From Cells to Virus Particles: Quantitative Methods to Monitor RNA Packaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
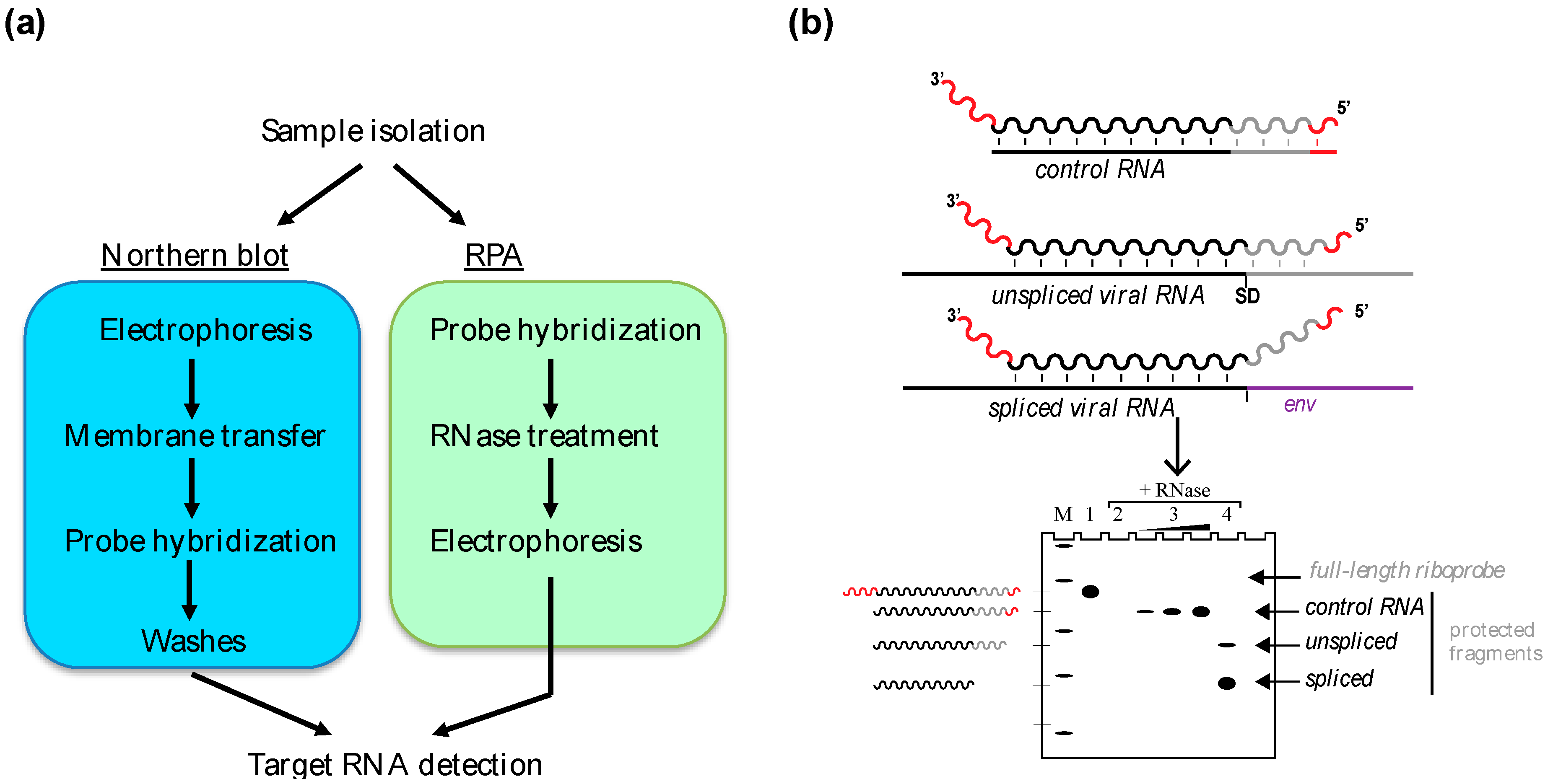
2. In Vitro Gel-Based Approaches: Northern Blot and Ribonuclease Protection Assay
2.1. The Northern Blot
2.2. The RPA
2.2.1. Sensitivity
2.2.2. Specificity and Accuracy
2.2.3. Multiplexing
2.3. Applications of Northern Blot and RPA
3. Quantitative RT-PCR
3.1. Absolute versus Relative Quantification
3.2. Choice of Fluorescence Approach
3.3. Priming Strategy
3.4. Quality of Templates
3.5. RT-qPCR to Monitor Retroviral RNA Encapsidation
3.6. Advantages of RT-qPCR.
4. Fluorescence Microscopy of Fixed- or Live-Cells
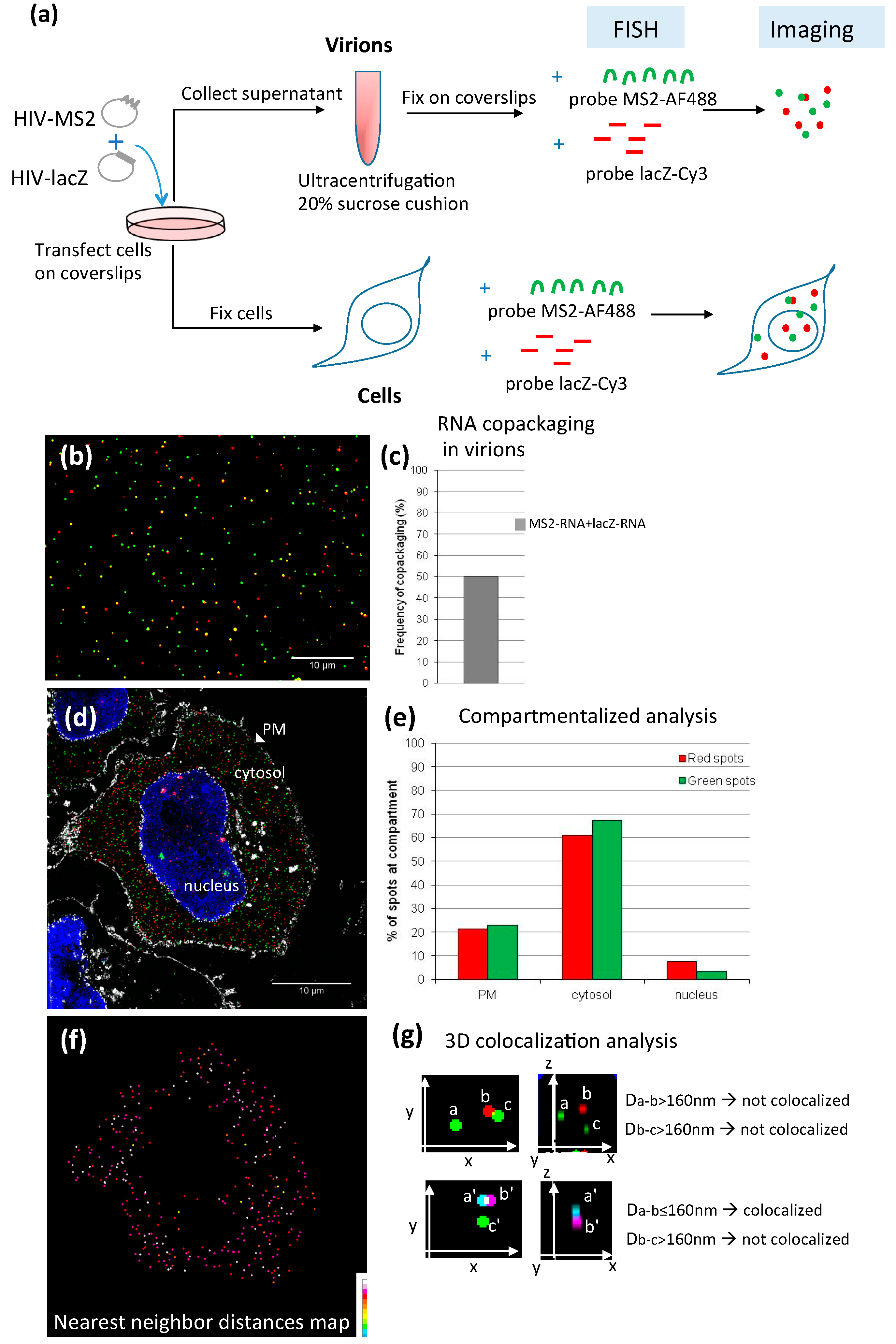
4.1. FISH
4.1.1. Methodology
4.1.2. Applications of FISH in the Study of Retroviral RNA Encapsidation
4.2. Live-Cell Imaging to Study Viral RNA Packaging
4.3. FISH versus Live-Cell Imaging
5. RNA Sequencing Opens New Perspectives for Studying the Virion Transcriptome
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jouvenet, N.; Lainé, S.; Pessel-Vivares, L.; Mougel, M. Cell biology of retroviral RNA packaging. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzembayeva, M.; Dilley, K.; Sardo, L.; Hu, W.S. Life of psi: How full-length HIV-1 RNAs become packaged genomes in the viral particles. Virology 2014, 454–455, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.S.; Liang, C.; Wainberg, M.A. Is HIV-1 RNA dimerization a prerequisite for packaging? Yes, no, probably? Retrovirology 2004, 1, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paillart, J.-C.; Shehu-Xhilaga, M.; Marquet, R.; Mak, J. Dimerization of retroviral RNA genomes: An inseparable pair. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rulli, S.J., Jr.; Hibbert, C.S.; Mirro, J.; Pederson, T.; Biswal, S.; Rein, A. Selective and nonselective packaging of cellular RNAs in retrovirus particles. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 6623–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didierlaurent, L.; Racine, P.J.; Houzet, L.; Chamontin, C.; Berkhout, B.; Mougel, M. Role of HIV-1 RNA and protein determinants for the selective packaging of spliced and unspliced viral RNA and host U6 and 7SL RNA in virus particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 8915–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onafuwa-Nuga, A.A.; Telesnitsky, A.; King, S.R. 7SL RNA, but not the 54-kd signal recognition particle protein, is an abundant component of both infectious HIV-1 and minimal virus-like particles. RNA 2006, 12, 542–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houzet, L.; Paillart, J.C.; Smagulova, F.; Maurel, S.; Morichaud, Z.; Marquet, R.; Mougel, M. HIV controls the selective packaging of genomic, spliced viral and cellular RNAs into virions through different mechanisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 2695–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurel, S.; Houzet, L.; Garcia, E.L.; Telesnitsky, A.; Mougel, M. Characterization of a natural heterodimer between MLV genomic RNA and the SD' retroelement generated by alternative splicing. RNA 2007, 13, 