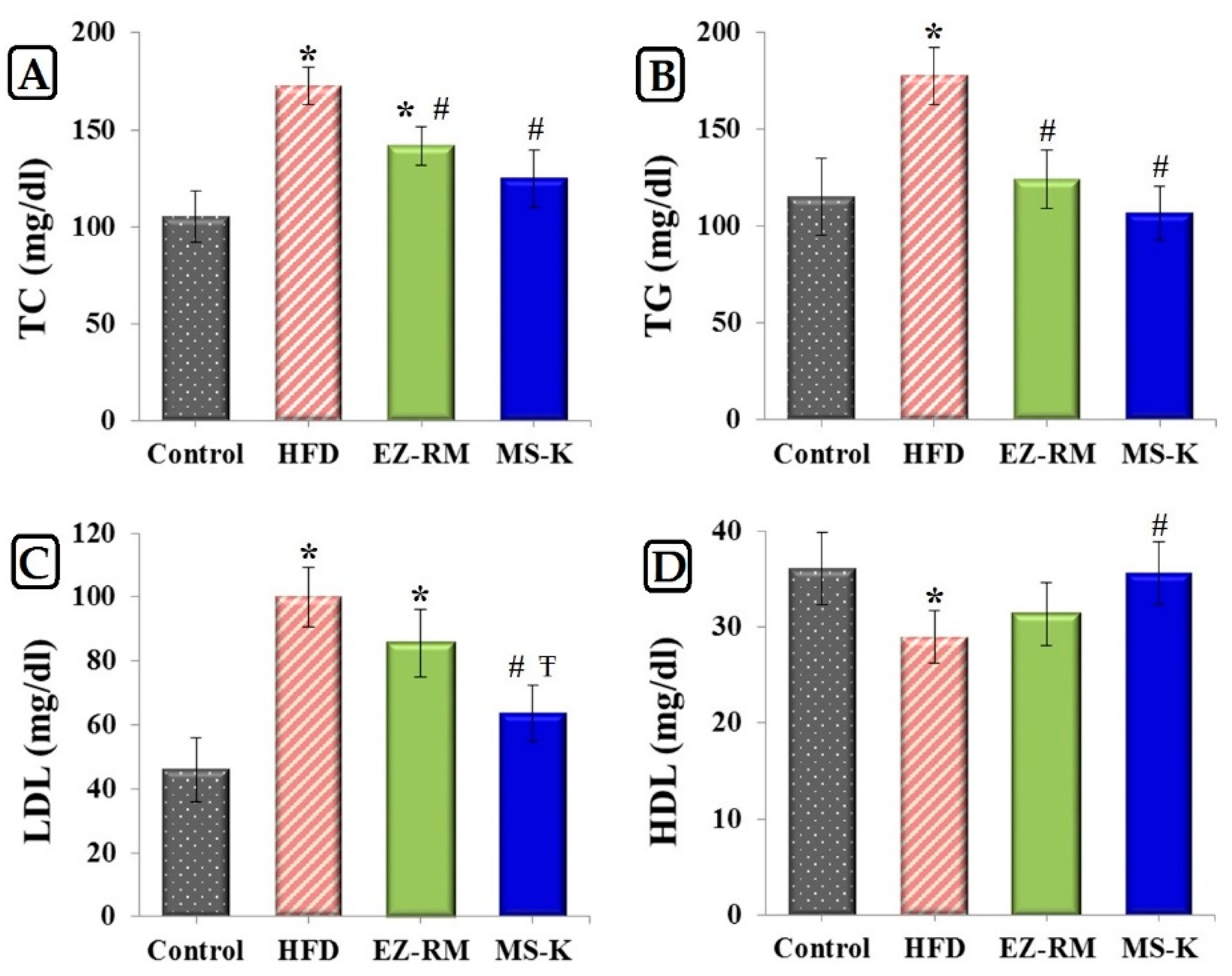
2.2.7. Lipid Profile Analysis
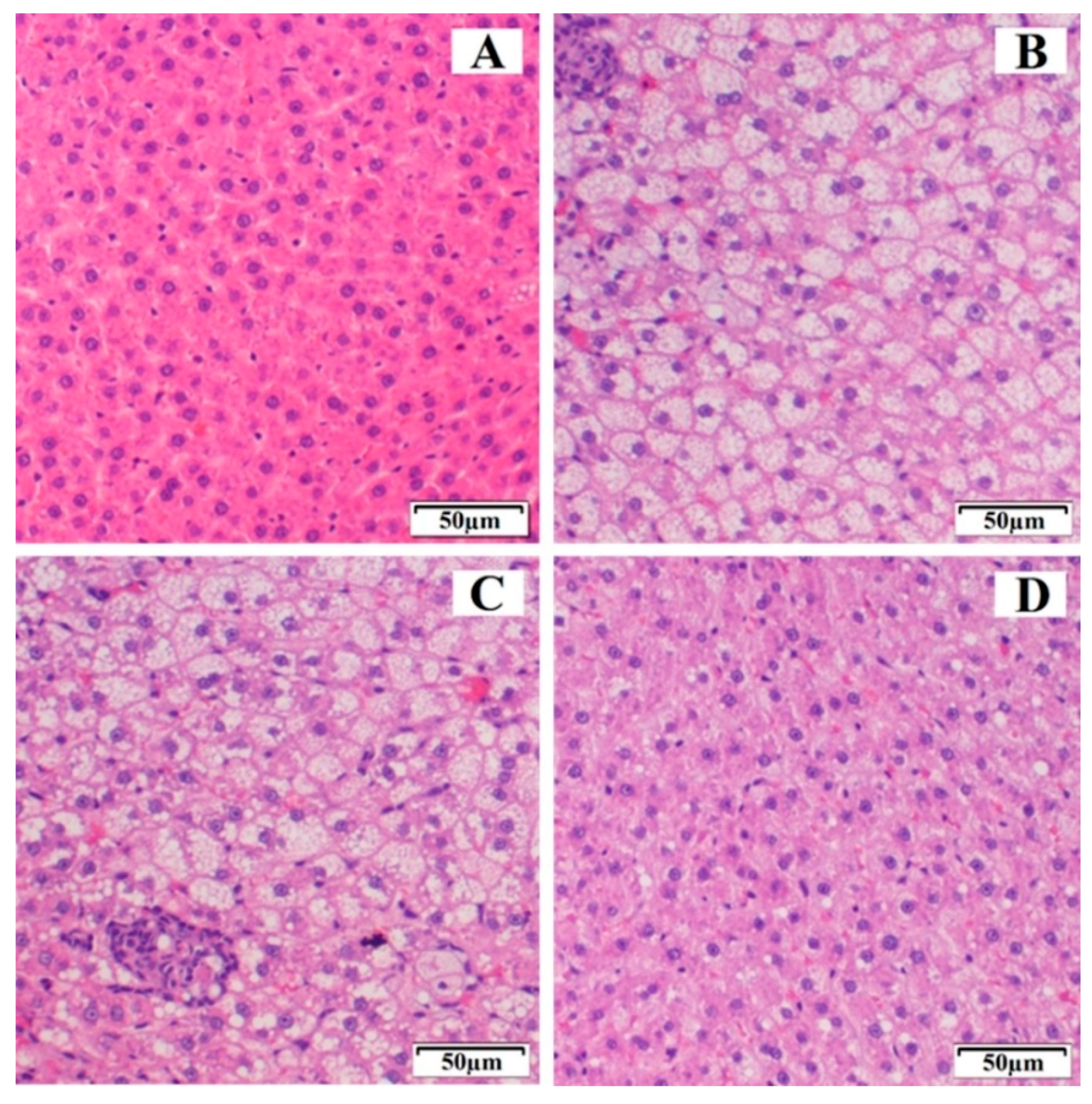
2.2.8. Histopathological Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SEM Characterization
3.2. X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD): Structure and Crystal Size Characterization
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.4. In Vitro Drug Release
3.5. Evaluation of the Efficacy of EZ Formulations
3.5.1. Total Lipid Profile
3.5.2. Histopathological Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ioannou, G.N.; Van Rooyen, D.M.; Savard, C.; Haigh, W.G.; Yeh, M.M.; Teoh, N.C.; Farrell, G.C. Cholesterol-lowering drugs cause dissolution of cholesterol crystals and disperse Kupffer cell crown-like structures during resolution of NASH. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckbauer, A.; Banerjee, J.; Fu, L.; Li, F.; Cao, Q.; Cui, X.; Wu, R.; Shi, H.; Xue, B.; Zemel, M.B. A Combination of Leucine, Metformin, and Sildenafil Treats Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Steatohepatitis in Mice. Int. J. Hepatol. 2016, 2016, 9185987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basha, M.; Salama, A.H.; El Awdan, S. Reconstitutable spray dried ultra-fine dispersion as a robust platform for effective oral delivery of an antihyperlipidemic drug. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bali, V.; Ali, M.; Ali, J. Nanocarrier for the enhanced bioavailability of a cardiovascular agent: In vitro, pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic and stability assessment. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 403, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, V.; Gazzin, S.; Gambaro, S.E.; Dal Ben, M.; Calligaris, S.; Anese, M.; Raseni, A.; Avellini, C.; Giraudi, P.J.; Tiribelli, C.; et al. Effects of Oral Administration of Silymarin in a Juvenile Murine Model of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Katare, O.P.; Singh, B. Development of optimized supersaturable self-nanoemulsifying systems of ezetimibe: Effect of polymers and efflux transporters. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, A.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Garjani, A.; Javadzadeh, Y.; Hamishehkar, H.; Rameshrad, M.; Adibkia, K. Physicochemical characterization and pharmacological evaluation of ezetimibe-PVP K30 solid dispersions in hyperlipidemic rats. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 134, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Katare, O.P.; Singh, B. Optimized self nano-emulsifying systems of ezetimibe with enhanced bioavailability potential using long chain and medium chain triglycerides. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 100, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivalli, K.M.; Mishra, B. Preparation and pharmacodynamic assessment of ezetimibe nanocrystals: Effect of P-gp inhibitory stabilizer on particle size and oral absorption. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 135, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riekes, M.K.; Dereymaker, A.; Berben, P.; Augustijns, P.; Stulzer, H.K.; Van den Mooter, G. Development of enteric-coated fixed dose combinations of amorphous solid dispersions of ezetimibe and lovastatin: Investigation of formulation and process parameters. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 30, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangiri, A.; Barzegar-Jalali, M.; Garjani, A.; Javadzadeh, Y.; Hamishehkar, H.; Asadpour-Zeynali, K.; Adibkia, K. Evaluation of physicochemical properties and in vivo efficiency of atorvastatin calcium/ezetimibe solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 82, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thadkala, K.; Nanam, P.K.; Rambabu, B.; Sailu, C.; Aukunuru, J. Preparation and characterization of amorphous ezetimibe nanosuspensions intended for enhancement of oral bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2014, 4, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelsen, R.; Holm, R.; Jacobsen, J.; Kristensen, J.; Abrahamsson, B.; Müllertz, A. Kolliphor surfactants affect solubilization and bioavailability of fenofibrate. Studies of in vitro digestion and absorption in rats. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1062–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.Q.; Wang, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, J.S.; Wang, L.N.; Cai, J.H.; Li, Z.Q.; Xiang, B.; Qi, X.R. Hot melt extrusion technology for improved dissolution, solubility and “spring-parachute” processes of amorphous self-micellizing solid dispersions containing BCS II drugs indomethacin and fenofibrate: Profiles and mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 130, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, K.; Cho, J.M.; Lee, H.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. Enhancement of Aqueous Solubility and Dissolution of Celecoxib through Phosphatidylcholine-Based Dispersion Systems Solidified with Adsorbent Carriers. Pharmaceutics 2018, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rodriguez, J.J.; Torre-Iglesias, P.M.; Vegas-Sánchez, M.C.; Torrado-Durán, S.; Bolás-Fernández, F.; Torrado-Santiago, S. Changed crystallinity of mebendazole solid dispersion: Improved anthelmintic. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 403, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Herrero, V.; Torrado, C.; García-Rodríguez, J.J.; López-Sánchez, A.; Torrado, S.; Torrado-Santiago, S. Improvement of the surface hydrophilic properties of naproxen particles with addition of hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose and sodium dodecyl sulphate: In vitro and in vivo studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfar, M.; Sheikh Salem, M.; Hawari, R. Formulation factors affecting the release of ezetimibe from different liquisolid compacts. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komersová, A.; Lochař, V.; Myslíková, K.; Mužíková, J.; Bartoš, M. Formulation and dissolution kinetics study of hydrophilic matrix tablets with tramadol hydrochloride and different co-processed dry binders. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 95, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse, W.L.; Grimsey, I.M.; De Matas, M. The impact of low-level inorganic impurities on key physicochemical properties of paracetamol. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 349, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Antunes, F.E.; Sousa, J.; Valente, A.; Alberto, A.; Pais, A. New insights on the interaction between hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose and sodium dodecyl sulfate. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanfar, M.; Al-Taani, B.; Alsmadi, M.; Zayed, A. Enhancement of the dissolution and bioavailability from freeze-dried powder of a hypocholesterolemic drug in the presence of Soluplus. Powder Technol. 2018, 329, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, R.; Kim, D.W.; Din, F.U.; Mustapha, O.; Yousaf, A.M.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.O.; Yong, C.S.; Choi, H.G. Effect of hydroxypropylcellulose and Tween 80 on physicochemical properties and bioavailability of ezetimibe-loaded solid dispersion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 130, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivalli, K.M.; Mishra, B. Improved Aqueous Solubility and Antihypercholesterolemic Activity of Ezetimibe on Formulating with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin and Hydrophilic Auxiliary Substances. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.; Giri, B.R.; Song, E.S.; Bae, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, D.W. Spray-Dried Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Atorvastatin Calcium for Improved Supersaturation and Oral Bioavailability. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajracharya, R.; Lee, S.H.; Song, J.G.; Kim, M.; Lee, K.; Han, H.K. Development of a Ternary Solid Dispersion Formulation of LW6 to Improve the In Vivo Activity as a BCRP Inhibitor: Preparation and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhayali, A.; Tavellin, S.; Velaga, S. Dissolution and precipitation behavior of ternary solid dispersions of ezetimibe in biorelevant media. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Herrero, V.; Torrado-Salmerón, C.; García-Rodríguez, J.J.; Torrado, G.; Torrado-Santiago, S. Submicellar liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection improves the analysis of naproxen in plasma and brain tissue. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhao, P.; Li, Y.; Deng, T.; Tian, L.; Li, H. Renoprotective effect of atorvastatin on STZ-diabetic rats through attenuating kidney-associated dysmetabolism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torrado-Salmerón, C.; Guarnizo-Herrero, V.; Cerezo-Garreta, J.; Torrado Durán, G.; Torrado-Santiago, S. Self-Micellizing Technology Improves the Properties of Ezetimibe and Increases Its Effect on Hyperlipidemic Rats. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120647
Torrado-Salmerón C, Guarnizo-Herrero V, Cerezo-Garreta J, Torrado Durán G, Torrado-Santiago S. Self-Micellizing Technology Improves the Properties of Ezetimibe and Increases Its Effect on Hyperlipidemic Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(12):647. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120647
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorrado-Salmerón, Carlos, Víctor Guarnizo-Herrero, Javier Cerezo-Garreta, Guillermo Torrado Durán, and Santiago Torrado-Santiago. 2019. "Self-Micellizing Technology Improves the Properties of Ezetimibe and Increases Its Effect on Hyperlipidemic Rats" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 12: 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120647
APA StyleTorrado-Salmerón, C., Guarnizo-Herrero, V., Cerezo-Garreta, J., Torrado Durán, G., & Torrado-Santiago, S. (2019). Self-Micellizing Technology Improves the Properties of Ezetimibe and Increases Its Effect on Hyperlipidemic Rats. Pharmaceutics, 11(12), 647. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11120647