2266–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, W.; Yu, X.F. Virion packaging determinants and reverse transcription of SRP RNA in HIV-1 particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 7288–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, K.E.; Caputi, M.; Beemon, K.L. Packaging and reverse transcription of snRNAs by retroviruses may generate pseudogenes. RNA 2004, 10, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckwahl, M.J.; Sim, S.; Smith, D.; Telesnitsky, A.; Wolin, S.L. A retrovirus packages nascent host noncoding RNAs from a novel surveillance pathway. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Heng, X.; Summers, M.F. Structural determinants and mechanism of HIV-1 genome packaging. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 410, 609–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Rahman, S.A.; Nikolaitchik, O.A.; Grunwald, D.; Sardo, L.; Burdick, R.C.; Plisov, S.; Liang, E.; Tai, S.; Pathak, V.K.; et al. HIV-1 RNA genome dimerizes on the plasma membrane in the presence of Gag protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E201–E208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrer, M.; Clerte, C.; Chamontin, C.; Basyuk, E.; Laine, S.; Hottin, J.; Bertrand, E.; Margeat, E.; Mougel, M. Imaging HIV-1 RNA dimerization in cells by multicolour super-resolution and fluctuation microscopies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharytonchyk, S.A.; Kireyeva, A.I.; Osipovich, A.B.; Fomin, I.K. Evidence for preferential copackaging of Moloney murine leukemia virus genomic RNAs transcribed in the same chromosomal site. Retrovirology 2005, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maurel, S.; Mougel, M. Murine leukemia virus RNA dimerization is coupled to transcription and splicing processes. Retrovirology 2010, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, S.V.; Pedersen, F.S. Co-localization of gammaretroviral RNAs at their transcription site favours co-packaging. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 2279–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, J.R. Q&A: What are exosomes, exactly? BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Belin, D. The use of RNA probes for the analysis of gene expression. Northern blot hybridization and ribonuclease protection assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 1998, 86, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azrolan, N.; Breslow, J.L. A solution hybridization/RNase protection assay with riboprobes to determine absolute levels of apoB, A-I, and E mRNA in human hepatoma cell lines. J. Lipid Res. 1990, 31, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Das, P.P.; Bagijn, M.P.; Goldstein, L.D.; Woolford, J.R.; Lehrbach, N.J.; Sapetschnig, A.; Buhecha, H.R.; Gilchrist, M.J.; Howe, K.L.; Stark, R.; et al. Piwi and piRNAs act upstream of an endogenous siRNA pathway to suppress tc3 transposon mobility in the Caenorhabditis elegans germline. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storch, G.A.; Park, C.S.; Dohner, D.E. RNA fingerprinting of respiratory syncytial virus using ribonuclease protection. Application to molecular epidemiology. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 83, 1894–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, C.I.; Holley, C.L.; Scruggs, B.S.; Sidhu, R.; Brookheart, R.T.; Listenberger, L.L.; Behlke, M.A.; Ory, D.S.; Schaffer, J.E. Small nucleolar RNAs U32a, U33, and U35a are critical mediators of metabolic stress. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, X.; Kharytonchyk, S.; Garcia, E.L.; Lu, K.; Divakaruni, S.S.; LaCotti, C.; Edme, K.; Telesnitsky, A.; Summers, M.F. Identification of a minimal region of the HIV-1 5′-leader required for RNA dimerization, NC binding, and packaging. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 417, 224–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cloutier, N.; Gravel, A.; Flamand, L. Multiplex detection and quantitation of latent and lytic transcripts of human herpesvirus-8 using RNase protection assay. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 122, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejardin, J.; Bompard-Marechal, G.; Audit, M.; Hope, T.J.; Sitbon, M.; Mougel, M. A novel subgenomic murine leukemia virus RNA transcript results from alternative splicing. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 3709–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houzet, L.; Battini, J.L.; Bernard, E.; Thibert, V.; Mougel, M. A new retroelement constituted by a natural alternatively spliced RNA of murine replication-competent retroviruses. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4866–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mougel, M.; Zhang, Y.; Barklis, E. Cis-active structural motifs involved in specific encapsidation of Moloney murine leukemia virus RNA. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5043–5050. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clever, J.L.; Mirandar, D., Jr.; Parslow, T.G. RNA structure and packaging signals in the 5′ leader region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genome. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 12381–12387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorman, N.; Lever, A. Comparison of viral genomic RNA sorting mechanisms in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), HIV-2, and Moloney murine leukemia virus. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 11413–11417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onafuwa-Nuga, A.A.; King, S.R.; Telesnitsky, A. Nonrandom packaging of host RNAs in Moloney murine leukemia virus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13528–13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrich, D.; Hooker, C.W.; Parry, E. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tar RNA upper stem-loop plays distinct roles in reverse transcription and RNA packaging. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 5639–5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Norris, K.M.; Mansky, L.M. Involvement of the matrix and nucleocapsid domains of the bovine leukemia virus Gag polyprotein precursor in viral RNA packaging. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9431–9438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktar, S.J.; Vivet-Boudou, V.; Ali, L.M.; Jabeen, A.; Kalloush, R.M.; Richer, D.; Mustafa, F.; Marquet, R.; Rizvi, T.A. Structural basis of genomic RNA (gRNA) dimerization and packaging determinants of mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV). Retrovirology 2014, 11, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dotsch, J.; Repp, R.; Rascher, W.; Christiansen, H. Diagnostic and scientific applications of TaqMan real-time PCR in neuroblastomas. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2001, 1, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arya, M.; Shergill, I.S.; Williamson, M.; Gommersall, L.; Arya, N.; Patel, H.R. Basic principles of real-time quantitative PCR. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2005, 5, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ririe, K.M.; Rasmussen, R.P.; Wittwer, C.T. Product differentiation by analysis of DNA melting curves during the polymerase chain reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 245, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessel-Vivares, L.; Ferrer, M.; Laine, S.; Mougel, M. MLV requires Tap/NXF1-dependent pathway to export its unspliced RNA to the cytoplasm and to express both spliced and unspliced RNAs. Retrovirology 2014, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, W.; Prasad, V.V.; Chen, J.; Nikolaitchik, O.; Hu, W.S. Molecular mechanisms of simian immunodeficiency virus SIV(agm) RNA encapsidation. Virology 2007, 363, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, F.; Al Amri, D.; Al Ali, F.; Al Sari, N.; Al Suwaidi, S.; Jayanth, P.; Philips, P.S.; Rizvi, T.A. Sequences within both the 5′ UTR and Gag are required for optimal in vivo packaging and propagation of mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) genomic RNA. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racine, P.J.; Chamontin, C.; de Rocquigny, H.; Bernacchi, S.; Paillart, J.C.; Mougel, M. Requirements for nucleocapsid-mediated regulation of reverse transcription during the late steps of HIV-1 assembly. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L'Hernault, A.; Weiss, E.U.; Greatorex, J.S.; Lever, A.M. HIV-2 genome dimerization is required for the correct processing of Gag: A second-site reversion in matrix can restore both processes in dimerization-impaired mutant viruses. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5867–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristic, N.; Chin, M.P. Mutations in matrix and sp1 repair the packaging specificity of a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutant by reducing the association of Gag with spliced viral RNA. Retrovirology 2010, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, S.; Blissenbach, M.; Grewe, B.; Konietzny, R.; Grunwald, T.; Uberla, K. Rev proteins of human and simian immunodeficiency virus enhance RNA encapsidation. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Femino, A.M.; Fay, F.S.; Fogarty, K.; Singer, R.H. Visualization of single RNA transcripts in situ. Science 1998, 280, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, E.; Chartrand, P.; Schaefer, M.; Shenoy, S.M.; Singer, R.H.; Long, R.M. Localization of ASH1 mRNA particles in living yeast. Mol. Cell 1998, 2, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shav-Tal, Y.; Singer, R.H.; Darzacq, X. Imaging gene expression in single living cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouvenet, N.; Bieniasz, P.D.; Simon, S.M. Imaging the biogenesis of individual HIV-1 virions in live cells. Nature 2008, 454, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanchenko, S.; Godinez, W.J.; Lampe, M.; Krausslich, H.G.; Eils, R.; Rohr, K.; Brauchle, C.; Muller, B.; Lamb, D.C. Dynamics of HIV-1 assembly and release. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chamontin, C.; Rassam, P.; Ferrer, M.; Racine, P.J.; Neyret, A.; Laine, S.; Milhiet, P.E.; Mougel, M. HIV-1 nucleocapsid and ESCRT-component TSG101 interplay prevents HIV from turning into a DNA-containing virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markaki, Y.; Smeets, D.; Cremer, M.; Schermelleh, L. Fluorescence in situ hybridization applications for super-resolution 3D structured illumination microscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 950, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vyboh, K.; Ajamian, L.; Mouland, A.J. Detection of viral RNA by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). J. Vis. Exp. 2012, e4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, A.; Tyagi, S. Detection of individual endogenous RNA transcripts in situ using multiple singly labeled probes. Methods Enzymol. 2010, 472, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mueller, F.; Senecal, A.; Tantale, K.; Marie-Nelly, H.; Ly, N.; Collin, O.; Basyuk, E.; Bertrand, E.; Darzacq, X.; Zimmer, C. FISH-quant: Automatic counting of transcripts in 3D FISH images. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ollion, J.; Cochennec, J.; Loll, F.; Escude, C.; Boudier, T. Tango: A generic tool for high-throughput 3D image analysis for studying nuclear organization. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1840–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Nikolaitchik, O.; Singh, J.; Wright, A.; Bencsics, C.E.; Coffin, J.M.; Ni, N.; Lockett, S.; Pathak, V.K.; Hu, W.S. High efficiency of HIV-1 genomic RNA packaging and heterozygote formation revealed by single virion analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13535–13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bann, D.V.; Parent, L.J. Application of live-cell RNA imaging techniques to the study of retroviral RNA trafficking. Viruses 2012, 963–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manival, X.; Yang, Y.; Strub, M.P.; Kochoyan, M.; Steinmetz, M.; Aymerich, S. From genetic to structural characterization of a new class of RNA-binding domain within the SacY/BglG family of antiterminator proteins. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5019–5029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocine, S.; Raymond, P.; Zenklusen, D.; Chao, J.A.; Singer, R.H. Single-molecule analysis of gene expression using two-color RNA labeling in live yeast. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigle, N.; Ellenberg, J. Lambdan-gfp: An RNA reporter system for live-cell imaging. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basyuk, E.; Galli, T.; Mougel, M.; Blanchard, J.M.; Sitbon, M.; Bertrand, E. Retroviral genomic RNAs are transported to the plasma membrane by endosomal vesicles. Dev. Cell 2003, 5, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouvenet, N.; Simon, S.M.; Bieniasz, P.D. Imaging the interaction of HIV-1 genomes and Gag during assembly of individual viral particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19114–19119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonas, E.; Lifland, A.W.; Gudheti, M.; Vanover, D.; Jung, J.; Zurla, C.; Kirschman, J.; Fiore, V.F.; Douglas, A.; Barker, T.H.; et al. Combining single RNA sensitive probes with subdiffraction-limited and live-cell imaging enables the characterization of virus dynamics in cells. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, U.; Dijk, F.; Sjollema, K.A.; Giepmans, B.N. Immunolabeling artifacts and the need for live-cell imaging. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juranic Lisnic, V.; Babic Cac, M.; Lisnic, B.; Trsan, T.; Mefferd, A.; Das Mukhopadhyay, C.; Cook, C.H.; Jonjic, S.; Trgovcich, J. Dual analysis of the murine cytomegalovirus and host cell transcriptomes reveal new aspects of the virus-host cell interface. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatherer, D.; Seirafian, S.; Cunningham, C.; Holton, M.; Dargan, D.J.; Baluchova, K.; Hector, R.D.; Galbraith, J.; Herzyk, P.; Wilkinson, G.W.; et al. High-resolution human cytomegalovirus transcriptome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19755–19760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushothaman, P.; Thakker, S.; Verma, S.C. Transcriptome analysis of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus during de novo primary infection of human B and endothelial cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 3093–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillies, M.A.; Rau, A.; Aubert, J.; Hennequet-Antier, C.; Jeanmougin, M.; Servant, N.; Keime, C.; Marot, G.; Castel, D.; Estelle, J.; et al. A comprehensive evaluation of normalization methods for illumina high-throughput RNA sequencing data analysis. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrer, M.; Henriet, S.; Chamontin, C.; Lainé, S.; Mougel, M. From Cells to Virus Particles: Quantitative Methods to Monitor RNA Packaging. Viruses 2016, 8, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080239
Ferrer M, Henriet S, Chamontin C, Lainé S, Mougel M. From Cells to Virus Particles: Quantitative Methods to Monitor RNA Packaging. Viruses. 2016; 8(8):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080239
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrer, Mireia, Simon Henriet, Célia Chamontin, Sébastien Lainé, and Marylène Mougel. 2016. "From Cells to Virus Particles: Quantitative Methods to Monitor RNA Packaging" Viruses 8, no. 8: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080239
APA StyleFerrer, M., Henriet, S., Chamontin, C., Lainé, S., & Mougel, M. (2016). From Cells to Virus Particles: Quantitative Methods to Monitor RNA Packaging. Viruses, 8(8), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/v8080239






